1. Introduction
Cisplatin (CIS) is a potent platinum chemotherapeutic compound immensely used for treatment of various solid tumors. However, renal toxicity, hepatotoxicity and gonadal toxicity restrict its use. After CIS treatment, approximately all patients suffer from testicular atrophy and azospermia that distress the social life of partners. Therefore, the prevention of CIS-related reproductive toxicity is a major challenge (Heeba, Hamza et al. 2016, Volarevic, Djokovic et al. 2019, Abdel-Latif, Fathy et al. 2022).
In spite of no exact pathophysiological mechanisms of CIS-induced gonadal injury, several earlier studies have revealed that direct DNA damage and oxidative stress in testicular tissue may associate its toxicity. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) overproduction triggers the inflammation-inducing mediators as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) which consequently causes necrosis and apoptosis of the testicular cells (Kohsaka, Minagawa et al. 2020, Mesbahzadeh, Hassanzadeh-Taheri et al. 2021). Therefore, the alleviation of these underlying mechanisms is rational strategies to hinder CIS reproductive toxicity.
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is a central intracellular second messenger for multiple intracellular signaling pathways (Hansson, Skålhegg et al. 2000). It regulates cell differentiation and growth and gene transcription in testicular cells. Moreover, cAMP is the intracellular messenger for steroidogenesis action of luteinizing hormone (Golkowski, Shimizu-Albergine et al. 2016). Regulation of cAMP is performed by superfamily of enzymes called phosphodiesterases (PDEs). However, inhibition of PDEs increases cAMP levels which, in turn, enhances cell function (Calamera, Moltzau et al. 2022). In the last decades, different phosphodiesterase inhibitors offered powerful protective effect against various diseases of testes (Özgür, Telli et al. 2014, Yao, Li et al. 2016, Mohamed, Hafez et al. 2018, Kölükçü, Atılgan et al. 2021). The potential chemoprotective effect of tadalafil (TDF) (Abdel-Wahab, Alkahtani et al. 2020, Kaku, Chiba et al. 2022), a selective long acting PDE-5 inhibitor, and pentoxifylline (PTX) (Fallahzadeh, Rezaei et al. 2017), a nonspecific PDE-4 inhibitor, was demonstrated against CIS-induced reproductive toxicity in males.
Meanwhile, cilostazol (Cilo), a selective PDE-3 inhibitor, abrogates platelets from aggregation and has vasodilator, as well as antithrombotic property (Hoshino, Toyoda et al. 2021). Cilo is safely indicated for intermittent claudication resulted from peripheral arterial disease (Real, Serna et al. 2018). According to recent studies, Cilo possesses pleiotropic effects that include anti-oxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory properties (Asal and Wojciak 2017, He, Kawamura et al. 2017, Mohamed, Hafez et al. 2018, Hafez, Ibrahim et al. 2019, Refaie, Ahmed Ibrahim et al. 2021). Moreover, it has showed a protective effect against different model of testicular injury as testicular ischemia reperfusion (Refaie, Ahmed Ibrahim et al. 2021) and diabetic testicular damage (Mohamed, Hafez et al. 2018). In these studies, Cilo significantly improved testicular inflammation and oxidative stress state.
To our knowledge, the impact of Cilo on CIS-induced male reproductive toxicity has not been clarified. The purpose of this study was to determine whether Cilo (in a dose-dependent manner) could possibly protect against testicular damage induced by CIS, examine the engaged underlying mechanisms and compare its proposed therapeutic potential with already published other PDE inhibitors on androgenic toxicity caused by CIS.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs and Chemicals
Cisplatin, TDF, PTX and Cilo were purchased from Bristol Mayers Co. (New Jersey, USA), Eva Pharma for Pharmaceutical industries (Egypt), Medical Union Pharmaceutical (Egypt) and Pharmacare for Pharmaceutical industries (Egypt), respectively. Polyclonal rabbit/anti-rat primary antibody against TNF-α was obtained from Thermo Fischer Scientific Inc. /Lab Vision, Fermont, CA, USA. Antibodies against nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and caspase-3 were purchased from Biolegend, San Diego, CA, USA and NSJ Bioreagents, San Diego,CA, respectively. All other chemicals of analytical grade were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Dorset, Germany).
2.2. Experimental Design
Seventy male Wistar rats, weighing 180–210 g, obtained from the Animal Care Unit, Faculty of Pharmacy, Nahda University, were used in this study. Through the experiment period, they were housed under constant environment of a 12 hours dark/light cycle and a temperature of 25 °C ± 2. The animals were allowed to feed on commercially available chow pellet diet and water ad libitum.
Before the beginning of the experiment, animals were allowed to adapt in the lab for 1 week. After that, twenty eight rats were randomly selected as control groups (7 rats each) received the corresponding vehicle, TDF group administered TDF (20 mg/kg/day, P.O), PTX group administered PTX (75 mg/kg/day, P.O) and Cilo 20 mg group received Cilo (20 mg/kg/day, P.O) for 14 successive days. The remaining (n=42) was randomly divided into 6 groups (7 rats each) and treated for duration of 14 consecutive days as follow:
CIS group was treated with a single i.p injection of CIS (7 mg/kg) dissolved in saline, a dose that is sufficient to induce testicular injury in male rats according to previous studies (Rezvanfar, Rezvanfar et al. 2013, Heeba, Hamza et al. 2016, Mesbahzadeh, Hassanzadeh-Taheri et al. 2021), on the 7th day of the experiment.
CIS +TDF group was given TDF (5 mg/kg/day, P.O) for 14 successive days while being injected with CIS (7 mg/kg, i.p) on the 7th day of the experiment.
CIS +PTX group received PTX (75 mg/kg/day, P.O) for 14 successive days while being injected with CIS (7 mg/kg, i.p) on the 7th day of the experiment.
CIS + Cilo 5 mg group received Cilo (5 mg/kg/day, P.O) for 14 successive days while being injected with CIS (7 mg/kg, i.p) on the 7th day of the experiment.
CIS + Cilo 10 mg group were treated with Cilo (10 mg/kg/day, P.O) for 14 successive days while being injected with CIS (7 mg/kg, i.p) on the 7th day of the experiment.
CIS + Cilo 20 mg group was exposed to the same regimen of the previous two groups except using higher dose of Cilo (20 mg/kg/day, P.O).
TDF and PTX were dissolved in normal saline while Cilo was dissolved in carboxy methyl cellulose solution. The dosages and timings for TDF and PTX administration were based on previous reports (Fallahzadeh, Rezaei et al. 2017, Abdel-Wahab, Alkahtani et al. 2020). Meanwhile, doses of Cilo were selected based on previous pharmacological studies. Cilo at these doses has been reported to suppress reproductive toxicity induced by cyclophosphamide, testicular ischemia/ reperfusion or streptozotocin (Mohamed, Hafez et al. 2018, Abdel-Aziz, Mohamed et al. 2020, Refaie, Ahmed Ibrahim et al. 2021).
All animals’ procedures were performed in accordance with Animal Care Community, Minia University, Egypt (Permit Number: 230103) in strict accordance with the international policies (Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the US National Institute of Health; NIH Publication No. 85-23, revised 1996).
2.3. Collection of Samples
At the end of the experiment, 12 h fasted rats were anaesthetized with pentobarbital sodium (50 mg/kg, i.p). Collection of blood samples was done by cardiac puncture and in order to separate the sera, blood samples were centrifuged for 10 min at 3000 rpm to measure testosterone level. Testes were excised, rinsed and dried. Testes were weighed to calculate the relative testicular weight (testicular weight /body weight x100). One testis of each animal was fixed in 10% formalin for histological examination. The other one was flash frozen in liquid nitrogen, stored at −80 °C and subsequently homogenized in cold potassium phosphate buffer (0.05 M, pH 7.4) for various biochemical and Western blot analyses.
2.4. Sperm Motility and Count
Assessment of the epididymal sperm motility and count were done immediately. With the aid of a TOX IVOS II, total sperm number was determined by Kenjale, Shah et al. (2008). Dissected Cauda epididymis was weighed and minced in 5 mL of physiological saline immediately, and then incubated for 30 min at 37 °C allowing sperms to leave the tubules of epididymis. A phase contrast microscope at 400 x magnification was used to record the percentage of motile sperm from left cauda epididymis. The total number of sperm was then calculated.
2.5. Determination of Serum Testosterone Level
Testosterone level in the serum was measured by using commercial rat-specific ELISA kit following the manufacturers’ guidelines, Cat. No. CSB-E05100r (Cusabio Biotech Co., Ltd., China).
2.6. Determination of Testicular Oxidative Stress Markers
Antioxidant status in testes was screened through determination of malondialdehyde (MDA), a lipid peroxidation, nitric oxide (NO) and reduced glutathione (GSH) in testicular homogenate. The process of MDA measurement is based on reaction of MDA with thiobarbituric acid to form a pink colored complex assessed spectrophotometrically at 535 nm (Buege and Aust 1978). The testicular NO was quantified as total nitrate/nitrite (the stable degradation products of NO). By using copperized cadmium, nitrate is reduced to nitrite followed by color development in acidic medium with Griess reagent (Sastry, Moudgal et al. 2002). The determination of GSH concentration is performed by using a commercially available spectrophotometric kit (Biodiagnostic, Cairo, Egypt). The thiol component of GSH reduces Ellman’s reagent (5,5-dithio-bis-2-nitrobenzoic acid) resulting in a yellow colored compound (5-thio-2-nitrobenzoic acid) which was measured spectrophotometrically at 405 nm.
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
Frozen testicular tissue samples were homogenized in ice-cold lysis buffer (Bio BASIC INC, Ontario, Canada). After quantitation of protein concentrations using the established Bradford dye-binding method (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA), aliquots of lysate with equal protein amount were electrophoresed on sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE).
Following the protein extraction, proteins were transferred to polyvinyl difluoride (PVDF) membrane. After incubation of membranes in blocking solution containing 5% (w/v) non-fat milk, they were incubated with primary antibodies, against the blotted target protein, TNF-α (catalog # PA5-19810, dilution1:3000), NF-κB (catalog # 622601, dilution 0.05 μg/mL) and caspase-3 (R31602, dilution 0.5 mg/ml) diluted in blocking buffer at 4 °C overnight. After extensive rinsing, membranes were incubated with secondary antibody (Goat anti-rabbit IgG- Novus Biologicals) conjugated to horseradish peroxidase for 1 h. Protein bands were visualized with a standard enhanced chemiluminescent method. The densitometry measurements of target protein band relative to that of their corresponding β-actin band were semi-quantified, presented as a ratio of the relative optical density and calibrated as fold-change value from control using image J software (freeware; rsbweb.nih.gov/ij).
2.8. Histopathological Examination
Collected testes from all experimental animals were washed with normal saline and fixed in Bouin’s solution for 1-2 days. After that, testes were dehydrated in graded ethanol series then cleared in xylene and embedded in paraffin blocks. Blocks were sectioned at 4-6 µm thickness. The obtained sections were deparaffinized by xylol and stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) for routine histopathological examination under a light microscope according to Suvarna (2013). In addition, the microscopic scoring for qualitative histopathological changes in seminiferous tubules were graded on a scale of (-) absence of pathological finding, (+) mild, (++) moderate and (+++) severe. Mild, moderate and severe represented pathological findings of <25%, 25–50% and >50% of the total examined area of seminiferous tubules, respectively. Scoring was applied on the following histological parameters [desquamation and disorganization in germinal cells, interstitial oedema, degeneration in germinal cells and reduction in germinal cell counts] (Tuglu, Yuvanc et al. 2015).
2.9. Statistical Analysis
Data were expressed as mean ± S.E.M and statistically analyzed through one way analysis of variance (ANOVA), then, comparisons between individual groups was performed by Tukey-Kramer post analysis test. The results were considered as statistically significant when differences were with the probability (P) value (<0.05). Statistical analysis was done using Graph Pad Prism® software (Version 5.0 for Windows, Graph Pad Software, San Diego, California, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Effect on Relative Testicular Weight, Testosterone Concentration and Epididymal Sperm Parameters
As listed in
Table 1, the relative weights of the testes in CIS group was significantly (
P < 0.05) lower than that of the control group. As compared to CIS group, relative testicular weight was significantly (
P < 0.05) higher in CIS-intoxicated rats treated with TDF, PTX and different doses of Cilo. In addition, CIS group exhibited significant decrease in serum testosterone level and sperm count and motility, as well as significant increase in the percent of sperms with abnormal morphology in comparison to control animals.
However, the impairment in testosterone concentration and the measured sperm parameters were significantly abolished with the pre-conditioning with TDF, PTX and Cilo (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg). Interestingly, middle dose of Cilo (10 mg) showed significant improvement in serum level of testosterone, motility of epipdidymal sperm and the percentage of abnormal sperm morphology when compared to CIS+ Cilo 5 mg group. Also, with the increasing dose of Cilo up to 20 mg/kg, a significant increase in testosterone concentration and the sperm indices was witnessed as compared to CIS+ Cilo 10 mg group.
In comparing the effect of Cilo 20 mg/kg with TDF and PTX in CIS-treated group, Cilo 20 mg/kg exhibited a significant elevation in testosterone concentration, sperm count and motility alongside a significant decrease in the percent of abnormal sperm morphology.
3.1. Histopathological Finding of Testicular Tissues
Representative images of H&E stained testicular sections showed active spermatogenesis and normal-size seminiferous tubules in testicular parenchyma of control, TDF, PTX and Cilo 20 mg groups. Each tubule was surrounded by an outer thin layer of connective tissue and lined with spermatogenic cells consisted of primary and secondary spermatocytes, spermatogonia and spermatids. These tubules are separated by interstitial cells in clusters characterized by large and ovoid nuclei (
Figure 1A–D).
On the other hand, the seminiferous tubules of CIS treated group revealed progressive histological abnormalities (
Figure 1E). Sections obtained from testes of CIS group revealed severe disorganized spermatogenic cells, reduced germinal cell layers and interstitial cells of distorted shrunken seminiferous tubules. Histological alterations as pyknotic nuclei and vacuolated cytoplasm were observed in spermatogenic cells. Moreover, spermatogenic cells apoptosis was appeared as deeply eosinophilic bodies with hyperactivity of Sertoli cell.
Contrary, this histological damage in testicular components was markedly improved with all used drugs (
Figure 1F–J). Moreover, CIS+ Cilo 20 mg group exhibited great protection of seminiferous tubules compared to groups treated with lower doses of Cilo or other two drugs. Most of the histopathological lesions seen in testicular tissues of CIS-intoxicated rats were disappeared in rats group protected by high dose of Cilo. Scoring of testes tissue injury in the ten groups was illustrated in
Table 2.
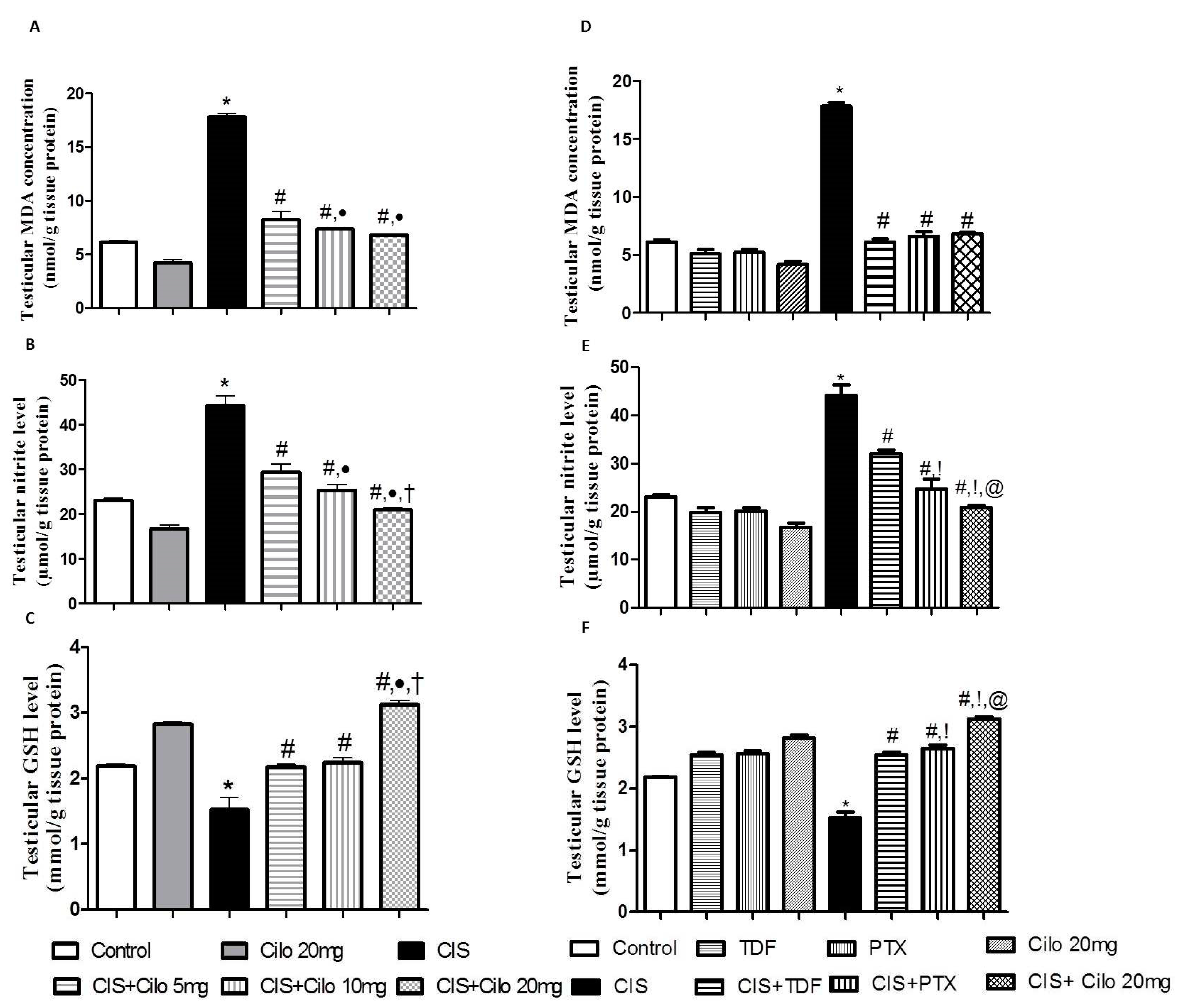
3.1. Effect on Testicular Malondialdehyde, Total Nitrite Content and Reduced Glutathione
Lipid peroxides and total nitrite levels were significantly elevated in testicular homogenates of CIS rats while antioxidant capacity of GSH was significantly attenuated (
Fig. 2 A, B, C).
However, testicular MDA and total nitrite levels were significantly diminished with all examined drugs compared to CIS-intoxicated rats. Noteworthy, the dose of 20 mg/kg Cilo further suppressed testicular total nitrite contents compared to those treated with either 5 or 10 mg/kg Cilo.
In consistent with the previous results, treatment with Cilo significantly increased the content of GSH. Of interest, high dose of Cilo (20 mg/kg) produced a more enhanced response in GSH capacity compared to those treated with lower doses (5 and 10 mg/kg).
Moreover, Cilo 20 mg compared to TDF and PTX had a greater effect on lowering total nitrite contents. This effect went along with the GSH capacity values which showed significant increase in GSH in CIS + Cilo 20 mg group compared to CIS + TDF and CIS + PTX groups.
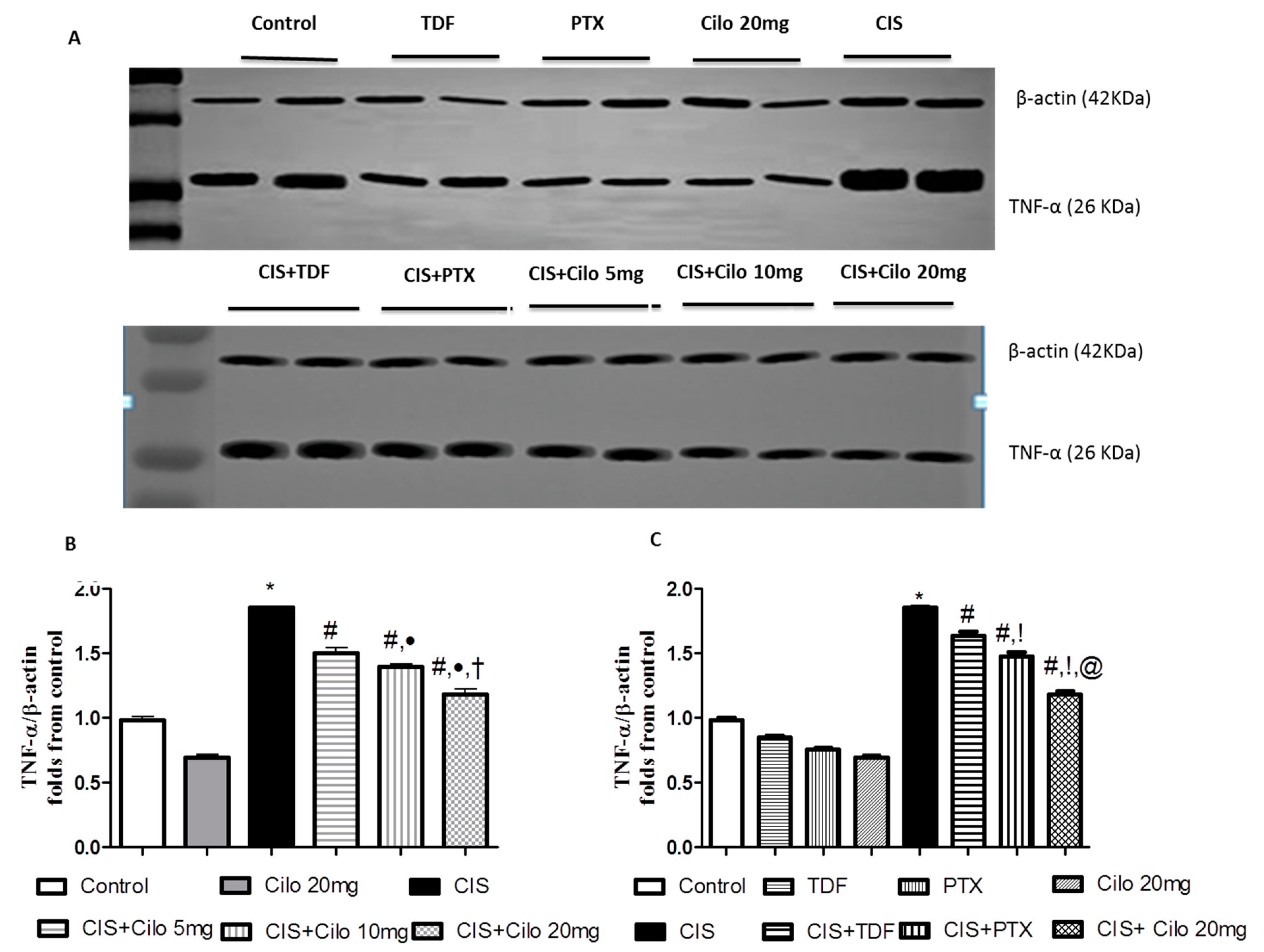
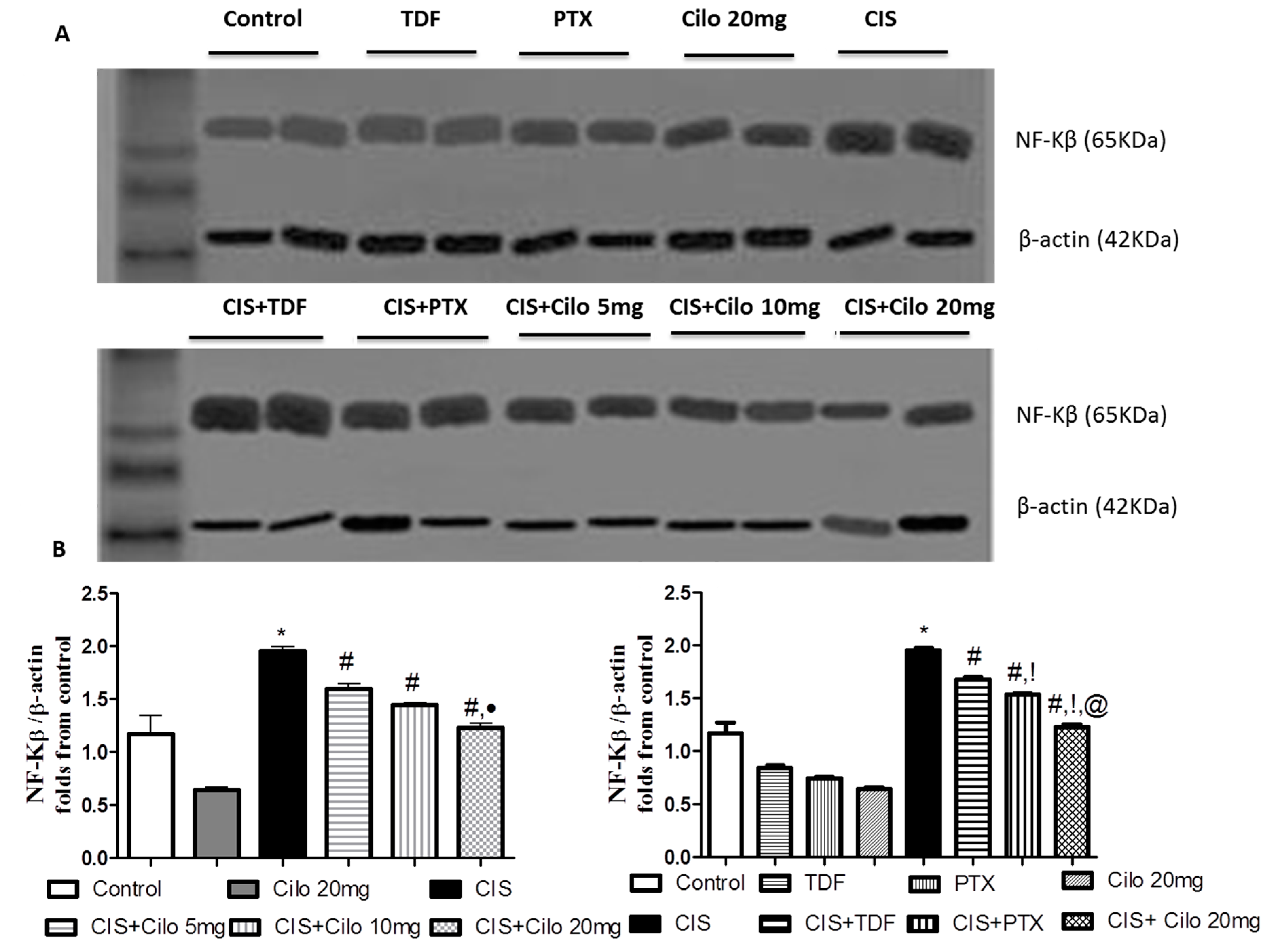
3.1. Effects on Testicular Inflammatory Mediators (TNF-α and NF-κB) Protein Expressions
Pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and NF-κB) protein expressions in testicular tissues were examined by Western blot analysis. As shown in
Figure 3 and
Figure 4, TNF-α and NF-Kβ protein expression in testes were significantly elevated in CIS group compared to control animals. However, different interventions significantly blunted CIS-induced abnormalities in the levels of these cytokines. Moreover, reduction of TNF-α and NF-Kβ expression was more pronounced in CIS rats treated by Cilo 20 mg/kg compared to either CIS+ Cilo 5 mg or CIS+ Cilo 10 mg groups.
In addition, testicular TNF-α and NF-ĸB protein expression were significantly decreased in CIS+ Cilo 20 mg groups when compared with their levels in groups treated with other PDE inhibitors.
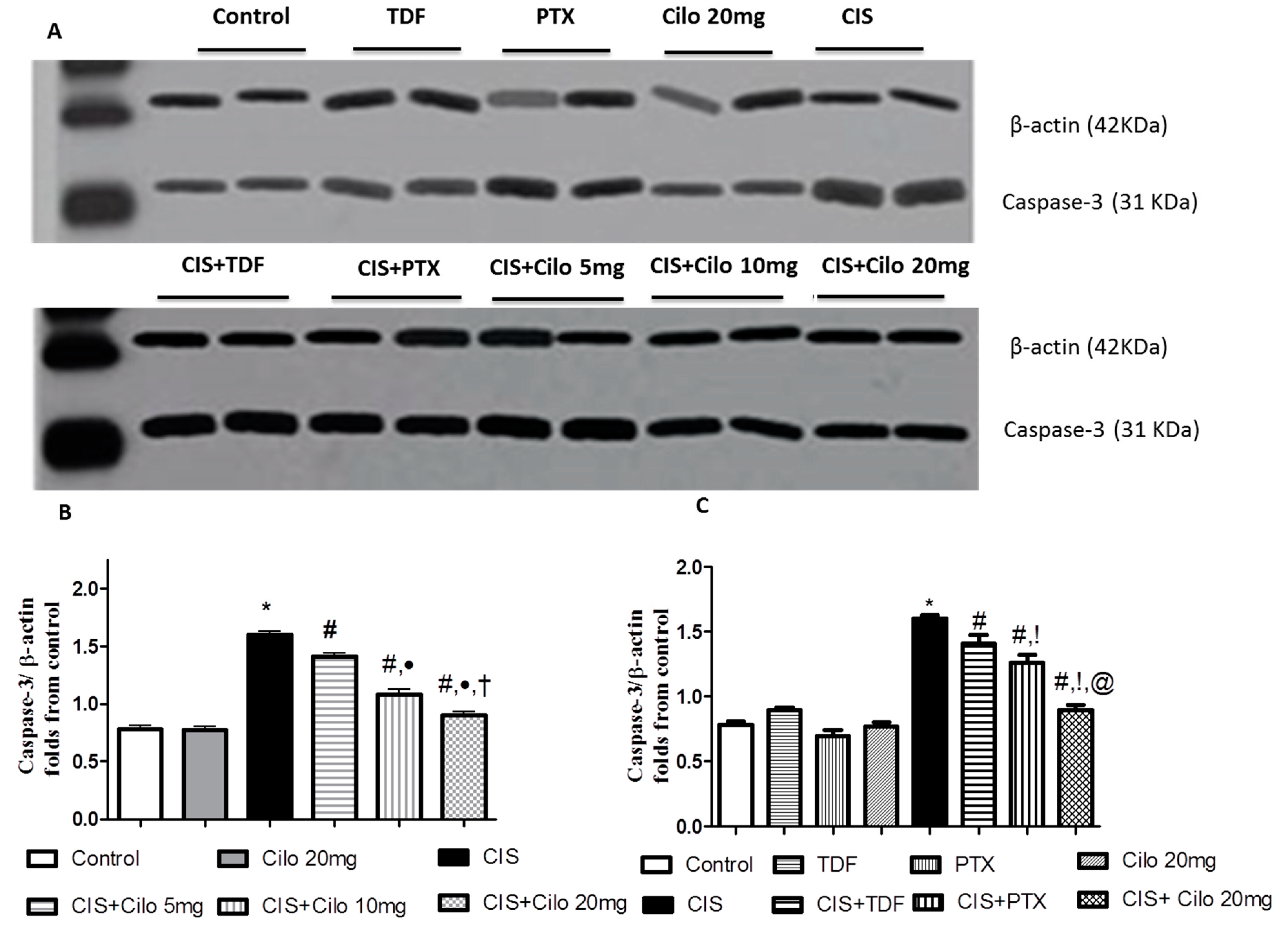
3.1. Effects on Testicular Caspase-3 Protein Expression
Protein expression level of caspase-3, a diagnostic apoptotic marker, was significantly increased in model group. This up-regulation of caspase-3 expression was remarkably counteracted by all groups treated by Cilo in a dose dependent manner and by the other investigated PDE inhibitors, TDF and PTX (
Figure 5).
On comparing the effect of Cilo 20 mg with TDF and PTX on caspase-3 protein expression, it was found that Cilo 20 mg significantly abolished the upregulation of caspase-3 expression caused by CIS relative to CIS+ TDF and CIS+ PTX groups.
4. Discussion
The clinical application of CIS was greatly restricted due to its hazards, particularly testicular toxicity. The current study demonstrated, for the first time, that PDE-3 inhibitor, Cilo, promoted potential protective effect against CIS-induced testicular damage as evident by a marked increase in serum testosterone, sperm motility and count, as well as reduction in the percent of abnormal sperms. Abrogation of oxidative stress along with reduction in NF-κB, TNF-α and caspase-3 expressions might be contributed to Cilo therapeutic effect. Moreover, Cilo afforded a stronger effect on dampening male reproductive toxicity achieved by CIS than that exerted by the other investigated PDE inhibitors, TDF and PTX.
Here, CIS- intoxicated rats exhibited a marked decline in relative testicular weight, a frequent measured indicator of spermatogenesis (Mesbahzadeh, Hassanzadeh-Taheri et al. 2021). Moreover, CIS administration showed a significant low epididymal sperm count, impaired sperm motility and increased sperm morphological abnormality with concomitant decline in testosterone level. The histopathological findings that showed desquamated and disorganized germinal cells, as well as degeneration in germinal cells confirmed deterioration of sperm quality indices in rats administered CIS alone. These observed effects of CIS were consistent with the results of previous studies (Fallahzadeh, Rezaei et al. 2017, Kohsaka, Minagawa et al. 2020, Mesbahzadeh, Hassanzadeh-Taheri et al. 2021, Adelakun, Ogunlade et al. 2022, Kaku, Chiba et al. 2022). On the other hand, pretreatment with TDF, PTX and the three doses of Cilo restored the loss of testicular weight and enhanced number and motility of the epididemal sperm, as well as serum testosterone level compared with CIS group. Also, Cilo- treated groups showed marked improvement in histopathological architecture, in a dose-dependent manner. These results are in parallel with previous studies that reported the ability of Cilo to mitigate testicular dysfunction caused by diabetes and testicular ischemia reperfusion injury (Mohamed, Hafez et al. 2018, Refaie, Ahmed Ibrahim et al. 2021).
The potential of TDF and PTX to ameliorate CIS-induced spermatogenic toxicity was demonstrated in the previous studies (Fallahzadeh, Rezaei et al. 2017, Abdel-Wahab, Alkahtani et al. 2020). Of interest, serum testosterone level, sperm indices and histological alteration were significantly improved in CIS+ Cilo 20 mg group compared to CIS-intoxicated rats treated with other PDE inhibitors. These observations provide insights on the possible effect of Cilo in abrogating testicular dysfunction induced by CIS. Based on these outcomes, we aimed to investigate molecular mechanisms that could partially illustrate the testicular preservative effect of Cilo in CIS setting.
In spite of no exact mechanism explaining CIS-induced cellular damage in testicular tissues, mechanistic studies revealed that oxidative stress remains the hallmark mechanism involved in CIS testicular toxicity (Soni, Kim et al. 2016). It is clearly demonstrated the strong relation between normal spermatozoa function and balanced oxidative status (Heeba and Hamza 2015, Sies 2015). Besides, CIS mitigated testosterone production by ROS-inhibited P450 side-chain cleavage enzyme (García, Acquier et al. 2012). In a harmony with several reports (Dasari and Tchounwou 2014, Adelakun, Ogunlade et al. 2022, Kaku, Chiba et al. 2022), impaired oxidative status in testicular tissues has been presented in the present work by a significant elevation in MDA content, a marker of lipid peroxidation, and total nitrite levels. In case of increased oxidative stress, the polyunsaturated phospholipids of the cell membrane are oxidized generating MDA. Hence, its elevated level indicates increased oxidative stress (Soni, Kim et al. 2016).
Moreover, increased ROS generation caused by CIS exceeded the antioxidant defense capacity which subsequently reduced these antioxidant tools presented as dramatic depletion in GSH level.
Of particular importance, administration of Cilo dampened oxidative stress which was confirmed by significant lower MDA and nitrite levels and higher GSH concentration. This effect was achieved by three different doses of Cilo but the higher dose afforded a more pronounced antioxidant activity which, indirectly, highlights a dose-dependent antioxidant effect of Cilo. These results can be explained in the light of published reports indicating that Cilo treatment significantly attenuated lipid peroxidation and restored GSH capacity in testes in streptozotocin diabetic model (Mohamed, Hafez et al. 2018) and testicular ischemia reperfusion (Refaie, Ahmed Ibrahim et al. 2021). Also, it has been demonstrated that milrinone, another PDE3 inhibitor, significantly attenuated MDA level in testicular torsion/detorsion rat model (Kölükçü, Atılgan et al. 2021).
In agreement with several reports, the antioxidant effect of TDF and PTX has been presented here by a significant depletion in testicular MDA and total nitrite and elevated GSH capacity (Saad, Najjar et al. 2004, Fallahzadeh, Rezaei et al. 2017, Abdel-Wahab, Alkahtani et al. 2020, Dhulqarnain, Takzaree et al. 2021, Kaku, Chiba et al. 2022). Improvement of sperm motility achieved by PTX in infertile patients is mediated by mitigation of oxidative stress (Garg and Kumar 2016). Of particular importance, the inhibitory effect of Cilo at high dose on oxidative stress was more profound relative to TDF or PTX therapy which indirectly highlights that Cilo, the PDE inhibitor, may be an effective regimen for alleviating testicular injury by scavenging free radical.
Additionally, exaggerated ROS generation evokes the inflammatory cascades which are clearly involved in the pathogenesis of CIS spermatoxicity and gonadotoxicity (Hamza, Elwy et al. 2016, Afsar, Razak et al. 2017). In this context, the present study showed that the exposure to CIS resulted in significant elaboration of pro-inflammatory mediators; TNF-α and NF-κB protein in testicular tissue compared to control group. The previous investigations reported that rats treated with CIS caused testicular inflammation which was evident by overexpression of inflammatory mediators as TNF-α, NF-κB and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) (Hamza, Elwy et al. 2016, Heeba, Hamza et al. 2016, H and B 2020, Moradi, Goodarzi et al. 2021).
It is worth mentioning that the elevated total nitrite level could be attributed to TNF-α capability to up-regulate iNOS expression which subsequently increases NO generation (Sherif, Abdel-Aziz et al. 2014). Elevated NO level, in turns, reacts with superoxide anion producing peroxynitrite radical that triggers harmful effects causing testicular toxicity (O’Bryan, Schlatt et al. 2000).
In contrast, treatment with Cilo (5, 10 or 20 mg/kg) was capable of ameliorating up-regulated TNF-α and NF-κB expressions induced by CIS. This result is in accordance with earlier studies which reported the anti-inflammatory properties of Cilo in different experimental models of testicular injury (Mohamed, Hafez et al. 2018, Refaie, Ahmed Ibrahim et al. 2021). Besides, protective effect of Cilo against diclofenac caused renal toxicity (Wadie, Abdel-Razek et al. 2021), high fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver (El-Deen, Heeba et al. 2020) and cyclophosphamide-induced cardiac damage (Elrashidy and Hasan 2021) was partially attributed to its ability to diminish the level of inflammatory markers. Milrinone also dramatically decreased TNF-α level which participated in its ameliorative effect against ischaemia-reperfusion testicular injury (Kölükçü, Atılgan et al. 2021).
Moreover, the inhibitory effect of Cilo on toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling mediated NF-κB activation could explain its anti-inflammatory effects. Cilo also cause direct interruption to NF-κB recruitment to promoters of pro-inflammatory gene which subsequently reduced transcriptional activation of pro-inflammatory gene mediated by TLR (El-Abhar, Abd El Fattah et al. 2018, Sakamoto, Ohashi et al. 2018). The observed anti-inflammatory properties of Cilo may also be attributed to increased cellular levels of cAMP which in turn, suppress production of TNF-α (Zidek 1999). Notably, inflammation was further halted by higher dose of Cilo (20 mg/kg).
Of interest, inhibition of PDE with TDA and PTX exhibited anti-inflammatory properties in CIS-induced male reproductive toxicity which was evident by significant decline in testicular TNF-α and NF-κB protein expression. These findings were in consistent with previous studies. Anti-inflammatory effect of TDF partially explained its ability to alleviate CIS-induced reproductive toxicity (Abdel-Wahab, Alkahtani et al. 2020) and thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in rats (Mansour, Salama et al. 2018). Besides, potent anti-inflammatory properties of PTX were documented in various illness (Mostafa-Hedeab, Al-Kuraishy et al. 2022). PTX decreased TNF-α and NF-κB in cerebral ischemia reperfusion (Dong, Yuan et al. 2018), high fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver (El-Deen, Heeba et al. 2020) and diclofenac-induced acute renal injury (Wadie, Abdel-Razek et al. 2021) models. Importantly, the decline in NF-κB and TNF-α expression was more pronounced in CIS rats treated with Cilo 20mg compared to either TDF or PTX groups.
Oxidative stress with its cascades of increasing expression of inflammatory mediators had been shown to induce cell death in testis of animals exposed to CIS either by necrosis or apoptosis (Amin and Hamza 2006, Hamza, Elwy et al. 2016). In vivo and in vitro studies had demonstrated that imbalance of mitochondrial redox processes caused by CIS led to cell death associated with caspases (Wang, Tang et al. 2018, Liu, Li et al. 2019). As, excess ROS mediates Ca2+ influx which subsequently activates apoptotic processes (Casares, Ramírez-Camacho et al. 2012). Translocation of cytosolic Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax), a pro-apoptotic factor, to the mitochondria and imbalance of the Bax/ B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), an anti-apoptotic factor, ratio induced by CIS result in caspase-3 activation. These events together attribute to cell apoptosis on exposure to CIS (Matsumoto, Nakajima et al. 2016).
In the present study, significant elevation of apoptosis related proteins, caspase 3, was displayed in testes of CIS group. In contrast, different PDE inhibitors protected the rats against CIS-induced testicular apoptosis as supported by significant decline in pro-apoptotic marker protein expression when compared to CIS alone. The anti-apoptotic activity of Cilo was demonstrated in several experimental models as cyclophosphamide-induced ovarian toxicity (Abdel-Aziz, Mohamed et al. 2020), testicular ischaemia/reperfusion (Refaie, Ahmed Ibrahim et al. 2021) and cochleo-vestibular dysfunction induced by CIS (Tian, Kim et al. 2013). This property of Cilo could be attributed to activating cAMP-dependent protein kinase. The anti-apoptotic impact of TDF and PTX was also observed in previous studies (Koka and Kukreja 2010, Abdel-Wahab, Alkahtani et al. 2020, Akbari, Reisi et al. 2020, Dhulqarnain, Takzaree et al. 2021). Interestingly, the higher dose of Cilo (20 mg/kg) exhibited further attenuation on testicular caspase-3 expression compared to lower doses (5 and 10 mg/kg) of Cilo and groups treated with TDF and PTX.
To that end, we collectively propose that treatment with PDE3 inhibitor, Cilo, may provide a marked protection over the use of TDF or PTX against CIS-induced testicular injury. The protective effect of Cilo can be possibly attributed to the restoration of unbalanced oxidative status alongside anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects.
5. Conclusion
The findings of the present study suggest that Cilo has a positive impact on male reproductive dysfunction in CIS intoxicated rats in a dose dependent manner. The protective effect of Cilo is possibly explained by scavenging free radicals. We also throw the light on the significance of molecular mechanisms involved in the protective role of this drug via targeting inflammatory and cell death signaling pathway through reduction of TNF-α, NF-κB and caspase-3 expressions. This invites clinical studies to evaluate the protective role of Cilo in cancerous patients treated with CIS to prevent the incidence of reproductive toxicity.
Ethical Approval
All animals’ procedures were performed in accordance with Animal Care Community, Minia University, Egypt (Permit Number: 230103) in strict accordance with the international policies (Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the US National Institute of Health; NIH Publication No. 85-23, revised 1996).
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Author Contributions
G. H. H.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing, Re-viewing and editing. H. A. H.: Methodology, Data analysis, Resources, Writing original draft. M. E. Z.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data analysis, Resources, E. M. O.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing, Re-viewing and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
All data and materials are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
- Abdel-Aziz, A. M., A. S. M. Mohamed, O. Abdelazem, A. M. M. Okasha and M. Y. Kamel (2020). “Cilostazol protects against cyclophosphamide-induced ovarian toxicity in female rats: role of cAMP and HO-1.” Toxicology Mechanisms and Methods 30(7): 526-535. [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, R., M. Fathy, H. A. Anwar, M. Naseem, T. Dandekar and E. M. Othman (2022). “Cisplatin-Induced Reproductive Toxicity and Oxidative Stress: Ameliorative Effect of Kinetin.” Antioxidants 11(5): 863. [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahab, B. A., S. A. Alkahtani and E. A. M. Elagab (2020). “Tadalafil alleviates cisplatin-induced reproductive toxicity through the activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and the inhibition of oxidative stress and apoptosis in male rats.” Reproductive Toxicology 96: 165-174.
- Adelakun, S. A., B. Ogunlade, O. P. Fidelis and O. D. Omotoso (2022). “Protective effect of nutritional supplementation of zinc-sulfate against cisplatin-induced spermatogonial and testicular dysfunctions in adult male Sprague-Dawley rats.” Endocrine and Metabolic Science 6: 100116. [CrossRef]
- Afsar, T., S. Razak, M. R. Khan and A. Almajwal (2017). “Acacia hydaspica ethyl acetate extract protects against cisplatin-induced DNA damage, oxidative stress and testicular injuries in adult male rats.” BMC Cancer 17(1): 883.
- Akbari, Z., P. Reisi, A. Torkaman-Boutorabi and M. Farahmandfar (2020). “Effect of Pentoxifylline on Apoptotic-Related Gene Expression Profile, Learning and Memory Impairment Induced by Systemic Lipopolysaccharide Administration in the Rat Hippocampus.” Int J Prev Med 11: 151.
- Amin, A. and A. A. Hamza (2006). “Effects of Roselle and Ginger on cisplatin-induced reproductive toxicity in rats.” Asian J Androl 8(5): 607-612. [CrossRef]
- Asal, N. J. and K. A. Wojciak (2017). “Effect of cilostazol in treating diabetes-associated microvascular complications.” Endocrine 56(2): 240-244. [CrossRef]
- Buege, J. A. and S. D. Aust (1978). [30] Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods in Enzymology. S. Fleischer and L. Packer, Academic Press. 52: 302-310.
- Calamera, G., L. R. Moltzau, F. O. Levy and K. W. Andressen (2022). “Phosphodiesterases and Compartmentation of cAMP and cGMP Signaling in Regulation of Cardiac Contractility in Normal and Failing Hearts.” Int J Mol Sci 23(4). [CrossRef]
- Casares, C., R. Ramírez-Camacho, A. Trinidad, A. Roldán, E. Jorge and J. R. García-Berrocal (2012). “Reactive oxygen species in apoptosis induced by cisplatin: review of physiopathological mechanisms in animal models.” Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269(12): 2455-2459.
- Dasari, S. and P. B. Tchounwou (2014). “Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action.” Eur J Pharmacol 740: 364-378. [CrossRef]
- Dhulqarnain, A. O., N. Takzaree, G. Hassanzadeh, H. Tooli, M. Malekzadeh, N. Khanmohammadi, M. Yaghobinejad, S. Solhjoo and T. Rastegar (2021). “Pentoxifylline improves the survival of spermatogenic cells via oxidative stress suppression and upregulation of PI3K/AKT pathway in mouse model of testicular torsion-detorsion.” Heliyon 7(4): e06868. [CrossRef]
- Dong, J., X. Yuan and W. Xie (2018). “Pentoxifylline exerts anti-inflammatory effects on cerebral ischemia reperfusion-induced injury in a rat model via the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.” Mol Med Rep 17(1): 1141-1147. [CrossRef]
- El-Abhar, H., M. A. Abd El Fattah, W. Wadie and D. M. El-Tanbouly (2018). “Cilostazol disrupts TLR-4, Akt/GSK-3β/CREB, and IL-6/JAK-2/STAT-3/SOCS-3 crosstalk in a rat model of Huntington’s disease.” PLOS ONE 13(9): e0203837.
- El-Deen, R. M., G. H. Heeba, R. G. Abdel-Latif and M. M. A. Khalifa (2020). “Comparative effectiveness of phosphodiesterase 3, 4, and 5 inhibitors in amelioration of high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver in rats.” Fundam Clin Pharmacol 34(3): 353-364.
- Elrashidy, R. A. and R. A. Hasan (2021). “Cilostazol preconditioning alleviates cyclophosphamide-induced cardiotoxicity in male rats: Mechanistic insights into SIRT1 signaling pathway.” Life Sci 266: 118822. [CrossRef]
- Fallahzadeh, A. R., Z. Rezaei, H. R. Rahimi, M. J. Barmak, H. Sadeghi, S. Mehrabi, S. M. Rabani, I. R. Kashani, V. Barati and R. Mahmoudi (2017). “Evaluation of the Effect of Pentoxifylline on Cisplatin-Induced Testicular Toxicity in Rats.” Toxicol Res 33(3): 255-263. [CrossRef]
- García, M. M., A. Acquier, G. Suarez, N. V. Gomez, A. Gorostizaga, C. F. Mendez and C. Paz (2012). “Cisplatin inhibits testosterone synthesis by a mechanism that includes the action of reactive oxygen species (ROS) at the level of P450scc.” Chem Biol Interact 199(3): 185-191. [CrossRef]
- Garg, H. and R. Kumar (2016). “An update on the role of medical treatment including antioxidant therapy in varicocele.” Asian Journal of Andrology 18(2): 222-228. [CrossRef]
- Golkowski, M., M. Shimizu-Albergine, H. W. Suh, J. A. Beavo and S. E. Ong (2016). “Studying mechanisms of cAMP and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase signaling in Leydig cell function with phosphoproteomics.” Cell Signal 28(7): 764-778. [CrossRef]
- H, A. A. A. and G. E. B (2020). “Cisplatin induced testicular damage through mitochondria mediated apoptosis, inflammation and oxidative stress in rats: impact of resveratrol.” Endocr J 67(9): 969-980.
- Hafez, H. M., M. A. Ibrahim, M. Z. Zedan, M. Hassan and H. Hassanein (2019). “Nephroprotective effect of cilostazol and verapamil against thioacetamide-induced toxicity in rats may involve Nrf2/HO-1/NQO-1 signaling pathway.” Toxicol Mech Methods 29(2): 146-152.
- Hamza, A. A., H. M. Elwy and A. M. Badawi (2016). “Fenugreek seed extract attenuates cisplatin-induced testicular damage in Wistar rats.” Andrologia 48(2): 211-221. [CrossRef]
- Hansson, V., B. S. Skålhegg and K. Taskén (2000). “Cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) in testicular cells. Cell specific expression, differential regulation and targeting of subunits of PKA.” J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 73(1-2): 81-92.
- He, P., H. Kawamura, M. Takemoto, Y. Maezawa, T. Ishikawa, R. Ishibashi, K. Sakamoto, M. Shoji, A. Hattori, M. Yamaga, S. Ide, K. Ide, A. Hayashi, H. Tokuyama, K. Kobayashi and K. Yokote (2017). “Combination of cilostazol and probucol protected podocytes from lipopolysaccharide-induced injury by both anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative mechanisms.” J Nephrol 30(4): 531-541. [CrossRef]
- Heeba, G. H. and A. A. Hamza (2015). “Rosuvastatin ameliorates diabetes-induced reproductive damage via suppression of oxidative stress, inflammatory and apoptotic pathways in male rats.” Life Sci 141: 13-19.
- Heeba, G. H., A. A. Hamza and S. O. Hassanin (2016). “Induction of heme oxygenase-1 with hemin alleviates cisplatin-induced reproductive toxicity in male rats and enhances its cytotoxicity in prostate cancer cell line.” Toxicology Letters 264: 38-50. [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, H., K. Toyoda, K. Omae, N. Ishida, S. Uchiyama, K. Kimura, N. Sakai, Y. Okada, K. Tanaka, H. Origasa, H. Naritomi, K. Houkin, K. Yamaguchi, M. Isobe, K. Minematsu, M. Matsumoto, T. Tominaga, H. Tomimoto, Y. Terayama, S. Yasuda and T. Yamaguchi (2021). “Dual Antiplatelet Therapy Using Cilostazol With Aspirin or Clopidogrel: Subanalysis of the CSPS.com Trial.” Stroke 52(11): 3430-3439. [CrossRef]
- Kaku, Y., K. Chiba, K. Sato, A. Onishi, T. Ishida, K. Okada and M. Fujisawa (2022). “Protective effects of tadalafil against cisplatin-induced spermatogenic dysfunction.” Biochem Biophys Res Commun 603: 123-129. [CrossRef]
- Kenjale, R., R. Shah and S. Sathaye (2008). “Effects of Chlorophytum borivilianum on sexual behaviour and sperm count in male rats.” Phytotherapy research : PTR 22(6): 796-801. [CrossRef]
- Kohsaka, T., I. Minagawa, M. Morimoto, T. Yoshida, T. Sasanami, Y. Yoneda, N. Ikegaya and H. Sasada (2020). “Efficacy of relaxin for cisplatin-induced testicular dysfunction and epididymal spermatotoxicity.” Basic and clinical andrology 30: 3-3. [CrossRef]
- Koka, S. and R. C. Kukreja (2010). “Attenuation of Doxorubicin-induced Cardiotoxicity by Tadalafil: A Long Acting Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitor.” Mol Cell Pharmacol 2(5): 173-178.
- Kölükçü, E., D. Atılgan, N. Uluocak, F. A. Deresoy, M. Katar and V. Unsal (2021). “Milrinone ameliorates ischaemia-reperfusion injury in experimental testicular torsion/detorsion rat model.” Andrologia 53(8): e14128. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z., C. Li, N. Kang, H. Malhi, V. H. Shah and J. L. Maiers (2019). “Transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) cross-talk with the unfolded protein response is critical for hepatic stellate cell activation.” J Biol Chem 294(9): 3137-3151. [CrossRef]
- Mansour, H. M., A. A. A. Salama, R. M. Abdel-Salam, N. A. Ahmed, N. N. Yassen and H. F. Zaki (2018). “The anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects of tadalafil in thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in rats.” Can J Physiol Pharmacol 96(12): 1308-1317. [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M., W. Nakajima, M. Seike, A. Gemma and N. Tanaka (2016). “Cisplatin-induced apoptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer cells is dependent on Bax- and Bak-induction pathway and synergistically activated by BH3-mimetic ABT-263 in p53 wild-type and mutant cells.” Biochem Biophys Res Commun 473(2): 490-496. [CrossRef]
- Mesbahzadeh, B., M. Hassanzadeh-Taheri, M.-s. Aliparast, P. Baniasadi and M. Hosseini (2021). “The protective effect of crocin on cisplatin-induced testicular impairment in rats.” BMC Urology 21(1): 117. [CrossRef]
- Mesbahzadeh, B., M. Hassanzadeh-Taheri, M. S. Aliparast, P. Baniasadi and M. Hosseini (2021). “The protective effect of crocin on cisplatin-induced testicular impairment in rats.” BMC Urol 21(1): 117. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M., H. Hafez, N. Zenhom and H. Mohammed (2018). “Cilostazol alleviates streptozotocin-induced testicular injury in rats via PI3K/Akt pathway.” Life Sciences 198. [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M., N. Goodarzi, A. Faramarzi, H. Cheraghi, A. H. Hashemian and C. Jalili (2021). “Melatonin protects rats testes against bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin-induced toxicity via mitigating nitro-oxidative stress and apoptosis.” Biomed Pharmacother 138: 111481. [CrossRef]
- Mostafa-Hedeab, G., H. M. Al-Kuraishy, A. I. Al-Gareeb, P. Jeandet, H. M. Saad and G. E. Batiha (2022). “A raising dawn of pentoxifylline in management of inflammatory disorders in Covid-19.” Inflammopharmacology 30(3): 799-809. [CrossRef]
- O’Bryan, M. K., S. Schlatt, O. Gerdprasert, D. J. Phillips, D. M. de Kretser and M. P. Hedger (2000). “Inducible nitric oxide synthase in the rat testis: evidence for potential roles in both normal function and inflammation-mediated infertility.” Biol Reprod 63(5): 1285-1293. [CrossRef]
- Özgür, B. C., O. Telli, C. N. Yuceturk, H. Sarici, E. Ozer, H. Surer, A. S. Kılınc, S. Hucumenoglu and M. Eroglu (2014). “The effect of sildenafil and udenafil on testicular damage following ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.” J Urol 192(4): 1272-1277.
- Real, J., M. C. Serna, M. Giner-Soriano, R. Forés, G. Pera, E. Ribes, M. Alzamora, J. R. Marsal, A. Heras and R. Morros (2018). “Safety of cilostazol in peripheral artery disease: a cohort from a primary healthcare electronic database.” BMC Cardiovasc Disord 18(1): 85. [CrossRef]
- Refaie, M. M. M., R. Ahmed Ibrahim and S. Shehata (2021). “Dose dependent effect of cilostazol in induced testicular ischemia reperfusion via modulation of HIF/VEGF and cAMP/SIRT1 pathways.” Int Immunopharmacol 101(Pt A): 108197. [CrossRef]
- Rezvanfar, M. A., M. A. Rezvanfar, A. R. Shahverdi, A. Ahmadi, M. Baeeri, A. Mohammadirad and M. Abdollahi (2013). “Protection of cisplatin-induced spermatotoxicity, DNA damage and chromatin abnormality by selenium nano-particles.” Toxicology and applied pharmacology 266(3): 356-365. [CrossRef]
- Saad, S. Y., T. A. Najjar and M. Alashari (2004). “Role of non-selective adenosine receptor blockade and phosphodiesterase inhibition in cisplatin-induced nephrogonadal toxicity in rats.” Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 31(12): 862-867. [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T., W. Ohashi, K. Tomita, K. Hattori, N. Matsuda and Y. Hattori (2018). “Anti-inflammatory properties of cilostazol: Its interruption of DNA binding activity of NF-κB from the Toll-like receptor signaling pathways.” Int Immunopharmacol 62: 120-131.
- Sastry, K., R. Moudgal, J. Mohan, d. j. s. Tyagi and G. Rao (2002). “Spectrophotometric Determination of Serum Nitrite and Nitrate by Copper-Cadmium Alloy.” Analytical biochemistry 306: 79-82. [CrossRef]
- Sherif, I. O., A. Abdel-Aziz and O. M. Sarhan (2014). “Cisplatin-induced testicular toxicity in rats: the protective effect of arjunolic acid.” J Biochem Mol Toxicol 28(11): 515-521. [CrossRef]
- Sies, H. (2015). “Oxidative stress: a concept in redox biology and medicine.” Redox Biol 4: 180-183. [CrossRef]
- Soni, K. K., H. K. Kim, B. R. Choi, K. K. Karna, J. H. You, J. S. Cha, Y. S. Shin, S. W. Lee, C. Y. Kim and J. K. Park (2016). “Dose-dependent effects of cisplatin on the severity of testicular injury in Sprague Dawley rats: reactive oxygen species and endoplasmic reticulum stress.” Drug Des Devel Ther 10: 3959-3968. [CrossRef]
- Suvarna, S. K. L. C. B. J. D. (2013). Bancroft’s theory and practice of histological techniques. [Oxford], Churchill Livingstone Elsevier.
- Tian, C. J., Y. J. Kim, S. W. Kim, H. J. Lim, Y. S. Kim and Y. H. Choung (2013). “A combination of cilostazol and Ginkgo biloba extract protects against cisplatin-induced Cochleo-vestibular dysfunction by inhibiting the mitochondrial apoptotic and ERK pathways.” Cell Death Dis 4(2): e509. [CrossRef]
- Tuglu, D., E. Yuvanc, E. Yilmaz, I. Y. Gencay, P. Atasoy, U. Kisa and E. Batislam (2015). “The antioxidant effect of dexmedetomidine on testicular ischemia-reperfusion injury.” Acta Cir Bras 30(6): 414-421. [CrossRef]
- Volarevic, V., B. Djokovic, M. G. Jankovic, C. R. Harrell, C. Fellabaum, V. Djonov and N. Arsenijevic (2019). “Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity: a balance on the knife edge between renoprotection and tumor toxicity.” J Biomed Sci 26(1): 25. [CrossRef]
- Wadie, W., N. S. Abdel-Razek and H. A. Salem (2021). “Phosphodiesterase (1, 3 & 5) inhibitors attenuate diclofenac-induced acute kidney toxicity in rats.” Life Sci 277: 119506. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F. Y., X. M. Tang, X. Wang, K. B. Huang, H. W. Feng, Z. F. Chen, Y. N. Liu and H. Liang (2018). “Mitochondria-targeted platinum(II) complexes induce apoptosis-dependent autophagic cell death mediated by ER-stress in A549 cancer cells.” Eur J Med Chem 155: 639-650. [CrossRef]
- Yao, C., G. Li, Y. Qian, M. Cai, H. Yin, L. Xiao, W. Tang, F. Guo and B. Shi (2016). “Protection of Pentoxifylline against Testis Injury Induced by Intermittent Hypobaric Hypoxia.” Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016: 3406802. [CrossRef]
- Zidek, Z. (1999). “Adenosine - cyclic AMP pathways and cytokine expression.” Eur Cytokine Netw 10(3): 319-328.
Figure 1.
Effect of cilostazol (5, 10 or 20 mg/kg), tadalafil (5 mg/kg) and pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) on testicular tissues stained with hematoxylin and eosin of CIS-treated rats. Photomicrograph of testis from control, TDF, PTX and Cilo 20 mg groups showing active spermatogenesis in normal-size seminiferous tubules with thin basement membranes (arrow, A1, B1, C1& D1, X200) and intact interstitial cells in-between (arrow, A2, B2, C2& D2 X400). Testicular tissues of CIS-treated rats presenting disorganized spermatogenic cells within distorted shrunken seminiferous tubules (arrow, E1, X200) and reduced germinal cell layers along with hyperactivity of Sertoli cells (arrow, E2, X400). Photomicrograph of testis obtained from CIS+TDF group showing partial reduction of seminiferous tubules size with depletion of germinal cells (arrow, F1, x200) and nuclear pyknosis of spermatogenic cells (arrow, F2, x400). Testicular tissue from CIS+PTX group represent eosinophilic oedematous area in-between seminiferous tubules with reduction of interstitial cells numbers (arrow, G1, x200) and germinal cells degeneration with pyknotic nuclei (arrow, G2, x400). Testis tissue micrographs of CIS+ Cilo 5 mg group exhibiting mild disorganization of spermatogenic cells with empty tubules from spermatids (arrow, H1, x200) and oedema in-between seminiferous tubules with attenuated interstitial cells number (arrow, H2, x400). Testis tissue of CIS+ Cilo 10 mg group represent reduction in size of seminiferous tubules with widened interstitium space (arrow, I1, X200) and pyknosis of germinal cells and depletion of interstitial cells (arrow, I2, X400). CIS+Cilo 20 mg group showing improvement in histological finding with regular arrangement of germinal cells within the seminiferous tubules (arrow, J1, X200) and normal tubular lumen contained spermatids (arrow, J2, X400). CIS: Cisplatin, TDF: Tadalafil, PTX: Pentoxifylline, Cilo: Cilostazol.
Figure 1.
Effect of cilostazol (5, 10 or 20 mg/kg), tadalafil (5 mg/kg) and pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) on testicular tissues stained with hematoxylin and eosin of CIS-treated rats. Photomicrograph of testis from control, TDF, PTX and Cilo 20 mg groups showing active spermatogenesis in normal-size seminiferous tubules with thin basement membranes (arrow, A1, B1, C1& D1, X200) and intact interstitial cells in-between (arrow, A2, B2, C2& D2 X400). Testicular tissues of CIS-treated rats presenting disorganized spermatogenic cells within distorted shrunken seminiferous tubules (arrow, E1, X200) and reduced germinal cell layers along with hyperactivity of Sertoli cells (arrow, E2, X400). Photomicrograph of testis obtained from CIS+TDF group showing partial reduction of seminiferous tubules size with depletion of germinal cells (arrow, F1, x200) and nuclear pyknosis of spermatogenic cells (arrow, F2, x400). Testicular tissue from CIS+PTX group represent eosinophilic oedematous area in-between seminiferous tubules with reduction of interstitial cells numbers (arrow, G1, x200) and germinal cells degeneration with pyknotic nuclei (arrow, G2, x400). Testis tissue micrographs of CIS+ Cilo 5 mg group exhibiting mild disorganization of spermatogenic cells with empty tubules from spermatids (arrow, H1, x200) and oedema in-between seminiferous tubules with attenuated interstitial cells number (arrow, H2, x400). Testis tissue of CIS+ Cilo 10 mg group represent reduction in size of seminiferous tubules with widened interstitium space (arrow, I1, X200) and pyknosis of germinal cells and depletion of interstitial cells (arrow, I2, X400). CIS+Cilo 20 mg group showing improvement in histological finding with regular arrangement of germinal cells within the seminiferous tubules (arrow, J1, X200) and normal tubular lumen contained spermatids (arrow, J2, X400). CIS: Cisplatin, TDF: Tadalafil, PTX: Pentoxifylline, Cilo: Cilostazol.
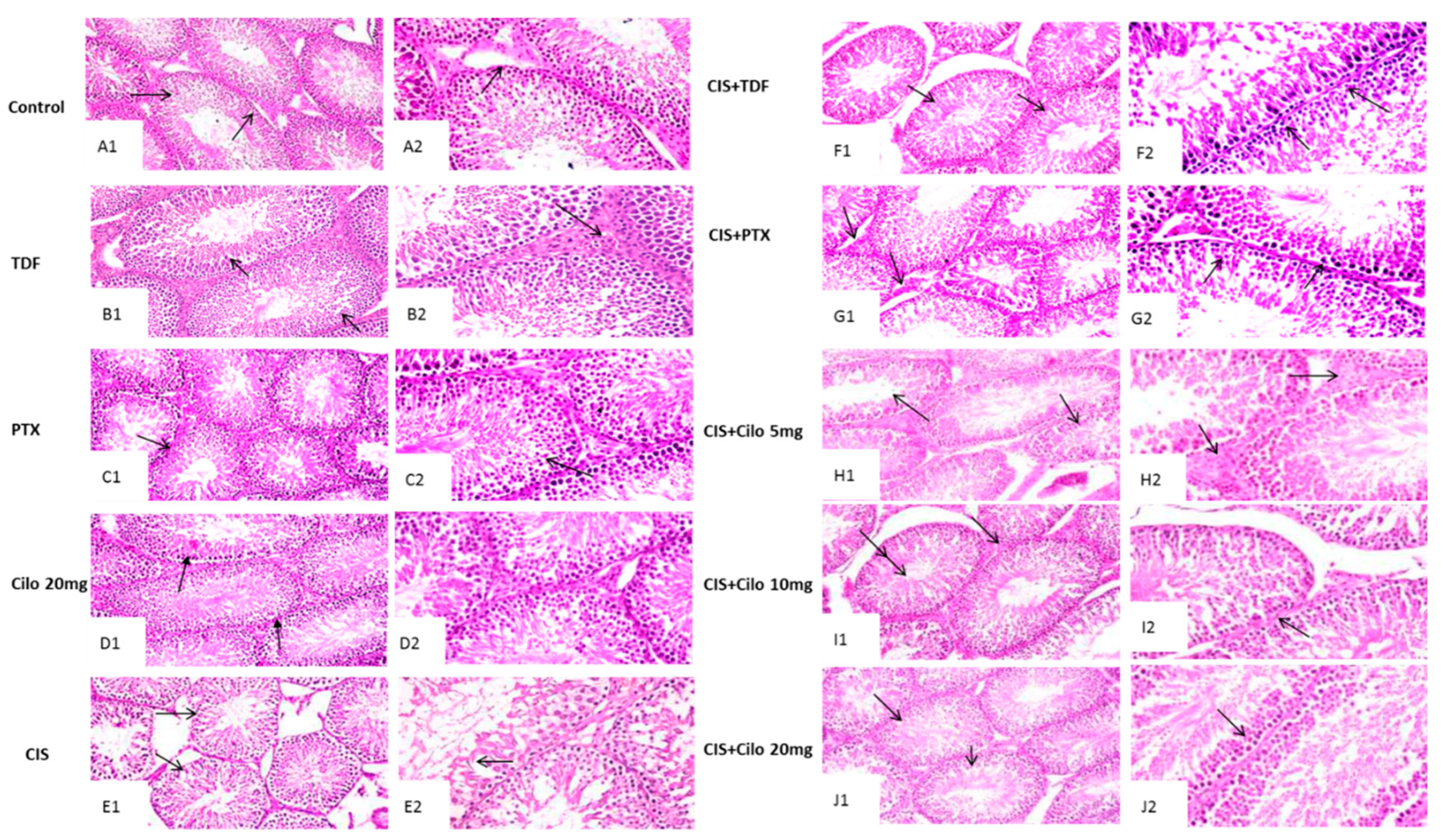
Figure 2.
Effect of cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg) on oxidative stress indicators of CIS-induced testicular dysfunction rat model accompanied by comparison between the levels of oxidative stress indicators in rat testes of groups treated with tadalafil (5 mg/kg), pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) and cilostazol (20 mg/kg). (A) testicular malondialdehyde, (B) total nitrite level, (C) reduced glutathione levels in rats treated with different doses of cilostazol (D) testicular malondialdehyde, (E) total nitrite level, (F) reduced glutathione levels of various phosphodieterase inhibitors groups. Data are represented as means ± S.E.M of 6 rats per group. *, #, ●, †,!, @ are significant (P˂0.05) difference from control, CIS group, CIS+ Cilo 5mg group, CIS+ Cilo 10mg, CIS+ TDF and CIS+ PTX group respectively. CIS: Cisplatin, TDF: Tadalafil, PTX: Pentoxifylline, Cilo: Cilostazol.
Figure 2.
Effect of cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg) on oxidative stress indicators of CIS-induced testicular dysfunction rat model accompanied by comparison between the levels of oxidative stress indicators in rat testes of groups treated with tadalafil (5 mg/kg), pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) and cilostazol (20 mg/kg). (A) testicular malondialdehyde, (B) total nitrite level, (C) reduced glutathione levels in rats treated with different doses of cilostazol (D) testicular malondialdehyde, (E) total nitrite level, (F) reduced glutathione levels of various phosphodieterase inhibitors groups. Data are represented as means ± S.E.M of 6 rats per group. *, #, ●, †,!, @ are significant (P˂0.05) difference from control, CIS group, CIS+ Cilo 5mg group, CIS+ Cilo 10mg, CIS+ TDF and CIS+ PTX group respectively. CIS: Cisplatin, TDF: Tadalafil, PTX: Pentoxifylline, Cilo: Cilostazol.
Figure 3.
Representative Western blots showing the effect of cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg), tadalafil (5 mg/kg) and pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) on TNF-α protein expression in testicular tissues of CIS-treated rats. (A) Representative Western blots showing target protein bands from each group. (B) The quantified densitometric analysis of testicular TNF-α protein expression in CIS groups treated with cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg). (C) Comparison between the levels of TNF-α in rat testes of CIS groups treated with tadalafil (5 mg/kg), pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) and cilostazol (20 mg/kg). Values for each bar represent the means ± S.E.M normalized to β-actin and are expressed as folds of the control, *, #, ●, †,!, @ are significant (P˂0.05) difference from control, CIS group, CIS+ Cilo 5mg group, CIS+ Cilo 10mg, CIS+ TDF and CIS+ PTX group respectively. TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha, CIS: Cisplatin, TDF: Tadalafil, PTX: Pentoxifylline, Cilo: Cilostazol.
Figure 3.
Representative Western blots showing the effect of cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg), tadalafil (5 mg/kg) and pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) on TNF-α protein expression in testicular tissues of CIS-treated rats. (A) Representative Western blots showing target protein bands from each group. (B) The quantified densitometric analysis of testicular TNF-α protein expression in CIS groups treated with cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg). (C) Comparison between the levels of TNF-α in rat testes of CIS groups treated with tadalafil (5 mg/kg), pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) and cilostazol (20 mg/kg). Values for each bar represent the means ± S.E.M normalized to β-actin and are expressed as folds of the control, *, #, ●, †,!, @ are significant (P˂0.05) difference from control, CIS group, CIS+ Cilo 5mg group, CIS+ Cilo 10mg, CIS+ TDF and CIS+ PTX group respectively. TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha, CIS: Cisplatin, TDF: Tadalafil, PTX: Pentoxifylline, Cilo: Cilostazol.
Figure 4.
Representative Western blots showing the effect of cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg), tadalafil (5 mg/kg) and pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) on NF-κB protein expression in testicular tissues of CIS-treated rats. (A) Representative Western blots showing target protein bands from each group. (B) The quantified densitometric analysis of testicular NF-κB protein expression in CIS groups treated with cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg). (C) Comparison between the levels of NF-κB in rat testes of groups treated with tadalafil (5 mg/kg), pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) and cilostazol (20 mg/kg). Values for each bar represent the means ± S.E.M normalized to β-actin and are expressed as folds of the control, *, #, ●, †,!, @ are significant (P˂0.05) difference from control, CIS group, CIS+ Cilo 5mg group, CIS+ Cilo 10mg, CIS+ TDF and CIS+ PTX group respectively. NF-κB: nuclear factor- kabba B, CIS: Cisplatin, TDF: Tadalafil, PTX: Pentoxifylline, Cilo: Cilostazol.
Figure 4.
Representative Western blots showing the effect of cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg), tadalafil (5 mg/kg) and pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) on NF-κB protein expression in testicular tissues of CIS-treated rats. (A) Representative Western blots showing target protein bands from each group. (B) The quantified densitometric analysis of testicular NF-κB protein expression in CIS groups treated with cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg). (C) Comparison between the levels of NF-κB in rat testes of groups treated with tadalafil (5 mg/kg), pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) and cilostazol (20 mg/kg). Values for each bar represent the means ± S.E.M normalized to β-actin and are expressed as folds of the control, *, #, ●, †,!, @ are significant (P˂0.05) difference from control, CIS group, CIS+ Cilo 5mg group, CIS+ Cilo 10mg, CIS+ TDF and CIS+ PTX group respectively. NF-κB: nuclear factor- kabba B, CIS: Cisplatin, TDF: Tadalafil, PTX: Pentoxifylline, Cilo: Cilostazol.
Figure 5.
Representative Western blots showing the effect of cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg), tadalafil (5 mg/kg) and pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) on Caspase-3 protein expression in testicular tissues of CIS-treated rats. A: Representative Western blots showing target protein bands from each group. B: The quantified densitometric analysis of testicular Caspase-3 protein expression in CIS groups treated with cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg). C: Comparison between the levels of Caspase-3 in rat testes of groups treated with tadalafil (5 mg/kg), pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) and cilostazol (20 mg/kg). Values for each bar represent the means ± S.E.M normalized to β-actin and are expressed as folds of the control, *, #, ●, †,!, @ are significant (P˂0.05) difference from control, CIS group, CIS+ Cilo 5mg group, CIS+ Cilo 10mg, CIS+ TDF and CIS+ PTX group respectively. CIS: Cisplatin, TDF: Tadalafil, PTX: Pentoxifylline, Cilo: Cilostazol.
Figure 5.
Representative Western blots showing the effect of cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg), tadalafil (5 mg/kg) and pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) on Caspase-3 protein expression in testicular tissues of CIS-treated rats. A: Representative Western blots showing target protein bands from each group. B: The quantified densitometric analysis of testicular Caspase-3 protein expression in CIS groups treated with cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg). C: Comparison between the levels of Caspase-3 in rat testes of groups treated with tadalafil (5 mg/kg), pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) and cilostazol (20 mg/kg). Values for each bar represent the means ± S.E.M normalized to β-actin and are expressed as folds of the control, *, #, ●, †,!, @ are significant (P˂0.05) difference from control, CIS group, CIS+ Cilo 5mg group, CIS+ Cilo 10mg, CIS+ TDF and CIS+ PTX group respectively. CIS: Cisplatin, TDF: Tadalafil, PTX: Pentoxifylline, Cilo: Cilostazol.
Table 1.
Effect of cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg), tadalafil (5 mg/kg) and pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) on CIS-induced changes in relative testicular weight, testosterone concentration and sperm quality indices.
Table 1.
Effect of cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg), tadalafil (5 mg/kg) and pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) on CIS-induced changes in relative testicular weight, testosterone concentration and sperm quality indices.
| Abnormal sperm morphology (%) |
Sperm motility
(%) |
Sperm Count
(×106/mm3) |
Serum
testosterone
level
(ng/ml) |
Relative testicular weight |
Groups
(dose:mg/kg) |
| 12.67 ±1.52 |
72.67 ± 1.53 |
38.50 ± 0.71 |
2.49±0.059 |
0.69 ±0.044 |
Control |
| 14.00 ±1.00 |
68.00 ±1.41 |
38.00 ±1.00 |
2.58±0.031 |
0.63 ±0.027 |
TDF 5 |
| 15.00 ±2.00 |
68.50 ± 0.71 |
35.00 ±2.65 |
2.63±0.042 |
0.65±0.033 |
PTX 75 |
| 15.50 ±0.71 |
68.00 ± 1.40 |
35.33 ±1.15 |
2.74±0.042 |
0.65±0.069 |
Cilo 20 |
| 35.00 ±1.41* |
32.67 ± 1.52* |
13.66 ± 1.53* |
0.93± 0.051* |
0.49 ±0.028* |
CIS |
| 27.67 ±0.57#
|
38.00 ±1.00#
|
20.66 ±0.58#
|
1.15±0.059#
|
0.64 ±0.027#
|
CIS+TDF |
| 24.67 ±1.53#
|
41.00 ±1.00#
|
23.00 ±1.00#
|
1.46 ±0.044#,!
|
0.73 ±0.064#
|
CIS+PTX |
| 23.50 ±0.71#
|
42.67 ±1.51#
|
25.50 ±0.71#
|
1.71 ±0.011#
|
0.73 ±0.027#
|
CIS+ Cilo 5 |
| 19.00 ±1.00#, ●
|
49.00 ±2.00#, ●
|
26.66 ±1.52#
|
1.84 ±0.040 #, ●
|
0.75 ±0.061#
|
CIS+ Cilo 10 |
| 19.00 ±0.99#, ●,!,@
|
59.67±1.52#, ●,†,!,@
|
31.50 ±0.70#, ●,†,!,@
|
1.97±0.020#, ●,†,!,@
|
0.70 ±0.098#
|
CIS+ Cilo 20 |
Table 2.
Histopathological scoring of testicular lesions summarizing effect of cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg), tadalafil (5 mg/kg) and pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) on histopathological changes of CIS-induced testicular injury.
Table 2.
Histopathological scoring of testicular lesions summarizing effect of cilostazol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg), tadalafil (5 mg/kg) and pentoxifylline (75 mg/kg) on histopathological changes of CIS-induced testicular injury.
| |
Lesions
Groups
|
Desquamation in germinal cells |
Disorganization
in germinal
cells |
Interstitial oedema |
Degeneration in germinal cells |
Reduction in
germinal cell
counts |
| (dose:mg/kg) |
|
| Control |
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
| TDF 5 |
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
| PTX 75 |
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
| Cilo 20 |
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
| CIS 7 |
++ |
++ |
+ |
++ |
++ |
| CIS+TDF |
++ |
+ |
+ |
++ |
+ |
| CIS+PTX |
+ |
+ |
++ |
+ |
+ |
| CIS+ Cilo 5 |
++ |
++ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
| CIS+ Cilo 10 |
++ |
++ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
| CIS+ Cilo 20 |
- |
- |
+ |
+ |
- |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).