1. Introduction
Phenol-formaldehyde (PF) resins have excellent properties, such as water resistance, bonding performance, and environmental stability [
2], and have been widely used as cross-linked agents in wood-based panels and composites. However, the high cost and toxicity restricted its broader applications. To overcome these shortcomings, many researchers have been focused on modifying PF resin using environmental and economic resources [
3,
4]. These materials included urea [
5,
6,
7], lignin [
8,
9], tannin [
10,
11], carbohydrate [
12], bio-oil [
13,
14], soybean meal [
15,
16], and so on [
17,
18].
In which soybean meal is a main byproduct of soybean oil processing. Using soybean meal to prepare soy-based adhesive has a long history. Soy-based adhesives are very popular in the late 1920s and 1930s [
19,
20]. However, the poor water resistance and biological stability limited its application [
21,
22,
23]. In the 1960s, soy-based adhesives were nearly completely replaced by petroleum-based adhesives in the wood industry [
24]. In recent decades, many efforts have been devoted to enhancing soy-based adhesive properties (such as water resistance and the bonding strength) [
25,
26,
27]. These efforts can be classified into three strategies: denaturing modification, cross-linking modification, and protein molecular modification [
25,
27,
28,
29]. Cross-linking modification has been proven to be the most efficient method to enhance the comprehensive performance of soy-based adhesives [
30]. Based on previous reports, many cross-linkers have been successfully used, such as epoxy resin, melamine-urea-formaldehyde resin, rubber, hyperbranched polymer, PF resin, and so on [
25,
31,
32]. Among them, PF have aroused researchers’ interest [
29,
30]. Some studies found that the hydroxymethyl groups of PF resin can react with the amino groups of soy protein under a basic condition. However, it’s still hard to meet the requirements of outdoor wood-based products by using these method to modified soy-based adhesives. Many studies also have been devoted to reduce the cost and improve the environmental properties of PF adhesives with soybean meal, which is a lower-cost, environmental friendly, and renewable materials for replacing part of phenol and formaldehyde in wood adhesives [
24,
29]. Many studies results showed that the soybean meal modified PF adhesives have good physical properties for bonding wood panels [
21,
29]. However, the properties of water resistance was decreased. In addition, a few research was focused on the effect of soybean meal for the structural, bonding and curing properties of PF resin. In fact, these properties are very important for its applications in wood industry.
In our previous research, it was found that soy protein isolate could promote the curing of phenolic resin at low temperature in our previous research. In fact, Soy protein isolate is very expensive to modify phenolic resin. To obtain a low-cost, excellent performance and environmentally friendly protein-based phenolic resin which was applied in wood industry, in this study, soybean meal-phenol-formaldehyde (SMPF) resins with varying contents of soybean meal were prepared and applied to plywood. The thermal performances of SMPF were detected by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermogravimetric (TG) and. At the same time, the physical performances of SMPF resin were also investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Urea (98%) was produced by PetroChina Ningxia petrochemical company. Sodium hydroxide (analytically pure) was produced by the Beijing chemical plant; Phenol (98%) and formaldehyde solution (37–40%) were produced by Xilong Scientific Co., Ltd. (Shantou, China). Soybean meal (industrial grade, containing 48% of soy protein) was provided by Tianguan Biotech Company Limited in Henan province of China.
2.2. Preparation of PF and SMPF Resins
PF resin was synthesized using our previous work (formaldehyde/phenol molar ratio of 2.2) [
1,
33]. NaOH solution with a concentration of 50% was used as the catalyst. First, phenol, one-third of formaldehyde, and half of NaOH were added into a four-necked flask. Then, heat the sample solution to 90 °C within 10 minutes and keep reacting for 60 minutes. Secondly, the same formaldehyde and NaOH solution were added and kept reacting for 40 min at 88 °C. Finally, the last formaldehyde and NaOH solution were added and reacted for 40 min at 88 °C. After that, cooling the reaction mixture to 40 °C and obtained the neat PF resin.
SMPF resins were synthesized by the same procedure as PF resin. The added amount of soybean meal is in the range of 10%-40% by weight of phenol. Firstly, phenol, one-third formaldehyde, half of the soybean meal, and NaOH solution were mixed in a four-necked flask. The mixture was reacted at 90 °C for 60 min. Then, another one-third of the formaldehyde, the rest of the soybean meal, and one-quarter of the NaOH solution (50%) were added for 40 min at 88 °C. Thirdly, the final formaldehyde and NaOH solution were added (reacting for 40 min at 88 °C). Colling the reaction samples to 40 °C to obtain the SMPF resins. These SMPF resins were marked with SMPF-1, SMPF-2, SMPF-3, and SMPF-4, respectively.
2.3. Characterization of the Phenolic Resins
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy was used to character the structure of SM, PF resins, and SMPF resins. All of the samples were freeze-dried at −60 °C for 18 hours. Then, these samples were ground meal in a mortar (200-mesh). Then, the SM, uncured PF and SMPF resin samples were performed with a Nicolet 6700 spectrometer (Nicolet Instrument Corporation, USA) [
1]. The PF and SMPF resins were detected by a TA Q2000 (Differential scanning calorimeter, TA instruments, USA). The DSC scanning temperature range is 30–180 °C; the heating rate is 10 °C/min [
34]. To measure the thermal stability, all resin samples were cured at 120 °C for 120 min. About 5–6 mg cured resin sample (200-mesh) were determined using a Q50 analyzer (TA instruments, USA). The condition of testing as follow: the temperature range is 30–800 °C, heating rate is 10 °C/min, N
2 atmosphere. After completely drying and curing in a 120 °C oven, breaking the cured resin to obtain a smooth and flat fracture surface. After spraying the gold coating on the fracture surface of the sample, it was analyzed and tested using a scanning electron microscope (SU8010, Hitachi, Japan).
For all resins, the performances of gel time, solid content, and pH value also were measured by the method from the reported of Li et al. [
11]. The measurement of residual rate is follow from the reported of Li et al. [
49]. Each resin sample was repeated three times and its average value was reported.
2.4. Plywood
Three-layer plywood was prepared with poplar veneer, which dimension is 400 mm × 400 mm × 1.5 mm. Both sides of the middle veneer were coated with adhesive, which is the mixture of phenolic resin and 15% flour (according to the weight ratio of phenolic resin). About 250–300 g/m
2 adhesive was coated on the veneer. Firstly, the plywood samples were cold-pressed under 0.8 MPa for 15 min and then hot-pressed at 135 °C under 1.05 MPa for 5 min. All of the plywood sample was stored at normal temperature for 3 days before testing. The shear strength of plywood was measured in accordance with the Chinese National Standard GB/T 17657-2013 [
33].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of PF and SMPF Resins
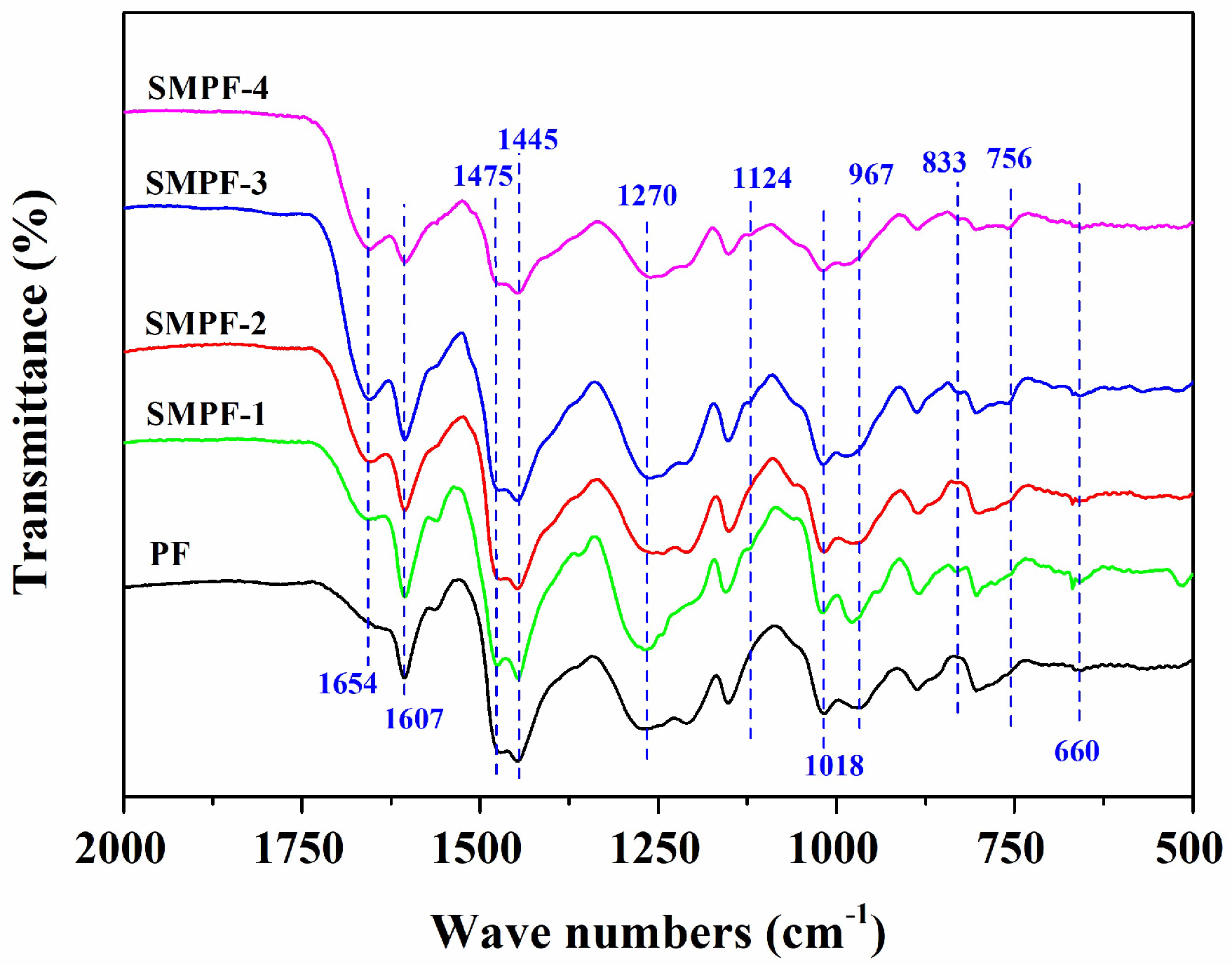
As seen in
Figure 1, the PF and SMPF resins samples shows intense peaks at around 3300–3400 cm
−1, which were belong to the hydroxyl groups of phenolic and aliphatic. The absorption peaks at 2900–2860 cm
−1 can be assigned to the stretching vibration of C–H in methylene groups. The characteristic peaks of aromatic rings in all phenolic resins were observed at 1606, 1457, and 1446 cm
−1 [
13]. The peak at 1244 cm
−1 was associated with the stretching vibration of C–O in the hydroxyl groups of phenolic. The absorption peaks at 829, 757, and 694 cm
−1 can be attributed to the aromatic C–H [
25,
29]. In addition, the peak at 978 cm
−1 was related to the C–H stretching vibration of vinyl [
26].
Comparing the FTIR spectra of PF and SMPF resins, we can see that all the samples have the similar functional groups, which indicated that PF and SMPF have similar molecules structure. However, the FTIR spectra of PF and SMPF resin also have some differences. Compared with PF resin, the spectra of all SMPF resins presented stronger absorption peaks at around 1667 and 1357 cm
−1, and showed weaker absorption at around 967 cm
−1. These differences can be attributed to the reaction between hydroxymethyl phenolic (HP) and soybean meal, which contained amounts of soy protein. As seen in
Figure 1 with the increase of substitution of phenol and formaldehyde by soybean meal, the peak at 1667 cm
−1 was become more stronger. The absorption peak as 1667 cm
−1 was belong to the C=O stretching vibration of amine groups in the molecular structure of soy protein [
35,
36], which implied that higher substitution of phenol by soybean meal, the higher reaction degree for PF and soy protein [
37]. In addition, soybean meal can react with formaldehyde, and formed hydroxymethylated soybean meal (HSM). The condensation reaction could be occurred between HSM and HP, or HSM and HSM.
Figure 1.
FTIR spectra of the PF and SMPF resins.
Figure 1.
FTIR spectra of the PF and SMPF resins.
3.2. Thermal Behaviors of the PF and SMPF Resins
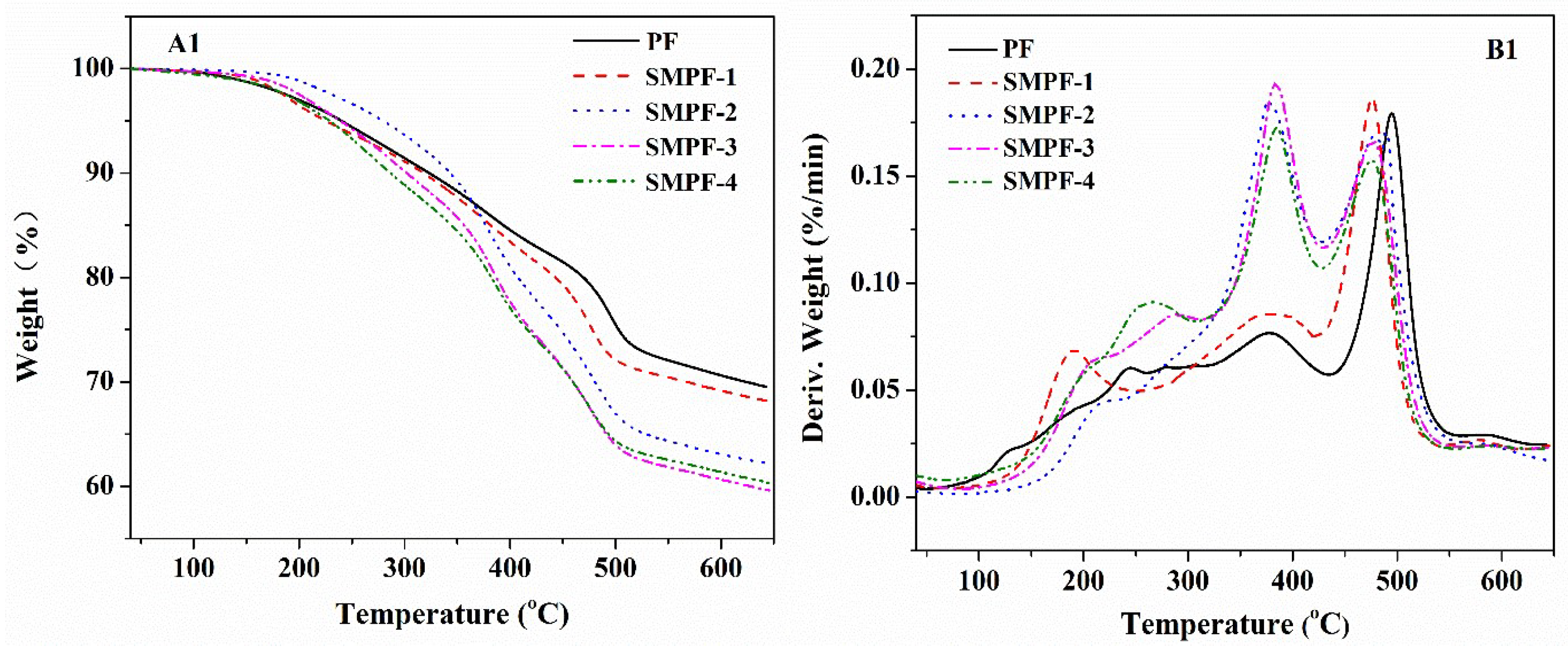
To investigate the effect of soybean meal on the thermal stability of phenolic resin, TGA analysis were performed. The TGA curve results are shown in
Figure 2. The weight loss ratio and the peak of the DTG curve (T
max) could be used to evaluate the thermal stability of resin. The weight loss and T
max of different decomposition stages of the resin samples are shown in
Table 1.
In general, the phenolic resins contained three main decomposition stages: post curing, thermal reforming, and ring stripping. According to the curves of TG and DTG in
Figure 2, it can be see that the mainly mass loss of all PF and SMPF resins were occurred in the region of 100–310 °C, 310–430 °C, and 430–550 °C, respectively. In the first region, the mass loss was attributed to the release of water, which main derived from the cross-linking/condensation reaction between methylol groups [
38,
39]. For the second region, the mass loss might be due to the decomposition of the methylene bridge bond in phenolic resin. In addition, some studies suggest that the mass loss in this stage might be due to the evaporation of water caused by the condensation reaction between two hydroxyl functional groups, as well as the reaction between methylene and phenolic –OH [
40,
41]. In the third mass loss region, the aromatic structure was degraded to a carbonaceous structure. Moreover, amounts of carbon monoxide and methane were produced from the decomposition of methylene linkage [
42,
43,
44].
The thermal properties of the cured PF and SMPF resins are shown in
Table 1. The weight loss and T
max of different thermal degradation steps of all samples were list. From
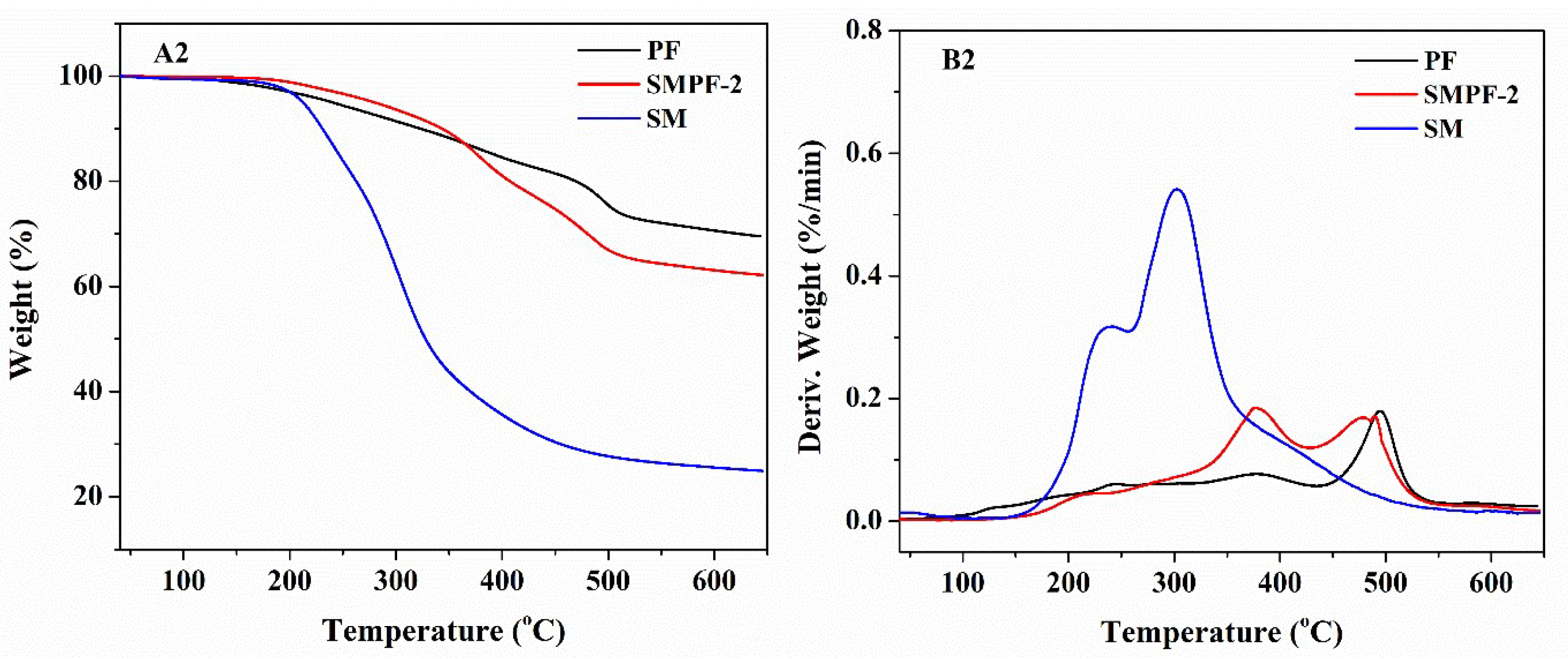
Table 1, we can see that the soybean meal had significant effect on the thermal stability of phenolic resin. All the SMPF resins showed lower weight residues at 600 °C than that of neat PF resin. It was indicated that soybean meal decreased the thermal stability of phenolic resin. This could be attributed to that the SMPF resin contained amount of carbohydrate compounds, which was derived from soybean meal. These carbohydrate compounds is difficult to react with soy protein and hydroxymethyl phenolic. Finally, the neat cured PF resin had a tighter network than all SMPF resins. For all SMPF resins, SMPF-1 has the highest thermal stability, the total weight loss is 31.86% in the temperature region of 100–550 °C.
Figure 2.
TG and DTG curves of the PF and SMPF resins (A1, B1); SM, PF and SMPF-2 resins (A2, B2).
Figure 2.
TG and DTG curves of the PF and SMPF resins (A1, B1); SM, PF and SMPF-2 resins (A2, B2).
Table 1.
Thermal degradation properties of SMPF resins.
Table 1.
Thermal degradation properties of SMPF resins.
| Resins |
Step 1
100–310 °C |
Step 2
310–430 °C |
Step 3
430–550 °C |
Total mass loss
(%) |
TP1
(°C) |
TP2
(°C) |
Mass loss
(%) |
TP3
(°C) |
Mass loss
(%) |
TP4
(°C) |
Mass loss
(%) |
| PF |
245 |
- |
7.89 |
378 |
9.05 |
494 |
9.72 |
30.47 |
| SMPF-1 |
191 |
- |
9.32 |
384 |
9.40 |
475 |
10.64 |
31.86 |
| SMPF-2 |
229 |
- |
6.97 |
379 |
15.70 |
482 |
12.87 |
37.80 |
| SMPF-3 |
226 |
289 |
11.37 |
383 |
15.52 |
476 |
11.92 |
40.32 |
| SMPF-4 |
215 |
265 |
11.41 |
384 |
14.46 |
475 |
10.98 |
39.60 |
3.3. Curing Behavior of the PF and SMPF Resins
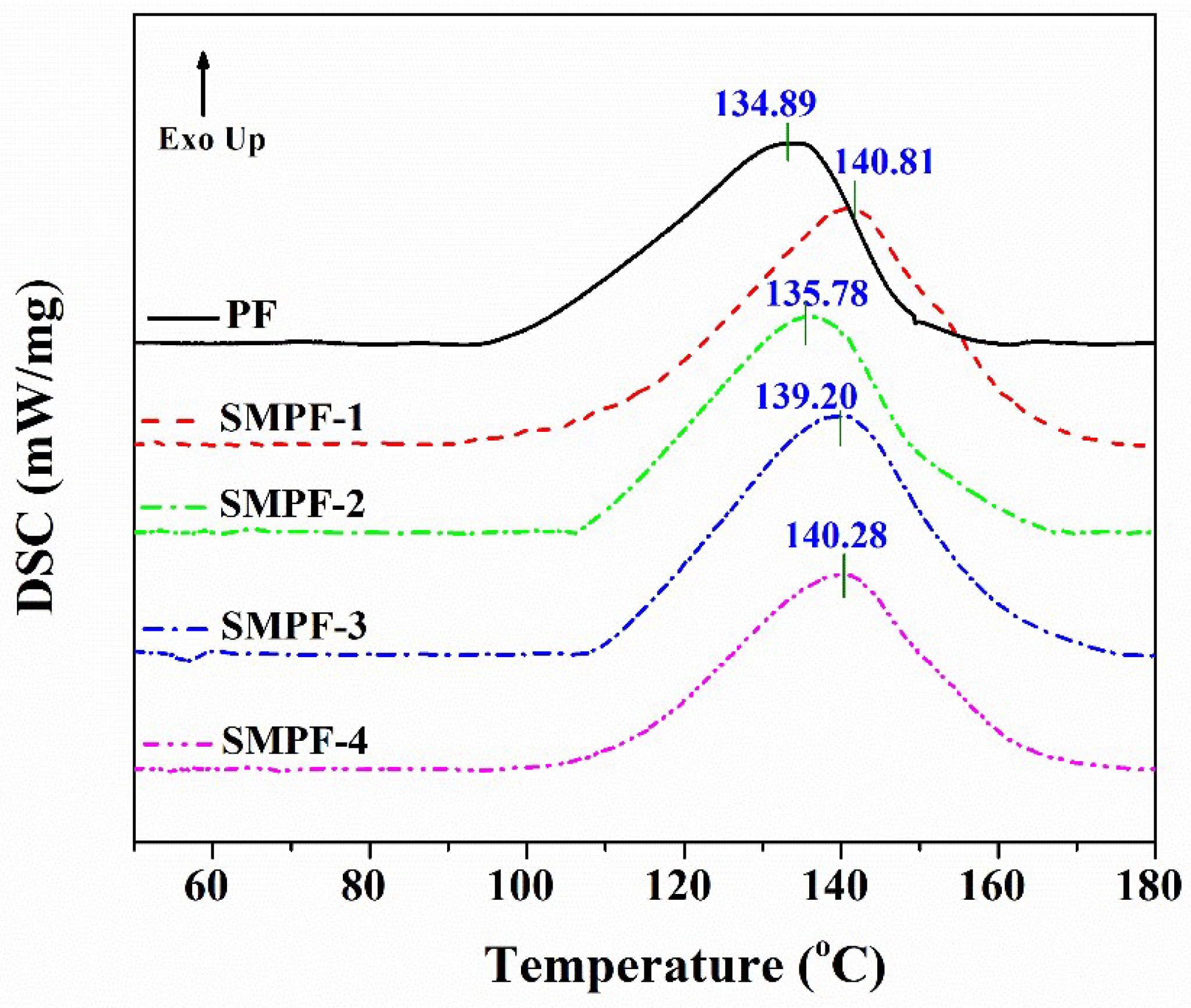
Differential scanning calorimetry analysis is a powerful method to investigate the curing behavior of thermosetting resins [
45,
46]. In this work, the influence of soybean meal on the curing properties of the PF and SMPF resins were studied. DSC analysis were conducted, and the results were recorded as shown in
Figure 3. The DSC curve (T
peak) were used to compare the curing properties of different resins.
As seen from
Figure 3, the obviously exothermic peaks were observed for all resins. The exothermic peak is attributed to the condensation reaction, which can release energy. In addition, it also indicated that the cross-linking/condensation reaction could be occurred between methylolated soybean meal and methylolated phenol. From
Figure 3, the onset temperature of PF resin was around 90 °C, but the SMPF resins were around 100 °C. Moreover, the exothermic peak temperature of PF, SMPF-1, SMPF-2, SMPF-3, and SMPF-4 are 134.89, 140.11, 135.78, 139.20, and 140.28 °C, respectively. This indicates that the curing temperature of the modified SMPF resins is higher than that of the neat PF resin. Therefore, it suggested that the requirement temperature of the condensation reaction between methylolated soybean protein and methylolphenol is higher than the condensation reaction between two methylolphenol groups.
Figure 3.
DSC curves of the PF and SMPF resins.
Figure 3.
DSC curves of the PF and SMPF resins.
3.4. The Properties of the PF and SMPF Resins
For all resins, the pH value, viscosity, solid content, gel time, and pot life were tested and listed in
Table 2. As it can been seen from
Table 2, all the SMPF resins almost have the similar pH values and solids content. Compared with PF resin, the viscosities of all modified resins were increased (from 87 to 1083 mPa‧s). This could be attributed to the amounts of hydrogen bond in SMPF resins. The soybean meals were contained amounts of soy protein and carbohydrate compounds. The molecular chains of these compounds will be broken under alkaline conditions, and then created a lot of hydrogen bonds [
47,
48]. The hydrogen bonds in the modified resins system were increased the viscosity of them. It should be point out that the pH value of all phenolic resins were controlled at about 12, because which is beneficial to the curing of resin in the process of plywood preparation. Gel time is an important property for phenolic resin, which can be used to evaluate the curing performance of resin. With the exception of SMPF-1, all the gel time of SMPF resins are shorter than PF resin. It indicated that the curing rate of these resins are faster than PF resin at 150 °C. In fact, the gel time of resins were tested at 150 °C. In addition, it’s worth noting that all of the SMPF resins had long pot life, which is benefits for its industrial application.
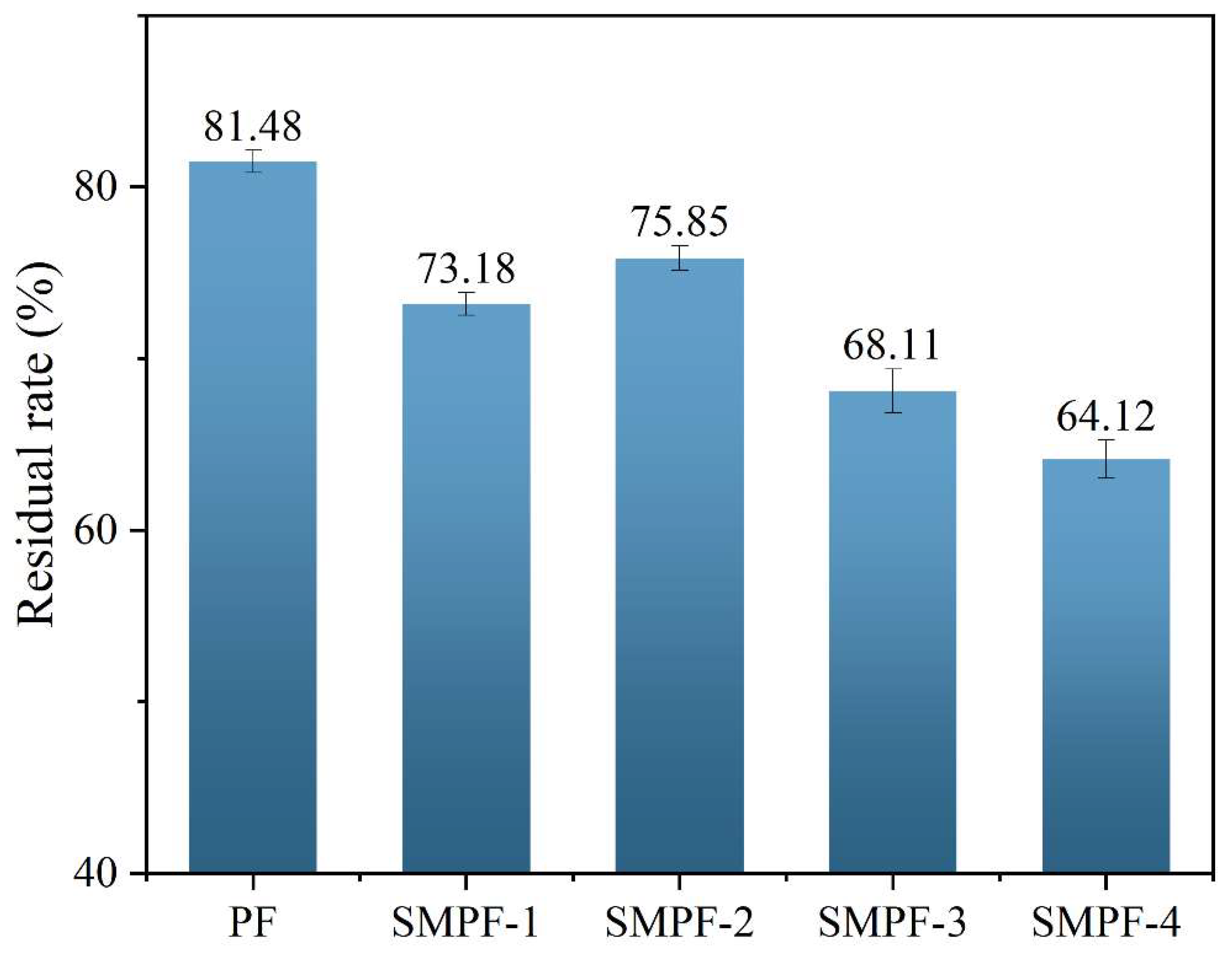
3.5. Residue Analysis
The residual rates of different SMPF resin adhesives are shown in
Figure 4. The residual rate of PF resin is 81.48%, higher than all SMPF resin adhesives. The main reason is that SM contains a large amount of starch. Starch molecules have hydrophilicity and cannot form a densely cross-linked network structure with PF. Ultimately, the residual rate of SMPF resin is lower than that of PF resin adhesive. The residual rates of SMPF-1 and SMPF-2 are 73.18% and 75.85%, respectively. This is because when appropriate SM is added, the active groups on the protein molecular chain in SM undergo cross-linking reaction with phenolic resin. The cross-linking density of SMPF resin after curing increases, effectively prevents water from entering the adhesive layer, thereby improving the water resistance of the adhesive. The residual rates of SMPF-3 and SMPF-4 decreased compared to SMPF-1 and SMPF-2, reaching 68.11% and 64.12%. Due to the excessive addition of SM, starch molecules in SM did not fully participate in the crosslinking and curing reaction of PF resin, thereby reducing the crosslinking density of the adhesive. By adjusting the amount of SM added to balance the optimal reaction ratio between SM and PF, the crosslinking reaction between them can be promoted. When 20% SM is added, the residual rate of SMPF-2 adhesive is relatively high, at 75.85%.
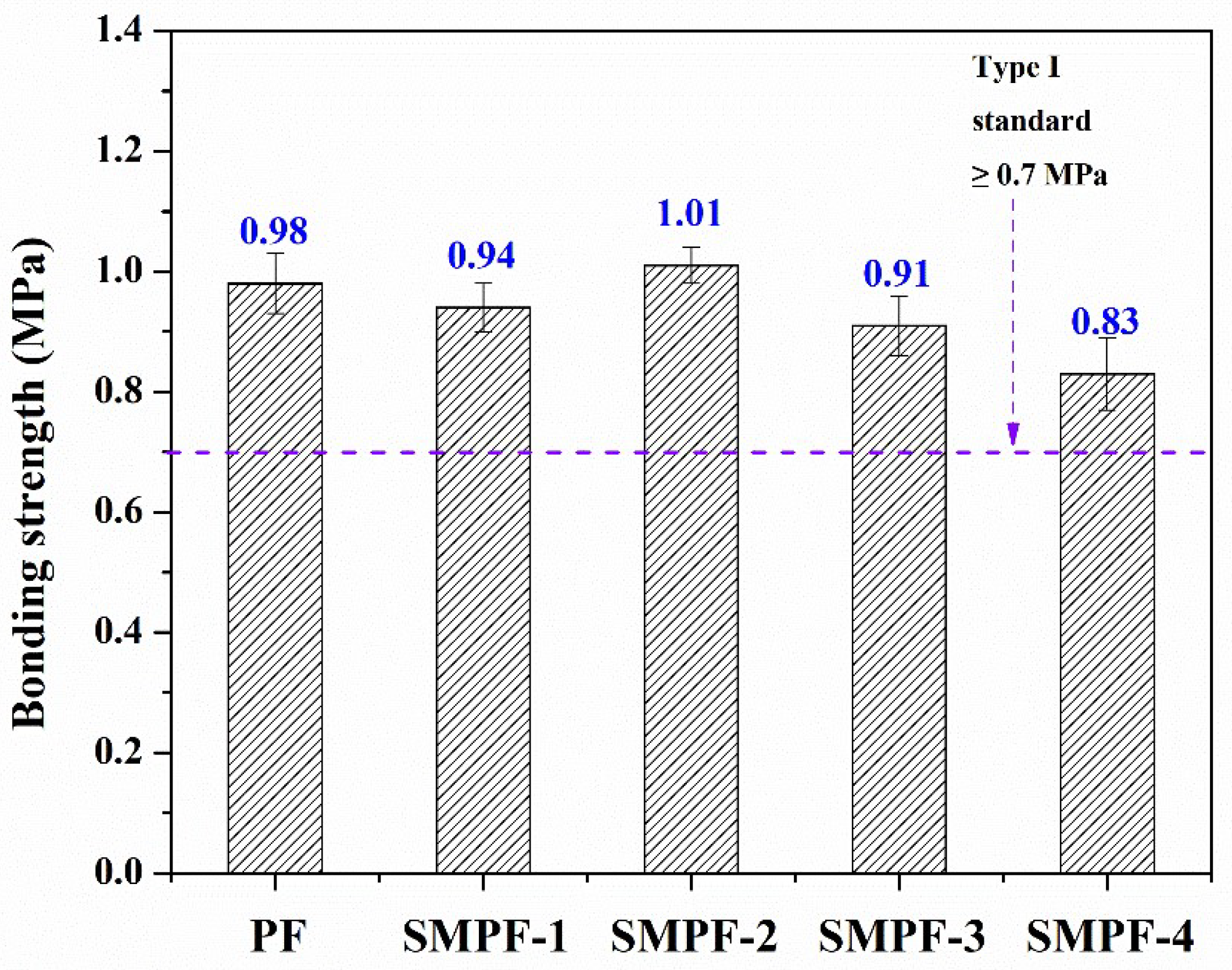
3.6. Bonding strength of Plywood by different SMPF adhesives
The effect of soybean meal on the performance of plywood was studied.
Figure 5 shows the wet bonding strength of all resins. As seen in
Figure 5, all of the plywood bonded with SMPF resins exhibited excellent water resistance and bonding strength, which could meet the requirement for plywood (the Chinese national standard, type I, ≥0.7 MPa). For all SMPF resin, the bonding strength was decreased with the soybean meal addition, except for the SMPF-2. When the addition of soybean meal is 20% (weight by phenol), the SMPF-2 plywood had the highest bonding strength (1.01 MPa). For PF resin, although the curing peak temperature was higher than SMPF resin, the bonding strength of the plywood was lower. This might be attributed to the favorable viscosity of SMPF-2 resin. From
Table 2, the SMPF-2 resins showed a suitable viscosity for plywood bonding. It indicate that SMPF-2 have a good coating behaviors. On the other hand, low viscosity might cause unevenly coating issues, which will influence the performance of PF resin and reduced the bonding strength.
In addition, the tighter network structures formed from the condensation reaction between the hydroxymethyl phenolic structure and soybean meal molecules, which enhanced the bonding strength and water resistance the SMPF-2 resin.
Figure 5.
The bonding strength of the PF and SMPF resins.
Figure 5.
The bonding strength of the PF and SMPF resins.
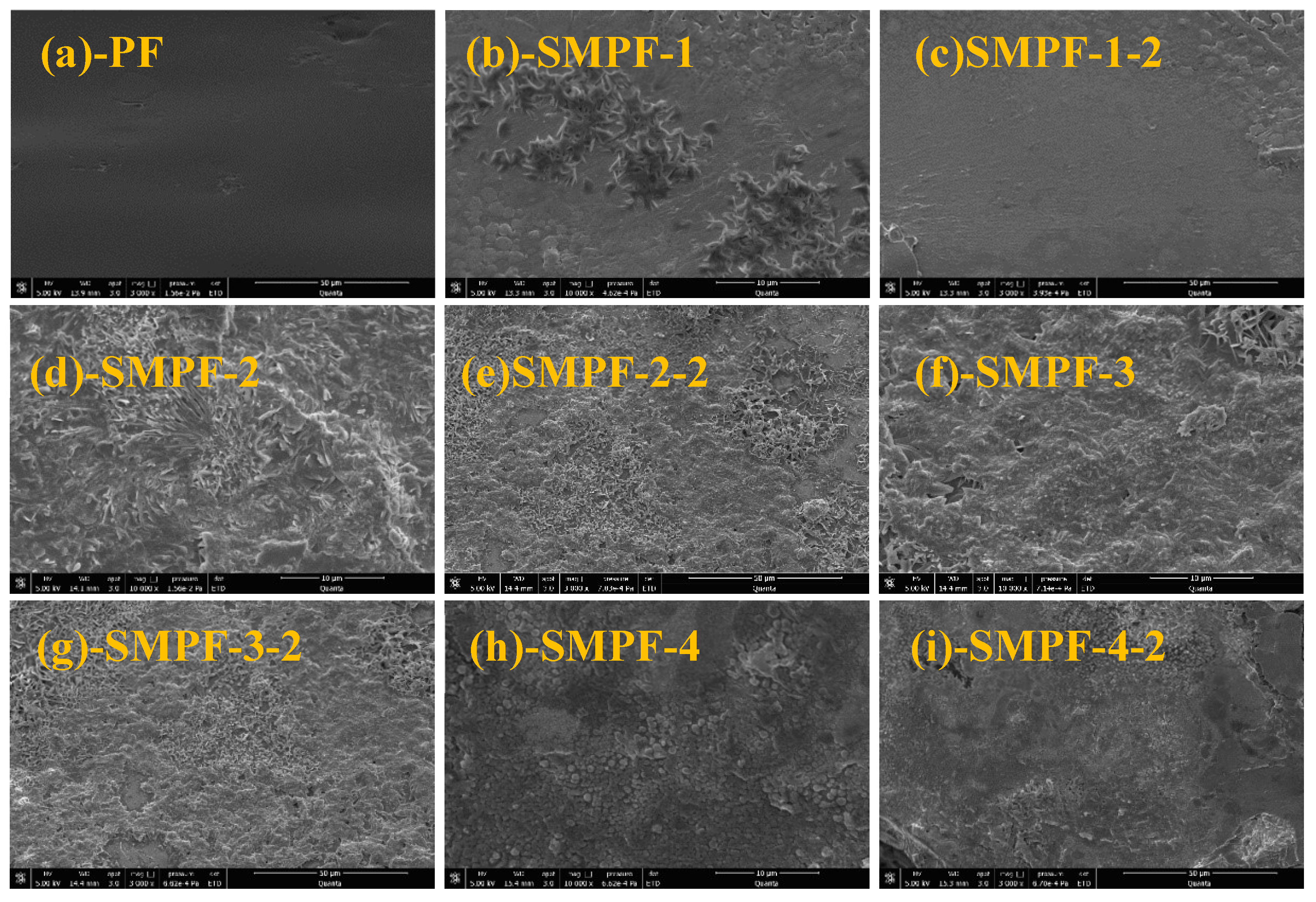
3.7. SEM analysis
Figure 6 shows an SEM image of the fracture morphology of the prepared adhesives. From
Figure 6, it can be seen that the surface of PF resin is very uniform and smooth. For the modified SMPF resin with liquefied SM, the cross sections of all samples become coarse and unsmooth. The main reason is that the density of rigid groups in the molecular structure of PF resin is large, and the toughness of the resin after crosslinking and curing is poor, so its cross-section is even and smooth. From
Figure 6, it also can be seen that the cross-section of SMPF resin has undergone significant changes, with a flocculent and irregular surface. The main reason is that SM reacts with hydroxymethylphenol and formaldehyde, forming a cross-linked network structure. SMPF resin has complex molecular structure and uneven curing compared to PF resin. Meanwhile, the starch components in SM cannot react with formaldehyde and phenol, thus affecting the curing of SMPF resin. The above reasons ultimately result in an uneven and irregular cross-section of the cured modified SMPF resin. The cured section of SMPF-4 resin modified with 40% SM addition showed obvious cracking, indicating that excessive SM addition increased the brittleness of the modified SMPF resin. The cracking of SMPF-4 resin after curing can reduce its water resistance, resulting in low wet bonding strength (0.83 MPa) and poor water resistance.
4. Conclusions
Environmentally friendly phenolic resin with low-cost, excellent water resistance, and bonding strength properties was prepared using soybean meal as a substitution. The FTIR and DSC analysis results suggested that the cross-linking reaction occurred between PF and soybean meal. The TG analysis results show that SMPF resins’ degradation increased compared to PF resin. The DSC results indicated that the addition of soybean meal increased the curing temperature of phenolic resins. Compared to other resins, the SMPF-2 resin has the highest bonding strength (1.01 MPa). In addition, the plywood performance results also show that all of the SMPF resins have favorable viscosity, short gel time, and excellent water resistance and bonding strength, meeting the Chinese National Standard for type I plywood. Therefore, the optimized SMPF resin can potentially replace part of PF resin in the wood industry.
Funding
The Special Fund for Young Talents in Henan Agricultural University (30500928).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors of this work declare that it does not have any conflict of interest, with people or financial institutions.
References
- Li, C.; Zhang, J.Z.; Yi, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.Z. Preparation and characterization of a novel environmentally friendly phenol–formaldehyde adhesive modified with tannin and urea. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2016, 66, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.Z.; Jing, J.L.; Zhu, Y.C.; Yang, X.M.; Wang, X.F.; Wang, Z.C. Preparation and performance of lignin–phenol–formaldehyde adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2016, 64, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ma, Y.F.; Wang, C.P.; Li, S.H.; Zhang, M.M.; Chu, F.X. Preparation and properties of lignin–phenol–formaldehyde resins based on different biorefinery residues of agricultural biomass. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 43, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.C.; Cui, Y.H.; Gou, G.J.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, S.L.; Hui, D.; Gou, J.H.; Zhou, Z.W. Liquefaction of lignin in hot-compressed water to phenolic feedstock for the synthesis of phenol-formaldehyde resins. Composites Part B 2017, 112, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turunen, M.; Alvila, L.; Pakkanen, T.T.; Rainio, J. Modification of phenol–formaldehyde resol resins by lignin, starch, and urea. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 88, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Grunwald, D.; Pasch, H. Preparation of phenol–urea–formaldehyde copolymer adhesives under heterogeneous catalysis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 2946–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.B.; Li, J.Z.; Chang, J.M. On the structure and cure acceleration of phenol–urea–formaldehyde resins with different catalysts. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 2849–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stücker, A.; Schütt, F.; Saake, B.; Lehnen, R. Lignins from enzymatic hydrolysis and alkaline extraction of steam refined poplar wood: Utilization in lignin-phenol-formaldehyde resins. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 85, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Li, S.J.; Guo, G.W.; Han, S.Y.; Ren, S.X.; Ma, Y.L. Synthesis and characterization of phenol-formaldehyde resin using enzymatic hydrolysis lignin. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabarsa, T.; Jahanshahi, S.; Ashori, A. Mechanical and physical properties of wheat straw boards bonded with a tannin modified phenol–formaldehyde adhesive. Composites Part B 2011, 42, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, S.; Zhou, X.; Segovia, C.; Pizzi, A.; Romagnoli, M.; Giovando, S.; Pasch, H.; Rode, K.; Delmotte, L. Phenolic resin adhesives based on chestnut (Castanea sativa) hydrolysable tannins. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanthan, T.; Toland, A. Whey modified phenol—formaldehyde resins as plywood adhesives. Carbohyd. Polym. 1991, 15, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.Y.; Yan, N.; Farnood, R.R. Synthesis and characterization of phenol formaldehyde novolac resin derived from liquefied mountain pine beetle infested lodgepole pine barks. Macromol. React. Eng. 2013, 7, 646–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.B.; Lu, Q.; Ye, X.N.; Li, W.T.; Hu, B.; Dong, C.Q. Production of phenolic-rich bio-oil from catalytic fast pyrolysis of biomass using magnetic solid base catalyst. Energy Convers. Manage. 2015, 106, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.K.; Sun, X.S. Plywood adhesives by blending soy protein polymer with phenol-formaldehyde resin. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2007, 1, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamatha, B.S.; Sujatha, D.; Nath, S.K.; Pandey, C.N. Soya based phenolic resin for plywood manufacture. Journal of the Indian Academy of Wood Science 2011, 8, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorov, S.A.; Denisov, D.E.; Vanicheva, L.L. Reaction of phenol-formaldehyde bond with refractory filler. Refract. Ind. Ceram. 1986, 27, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, N.; Feng, M.W. Bark extractives-based phenol–formaldehyde resins from beetle-infested lodgepole pine. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 2112–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhao, S.J.; Zhang, S.F.; Li, J.J. Development of mainly plant protein-derived plywood bioadhesives via soy protein isolate fiber self-reinforced soybean meal composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 133, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.H.; Li, K.C. An all-natural adhesive for bonding wood. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2015, 92, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Wu, Z.G.; Cao, M.; Du, G.B. Study on the Soy protein-based wood adhesive modified by hydroxymethyl phenol. Polymers 2016, 8, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.D.; Liu, X.R.; Ye, Q.Q.; Gao, Q.; Gong, S.S.; Li, J.Z.; Shi, S.Q. Bio-inspired co-deposition strategy of aramid fibers to improve performance of soy protein isolate-based adhesive. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 150, 112424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamaming, S.Z.; Lamaming, J.; Rawi, N.F.M.; Hashim, R.; Kassim, M.H.M.; Hussin, M.H.; Bustami, Y.; Sulaiman, O.; Amini, M.H.M.; Hiziroglu, S. Improvements and limitation of soy protein-based adhesive: A review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2021, 61, 2393–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, I.; Kuo, M.; Myers, D.J. Bond quality of soy-based phenolic adhesives in southern pine plywood. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2006, 73, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Luo, J.L.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.Z.; Gao, Q.; Chen, H. An eco-friendly wood adhesive from soy protein and lignin: performance properties. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 100849–100855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, X.N.; Zhang, H.X.; Gao, Q.; Li, J.Z. Properties of a soybean meal-based plywood adhesive modified by a commercial epoxy resin. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2016, 71, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, K.C. Modification of soy protein for wood adhesives using mussel protein as a model: the influence of a mercapto group. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2004, 25, 1835–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Gupta, A.; Beg, M.; Chua, G.K.; Kumar, A. Physical and mechanical properties of medium-density fibreboards using soy-lignin adhesives. J. Trop. For. Sci. 2014, 26, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.G.; Xi, X.D.; Lei, H.; Du, G.B. Soy-based adhesive cross-linked by phenol-formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde. Polymers 2017, 9, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.G.; Lei, H.; Cao, M.; Xi, X.D.; Liang, J.K.; Du, G.B. Soy-based adhesive cross-linked by melamine–glyoxal and epoxy resin. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 2120–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.Q.; Sun, X.S. Soy proteins as plywood adhesives: formulation and characterization. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 2014–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.N.; Luo, J.; Gao, Q.; Li, J.Z. “Green” bio-thermoset resins derived from soy protein isolate and condensed tannins. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 108, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, W.; Mu, Y.B.; Zhang, J.Z.; Zhang, S.F.; Li, J.Z.; Zhang, W. Structural properties and copolycondensation mechanism of valonea tannin-modified phenol-formaldehyde resin. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.D.; Li, F.; Liu, X.R.; Gao, Q.; Gong, S.S.; Li, J.Z.; Shi, S.Q. Borate chemistry inspired by cell walls converts soy protein into high-strength, antibacterial, flame-retardant adhesive. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.C.; Xu, P.W.; Yang, W.J.; Chu, H.; Wang, W.; Dong, W.F.; Chen, M.Q.; Bai, H.Y.; Ma, P.M. Soy protein-based adhesive with superior bonding strength and water resistance by designing densely crosslinking networks. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 142, 110128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.J.; Xu, Y.C.; Chen, M.S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.Z.; Gao, Q.; Shi, S.Q. Soy protein adhesive with bio-based epoxidized daidzein for high strength and mildew resistance. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, R.Q.; Xu, Y.C.; Chen, M.S.; Zhang, J.Y.; Gao, Q.; Li, J.Z. Developing a stable high-performance soybean meal-based adhesive using a simple high-pressure homogenization technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.L.; Li, J.J.; Li, C.; Zhang, S.F.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.Z. Degradation mechanism of Acacia mangium tannin in NaOH/urea aqueous solution and application of degradation products in phenolic adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2020, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.L.; Li, C.F. Preparation and performance study of modified silica sol/phenolic resin. BioResources 2021, 16, 6669–6683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.V.; Oliet, M.; Domínguez, J.C.; Rojo, E.; Rodríguez, F. Thermal degradation of lignin–phenol–formaldehyde and phenol–formaldehyde resol resins. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 105, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, J.C.; Oliet, M.; Alonso, M.V.; Rojo, E.; Rodríguez, F. Structural, thermal and rheological behavior of a bio-based phenolic resin in relation to a commercial resol resin. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 42, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.G.; Liu, Y.F.; Yang, L.T. Thermal stability of boron-containing phenol formaldehyde resin. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 1999, 63, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, F.H.; Zhang, B.X.; Luo, Z.H.; Li, H.; Zhao, T. Structure and improved thermal stability of phenolic resin containing silicon and boron elements. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2016, 133, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.M.; Fernández, A. Thermal stability and pyrolysis kinetics of lignin-phenol-formaldehyde resins. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 123, 3036–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.B.; Riedl, B.; Ait-Kadi, A. Curing process of powdered phenol–formaldehyde resole resins and the role of water in the curing systems. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, G.; González-Alvarez, J.; Antorrena, G. Curing of a phenol-formaldehyde-tannin adhesive in the presence of wood: analysis by differential scanning calorimetry. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2004, 84, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.X.; Chang, Z.W.; Bai, Y.M.; Gao, Z.H. Effects of working time on properties of a soybean meal-based adhesive for engineered wood flooring. J. Adhesion. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Y.F.; Sun, B.; Kan, H.F.; Bai, Y.M.; Guo, Z.H. Preparation and characterization of a melamine-urea-glyoxal resin and its modified soybean adhesive. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2021, 111, 102986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, W.; Tang, Y.; Yang, F.; Gong, C.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Li, C. Preparation and Characterization of Soybean Protein Adhesives Modified with an Environmental-Friendly Tannin-Based Resin. Polymers 2023, 15, 2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).