Submitted:
26 May 2023
Posted:
29 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrate material and plasma nitriding
2.2. Corrosion tests
2.3. Tribocorrosion tests
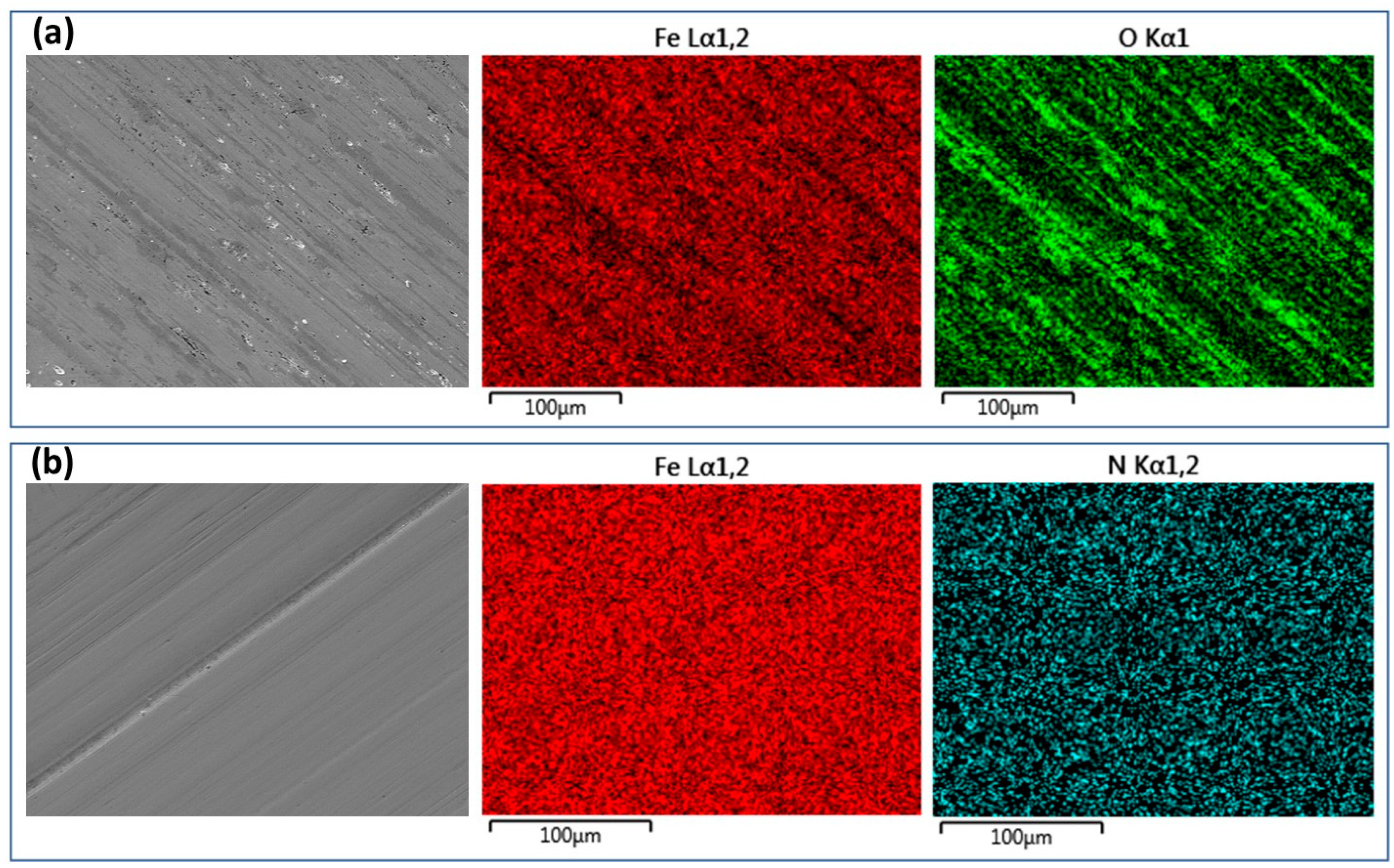
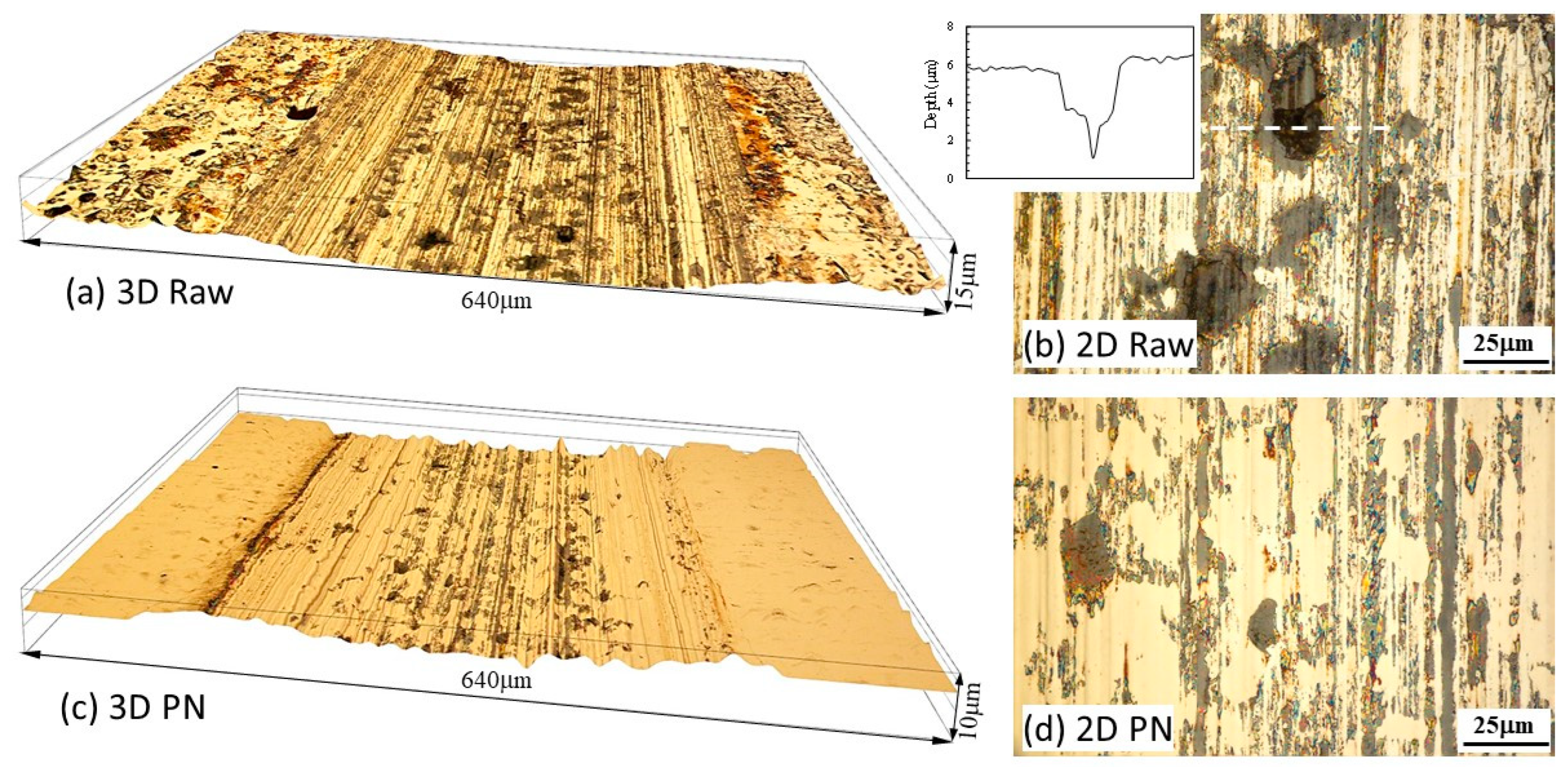
2.4. Specimen characterisation
3. Results
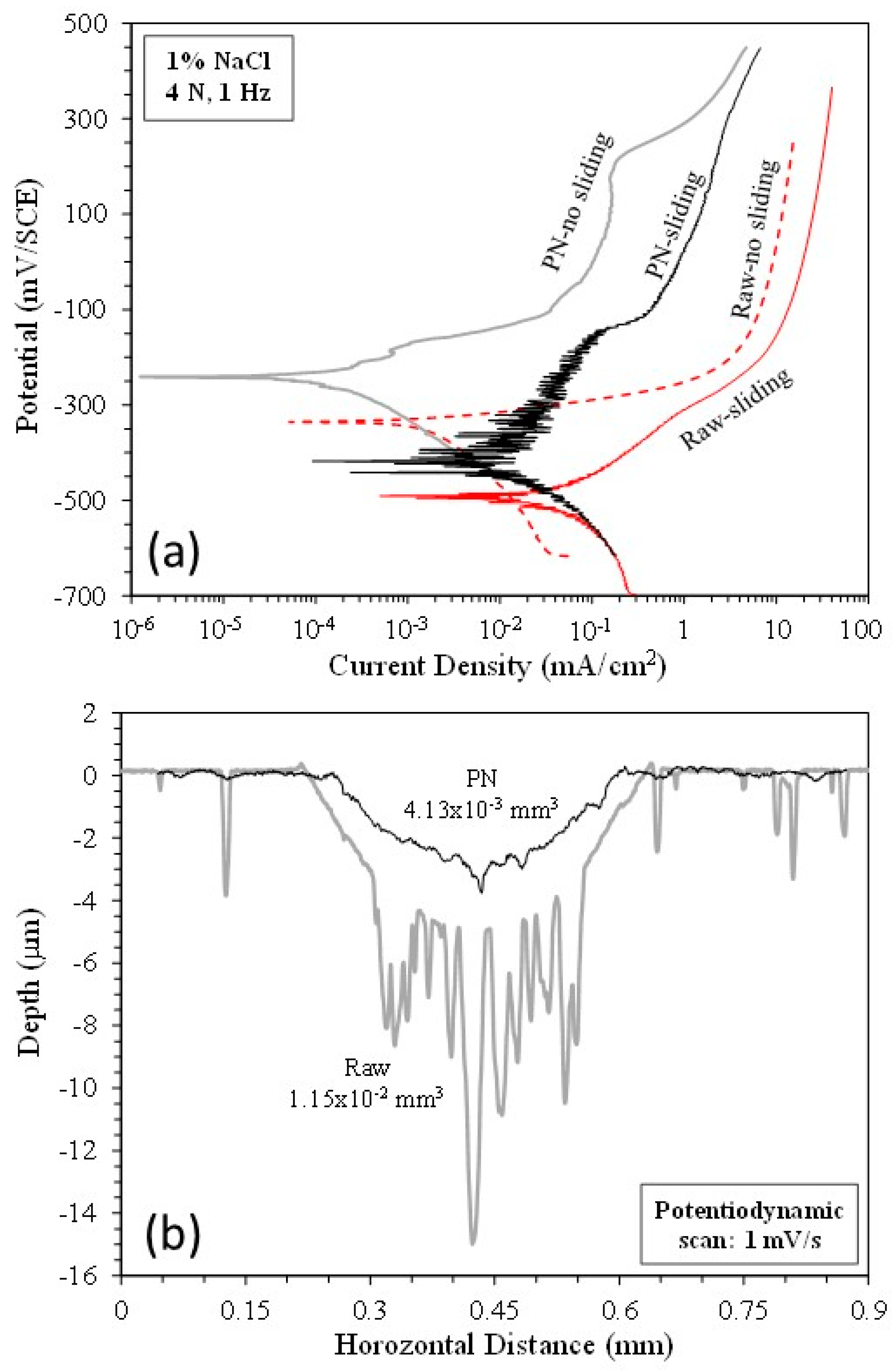
3.1. Potentiodynamic tests
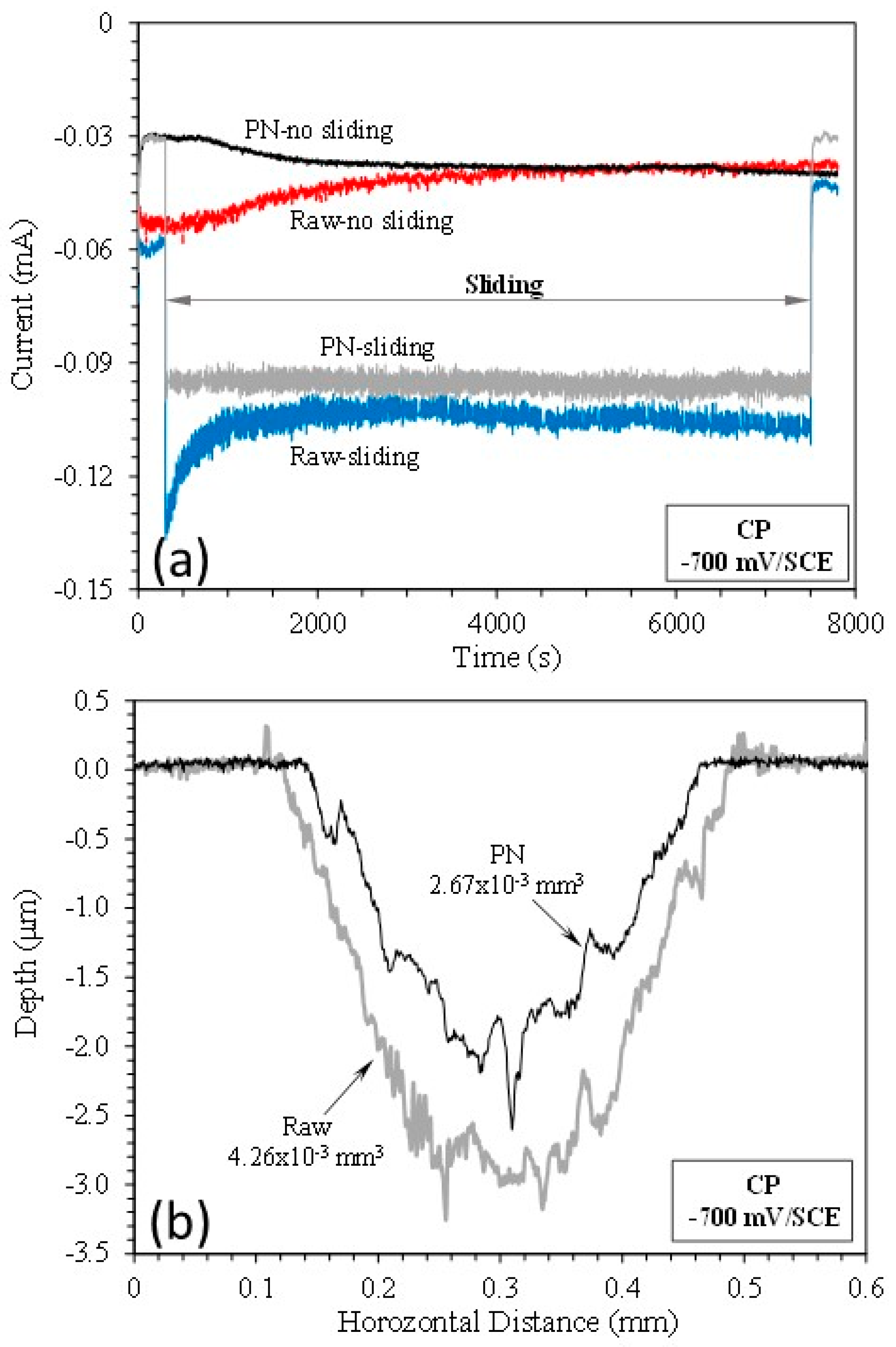
3.2. Cathodic potential tests
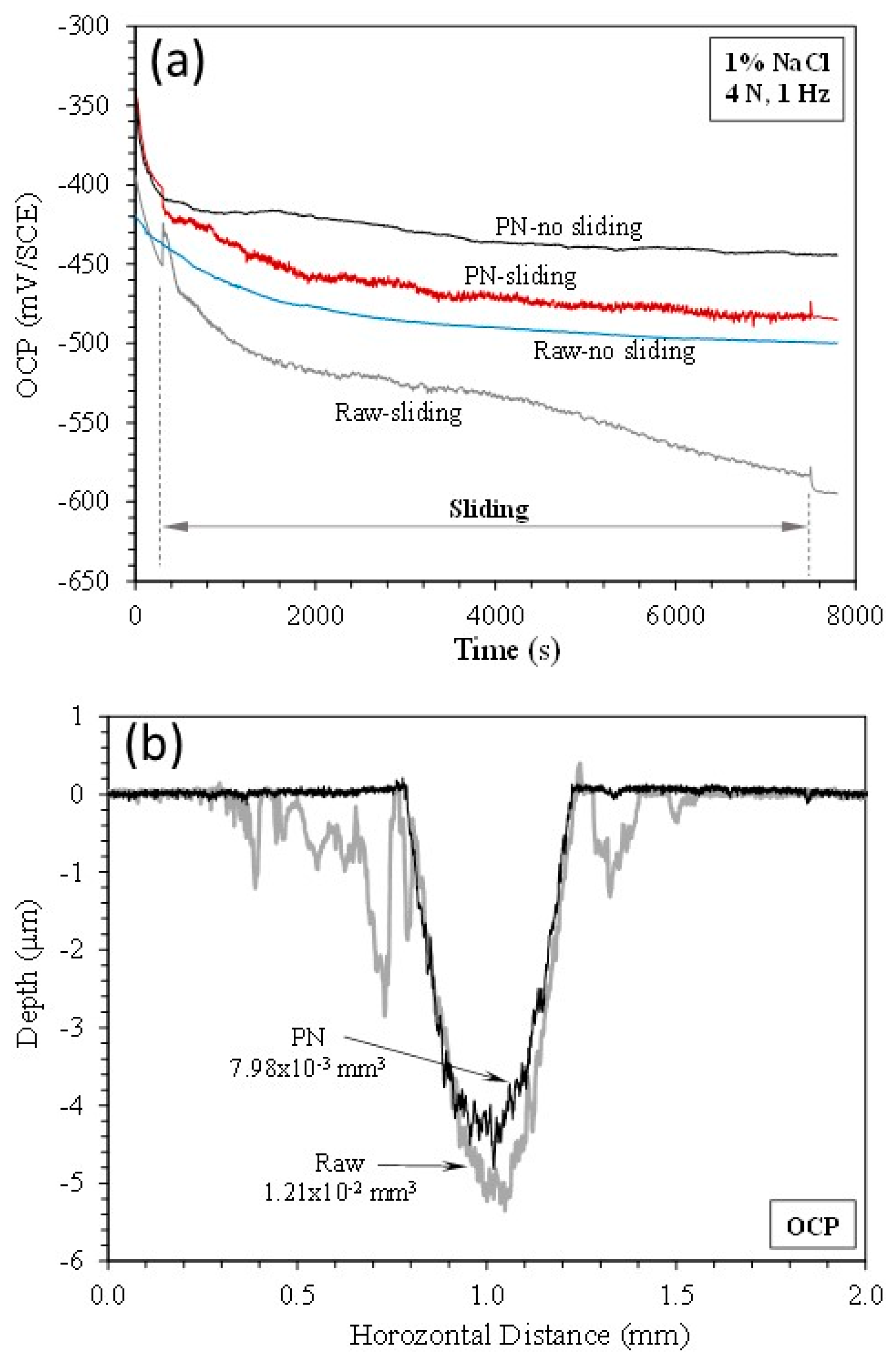
3.3. Open circuit potential (OCP) tests
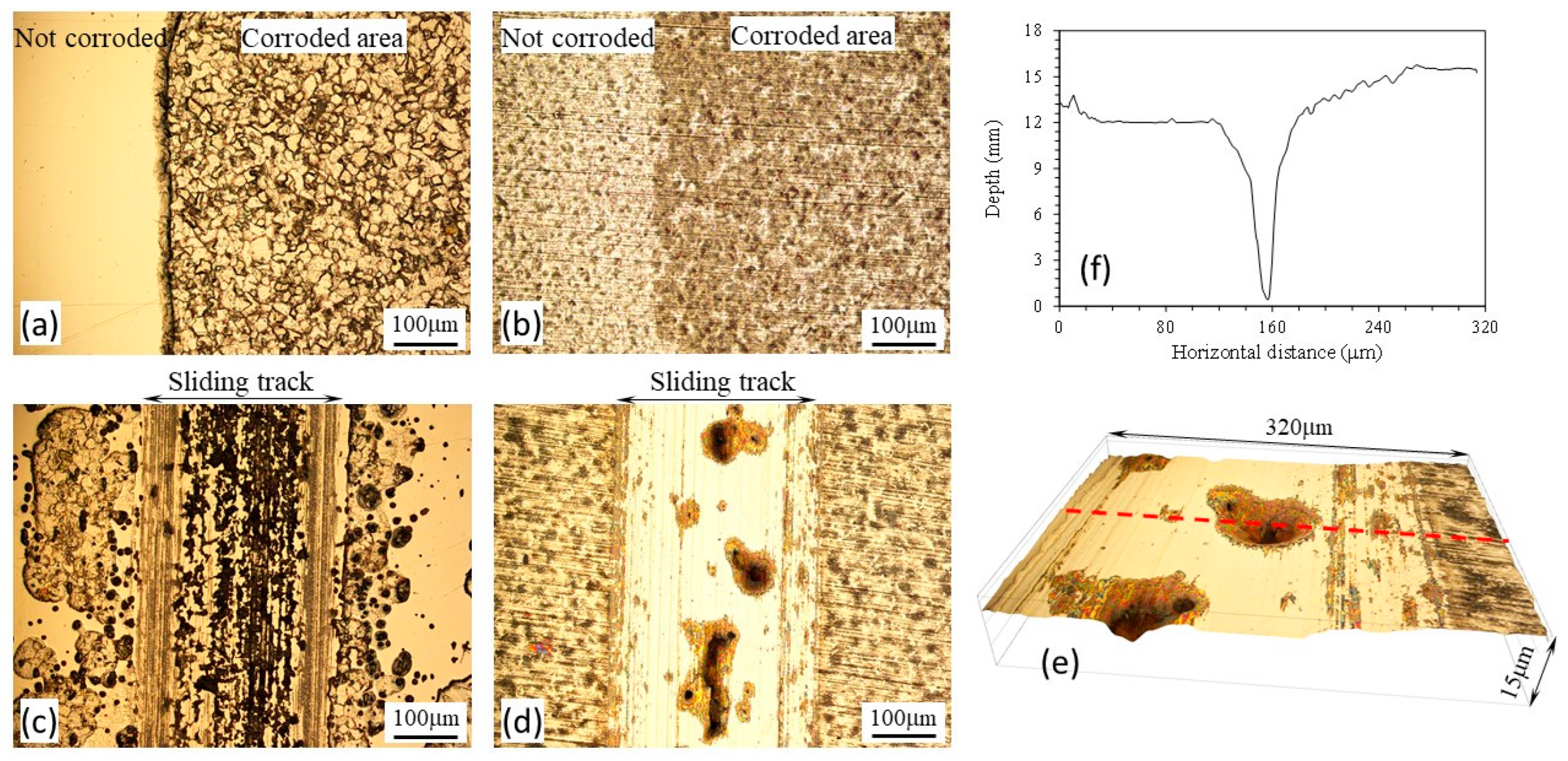
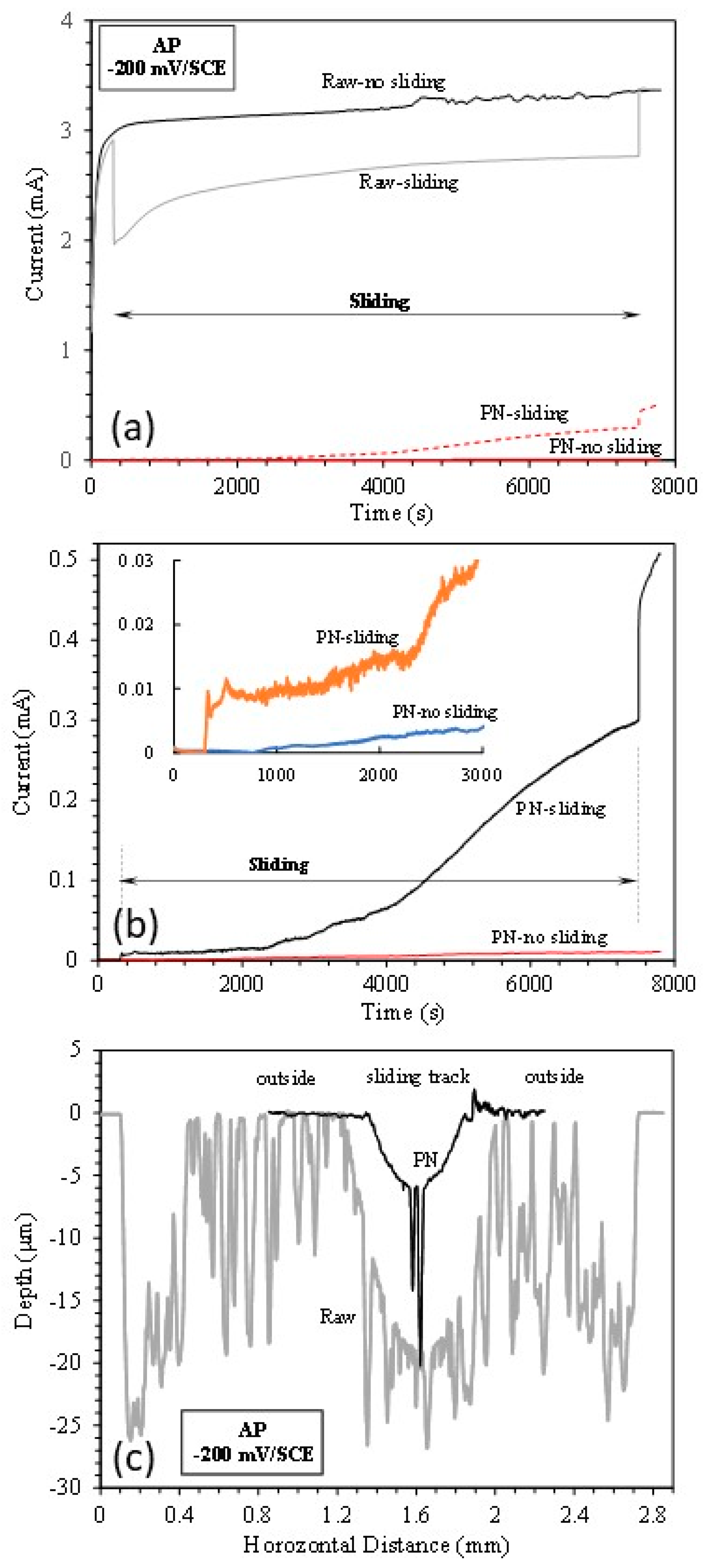
3.4. Anodic potential tests
4. Discussion
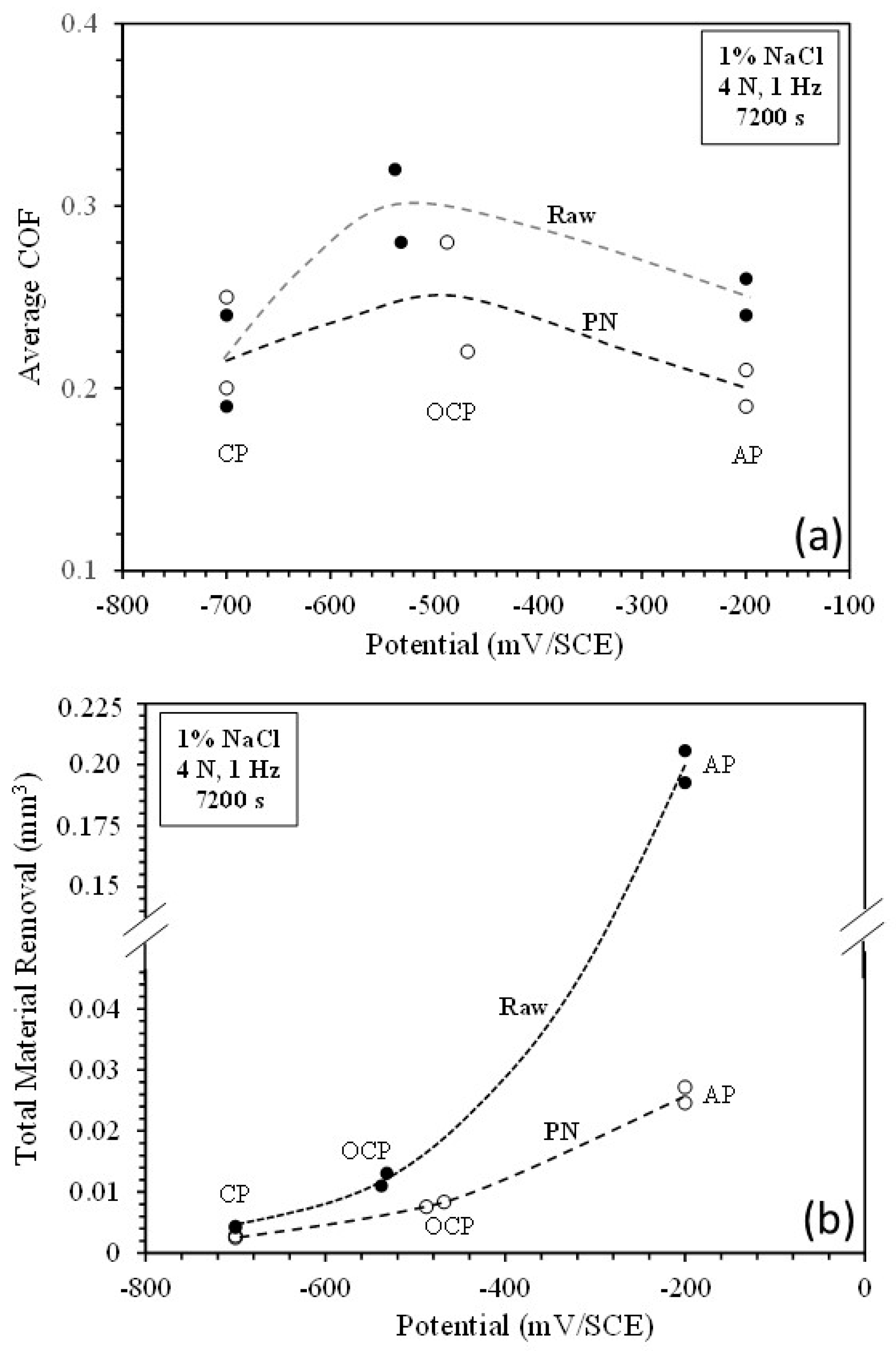
4.1. Effect of potential on tribocorrosion behaviour
4.2. Contribution of mechanical wear and chemical wear
5. Conclusions
- In the NaCl containing solution, both the raw mild steel and γ’-Fe4N layer are in the active state in the anodic region. The γ’-Fe4N layer has the ability to reduce metal dissolution and improve corrosion resistance of mild steel.
- At the cathodic potential, where mechanical wear dominates, the γ’-Fe4N layer can reduce total material removal by 37% due to its higher hardness than that of raw mild steel.
- At open circuit potential, where both mechanical wear and chemical wear are involved, the γ’-Fe4N layer has the ability to reduce chemical wear due to its better resistance to metal dissolution, such that the total material removal is reduced by 35% as compared to that from the raw mild steel.
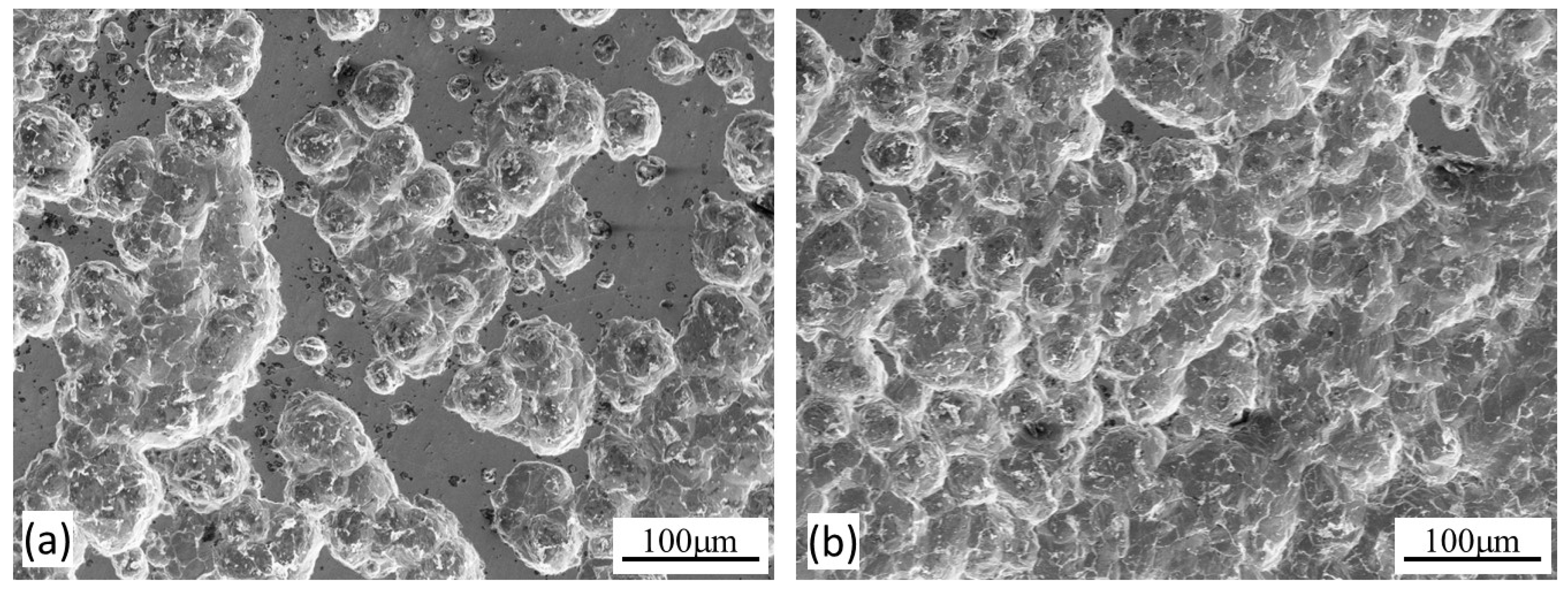
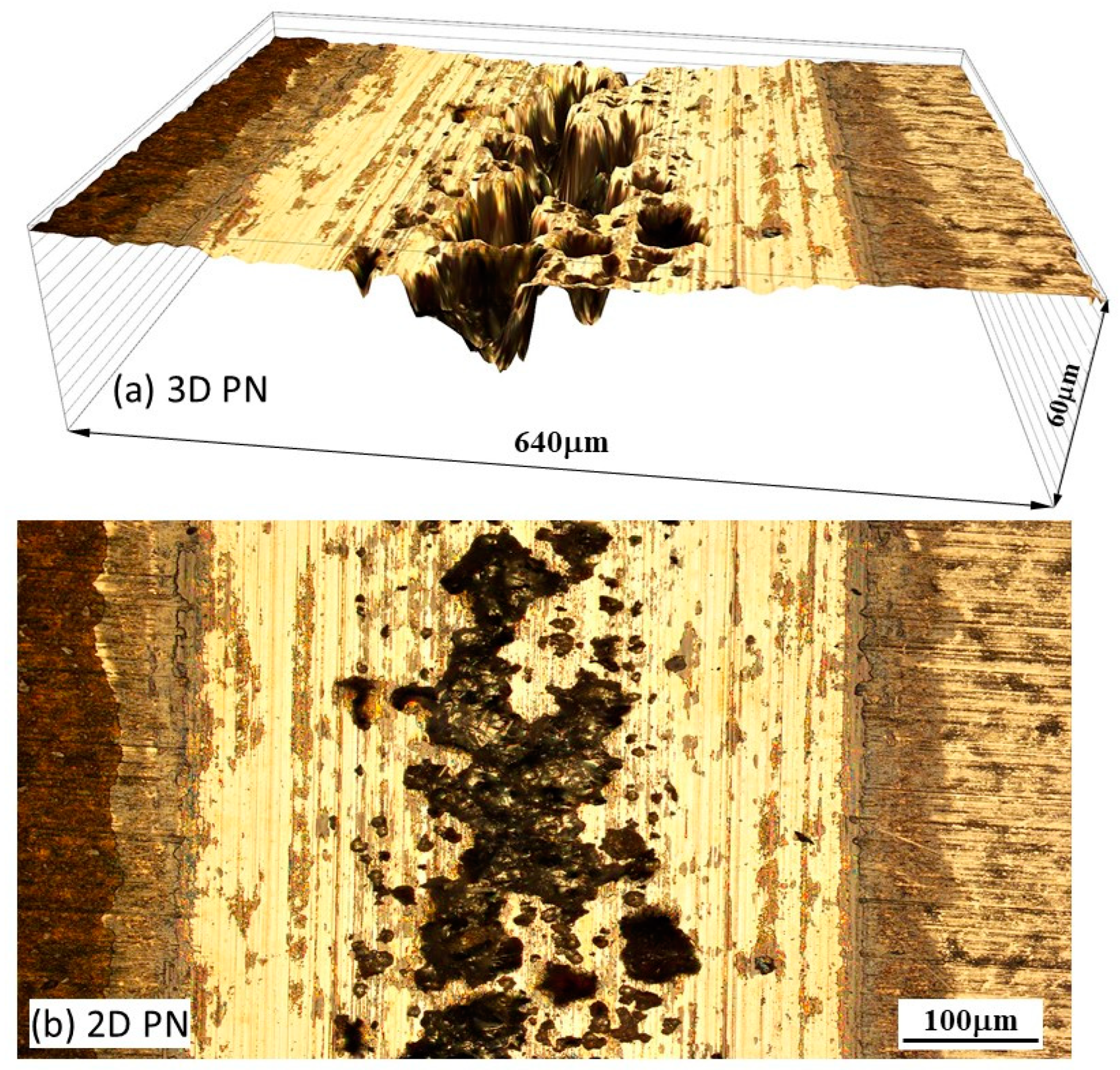
- At the anodic potential, where chemical wear plays an increasing role, the γ’-Fe4N layer can reduce total material removal by 87%. However, local breakdown of the γ’-Fe4N layer can happen in the sliding track, leading to accelerated pitting corrosion.
- The γ’-Fe4N layer has the ability to improve the tribocorrosion behaviour of mild steel in the NaCl containing solution under all test conditions. But there is a concern regarding the sustainability of the layer when localised breakdown or wearing-through occurs, which can lead to accelerated pitting and accelerated material removal.
References
- Staines, A.M.; Bell, T. Technological importance of plasma-induced nitrided and carburized layers on steel. Thin Solid Films 1981, 86, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spies, H.J.; Thien, H.L.; Biermann, H.B. Controlled nitriding. Metal Science and Heat Treatment 2004, 46, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B.J. Lightfoot, B.J.; Jack, D.H. Kinetics of nitriding with and without white-layer formation. Heat Treatment ’73, The Metals Society, December 1973 (republished in the Source Book on Nitriding, American Society for Metals, Metals Park, Ohio, 1977, pp.248−254).
- Thermochemical Surface Engineering of Steels. Edited by Mittemeijer, E.J; Somers, A.L. 2015, Elsevier.
- Menthe, E.; Rie, K.T.; Schultze, J.W.; Simson, S. Structure and properties of plasma-nitrided stainless steel. Surface and Coatings Technology 1995, 74–75, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yi, X.; Yan, J.; Zhou, Z.; Fang, D.; He, Y.; Li, Y. Corrosion behaviour of nitrided layer of Ti6Al4V titanium alloy by hollow cathodic plasma source nitriding. Materials 2023, 16, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhecheva, A.; Malinov, S. Titanium alloys after surface gas nitriding. Surface and Coatings Technology 2006, 201, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchwalder, A.; Bocker, J.; Hegelmann, E.; Klemm, V. Investigations on the microstructure of an aluminium nitride layer and its interface with the aluminium substrate (Part I). Coatings 2022, 12, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visuttipitukul, P.; Aizawa, T.; Kuwahara, H. Advanced plasma nitriding for aluminium and aluminium alloys. Materials Transactions 2003, 44, 2695–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. Kinetics of layer growth during plasma nitriding of nickel based alloy Inconel 600. Journal of alloys and compounds 2003, 351, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Kavanagh, J.; Li, X.; Dong, H.; Matthews, A.; Leyland, A. An investigation of precipitation strengthened Inconel 718 superalloy after triode plasma nitriding. Surface and Coatings Technology 2022, 442, 128401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Dong, H. Tribocorrosion behaviour of S-phase surface engineered medical grade Co-Cr alloy. Wear 2013, 302, 1615–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purandare, Y.; Shukla, K.; Sugumaran, A.; Ehiasarian, A.; Khan, I.; Hovsepian, P. Improving tribocorrosion resistance of a medical grade CoCrMo alloy by the novel HIPIMS nitriding technique. Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices 2023, 8, 100570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spies, H.J. Corrosion behaviour of nitrided, nitrocarburised and carburised steels, in Thermochemical Surface Engineering of Steels, edited by Mittemeijer, E.J; Somers, A.L. 2015, Elsevier.
- Mittemeijer, E.J. Nitriding of binary and ternary iron-based alloy. in Thermochemical Surface Engineering of Steels, edited by Mittemeijer, E.J; Somers, A.L. 2015, Elsevier.
- Jasinski, J.J; Kurpaska, L.; Frazek, T.; Lubas, M.; Sitarz, M. Structural characterisation of fine ’-Fe4N nitrides form by active screen plasma nitriding. Metals 2020, 10, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.; Loh, N.L. The fatigue characteristics of plasma nitrided three Pct Cr-Mo steel. Journal of Heat Treating 1982, 2, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Eyre, T.S.; Ralph, B. Wear mechanism map of nitrided steel. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia 1994, 42, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.; Sun, Y. Load bearing capacity of plasma nitrided low alloy steel under combined rolling-sliding contact. Surface Engineering 1990, 6, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boztepe, E; Alves, A. C; Ariza, E; Rocha, L.A.; Cansever, N.; Toptan, F. A comparative investigation of the corrosion and tribocorrosion behaviour of nitrocarburized, gas nitrided, fluidized-bed nitrided, and plasma nitrided plastic mould steel. Surface & Coatings Technology 2018, 334, 116–123. [Google Scholar]
- Ram Mohan Rao, K.; Nouveau, C; Lakshman, S. ; Muralidhar, P.; Trinadh, K. Effect of low and high temperature plasma nitriding on electrochemical corrosion of steel. Materials Today: Proceedings 2020, 39, 1367–1371. [Google Scholar]
- Valdes, J.; Huape, E.; Oseguern, J.; Ruiz, A.; Ibarrra, J.; Bernal, J.L.; Medina, A. Effects of plasma nitriding in corrosion behaviour of an AISI 4140 steel using a seawater medium solution. Materials Letters 2022, 316, 131991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S.W. Watson, F.J. Friedersdorf, B.W. Madsen, S.D. Gramer, Methods of measuring wear-corrosion synergism, Wear, 1995, 181-183, p476-484.
- P. Ponthiaux, F. Wenger, D. Drees, J.P. Celis, Electrochemical techniques for studying tribocorrosion processes, Wear, 2004, 256, 459–468.
- A.I. Munoz, N. Espallargas, S. Mischler, Ed., Tribocorrosion, Springer, 2020.
- Mindivan, F.; Aktas, G.R.; Bayram, A. Influence of plasma nitriding on dry wear, corrosion and tribocorrosion performance of 17-4 precipitation hardening stainless steel. Materialwiss. Werkstofftech 2022, 53, 963–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li. X.; Dou, W.; Tian, L.; Dong, H. Combating the tribo-corrosion of LDX2404 lean duplex stainless steel by low temperature plasma nitriding. Lubricants 2018, 93, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Hacisalihoglu, I.; Yildiz, F.; Celik, A. Tribocorrosion behavior of plasma nitrided Hardox steels in NaCl solution. Tribology International 2018, 120, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Angel, W.D.; Martinez-Trinidad, J.; Campos-Silva, V.; Hernandez-Hernandez; Silva-Rivera, U. S.; Garcia-Leon, R.A. Wear-corrosion synergy on Din-16MnCr5 steel under nitriding and post-oxidizing treatments. Journal of Bio- and Tribo-Corrosion 2021, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Burghaus, J.; Music, D.; Dronskowski, R.; Schneider, J.M. Elastric properties of ’-Fe4N probed by nanoindentation and ab initio calculation. Acta Materialia 2012, 60, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Bailey, R. Comparison of wear performance of low temperature nitrided and carburized 316L stainless steel under dry sliding and corrosive-wear condition. J Mater Eng Perform. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casar, J.; Malia, B.; Mazzonello, A.; Karl, A.; Buhagiar, J. Improved tribocorrosion resistance of a CoCrMo implant material by carburising. Lubricants 2018, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, G.; Shafei, Y.E.; Stack, M.M. Mapping tribo-corrosion behaviour of Ti-6Al-4V Eli in laboratory simulated hip joint environments. Lubricants 2020, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, R.A.; Ichikawa, R.U.; Martinez, L. G.; Costa, I. Characterisation of corrosion products on carbon steel exposed to natural weathering and to accelerated corrosion tests. International Journal of Corrosion 2014, 2014, 419570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonna, S.; Ibrahim, I.B.M.; Gunawarman; Huzni, S. ; Lksan, M.; Thalib, S. Investigation of corrosion products formed on the surface of carbon steel exposed in Banda Aceh’s atmosphere. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Stack, M.M.; Neville, A. Modelling the tribo-corrosion interaction in aqueous sliding conditions. Tribology International 2002, 35, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Dearnley, P.A.; Bertram, M. Response of duplex Cr(N)/S and Cr(C)/S coatings on 316L stainless steel to tribocorrosion in 0.89% NaCl solution under plastic contact conditions. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, Part B 2017, 105, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
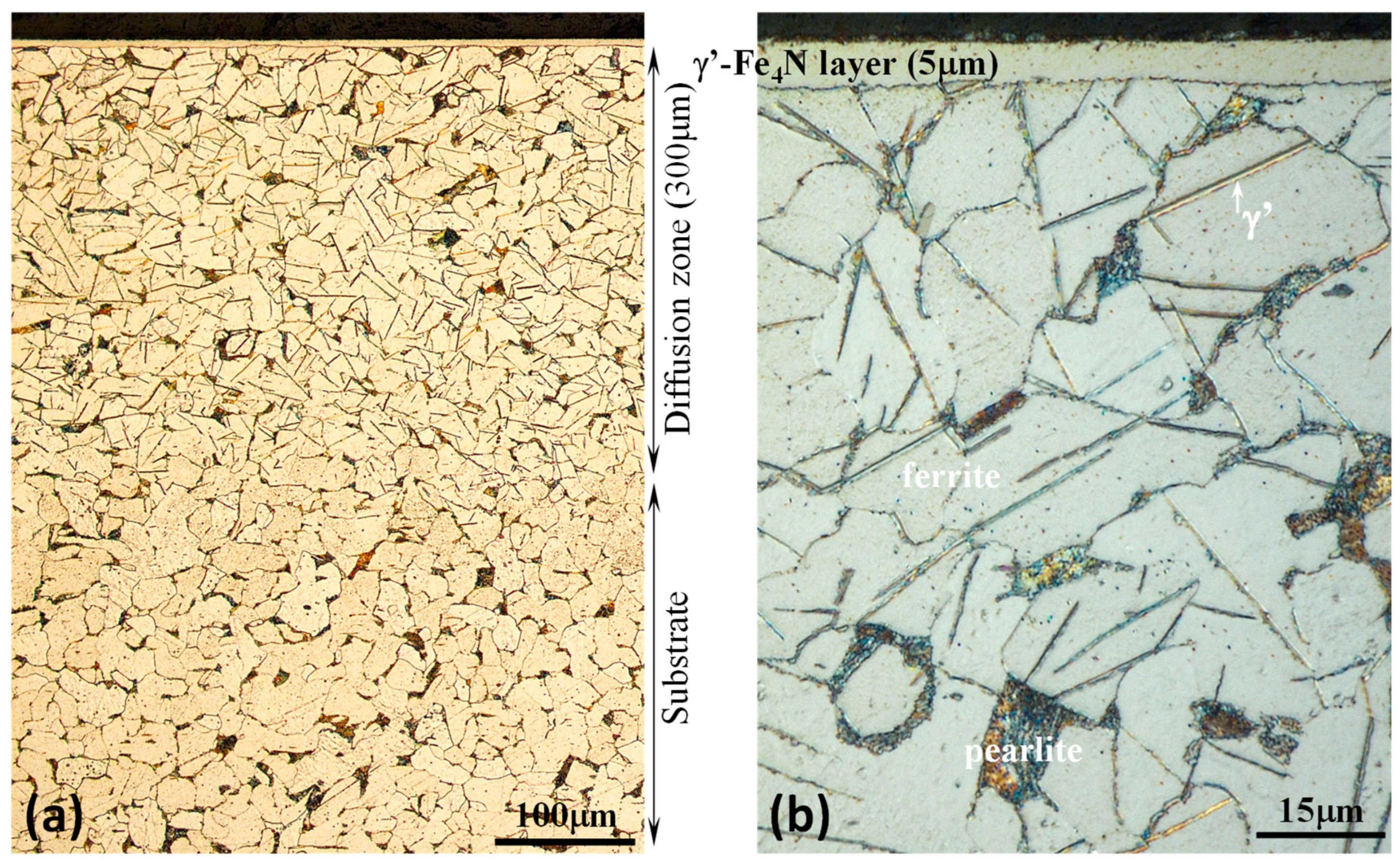
| Structure | Surface Hardness | |||||
| Specimen | Surface layer | Diffusion zone | HV0.025 | HV0.05 | HV0.1 | HV0.2 |
| PN MS | ’-Fe4N 5 m thick |
’-Fe4N needles in +P matrix |
760 | 540 | 370 | 292 |
| Raw MS | +P | +P | 266 | 258 | 248 | 245 |
| Corrosion | Tribocorrosion | |
| Potentiodynamic | -200 mV to 800 mV, 1 mV/s No sliding |
-200 mV to 800 mV, 1 mV/s Sliding at 4 N & 1 Hz |
| Potentiostatic | -700 mV(SCE) no sliding OCP no sliding -200 mV(SCE) no sliding |
-700 mV(SCE) sliding at 4 N & 1 Hz OCP sliding at 4 N and 1 Hz -200 mV(SCE) sliding at 4 N & 1 Hz |
| Ecorr (mV/SCE) | icorr (mA/cm2) | |||
| Specimen | No sliding | Sliding | No sliding | Sliding |
| Raw MS | -335 | -490 | 4.28x10-3 | 4.95x10-2 |
| PN MS | -241 | -418 | 2.05x10-4 | 1.91x10-2 |
| Specimen | TMR (mm3) | Vmech (mm3) | Vchem (mm3) | % of Vchem |
| Raw | 1.20410-2 | 6.26510-3 | 5.77510-3 | 48 |
| PN | 7.98310-3 | 5.75510-3 | 2.22810-3 | 28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





