Submitted:
02 June 2023
Posted:
05 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Antibiotic Therapy, Antibiotic Resistance
3. Evolutionary Medicine
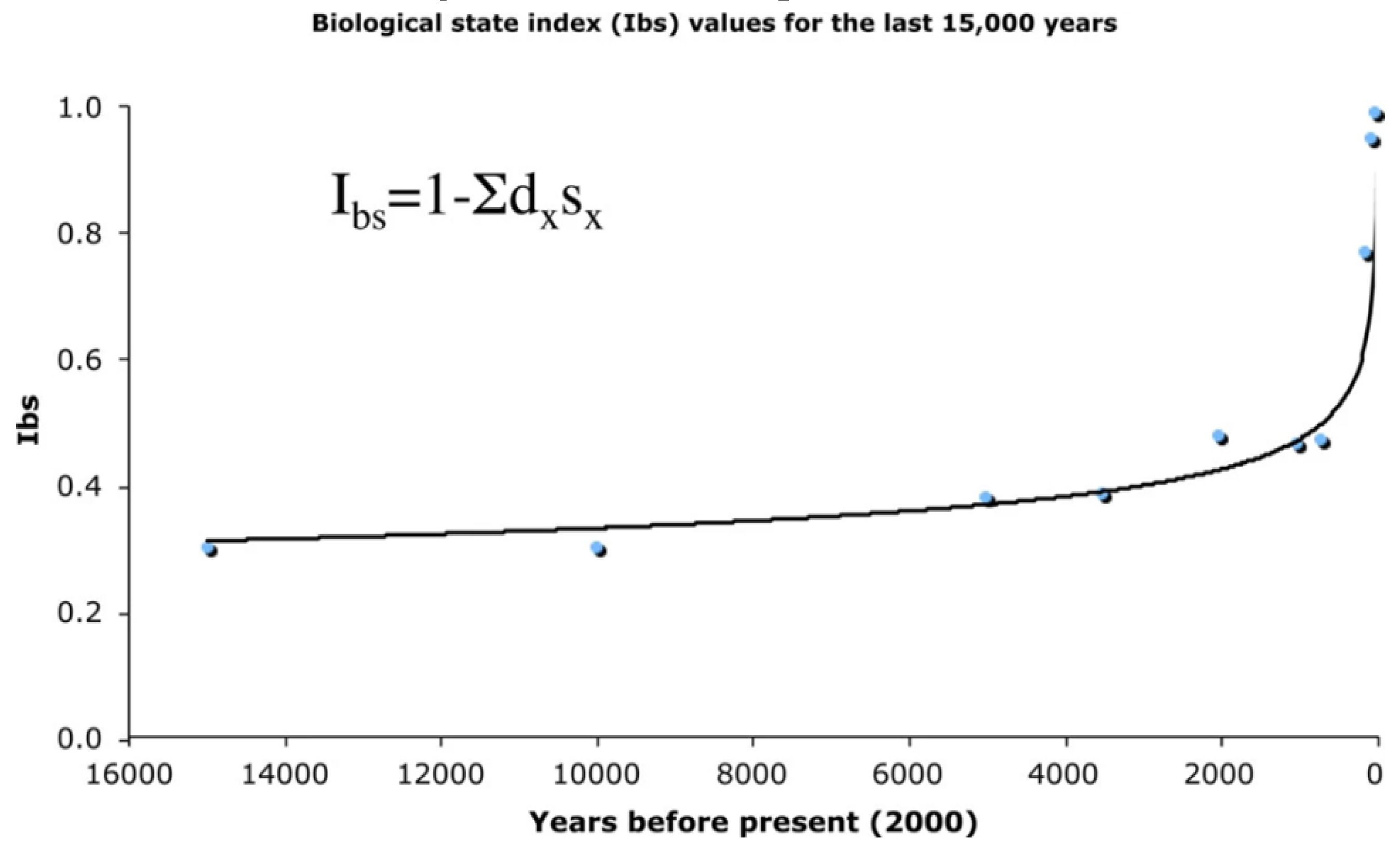
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vernadsky, V. I. The Biosphere./Forward by Linn Margulis and colleagues; introduction by Jacques Grinevald; translated by David B. Langmuir; revised and annotated by Mark A. S. McMenamin. New York, Copernicus, 1998.
- Vernadsky, V. I. Thoughts of the Naturalist. Moscow, Nauka, 1977, 18.
- Wells, J.C.K.; Nesse, R.M.; Sear, R.; A Johnstone, R.; Stearns, S.C. Evolutionary public health: introducing the concept. Lancet 2017, 390, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunspan, D.Z.; Nesse, R.M.; Barnes, M.E.; E Brownell, S. Core principles of evolutionary medicine. Evol. Med. Public Heal. 2017, 2018, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluckman, P. , Beedle A., Buklijas T., Low FHM (2016) Principles of evolutionary medicine, 2nd ed. Oxford University Press.
- Tiganov, A.S. The pathomorphosis of schizophrenia. Zhurnal Nevrol. i psikhiatrii im. S.S. Korsakova 2015, 115, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, W. Piraino, Simon J. Furney et al. Mutations: Driver Versus Passenger. In Encyclopedia of Cancer (Third Edition), 2019. Editors-in-Chief: Paolo Boffetta, Pierre Hainaut. eBook ISBN: 9780128124857. Hardcover ISBN: 9780128124840.
- Berger, M.F.; Mardis, E.R. The emerging clinical relevance of genomics in cancer medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potievskii, M.B.; Shegai, P.V.; Kaprin, A.D. Prospects for the Application of Methods of Evolutionary Biology in Oncology. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 58, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanSteelandt, A. , Stone A.C. Genetics, Evolutionary Medicine, and the Evolution of Human Pathogens. In: A Companion to Anthropological Genetics. Dennis H. O’Rourke (Editor), 19, Wiley-Blackwell, 496 Pages. ISBN: 978-1-118-76899-0. 20 March.
- Ewald, P.W. Evolutionary biology and the treatment of signs and symptoms of infectious disease. J. Theor. Biol. 1980, 86, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global antimicrobial resistance and use surveillance system (GLASS) report: 2022 (who.int)). Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240062702.
- Friedman, N.; Temkin, E.; Carmeli, Y. The negative impact of antibiotic resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 22, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spread of Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococci. New Engl. J. Med. 1953, 249, 711–713. [CrossRef]
- Finland, M.; Weinstein, L. Complications Induced by Antimicrobial Agents. New Engl. J. Med. 1953, 248, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sir Alexander Fleming – Banquet speech. NobelPrize.org. Available online: https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/medicine/1945/fleming/speech/.
- O’Neill, J. Antimicrobial resistance: tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations. London: Review on Antimicrobial Resistance, 2014.
- Abat, C.; Fournier, P.-E.; Jimeno, M.-T.; Rolain, J.-M.; Raoult, D. Extremely and pandrug-resistant bacteria extra-deaths: myth or reality? Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 1687–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abat, C.; Rolain, J.-M.; Dubourg, G.; Fournier, P.-E.; Chaudet, H.; Raoult, D. Evaluating the Clinical Burden and Mortality Attributable to Antibiotic Resistance: The Disparity of Empirical Data and Simple Model Estimations. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, S58–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet 2022; 399: 629–55 Published Online January 20, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Requires a Manifold Response - Medscape - Apr 07, 2023.
- Johnson, ET. Nosocomial infection: update. J Natl Med Assoc. 1983 Feb;75(2):147-54. PMID: 6827607; PMCID: PMC2561458.
- Miles, A.A. OBSERVATIONS ON THE CONTROL OF HOSPITAL INFECTION. Br. Med Bull. 1944, 2, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.E. Nosocomial infection a continuing problem. Postgrad. Med. 1977, 62, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, R. Nosocomial Infection Update. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1998, 4, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therapeutic evaluation of National Formulary drugs. Bull Am Pharm Assoc. 1946 Sep-Oct;14(9-10):161-204. [PubMed]
- Boetzkes, H. [The drug list of the American Hospital Formulary Service]. . 1961, 7, 114–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Letourneau, CU. The hospital drug formulary. I. Hosp Manage. 1961 Apr;91:38-9. [PubMed]
- Deuster, S.; Roten, I.; Muehlebach, S. Implementation of treatment guidelines to support judicious use of antibiotic therapy. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2010, 35, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sermet, C.; Andrieu, V.; Godman, B.; Van Ganse, E.; Haycox, A.; Reynier, J.-P. Ongoing pharmaceutical reforms in France. Appl. Heal. Econ. Heal. Policy 2010, 8, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuster, S.; Roten, I.; Muehlebach, S. Implementation of treatment guidelines to support judicious use of antibiotic therapy. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2010, 35, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastine, S.; Hsia, Y.; Clements, M.; Barker, C.I.; Bielicki, J.; Hartmann, C.; Sharland, M.; Standing, J.F. Variation in Target Attainment of Beta-Lactam Antibiotic Dosing Between International Pediatric Formularies. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 109, 958–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellit, T.H.; Owens, R.C.; McGowan, J.E.; Gerding, D.N.; Weinstein, R.A.; Burke, J.P.; Huskins, W.C.; Paterson, D.L.; Fishman, N.O.; Carpenter, C.F.; et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America Guidelines for Developing an Institutional Program to Enhance Antimicrobial Stewardship. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, S.; Rzewuska, M.; Duncan, E.; Ramsay, C. Identification of outcomes reported for hospital antimicrobial stewardship interventions using a systematic review of reviews. JAC-Antimicrobial Resist. 2022, 5, dlac127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garwan, Y.M.; Alsalloum, M.A.; Thabit, A.K.; Jose, J.; Eljaaly, K. Effectiveness of antimicrobial stewardship interventions on early switch from intravenous-to-oral antimicrobials in hospitalized adults: A systematic review. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2023, 51, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Sobalvarro, J.V.; Júnior, A.A.P.; Pereira, L.B.; Baldoni, A.O.; Ceron, C.S.; dos Reis, T.M. Antimicrobial stewardship for surgical antibiotic prophylaxis and surgical site infections: a systematic review. Pharm. Weekbl. 2021, 44, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selwyn, S. Hospital infection: the first 2500 years. J. Hosp. Infect. 1991, 18, 5–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, P.J.; Ali, M.; Rana, M.; Patel, G.; Sullivan, T.; Murphy, J.; Pinney, S.; Anyanwu, A.; Huprikar, S.; Taimur, S. Infections due to multidrug-resistant organisms following heart transplantation: Epidemiology, microbiology, and outcomes. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2019, 22, e13215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, B.; Wu, J.; Wan, Q.; Zhang, S.; Ye, Q. Factors influencing mortality in abdominal solid organ transplant recipients with multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteremia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, R.; Casella, T. Healthcare-associated infections in patients who are immunosuppressed due to chemotherapy treatment: a narrative review. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2022, 16, 1784–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitmann, L.; Gaudet, A.; Nseir, S. Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in Immunosuppressed Patients. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Zarza, J.; Álvarez-Hernández, E.; Casasola-Vargas, J.; Estrada-Castro, E.; Burgos-Vargas, R. Prevalence of community-acquired and nosocomial infections in hospitalized patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2009, 19, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo-Escobar, M.M.; Granda-Carvajal, P.A.M.; Aguirre-Acevedo, D.C.M.; Jaimes, F.M.; Vásquez, G.M. Predictive Factors of Hospital-Acquired Bacterial Infections in Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 29, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, F.; Evans, R.; Ghazal, P.; MacGowan, A. Patients with transplantation have reduced mortality in bacteraemia: Analysis of data from a randomised trial. J. Infect. 2022, 85, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Q.; Ye, Q.; Zhou, J. Mortality Predictors of Bloodstream Infections in Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients. Transplantation 2013, 11, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elward, A.M.; Fraser, V.J. Risk Factors for Nosocomial Primary Bloodstream Infection in Pediatric Intensive Care Unit Patients: A 2-Year Prospective Cohort Study. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiology 2006, 27, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lode, H. Combination versus monotherapy for nosocomial pneumonia. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2007, 16, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.Y.; Zhang, S.W.; Wu, J.D.; Wu, F.; Zhang, J.; Dong, J.T.; Guo, P.; Zhang, D.L.; Yang, J.T.; Zhang, W.J. Comparison of mono- and combination antibiotic therapy for the treatment of Pseudomonas�aeruginosa bacteraemia: A cumulative meta-analysis of cohort studies. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 2418–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogorelić, Z.; Silov, N.; Jukić, M.; Baloević, S.E.; Peričić, T.P.; Jerončić, A. Ertapenem Monotherapy versus Gentamicin Plus Metronidazole for Perforated Appendicitis in Pediatric Patients. Surg. Infect. 2019, 20, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigin, E.; Samuk, I.; Kravarusic, D.; Baazov, A.; Levy, I.; Livni, G.; Freud, E.; Dreznik, Y. Dual versus Triple Antibiotics Regimen in Children with Perforated Acute Appendicitis. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 28, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino’s The ICU Book International Edition (Paperback, Fourth, International Edition, LWW; Fourth, North American edition (, 2013). 5 November.
- Liu, X.; Long, Y.; Greenhalgh, C.; Steeg, S.; Wilkinson, J.; Li, H.; Verma, A.; Spencer, A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of risk factors associated with healthcare-associated infections among hospitalized patients in Chinese general hospitals from 2001 to2022. J. Hosp. Infect. 2023, 135, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/sinus-infection. html#:~:text=Most%20sinus%20infections%20usually%20get,to%20more%20serious%20health%20problems.
- Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/acute-sinusitis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20351677.
- Rosenfeld, R.M. Acute Sinusitis in Adults. New Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraki, S.; Mantadakis, E.; Mavromanolaki, V.E.; Kofteridis, D.P.; Samonis, G. A 5-year Surveillance Study on Antimicrobial Resistance ofAcinetobacter baumanniiClinical Isolates from a Tertiary Greek Hospital. Infect. Chemother. 2016, 48, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiz, T.A.; Alghamdi, S.S.; Mubaraki, M.A.; Alghamdi, S.S.; Alothaybi, A.; Aldawood, E.; Alotaibi, F. A two-year retrospective study of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii respiratory infections in critically Ill patients: Clinical and microbiological findings. J. Infect. Public Heal. 2023, 16, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-J.; Xiao, Z.-G.; Lv, X.-J.; Huang, H.-T.; Liao, C.; Hui, C.-Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.-F. Drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: From molecular mechanisms to potential therapeutics (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2023, 25, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elisa, M. Jukemura, Marcelo N. Burattini. Control of Multi-Resistant Bacteria and Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: Is It Possible with Changes in Antibiotics? The Brazilian Journal of Infectious Diseases 2007;11(4):418-422.
- Dat, V.Q.; Dat, T.T.; Hieu, V.Q.; Giang, K.B.; Otsu, S. Antibiotic use for empirical therapy in the critical care units in primary and secondary hospitals in Vietnam: a multicenter cross-sectional study. Lancet Reg. Heal. - West. Pac. 2021, 18, 100306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. World Health Organization; 2019. The 2019 WHO AWaRe classification of antibiotics for evaluation and monitoring of use. Geneva. 2019. Contract No.: WHO/EMP/IAU/2019.11.
- Rehab, H. El-sokkary, Shahenda G. Badran, Omnia S. El Seifi, Yara M. El-Fakharany, Rehab M. Elsaid Tash, El-sokkary et al. Antibiotic prescribing etiquette” an elective course for medical students: could we recruit potential physicians to fight resistance? BMC Medical Education (2023) 23:8).
- Tiseo, G.; Brigante, G.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Maraolo, A.E.; Gona, F.; Falcone, M.; Giannella, M.; Grossi, P.; Pea, F.; Rossolini, G.M.; et al. Diagnosis and management of infections caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria: guideline endorsed by the Italian Society of Infection and Tropical Diseases (SIMIT), the Italian Society of Anti-Infective Therapy (SITA), the Italian Group for Antimicrobial Stewardship (GISA), the Italian Association of Clinical Microbiologists (AMCLI) and the Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM). Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2022, 60, 106611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kish, T. New Antibiotics in Development Target Highly Resistant Gram-Negative Organisms. 2018, 43, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karvouniaris, M.; Almyroudi, M.P.; Abdul-Aziz, M.H.; Blot, S.; Paramythiotou, E.; Tsigou, E.; Koulenti, D. Novel Antimicrobial Agents for Gram-Negative Pathogens. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provenzani, A.; Hospodar, A.R.; Meyer, A.L.; Vinci, D.L.; Hwang, E.Y.; Butrus, C.M.; Polidori, P. Multidrug-resistant gram-negative organisms: a review of recently approved antibiotics and novel pipeline agents. Pharm. Weekbl. 2020, 42, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, D.L. “Collateral Damage” from Cephalosporin or Quinolone Antibiotic Therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, S341–S345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertsalmi, T.H.; Pekkonen, E.; Scheperjans, F. Antibiotic Exposure and Risk of Parkinson’s Disease in Finland: A Nationwide Case-Control Study. Mov. Disord. 2019, 35, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, L.; Goemans, C.V.; Wirbel, J.; Kuhn, M.; Eberl, C.; Pruteanu, M.; Müller, P.; Garcia-Santamarina, S.; Cacace, E.; Zhang, B.; et al. Unravelling the collateral damage of antibiotics on gut bacteria. Nature 2021, 599, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubser, C.; Liese, J.; Serna-Higuita, L.M.; Müller, A.; Vochem, M.; Arand, J.; Karck, U.; Gross, M.; Poets, C.F.; Härtel, C.; et al. Impact of early antibiotic exposure on the risk of colonization with potential pathogens in very preterm infants: a retrospective cohort analysis. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2022, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melenotte, C.; Pontarotti, P.; Pinault, L.; Mège, J.-L.; Devaux, C.; Raoult, D. Could β-Lactam Antibiotics Block Humoral Immunity? Front. Immunol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atamna, A.; Eliakim-Raz, N.; Mohana, J.; Ben-Zvi, H.; Sorek, N.; Shochat, T.; Bishara, J. Predicting candidemia in the internal medicine wards: a comparison with gram-negative bacteremia—a retrospectives study. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 95, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torosantucci, A.; Tumbarello, M.; Bromuro, C.; Chiani, P.; Posteraro, B.; Sanguinetti, M.; Cauda, R.; Cassone, A. Antibodies against a β-glucan-protein complex of Candida albicans and its potential as indicator of protective immunity in candidemic patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilov, A.I. , Alekseeva I.V., Asner T.V., Vlasova E.E., Danilova E.M., Dehnich A.V. i soavt. Jetiologija infekcionnogo jendokardita v Rossii. Klin Mikrobiol Antimikrob Khimioter. 2015; 17 (1): 4–10.
- Belov, B.S. Acute rheumatic fever and chronic rheumatic heart disease. From: Rational Pharmacotherapy of Cardiovascular Diseases: Guide for Practitioners / edited by E.I. Chazov, Yu.A. Karpov - 2nd ed., amended and suppl. M, Litterra, 2017. 623-632.
- Carapetis, J.R.; Steer, A.C.; Mulholland, E.K.; Weber, M. The global burden of group A streptococcal diseases. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, D.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Colquhoun, S.M.; Karthikeyan, G.; Beaton, A.; Bukhman, G.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Longenecker, C.T.; Mayosi, B.M.; Mensah, G.A.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Rheumatic Heart Disease, 1990–2015. New Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dooley, L.M.; Ahmad, T.B.; Pandey, M.; Good, M.F.; Kotiw, M. Rheumatic heart disease: A review of the current status of global research activity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 20, 102740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Xu, W.; Wu, S.; Zhang, J. Rheumatic heart disease burden, trends, and inequalities in Asia, 1990–2019. Glob. Heal. Action 2023, 16, 2215011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvind, B.; Ramakrishnan, S. Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease in Children. Indian J. Pediatr. 2020, 87, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedo, S.E.; Leonard, H.L.; Garvey, M.A.; Mittleman, B.B.; Allen, A.J.; Dow, S.; Zamkoff, J.; Dubbert, B.K.; Lougee, L.; Colvin, M.K.; et al. Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated With Streptococcal Infections: Clinical Description of the First 50 Cases. Am. J. Psychiatry 1998, 155, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPenta, D.; Rubens, C.; Chi, E.; Cleary, P.P. Group A streptococci efficiently invade human respiratory epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1994, 91, 12115–12119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, R.; De Martino, L.; Donnarumma, G.; Conte, M.; Seganti, L.; Valenti, P. Invasion of cultured human cells by Streptococcus pyogenes. Res. Microbiol. 1995, 146, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohde M, Cleary PP. Adhesion and invasion of Streptococcus pyogenes into host cells and clinical relevance of intracellular streptococci. 2022 Sep 4 [updated 2022 Oct 4]. In: Ferretti JJ, Stevens DL, Fischetti VA, editors. Streptococcus pyogenes: Basic Biology to Clinical Manifestations [Internet]. 2nd ed. Oklahoma City (OK): University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center; 2022 Oct 8. Chapter 17. [PubMed]
- Herman, J. Medicine and evolution: time for a new paradigm? Med Hypotheses 1997, 48, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rühli, F.J.; Henneberg, M. New perspectives on evolutionary medicine: the relevance of microevolution for human health and disease. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 115–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauduer, F. La médecine évolutionniste : un nouveau regard sur la santé et les maladies. La Rev. de Médecine Interne 2017, 38, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katelaris, P.; Hunt, R.; Bazzoli, F.; Cohen, H.; Fock, K.M.; Gemilyan, M.; Malfertheiner, P.; Mégraud, F.; Piscoya, A.; Quach, D.; et al. Helicobacter pylori World Gastroenterology Organization Global Guideline. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2022, 57, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mégraud, F.; Graham, D.Y.; Howden, C.W.; Trevino, E.; Weissfeld, A.; Hunt, B.; Smith, N.; Leifke, E.; Chey, W.D. Rates of Antimicrobial Resistance in Helicobacter pylori Isolates From Clinical Trial Patients Across the US and Europe. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 118, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Time to Ditch Clarithromycin for H pylori? - Medscape – Oct 21, 2022.
- Usui, Y.; Taniyama, Y.; Endo, M.; Koyanagi, Y.N.; Kasugai, Y.; Oze, I.; Ito, H.; Imoto, I.; Tanaka, T.; Tajika, M.; et al. Helicobacter pylori, Homologous-Recombination Genes, and Gastric Cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



