Submitted:
29 May 2023
Posted:
30 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
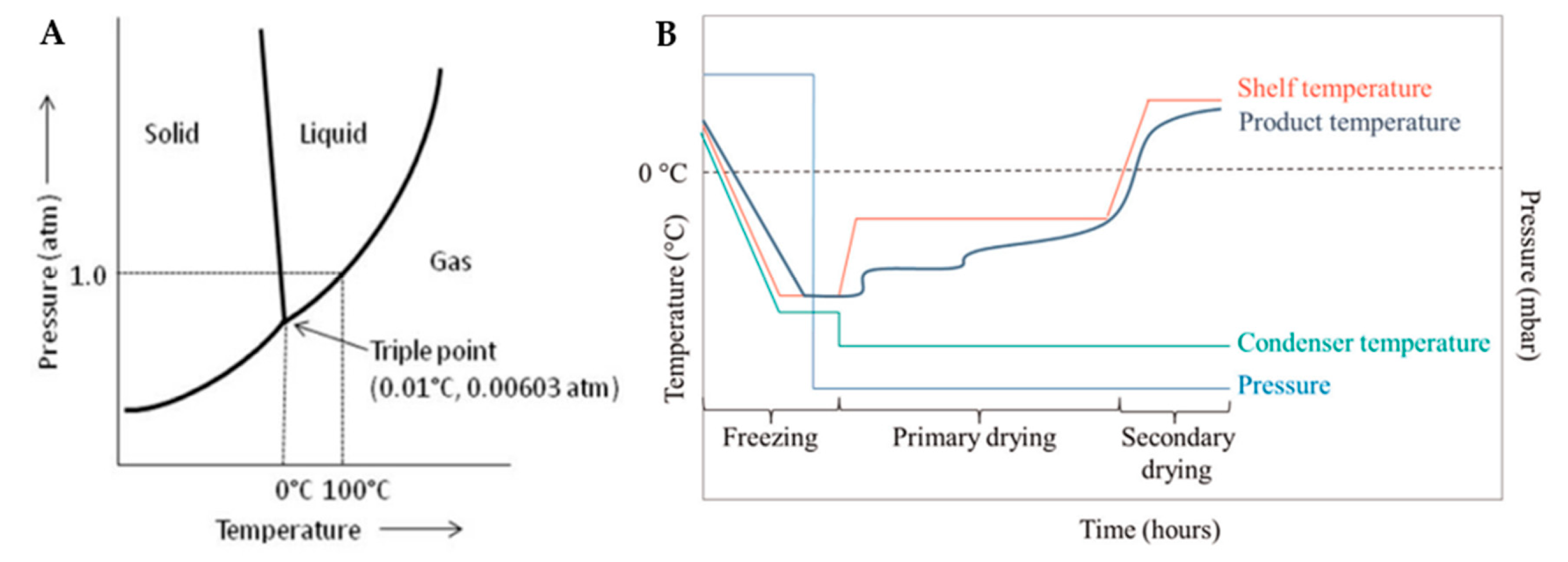
2. Freeze-drying
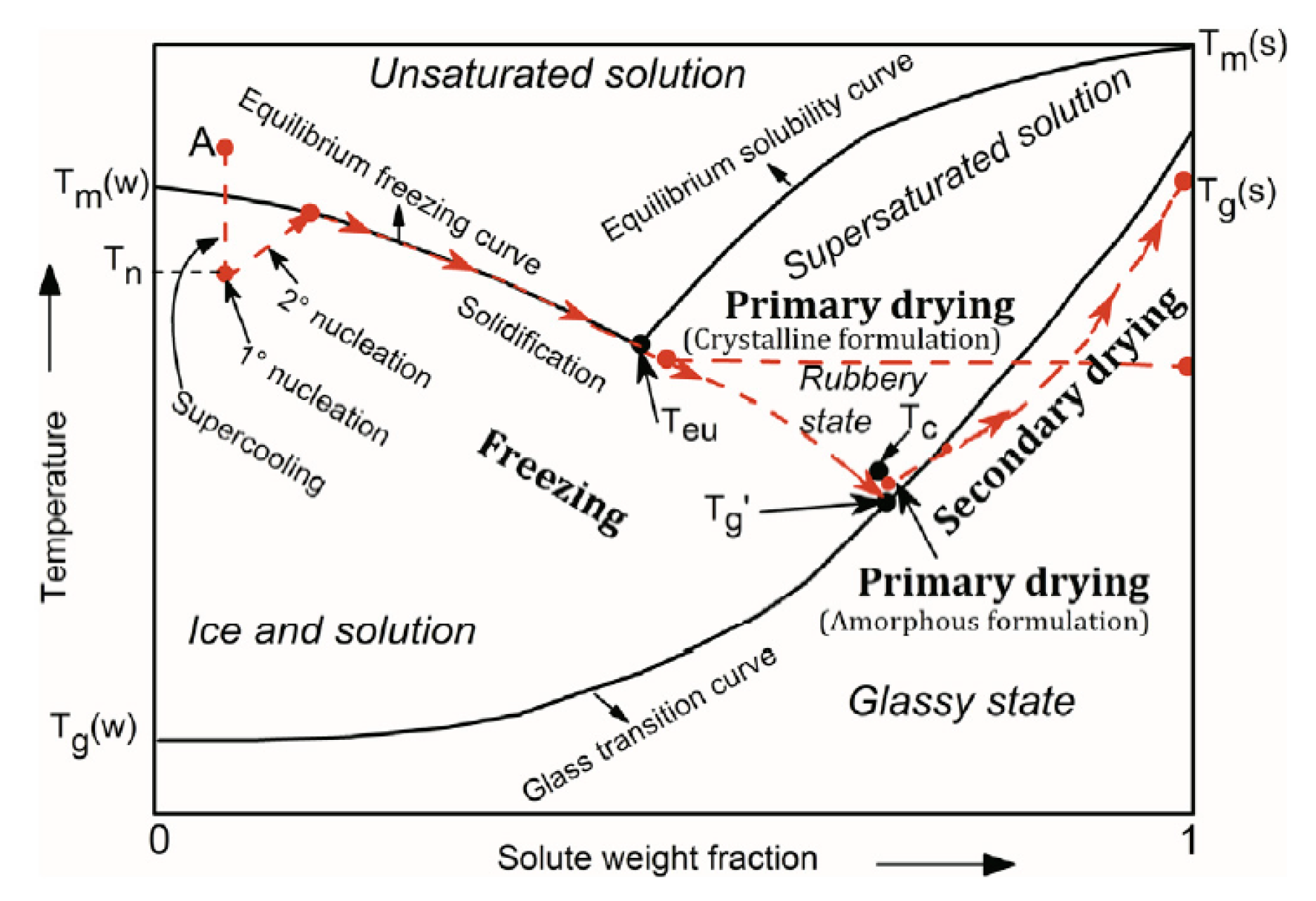
2.1. Freezing
2.2. Primary Drying
2.3. Secondary Drying
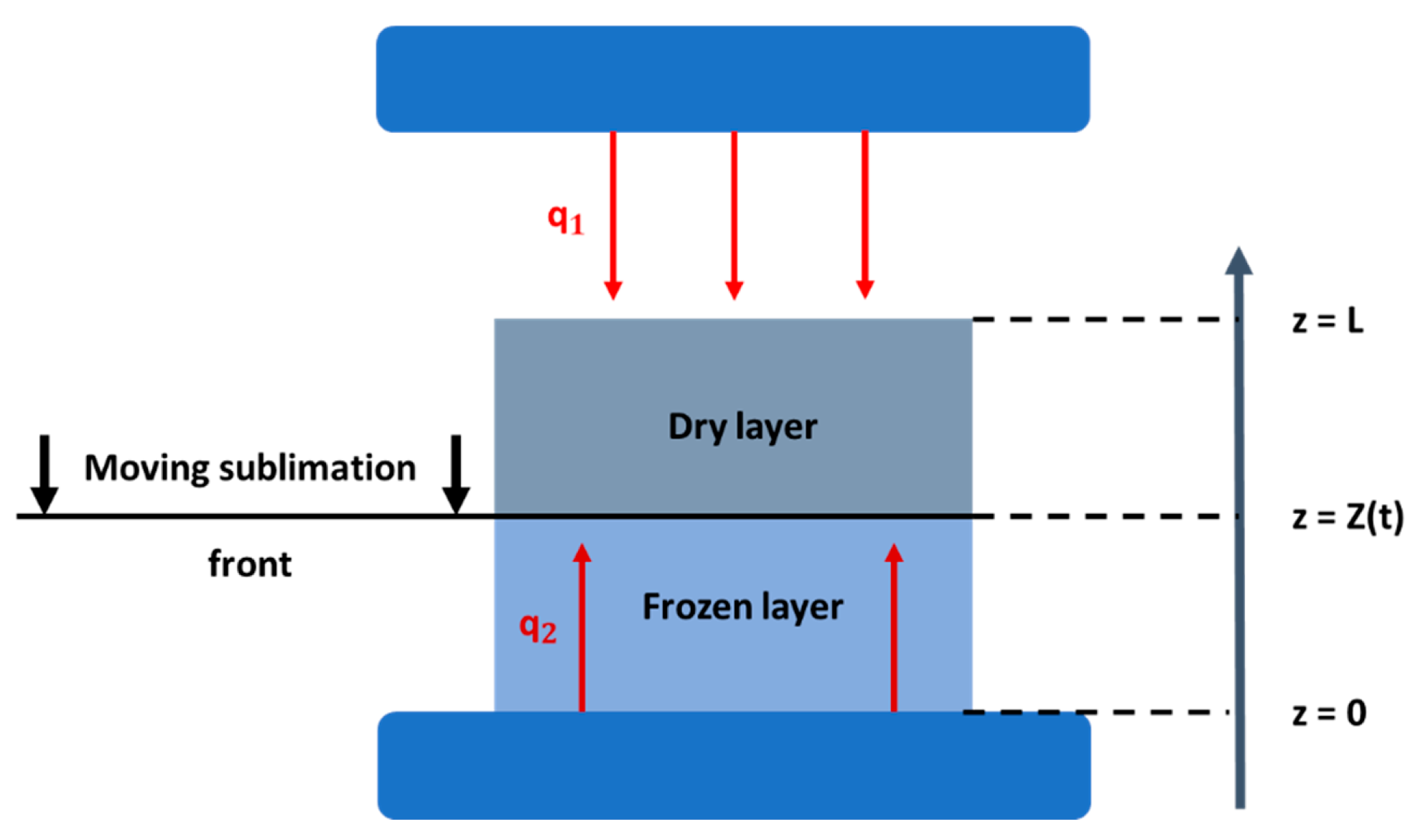
2.4. Mathematical modeling of the freeze-drying process
- Heat transfer in the frozen phase:
- Heat transfer in the dried phase:
- Mass transfer in the frozen phase:
- Mass transfer in the frozen phase:
3. Freeze-dried collagen-based sponges in biomedical engineering
3.1. Parameters affecting the properties of collagen-based sponges
3.2. Commercially available collagen-based sponges
4. Design of Experiments and Artificial Intelligence
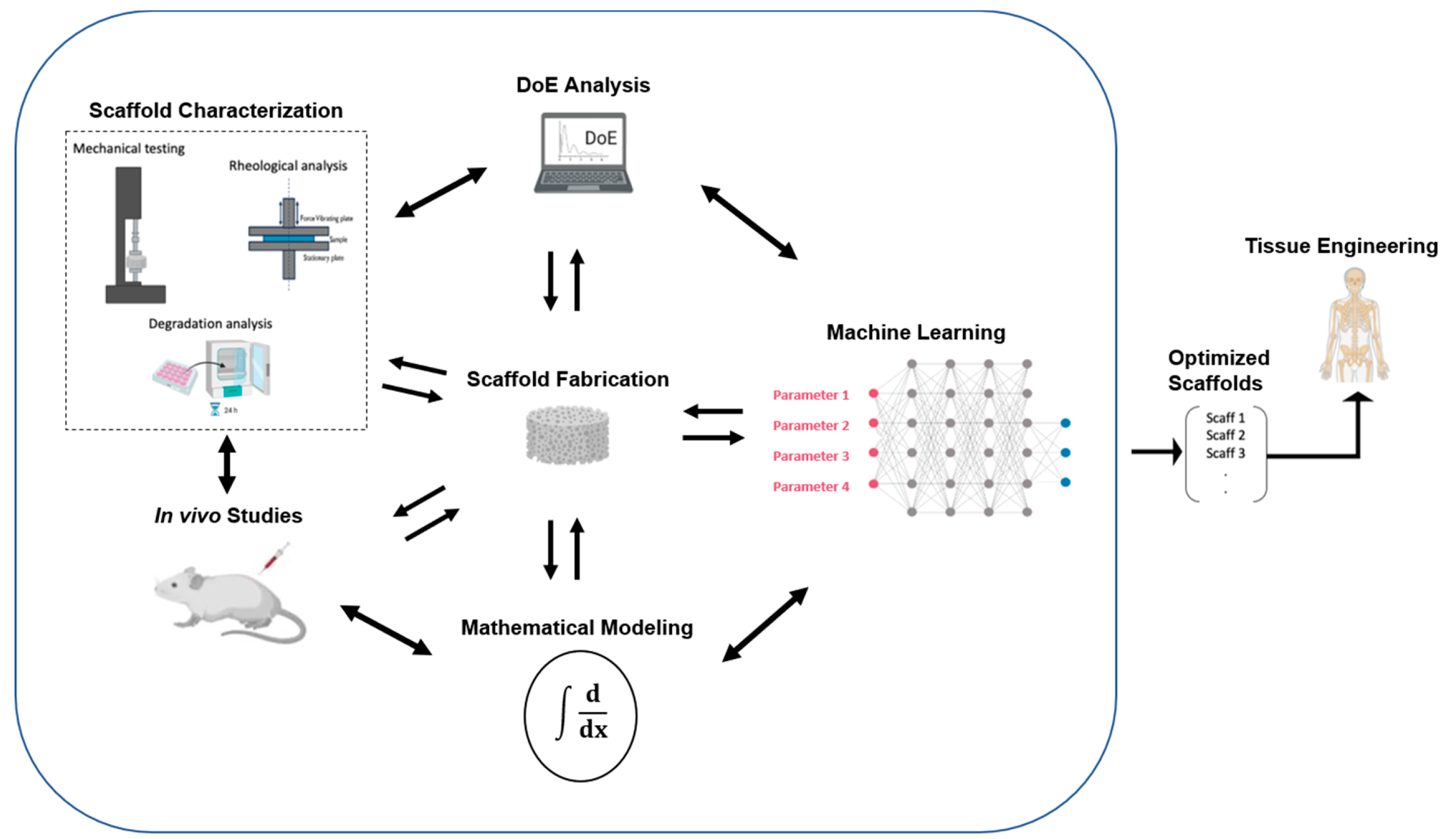
5. Discussion /Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.-Y. Biomedical Engineering for Health Research and Development. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2015, 19, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Christy, P.N.; Basha, S.K.; Kumari, V.S.; Bashir, A.K.H.; Maaza, M.; Kaviyarasu, K.; Arasu, M.V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Ignacimuthu, S. Biopolymeric Nanocomposite Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering Applications – A Review. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 2020, 55, 101452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttappan, S.; Mathew, D.; Nair, M.B. Biomimetic Composite Scaffolds Containing Bioceramics and Collagen/Gelatin for Bone Tissue Engineering - A Mini Review. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2016, 93, 1390–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico Llanos, G.A.; Borrego-González, S.; Moncayo, M.; Becerra, J.; Visser, R. Collagen Type I Biomaterials as Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2021, 13, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ma, P.X. Polymeric Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Annals of Biomedical Engineering 2004, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, M.; Born, G.; Chaaban, M.; Scherberich, A. Natural Polymeric Scaffolds in Bone Regeneration. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Puyana, V.; Felix, M.; Romero, A.; Guerrero, A. Influence of the Processing Variables on the Microstructure and Properties of Gelatin-Based Scaffolds by Freeze-Drying. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 2019, 136, 47671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Teo, W.E.; Zhu, X.; Beuerman, R.W.; Ramakrishna, S.; Yung, L.Y.L. An Aligned Nanofibrous Collagen Scaffold by Electrospinning and Its Effects on in Vitro Fibroblast Culture. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A 2006, 79A, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varley, M.C.; Neelakantan, S.; Clyne, T.W.; Dean, J.; Brooks, R.A.; Markaki, A.E. Cell Structure, Stiffness and Permeability of Freeze-Dried Collagen Scaffolds in Dry and Hydrated States. Acta Biomaterialia 2016, 33, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadikoglu, H.; Ozdemir, M.; Şeker, M. Freeze-Drying of Pharmaceutical Products: Research and Development Needs. Drying Technology - DRY TECHNOL 2006, 24, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachlos, E.; Czernuszka, J.T. Making Tissue Engineering Scaffolds Work. Review: The Application of Solid Freeform Fabrication Technology to the Production of Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Eur Cell Mater 2003, 5, 29–39, discussion 39-40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, H. Drying Technologies of Foods -Their History and Future. Drying Technology 1989, 7, 315–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.; Jakubczyk, E. The Freeze-Drying of Foods—The Characteristic of the Process Course and the Effect of Its Parameters on the Physical Properties of Food Materials. Foods 2020, 9, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Arnoult, O.; Smith, M.E.; Wnek, G.E. Electrospinning of Collagen Nanofiber Scaffolds from Benign Solvents. Macromolecular Rapid Communications 2009, 30, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, C.J.; Reucroft, I.M.; Grota, M.C.; Shreiber, D.I. Production of Highly Aligned Collagen Scaffolds by Freeze-Drying of Self-Assembled, Fibrillar Collagen Gels. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Cheung, K.C. Biodegradable Cell-Seeded Nanofiber Scaffolds for Neural Repair. Polymers 2011, 3, 1684–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Murugan, R.; Wang, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospinning of Nano/Micro Scale Poly(l-Lactic Acid) Aligned Fibers and Their Potential in Neural Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2603–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, J.T.; Li, D.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of Nanofibers with Core-Sheath, Hollow, or Porous Structures. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.G.; Shin, H.; Lim, D.W. Biomimetic Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Advanced Functional Materials 2012, 22, 2446–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shen, Q.; Shen, J.; Ding, X.; Liu, T.; He, J.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, D.; Zhu, J. Multifunctional Fibroblasts Enhanced via Thermal and Freeze-Drying Post-Treatments of Aligned Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2021, 3, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiono, V.; Tonda-Turo, C. Trends in the Design of Nerve Guidance Channels in Peripheral Nerve Tissue Engineering. Progress in Neurobiology 2015, 131, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girton, T.S.; Dubey, N.; Tranquillo, R.T. Magnetic-Induced Alignment of Collagen Fibrils in Tissue Equivalents. In Tissue Engineering Methods and Protocols; Morgan, J.R., Yarmush, M.L., Eds.; Methods in Molecular MedicineTM; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, 1999; pp. 67–73. ISBN 978-1-59259-602-7. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Gurkan, U.A.; Dehen, C.J.; Tate, M.P.; Hillhouse, H.W.; Simpson, G.J.; Akkus, O. An Electrochemical Fabrication Process for the Assembly of Anisotropically Oriented Collagen Bundles. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3278–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacko, C.S.; Singh, I.; Wall, M.A.; Garcia, A.R.; Porvasnik, S.L.; Rinaldi, C.; Schmidt, C.E. Magnetic Particle Templating of Hydrogels: Engineering Naturally Derived Hydrogel Scaffolds with 3D Aligned Microarchitecture for Nerve Repair. J. Neural Eng. 2020, 17, 016057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vader, D.; Kabla, A.; Weitz, D.; Mahadevan, L. Strain-Induced Alignment in Collagen Gels. PLOS ONE 2009, 4, e5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girton, T.S.; Barocas, V.H.; Tranquillo, R.T. Confined Compression of a Tissue-Equivalent: Collagen Fibril and Cell Alignment in Response to Anisotropic Strain. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering 2002, 124, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whang, K.; Thomas, C.H.; Healy, K.E.; Nuber, G. A Novel Method to Fabricate Bioabsorbable Scaffolds. Polymer 1995, 36, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, S.; Agarwal, T.; Das, J.; Maiti, T.K. Development of Gelatin/Carboxymethyl Chitosan/Nano-Hydroxyapatite Composite 3D Macroporous Scaffold for Bone Tissue Engineering Applications. Carbohydrate Polymers 2018, 189, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, G.D.J.; Cook, I.; Ward, K.R. The Principles of Freeze-Drying. In Cryopreservation and Freeze-Drying Protocols; Wolkers, W.F., Oldenhof, H., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 121–143. ISBN 978-1-4939-2193-5. [Google Scholar]
- Khairnar, S.; Kini, R.; Harwalkar, M.; Salunkhe, K.; Chaudhari, S. A Review on Freeze Drying Process of Pharmaceuticals. International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and science 2012, IJRPS 2013, 76–94. [Google Scholar]
- Baheti, A.; Lokesh, K.; Bansal, A. Excipients Used in Lyophilization of Small Molecules. Journal of Excipients and Food Chemicals 2010, 1. [Google Scholar]
- do V. Morais, A.R. Alencar, É. do N.; Xavier Júnior, F.H.; Oliveira, C.M. de; Marcelino, H.R.; Barratt, G.; Fessi, H.; Egito, E.S.T. do; Elaissari, A. Freeze-Drying of Emulsified Systems: A Review. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2016, 503, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assegehegn, G.; la Fuente, E.B.; Franco, J.M.; Gallegos, C. The Importance of Understanding the Freezing Step and Its Impact on Freeze-Drying Process Performance. JPharmSci 2019, 108, 1378–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Chen, M.; Chen, G. Issues in Freeze Drying of Aqueous Solutions. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering 2012, 20, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambhatla, S.; Ramot, R.; Bhugra, C.; Pikal, M.J. Heat and Mass Transfer Scale-up Issues during Freeze Drying: II. Control and Characterization of the Degree of Supercooling. AAPS PharmSciTech 2004, 5, e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujumdar, A.S. (Ed.) Handbook of Industrial Drying, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 2006; ISBN 978-0-429-13609-2. [Google Scholar]
- Fereshteh, Z. 7 - Freeze-Drying Technologies for 3D Scaffold Engineering. In Functional 3D Tissue Engineering Scaffolds; Deng, Y., Kuiper, J., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing, 2018; pp. 151–174 ISBN 978-0-08-100979-6.
- Vasanthan, K.S.; Subramaniam, A.; Krishnan, U.M.; Sethuraman, S. Influence of 3D Porous Galactose Containing PVA/Gelatin Hydrogel Scaffolds on Three-Dimensional Spheroidal Morphology of Hepatocytes. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 2015, 26, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X. (Charlie); Pikal, M.J. Design of Freeze-Drying Processes for Pharmaceuticals: Practical Advice. Pharm Res 2004, 21, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.J. Freeze-drying of foods; London, UK: Butterworth & Co. (Publishers) Ltd., 1971; pp. 10–76. ISBN 978-0-408-70189-1. [Google Scholar]
- Daraoui, N.; Dufour, P.; Hammouri, H.; Hottot, A. Model Predictive Control during the Primary Drying Stage of Lyophilisation. Control Engineering Practice 2010, 18, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.-Y.; Kang, J.-S.; Chang, Y.S. Analysis of Primary Drying of Poly-γ-Glutamic Acid during Vacuum Freeze Drying. J Mech Sci Technol 2020, 34, 4323–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhova, E.; Gordienko, M.; Menshutina, N. Mathematical Model of Freeze Drying Taking into Account Uneven Heat and Mass Transfer over the Volume of the Working Chamber. Drying Technology 2022, 40, 2470–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antelo, L.T.; Passot, S.; Fonseca, F.; Trelea, I.C.; Alonso, A.A. Toward Optimal Operation Conditions of Freeze-Drying Processes via a Multilevel Approach. Drying Technology 2012, 30, 1432–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liapis, A.I.; Litchfield, R.J. Numerical Solution of Moving Boundary Transport Problems in Finite Media by Orthogonal Collocation. Computers & Chemical Engineering 1979, 3, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadikoglu, H.; Liapis, A.I.; Crosser, O.K. Optimal Control of the Primary and Secondary Drying Stages of Bulk Solution Freeze Drying in Trays. Drying Technology 1998, 16, 399–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boss, E.A.; Filho, R.M.; de Toledo, E.C.V. Freeze Drying Process: Real Time Model and Optimization. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification 2004, 43, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koganti, V.R.; Shalaev, E.Y.; Berry, M.R.; Osterberg, T.; Youssef, M.; Hiebert, D.N.; Kanka, F.A.; Nolan, M.; Barrett, R.; Scalzo, G.; et al. Investigation of Design Space for Freeze-Drying: Use of Modeling for Primary Drying Segment of a Freeze-Drying Cycle. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisano, R.; Fissore, D.; Barresi, A.A.; Rastelli, M. Quality by Design: Scale-Up of Freeze-Drying Cycles in Pharmaceutical Industry. AAPS PharmSciTech 2013, 14, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Chen, G.; Mujumdar, A.S. Physical Interpretation of Solids Drying: An Overview on Mathematical Modeling Research. Drying Technology 2007, 25, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Stawczyk, J.; Zbicinski, I. CFD Model of Apple Atmospheric Freeze Drying at Low Temperature. Drying Technology 2007, 25, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barresi, A.A.; Pisano, R.; Rasetto, V.; Fissore, D.; Marchisio, D.L. Model-Based Monitoring and Control of Industrial Freeze-Drying Processes: Effect of Batch Nonuniformity. Drying Technology 2010, 28, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.P.; Leong, K.W. Scaffolding in Tissue Engineering: General Approaches and Tissue-Specific Considerations. Eur Spine J 2008, 17, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brougham, C.M.; Levingstone, T.J.; Shen, N.; Cooney, G.M.; Jockenhoevel, S.; Flanagan, T.C.; O’Brien, F.J. Freeze-Drying as a Novel Biofabrication Method for Achieving a Controlled Microarchitecture within Large, Complex Natural Biomaterial Scaffolds. Advanced Healthcare Materials 2017, 6, 1700598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lam, W.M.R.; Yang, Z.; Wang, M.; Ren, X.; Hu, T.; Li, J.; Goh, J.C.-H.; Wong, H.-K. Improving the Handling Properties and Long-Term Stability of Polyelectrolyte Complex by Freeze-Drying Technique for Low-Dose Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 Delivery. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials 2020, 108, 2450–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, D.E.L.; do Amaral Sobral, P.J. The Effect of Processing Parameters and Solid Concentration on the Microstructure and Pore Architecture of Gelatin-Chitosan Scaffolds Produced by Freeze-Drying. Mat. Res. 2016, 19, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albu, G.; Titorencu, I.; Ghica, M.V. Collagen-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Tissue Engineering. In; 2011 ISBN 978-953-307-661-4.
- Kirkness, M.W.; Lehmann, K.; Forde, N.R. Mechanics and Structural Stability of the Collagen Triple Helix. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 2019, 53, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M. Processing of Collagen Based Biomaterials and the Resulting Materials Properties. BioMedical Engineering OnLine 2019, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owczarzy, A.; Kurasiński, R.; Kulig, K.; Rogóż, W.; Szkudlarek, A.; Maciążek-Jurczyk, M. Collagen - Structure, Properties and Application. Engineering of Biomaterials 2020, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Kawazoe, N.; Tateishi, T. 15 - Collagen-Based Scaffolds. In Natural-Based Polymers for Biomedical Applications; Reis, R.L., Neves, N.M., Mano, J.F., Gomes, M.E., Marques, A.P., Azevedo, H.S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Biomaterials; Woodhead Publishing, 2008; pp. 396–415 ISBN 978-1-84569-264-3.
- Liu, X.; Zheng, C.; Luo, X.; Wang, X.; Jiang, H. Recent Advances of Collagen-Based Biomaterials: Multi-Hierarchical Structure, Modification and Biomedical Applications. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2019, 99, 1509–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.-W.; Tabata, Y.; Ikada, Y. Fabrication of Porous Gelatin Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.; Wong, M.; Tabata, Y.; Mikos, A.G. Gelatin as a Delivery Vehicle for the Controlled Release of Bioactive Molecules. Journal of Controlled Release 2005, 109, 256–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echave, M.C.; Sánchez, P.; Pedraz, J.L.; Orive, G. Progress of Gelatin-Based 3D Approaches for Bone Regeneration. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 2017, 42, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Wang, C. Recent Advances in the Use of Gelatin in Biomedical Research. Biotechnol Lett 2015, 37, 2139–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aramwit, P.; Jaichawa, N.; Ratanavaraporn, J.; Srichana, T. A Comparative Study of Type A and Type B Gelatin Nanoparticles as the Controlled Release Carriers for Different Model Compounds. Materials Express 2015, 5, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, E.; Azami, M.; Kajbafzadeh, A.-M.; Moztarzadeh, F.; Faridi-Majidi, R.; Shamousi, A.; Karimi, R.; Ai, J. Preparation of Biomimetic Composite Scaffold from Gelatin/Collagen and Bioactive Glass Fibers for Bone Tissue Engineering. Materials Science and Engineering C 2016, 59, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toosi, S.; Naderi-Meshkin, H.; Kalalinia, F.; HosseinKhani, H.; Heirani-Tabasi, A.; Havakhah, S.; Nekooei, S.; Jafarian, A.H.; Rezaie, F.; Peivandi, M.T.; et al. Bone Defect Healing Is Induced by Collagen Sponge/Polyglycolic Acid. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 2019, 30, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujioka-Kobayashi, M.; Schaller, B.; Saulacic, N.; Pippenger, B.E.; Zhang, Y.; Miron, R.J. Absorbable Collagen Sponges Loaded with Recombinant Bone Morphogenetic Protein 9 Induces Greater Osteoblast Differentiation When Compared to Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2. Clinical and Experimental Dental Research 2017, 3, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, A.W.; LaChaud, G.; Shen, J.; Asatrian, G.; Nguyen, V.; Zhang, X.; Ting, K.; Soo, C. A Review of the Clinical Side Effects of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2. Tissue Eng Part B Rev 2016, 22, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovrlj, B.; Koehler, S.M.; Anderson, P.A.; Qureshi, S.A.; Hecht, A.C.; Iatridis, J.C.; Cho, S.K. Association Between BMP-2 and Carcinogenicity. Spine 2015, 40, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrejon, V.M.; Song, J.; Yu, Z.; Hang, S. Gelatin-Based Cellular Solids: Fabrication, Structure and Properties. Journal of Cellular Plastics 2022, 58, 797–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vlierberghe, S.; Cnudde, V.; Dubruel, P.; Masschaele, B.; Cosijns, A.; De Paepe, I.; Jacobs, P.J.S.; Van Hoorebeke, L.; Remon, J.P.; Schacht, E. Porous Gelatin Hydrogels: 1. Cryogenic Formation and Structure Analysis. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, C.; Besse, J.; Boyce, S. Controlled-Rate Freezing to Regulate the Structure of Collagen–Glycosaminoglycan Scaffolds in Engineered Skin Substitutes. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials 2015, 103, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forero, J.C.; Roa, E.; Reyes, J.G.; Acevedo, C.; Osses, N. Development of Useful Biomaterial for Bone Tissue Engineering by Incorporating Nano-Copper-Zinc Alloy (NCuZn) in Chitosan/Gelatin/Nano-Hydroxyapatite (Ch/G/NHAp) Scaffold. Materials 2017, 10, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, D.; Qin, C.; Shi, Y. A Review of Preparation Methods of Porous Skin Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Materials Today Communications 2022, 32, 104109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merivaara, A.; Zini, J.; Koivunotko, E.; Valkonen, S.; Korhonen, O.; Fernandes, F.M.; Yliperttula, M. Preservation of Biomaterials and Cells by Freeze-Drying: Change of Paradigm. Journal of Controlled Release 2021, 336, 480–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-Y.; Chen, L.-H.; Li, Y.; Rooke, J.C.; Sanchez, C.; Su, B.-L. Hierarchically Porous Materials: Synthesis Strategies and Structure Design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 481–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Long, J.; Cooper, A.I. Aligned Porous Materials by Directional Freezing of Solutions in Liquid CO2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 13482–13483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hussain, I.; Brust, M.; Butler, M.F.; Rannard, S.P.; Cooper, A.I. Aligned Two- and Three-Dimensional Structures by Directional Freezing of Polymers and Nanoparticles. Nature Mater 2005, 4, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Long, X.; Lin, W.; Du, B.; Yin, H.; Lan, W.; Zhao, D.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Luo, F.; et al. Bioactive 3D Porous Cobalt-Doped Alginate/Waterborne Polyurethane Scaffolds with a Coral Reef-like Rough Surface for Nerve Tissue Engineering Application. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, V.; Tekinay, A.; Müller, H.W. Chapter 16 - Neural ECM Mimetics. In Progress in Brain Research; Dityatev, A., Wehrle-Haller, B., Pitkänen, A., Eds.; Brain Extracellular Matrix in Health and Disease; Elsevier, 2014; Vol. 214, pp. 391–413.
- Powell, R.; Eleftheriadou, D.; Kellaway, S.; Phillips, J.B. Natural Biomaterials as Instructive Engineered Microenvironments That Direct Cellular Function in Peripheral Nerve Tissue Engineering. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Ding, F.; Williams, D.F. Neural Tissue Engineering Options for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6143–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantha, S.; Pillai, S.; Khayambashi, P.; Upadhyay, A.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, O.; Pham, H.M.; Tran, S.D. Smart Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Materials 2019, 12, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannino, A.; Madaghiele, M. Tuning the Porosity of Collagen-Based Scaffolds for Use as Nerve Regenerative Templates. Journal of Cellular Plastics 2009, 45, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokols, S.; Tuszynski, M.H. Freeze-Dried Agarose Scaffolds with Uniaxial Channels Stimulate and Guide Linear Axonal Growth Following Spinal Cord Injury. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basurto, I.M.; Mora, M.T.; Gardner, G.M.; Christ, G.J.; Caliari, S.R. Aligned and Electrically Conductive 3D Collagen Scaffolds for Skeletal Muscle Tissue Engineering. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 4040–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Nakamoto, T.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G. Engineering Multi-Layered Skeletal Muscle Tissue by Using 3D Microgrooved Collagen Scaffolds. Biomaterials 2015, 73, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozkurt, A.; Lassner, F.; O’Dey, D.; Deumens, R.; Böcker, A.; Schwendt, T.; Janzen, C.; Suschek, C.V.; Tolba, R.; Kobayashi, E.; et al. The Role of Microstructured and Interconnected Pore Channels in a Collagen-Based Nerve Guide on Axonal Regeneration in Peripheral Nerves. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidenko, N.; Gibb, T.; Schuster, C.; Best, S.M.; Campbell, J.J.; Watson, C.J.; Cameron, R.E. Biomimetic Collagen Scaffolds with Anisotropic Pore Architecture. Acta Biomaterialia 2012, 8, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, L.; Cohen, S. Novel Alginate Sponges for Cell Culture and Transplantation. Biomaterials 1997, 18, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokols, S.; Tuszynski, M.H. The Fabrication and Characterization of Linearly Oriented Nerve Guidance Scaffolds for Spinal Cord Injury. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5839–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, L.J.; Yannas, I.V.; Hsu, H.-P.; Strichartz, G.; Spector, M. Collagen-GAG Substrate Enhances the Quality of Nerve Regeneration through Collagen Tubes up to Level of Autograft. Experimental Neurology 1998, 154, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, L.J.; Yannas, I.V.; Arrizabalaga, A.; Hsu, H.-P.; Norregaard, T.V.; Spector, M. Early Peripheral Nerve Healing in Collagen and Silicone Tube Implants: Myofibroblasts and the Cellular Response. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, L.J.; Yannas, I.V.; Hsu, H.-P.; Spector, M. Connective Tissue Response to Tubular Implants for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration: The Role of Myofibroblasts. Journal of Comparative Neurology 2000, 417, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, L.J.; Yannas, I.v.; Hsu, H.-P.; Strichartz, G.r.; Spector, M. Near-Terminus Axonal Structure and Function Following Rat Sciatic Nerve Regeneration through a Collagen-GAG Matrix in a Ten-Millimeter Gap. Journal of Neuroscience Research 2000, 60, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Xu, Z. Ultralight, Highly Compressible, Hydrophobic and Anisotropic Lamellar Carbon Aerogels from Graphene/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Cellulose Nanofiber Aerogel as Oil Removing Absorbents. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2020, 388, 121804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Pang, B.; Xu, W.; Duan, G.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, K. Recent Progress on Nanocellulose Aerogels: Preparation, Modification, Composite Fabrication, Applications. Advanced Materials 2021, 33, 2005569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Wen, P.; Zhang, Y.; Long, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Xing, F.; Gao, J. Preparation of Aligned Porous Gelatin Scaffolds by Unidirectional Freeze-Drying Method. Acta Biomaterialia 2010, 6, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoof, H.; Bruns, L.; Fischer, A.; Heschel, I.; Rau, G. Dendritic Ice Morphology in Unidirectionally Solidified Collagen Suspensions. Journal of Crystal Growth 2000, 209, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaghiele, M.; Sannino, A.; Yannas, I.V.; Spector, M. Collagen-Based Matrices with Axially Oriented Pores. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A 2008, 85A, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Zhao, H.-B.; Liu, Z.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.-Z. On Controlling Aerogel Microstructure by Freeze Casting. Composites Part B: Engineering 2019, 173, 107036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divakar, P.; Yin, K.; Wegst, U.G.K. Anisotropic Freeze-Cast Collagen Scaffolds for Tissue Regeneration: How Processing Conditions Affect Structure and Properties in the Dry and Fully Hydrated States. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials 2019, 90, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinle, A.; Elsaesser, M.S.; Hüsing, N. Sol–Gel Synthesis of Monolithic Materials with Hierarchical Porosity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3377–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schardosim, M.; Soulié, J.; Poquillon, D.; Cazalbou, S.; Duployer, B.; Tenailleau, C.; Rey, C.; Hübler, R.; Combes, C. Freeze-Casting for PLGA/Carbonated Apatite Composite Scaffolds: Structure and Properties. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2017, 77, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, M.-A.; Ghalkhani, M.; Maleki, H. Directional Freeze-Casting: A Bioinspired Method to Assemble Multifunctional Aligned Porous Structures for Advanced Applications. Advanced Engineering Materials 2020, 22, 2000033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oryan, A.; Kamali, A.; Moshiri, A.; Baharvand, H.; Daemi, H. Chemical Crosslinking of Biopolymeric Scaffolds: Current Knowledge and Future Directions of Crosslinked Engineered Bone Scaffolds. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2018, 107, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azami, M.; Orang, F.; Moztarzadeh, F. Nanocomposite Bone Tissue-Engineering Scaffolds Prepared from Gelatin and Hydroxyapatite Using Layer Solvent Casting and Freeze-Drying Technique. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference on Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Engineering; September 2006; pp. 259–264.
- Shabafrooz, V.; Mozafari, M.; Köhler, G.A.; Assefa, S.; Vashaee, D.; Tayebi, L. The Effect of Hyaluronic Acid on Biofunctionality of Gelatin–Collagen Intestine Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A 2014, 102, 3130–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tylingo, R.; Gorczyca, G.; Mania, S.; Szweda, P.; Milewski, S. Preparation and Characterization of Porous Scaffolds from Chitosan-Collagen-Gelatin Composite. Reactive and Functional Polymers 2016, 103, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Puyana, V.; Jiménez-Rosado, M.; Rubio-Valle, J.F.; Guerrero, A.; Romero, A. Gelatin vs Collagen-Based Sponges: Evaluation of Concentration, Additives and Biocomposites. J Polym Res 2019, 26, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; An, M.; Qiu, H.-X.; Wang, L. The Properties of Chitosan-Gelatin Scaffolds by Once or Twice Vacuum Freeze-Drying Methods. Polymer-Plastics Technology and Engineering 2013, 52, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banafati Zadeh, F.; Zamanian, A. Glutaraldehyde: Introducing Optimum Condition for Cross-Linking the Chitosan/Gelatin Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. International Journal of Engineering 2022, 35, 1967–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugh, M.G.; Jaasma, M.J.; O’Brien, F.J. The Effect of Dehydrothermal Treatment on the Mechanical and Structural Properties of Collagen-GAG Scaffolds. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A 2009, 89A, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnakumar, G.S.; Sampath, S.; Muthusamy, S.; John, M.A. Importance of Crosslinking Strategies in Designing Smart Biomaterials for Bone Tissue Engineering: A Systematic Review. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2019, 96, 941–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, D.B.; Larsson, D.; Mrkonjic, F.; Isaksson, H.; Kumar, A.; Lidgren, L.; Tägil, M. Gelatin- Hydroxyapatite- Calcium Sulphate Based Biomaterial for Long Term Sustained Delivery of Bone Morphogenic Protein-2 and Zoledronic Acid for Increased Bone Formation: In-Vitro and in-Vivo Carrier Properties. Journal of Controlled Release 2018, 272, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Chen, L.; Cai, X.; Tong, T.; Tong, H.; Hu, J. A Novel Method for the Fabrication of Homogeneous Hydroxyapatite/Collagen Nanocomposite and Nanocomposite Scaffold with Hierarchical Porosity. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 2011, 22, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunniffe, G.M.; Dickson, G.R.; Partap, S.; Stanton, K.T.; O’Brien, F.J. Development and Characterisation of a Collagen Nano-Hydroxyapatite Composite Scaffold for Bone Tissue Engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med 2010, 21, 2293–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, R.J.; Roeder, R.K. Effects of Hydroxyapatite Reinforcement on the Architecture and Mechanical Properties of Freeze-Dried Collagen Scaffolds. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials 2012, 7, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Tong, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, T.; Wang, X. In Vitro Evaluation of a Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Nanometer Hydroxyapatite Collagen Scaffold for Bone Regeneration. Mol Med Rep 2018, 17, 5830–5836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, E.; Thompson, E.M.; Matsiko, A.; O’Brien, F.J.; López-Noriega, A. Long-Term Controlled Delivery of RhBMP-2 from Collagen-Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds for Superior Bone Tissue Regeneration. J Control Release 2015, 207, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-W.; Knowles, J.C.; Kim, H.-E. Hydroxyapatite and Gelatin Composite Foams Processed via Novel Freeze-Drying and Crosslinking for Use as Temporary Hard Tissue Scaffolds. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A 2005, 72A, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackington, W.; Gehweiler, D.; Zderic, I.; Nehrbass, D.; Zeiter, S.; González-Vázquez, A.; O’Brien, F.; Stoddart, M.; Thompson, K. Incorporation of Hydroxyapatite into Collagen Scaffolds Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of RhBMP-2 in a Weight-Bearing Femoral Defect Model. Materials Today Communications 2021, 29, 102933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, E.; López-Noriega, A.; Thompson, E.; Kelly, H.M.; Cryan, S.A.; O’Brien, F.J. Development of Collagen–Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds Incorporating PLGA and Alginate Microparticles for the Controlled Delivery of RhBMP-2 for Bone Tissue Engineering. Journal of Controlled Release 2015, 198, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Hwangbo, H.; Koo, Y.; Kim, G. Fabrication of Mechanically Reinforced Gelatin/Hydroxyapatite Bio-Composite Scaffolds by Core/Shell Nozzle Printing for Bone Tissue Engineering. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Lin, K. The Development of Collagen Based Composite Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. Bioactive Materials 2018, 3, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X. Chemical and Biochemical Basis of Cell-Bone Matrix Interaction in Health and Disease. Curr Chem Biol 2009, 3, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, E.; Partap, S.; Azevedo, M.M.; Jell, G.; Stevens, M.M.; O’Brien, F.J. Hypoxia-Mimicking Bioactive Glass/Collagen Glycosaminoglycan Composite Scaffolds to Enhance Angiogenesis and Bone Repair. Biomaterials 2015, 52, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugh, M.; Murphy, C.; O’Brien, F. Novel Freeze-Drying Methods to Produce a Range of Collagen–Glycosaminoglycan Scaffolds with Tailored Mean Pore Sizes. Tissue engineering. Part C, Methods 2009, 16, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.M.; Haugh, M.G.; O’Brien, F.J. The Effect of Mean Pore Size on Cell Attachment, Proliferation and Migration in Collagen–Glycosaminoglycan Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irawan, V.; Sung, T.-C.; Higuchi, A.; Ikoma, T. Collagen Scaffolds in Cartilage Tissue Engineering and Relevant Approaches for Future Development. Tissue Eng Regen Med 2018, 15, 673–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Lu, H.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G. Pore Size Effect of Collagen Scaffolds on Cartilage Regeneration. Acta Biomaterialia 2014, 10, 2005–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eviana Putri, N.R.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G. Preparation of PLGA-Collagen Hybrid Scaffolds with Controlled Pore Structures for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International 2020, 30, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooeaid, P.; Chuysinuan, P.; Pengsuk, C.; Dechtrirat, D.; Lirdprapamongkol, K.; Techasakul, S.; Svasti, J. Polylactic Acid Microparticles Embedded Porous Gelatin Scaffolds with Multifunctional Properties for Soft Tissue Engineering. Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices 2020, 5, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahnama, H.; Dadbin, S.; Frounchi, M.; Rajabi, S. Preparation of Biodegradable Gelatin/PVA Porous Scaffolds for Skin Regeneration. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology 2017, 45, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorczyca, G.; Tylingo, R.; Szweda, P.; Augustin, E.; Sadowska, M.; Milewski, S. Preparation and Characterization of Genipin Cross-Linked Porous Chitosan–Collagen–Gelatin Scaffolds Using Chitosan–CO2 Solution. Carbohydrate Polymers 2014, 102, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karipidou, N.; Tzavellas, A.-N.; Petrou, N.; Katrilaka, C.; Theodorou, K.; Pitou, M.; Tsiridis, E.; Choli-Papadopoulou, T.; Aggeli, A. Comparative Studies of Sterilization Processes for Sensitive Medical Nano-Devices. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, M.J.C.; Colaço, B.J.A.; Ventura, J.; Monteiro, F.J.M.; Salgado, C.L. Translational Research for Orthopedic Bone Graft Development. Materials 2021, 14, 4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabska-Zielińska, S.; Sionkowska, A.; Carvalho, Â.; Monteiro, F.J. Biomaterials with Potential Use in Bone Tissue Regeneration—Collagen/Chitosan/Silk Fibroin Scaffolds Cross-Linked by EDC/NHS. Materials 2021, 14, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asamura, S.; Mochizuki, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Tabata, Y.; Isogai, N. Bone Regeneration Using a Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Saturated Slow-Release Gelatin Hydrogel Sheet: Evaluation in a Canine Orbital Floor Fracture Model. Annals of Plastic Surgery 2010, 64, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caliari, S.R.; Harley, B.A.C. The Effect of Anisotropic Collagen-GAG Scaffolds and Growth Factor Supplementation on Tendon Cell Recruitment, Alignment, and Metabolic Activity. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 5330–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, K.S.; Haszman, S.; Wong, Y.N.; Soidin, E.; Hesham, N.; Mior, M.A.A.; Tabata, Y.; Ahmad, I.; Fauzi, M.B.; Mohd Yunus, M.H. Physicochemical Characterization of Bilayer Hybrid Nanocellulose-Collagen as a Potential Wound Dressing. Materials 2020, 13, 4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.J.; Husmann, A.; Hume, R.D.; Watson, C.J.; Cameron, R.E. Development of Three-Dimensional Collagen Scaffolds with Controlled Architecture for Cell Migration Studies Using Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Biomaterials 2017, 114, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, W.F.; Peckham, S.M.; Badura, J.M. A Comprehensive Clinical Review of Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (INFUSE® Bone Graft). International Orthopaedics (SICO 2007, 31, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bialy, I.; Jiskoot, W.; Reza Nejadnik, M. Formulation, Delivery and Stability of Bone Morphogenetic Proteins for Effective Bone Regeneration. Pharm Res 2017, 34, 1152–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA Inductos. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/inductos (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Katti, D.R.; Sharma, A.; Katti, K.S. Chapter 10 - Predictive Methodologies for Design of Bone Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. In Materials for Bone Disorders; Bose, S., Bandyopadhyay, A., Eds.; Academic Press, 2017; pp. 453–492 ISBN 978-0-12-802792-9.
- Morin, R.; Kaplan, D.; Perez-Ramirez, B. Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Binds As Multilayers To A Collagen Delivery Matrix: An Equilibrium Thermodynamic Analysis. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration Summary of Safety and Effectiveness Data 2002.
- Winn, S.R.; Uludag, H.; Hollinger, J.O. Carrier Systems for Bone Morphogenetic Proteins. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1999, S95–S106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uludag, H.; D’Augusta, D.; Palmer, R.; Timony, G.; Wozney, J. Characterization of RhBMP-2 Pharmacokinetics Implanted with Biomaterial Carriers in the Rat Ectopic Model. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research 1999, 46, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uludag, H.; D’Augusta, D.; Golden, J.; Li, J.; Timony, G.; Riedel, R.; Wozney, J.M. Implantation of Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Proteins with Biomaterial Carriers: A Correlation between Protein Pharmacokinetics and Osteoinduction in the Rat Ectopic Model. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research 2000, 50, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Integra Helistat® and Helitene® Absorbable Collagen Hemostats. Available online: https://instrumed-int.com.mx/uploads/CatalogoHelitene&Helistat2014.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2023).
- di Summa, P.G.; Kingham, P.J.; Campisi, C.C.; Raffoul, W.; Kalbermatten, D.F. Collagen (NeuraGen®) Nerve Conduits and Stem Cells for Peripheral Nerve Gap Repair. Neuroscience Letters 2014, 572, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, W.W.; Weatherly, T.; Park, T.S. Collagen Nerve Guides for Surgical Repair of Brachial Plexus Birth Injury. J Neurosurg 2006, 105, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushnell, B.D.; McWilliams, A.D.; Whitener, G.B.; Messer, T.M. Early Clinical Experience With Collagen Nerve Tubes in Digital Nerve Repair. The Journal of Hand Surgery 2008, 33, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Luca, A.C.; Lacour, S.P.; Raffoul, W.; di Summa, P.G. Extracellular Matrix Components in Peripheral Nerve Repair: How to Affect Neural Cellular Response and Nerve Regeneration? Neural Regeneration Research 2014, 9, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Giusti, G.; Friedrich, P.F.; Archibald, S.J.; Kemnitzer, J.E.; Patel, J.; Desai, N.; Bishop, A.T.; Shin, A.Y. The Effect of Collagen Nerve Conduits Filled with Collagen-Glycosaminoglycan Matrix on Peripheral Motor Nerve Regeneration in a Rat Model. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2012, 94, 2084–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmeyer, J.A.; Siemers, F.; Machens, H.-G.; Mailänder, P. The Clinical Use of Artificial Nerve Conduits for Digital Nerve Repair: A Prospective Cohort Study and Literature Review. J Reconstr Microsurg 2009, 25, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taras, J.S.; Nanavati, V.; Steelman, P. Nerve Conduits. Journal of Hand Therapy 2005, 18, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyner, T.R.; Parks, N.; Faria, S.; Simons, M.; Stapp, B.; Curtis, B.; Sian, K.; Yamaguchi, K.T. Effects of Collagen Nerve Guide on Neuroma Formation and Neuropathic Pain in a Rat Model. The American Journal of Surgery 2007, 193, e1–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.; Sullivan, N.; Margolis, D.; Schoelles, K. Commercially Available Skin Substitute Products; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US), 2020.
- GRAFTJACKET NOWTM. Available online: https://www.wright.com/healthcare-professionals/graftjacket-now (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- Sbricoli, L.; Guazzo, R.; Annunziata, M.; Gobbato, L.; Bressan, E.; Nastri, L. Selection of Collagen Membranes for Bone Regeneration: A Literature Review. Materials 2020, 13, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kharusi, G.; Dunne, N.J.; Little, S.; Levingstone, T.J. The Role of Machine Learning and Design of Experiments in the Advancement of Biomaterial and Tissue Engineering Research. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freiesleben, J.; Keim, J.; Grutsch, M. Machine Learning and Design of Experiments: Alternative Approaches or Complementary Methodologies for Quality Improvement? Quality and Reliability Engineering International 2020, 36, 1837–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebala, G.; Ravi, A.; Churiwala, S. Machine Learning Definition and Basics. In An Introduction to Machine Learning; Rebala, G., Ravi, A., Churiwala, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2019; pp. 1–17. ISBN 978-3-030-15729-6. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press, 2016; ISBN 978-0-262-33737-3.
- Colucci, D.; Morra, L.; Zhang, X.; Fissore, D.; Lamberti, F. An Automatic Computer Vision Pipeline for the In-Line Monitoring of Freeze-Drying Processes. Computers in Industry 2020, 115, 103184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, M.; Bica, I.; Best, S.M.; Cameron, R.E. Feature Importance in Multi-Dimensional Tissue-Engineering Datasets: Random Forest Assisted Optimization of Experimental Variables for Collagen Scaffolds. Applied Physics Reviews 2021, 8, 041403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
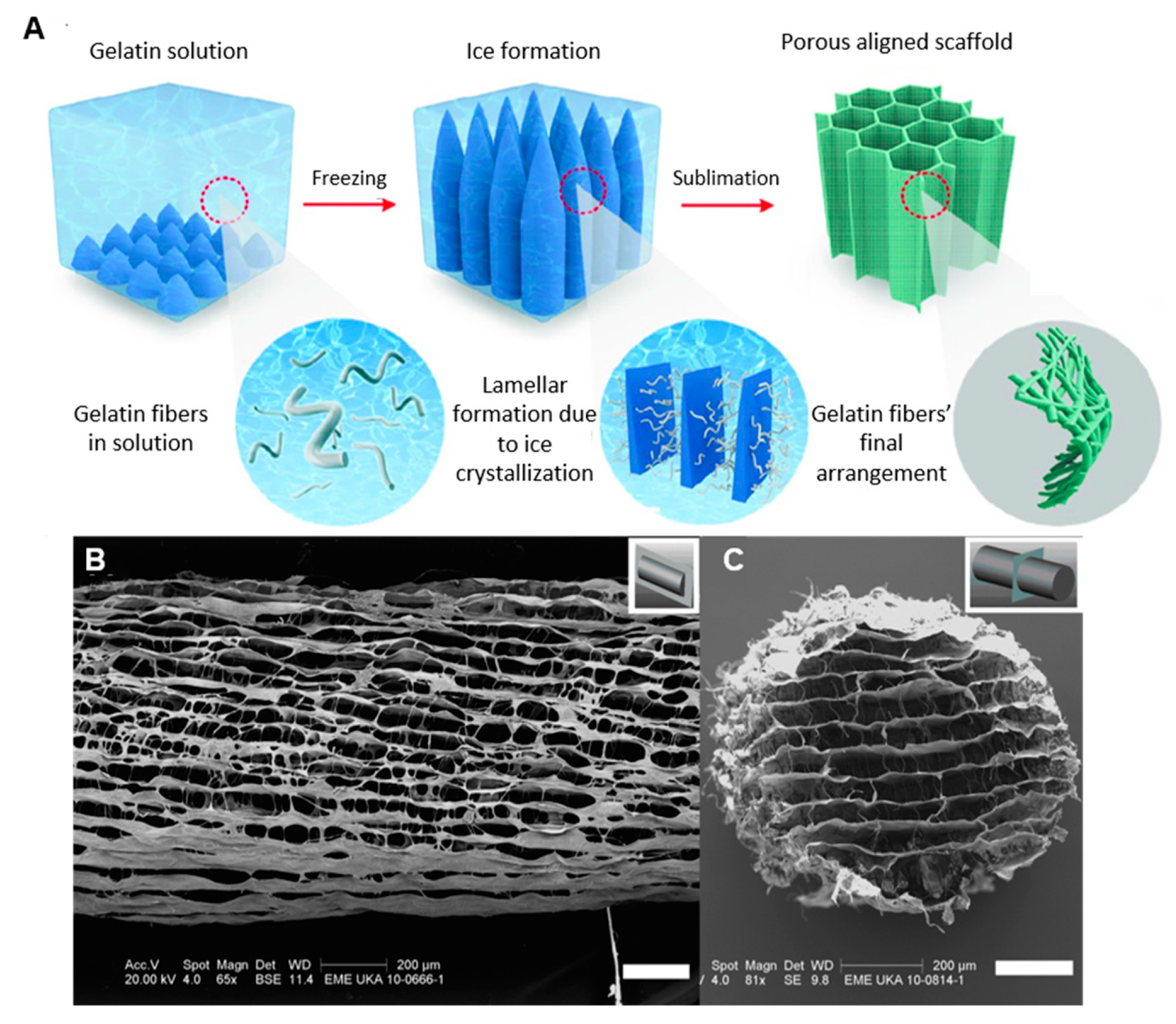
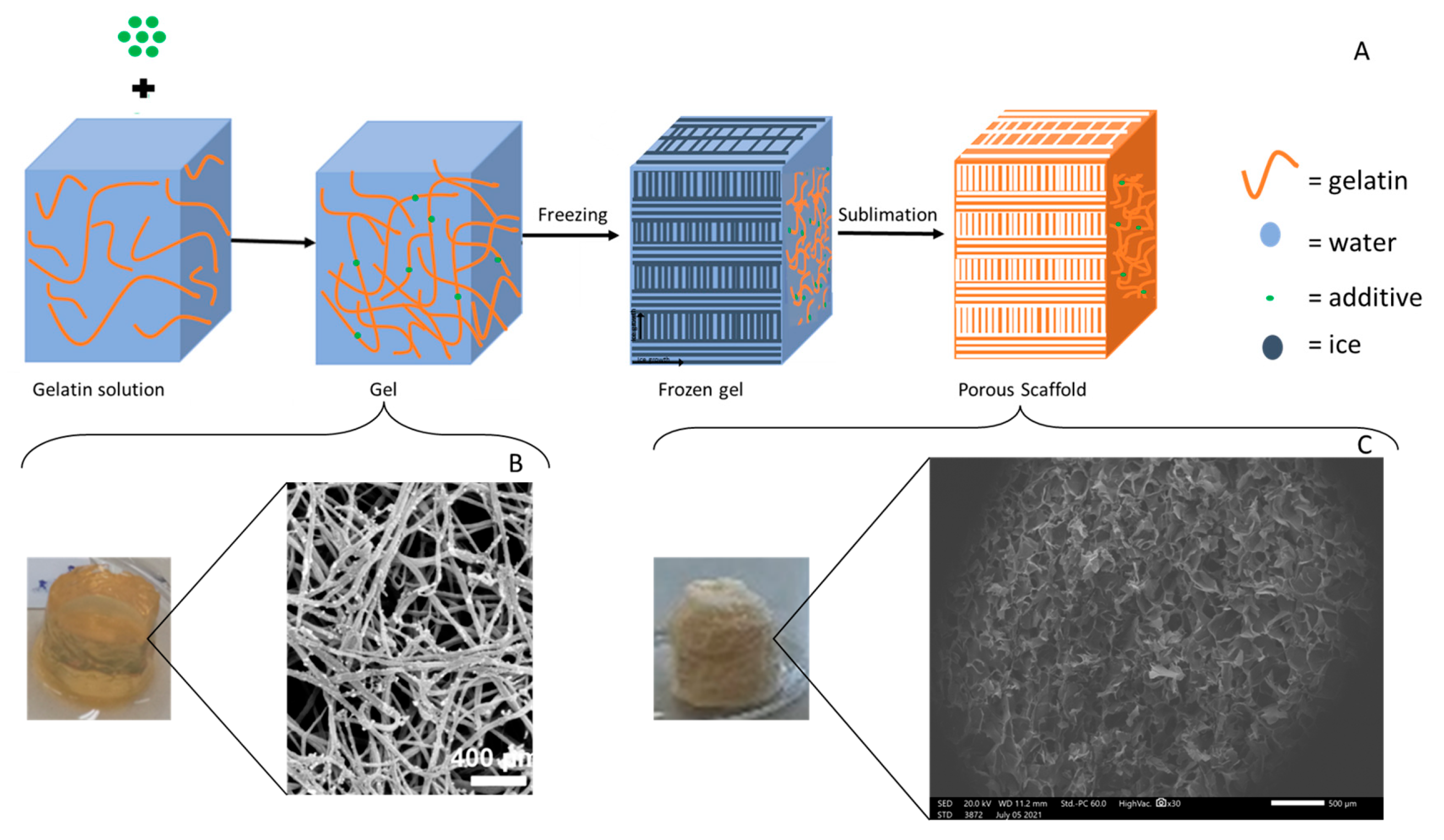
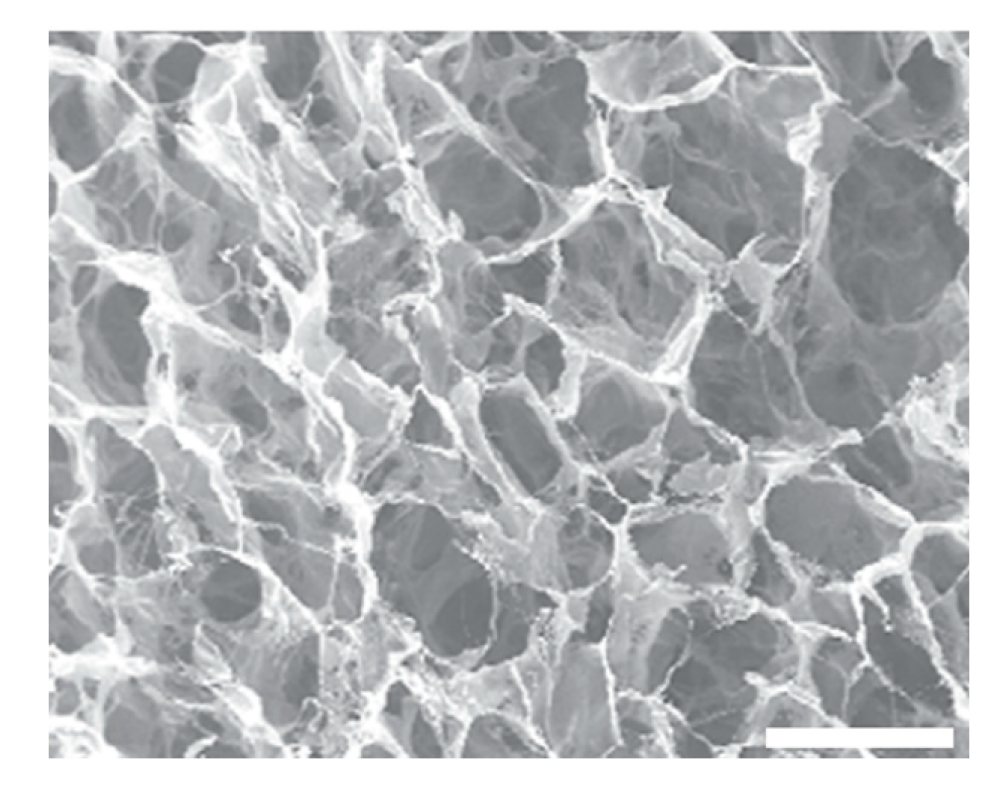
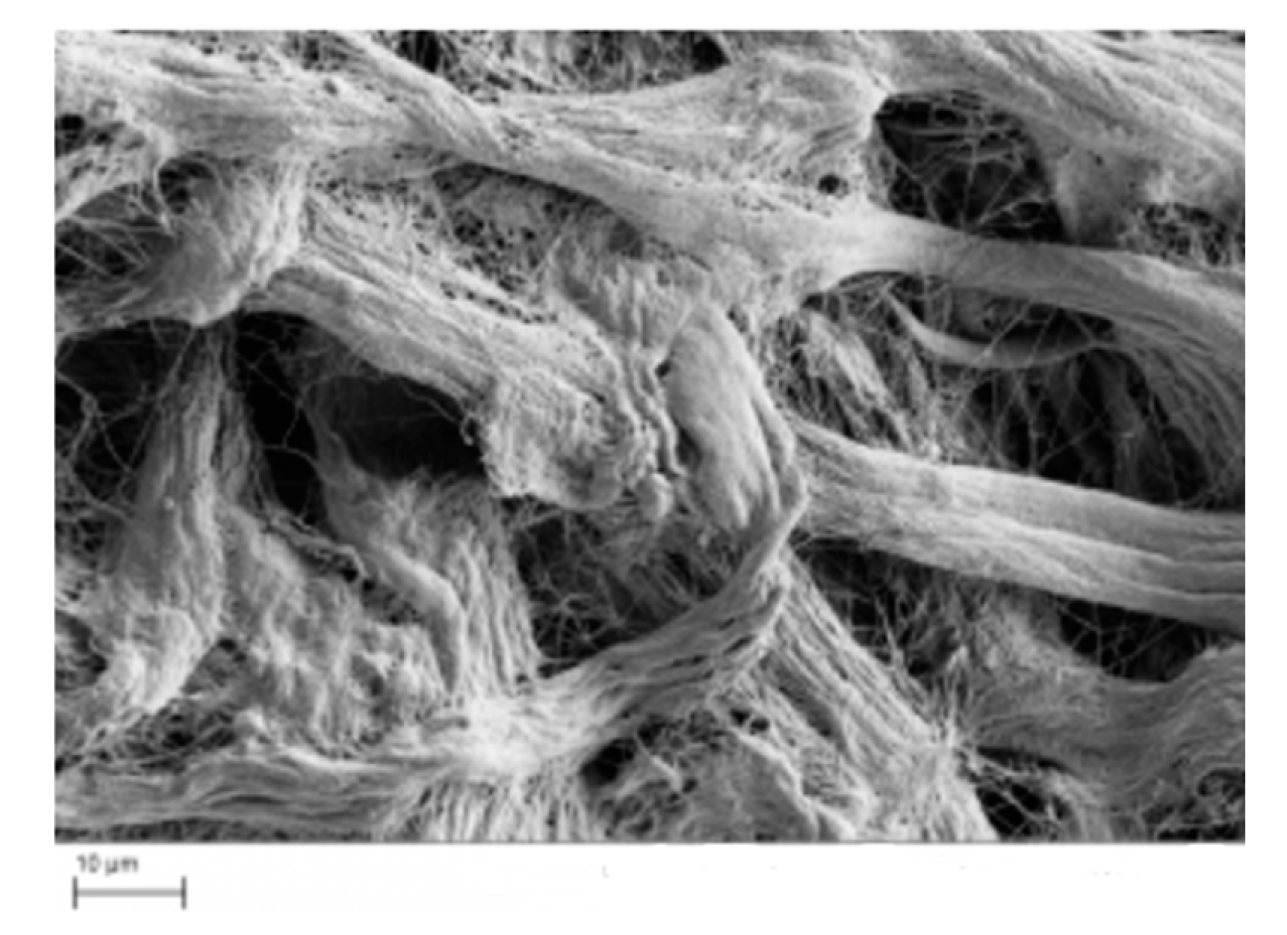
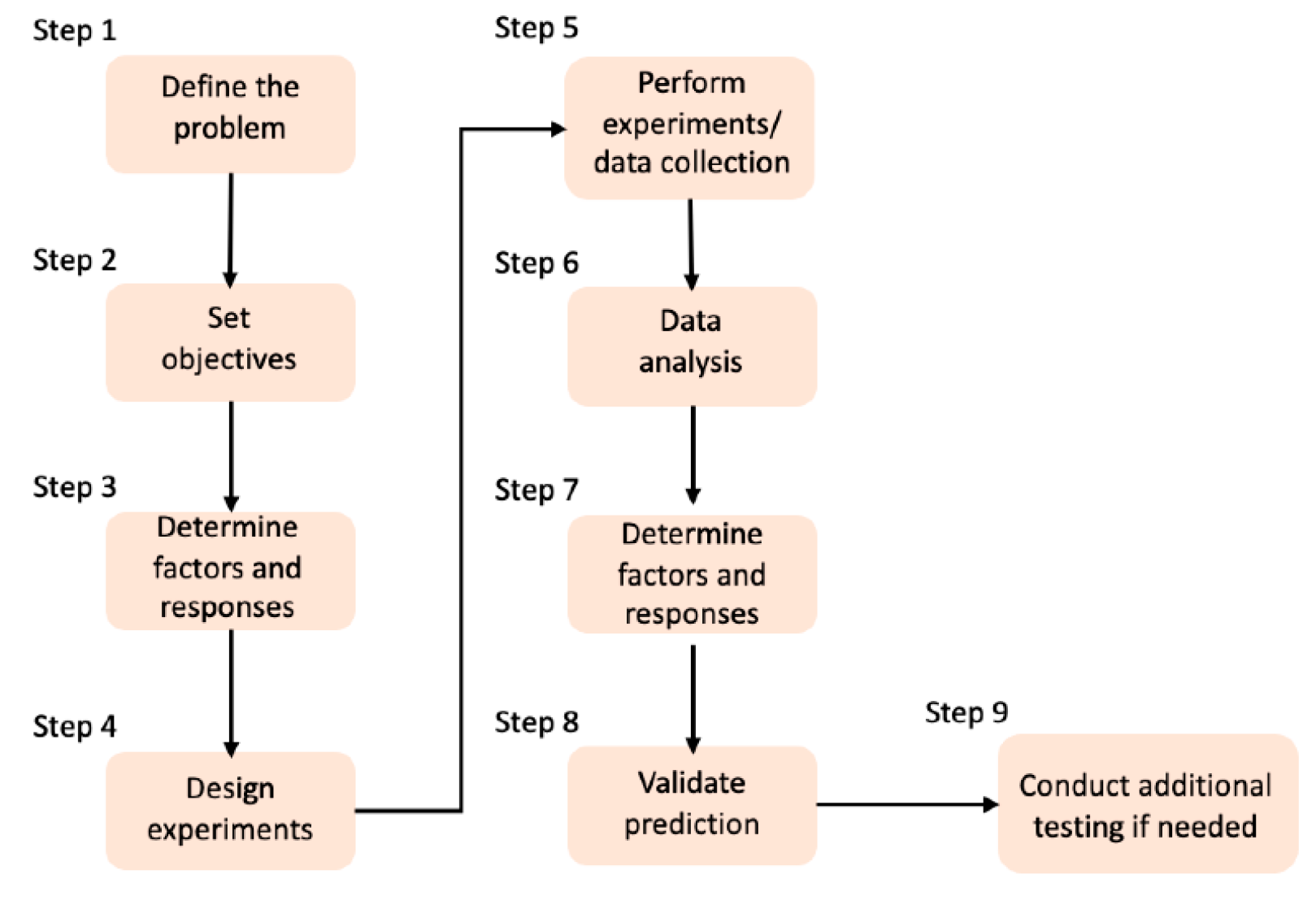
| Type | Percentage | Additive | Cross-linking Method | Freezing conditions |
Freeze-drying conditions | Porosity & Pore size | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type-I collagen from porcine dermis | - | HA | GA | -20°C (12h) | 24h at -40°C | 50–100μm | Bone Tissue Engineering |
[119] |
| Type-I collagen from bovine | 0.5% (w/v) | HA | DHT | -40°C | 17h at 0°C | porosity > 98.9% |
Bone Tissue Engineering |
[120] |
| Type-I collagen from bovine dermis |
50 mg/mL | HA | DHT | -80°C | 24h at -30°C | porosity 90%-96% 20-90μm |
Bone Tissue Engineering |
[121] |
| Type-I collagen from bovine tendon |
- | GAG, BG | DHT & N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N’-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride & NHS | - | 24h at -40°C | porosity > 97% |
Bone Tissue Engineering |
[130] |
| Type-I collagen from bovine achilles tendon |
- | nano-HA | EDC/NHS | -20°C | 24h | 50–900μm | Bone Tissue Engineering |
[140] |
| Collagen from young rats’ tail tendons | 1% | CH, SF | EDC/NHS | -80°C | 48h | 200μm | Bone Tissue Engineering |
[141] |
| Gelatin from porcine skin Collagen |
3% | - | GA | -40°C | 12h at -40°C | porosity 95% 50-100μm |
Bone Tissue Engineering |
[142] |
| Type-B gelatin from bovine skin | 0.5% (w/v) | HA | Acetone-water-based solution | -20°C (24h) | 72h | porosity 88%/85% 250/300μm |
Hard Tissue Engineering |
[124] |
| Gelatin from porcine skin | 0.6% (w/v) | TCH-PLA | EDC & NHS | -20°C (12h) | 24h at -50°C | 261μm | Soft Tissue Engineering |
[136] |
| Type-I collagen from porcine | 2% (w/v) | - | GA | -80°C (6h) | 72h | 150–250μm | Cartilage Tissue Engineering | [134] |
| Type-I collagen from porcine | 2% (w/v) | PLGA | EDC, NHS | -12°C (4h) & -80°C (6h) |
48h | porosity 99% 441/50μm |
Cartilage Tissue Engineering | [135] |
| Type-I collagen from bovine dermis |
- | GAG | DHT, EDC & NHS | -60°C to -10°C |
0°C | 55–243μm | Tendon Tissue Engineering | [143] |
| Type-I collagen from bovine tendon |
- | nano-CE | GNP | -80°C | 24 -48h | 90–140μm | Wound Dressing |
[144] |
| Type-A gelatin from pig skin | 2% | CH | GA | -190°C or -27°C |
18h at -55°C | 119-196μm | Skin Regeneration |
[56] |
| Collagen from bovine achilles tendon |
1% (w/w) | - | Ethanol & 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide hydrochloride & NHS | -40°C (2h) | 18h | 100μm | Cancer Cell Invasion and Migration |
[145] |
| Type-I collagen from bovine | 0.5-1% | GAG | EDC & NHS | -10°C & -40°C |
18h | 137μm | Tissue Engineering |
[54] |
| Type-I collagen from bovine | 0.5% (w/v) | GAG | DHT | -70°C to -10°C |
17h at 0°C | 85-325μm | Tissue Engineering |
[131] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




