Submitted:
30 May 2023
Posted:
31 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study design and participants
2.2. Laboratory testing
2.3. Statistical analysis
3. Results
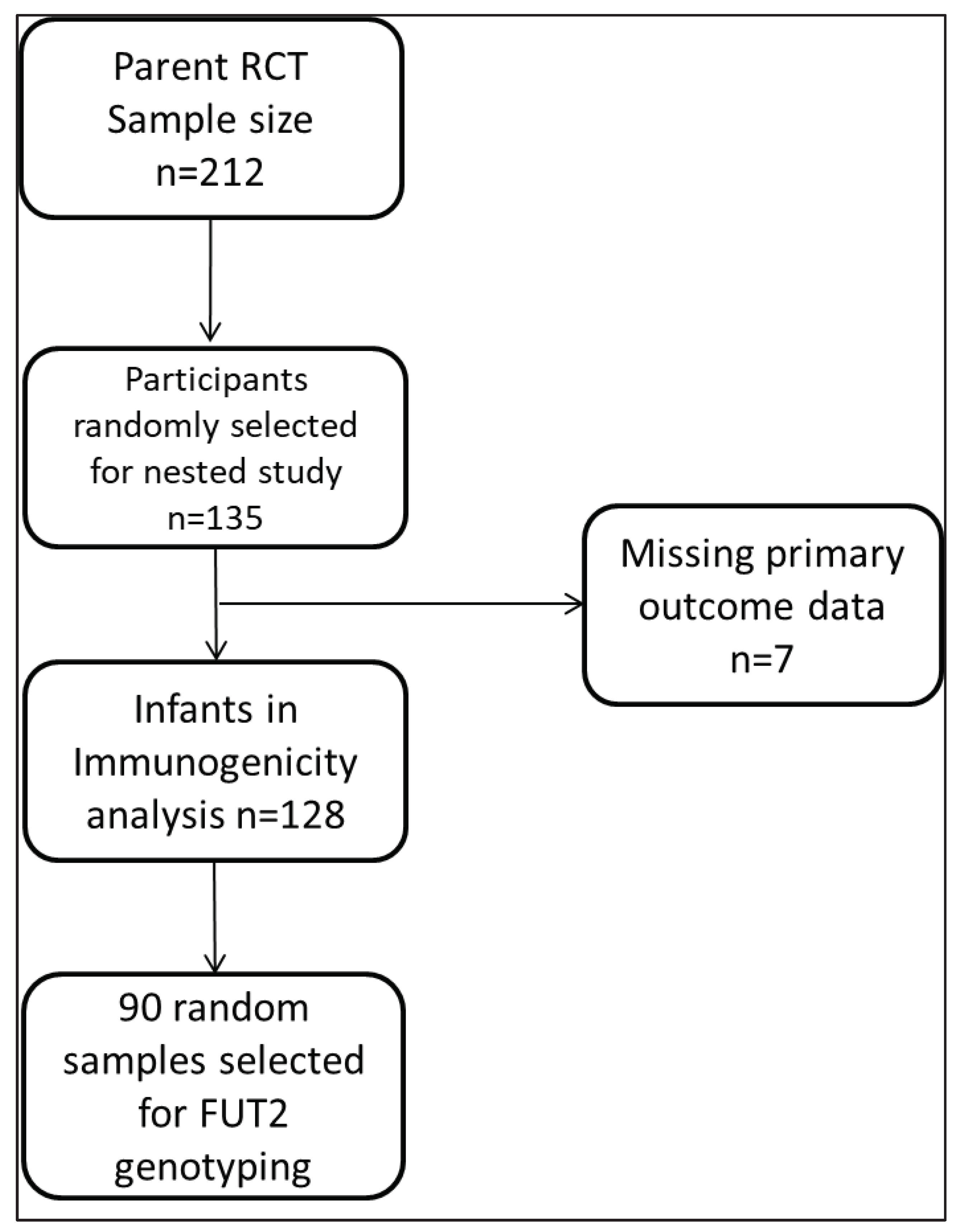
3.1. Participant and Sampling flow chart
3.2. Study population characteristics and overall seroconversion frequency
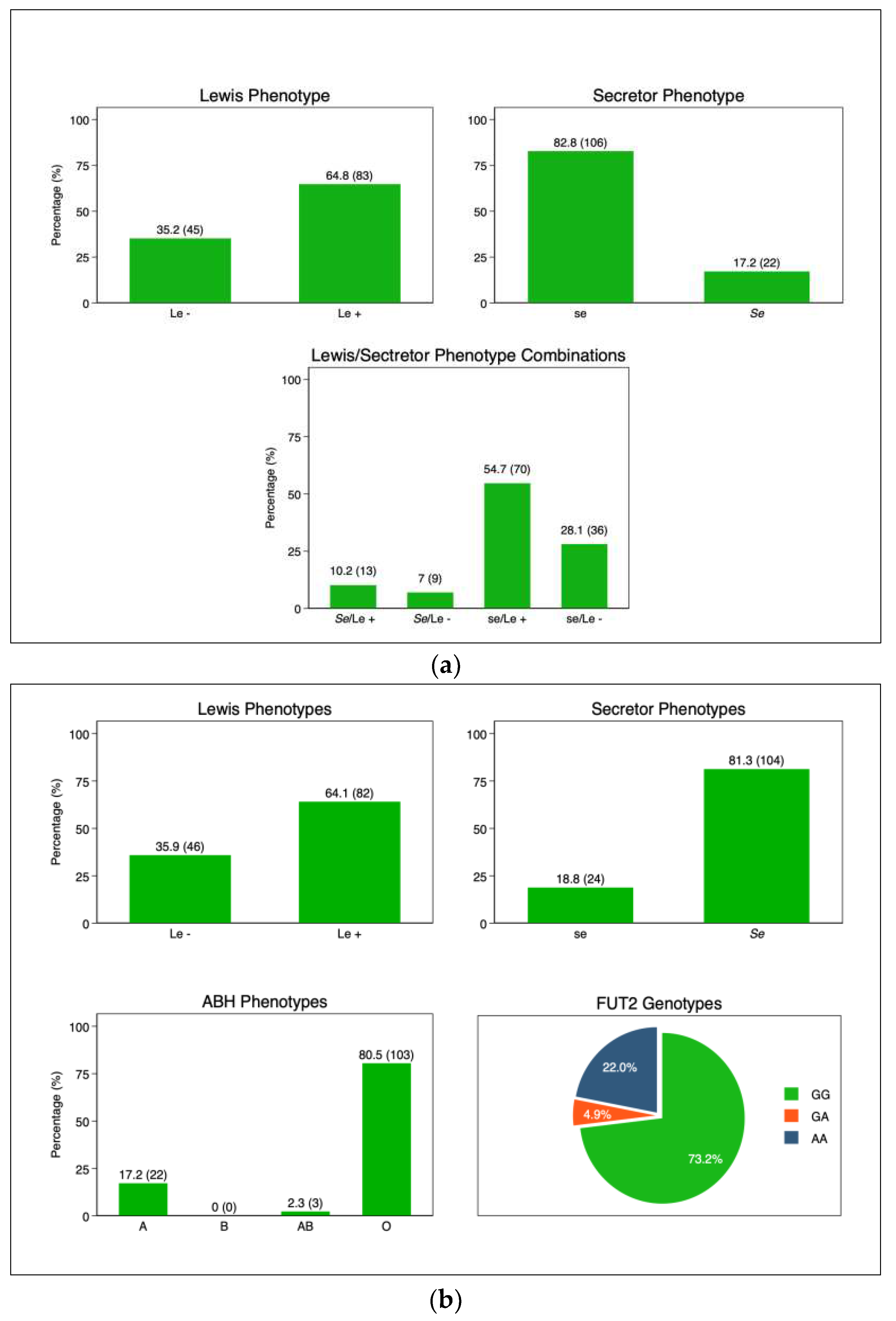
3.3. Mother and infant HBGA profiles
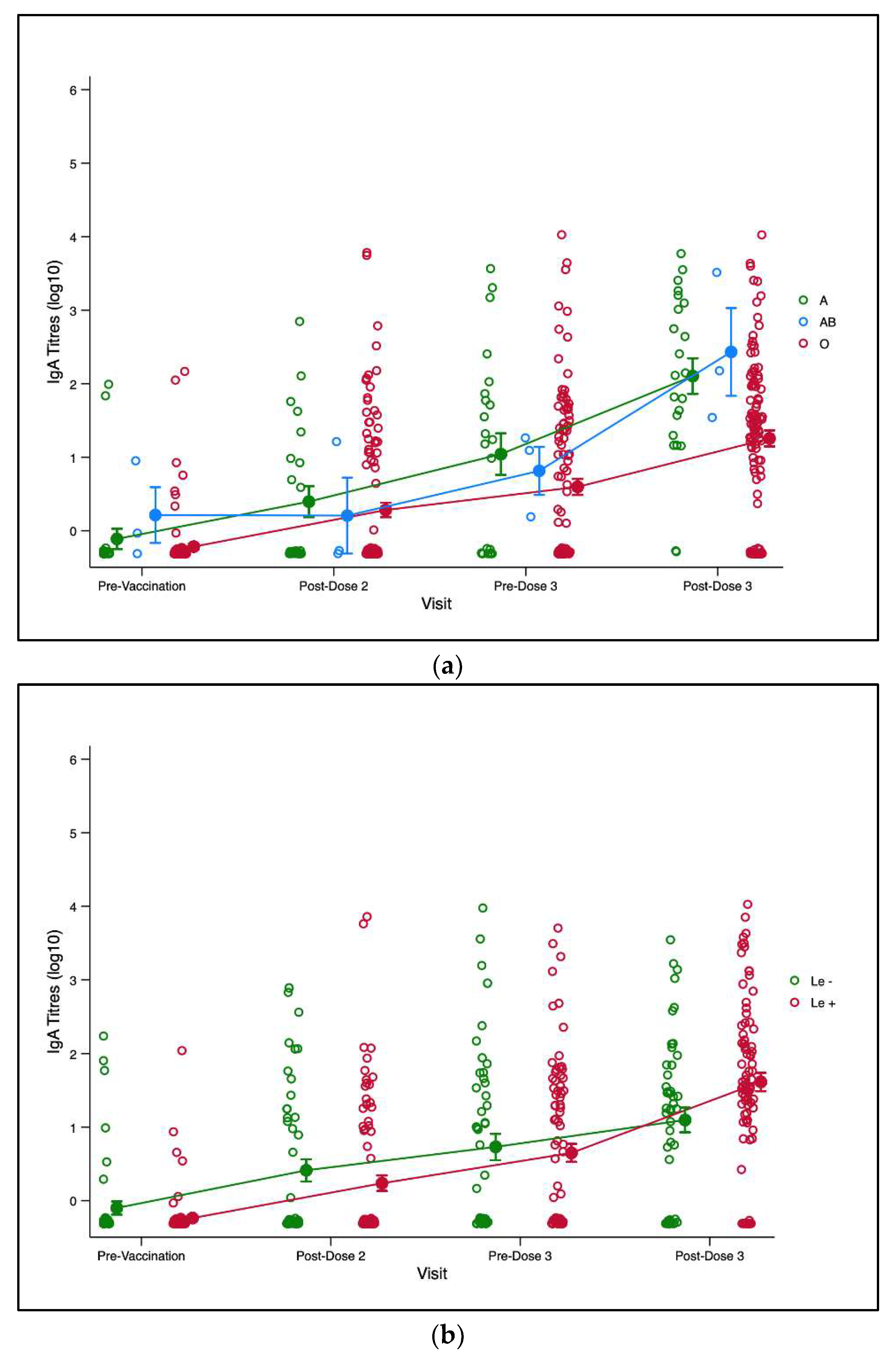
3.3. Maternal and Infant HBGA and RV-IgA Immunogenicity
3.3. Maternal and Infant HBGA and RV-IgA Immunogenicity 3-months post dose-3
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lanata, C.F.; Fischer-Walker, C.L.; Olascoaga, A.C.; Torres, C.X.; Aryee, M.J.; Black, R.E. ; for the Child Health Epidemiology Reference Group of the World Health Organization and UNICEF Global Causes of Diarrheal Disease Mortality in Children <5 Years of Age: A Systematic Review. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e72788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbafati C, Abbas KM, Abbasi-Kangevari M, Abd-Allah F, Abdelalim A, Abdollahi M, et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [CrossRef]
- Chilengi, R.; Rudd, C.; Bolton, C.; Guffey, B.; Masumbu, P.K.; Stringer, J. Successes, Challenges and Lessons Learned in Accelerating Introduction of Rotavirus Immunisation in Zambia. World J. Vaccines 2015, 05, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, E.; Jonesteller, C.L.; Tate, J.E.; Yen, C.; Parashar, U.D. Global Impact of Rotavirus Vaccination on Childhood Hospitalizations and Mortality From Diarrhea. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 1666–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James A Church, Edward P Parker, Beth Kirkpatrick4, Nicholas C Grassly AJ, Prendergast. Interventions to Improve Oral Vaccine Performance in developing countries : A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Protocol Information. 2017;(December):1–41.
- Kazimbaya, K.M.; Bosomprah, S.; Simuyandi, M.; Chisenga, C.C.; Chilengi, R.; Munsaka, S. Efficacy and Effectiveness of Rotavirus Vaccine on Incidence of Diarrhoea among Children: A Meta-analysis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Open Access 2018, 03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasquez DE, Parashar U, Jiang B. Decreased performance of live attenuated, oral rotavirus vaccines in low-income settings : causes and contributing factors. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2018;00(00):1–17.
- Mwape, I.; Bosomprah, S.; Mwaba, J.; Mwila-Kazimbaya, K.; Laban, N.M.; Chisenga, C.C.; Sijumbila, G.; Simuyandi, M.; Chilengi, R. Immunogenicity of rotavirus vaccine (RotarixTM) in infants with environmental enteric dysfunction. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0187761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwila-Kazimbaya, K.; Garcia, M.P.; Bosomprah, S.; Laban, N.M.; Chisenga, C.C.; Permar, S.R.; Simuyandi, M.; Munsaka, S.; Chilengi, R. Effect of innate antiviral glycoproteins in breast milk on seroconversion to rotavirus vaccine (Rotarix) in children in Lusaka, Zambia. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0189351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilengi, R.; Simuyandi, M.; Beach, L.; Mwila, K.; Becker-Dreps, S.; Emperador, D.M.; Velasquez, D.E.; Bosomprah, S.; Jiang, B. Association of Maternal Immunity with Rotavirus Vaccine Immunogenicity in Zambian Infants. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0150100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu S, Liu Y, Tan M, Zhong W, Zhao D, Jiang X, et al. Molecular basis of P [ 6 ] and P [ 8 ] major human rotavirus VP8 * domain interactions with histo-blood group antigens. 2019.
- E Armah, G.; Cortese, M.M.; E Dennis, F.; Yu, Y.; Morrow, A.L.; McNeal, M.M.; Lewis, K.D.C.; A Awuni, D.; Armachie, J.; Parashar, U.D. Rotavirus Vaccine Take in Infants Is Associated With Secretor Status. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 219, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock L, Bennett A, Jere KC, Dube Q, Mandolo J, Bar-Zeev N, et al. Non-secretor histo-blood group antigen phenotype is associated with reduced risk of clinical rotavirus vaccine failure in Malawian infants. Clin Infect Dis. 2018;(Xx):1–7.
- Bucardo, F.; Nordgren, J.; Reyes, Y.; Gonzalez, F.; Sharma, S.; Svensson, L. The Lewis A phenotype is a restriction factor for Rotateq and Rotarix vaccine-take in Nicaraguan children. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Dickson, D.M.; Decamp, A.C.; Colgate, E.R.; A Diehl, S.; Uddin, M.I.; Sharmin, S.; Islam, S.; Bhuiyan, T.R.; Alam, M.; et al. Histo–Blood Group Antigen Phenotype Determines Susceptibility to Genotype-Specific Rotavirus Infections and Impacts Measures of Rotavirus Vaccine Efficacy. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 217, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordgren, J.; Sharma, S.; Bucardo, F.; Nasir, W.; Günaydın, G.; Ouermi, D.; Nitiema, L.W.; Becker-Dreps, S.; Simpore, J.; Hammarström, L.; et al. Both Lewis and Secretor Status Mediate Susceptibility to Rotavirus Infections in a Rotavirus Genotype–Dependent Manner. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, P.; Tan, M.; Liu, Y.; Biesiada, J.; Meller, J.; Castello, A.A.; Jiang, B.; Jiang, X. Rotavirus VP8*: Phylogeny, Host Range, and Interaction with Histo-Blood Group Antigens. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 9899–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abegaz, S.B. Human ABO Blood Groups and Their Associations with Different Diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, G. Human Blood groups, Second Edition. 2016. 1–23 p.
- Jiang X, Huang P, Zhong W, Tan M, Farkas T, Morrow AL, et al. Human Milk Contains Elements That Block Binding of Noroviruses to Human Histo – Blood Group Antigens in Saliva. 2004;3039.
- Williams, F.B.; Kader, A.; Colgate, E.R.; Dickson, D.M.; Carmolli, M.; Uddin, M.I.; Sharmin, S.; Islam, S.; Bhuiyan, T.R.; Alam, M.; et al. Maternal Secretor Status Affects Oral Rotavirus Vaccine Response in Breastfed Infants in Bangladesh. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 224, 1147–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colston, J.M.; Francois, R.; Pisanic, N.; Yori, P.P.; McCormick, B.J.J.; Olortegui, M.P.; Gazi, A.; Svensen, E.; Ahmed, M.M.M.; Mduma, E.; et al. Effects of Child and Maternal Histo-Blood Group Antigen Status on Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Enteric Infections in Early Childhood. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, E.P.; Ramani, S.; A Lopman, B.; A Church, J.; Iturriza-Gómara, M.; Prendergast, A.J.; Grassly, N.C.; Colvin, E.; Kosek, M.N.; Kang, G.; et al. Causes of impaired oral vaccine efficacy in developing countries. Futur. Microbiol. 2018, 13, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laban, N.M.; Bosomprah, S.; Simuyandi, M.; Chibuye, M.; Chauwa, A.; Chirwa-Chobe, M.; Sukwa, N.; Chipeta, C.; Velu, R.; Njekwa, K.; et al. Evaluation of ROTARIX® Booster Dose Vaccination at 9 Months for Safety and Enhanced Anti-Rotavirus Immunity in Zambian Children: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Vaccines 2023, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Armah, G.; O Sow, S.; Breiman, R.F.; Dallas, M.J.; Tapia, M.D.; Feikin, D.R.; Binka, F.N.; Steele, A.D.; Laserson, K.F.; A Ansah, N.; et al. Efficacy of pentavalent rotavirus vaccine against severe rotavirus gastroenteritis in infants in developing countries in sub-Saharan Africa: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmgren ASDS and S for PM in the HL( F) GEMG of the HLBGS, Larson G. DNA Sequencing and Screening for Point Mutations in the Human Lewis ( FUT3 ) Gene Enables Molecular Genotyping of the Human Lewis Blood Group Sytem. 1996;97–103.
- Silva, L.M.; Carvalho, A.S.; Guillon, P.; Seixas, S.; Azevedo, M.; Almeida, R.; Ruvoën-Clouet, N.; Reis, C.A.; Le Pendu, J.; Rocha, J.; et al. Infection-associated FUT2 (Fucosyltransferase 2) genetic variation and impact on functionality assessed by in vivo studies. Glycoconj. J. 2009, 27, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Guo, N.; Li, J.; Yan, X.; He, Z.; Li, D.; Jin, M.; Xie, G.; Pang, L.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Rotavirus infection and histo-blood group antigens in the children hospitalized with diarrhoea in China. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 740–e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mattos, L.C. Structural diversity and biological importance of ABO, H, Lewis and secretor histo-blood group carbohydrates. Rev. Bras. de Hematol. e Hemoter. 2016, 38, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasquez, D.E.; Parashar, U.; Jiang, B. Decreased performance of live attenuated, oral rotavirus vaccines in low-income settings: causes and contributing factors. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2017, 17, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, D.C.; Currier, R.L.; Staat, M.A.; Sahni, L.C.; Selvarangan, R.; Halasa, N.B.; Englund, J.A.; Weinberg, G.A.; Boom, J.A.; Szilagyi, P.G.; et al. Epidemiologic Association Between FUT2 Secretor Status and Severe Rotavirus Gastroenteritis in Children in the United States. JAMA Pediatrics 2015, 169, 1040–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heggelund, J.E.; Varrot, A.; Imberty, A.; Krengel, U. Histo-blood group antigens as mediators of infections. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2017, 44, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, L.; Bennett, A.; Jere, K.C.; Dube, Q.; Mandolo, J.; Bar-Zeev, N.; Heyderman, R.S.; A Cunliffe, N.; Iturriza-Gomara, M. Nonsecretor Histo–blood Group Antigen Phenotype Is Associated With Reduced Risk of Clinical Rotavirus Vaccine Failure in Malawian Infants. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 69, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Tan, M. Histo-blood group antigens as receptors for rotavirus, new understanding on rotavirus epidemiology and vaccine strategy. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi, A.M.; Cortese, M.M.; Yu, Y.; Lopman, B.; Morrow, A.L.; Fleming, J.A.; McNeal, M.M.; Steele, A.D.; Parashar, U.D.; Zaidi, A.K.M.; et al. Secretor and Salivary ABO Blood Group Antigen Status Predict Rotavirus Vaccine Take in Infants. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 786–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Armah, G.; Cortese, M.M.; E Dennis, F.; Yu, Y.; Morrow, A.L.; McNeal, M.M.; Lewis, K.D.C.; A Awuni, D.; Armachie, J.; Parashar, U.D. Rotavirus Vaccine Take in Infants Is Associated With Secretor Status. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 219, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Dickson, D.M.; Decamp, A.C.; Colgate, E.R.; A Diehl, S.; Uddin, M.I.; Sharmin, S.; Islam, S.; Bhuiyan, T.R.; Alam, M.; et al. Histo–Blood Group Antigen Phenotype Determines Susceptibility to Genotype-Specific Rotavirus Infections and Impacts Measures of Rotavirus Vaccine Efficacy. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 217, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.-A.; Hou, J.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-J. Genetic Susceptibility to Rotavirus Gastroenteritis and Vaccine Effectiveness in Taiwanese Children. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6412–6412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, V.; Ali, A.; Fuentes, S.; Korpela, K.; Kazi, M.; Tate, J.; Parashar, U.; Wiersinga, W.J.; Giaquinto, C.; de Weerth, C.; et al. Rotavirus vaccine response correlates with the infant gut microbiota composition in Pakistan. Gut Microbes 2017, 9, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Nordgren, J. Effect of Infant and Maternal Secretor Status on Rotavirus Vaccine Take—An Overview. Viruses 2021, 13, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, R.; Fleming, F.E.; Maggioni, A.; Dang, V.T.; Holloway, G.; Coulson, B.S.; von Itzstein, M.; Haselhorst, T. Revisiting the role of histo-blood group antigens in rotavirus host-cell invasion. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5907–5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Xia, M.; Tan, M.; Zhong, W.; Wei, C.; Wang, L.; Morrow, A.; Jiang, X. Spike Protein VP8* of Human Rotavirus Recognizes Histo-Blood Group Antigens in a Type-Specific Manner. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4833–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooling, L. Blood Groups in Infection and Host Susceptibility. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 801–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Trang N, Vu HT, Le NT, Huang P, Jiang X, Anh DD. Association between norovirus and rotavirus infection and histo-blood group antigen types in vietnamese children. J Clin Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1366–1374. [CrossRef]
- Bekdas M, Demircioglu F, Goksugur SB, Kucukbayrak B. Is there a relationship between rotavirus positive gastroenteritis and ABO blood groups? A retrospective cohort study. Arch Argent Pediatr. 2014, 112, 345–348.
- Mihala G, Ware RS, Cheung C, Lambert SB, Sly PD, Whiley DM, et al. Intestinal shedding of enteric agents in histo-blood group antigen-secretor children in an Australian community-based birth cohort study. J Pediatr Neonatal Individ Med. 2022, 11, 1–13.
- Ramani, S.; Giri, S. Influence of histo blood group antigen expression on susceptibility to enteric viruses and vaccines. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 32, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, F.B.; Kader, A.; Colgate, E.R.; Dickson, D.M.; Carmolli, M.; Uddin, M.I.; Sharmin, S.; Islam, S.; Bhuiyan, T.R.; Alam, M.; et al. Maternal Secretor Status Affects Oral Rotavirus Vaccine Response in Breastfed Infants in Bangladesh. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 224, 1147–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu S, Liu Y, Tan M, Zhong W, Zhao D, Jiang X, et al. Molecular basis of P[6] and P[8] major human rotavirus VP8* domain interactions with histo-blood group antigens. bioRxiv [Internet]. 2019;512301. [CrossRef]
- Ayouni, S.; Sdiri-Loulizi, K.; de Rougemont, A.; Estienney, M.; Ambert-Balay, K.; Aho, S.; Hamami, S.; Aouni, M.; Neji-Guediche, M.; Pothier, P.; et al. Rotavirus P[8] Infections in Persons with Secretor and Nonsecretor Phenotypes, Tunisia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 2055–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Seroconverted | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother-infant pairs (N=128) | No。(n = 91, 71.1%) | Yes。(n = 37, 28.9%)) | P-value | |
| n (% of total) | n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Infant Characteristics | ||||
| Age (Weeks) | ||||
| Median (IQR) | 6 (6-6) | 6 (6-6) | 6 (6-6) | 0.442 |
| Mean (SD) | 6 (0.6) | 6 (0.6) | 5.9 (0.7) | |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 69 (53.9) | 51 (73.9) | 18 (26.0) | 0.447 |
| Female | 59 (46.1) | 40 (67.7) | 19 (32.2) | |
| Feeding | ||||
| Exclusive Breastfeeding | 122 (95.3) | 86 (70.4) | 36 (29.5) | 0.672 |
| Mixed Feeding | 6 (4.7) | 5 (83.3) | 1 (16.6) | |
| Birthweight (kg) | ||||
| < 2.5 | 5 (3.9) | 3 (60.0) | 2 (40.0) | 0.626 |
| ≥ 2.5 | 123 (96.1) | 88 (71.5) | 35 (28.4) | |
| HIV Exposure | ||||
| Not Exposed | 89 (69.5) | 62 (69.6) | 27 (30.3) | 0.590 |
| Exposed | 39 (30.5) | 28 (73.6) | 10 (26.3) | |
| Nutritional Status | ||||
| Stunted | ||||
| No (HAZ ≥ -2) | 107 (83.6) | 78 (72.8) | 29 (27.1) | 0.310 |
| Yes (HAZ < -2) | 21 (16.4) | 13 (61.9) | 8 (38.0) | |
| Wasted | ||||
| No (WAZ ≥ -2) | 119 (93.0) | 86 (72.2) | 33 (27.7) | 0.281 |
| Yes (WAZ < -2) | 9 (7.0) | 5 (55.5) | 4 (44.4) | |
| Mother’s Characteristics | ||||
| Age (years) | ||||
| <20 | 20 (15.6) | 15 (75.0) | 5 (25.0) | 0.080 |
| 20-24 | 45 (35.2) | 37 (82.2) | 8 (17.7) | |
| 25-29 | 34 (26.6) | 19 (55.8) | 15 (44.1) | |
| ≥30 | 29 (22.7) | 20 (68.9) | 9 (31.0) | |
| Highest Education Level | ||||
| None | 6 (4.7) | 4 (66.7) | 2 (33.3) | 0.470* |
| Primary | 40 (31.3) | 25 (62.5) | 15 (37.5) | |
| Secondary | 81 (63.3) | 61 (75.3) | 20 (24.6) | |
| Tertiary | 1 (0.8) | 1 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Water Source | ||||
| Piped into house/yard | 45 (35.2) | 33 (75.0) | 12 (25.0) | 0.882 |
| Protected well | 5 (3.9) | 4 (80.0) | 1 (20.0) | |
| Public borehole/tap and pipe | 78 (60.9) | 54 (80.0) | 24 (20.0) | |
| Shared Toilet Facility | ||||
| No | 24 (18.8) | 17 (70.8) | 7 (29.1) | 0.975 |
| Yes | 104 (81.3) | 74 (71.1) | 30 (28.8) | |
| Type of Toilet Facility | ||||
| Flushing toilet | 26 (20.3) | 17 (65.4) | 9 (34.6) | 0.476 |
| Pit latrine | 102 (79.7) | 74 (72.6) | 28 (27.5) | |
| Seroconverted | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother-infant pairs (N=128) | No。(n = 91, 71.1%) | Yes。(n = 37, 28.9%)) | P-value | |
| n (% of total) | n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Infant Characteristics | ||||
| Age (Weeks) | ||||
| Median (IQR) | 6 (6-6) | 6 (6-6) | 6 (6-6) | 0.442 |
| Mean (SD) | 6 (0.6) | 6 (0.6) | 5.9 (0.7) | |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 69 (53.9) | 51 (73.9) | 18 (26.0) | 0.447 |
| Female | 59 (46.1) | 40 (67.7) | 19 (32.2) | |
| Feeding | ||||
| Exclusive Breastfeeding | 122 (95.3) | 86 (70.4) | 36 (29.5) | 0.672 |
| Mixed Feeding | 6 (4.7) | 5 (83.3) | 1 (16.6) | |
| Birthweight (kg) | ||||
| < 2.5 | 5 (3.9) | 3 (60.0) | 2 (40.0) | 0.626 |
| ≥ 2.5 | 123 (96.1) | 88 (71.5) | 35 (28.4) | |
| HIV Exposure | ||||
| Not Exposed | 89 (69.5) | 62 (69.6) | 27 (30.3) | 0.590 |
| Exposed | 39 (30.5) | 28 (73.6) | 10 (26.3) | |
| Nutritional Status | ||||
| Stunted | ||||
| No (HAZ ≥ -2) | 107 (83.6) | 78 (72.8) | 29 (27.1) | 0.310 |
| Yes (HAZ < -2) | 21 (16.4) | 13 (61.9) | 8 (38.0) | |
| Wasted | ||||
| No (WAZ ≥ -2) | 119 (93.0) | 86 (72.2) | 33 (27.7) | 0.281 |
| Yes (WAZ < -2) | 9 (7.0) | 5 (55.5) | 4 (44.4) | |
| Mother’s Characteristics | ||||
| Age (years) | ||||
| <20 | 20 (15.6) | 15 (75.0) | 5 (25.0) | 0.080 |
| 20-24 | 45 (35.2) | 37 (82.2) | 8 (17.7) | |
| 25-29 | 34 (26.6) | 19 (55.8) | 15 (44.1) | |
| ≥30 | 29 (22.7) | 20 (68.9) | 9 (31.0) | |
| Highest Education Level | ||||
| None | 6 (4.7) | 4 (66.7) | 2 (33.3) | 0.470* |
| Primary | 40 (31.3) | 25 (62.5) | 15 (37.5) | |
| Secondary | 81 (63.3) | 61 (75.3) | 20 (24.6) | |
| Tertiary | 1 (0.8) | 1 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Water Source | ||||
| Piped into house/yard | 45 (35.2) | 33 (75.0) | 12 (25.0) | 0.882 |
| Protected well | 5 (3.9) | 4 (80.0) | 1 (20.0) | |
| Public borehole/tap and pipe | 78 (60.9) | 54 (80.0) | 24 (20.0) | |
| Shared Toilet Facility | ||||
| No | 24 (18.8) | 17 (70.8) | 7 (29.1) | 0.975 |
| Yes | 104 (81.3) | 74 (71.1) | 30 (28.8) | |
| Type of Toilet Facility | ||||
| Flushing toilet | 26 (20.3) | 17 (65.4) | 9 (34.6) | 0.476 |
| Pit latrine | 102 (79.7) | 74 (72.6) | 28 (27.5) | |
| Seroconverted | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother-infant pairs (N=128) | No。(n = 91, 71.1%) | Yes。(n = 37, 28.9%)) | P-value | |
| n (% of total) | n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Infant Characteristics | ||||
| Age (Weeks) | ||||
| Median (IQR) | 6 (6-6) | 6 (6-6) | 6 (6-6) | 0.442 |
| Mean (SD) | 6 (0.6) | 6 (0.6) | 5.9 (0.7) | |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 69 (53.9) | 51 (73.9) | 18 (26.0) | 0.447 |
| Female | 59 (46.1) | 40 (67.7) | 19 (32.2) | |
| Feeding | ||||
| Exclusive Breastfeeding | 122 (95.3) | 86 (70.4) | 36 (29.5) | 0.672 |
| Mixed Feeding | 6 (4.7) | 5 (83.3) | 1 (16.6) | |
| Birthweight (kg) | ||||
| < 2.5 | 5 (3.9) | 3 (60.0) | 2 (40.0) | 0.626 |
| ≥ 2.5 | 123 (96.1) | 88 (71.5) | 35 (28.4) | |
| HIV Exposure | ||||
| Not Exposed | 89 (69.5) | 62 (69.6) | 27 (30.3) | 0.590 |
| Exposed | 39 (30.5) | 28 (73.6) | 10 (26.3) | |
| Nutritional Status | ||||
| Stunted | ||||
| No (HAZ ≥ -2) | 107 (83.6) | 78 (72.8) | 29 (27.1) | 0.310 |
| Yes (HAZ < -2) | 21 (16.4) | 13 (61.9) | 8 (38.0) | |
| Wasted | ||||
| No (WAZ ≥ -2) | 119 (93.0) | 86 (72.2) | 33 (27.7) | 0.281 |
| Yes (WAZ < -2) | 9 (7.0) | 5 (55.5) | 4 (44.4) | |
| Mother’s Characteristics | ||||
| Age (years) | ||||
| <20 | 20 (15.6) | 15 (75.0) | 5 (25.0) | 0.080 |
| 20-24 | 45 (35.2) | 37 (82.2) | 8 (17.7) | |
| 25-29 | 34 (26.6) | 19 (55.8) | 15 (44.1) | |
| ≥30 | 29 (22.7) | 20 (68.9) | 9 (31.0) | |
| Highest Education Level | ||||
| None | 6 (4.7) | 4 (66.7) | 2 (33.3) | 0.470* |
| Primary | 40 (31.3) | 25 (62.5) | 15 (37.5) | |
| Secondary | 81 (63.3) | 61 (75.3) | 20 (24.6) | |
| Tertiary | 1 (0.8) | 1 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Water Source | ||||
| Piped into house/yard | 45 (35.2) | 33 (75.0) | 12 (25.0) | 0.882 |
| Protected well | 5 (3.9) | 4 (80.0) | 1 (20.0) | |
| Public borehole/tap and pipe | 78 (60.9) | 54 (80.0) | 24 (20.0) | |
| Shared Toilet Facility | ||||
| No | 24 (18.8) | 17 (70.8) | 7 (29.1) | 0.975 |
| Yes | 104 (81.3) | 74 (71.1) | 30 (28.8) | |
| Type of Toilet Facility | ||||
| Flushing toilet | 26 (20.3) | 17 (65.4) | 9 (34.6) | 0.476 |
| Pit latrine | 102 (79.7) | 74 (72.6) | 28 (27.5) | |
| Characteristics | Number of mother-infant pairs (% of total) | GMTs (95% CI) | ANOVA P-value | Seroconversion (n = 37, 28.9%) | Chi-Square P-value | Crude Odds Ratio (95% CI) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | |||||||
| Infant | |||||||
| Infant HBGA Phenotype | |||||||
| A | 22 (17.2) | 2.5 (0.9, 6.8) | 0.874 | 7 (31.8) | 0.929 | ref | |
| AB | 3 (2.3) | 1.6 (0, 270.6) | 1 (33.3) | 1.1 (0.1, 13.9) | 0.958 | ||
| O | 103 (80.5) | 1.9 (1.2, 3) | 29 (28.2) | 0.8 (0.3, 2.3) | 0.731 | ||
| Infant Lewis Phenotype | |||||||
| Le- (Le a-b-) | 46 (35.9) | 2.6 (1.3, 5.2) | 0.332 | 14 (30.4) | 0.775 | ref | |
| Le+ (Le a+b-,Le a-b+, or Le a+b+) | 82 (64.1) | 1.7 (1.1, 2.8) | 23 (28.2) | 0.9 (0.4, 2) | 0.775 | ||
| Secretor Phenotype | |||||||
| Non-secretor (se) | 24 (18.8) | 1.3 (0.6, 2.8) | 0.279 | 5 (20.8) | 0.24 | ref | |
| Secretor Phenotype (Se) | 104 (81.3) | 2.2 (1.4, 3.5) | 32 (30.8) | 1.7 (0.6, 4.9) | 0.337 | ||
| Infant FUT2 Genotype* | |||||||
| Homozygous secretor (GG) | 60 (46.9) | 1.4 (0.8, 2.5) | 0.093 | 15 (25.0) | 0.289 | ref | |
| Heterozygous secretor (GA) | 4 (3.1) | 5.6 (0, 1426.5) | 2 (50.0) | 3 (0.4, 23.2) | 0.292 | ||
| Non-secretor (AA) | 18 (14.1) | 4.9 (1.5, 16.3) | 7 (38.9) | 1.9 (0.6, 5.8) | 0.255 | ||
| Missing | 46 (35.9) | 2 (1, 3.8) | 13 (28.3) | - | - | ||
| Mother | |||||||
| Lewis Phenotype | |||||||
| Le- (Le a-b-) | 45 (35.2) | 1.6 (0.9, 2.8) | 0.358 | 13 (28.9) | 0.997 | ref | |
| Le+ (Le a+b-,Le a-b+, or Le a+b+) | 83 (64.8) | 2.3 (1.4, 3.9) | 24 (28.9) | 1.0 (0.4, 2.2) | 0.997 | ||
| Secretor Phenotype | |||||||
| Non-secretor (se) | 106 (82.8) | 2 (1.3, 3.1) | 0.85 | 32 (30.2) | 0.336 | ref | |
| Secretor Phenotype (Se) | 22 (17.2) | 1.8 (0.7, 5.2) | 5 (22.7) | 0.7 (0.2, 2.0) | 0.484 | ||
| Characteristics | V12 GMTs | ANOVA, P-value | GMT Ratio (95% CI) | P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GMT (95% CI) | ||||||
| Infant | ||||||
| Infant ABO Phenotype | ||||||
| A | 5.02 (4.14, 6.07) | 0.002 | ref | |||
| AB | 5.28 (1.86, 15) | 0.59 (0.10, 3.47) | 0.560 | |||
| O | 3.7 (3.35, 4.08) | 0.36 (0.09, 1.41) | 0.140 | |||
| Infant Lewis Phenotype | ||||||
| Le- (Le a-b-) | 3.57 (3.03, 4.22) | 0.015 | ref | |||
| Le+ (Le a+b-, Le a-b+, or Le a+b+) | 4.17 (3.75, 4.63) | 0.83 (0.31, 2.23) | 0.705 | |||
| Secretor Phenotype | ||||||
| Non-secretor (se) | 2.89 (2.26, 3.71) | < 0.001 | ref | |||
| Secretor Phenotype (Se) | 4.14 (3.78, 4.54) | 1.94 (0.59, 6.4) | 0.276 | |||
| Infant FUT2 Genotype | ||||||
| Secretor (GG)/(GA) | 3.95 (3.45, 4.52) | 0.063 | ref | |||
| Non-secretor (AA) | 3.24 (2.44, 4.31) | 1.66 (0.96, 2.83) | 0.543 | |||
| Mother | ||||||
| Lewis Phenotype | ||||||
| Le- (Le a-b-) | 4.02 (3.52, 4.58) | 0.521 | ref | |||
| Le+ (Le a+b-, Le a-b+, or Le a+b+) | 3.95 (3.51, 4.44) | 1.09 (0.41, 2.88) | 0.863 | |||
| Secretor Phenotype | ||||||
| Non-secretor (se) | 4.08 (3.72, 4.48) | 0.368 | ref | |||
| Secretor Phenotype (Se) | 3.45 (2.64, 4.51) | 0.83 (0.25, 2.70) | 0.751 | |||
| Treatment Arm | ||||||
| Control (MR) | 4.08 (3.56, 4.67) | 0.260 | ref | |||
| Intervention (ROTARIX®+MR) | 3.88 (3.44, 4.37) | 1.39 (0.55, 3.49) | 0.479 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





