Submitted:
23 May 2023
Posted:
24 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
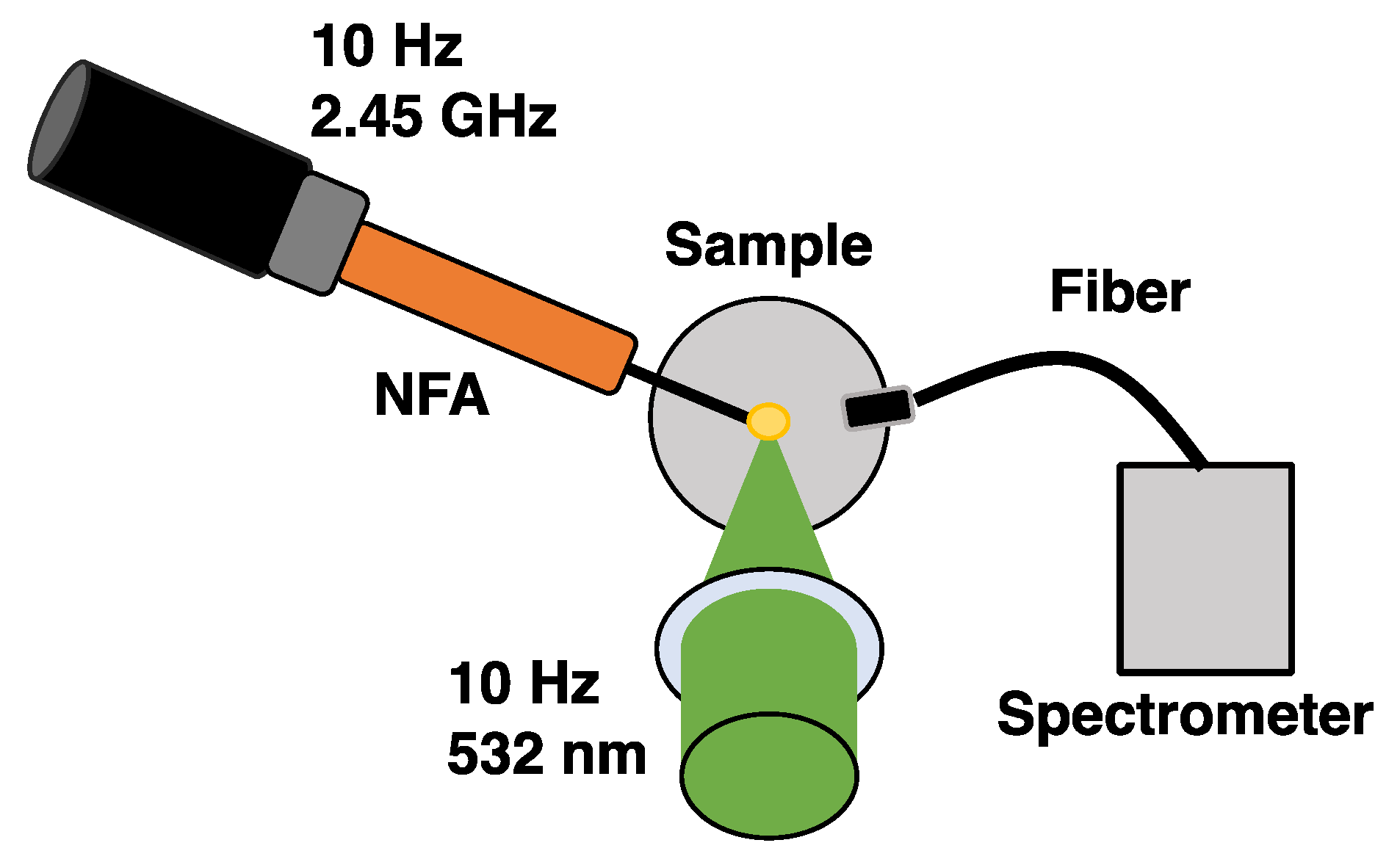
2. Experimental Arrangement
3. Results
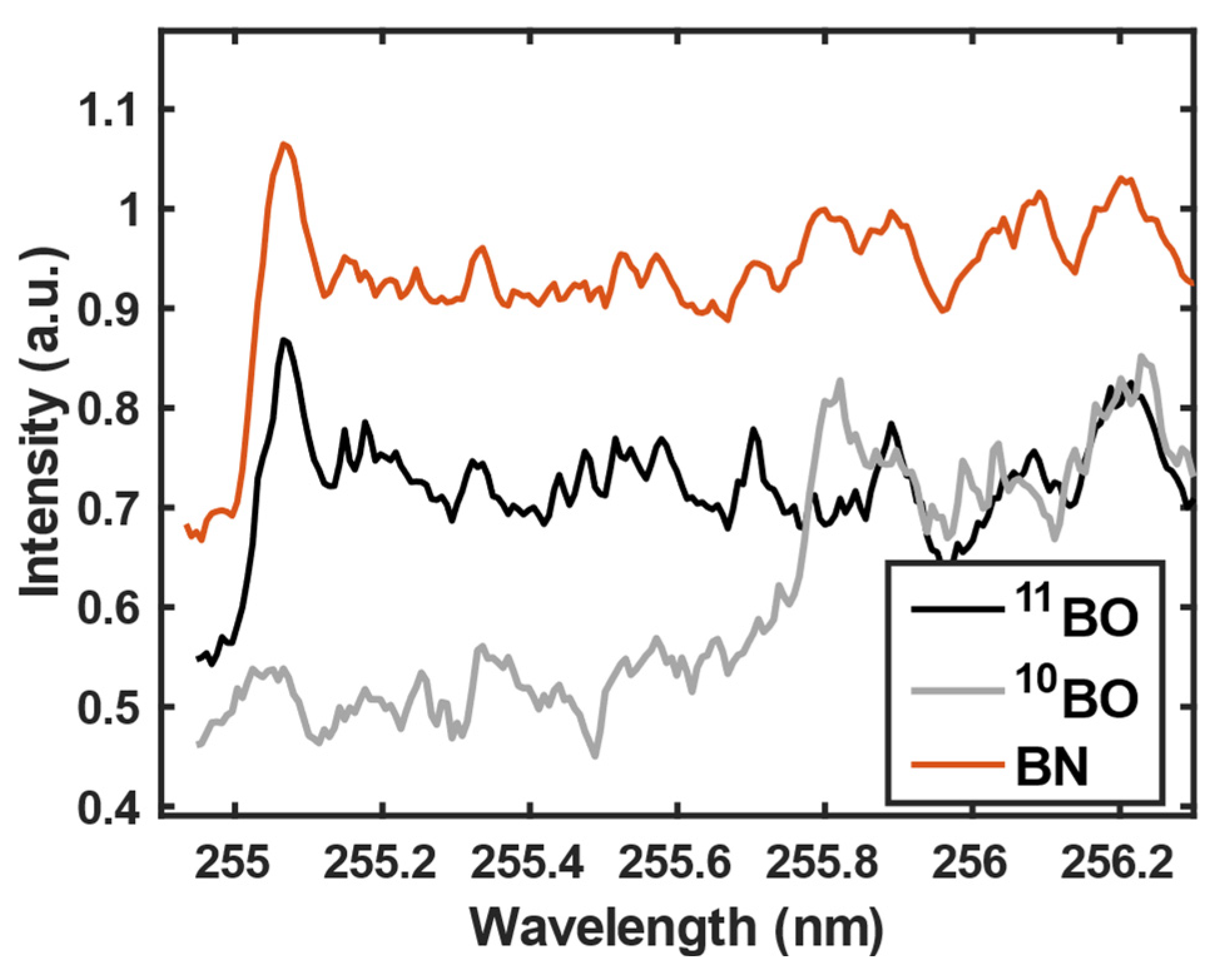
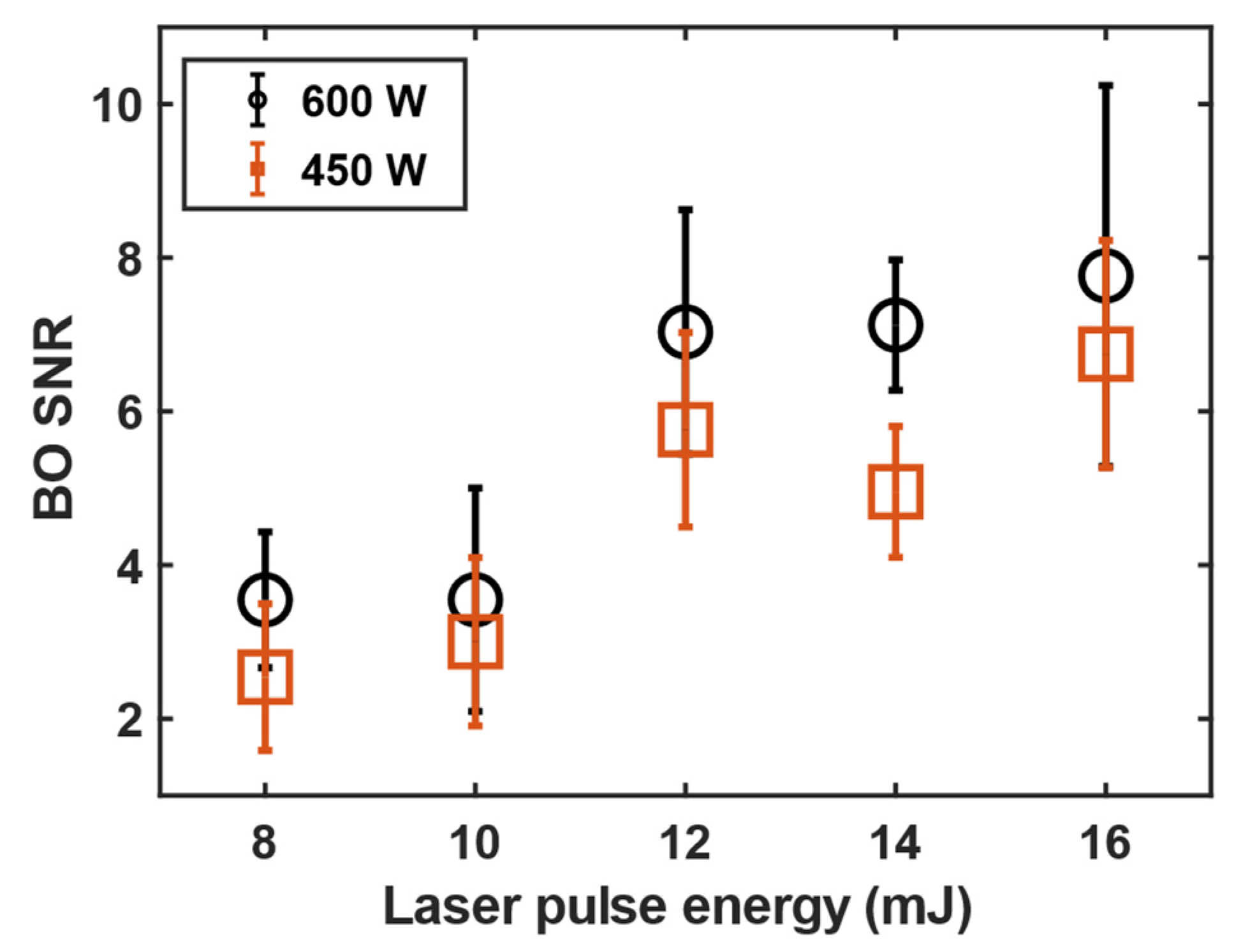
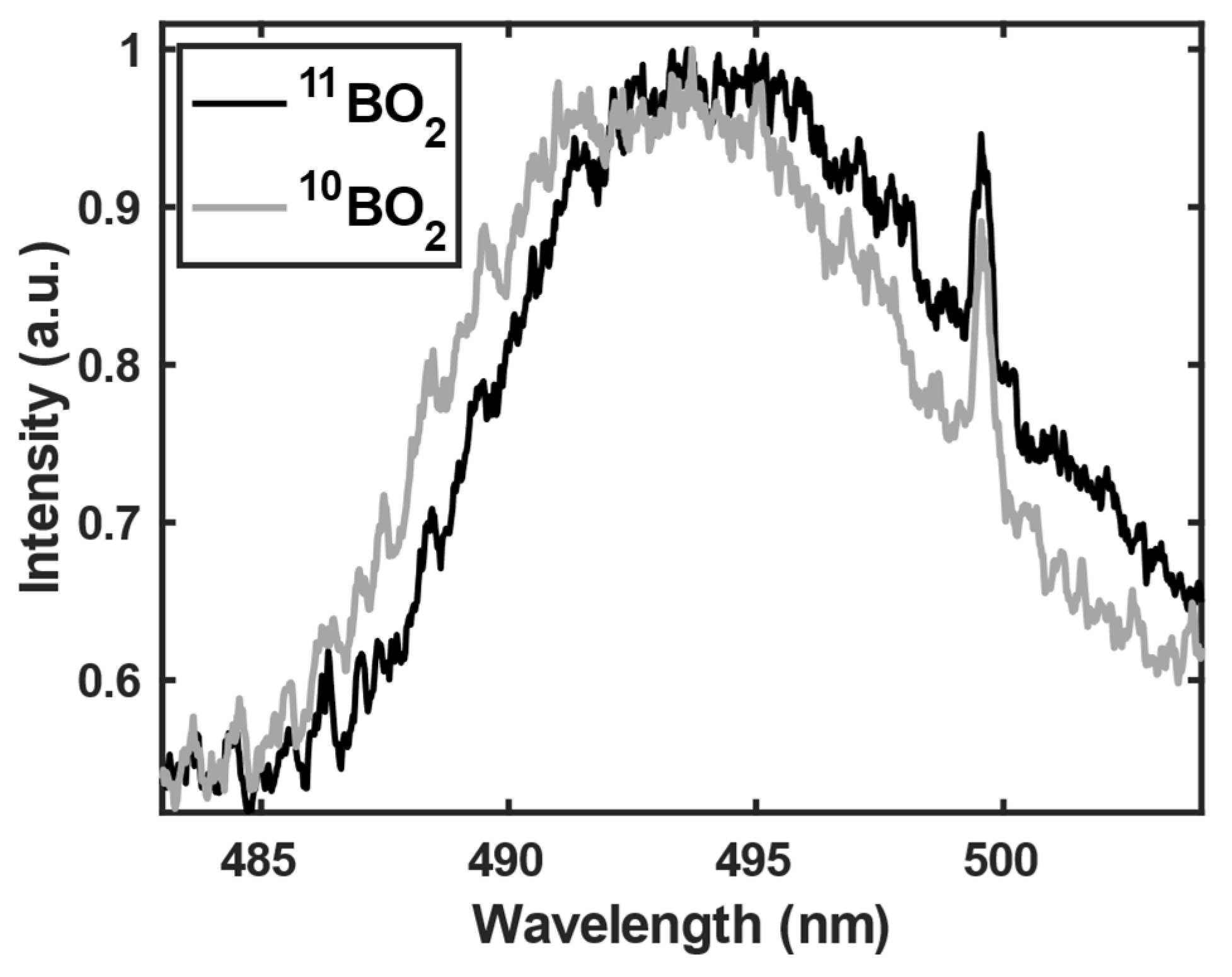
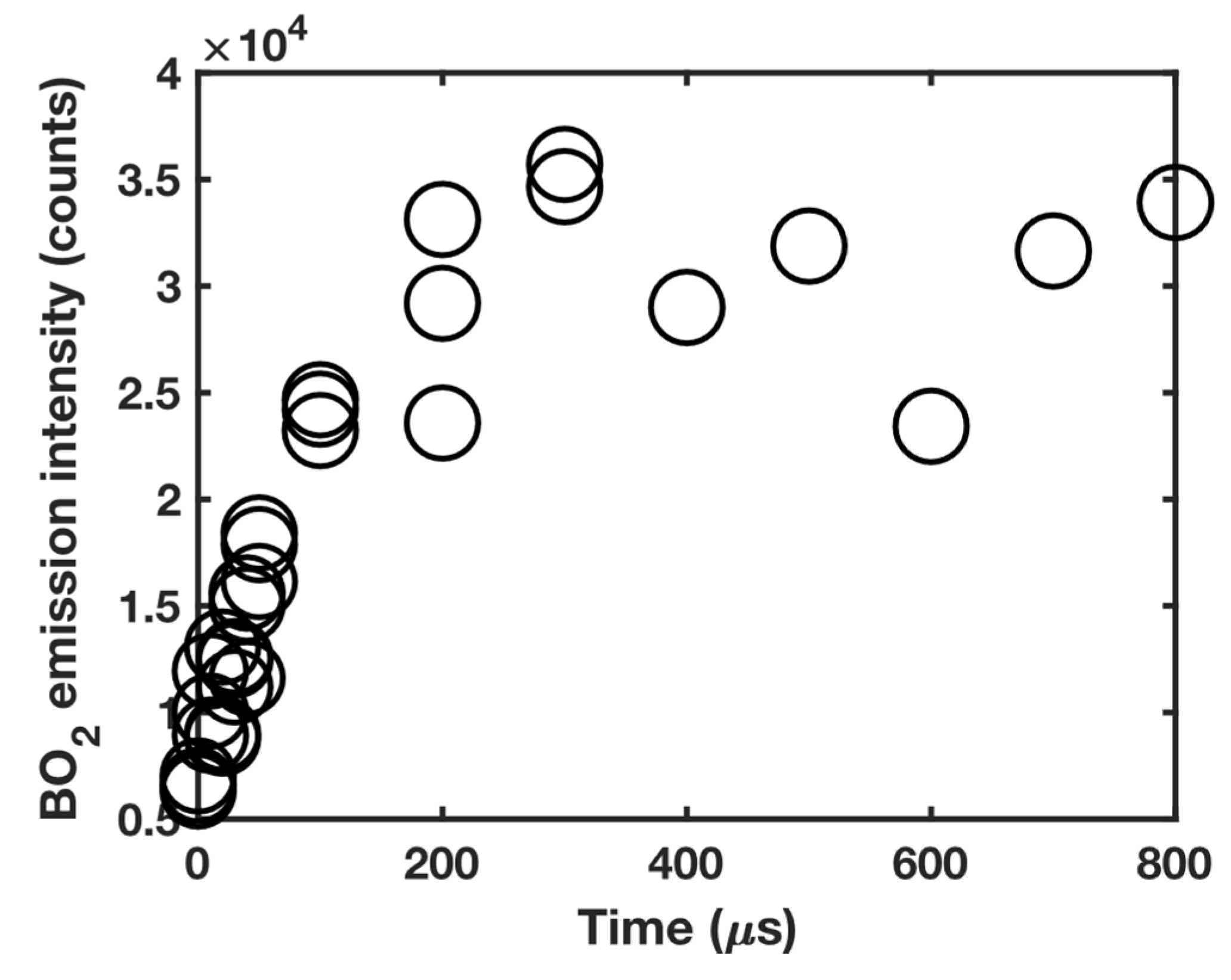
3.1. 11B and 10B isotope detection
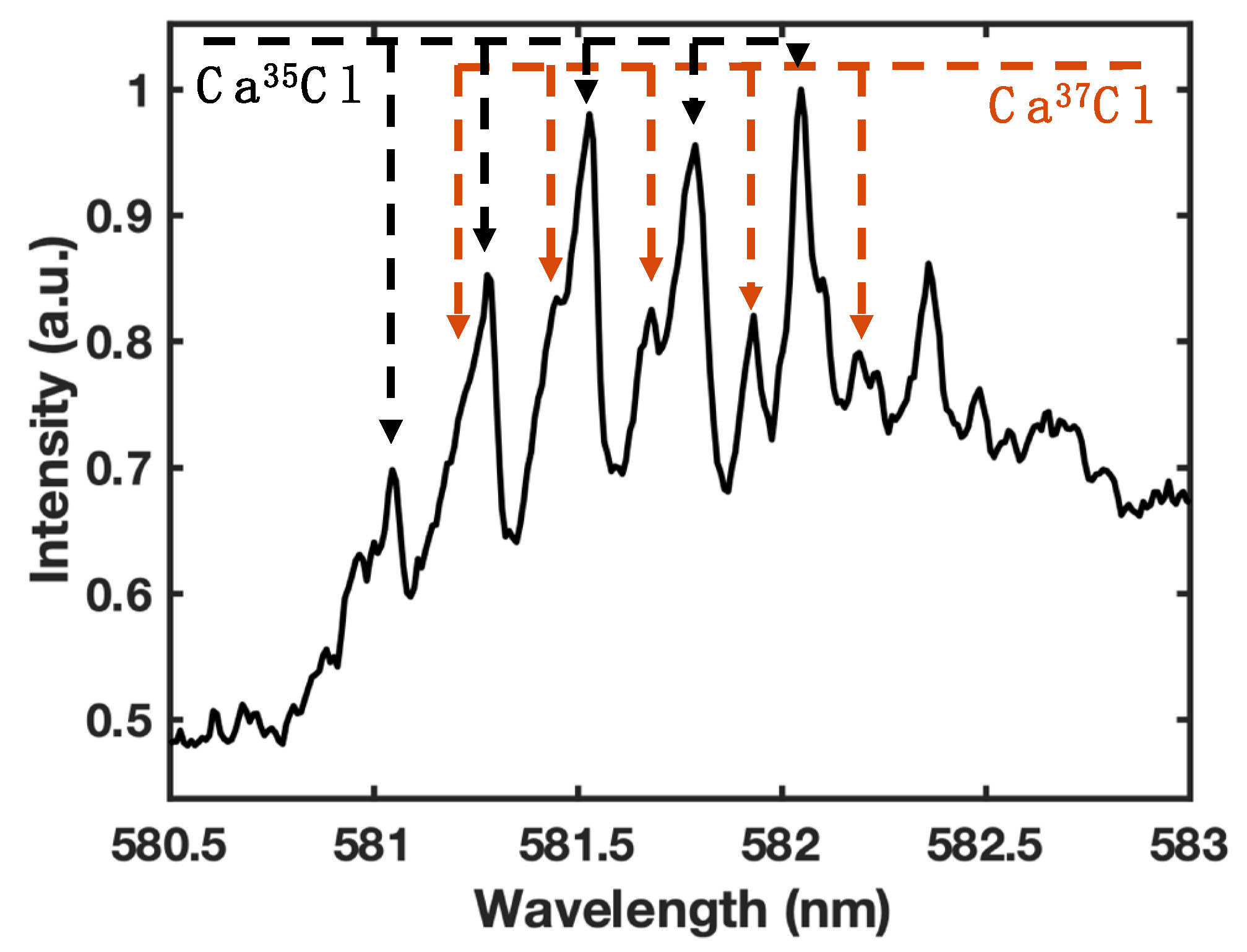
3.2. 35Cl and 37Cl isotope detection
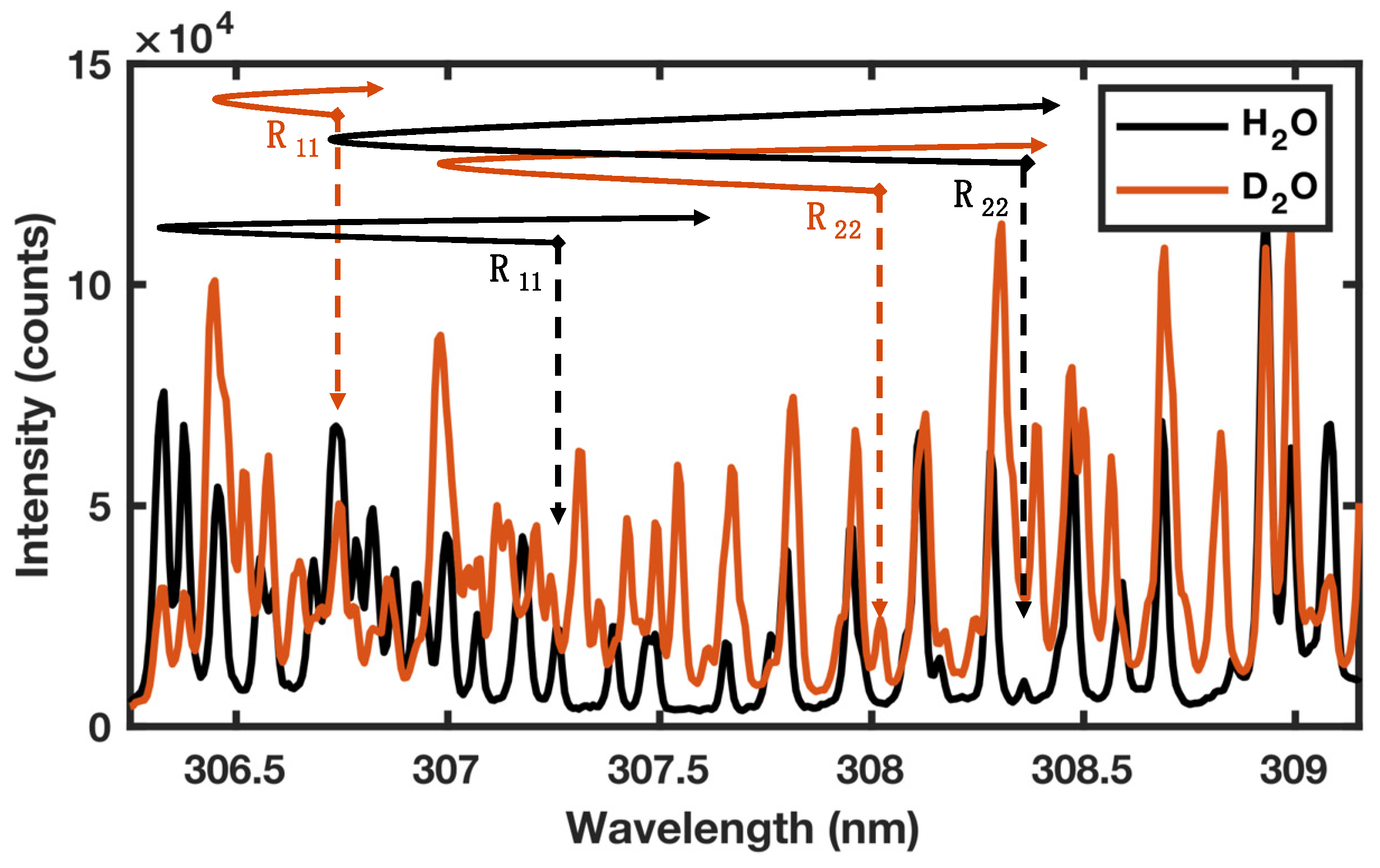
3.3. 1H and 2D isotope detection
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hahn, D.W.; Omenetto, N. "Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), part II: review of instrumental and methodological approaches to material analysis and applications to different fields." Applied spectroscopy 66, no. 4 (2012): 347-419. [CrossRef]
- Hahn, D.W.; Omenetto, N. "Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), part I: review of basic diagnostics and plasma—particle interactions: still-challenging issues within the analytical plasma community." Applied spectroscopy 64, no. 12 (2010): 335A-336A. [CrossRef]
- Guezenoc, J.; Gallet-Budynek, A.; Bousquet, B. "Critical review and advices on spectral-based normalization methods for LIBS quantitative analysis." Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy 160 (2019): 105688. [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Perry, D.L.; Bol'shakov, A.A.; Russo, R.E. "Laser ablation molecular isotopic spectrometry for rare isotopes of the light elements." Spectroscopy 29, no. 6 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Menéndez, L. J.; Méndez-López, C.; Abad, C.; Fandino, J. González-Gago, C.; Pisonero, J.; Bordel, N. "A critical evaluation of the chlorine quantification method based on molecular emission detection in LIBS." Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy 190 (2022): 106390. [CrossRef]
- Moros, J.; Laserna, J. "Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) of organic compounds: A review." Applied Spectroscopy 73, no. 9 (2019): 963-1011. [CrossRef]
- Russo, R. E.; Bol'shakov, A.A.; Mao, X.; McKay, C.P.; Perry, D.L.; Sorkhabi, O. "Laser ablation molecular isotopic spectrometry." Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy 66, no. 2 (2011): 99-104. 10.1016/j.sab.2011.01.007.
- Bol'shakov, A.A.; Mao, X.; González, J.J. ; Russo; R. E. "Laser ablation molecular isotopic spectrometry (LAMIS): current state of the art." Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry 31, no. 1 (2016): 119-134. [CrossRef]
- Dong, M. ; Mao,X.; Gonzalez, J.J.; Lu, J.; Russo, R.E. "Carbon isotope separation and molecular formation in laser-induced plasmas by laser ablation molecular isotopic spectrometry." Analytical chemistry 85, no. 5 (2013): 2899-2906. [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Mao, X.; Chan, G.C.Y.; Russo, R.E. "Laser ablation molecular isotopic spectrometry of water for 1D2/1H1 ratio analysis." Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy 88 (2013): 46-53. [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Chan, G.C.Y.; Choi, C.; Zorba, V.; Russo, R.E. "Combination of atomic lines and molecular bands for uranium optical isotopic analysis in laser induced plasma spectrometry." Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry 312 (2017): 121-131. [CrossRef]
- Silverman, S.N. , Phillips, A.A.; Weiss, G.M.; Wilkes, E.B.; Eiler, J.M.; Sessions, A.L. "Practical considerations for amino acid isotope analysis." Organic Geochemistry 164 (2022): 104345. [CrossRef]
- Di, Y.; Krestianinov, E.; Zink, S.; Amelin, Y. "High-precision multidynamic Sr isotope analysis using thermal ionization mass spectrometer (TIMS) with correction of fractionation drift." Chemical Geology 582 (2021): 120411. [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, J.; Nemchin, A.A.; Kinny, P.D.; Martin, L.; Aleshin, M.; Roberts, M.P.; Ireland, T.R.; et al. "Strontium isotope analysis of apatite via SIMS." 1: Chemical Geology 559 (2021): 119979. [CrossRef]
- Vanhaecke, F.; Degryse, P. (Eds.) Isotopic analysis: fundamentals and applications using ICP-MS. John Wiley & Sons, 2012.
- Bol'shakov, A.A. ; Mao, X,; Russo, R.E. "Spectral emission enhancement by an electric pulse for LIBS and LAMIS." Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry 32, no. 3 (2017): 657-670. [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Bol'shakov, A.A.; Perry, D.L.; Sorkhabi, O.; Russo, R.E. "Laser ablation molecular isotopic spectrometry: parameter influence on boron isotope measurements." Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy 66, no. 8 (2011): 604-609. [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Han, S.C.; Lee, J.; Yun, J. "Isotope analysis of iron on structural materials of nuclear power plants using double-pulse laser ablation molecular isotopic spectrometry." Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry 36, no. 6 (2021): 1287-1296. [CrossRef]
- Wakil, M.A.; Alwahabi, Z.T. “Gated and non-gated silver detection using microwave-assisted laser induced breakdown spectroscopy.” Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 36(1), (2021):185-193. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Baudelet, M.; Richardson, M. “Elemental analysis by microwave-assisted laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: Evaluation on ceramics.” Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 25(8), (2010): 1316-1323. [CrossRef]
- Khumaeni, A.; Motonobu, T.; Katsuaki, A.; Masabumi, M.; & Ikuo, W. ”Enhancement of LIBS emission using antenna-coupled microwave.” Optics Express, 21(24), (2013): 29755-29768. [CrossRef]
- Oba, M.; Miyabe, M.; Akaoka, K.; Wakaida, I. ”Development of microwave-assisted, laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy without a microwave cavity or waveguide.” Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 59(6), (2020): 062001. [CrossRef]
- Wall, M.; Sun, Z.; Alwahabi, Z.T. . Quantitative detection of metallic traces in water-based liquids by microwave-assisted laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Optics Express, 24(2), (2016): 1507-1517. [CrossRef]
- Viljanen, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Toivonen, J.; Alwahabi, Z.T. ”Real-time release of Na, K and Ca during thermal conversion of biomass using quantitative microwave-assisted laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy.” Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 149, (2018): 76-83. [CrossRef]
- Viljanen, J.; Sun, Z.; Alwahabi, Z.T. ”Microwave assisted laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy at ambient conditions.” Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 118, (2016): 29-36. [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Ofosu, J.A.; Wakaida, I. ”Development of microwave-enhanced fibre-coupled laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for nuclear fuel debris screening at Fukushima.” Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 171, (2020): 105933. [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Soriano, J.K.; Kawahara, N. and Wakaida, I. "Spatially and temporally resolved plasma formation on alumina target in microwave-enhanced laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy". 1: Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy 197 (2022): 106533. [CrossRef]
- Wakil, M.A.; Alwahabi, Z.T. “Quantitative fluorine and bromine detection under ambient conditions via molecular emission.” Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 35(11), (2020): 2620-2626. [CrossRef]
- Wakil, M.A.; Alwahabi, Z.T. Microwave-assisted laser induced breakdown molecular spectroscopy: quantitative chlorine detection. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 34(9), (2019): 1892-1899. [CrossRef]
- Alamri, A.M.; Viljanen, J.; Alwahabi, Z.T. ”Properties of Microwave-Assisted Laser-Induced Breakdown Plasma.” Spectrochim. Act. B Submitted.
- Chen, S.J.; Iqbal, A.; Wall, M.; Fumeaux, C.; Alwahabi, Z.T. “Design and application of near-field applicators for efficient microwave-assisted laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy.” Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 32(8), (2017): 1508-1518. [CrossRef]
- Akpovo, C.A.; Helms, L.; Profeta, L.T.; Johnson, L. “Multivariate determination of 10B isotopic ratio by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy using multiple BO molecular emissions.” Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy. 162 (2019): 105710. [CrossRef]
- Amiri, S.H.; Darbani, S.M.R.; Saghafifar, H. "Detection of BO2 isotopes using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy." Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy 150 (2018): 86-91. [CrossRef]
- Berglund, M.; Wieser, M.E. "Isotopic compositions of the elements 2009 (IUPAC Technical Report)." Pure and applied chemistry 83, no. 2 (2011): 397-410. [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.A.; Arthur, J.S. "The stable-chlorine isotope compositions of natural and anthropogenic materials." Reviews in mineralogy and geochemistry 55, no. 1 (2004): 231-254. [CrossRef]
- Pirali, T.; Serafini, M.; Cargnin, S.; Genazzani, A.A. "Applications of deuterium in medicinal chemistry." Journal of medicinal chemistry, vol. 62, no. 11, (2019) 5276-5297. [CrossRef]
- Atzrodt, J.; Derdau, V.; Kerr, W.J.; Reid, M. "Deuterium-and tritium-labelled compounds: applications in the life sciences." Angewandte chemie international edition, vol. 57, no. 7, (2018): 1758-1784. [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, D.A.; Miller, A.I. "The CECE alternative for upgrading/detritiation in heavy water nuclear reactors and for tritium recovery in fusion reactors." Fusion technology, vol. 28, no. 3P1, (1995) 748-754. [CrossRef]
- Stark, G.; Brault, J.; Abrams, M. "Fourier-transform spectra of the A 2 Σ+–X 2 Π Δv= 0 bands of OH and OD," JOSA B, vol. 11, no. 1, (1994): 3-32. [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.U.; Han, S.C.; Yun, J.I. “Hydrogen isotopic analysis using molecular emission from laser-induced plasma on liquid and frozen water.” Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 162 (2019): 105716. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




