Submitted:
31 May 2023
Posted:
01 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Principle of cancer theranostics
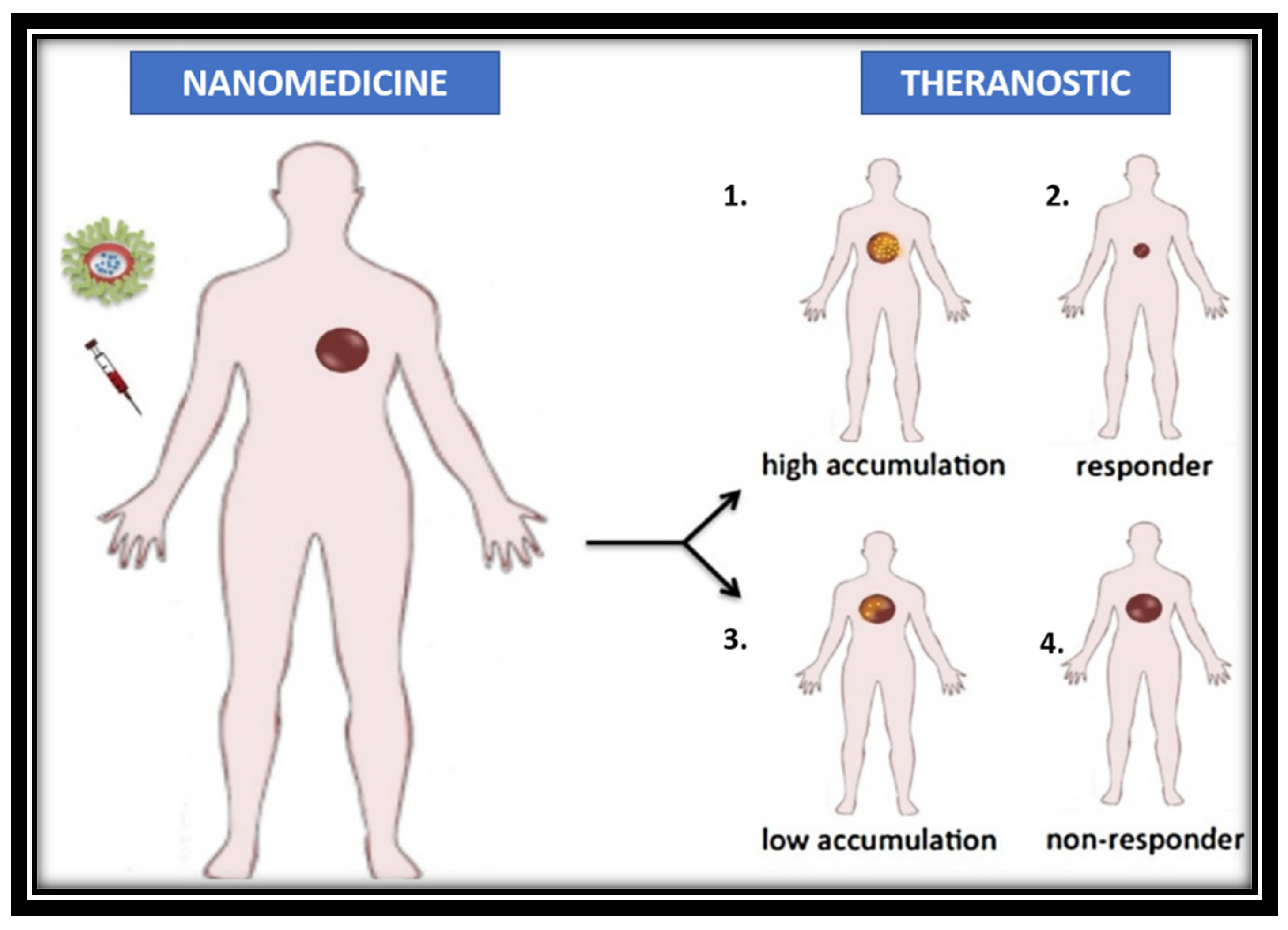
3. Application of cancer theranostics
| Contrast Agent | Drug used | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Gold | DOX | Diagnosis, tumour targeting and PTT |
| Silica | Pyro pheophorbide (HPPH), DOX | Drug carrier, X-ray/CT imaging, Photodynamic therapy |
| Manganese oxide | siRNA | MRI plus RNA delivery |
| CNTs | DNA plasmid, DOX, PTX | Diagnosis, DNA and drug delivery |
| QDs | DOX, MTX | Imaging, therapy and sensing |
| Iron oxide | siRNA, DOX, docetaxel | Targeting, MRI and therapy |
3.1. Quantum dots
3.2. Liposomes
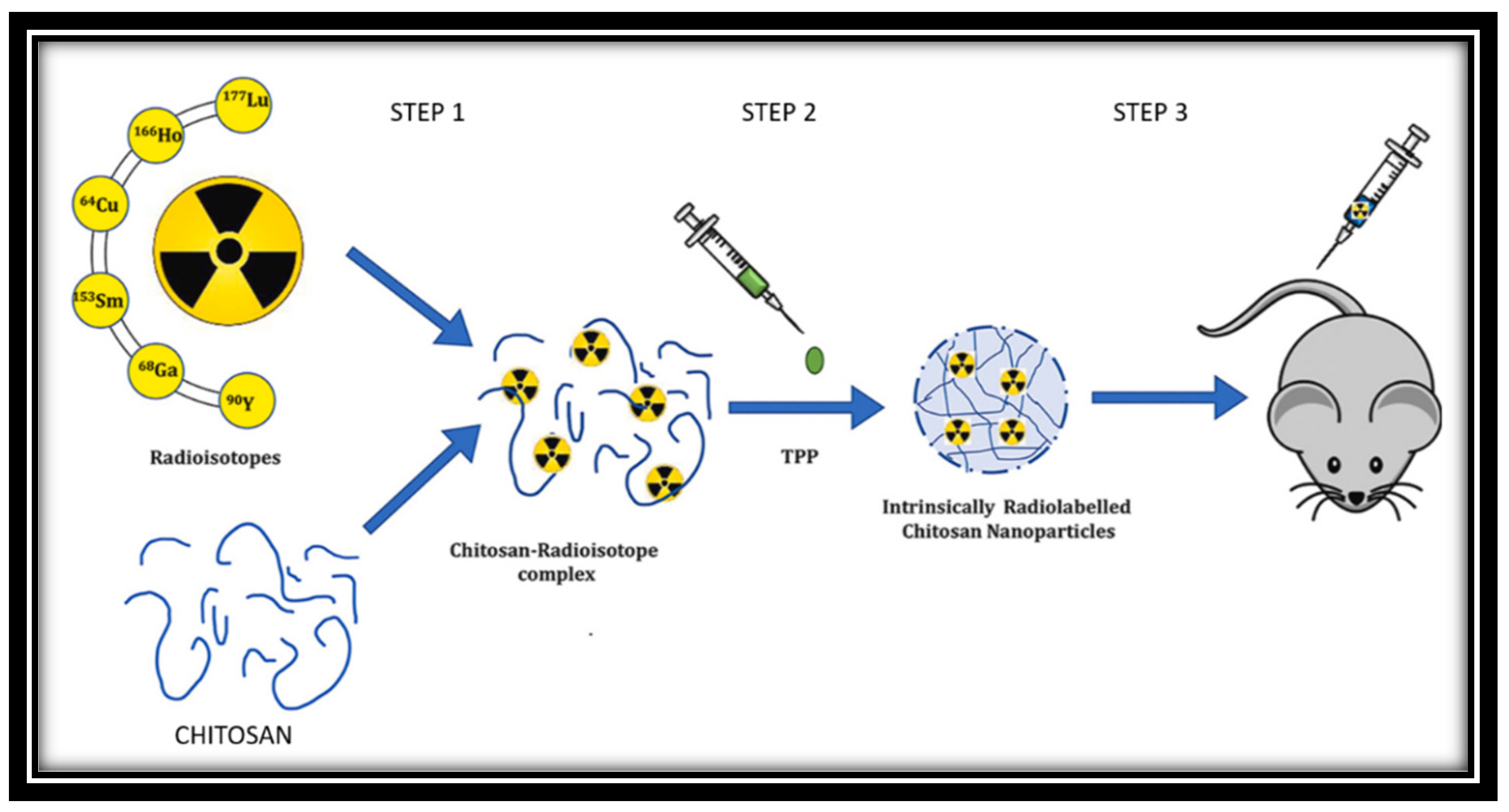
3.3. Radioisotopes
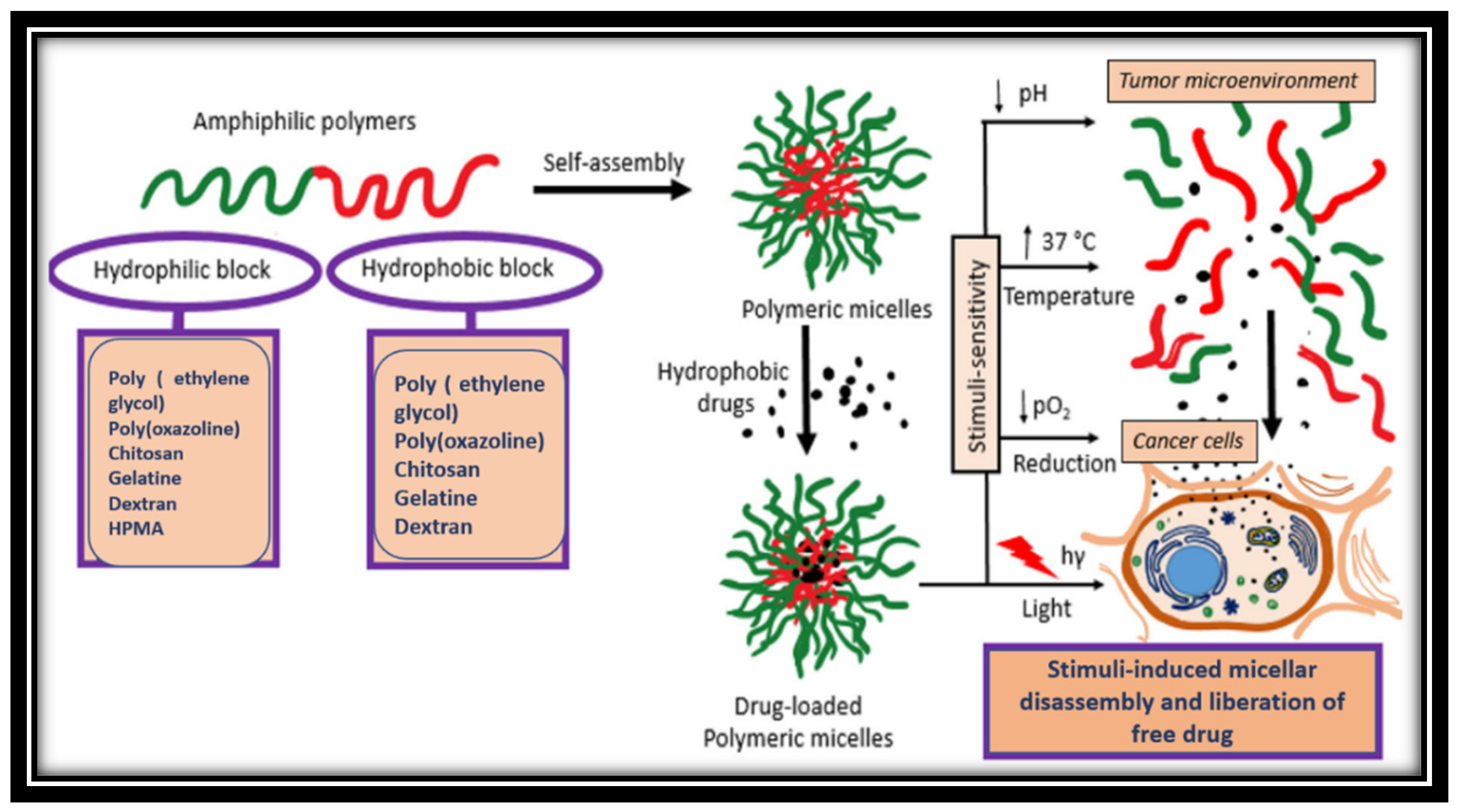
3.4. Micelles
3.5. Nanobubbles
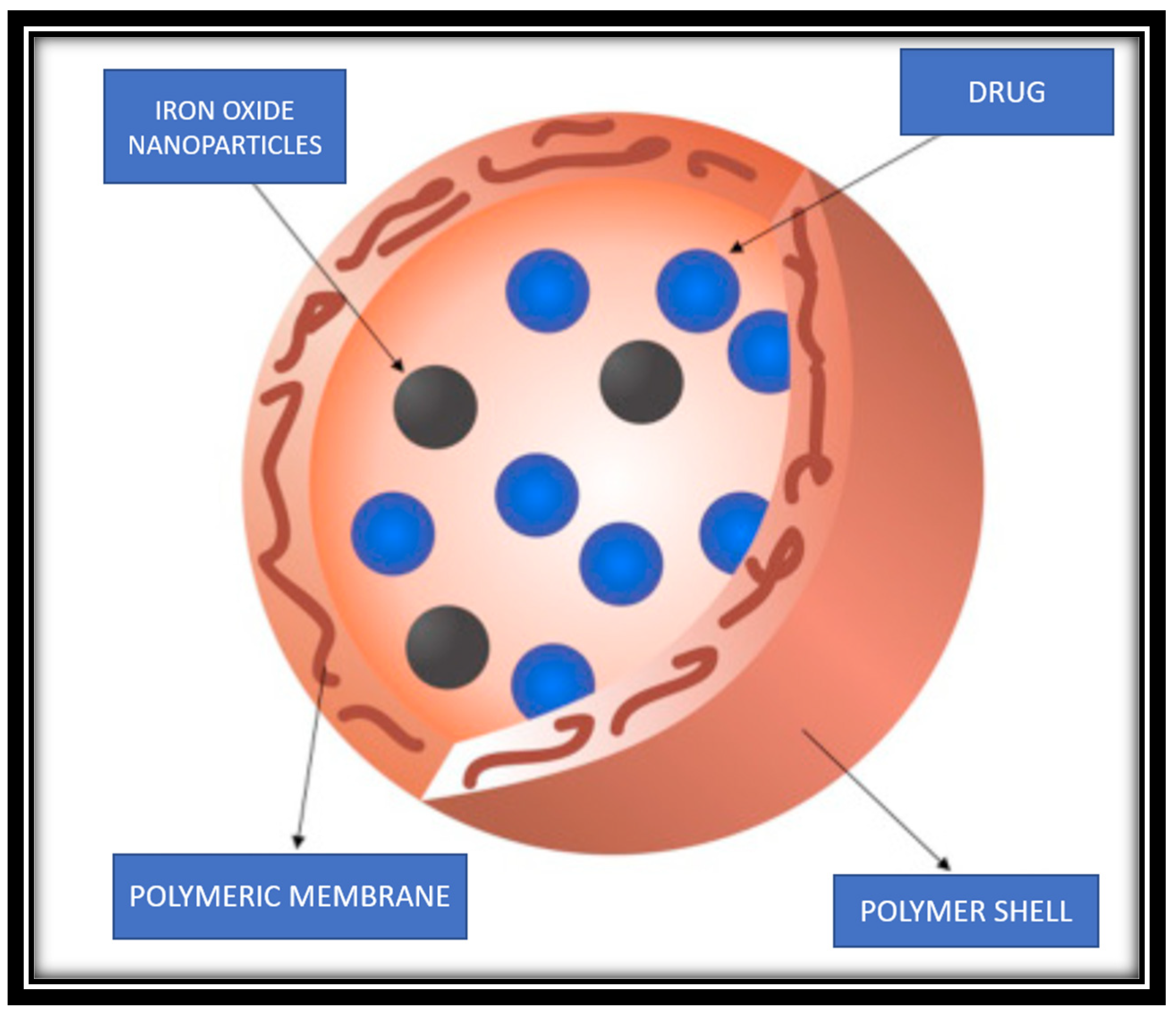
3.6. Diagnosis using cancer theranostics
4. Clinical trials of cancer theranostics
| PROJECT | CONSORTIUM | AIM |
|---|---|---|
| Vibrant | 10 groups | Contrast agent for pancreatic beta-cell imaging in diabetes Mellitus type I |
| Magnifyco | 11 groups | Magnetic nanoparticles have the potential to be used theranostically to treat ovarian cancer. |
| SaveMe | 19 groups | Nano core platforms to advance cancer treatment and diagnosis |
| NAD | 19 groups | Alzheimers’ treatment |
| Namdiatream | 22 groups | Molecular biomarker and detection |
| Multifun | 15 groups | Breast and pancreatic cancer early detection using iron oxide nanoparticles with cancer stem cells |
| Nanomagdye | 8 groups | Iron oxide nanoparticles as a new contrast agent in cancer patients' lymph node imaging |
| Responses | TACE group (n=32) | TACE+HIFU group (n=25) |
|---|---|---|
| SD | 4(13%) | 5(20%) |
| CR | 9(28%) | 5(20%) |
| PD | 17(53%) | 13(52%) |
| PR | 2(6%) | 2(8%) |
| Disease control rate | 15/32(47%) | 12/25(48%) |
5. Limitations and challenges
6. Discussion
7. Conclusion
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavas, S.; Quazi, S.; Karpiński, T.M. Nanoparticles for cancer therapy: current progress and challenges. Nanoscale research letters 2021, 16, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, K.; Zunbul, Z.; Lee, I.; Kim, E.; Chi, S.G.; Kim, J.S. Covalent organic framework nanomedicines: Biocompatibility for advanced nanocarriers and cancer theranostics applications. Bioactive Materials 2023, 21, 358–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, K.; Zunbul, Z.; Lee, I.; Kim, E.; Chi, S.G.; Kim, J.S. Covalent organic framework nanomedicines: Biocompatibility for advanced nanocarriers and cancer theranostics applications. Bioactive Materials 2023, 21, 358–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, M.; Liu, W.; Gref, R. Nanoscale MOFs: From synthesis to drug delivery and theranostics applications. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2022, 114496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Ma, K.; Wang, D.; Su, L.; Zhang, X.; Tang, B.Z. Nanolab in a Cell: Crystallization-Induced In Situ Self-Assembly for Cancer Theranostic Amplification. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2022, 144, 14388–14395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.G.; Liu, S.L.; Pang, D.W. Near-Infrared-II Quantum Dots for In Vivo Imaging and Cancer Therapy. Small 2022, 18, 2104567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, F.; Avatefi, M.; Moghadam, N.B.; Asghari, S.; Ekrami, E.; Mahmoudifard, M. A review of graphene quantum dots and their potential biomedical applications. Journal of Biomaterials Applications 2023, 37, 1137–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campora, S.; Ghersi, G. Recent developments and applications of smart nanoparticles in biomedicine. Nanotechnology Reviews 2022, 11, 2595–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavda, V.P.; Vihol, D.; Mehta, B.; Shah, D.; Patel, M.; Vora, L.K.; Pereira-Silva, M.; Paiva-Santos, A.C. Phytochemical-loaded liposomes for anticancer therapy: An updated review. Nanomedicine 2022, 17, 547–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karges, J. Clinical development of metal complexes as photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy of cancer. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2022, 61, e202112236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, Y.; Zhang, P.; Lai, W.F.; Zhang, D. Design and applications of liposome-in-gel as carriers for cancer therapy. Drug Delivery 2022, 29, 3245–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, J.; Gulati, M.; Jha, N.K.; Disouza, J.; Patravale, V.; Dua, K.; Singh, S.K. Recent advances in developing polymeric micelles for treating cancer: Breakthroughs and bottlenecks in their clinical translation. Drug Discovery Today 2022. [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Tian, W.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, J.; He, Q.; Tang, Z.; Shen, W.; Wang, J. A dual drug delivery platform based on thermo-responsive polymeric micelle capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 2022, 338, 111943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.; Choudhary, S. Physicochemical insights into the micelle-based drug-delivery of bioactive compounds to the carrier protein. New Journal of Chemistry 2022, 46, 19124–19135. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S. and Streeter, P.R., 2022. Micelle-Based Nanocarriers for Targeted Delivery of Cargo to Pancreas. In Type-1 Diabetes: Methods and Protocols (pp. 175-184). New York, NY: Springer US. [CrossRef]
- Siddique, S.; Chow, J.C. Recent advances in functionalized nanoparticles in cancer theranostics. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khursheed, R.; Dua, K.; Vishwas, S.; Gulati, M.; Jha, N.K.; Aldhafeeri, G.M.; Alanazi, F.G.; Goh, B.H.; Gupta, G.; Paudel, K.R.; Hansbro, P.M. Biomedical applications of metallic nanoparticles in cancer: Current status and future perspectives. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2022, 150, 112951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.; Khurana, S.; Choudhari, R.; Kesari, K.K.; Kamal, M.A.; Garg, N.; Ruokolainen, J.; Das, B.C.; Kumar, D. Specific targeting cancer cells with nanoparticles and drug delivery in cancer therapy. In Seminars in cancer biology 2021, 69, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, D.; Kiselev, M.A. Methods of liposomes preparation: formation and control factors of versatile nanocarriers for biomedical and nanomedicine application. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, N.; Lin, X.; Xie, M.; Zeng, D. Effect of surface ligand modification on the properties of anti-tumor nanocarrier. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2022, 112944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, M.I.; Lopes, C.M.; Amaral, M.H.; Costa, P.C. Surface-modified lipid nanocarriers for crossing the blood-brain barrier (BBB): a current overview of active targeting in brain diseases. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2022, 112999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soman, S.; Kulkarni, S.; Pandey, A.; Dhas, N.; Subramanian, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Mutalik, S. 2D Hetero-Nanoconstructs of Black Phosphorus for Breast Cancer Theragnosis: Technological Advancements. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.; Heo, Y.J.; Han, D.K. New opportunities for nanoparticles in cancer immunotherapy. Biomaterials research 2018, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasirmoghadas, P.; Mousakhani, A.; Behzad, F.; Beheshtkhoo, N.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Nikoo, M.; Mehrabi, M.; Kouhbanani, M.A.J. Nanoparticles in cancer immunotherapies: An innovative strategy. Biotechnology progress 2021, 37, e3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargazi, S.; Laraib, U.; Er, S.; Rahdar, A.; Hassanisaadi, M.; Zafar, M.N.; Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Bilal, M. Application of green gold nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasan, M.S. Cytology of a spontaneous triploid Coffea canephora Pierre ex Froehner. Caryologia 1981, 34, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jortner, J. and Ratner, M.A. eds., 1997. Molecular electronics (p. 255). Oxford: Blackwell Science.
- Kastner, M.A. Mesoscopic physics and artificial atoms. AIP Conference Proceedings 1993, 275, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, C.P.; Vossmeyer, T.; Heath, J.R. Nanoparticles Superlattices. Anu. Rev. Phys. Phys. Chem 1998, 49, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.K.; Sahu, M.; Kumar, G.; Ashourian, M. Pivotal Role of Quantum Dots in the Advancement of Healthcare Research. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience 2021, 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malavika, J.P.; Shobana, C.; Sundarraj, S.; Ganeshbabu, M.; Kumar, P.; Selvan, R.K. Green synthesis of multifunctional carbon quantum dots: An approach in cancer theranostics. Biomaterials Advances 2022, 212756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhas, N.; Pastagia, M.; Sharma, A.; Khera, A.; Kudarha, R.; Kulkarni, S.; Soman, S.; Mutalik, S.; Barnwal, R.P.; Singh, G.; Patel, M. Organic quantum dots: An ultrasmall nanoplatform for cancer theranostics. Journal of Controlled Release 2022, 348, 798–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.L.; Liu, H.R.; Lou, Q.; Wang, F.; Liu, K.K.; Dong, L.; Shan, C.X. Recent progress of carbon dots in targeted bioimaging and cancer therapy. Theranostics 2022, 12, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, S.; Kumar, M.; Tiwari, A.; Tiwari, V.; Kaushik, D.; Verma, R.; Bhatt, S.; Sahoo, B.M.; Bhattacharya, T.; Alshehri, S.; Ghoneim, M.M. Quantum dots: An emerging approach for cancer therapy. Frontiers in Materials 2022, 8, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Da Silva, C.G.; Van der Maaden, K.; Ossendorp, F.; Cruz, L.J. Liposome-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Cancer Immunotherapy. Pharmaceutics. 2020, 12, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.; Hu, X.L.; Saeed, M.; Chen, B.F.; Li, Y.P.; Yu, H.J. Overview of recent advances in liposomal nanoparticle-based cancer immunotherapy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zununi Vahed, S.; Salehi, R.; Davaran, S.; Sharifi, S. Liposome-based drug co-delivery systems in cancer cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 1327–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.J.; Masin, D.; Madden, T.D.; Bally, M.B. Influence of drug release characteristics on the therapeutic activity of liposomal mitoxantrone. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 1997, 281, 566–573. [Google Scholar]
- Forssen, E.A.; Male-Brune, R.; Adler-Moore, J.P.; Lee, M.J.A.; Schmidt, P.G.; Krasieva, T.B.; Shimizu, S.; Tromberg, B.J. Fluorescence imaging studies for the disposition of daunorubicin liposomes (DaunoXome) within tumor tissue. Cancer research 1996, 56, 2066–2075. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krishna, R.; Webb, M.S.; Onge, G.S.; Mayer, L.D. Liposomal and nonliposomal drug pharmacokinetics after administration of liposome-encapsulated vincristine and their contribution to drug tissue distribution properties. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2001, 298, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhigaltsev, I.V.; Maurer, N.; Akhong, Q.F.; Leone, R.; Leng, E.; Wang, J.; Semple, S.C.; Cullis, P.R. Liposome-encapsulated vincristine, vinblastine and vinorelbine: a comparative study of drug loading and retention. Journal of controlled release 2005, 104, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.C.; Ozols, R.F.; Myers, C.E. The anthracycline antineoplastic drugs. New England Journal of Medicine 1981, 305, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, J.W.; Deamer, D.W. Catecholamine uptake and concentration by liposomes maintaining pH gradients. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes 1976, 455, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, L.D.; Bally, M.B.; Hope, M.J.; Cullis, P.R. Uptake of antineoplastic agents into large unilamellar vesicles in response to a membrane potential. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes 1985, 816, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, T.D.; Harrigan, P.R.; Tai, L.C.; Bally, M.B.; Mayer, L.D.; Redelmeier, T.E.; Loughrey, H.C.; Tilcock, C.P.; Reinish, L.W.; Cullis, P.R. The accumulation of drugs within large unilamellar vesicles exhibiting a proton gradient: a survey. Chemistry and physics of lipids 1990, 53, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasic, D.D.; Frederik, P.M.; Stuart, M.C.A.; Barenholz, Y.; McIntosh, T.J. Gelation of liposome interior A novel method for drug encapsulation. FEBS letters 1992, 312, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANDREWS, G.A. A few notions involved in the clinical use of radioisotopes. Annals of Internal Medicine 1957, 47, 922–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otuka, N.; Takács, S. Definitions of radioisotope thick target yields. Radiochimica Acta 2015, 103, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnaduwage, D.S.; Srivastava, S.P.; Yan, X.; Jani, S.; Brachman, D.G.; Sorensen, S.P. Dosimetric impacts of source migration, radioisotope type, and decay with permanent implantable collagen tile brachytherapy for brain tumors. Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment 2022, 21, 15330338221106852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculae, D.; Dusman, R.; Leonte, R.A.; Chilug, L.E.; Dragoi, C.M.; Nicolae, A.; Serban, R.M.; Niculae, D.A.; Dumitrescu, I.B.; Draganescu, D. Biological pathways as substantiation of the use of copper radioisotopes in cancer theranostics. Frontiers in Physics 2021, 8, 568296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vretenar, M.; Mamaras, A.; Bisoffi, G.; Foka, P. Production of radioisotopes for cancer imaging and treatment with compact linear accelerators. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2023, 2420, 012104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, G.; Rohra, N.; Kumar, C.; Jadhav, S.; Sarma, H.D.; Borade, L.; Chakraborty, S.; Bhagwat, S.; Dandekar, P.; Jain, R.; Chakravarty, R. A facile strategy for synthesis of a broad palette of intrinsically radiolabeled chitosan nanoparticles for potential use in cancer theranostics. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 2021, 63, 102485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Biswas, S. Polymeric micelles in cancer therapy: State of the art. Journal of Controlled Release 2021, 332, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, M.; Pavlopoulou, A.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Kyrodimos, E. The challenge of drug resistance in cancer treatment: a current overview. Clinical & Experimental Metastasis 2018, 35, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, R.R.; Torchilin, V.P. Multifunctionality of lipid-core micelles for drug delivery and tumour targeting. Molecular membrane biology 2010, 27, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, D.; Tezcaner, A. Micelles as delivery system for cancer treatment. Current Pharmaceutical Design 2017, 23, 5230–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.; Son, S.; Park, K.S.; Zou, W.; Shea, L.D.; Moon, J.J. Cancer nanomedicine for combination cancer immunotherapy. Nature Reviews Materials 2019, 4, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Zheng, R.; Moharil, P.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, R.; Song, X.; Ao, Q. Polymeric micelles in cancer immunotherapy. Molecules 2021, 26, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Min, Y.; Rodgers, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, A.Z. Nanomedicine approaches to improve cancer immunotherapy. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology 2017, 9, e1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusoff, A.H.M.; Salimi, M.N. Superparamagnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Applications of Nanocomposite Materials in Drug Delivery 2018, 843–859. [Google Scholar]
- Lapotko, D. Plasmonic nanobubbles as tunable cellular probes for cancer theranostics. Cancers 2011, 3, 802–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, A.D.; Wu, Z.; Thakur, S.S. A comprehensive update of micro-and nanobubbles as theranostics in oncology. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 2022. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.C.; Chua, Q.W.; Ong, X.J.; Sharma, V.K.; Tong, Y.W.; Wang, C.H. Fabrication of ultrasound-responsive microbubbles via coaxial electrohydrodynamic atomization for triggered release of tPA. Journal of colloid and interface science 2017, 501, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wande, D.P.; Trevaskis, N.; Farooq, M.A.; Jabeen, A.; Nayak, A.K. Theranostic nanostructures as nanomedicines: benefits, costs, and future challenges. Design and Applications of 2023, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, S.; Sharma, D.; Kalia, K.; Tekade, R.K. Tumor microenvironment targeted nanotherapeutics for cancer therapy and diagnosis: A review. Acta biomaterialia 2020, 101, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, B.; Chen, Q.; Sun, J.; He, Z.; Luo, C. Nanotherapeutics for antimetastatic treatment. Trends in Cancer 2020, 6, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu, M.S.; Leong, D.T.; Mei, L.; Feng, S.S. Nanotheranostics˗ application and further development of nanomedicine strategies for advanced theranostics. Theranostics 2014, 4, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, F.; Asad, M.I.; Qindeel, M.; Afzal, I.; Dar, M.J.; Shah, K.U.; Zeb, A.; Khan, G.M.; Ahmed, N.; Din, F.U. Polymeric nanogels as versatile nanoplatforms for biomedical applications. Journal of nanomaterials 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Li, Q.; Zhao, C.; Lu, J.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Deng, X.; Ge, G.; Wu, Y. Auto-fluorescent polymer nanotheranostics for self-monitoring of cancer therapy via triple-collaborative strategy. Biomaterials 2019, 194, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panigrahi, B.K.; Nayak, A.K. Carbon nanotubes: an emerging drug delivery carrier in cancer therapeutics. Current Drug Delivery 2020, 17, 558–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.M.; Wang, J.T.W.; Morfin, J.F.; Khanum, T.; To, W.; Sosabowski, J.; Tóth, E.; Al-Jamal, K.T. Functionalised carbon nanotubes enhance brain delivery of amyloid-targeting Pittsburgh compound B (PiB)-derived ligands. Nanotheranostics 2018, 2, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.T.; Hodgins, N.O.; Maher, J.; Sosabowski, J.K.; Al-Jamal, K.T. Organ biodistribution of radiolabelled γδ T cells following liposomal alendronate administration in different mouse tumour models. Nanotheranostics 2020, 4, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medalsy, I.; Dgany, O.; Sowwan, M.; Cohen, H.; Yukashevska, A.; Wolf, S.G.; Wolf, A.; Koster, A.; Almog, O.; Marton, I.; Pouny, Y. SP1 protein-based nanostructures and arrays. Nano letters 2008, 8, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wen, S.; Shen, M.; Shi, X. Multifunctional lactobionic acid-modified dendrimers for targeted drug delivery to liver cancer cells: investigating the role played by PEG spacer. ACS applied materials & interfaces 2014, 6, 16416–16425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Meza, L.R.; Greer, F.; Greer, J.R. Fabrication and deformation of three-dimensional hollow ceramic nanostructures. Nature materials 2013, 12, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardhian, D.F.; Vrynas, A.; Storm, G.; Bansal, R.; Prakash, J. FGF2 engineered SPIONs attenuate tumor stroma and potentiate the effect of chemotherapy in 3D heterospheroidal model of pancreatic tumor. Nanotheranostics 2020, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, S.Y.; Su, Y.L.; Cheng, W.; Hu, P.F.; Chiang, C.S.; Chen, W.T.; Hu, S.H. Graphene quantum dots-mediated theranostic penetrative delivery of drug and photolytics in deep tumors by targeted biomimetic nanosponges. Nano letters 2018, 19, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sahoo, S.K. Magnetic nanoparticles: a novel platform for cancer theranostics. Drug discovery today 2014, 19, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, K.K.; Rabha, B.; Pati, S.; Sarkar, T.; Choudhury, B.K.; Barman, A.; Bhattacharjya, D.; Srivastava, A.; Baishya, D.; Edinur, H.A.; Abdul Kari, Z. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using plant extracts as beneficial prospect for cancer theranostics. Molecules 2021, 26, 6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kargozar, S.; Mollazadeh, S.; Kermani, F.; Webster, T.J.; Nazarnezhad, S.; Hamzehlou, S.; Baino, F. Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for improved cancer theranostics. Journal of Functional Biomaterials 2022, 13, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Yin, J.; Chen, Y.; Pan, S.; Yao, H.; Gao, Y.; Shi, J. 2D-black-phosphorus-reinforced 3D-printed scaffolds: a stepwise countermeasure for osteosarcoma. Advanced Materials 2018, 30, 1705611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Tang, W.; Hu, L.; Chen, X.; Su, Y.; Zou, C.; Wang, J.; Lu, W.W.; Zhen, W.; Zhang, R. Multifunctional nanoengineered hydrogels consisting of black phosphorus nanosheets upregulate bone formation. Small 2019, 15, 1901560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, S.; Pan, T.; Zhou, W.; Cui, H.; Wu, L.; Li, Z.; Chu, P.K.; Yu, X.F. Bioactive phospho-therapy with black phosphorus for in vivo tumor suppression. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, X.; Liang, D.; Liang, X.; Mi, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, J. Gold nanobipyramid-loaded black phosphorus nanosheets for plasmon-enhanced photodynamic and photothermal therapy of deep-seated orthotopic lung tumors. Acta Biomaterialia 2020, 107, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, H.; Shao, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, F.; Lin, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Huang, P. Polydopamine-functionalized black phosphorus quantum dots for cancer theranostics. Applied Materials Today 2019, 15, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, P.; Wang, C.; Miao, W.; Huang, H. Black phosphorus nanophototherapeutics with enhanced stability and safety for breast cancer treatment. Chemical Engineering Journal 2020, 400, 125851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Shi, Y.; Zou, J.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, W.; Shao, J.; Xie, X.; Dong, X. Black phosphorus nanosheets immobilizing Ce6 for imaging-guided photothermal/photodynamic cancer therapy. ACS applied materials & interfaces 2018, 10, 12431–12440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, S.T.; Hall, J.B.; Lee, L.Y.; Wood, L.J.; Paciotti, G.F.; Tamarkin, L.; Long, S.E.; McNeil, S.E. Translational considerations for cancer nanomedicine. Journal of Controlled Release 2010, 146, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Hirst, D.G.; O'Sullivan, J. Gold nanoparticles as novel agents for cancer therapy. The British journal of radiology 2012, 85, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staves, B. Pilot study of AurolaseTM therapy in refractory and/or recurrent tumors of the head and neck. ClinicalTrials. gov Identifier: NCT00848042, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sayed, I.H. Nanotechnology in head and neck cancer: the race is on. Current oncology reports 2010, 12, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, E.S., Morton, J.G. and West, J.L., 2009. Nanoparticles for thermal cancer therapy. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Chung, D.J.; Jung, S.E.; Cho, S.H.; Hahn, S.T.; Lee, J.M. Therapeutic effect of high-intensity focused ultrasound combined with transarterial chemoembolisation for hepatocellular carcinoma< 5 cm: comparison with transarterial chemoembolisation monotherapy—preliminary observations. The British journal of radiology 2012, 85, e940–e946. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sargazi, S.; Laraib, U.; Er, S.; Rahdar, A.; Hassanisaadi, M.; Zafar, M.N.; Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Bilal, M. Application of green gold nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhosi, S.R.; Mdlalose, W.; Nhlapo, A.; Singh, M. Advances in the synthesis and application of magnetic ferrite nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.Z.; Rizwanullah, M.; Ahmad, J.; Alasmary, M.Y.; Akhter, M.H.; Abdel-Wahab, B.A.; Warsi, M.H.; Haque, A. Progress in nanomedicine-based drug delivery in designing of chitosan nanoparticles for cancer therapy. International Journal of Polymeric Materials and Polymeric Biomaterials 2022, 71, 602–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, F.; Gigli, G.; Leporatti, S. Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles in cancer therapy: Current overview and future directions. Nano Express 2021, 2, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodley, T.; Singh, M. Current stimuli-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.I.; Imam, S.S.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Vuddanda, P.R.; Alshehri, S.; Mahdi, W.A.; Ahmad, J. Recent progress in lipid nanoparticles for cancer theranostics: opportunity and challenges. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, V.; Singh, K.R.; Verma, R.; Pandey, M.D.; Singh, J.; Singh, R.P. Recent advancements of biogenic iron nanoparticles in cancer theranostics. Materials Letters 2022, 313, 131769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.W.; Tsao, H.Y.; Chiang, C.S.; Chen, S.Y. Advances in magnetic nanoparticle-mediated cancer immune-theranostics. Advanced healthcare materials 2021, 10, 2001451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calero, M.; Chiappi, M.; Lazaro-Carrillo, A.; Rodríguez, M.J.; Chichón, F.J.; Crosbie-Staunton, K.; Prina-Mello, A.; Volkov, Y.; Villanueva, A.; Carrascosa, J.L. Characterization of interaction of magnetic nanoparticles with breast cancer cells. Journal of nanobiotechnology 2015, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, A.; Canete, M.; Roca, A.G.; Calero, M.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S.; Serna, C.J.; del Puerto Morales, M.; Miranda, R. The influence of surface functionalization on the enhanced internalization of magnetic nanoparticles in cancer cells. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 115103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Rojas, G.G.; López-Saucedo, F.; Vera-Graziano, R.; Mendizabal, E.; Bucio, E. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Medical Applications: Updated Review. Macromol 2022, 2, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, H.; Shukrullah, S.; Naz, M.Y.; Fatima, H.; Hussain, H.; Ullah, S.; Assiri, M.A. Current and future perspectives of multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles based controlled drug delivery systems. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 2022, 67, 102946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanicki, D.; Vangijzegem, T.; Ternad, I.; Laurent, S. An update on the applications and characteristics of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for drug delivery. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery 2022, 19, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Rojas, G.G.; López-Saucedo, F.; Vera-Graziano, R.; Mendizabal, E.; Bucio, E. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Medical Applications: Updated Review. Macromol 2022, 2, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo-Takahashi, Y.; Negishi, Y. Gene and oligonucleotide delivery via micro-and nanobubbles by ultrasound exposure. Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 2022, 100445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bismuth, M.; Katz, S.; Mano, T.; Aronovich, R.; Hershkovitz, D.; Exner, A.A.; Ilovitsh, T. Low frequency nanobubble-enhanced ultrasound mechanotherapy for noninvasive cancer surgery. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 13614–13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafary, S.M.; Rahimjazi, E.; Hamzehil, H.; Mousavi, S.M.M.; Nikkhah, M.; Hosseinkhani, S. Design and preparation of a theranostic peptideticle for targeted cancer therapy: Peptide-based codelivery of doxorubicin/curcumin and graphene quantum dots. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine 2022, 42, 102544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, M.; Webster, T.J.; Li, L. Theranostic safe quantum dots for anticancer and bioimaging applications. Micro Nano Bio Aspects 2022, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Wang, J.; Xiong, B.; Hu, J.; Zeng, P.; Liu, X.; Liang, H. Biologically Safe, Versatile, and Smart Bismuthene Functionalized with a Drug Delivery System Based on Red Phosphorus Quantum Dots for Cancer Theranostics. Angewandte Chemie 2022, 134, e202117679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salkho, N.M.; Awad, N.S.; Pitt, W.G.; Husseini, G.A. Photo-induced drug release from polymeric micelles and liposomes: Phototriggering mechanisms in drug delivery systems. Polymers 2022, 14, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, M.; Nokhodchi, A. Micro-and nanoformulations of paclitaxel based on micelles, liposomes, cubosomes, and lipid nanoparticles: Recent advances and challenges. Drug Discovery Today 2022, 27, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Delfi, M.; Zarrabi, A.; Bigham, A.; Sharifi, E.; Rabiee, N.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Kumar, A.P.; Tan, S.C.; Hushmandi, K.; Ren, J. Stimuli-responsive liposomal nanoformulations in cancer therapy: Pre-clinical & clinical approaches. Journal of Controlled Release 2022, 351, 50–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y.; Lin, Q.; Gong, T.; Sun, X. Live macrophage-delivered doxorubicin-loaded liposomes effectively treat triple-negative breast cancer. ACS nano 2022, 16, 9799–9809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Y.; Su, H.; Zhu, X.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Hao, R.Y.; Yan, X.Y. Long-circulating doxorubicin and schizandrin A liposome with drug-resistant liver cancer activity: preparation, characterization, and pharmacokinetic. Journal of Liposome Research 2022, 32, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Silva, J.; Fernandes, R.S.; Oda, C.M.R.; Ferreira, T.H.; Botelho, A.F.M.; Melo, M.M.; de Miranda, M.C.; Gomes, D.A.; Cassali, G.D.; Townsend, D.M.; Rubello, D. Folate-coated, long-circulating and pH-sensitive liposomes enhance doxorubicin antitumor effect in a breast cancer animal model. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy 2019, 118, 109323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, U.; Onyesom, I.; Douroumis, D. Anti-cancer activity of sirolimus loaded liposomes in prostate cancer cell lines. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 2021, 61, 102200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.J.; Ju, R.J.; Zeng, F.; Qi, X.R.; Lu, W.L. Liposomes in drug delivery: status and advances. Liposome-Based Drug Delivery Systems 2021, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrisse, S.; Karamouza, E.; Parker, C.C.; Sartor, A.O.; James, N.D.; Pirrie, S.; Collette, L.; Tombal, B.F.; Chahoud, J.; Smeland, S.; Erikstein, B. Overall survival in men with bone metastases from castration-resistant prostate cancer treated with bone-targeting radioisotopes: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomized clinical trials. JAMA oncology 2020, 6, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, P.; Liu, T.; Shen, W.; Liu, Z.; Yang, K. Biomaterial-mediated internal radioisotope therapy. Materials Horizons 2021, 8, 1348–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Chao, Y.; Yi, X.; Xu, J.; Feng, L.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, K.; Liu, Z. Nanoparticle-mediated internal radioisotope therapy to locally increase the tumor vasculature permeability for synergistically improved cancer therapies. Biomaterials 2019, 197, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Meng, X.; Wen, L.; Zhou, N.; Liu, T.; Xu, X.; Wang, F.; Cheng, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, H. A Highly Specific Multiple Enhancement Theranostic Nanoprobe for PET/MRI/PAI Image-Guided Radioisotope Combined Photothermal Therapy in Prostate Cancer. Small 2021, 17, 2100378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choiński, J.; Łyczko, M. Prospects for the production of radioisotopes and radiobioconjugates for theranostics. Bio-Algorithms and Med-Systems 2021, 17, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyamogan, S.; Khan, N.A.; Siddiqui, R. Application and Importance of Theranostics in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Cancer. Archives of medical research 2021, 52, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naskar, N.; Lahiri, S. Theranostic terbium radioisotopes: challenges in production for clinical application. Frontiers in medicine 2021, 8, 675014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadag, S.N.; Ustun, O.; Yilmaz, A.; Yilmaz, M. The fabrication of excitation-dependent fluorescence boron/nitrogen co-doped carbon quantum dots and their employment in bioimaging. Chemical Physics 2022, 562, 111678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeroslavsky, G.; Umezawa, M.; Okubo, K.; Nigoghossian, K.; Dung, D.T.K.; Miyata, K.; Kamimura, M.; Soga, K. Stabilization of indocyanine green dye in polymeric micelles for NIR-II fluorescence imaging and cancer treatment. Biomaterials science 2020, 8, 2245–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuggino, J.C.; Picchio, M.L.; Gugliotta, A.; Bürgi, M.; Ronco, L.I.; Calderón, M.; Etcheverrigaray, M.; Igarzabal, C.I.A.; Minari, R.J.; Gugliotta, L.M. Crosslinked casein micelles bound paclitaxel as enzyme activated intracellular drug delivery systems for cancer therapy. European Polymer Journal 2021, 145, 110237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, C.H.; Fernandes, R.S.; de Oliveira Silva, J.; Oda, C.M.R.; Leite, E.A.; Cassali, G.D.; Charlie-Silva, I.; Fernandes, B.H.V.; Ferreira, L.A.M.; de Barros, A.L.B. Doxorubicin-loaded pH-sensitive micelles: A promising alternative to enhance antitumor activity and reduce toxicity. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2021, 134, 111076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamkhari, A.; Pouyafar, A.; Salehi, R.; Rahbarghazi, R. Chrysin and docetaxel loaded biodegradable micelle for combination chemotherapy of cancer stem cell. Pharmaceutical Research 2019, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junnuthula, V.; Kolimi, P.; Nyavanandi, D.; Sampathi, S.; Vora, L.K.; Dyawanapelly, S. Polymeric Micelles for Breast Cancer Therapy: Recent Updates, Clinical Translation and Regulatory Considerations. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Beaudoin, J.J.; Vinod, N.; Min, Y.; Makita, N.; Bludau, H.; Jordan, R.; Wang, A.; Sokolsky, M.; Kabanov, A.V. Co-delivery of paclitaxel and cisplatin in poly (2-oxazoline) polymeric micelles: Implications for drug loading, release, pharmacokinetics and outcome of ovarian and breast cancer treatments. Biomaterials 2019, 192, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Ning, Q.; Mo, Z.; Tang, S. Intelligent polymeric micelles for multidrug co-delivery and cancer therapy. Artificial cells, nanomedicine, and biotechnology, 2019, 47, 1476–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Deng, J.; Liu, F.; Fan, A.; Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Ding, D.; Kong, D.; Wang, Z.; Peer, D.; Zhao, Y. Triggered ferroptotic polymer micelles for reversing multidrug resistance to chemotherapy. Biomaterials 2019, 223, 119486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelopoulou, A.; Kolokithas-Ntoukas, A.; Fytas, C.; Avgoustakis, K. Folic acid-functionalized, condensed magnetic nanoparticles for targeted delivery of doxorubicin to tumor cancer cells overexpressing the folate receptor. ACS omega 2019, 4, 22214–22227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzin, A.; Etesami, S.A.; Quint, J.; Memic, A.; Tamayol, A. Magnetic nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Advanced healthcare materials 2020, 9, 1901058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.W.; Tsao, H.Y.; Chiang, C.S.; Chen, S.Y. Advances in magnetic nanoparticle-mediated cancer immune-theranostics. Advanced healthcare materials 2021, 10, 2001451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, X.; Si, J.; Mou, X.; Dong, X. All-in-One Nanomedicine: Multifunctional Single-Component Nanoparticles for Cancer Theranostics. Small 2021, 17, 2103072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ge, J.; Miao, Q.; Zhu, R.; Wen, L.; Zeng, J.; Gao, M. Biodegradable inorganic nanoparticles for cancer theranostics: insights into the degradation behavior. Bioconjugate chemistry 2019, 31, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavaleta, C.; Ho, D.; Chung, E.J. Theranostic nanoparticles for tracking and monitoring disease state. SLAS technology 2018, 23, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharmiladevi, P.; Girigoswami, K.; Haribabu, V.; Girigoswami, A. Nano-enabled theranostics for cancer. Materials Advances 2021, 2, 2876–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revia, R.A.; Stephen, Z.R.; Zhang, M. Theranostic nanoparticles for RNA-based cancer treatment. Accounts of Chemical research 2019, 52, 1496–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhari, S.I.; Imam, S.S.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Vuddanda, P.R.; Alshehri, S.; Mahdi, W.A.; Ahmad, J. Recent progress in lipid nanoparticles for cancer theranostics: opportunity and challenges. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehnke, N.; Correa, S.; Hao, L.; Wang, W.; Straehla, J.P.; Bhatia, S.N.; Hammond, P.T. Theranostic Layer-by-Layer Nanoparticles for Simultaneous Tumor Detection and Gene Silencing. Angewandte Chemie 2020, 132, 2798–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.Z.; Zeth, K.; Iftikhar, M.; Rehman, M.; Munir, M.U.; Khan, W.S.; Ihsan, A. Supramolecular lipid nanoparticles as delivery carriers for non-invasive cancer theranostics. Current Research in Pharmacology and Drug Discovery 2021, 2, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, M.; Belmonte-Reche, E.; Gallo, J.; Baltazar, F.; Bañobre-López, M. Magnetic solid nanoparticles and their counterparts: recent advances towards cancer theranostics. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





