Submitted:
26 May 2023
Posted:
29 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Benzoic Acid: General Introduction
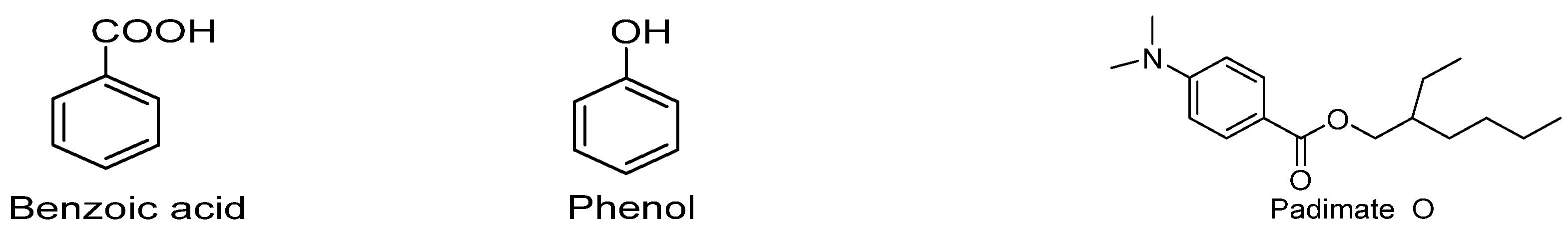
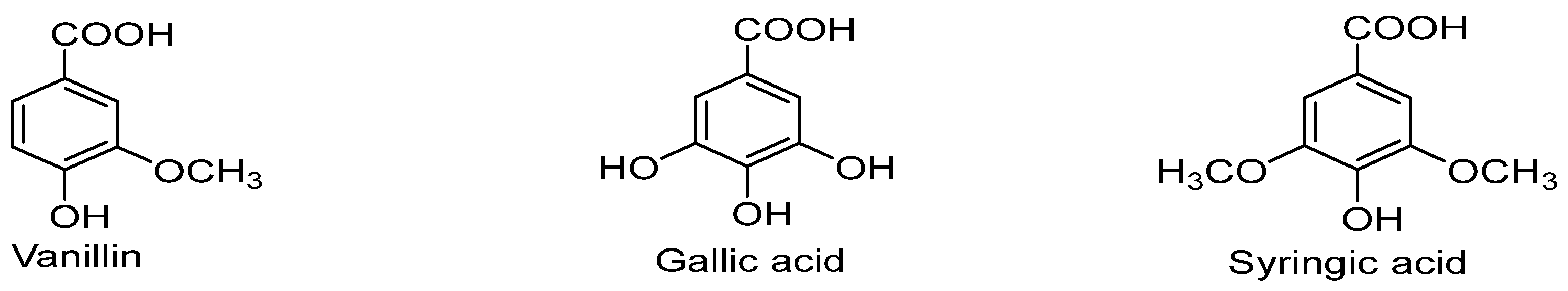
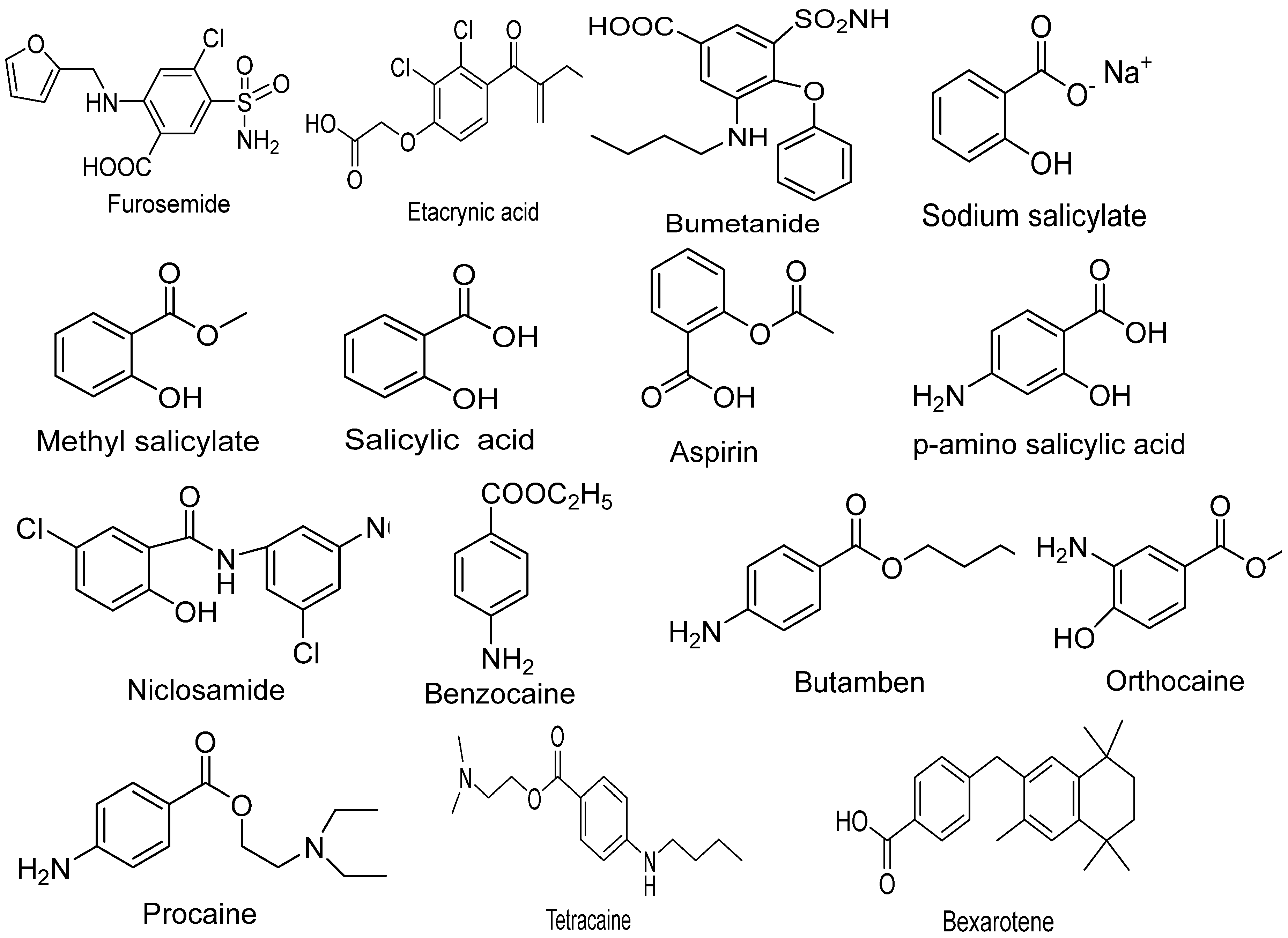
3. Clinical and Biological uses of Benzoic Acid (BA) derivatives for the treatment of Cancer
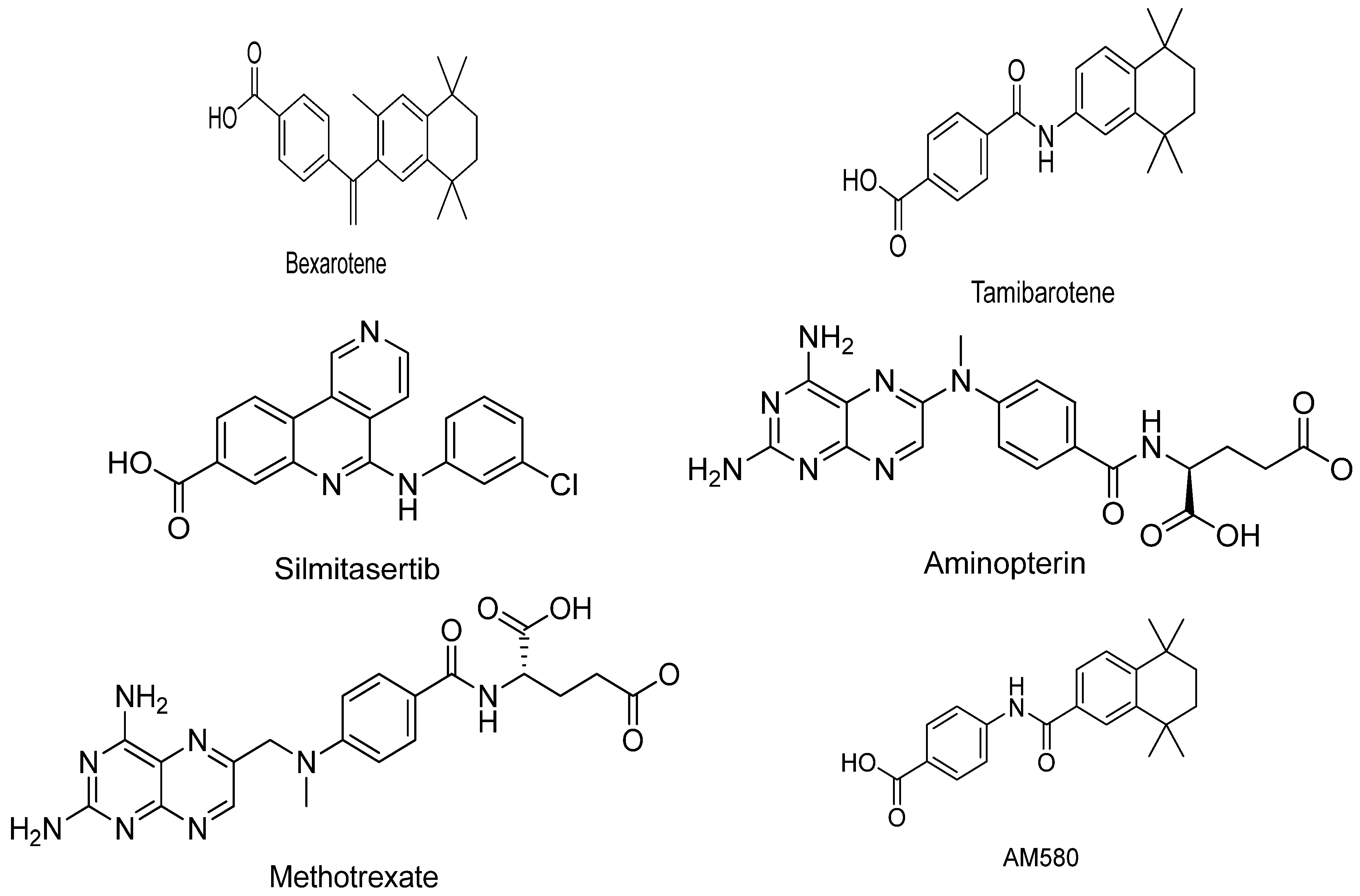
3.1. Bexarotene:
3.2. Tallimustine:
3.3. Tamibarotene:
3.4. Silmitasertib:
3.5. Aminopterin:
3.6. Methotrexate:
3.7. AM580:
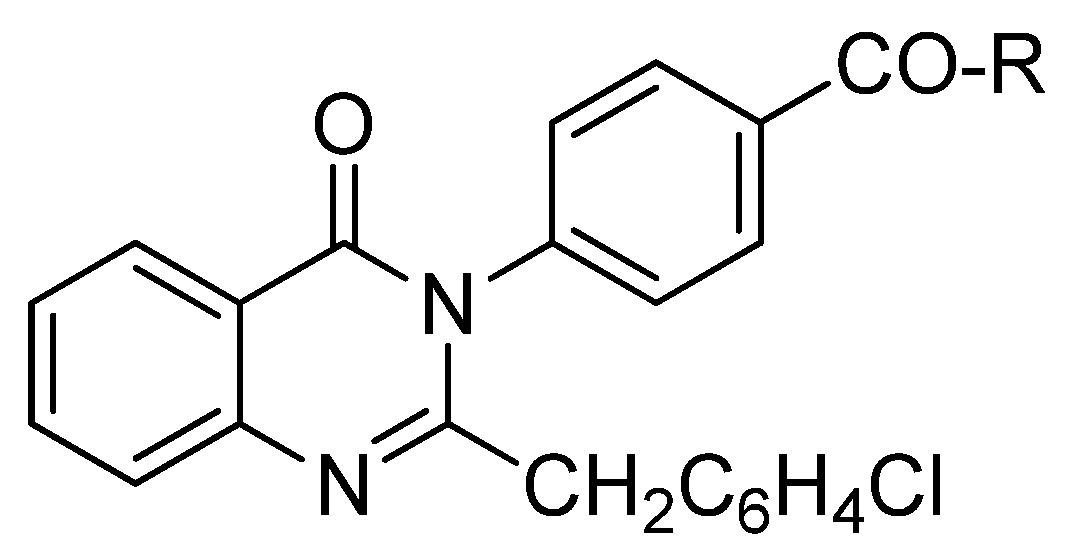
4. Recently Developed BA Analogues for Anti-Cancer Activity
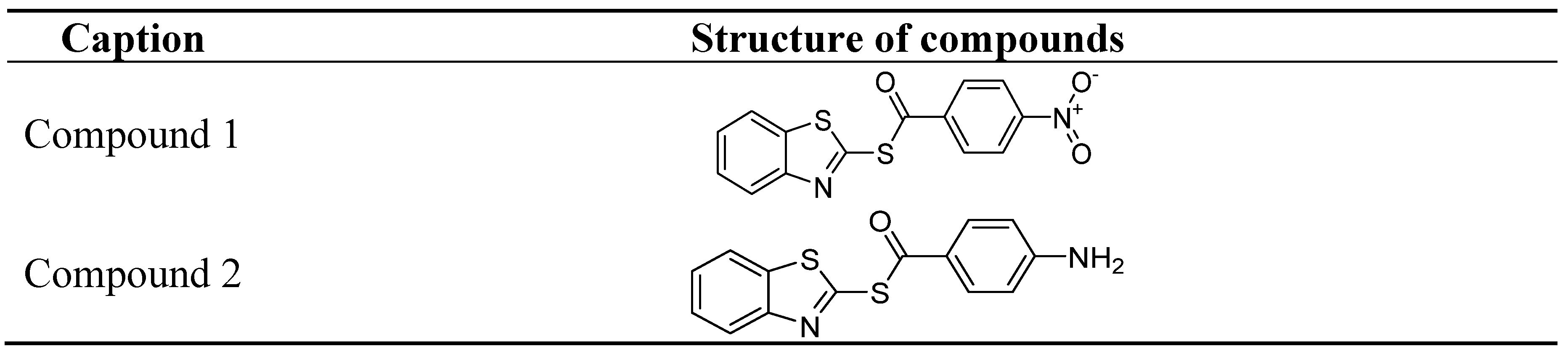
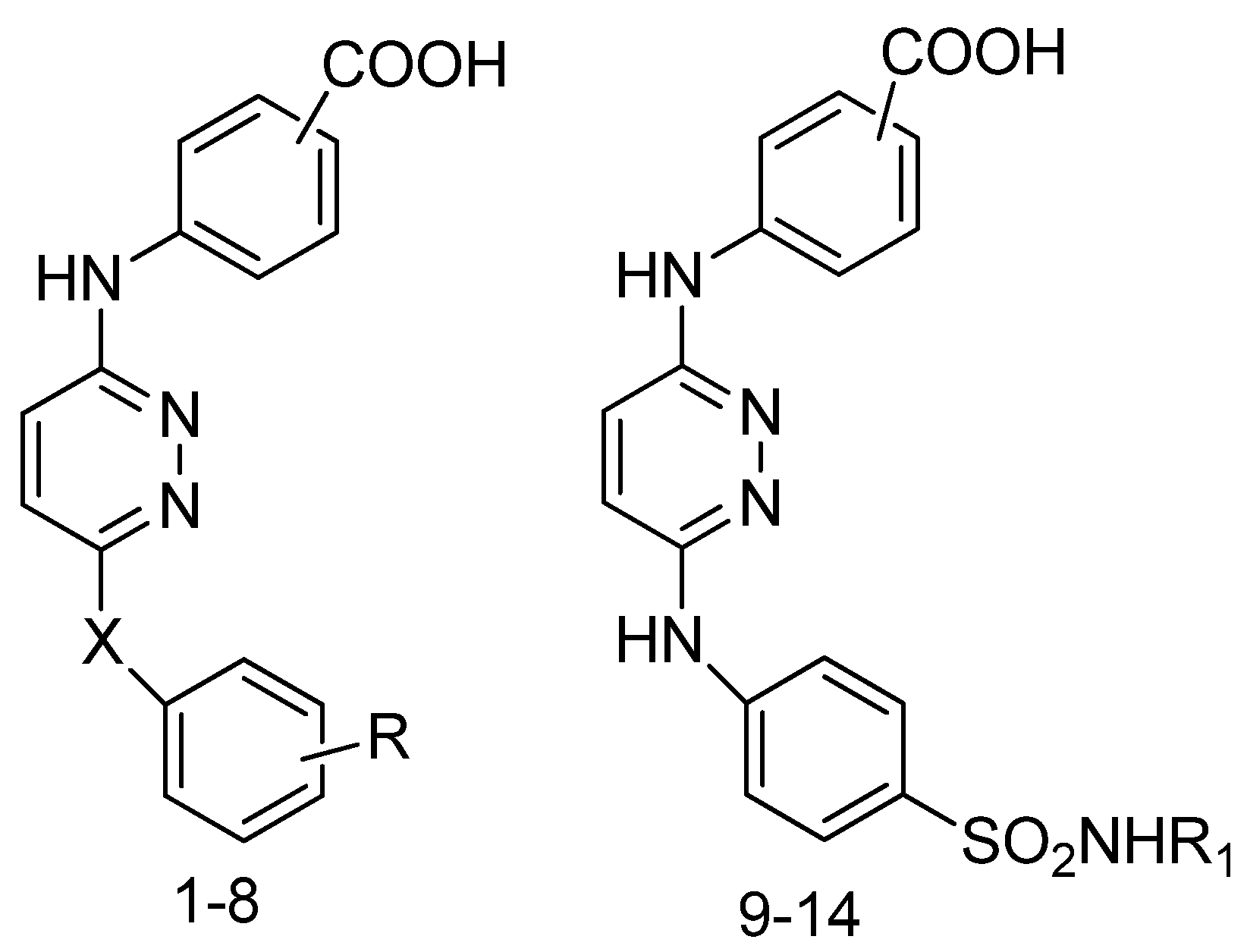
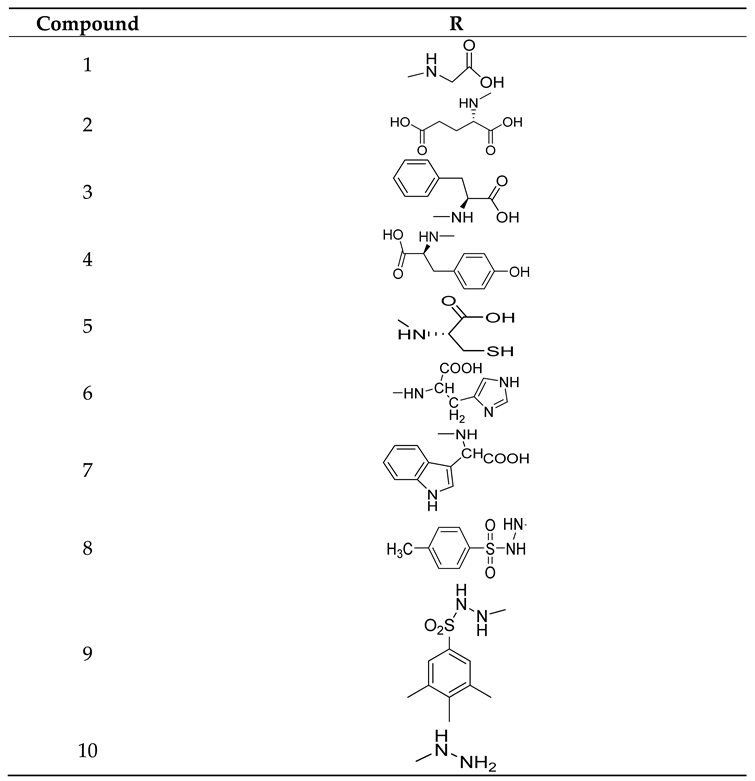
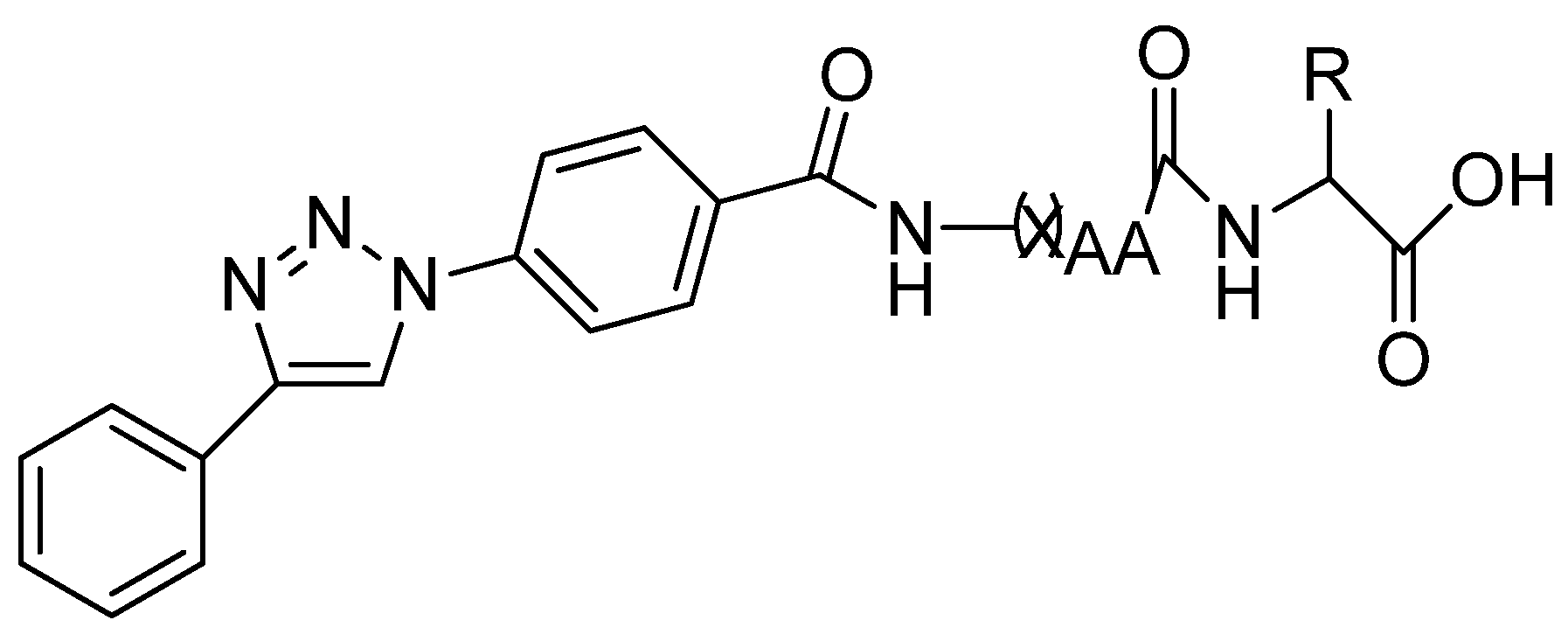
| S. No. | X | R | R1 |
| 1 | NH | 4-Cl | 4-Cl |
| 2 | NH | 4-Cl | 4-Cl |
| 3 | NH | 2,4-Cl2 | 2,4-Cl2 |
| 4 | NH | 2,4-Cl2 | 2,4-Cl2 |
| 5 | NH | 2,6-Cl2 | 2,6-Cl2 |
| 6 | NH | 2,6-Cl2 | 2,6-Cl2 |
| 7 | - | - | - |
| 8 | - | - | - |
| 9 | O | 2-CONH2 | 2-CONH2 |
| 10 | O | 2-CONH2 | 2-CONH2 |
| 11 | - | H | H |
| 12 | - | H | H |
| 13 | - | C(NH)NH2 | C(NH)NH2 |
| 14 | - | C(NH)NH2 | C(NH)NH2 |

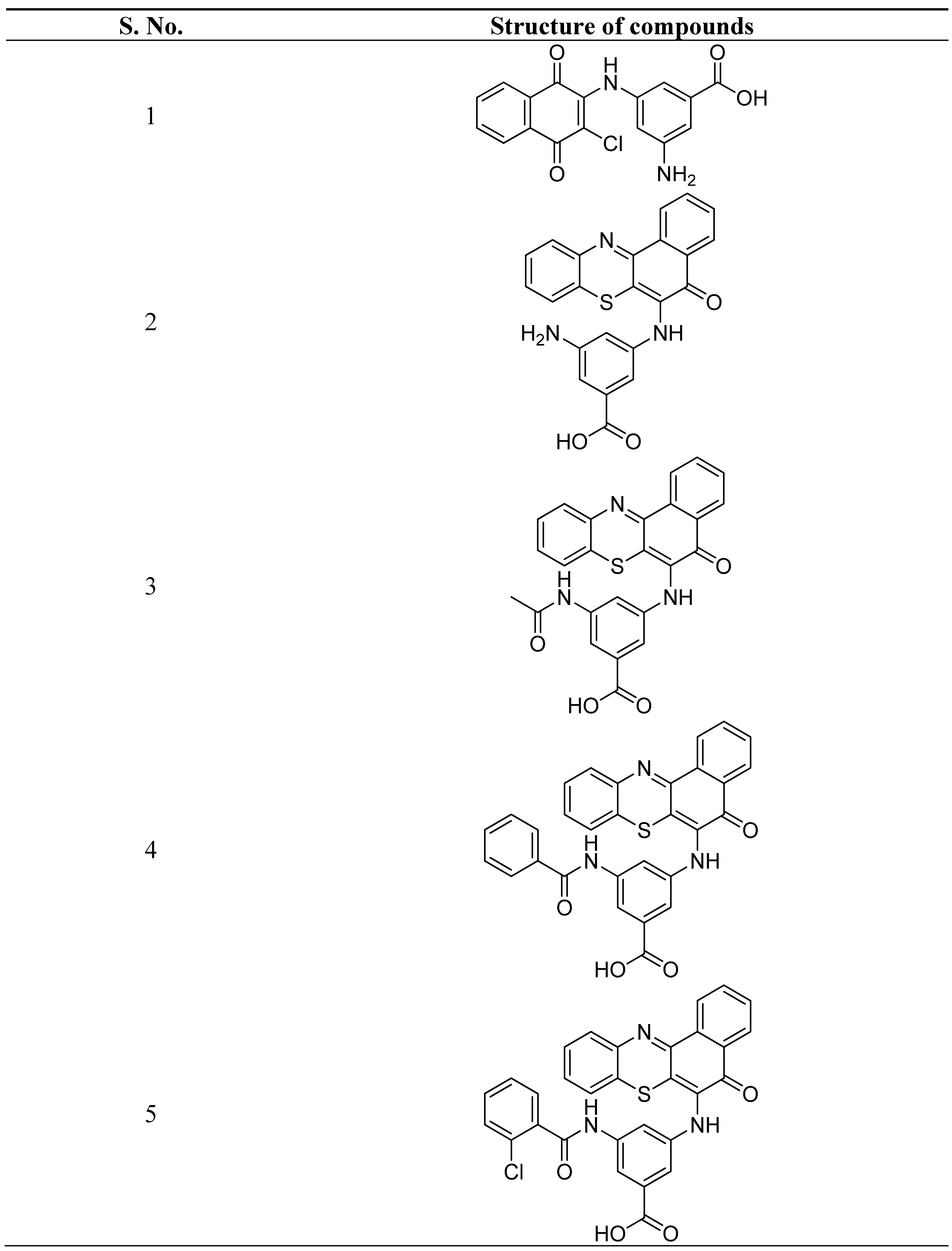
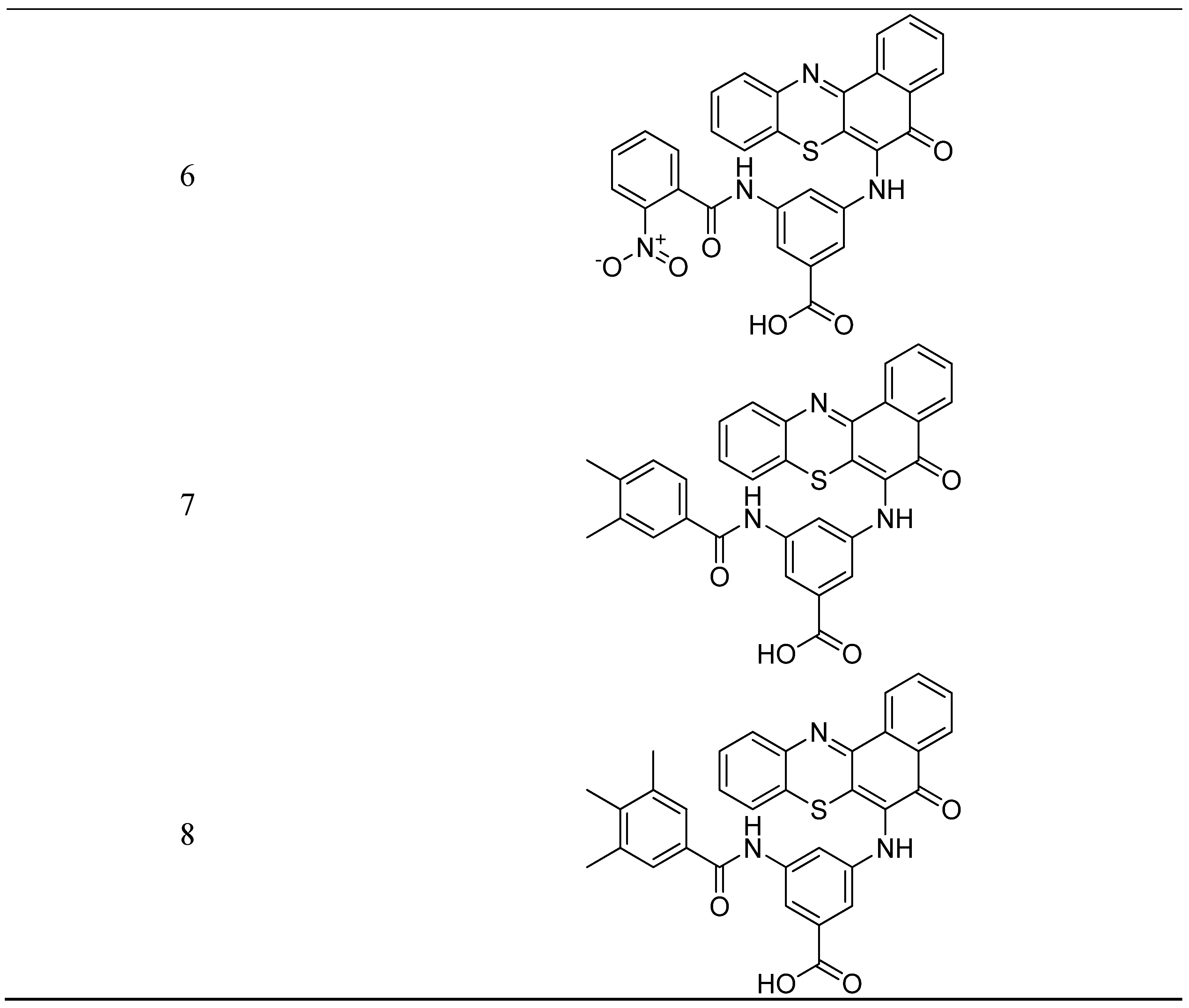

| S. No. | Structure | Name of Compound | Type of Cancer for which it is potent | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 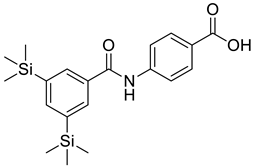 |
4-[3,5 Bis(trimethylsilyl)benzamido] Benzoic Acid (TAC-101) | Colon Cancer | Caspase-3 and -8 Activation and Fas Expression in a DLD-1 Colon Cancer Cell Line | [75] |
| 2 | 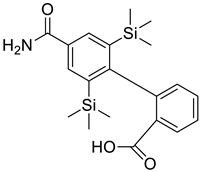 |
(4-[3,5-bis(trimethylsilyl) benzamide] benzoic acid) | Gastrointestinal Cancer | Orthotopic implantation to athymic nude mice inhibited spontaneous liver metastasis of AZ-521 (human gastric cancer). Furthermore, by intrahepatic implantation, it inhibited the proliferation of Co-3 (human colon adenocarcinoma), which formed a single nodule in the liver of athymic nude mice. | [73] |
| 3 | 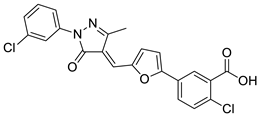 |
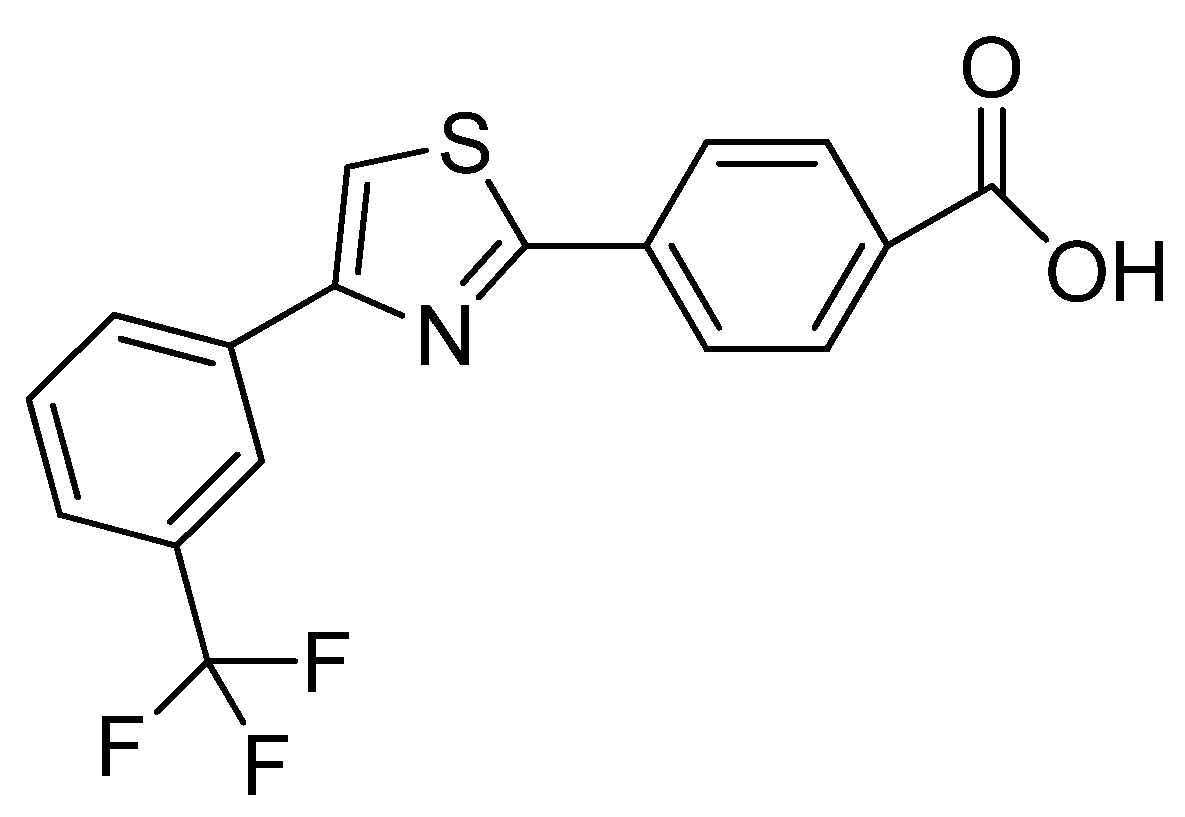
2-chloro-5-[5-[(E)-[1-(3-chlorophenyl)-3-methyl-5-oxo-pyrazol-4-ylidene]methyl]-2-furyl]benzoic acid | Various Cancers | EP300 histone acetyltransferase inhibitors | [76] |
| 4 | 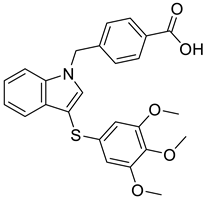 |
4-({3-[(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)sulfanyl]-1H-indol-1-yl}methyl)benzoic acid | Castration-resistant prostate cancer | Potential AKR1C3 Inhibitors | [77] |
| 5 | 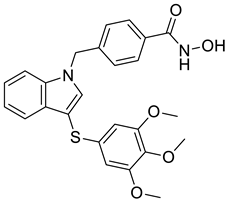 |
N-hydroxy-4-({3-[(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)sulfanyl]-1H-indol-1-yl}methyl)benzamide | Castration-resistant prostate cancer | Potential AKR1C3 Inhibitors | [77] |
| 6 | 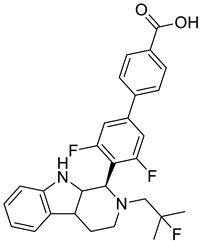 |
3',5'-difluoro-4'-((1R)-2-(2-fluoro-2-methylpropyl)-2,3,4,4a,9,9a-hexahydro-1H-pyrido [3,4-b]indol-1-yl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-carboxylic acid | Breast Cancer | It has a strong affinity for binding to ERα,, a good ability to break down ERα, and an inhibiting effect on the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. | [78] |
| 7 | 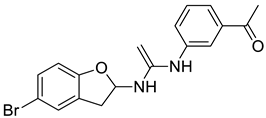 |
1-(3-((1-((5-bromo-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-2-yl)amino)vinyl)amino)phenyl)ethanone | Breast Cancer | Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor | [79] |
| 8 | 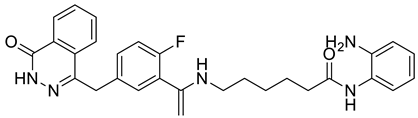 |
N-(2-aminophenyl)-6-((1-(2-fluoro-5-((4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazin-1-yl)methyl)phenyl)vinyl)amino)hexanamide | Various Cancers | Dual poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1/histone deacetylase-1 inhibitors | [80] |
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hurmath, U.S.; Reddy, G.K.; Aravazhi, T. Synthesis and in Vitro Anti Tumor Activity of Some Novel 2, 3-Disubstituted Quinazolin 4(3H)-one Derivatives. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 3, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.W.; Hong, D.H.; Han, S.B.; Jong, S.H.; Kim, H.C.; Fine, R.L.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.M. A novel stereo-selective sulfonylurea, 1-[1-(4-aminobenzoyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-6-sulfonyl]-4-phenyl-imidazolidin-2-one, has antitumor efficacy in in vitro and in vivo tumor models. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 64, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckhardt, S. Recent progress in the development of anticancer agents. Current Med. Chem. Anti-Cancer Agents. 2002, 2, 419–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Synthesis, characterization and anti cancer activity of some fluorinated 3,6-diaryl-[1,2,4]triazolo [3,4-b][1,3,4]thiadiazoles. Arabian Journal of Chem. 2017, 10, S2424–S2428. [CrossRef]
- Rojo, F.; Albanell, J.; Rovira, A.; Corominas, J.M.; Manzarbeitia, F. Targeted therapies in breast cancer. Seminars in Diagnost. Pathol. 2008, 25, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Li, J.J.; Tian, Y.S. Synthesis and bioactivity evaluation of 2,3-diaryl acrylonitrile derivatives as potential anticancer agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 81–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.C.; Jin, L.; Wang, M. Design, synthesis and in vitro evaluation of novel dehydroabietic acid derivatives containing a dipeptide moiety as potential anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 370–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaid, A.M.; Abdel-Hamide, S.G.; El-Kashef, H.A.; El-Azab, A.S.; Al-Khamees, H.A.; El-Subbagh, H.I. Substituted quinazolines, part 3. Synthesis, in vitro antitumor activity and molecular modeling study of certain 2-thieno-4(3H)-quinazolinone analogs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 2379–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, G.M. ; Newman. D.J. Nature: a vital source of leads for anticancer drug development. Phytochem. Rev. 2009, 8, 313–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelizz, H.A.; Marzouk, M.; Ghabbour, H.; Al-Salahi, R. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 1047–1054.
- Del, O.A.; Calzada, J.; Nuñez, M. Benzoic acid and its derivatives as naturally occurring compounds in foods and as additives: Uses, exposure, and controversy. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3084–3103. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, H.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Michael, F. Green, Add-on Treatment of Benzoate for Schizophrenia: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of d-Amino Acid Oxidase Inhibitor. JAMA Psychiat. 2013, 70, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safety and efficacy of benzoic acid as a feed additive for pigs for fattening when used as acidity regulator and all animal species when used as flavouring. Scientific Opinion. 2016, 14, 4353–4362.
- Maki, Takao; Takeda, Kazuo (2000). "Benzoic Acid and Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, ISBN 978-3527306732. [CrossRef]
- Sung,C. R..; Kim, K.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, B.M.; Kwack, S.J.Risk Assessment of Ethylhexyl Dimethyl PABA in Cosmetics. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 35, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.K.; Sharma, U.K.; Sharma, N. Comprehensive Review on Vanilla Flavor: Extraction, Isolation and Quantification of Vanillin and Others Constituents. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2008, 59, 299–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.P.; Gupta, A.; Sisodia, S.S. Gallic Acid: Pharmacogical Promising Lead Molecule: A Review. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 2018, 10, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, K.P. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity and Fungitoxicity of Syringic Acid, Caffeic Acid and 4-hydroxybenzoic Acid against Ganoderma Boninense. J. Agricul. Sci. 2009, 1, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, S.; Qamar, F.; Zainab, S. Simple UV spectrophotometric assay of Furosemide. J. Innovat. Pharm. Biolog. Sci. 2014, 1, 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Murchison, L.E.; Bewsher, P.D. Lack of effect of bumetanide on body potassium content in hypertension. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1975, 2, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.A.; Saunders, M.; Barnes, P.J.; Newton, R.; Maria, G. Belvisi. Sodium Salicylate Inhibits Cyclo-Oxygenase-2 Activity Independently of Transcription Factor (Nuclear Factor κB) Activation: Role of Arachidonic Acid. Molecular Pharmacol. 1997, 51, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, F.E.; Luciuk, G.H.; Becker, A.B.; Gillespie, C.A. Ketotifen: a new drug for prophylaxis of asthma in children. Ann. Allergy. 1982, 48, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Hartog, E.; Menashe, O.; Kler, E.; Yaron, S. Salicylate reduces the antimicrobial activity of ciprofloxacin against extracellular Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, but not against Salmonella in macrophages. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Albeniz, X.; Chan, A.T. Aspirin for the prevention of colorectal cancer. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 25, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, R.T.; Coleman, H.G.; Hughes, C.; Murray, L.J.; Cardwell, C.R. Low-dose aspirin use and survival in colorectal cancer: results from a population-based cohort study. BMC Cancer. 2018, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadri, H.; Lambourne, O.A.; Mehellou, Y. Niclosamide, a Drug with Many (Re)purposes. Chem. Med. Chem. 2018, 13, 1088–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Chawla, R.; Goyal, M. Topical anesthesia. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 31, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, I.C. Chemical structure of local anaesthetics. Brit. J. Anaesth. 1962, 34, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst,R. E.. Bexarotene ligand pharmaceuticals. Bexarotene: a clinical review. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2000, 1, 514–523. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, D.; Yu, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Cheng, F.; Xia, L. Emerging roles of bexarotene in the prevention, treatment and anti-drug resistance of cancers. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2018, 18, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punt, C.J.; Humblet, Y.; Roca, E.; Dirix, L.Y.; Wainstein, R.; Polli, A.; Corradino, I. Tallimustine in advanced previously untreated colorectal cancer, a phase II study. Br. J. Cancer. 1996, 73, 803–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beran, M.; Jeha, S.; Estey, E.; Vitek, L.; Zurlo, M.G.; Rios, M.B.; Keating, M.; Kantarjian. Tallimustine, an Effective Antileukemic Agent in a Severe Combined Immunodeficient Mouse Model of Adult Myelogenous Leukemia, Induces Remissions in a Phase I Study’. Cli. Cancer Res. 1997, 3, 2377–2384. [Google Scholar]
- Durães, F.; Pinto, M.; Sousa, E. Old Drugs as New Treatments for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2018, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, F.S. Tamibarotene: a new hope for therapeutic efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Hepatol. Int. 2014, 8, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarno, S.; Papinutto, E.; Franchin, C.; Bain, J.; Elliott, M.; Meggio, F.; Kazimierczuk, Z.; Orzeszko, A.; Zanotti, G.; Battistutta, R.; Pinna, L.A. ATP site-directed inhibitors of protein kinase CK2: an update. Curr. Topics Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masłyk, M.; Janeczko, M.; Martyna, A.; Kubiński, K. CX-4945: the protein kinase CK2 inhibitor and anti-cancer drug shows anti-fungal activity. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2017, 435, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menter, A.; Thrash, B.; Cherian, C.; Matherly, L.H.; Wang, L.; Gangjee, A.; Morgan, J.R.; Maeda, D.Y.; Schuler, A.D.; Kahn, S.J.; Zebala, J.A. Intestinal Transport of Aminopterin Enantiomers in Dogs and Humans with Psoriasis Is Stereoselective: Evidence for a Mechanism Involving the Proton-Coupled Folate Transporter. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 342, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldin, A.; Venditti, J.M.; Humphreys, S.R.; Denis, D.; Mantel, N.; Greenhouse, S.W. A quantitative comparison of the antileukemic effectiveness of two folic acid antagonists in mice. J. Nat. Cancer Inst. 1955, 15, 1657–1664. [Google Scholar]
- Falzone, L. , Salomone, S., Libra, M. Evolution of Cancer Pharmacological Treatments at the Turn of the Third Millennium. Front Pharmacology. 2018, 9, 1300–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleyer, W.A. The clinical pharmacology of methotrexate: new applications of an old drug. Cancer. 1978, 41, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conserva, M.R.; Anelli, L.; Zagaria, A.; Specchia, G.; Albano, F. The Pleiotropic Role of Retinoic Acid/Retinoic Acid Receptors Signaling: From Vitamin A Metabolism to Gene Rearrangements in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reversal by RARα agonist Am580 of c-Myc-induced imbalance in RARα/RARγ expression during MMTV-Myc tumorigenesis. Breast Cancer Rev. 2012, 14, R121–1229. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devmurari, V.P.; Shivan, P.; Goyani, M.B.; Jivani, N.P. Synthesis and anticancer activity of some novel 2-substituted benzothiazole. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2010, 8, 663–675. [Google Scholar]
- Abouzid, K.A.M.; Khalil, N.A.; Ahmed, E.M. Mohamed, K. O. 3-[(6-Arylamino)pyridazinylamino]benzoic acids: design, synthesis and in vitro evaluation of anticancer activity. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Hurmath, U.S.; Reddy, G.K.; Aravazhi, T. Synthesis and in vitro anti tumor activity of some novel 2, 3-disubstituted quinazolin 4(3h)-one derivatives. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 10, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
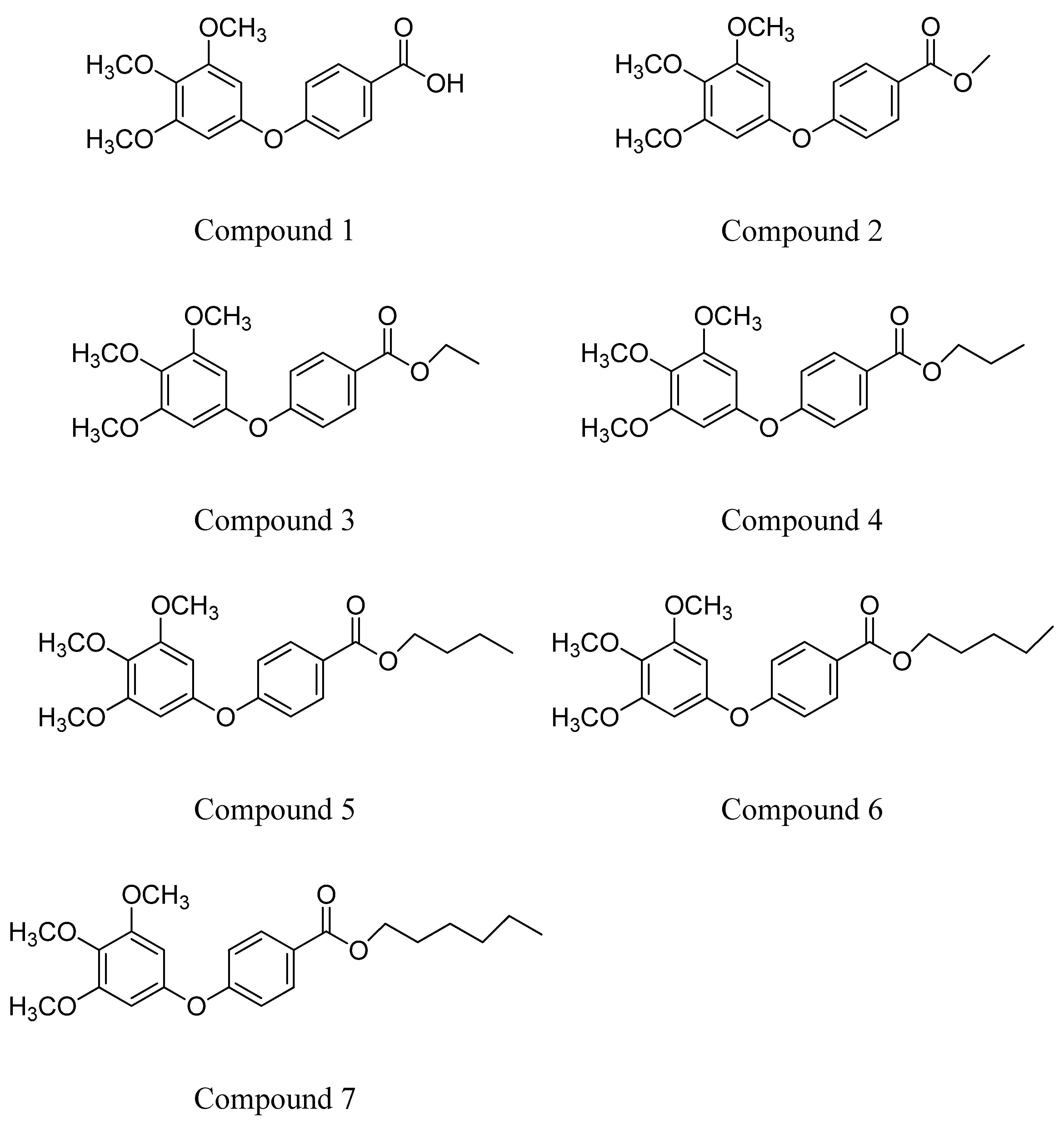
- Lee, K.H.; Ho, W.Y.; Wu, S.J.; Cheng, T.L.; Huang, P.J.; Wang, C.C.; Hung, J.H. Behavior-selective apoptotic capacity of 4-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenoxy) benzoic acid and its methyl derivatives on two breast cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
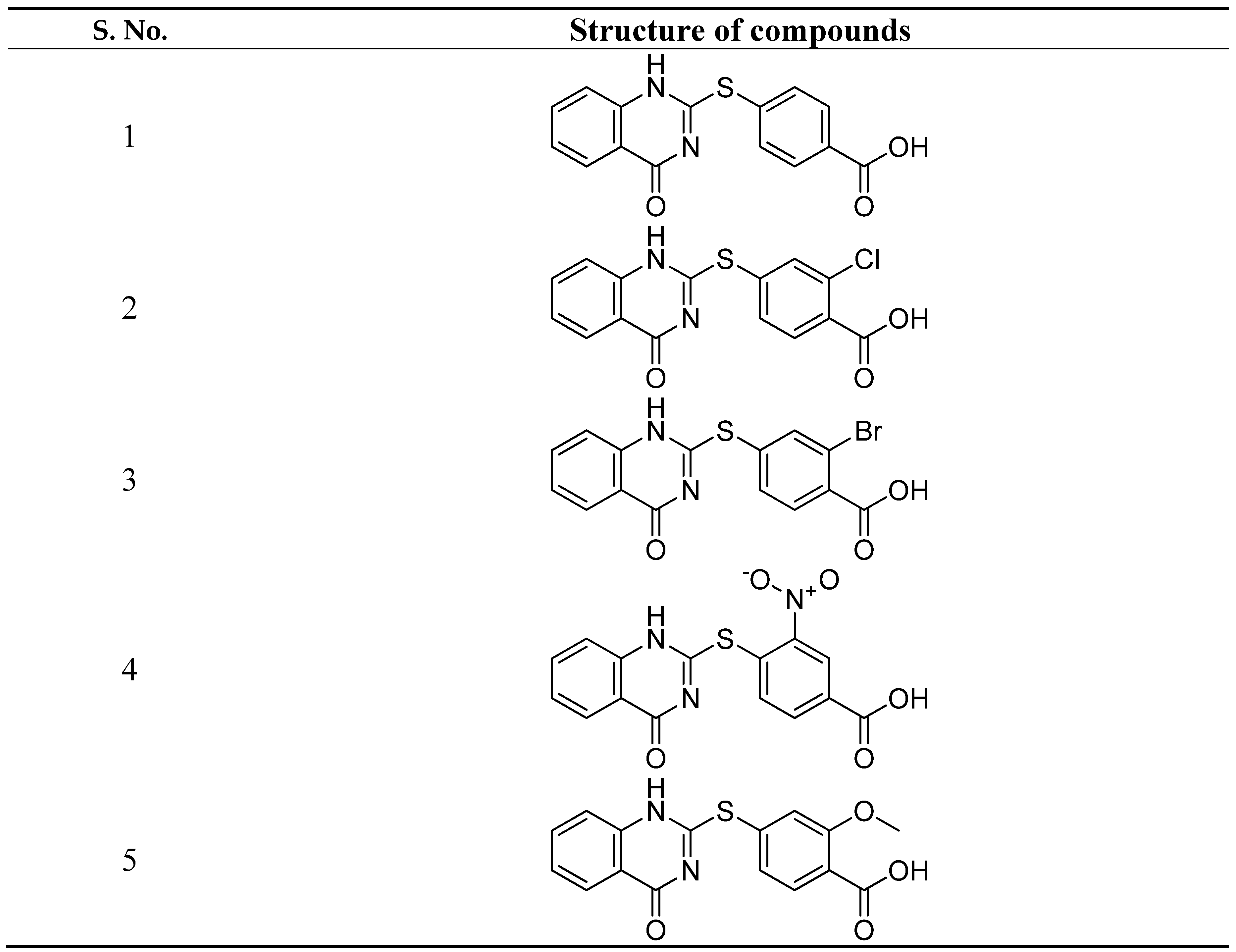
- Maruthamuthu, Alex, Dileepan, B. ; Rajam, S.; Stella, C.R. Synthesis, docking study and anticancer activity of benzoic acid substituted derivatives of quinazolinones. Der Pharma Chemica. 2015, 7, 130–136. [Google Scholar]
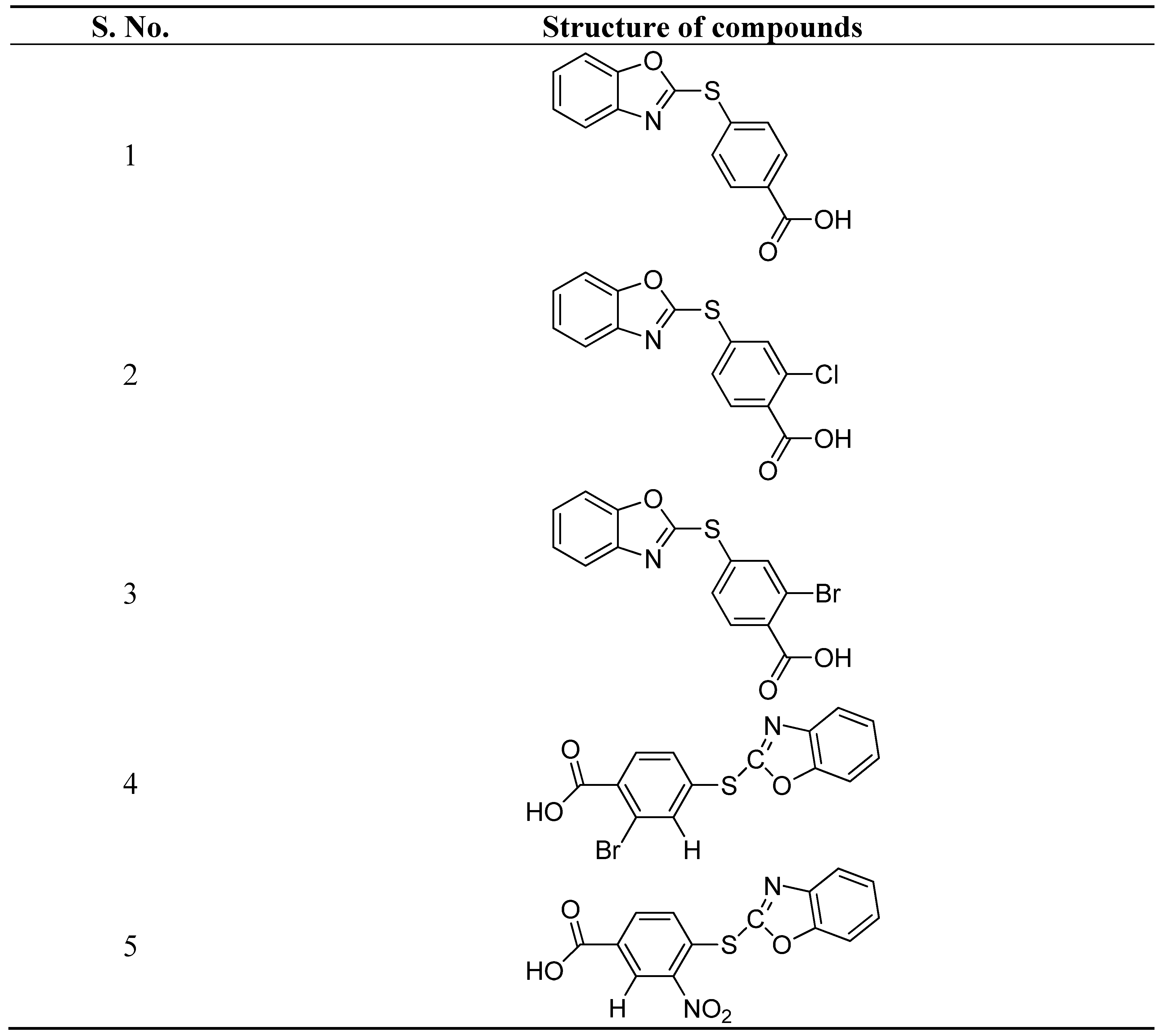
- Maruthamuthu, Bharathi Dileepan, B. ; Rajam, S.; Stella, C.R.; Ranjith, R. Synthesis, characterization, and anticancer activity of benzoxazole derivatives. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 380–387. [Google Scholar]
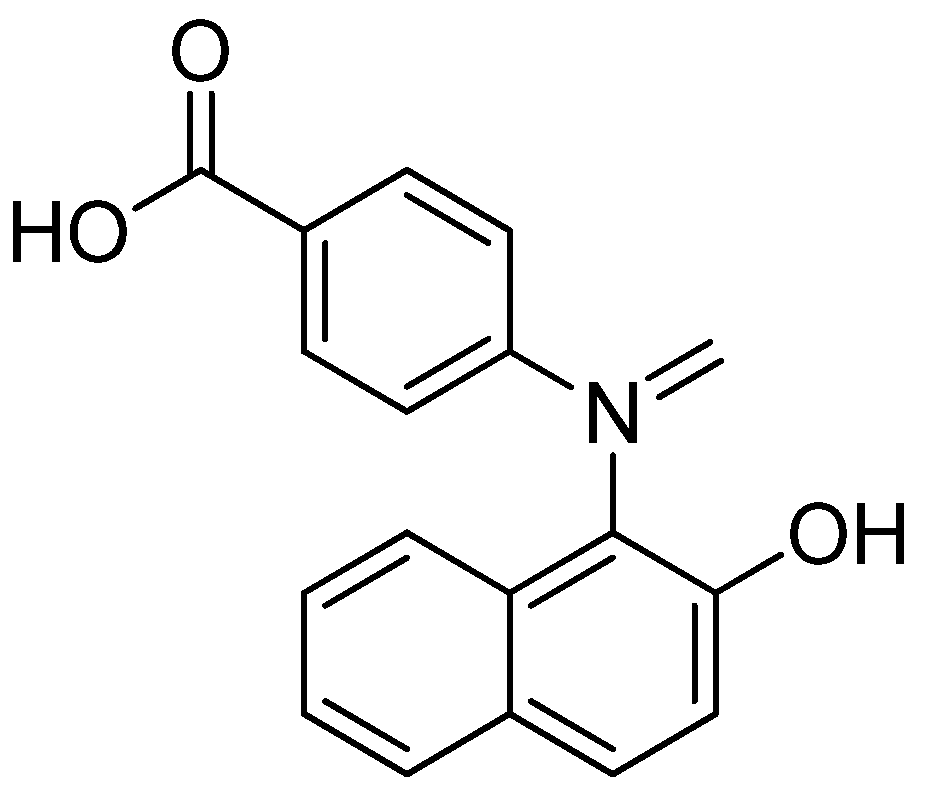
- Jebastin, J.N.S.; Kumar, T.R.; Evangelin, D. Molecular docking study, synthesis and invitro evaluation of antitumor activity of novel naphthylidene base of benzoic acid derivatives. Int. J. Life Sci. Pharm. Res. 2016, 6, L-36–L-44. [Google Scholar]
- Chowrasia, D.; Karthikeyan, C.; Choure, L.; Sahabjada, Gupta, M. ; Md Arshad, Trivedi, P. Synthesis, characterization and anti cancer activity of some fluorinated 3,6-diaryl-[1,2,4]triazolo [3,4-b] [1,3,4]thiadiazoles. Arabian J. Chem. 2017, 10, S2424–S2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, G.C.; Franchi, G.C.; Nowill, A.E.; Santos, L.S.; Alves, C.N.; Barata, L.E.S.; Andrade, C.K.Z. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro anticancer activity of novel 8,4’-oxyneolignan analogues. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2017, 28, 2229–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahlan, S.; Ramasamy, K.; Lim, S.M.; Ali, S.A. ; Shah; Mani, V.; Narasimhan, B. Design, synthesis and therapeutic potential of 3-(2-(1H-benzo [d]imidazol-2-ylthio) acetamido)-N-(substituted phenyl)benzamide analogues. Chem. Central J. 2018, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, R.; Jain, S.K.; Trivedi, P. ; Synergistic anti-cancer activity of combined 5-fuorouracil and gallic acid-stearylamine conjugate in A431 human squamous carcinoma cell line. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelizz, H.A.; Awad, H.M.; Marzouk, M.; Nasr, F.A.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Bakheit, A.H.; Naglahgh, A.M.; Al-Salahi, R. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoic acid hybrids as anticancer agents. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 19065–19074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
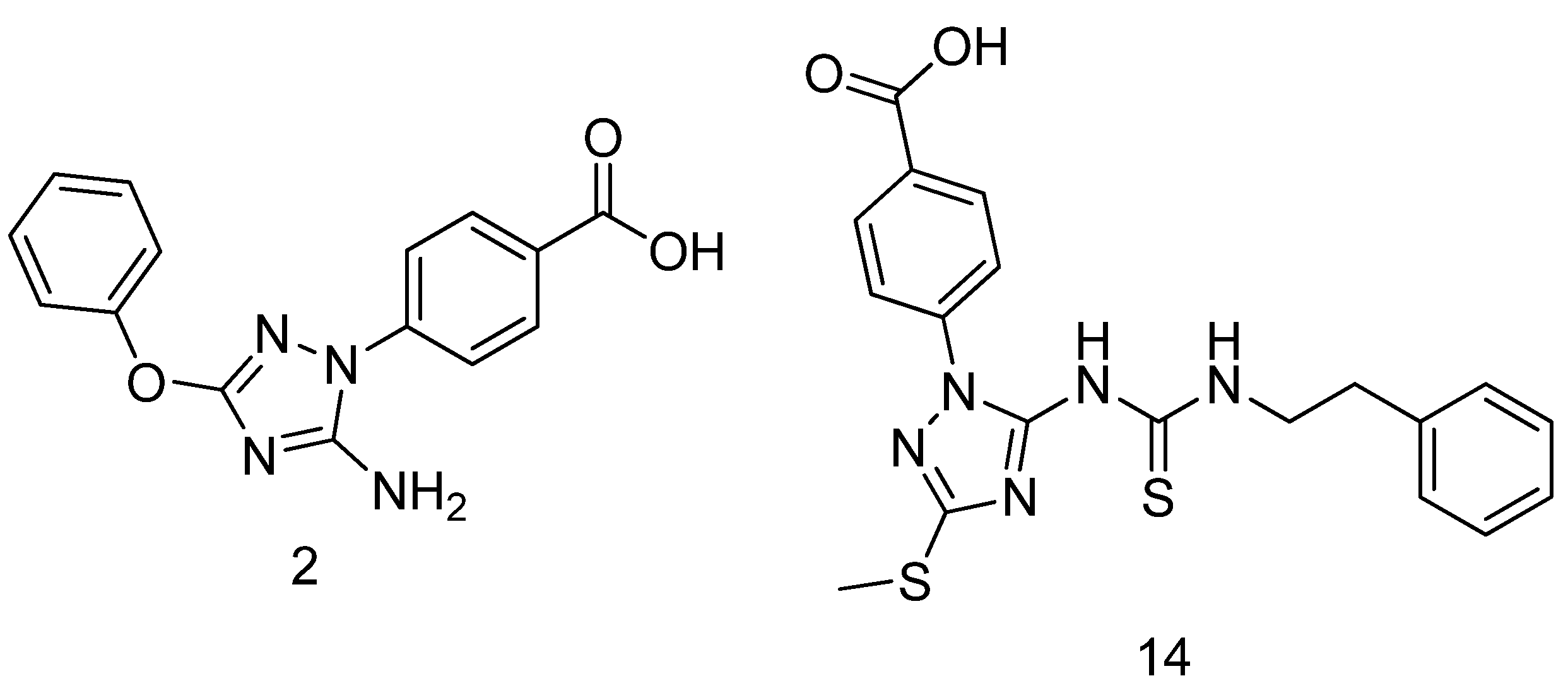
- Baharloui, M.; Mirshokraee, S.A.; Monfared, A.; Tehrani, M.H.H. Design and synthesis of novel triazole-based peptide analogues as anticancer agents. Iranian J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar]
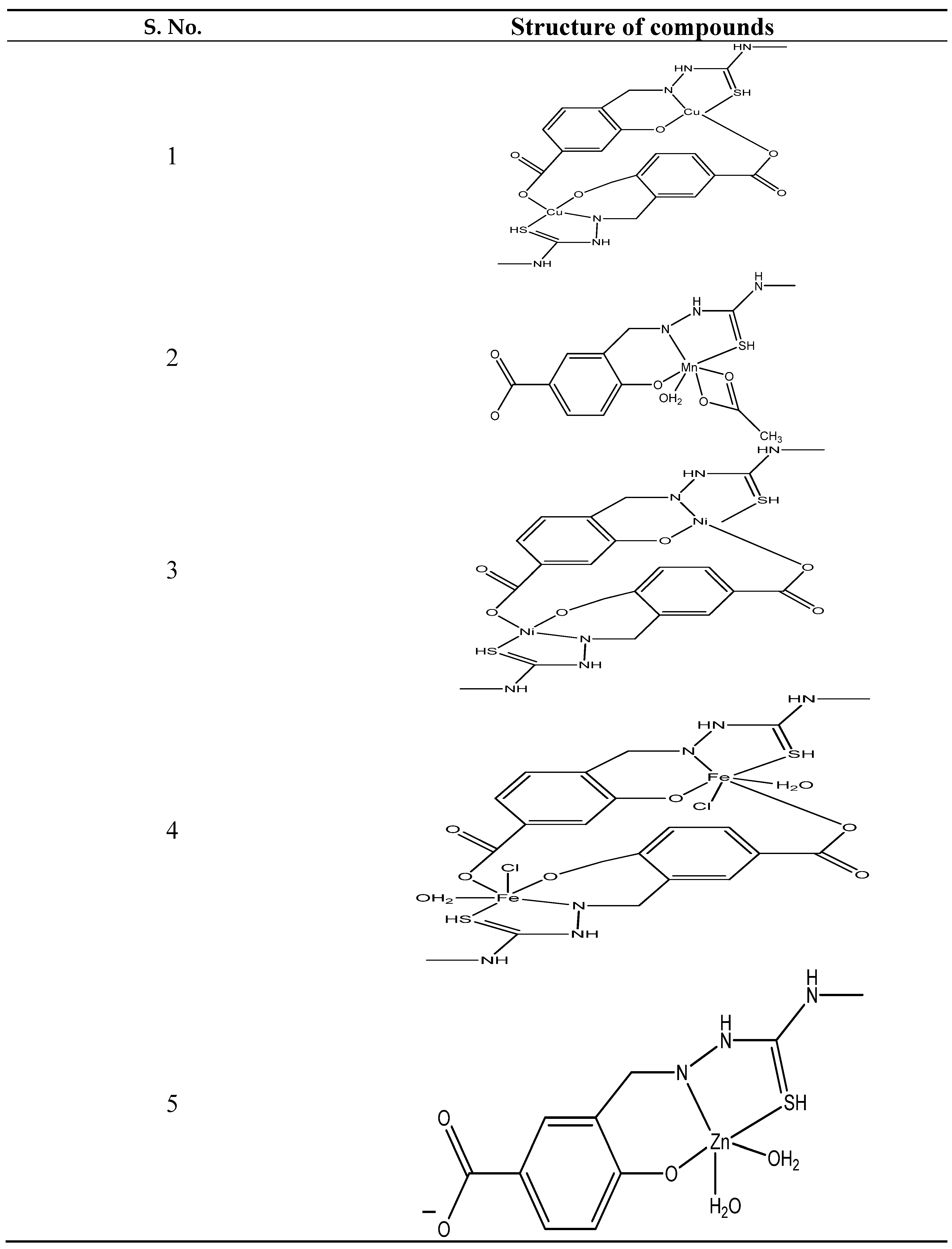
- Sardroud, S.J.; Hosseini-Yazdi, S.A.; Mahdavi, M.; Poupon, M.; Skorepova, E. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro evaluation of anticancer activity of a new water-soluble thiosemicarbazone ligand and its complexes. Polyhedron. 2020, 175, 114218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
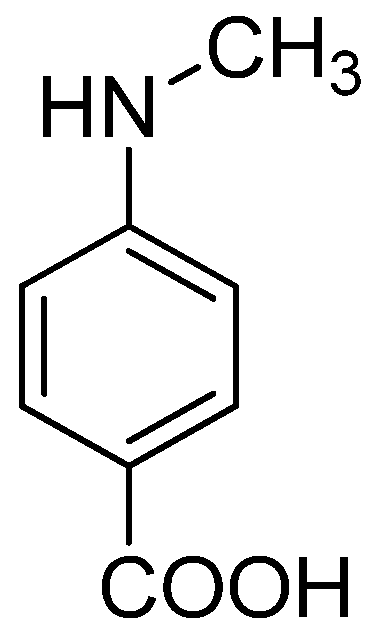
- AlSalhi, M.S.; Elangovan, K.; Ranjitsingh, A.J.A.; Murali, P.; Devanesan, S. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant derived 4-N-methyl benzoic acid and evaluation of antimicrobial, antioxidant and antitumor activity. Saudi J. Bio. Sci. 2019, 26, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
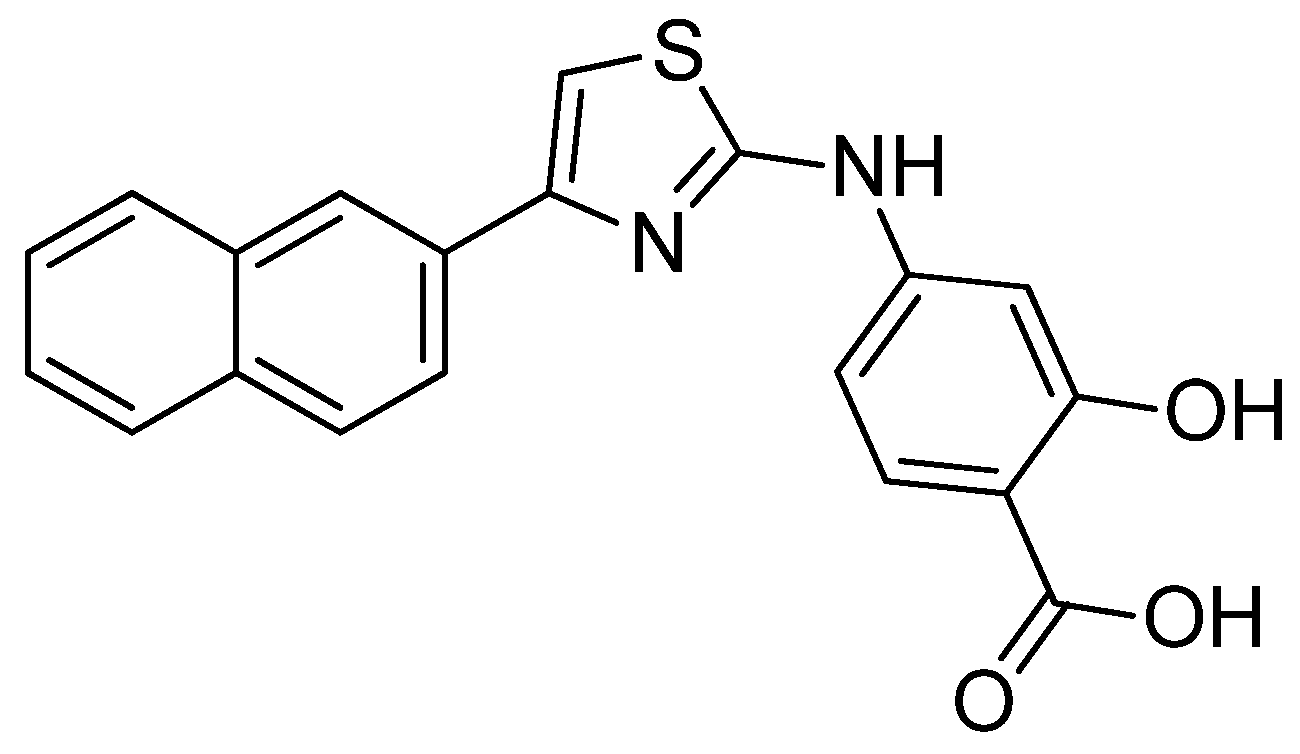
- Koshiishi, C.; Kanazawa, T.; Vangrevelinghe, E.; Honda, T.; Hatakeyama, S. Identification and characterization of a phenyl-thiazolyl-benzoic acid derivative as a novel RAR/RXR agonist. Heliyon, 2019, 5, e02849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
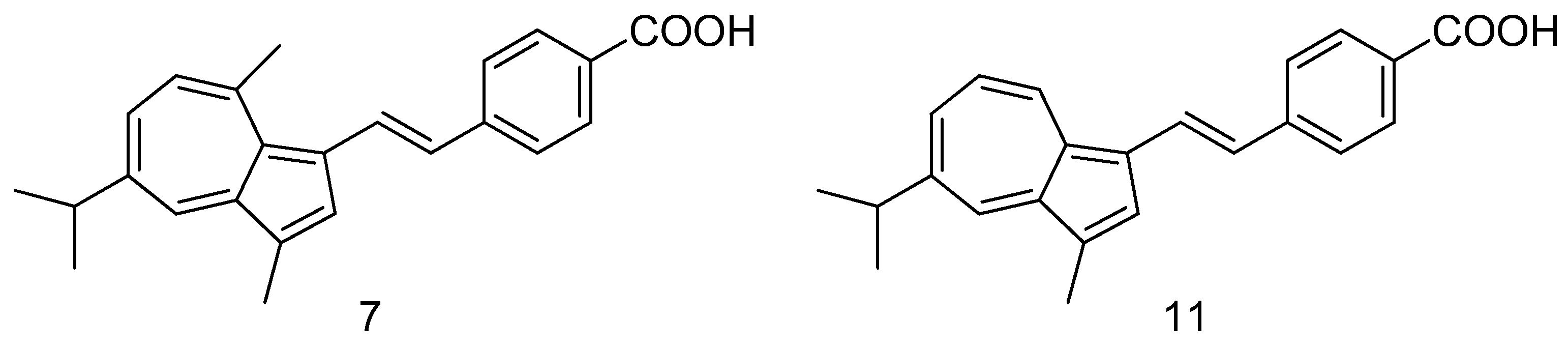
- Asato, A.E.; Peng, A.; Hossain, M.Z.; Mirzadegan, T.; Bertram, J.S. Azulenic retinoids: novel nonbenzenoid aromatic retinoids with anticancer activity. J. Med. Chem. 1993, 36, 3137–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
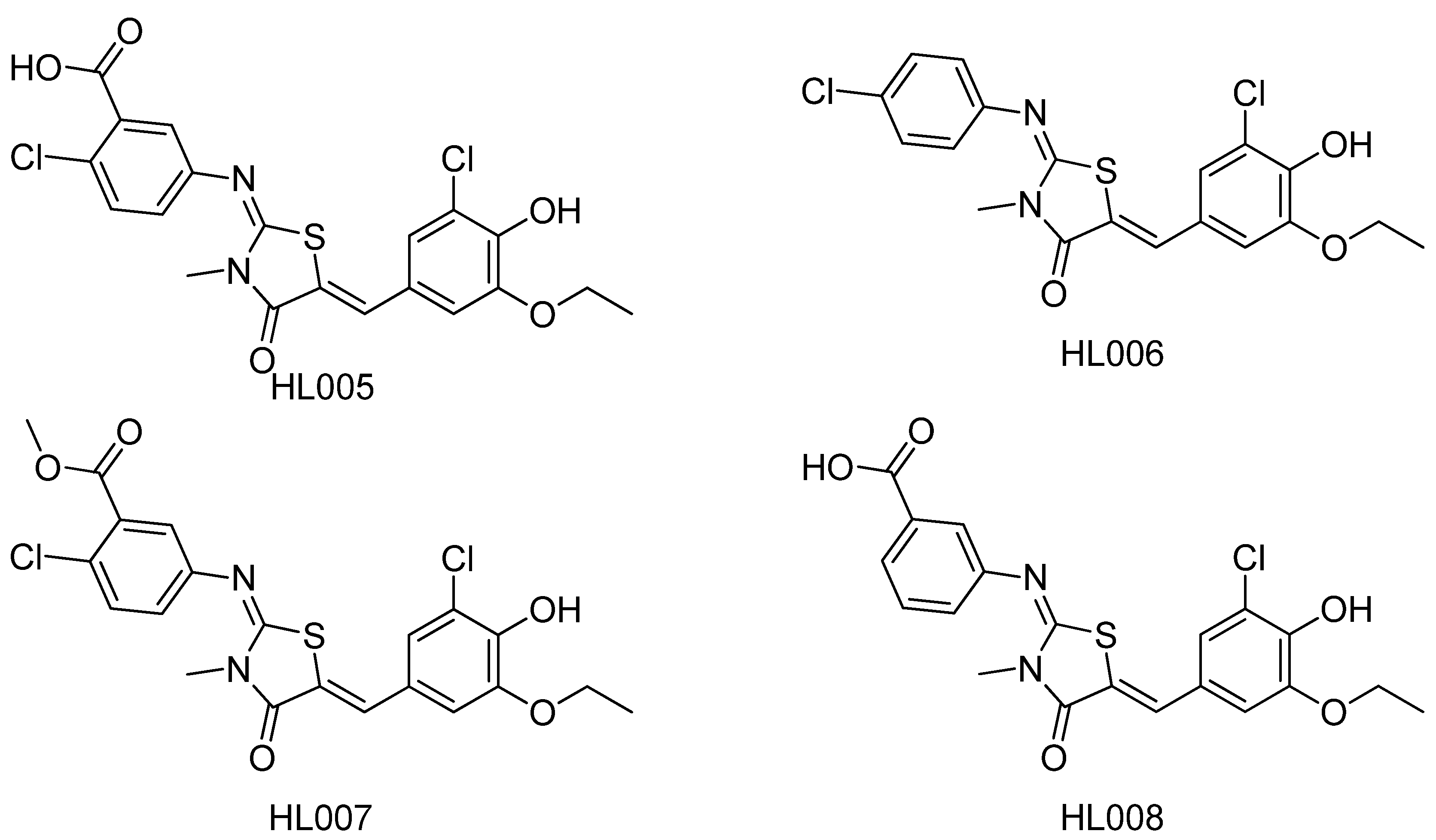
- Lua, W.; Chea, P.; Zhanga, Y.; Li, H.; Zoub, S.; Zhua, J.; Denga, J.; Shena, X.; Jianga, H.; Li, J.; Huang, J. HL005—A new selective PPARα antagonist specifically inhibits the proliferation of MCF-7. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 124, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestgen, B.; Kufareva, I.; Seetoh, W.; Abell, C.; Hartmann, R.W.; Abagyan, R.; Borgne, M.L.; Filhol, O.; Cochet, C.; Lomberget, T.; Engel, M. 2-Aminothiazole Derivatives as Selective Allosteric Modulators of the Protein Kinase CK2. 2. Structure-Based Optimization and Investigation of Effects Specific to the Allosteric Mode of Action. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1817–1836. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.S.; Premnath, D.; Obadiah, A.; Durairaj, A.; Ramanathan, S.; Vasanthkumar, S. Synthesis, structure characterization, and biological evaluation of 3-amino-5-(5-oxo-5h-benzo[a]phenothiazin-6-ylamino) benzoic acid derivatives via molecular docking, cytotoxicity, and antioxidant studies. Curr. Pharmacol. Reports. 2019, 5, 440–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
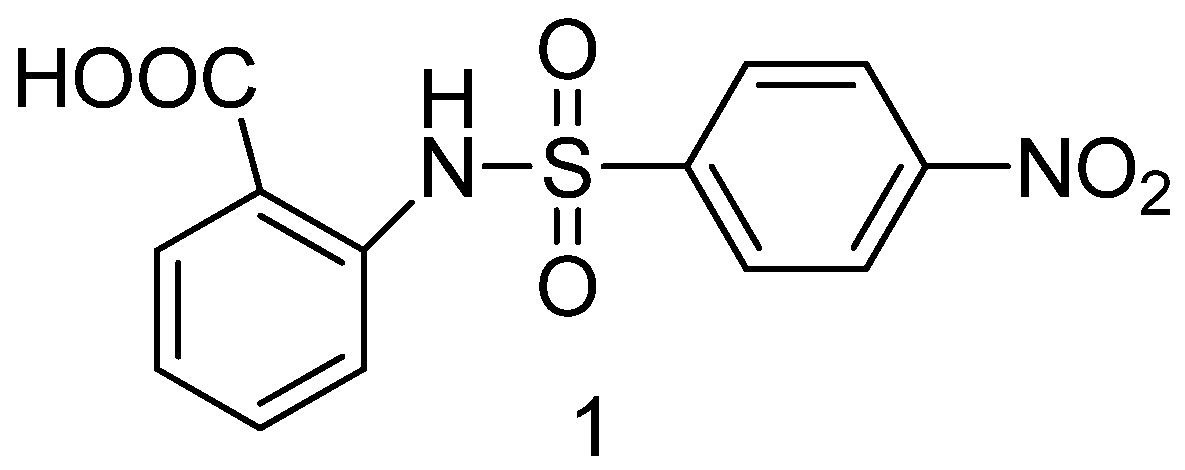
- Doungsoongnuen, S.; Worachartcheewan, A.; Pingaew, R.; Suksrichavalit, T.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Ruchirawat, S.; Prachayasittiku, V. Investigation on biological activities of anthranilic acid sulfonamide analogs. EXCLI J., 2011, 10, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wasfy, A.A.F.; Fathalla, O.A.; Salman, A.A. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel quinazoline derivatives as potential anticancer agent. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Chem. 2014, 4, 501–508. [Google Scholar]
- Unver, H.; Canturk, Z. Synthesis and characterization of two new thiophene acetyl salicylic acid esters and their ortho- and para-effect on anticancer activity. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
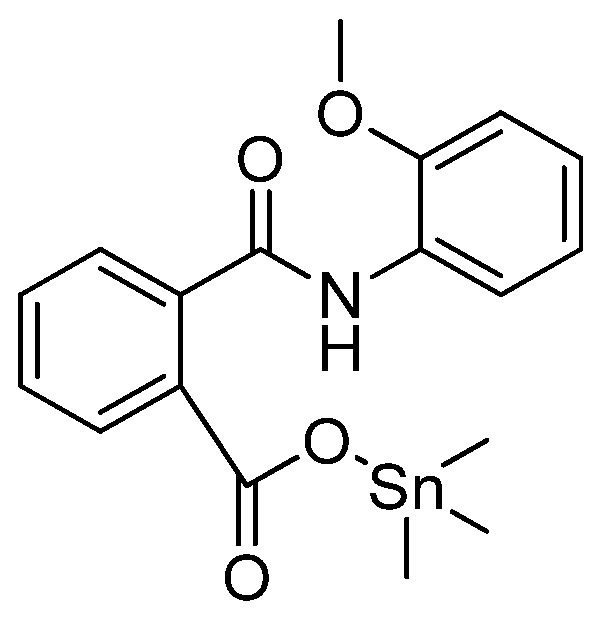
- Sirajuddin, M.; Ali, S.; Tahir, M.N. Organotin(IV) derivatives based on 2-((2-methoxyphenyl)carbamoyl)benzoic acid: Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, assessment of antibacterial, DNA interaction, anticancer and antileishmanial potentials. J. Mol. Str. 2020, 1229, 129600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelizz, H.A.; Awad, H.M.; Marzouk, M.; Nasr, F.A. Exploiting the 4-hydrazinobenzoic acid moiety for the development of anticancer agents: Synthesis and biological profile. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 102, 104098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anantharaju, P.G.; Reddy, B.D.; Padukudru, M.A.; Kumari, C.C.M.; Vimalambike, M.G.; Madhunapantula, S.V. Naturally occurring benzoic acid derivatives retard cancer cell growth by inhibiting histone deacetylases (HDAC). Can. Bio. Ther. 2017, 18, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, W.W.; Shao, L.D.; Pan, Z.H.; Chen, C.H.; Li, D. Design, synthesis, and anti-triple negative breast cancer activity of novel Toosendanin derivatives. Bio. Med. Chem. Let. 2023, 129187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.N.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, B.; Hong, J.-H.; Jang, Y.S.; Lee, D.E.; Pang, C.; Kang, K.S.; Kim, K.H. Estrogenic Activity of 4-Hydroxy-Benzoic Acid from Acer tegmentosum via Estrogen Receptor α-Dependent Signaling Pathways. Plant. 2022, 11, 3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco-Morales, M.; Hernández-Pedro, N.Y.; Barrios-Bernal, P.; Arrieta, O.; Ruiz-Godoy, L.M.; Aschner, M.; Santamaría, A.; Colín-González, A.L. S-allylcysteine induces cytotoxic effects in two human lung cancer cell lines via induction of oxidative damage, downregulation of Nrf2 and NF-κB, and apoptosis. Anti-Cancer Drug. 2021, 32, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
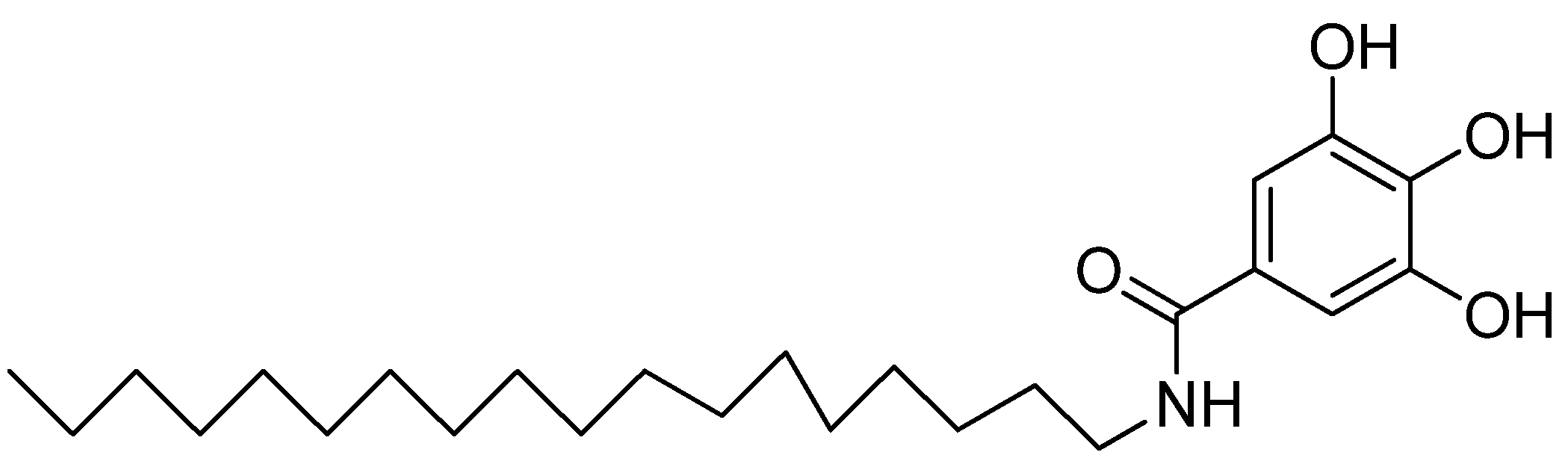
- Lee, H.L.; Lin, C.S.; Kao, S.H.; Chou, M.C. Gallic acid induces G1 phase arrest and apoptosis of triple-negative breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231 via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/p21/p27 axis. Anti-Can. Drug. 2017, 28, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Wierzba, K.; Sano, M.; Shibata, J.; Yonekura, K.; Hashimoto, A.; Sato, K.; Yamada, Y. TAC-101, a benzoic acid derivative, inhibits liver metastasis of human gastrointestinal cancer and prolongs the life-span. Clin. & Exp. Meta. 1998, 16, 323–331. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, L.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Sheng, X.; Wang, A.; Zheng, S.; Lu, Y. Phenolcarboxylic acids from medicinal herbs exert anticancer effects through disruption of COX-2 activity. Phyto. 2014, 21, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, Y.; Nakayama, Y.; Sako, T.; Minagawa, N.; Abe, Y.; Nagato, M.; Kadowaki, K.; Katsuki, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Tsurudome, Y.; Shibao, K. 4-[3, 5-Bis (trimethylsilyl) benzamido] benzoic acid (TAC-101) induced Fas expression and activated caspase-3 and-8 in a DLD-1 colon cancer cell line. in vivo. 2007, 21, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kanada, R.; Suzuki, T.; Murata, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Shimada, T.; Kuroha, M.; Minami, M.; Higuchi, S.; Tominaga, Y.; Naito, H. 4-Pyridone-3-carboxylic acid as a benzoic acid bioisostere: Design, synthesis, and evaluation of EP300/CBP histone acetyltransferase inhibitors. Bio. Med. Chem. Let. 2021, 51, 128358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhuo, X.; Wang, S.; Jiang, S.; Peng, Z.; Kang, K.; Zheng, X.; Sun, M. Design, Synthesis and Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Novel Indole Derivatives Containing Benzoic Acid Group as Potential AKR1C3 Inhibitors. Chem. Bio. 2020, 17, e2000519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, W.; Liu, J. Dynamics-based discovery of novel, potent benzoic acid derivatives as orally bioavailable selective estrogen receptor degraders for ERα+ breast cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 7575–7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldehna, W.M.; Nocentini, A.; Elsayed, Z.M.; Al-Warhi, T.; Aljaeed, N.; Alotaibi, O.J.; Al-Sanea, M.M.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; Supuran, C.T. Benzofuran-based carboxylic acids as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and antiproliferative agents against breast cancer. ACS Med. Chem. Let. 2020, 11, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Xie, Z.; Liao, C. Design, synthesis and anticancer activities of novel dual poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1/histone deacetylase-1 inhibitors. Bio. & Med. Chem. Let. 2020, 30, 127036. [Google Scholar]
| S. No. | Structure | Name of Compound | Type of Cancer for which it is potent | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 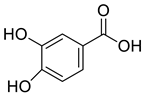 |
Dihydroxy Benzoic Acid | Cervical and Colon Cancer | Histone deacetylases (HDAC) activity was inhibited, resulting in cancer cell growth inhibition via ROS induction and cellular apoptosis mediated by Caspase-3. Furthermore, DHBA arrested cells in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle and increased the population of sub-G0-G1 cells. | [68] |
| 2 | 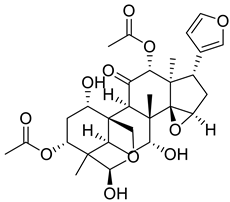 |
Toosendanin | Triple Negative Breast Cancer | Induction of S-phase arrest and a decrease in G2/M cell number in HCC1806 cells. Toosendanin also significantly reduced the protein level of the well-known cancer suppressor gene p53, inhibited AKT and ERK phosphorylation, and induced the accumulation of phosphorylated p38 and p21. | [69] |
| 3 | 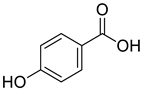 |
4-hydroxy-benzoic acid | Breast Cancer | Concentration-dependently increased the protein expression levels of p-ERK, p-AKT, p-PI3K, and p-Er. 4-hydroxybenzoic acid is responsible for the estrogen-like effects of A. tegmentosum and may assist in the regulation of estrogenic effects during menopause. | [70] |
| 4 | 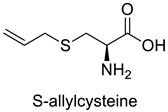 |
S-allylcysteine | Lung Cancer | Oxidative damage induction, Nrf2 and NF-B downregulation, and apoptosis | [71] |
| 5 | 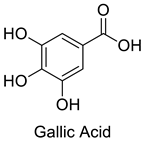 |
Gallic Acid | Triple-Negative Breast Cancer | MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cell G1 arrest and apoptosis via the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/p21/p27 axis. | [72] |
| 6 | 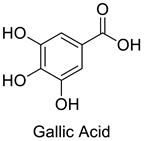 |
Gallic Acid | Lung Cancer | Disruption of COX-2 Activity | [74] |
| 7 | 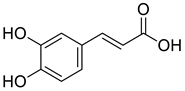 |
3,4-Dihydroxycinnamic acid | Lung Cancer | Disruption of COX-2 Activity | [74] |
| 8 | 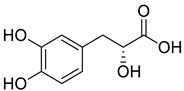 |
Danshensu | Lung Cancer | Disruption of COX-2 Activity | [74] |
| 9 | 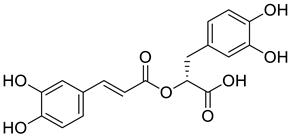 |
Rosmarinic acid | Lung Cancer | Disruption of COX-2 Activity | [74] |
| 10 | 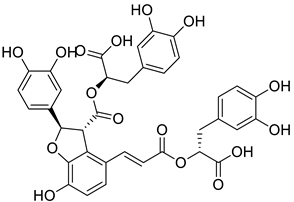 |
Salvianolic acid B | Lung Cancer | Disruption of COX-2 Activity | [74] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





