1. Introduction
A majority of deaths worldwide are caused by cardiovascular diseases (CVD) and cancer [
1,
2]. Over the last decades, it has been discovered that both CVD and cancer are more common in individuals with traditional cardiovascular risk factors accumulation. Several risk factors that are common to CVD and cancer make preventative measures extremely effective in reducing disease incidence [
3,
4]. In recent years, the bidirectional association between myocardial infarction (MI) and cancer has been established. One prospective cohort study described the future risk of incident cancer in patients diagnozed with MI. The study (n = 28 763) included participants without previous history of MI or cancer and had a follow-up period of more than 15 years. There were 1747 subjects with MI, 146 of whom developed cancer afterwards. Patients with MI had an increased risk of 46% to develop cancer compared with those without MI [
5]. On the other hand, a significant increase of arterial thromboembolism risk is associated with incident cancer [
6]. Lung cancer had the greatest excess risk, which also correlated with cancer stage. In newly diagnosed cancer patients, the 6-month cumulative incidence of myocardial infarction was found to be markedly higher than that of matched control patients (HR = 2.9). [
6]
During cancer treatment, patients may suffer cardiovascular side effects or a worsening of an underlying cardiovascular condition. More and more patients are living longer due to improved oncology treatments. Cancer chemotherapy can be associated with coronary disease, severe hypertension and thromboembolic ischemia, as well as cardiac arrhythmias. It has been established that cancer treatment can exert late effects many years after treatment. Myocardial disease, myocardial fibrosis, cardiomyopathy, coronary artery disease, and valve disease can all be induced by chest radiation, early or late [
7]. Oncology patients suffering from cardiotoxicity, specifically left ventricular dysfunction, are at high risk of morbidity and mortality long-term. Currently, there is an increase in the use of biomarkers to detect cardiotoxicity at an early stage that can be reversed [
8]. Patients with cancer and cancer survivors are at increased risk for incident heart failure (HF) and other cardiovascular events. In Paterson et al. study [
9] a total of 224,016 participants with new cancer diagnoses were identified, as well as 73,360 cardiovascular deaths and 470,481 nonfatal cardiovascular events. Cardiovascular risk was highest for patients with genitourinary, gastrointestinal, thoracic, nervous system, and hematologic malignancies [
9]. According to other retrospective cohort study including 27,195,088 individuals, subjects with CVD had an increased risk (12%) of incident cancer compared with those without CVD. The risk was most pronounced among individuals with atherosclerotic CVD, who had a higher risk of cancer than those without CVD. Results showed that atherosclerotic CVD was particularly linked with several malignancies, including lung, bladder, liver, colon, and hematologic cancers [
10].
2. Case Presentation Section
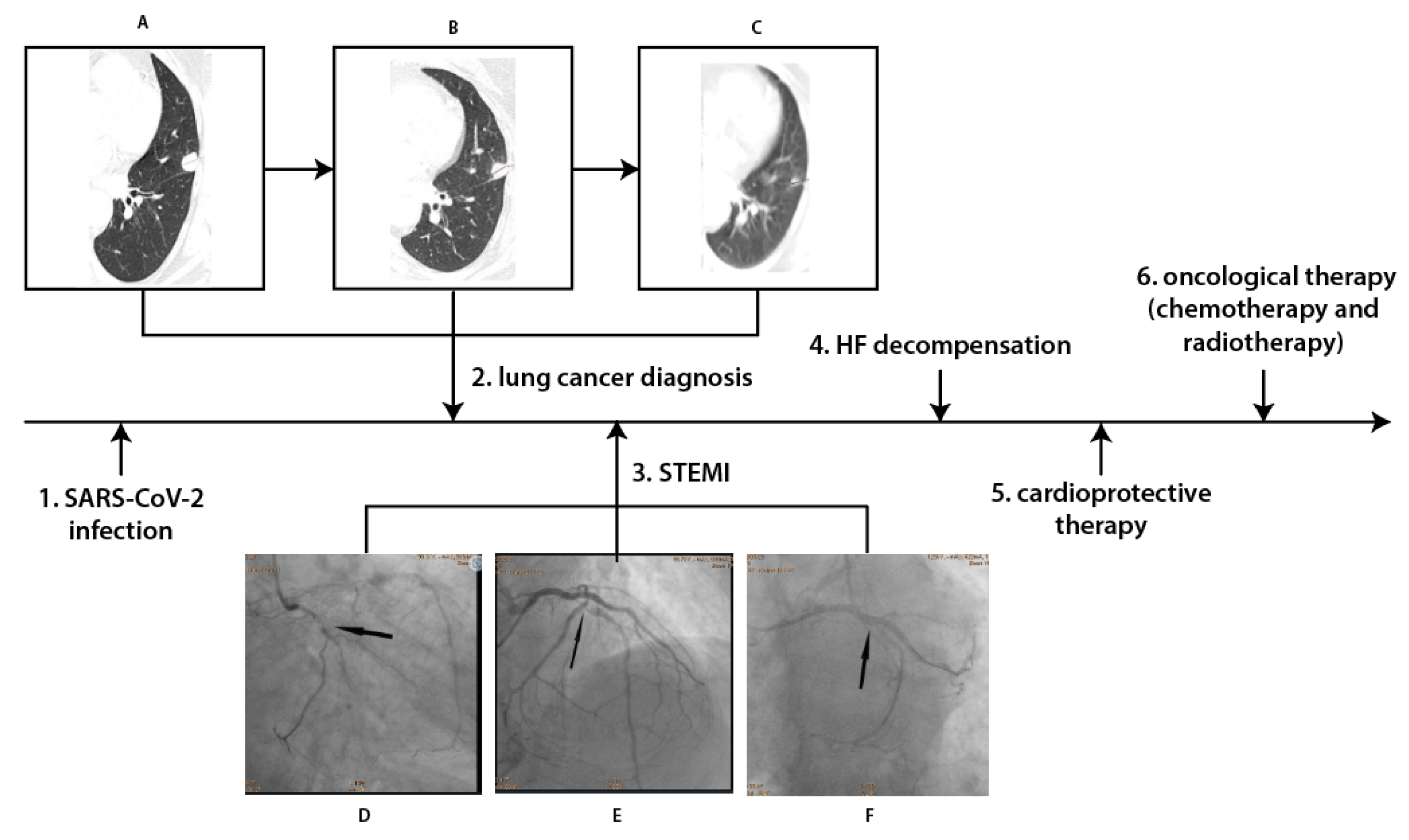
A 73-year-old former male smoker with hyperlipidaemia, type 2 diabetes and hypertension, after partial right nephrectomy in 2005 due to the kidney cancer, in April 2022 was diagnosed with SARS-COV-2 infection. Due to the symptomatic course of COVID-19 disease the chest X-ray was performed which revealed pathological changes in left lung. Therefore, subsequent angio-chest tomography (CT) was performed, which excluded pulmonary embolism but confirmed a 20-mm diameter subpleural focal lesion in 4 segment of the left lung. According to the classification of tumors (T), nodes (N) and metastases (M), this was diagnosed as cT1bN1M0, grade IIB, a small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.
One month later, the patient was admitted to Hemodynamic Lab with inferior wall ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. On admission, significant elevation in troponin T and N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) were noted as well as poor glycemia control (
Table 1).
Coronarography revealed multivessel coronary disease with significant stenoses in circumflex artery (Cx), first marginal artery and left anterior artery (LAD) (
Figure 1). They were subsequently treated by percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with drug-eluting stent (DES) implantation in Cx and first marginal artery on 26 May 2022. One day later, PCI of LAD was performed with two DES implantation. HF with reduced left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) was diagnosed with LVEF 30% in echocardiography. The patient was discharged 4 days later on dual antiplatelet therapy (aspirin and clopidogrel), beta-blocker, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, furosemide and statin.
He was hospitalized again in Cardiology Department in June 2022 due to acute HF decompensation. Upon admission oxygen saturation was 86%, and the following abnormalities were observed on laboratory examination: C-reactive protein (CRP) 7.21 mg/d (max 0.5), D-dimers 4228 ng/ml (max 500), NT pro BNP 8163.1 pg/ml (max 125), and blood glucose 207 mg/dl (max 99). Due to clinical symptoms and congestion in the pulmonary circulation noted on chest X-ray, intensive diuretic treatment with intravenous furosemide was initiated, resulting in a gradual improvement of the patient's clinical condition and remission of dyspnea. On discharge patients’ estimated glomerular filtration rate was 57 ml/min/1.73m2 and in addition to previous therapy dapagliflozin 10 mg once daily was introduced.
One month later the patient was admitted to the Department of Clinical Oncology to qualify for systemic treatment. The patient was stable with no HF decompensation events in the previous month with still reduced LVEF of 30% in echocardiography. The cardiological treatment was maintained and after multidisciplinary team discussion chemotherapy was initiated based on cisplatin-etoposide (PE) combination scheme. During the hospitalization the patient received the first course of PE regiment without complications.
A chest CT scan performed in August 2022 revealed a regression of the left lung neoplastic lesion (
Figure 1). There were also no signs of metastases on CT scans of the head and abdomen. Chemotherapy was continued for 6 months with no HF decompensations events and no significant renal function worsening. Futhermore the patient was also qualified and completed radical radiotherapy. Two months later the patient was still stable with no HF decompensation events, no significant renal function worsening and improvement of glycemia control (glycated haemoglobin 7.4%). In December an improvement in LVEF was also noticed from 30 to 40%.
3. Discussion
The Hiob avalanche of adverse events in our patient followed an interesting se-quence. The diagnosis of COVID-19 disease with related tests were decisive in the detection of the lung cancer, which contributed to early diagnosis and radical oncological treatment. Since there is a positive correlation between time of diagnosis and cancer prognosis, we might speculate that in this case post-COVID tests saved patients’ life.
In our case, a strong correlation between COVID-19 disease, cancer, and myocardial infarction needs to be addressed. CVD and cancer share many common cardiovascular risk factors and mechanisms, including inflammatory processes, impaired endothelium function and altered platelet function. On the one side it causes that these two diseases frequently co-exist; on the other- patients are more prone to thrombotic events [
11]. COVID-19 additionally increases the risk of thrombotic complications which triggered in our case the cascade of adverse events [
12].
The severity of COVID-19 and mortality rates are higher when there is an underlying CVD. Depending on the severity of the condition, COVID-19 may result in primary (myocarditis, MI, and arrhythmias) or secondary cardiac complications (usually due to systemic inflammatory syndrome resulting in acute myocardial injury or congestive heart failure). In some cases severe circulatory failure may develop [
13].
Several mechanisms of MI in cancer patients have been proposed [14-16]. The metastases of lung cancer to the heart can block coronary arteries directly, causing acute myocardial infarctions. The possibility of such a situation does exist, although it is relatively rare. In the literature, several cases of myocardial infarction associated with metastatic lung cancer have been reported [
14,
15,
16]. As the patient we describe did not have a diagnosed metastatic disease, we may suspect that COVID-19 infection and the accumulation of other patients’ traditional risk factors (smoking, diabetes type 2, hyperlipidaemia, hypertension) could have contributed to the MI.
As a final point, we would like to discuss one more important clinical issue. The treatment of HF involves many different approaches. In 2021, sodium glucose cotrans-porter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors were introduced by European Society of Cardiology guide-lines to the treatment of HF with reduced EF as class I agents due to the breakthrough studies documenting their efficacy in reduction of hospitalization rates and mortality [
17,
18]. However, few studies have been conducted on the effectiveness of SGLT2-inhibitors in HF concerning cancer sub-population [
19,
20]. In our opinion, in reported patient case, the addition of dapagliflozin to the standard HF therapy potentially might contribute to the prevention of next HF worsening episodes. Moreover, it allowed on proceeding with chemotherapy requiring intensive fluid therapy to counteract the potential risk of cisplatin-related nephrotoxicity in patient with past renal cancer history.
We introduce this vignette to document how COVID disease being terrific in the last years, might contribute and provoke serious adverse events however paradoxically with the help of modern diagnostic and therapeutic options might lead to saving patients’ life in the end.
4. Conclusions
Cancer and cardiovascular diseases frequently coexist, meaning that an oncological patient is also often a cardiological patient. Diagnostics and cardiological treatments must be carried out simultaneously with anticancer therapies. In order to reduce long-term cardiovascular complications and to prevent the potential discontinuation of cancer therapy due to deterioration of the cardiovascular system condition, early and periodic assessment of the risk of cardiotoxicity and optimal pharmacotherapy are essential.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The data are not publicly available due to nature of article (case report).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Timmis, A.; Townsend, N.; Gale, C.P.; Torbica, A.; Lettino, M.; Petersen, S.E.; Mossialos, E.A.; Maggioni, A.P.; Kazakiewicz, D.; May, H.T.; et al. European society of cardiology: Cardiovascular disease statistics 2019. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 12–85. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehz859. [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Steliarova-Foucher, E.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Rosso, S.; Coebergh, J.W.W.; Comber, H.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: Estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 1374–1403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2012.12.027. [CrossRef]
- Bayliss, E.A.; Reifler, L.M.; Zeng, C.; McQuillan, D.B.; Ellis, J.L.; Steiner, J.F. Competing Risks of Cancer Mortality and Cardiovascular Events in Individuals with Multimorbidity. J. Comorbidity 2014, 4, 29–36. https://doi.org/10.15256/joc.2014.4.41. [CrossRef]
- Meijers, W.C.; De Boer, R.A. Common risk factors for heart failure and cancer. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 844–853. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvz035. [CrossRef]
- Rinde, L.B.; Småbrekke, B.; Hald, E.M.; Brodin, E.E.; Njølstad, I.; Mathiesen, E.B.; Løchen, M.L.; Wilsgaard, T.; Brækkan, S.K.; Vik, A.; et al. Myocardial infarction and future risk of cancer in the general population—the Tromsø Study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 193–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-017-0231-5. [CrossRef]
- Navi, B.B.; Reiner, A.S.; Kamel, H.; Iadecola, C.; Okin, P.M.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Panageas, K.S.; DeAngelis, L.M. Risk of Arterial Thromboembolism in Patients With Cancer. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 926–938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2017.06.047. [CrossRef]
- Curigliano, G.; Cardinale, D.; Dent, S.; Criscitiello, C.; Aseyev, O.; Lenihan, D.; Cipolla, C.M. Cardiotoxicity of anticancer treatments: Epidemiology, detection, and management. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 309–325. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21341. [CrossRef]
- Ananthan, K.; Lyon, A.R. The Role of Biomarkers in Cardio-Oncology. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2020, 13, 431–450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-020-10042-3. [CrossRef]
- Paterson, D.I.; Wiebe, N.; Cheung, W.Y.; Mackey, J.R.; Pituskin, E.; Reiman, A.; Tonelli, M. Incident Cardiovascular Disease Among Adults With Cancer: A Population-Based Cohort Study. JACC CardioOncology 2022, 4, 85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaccao.2022.01.100. [CrossRef]
- Caitlin F. Bell, Xiudong Lei, Allen Haas, Richard A. Baylis, Hua Gao, Lingfeng Luo, Sharon H. Giordano, Mackenzie R. Wehner, Kevin T. Nead, N.J.L. Risk of cancer after diagnosis of Cardiovascular Disease. 2023, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaccao.2023.01.010. [CrossRef]
- Leiva, O.; AbdelHameid, D.; Connors, J.M.; Cannon, C.P.; Bhatt, D.L. Common Pathophysiology in Cancer, Atrial Fibrillation, Atherosclerosis, and Thrombosis: JACC: CardioOncology State-of-the-Art Review. JACC CardioOncology 2021, 3, 619–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaccao.2021.08.011. [CrossRef]
- Kanth Manne, B.; Denorme, F.; Middleton, E.A.; Portier, I.; Rowley, J.W.; Stubben, C.; Petrey, A.C.; Tolley, N.D.; Guo, L.; Cody, M.; et al. Platelet gene expression and function in patients with COVID-19. Blood 2020, 136, 1317–1329. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2020007214. [CrossRef]
- Ranard, L.S.; Fried, J.A.; Abdalla, M.; Anstey, D.E.; Givens, R.C.; Kumaraiah, D.; Kodali, S.K.; Takeda, K.; Karmpaliotis, D.; Rabbani, L.R.E.; et al. Approach to Acute Cardiovascular Complications in COVID-19 Infection. Circ. Hear. Fail. 2020, 13, 167–176. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.120.007220. [CrossRef]
- Kuramoto, M.; Okada, M.; Saeki, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Hasegawa, S. Acute Myocardial Infarction Due to Coronary Occlusion Caused by a Metastatic Cardiac Tumor Arising from Squamous Cell Lung Cancer: An Evaluation with Three-dimensional Transthoracic Echocardiography. Intern. Med. 2022, 61, 345–350. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.7580-21. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Xie, X.; Yang, Y.; Tang, S. Lung tumor presenting with acute myocardial infarction and lower extremity arterial embolism. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-020-01770-0. [CrossRef]
- Daher, I.N.; Luh, J.Y.; Duarte, A.G. Squamous cell lung cancer simulating an acute myocardial infarction. Chest 2003, 123, 304–306. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.123.1.304. [CrossRef]
- Sławiński G., Jankowska H. Liżewska-Springer A., L.E. Effective cardioprotection with early initiation of sacubitril- valsartan in a patient with breast cancer and cancer treatment-induced heart failure. Kardiol. Pol. 2022, 78, 131–137. https://doi.org/10.33963/KP.15163. [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Čelutkiene, J.; Chioncel, O.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Coats, A.J.S.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab368. [CrossRef]
- Daniele, A.J.; Gregorietti, V.; Costa, D.; Lopez-Fernandez, T. Use of emgliflozine in cardiotoxicity treatment. EMPACARD-treatment registry. Six-months follow-up. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 2590. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehac544.2590. [CrossRef]
- Lyon, A.R.; López-Fernánde, T.; Couch, L.S.; Asteggiano, R.; Aznar, M.C.; Bergler-Klei, J.; Boriani, G.; Cardinale, D.; Cordoba, R.; Cosyns, B.; et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines on cardio-oncology developed in collaboration with the European Hematology Association (EHA), the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ESTRO) and the International Cardio-Oncology Society (IC-OS). Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 4229–4361. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehac244. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).