1. Introduction
Balance in diet, sleep and physical activity are so crucial to maintain homeostasis. But, continued overeating and prolonged sleep deprivation may change the metabolism of the body and finally it may lead to obesity as both sleep and eating are partly regulated by common neural mechanisms.[
1] Energy homeostasis is the balance between food intake and the energy expenditure, but when it gets disrupted it results as an altered homeostatic response which leads to abnormal metabolism (
Figure 1). Some of the other comorbid conditions such as genetic, endocrine and nutritional deficiencies may further induce obesity.[
2] Environmental and lifestyle processes including diet, exercise, light, temperature, etc. regulates energy homeostasis and modulates the decision of energy consumption or storage.[
3] Although exercise and regular physical activity promotes sleep quality, excess sleep in absence of physical activity leads to less energy expenditure causing metabolic disorders including obesity.
Sleep is an essential physiological phenomenon that is intricately related and crucial to the normal functioning of all the metabolic and physiologic processes. The ability to fall asleep, the quality and quantity of sleep for an adequate period of time daily carries utmost importance to ensure optimal health and overall wellbeing. Loss of sleep is among the common symptoms seen in several neurological, cardiovascular, respiratory, and metabolic dysfunctions which includes hypertension, diabetes, obesity, Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), mood disorders, depression, narcolepsy, epilepsy, cognitive impairment, infections, immune dysfunction and other associated disorders, .
[1-3] The deprivation or fragmentation of sleep reduces sleep quality and duration which in turn can enhance the risk of mental stress.[
7] This stress thereby directly or indirectly influences several processes including eating behavior and other metabolic processes which may cause weight gain, increase in adiposity and its related anomalies.[
7] Thus, sleep discipline corroborates healthy living, ensures disease-free living and strikes a balance between sleep and wakefulness that is crucial for the maintenance of homeostasis. Many sleep disorders such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), restless legs syndrome (RLS) insomnia, and narcolepsy are induced by the modern lifestyle which influences the sleep quality and duration.[
8]
A strong correlation exists between the sleep disorders and obesity which needs immediate consideration. In the present review, we will elaborate upon the phenomenon of homeostasis and its importance. Obesity as a result of disturbance in homeostasis, sleep loss causing perturbed homeostasis, the crosstalk between sleep and obesity and finally the pharmacological interventions that would benefit sleep or its loss mediated metabolic disorders including obesity (
Figure 2).
2. Maintenance of homeostasis
Every living cell tries to maintain stability and constancy to function properly. The balance between acidity and alkalinity and regulation of body temperature are few examples of homeostasis. It works in maintaining the stability of the organism’s internal environment in response to fluctuations in external environmental conditions. There are three key components required to maintenance the homeostasis, a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.[
9] Irrespective to the unicellular organism to the multicellular plants and animals, an intricate metabolic system is regulated by chemical reactions that maintains its internal process independent of the external environment and this mechanism is called homeostasis.[
10] Homeostatic processes are practiced across a wide range that includes the cell, the tissue, the organ, as well as at the organism. At least three interdependent components are essential for the homeostatic control mechanism for any variable being regulated. The receptor is the sensing component that detects and responds to any change in the environment. When a stimulus is senses by the receptor, it sends information to the nucleus, which sets the range at which the variable is maintained.[
11,
12] The stimulus specific response is determines at the level of nucleus. The nucleus then sends signals to an effector site, which can be other cells, tissues, organs, or any distinct structures that receive signals for homeostasis.[
13] After receiving the signal, a corrective change occurs to counter the deviation by depressing or damping it by utilizing negative feedback. The classical view of homeostasis is that it is maintained by signals from the endocrine and autonomic nervous systems. Kotas et al. used the recent approach of ‘stock and flow model’ to explain homeostasis in humans.[
11,
14] They studied homeostasis primarily concerning systemically regulated variables for instance plasma glucose level and core body temperature at the cellular level within tissues. Therefore, while blood glucose level is maintained by insulin, glucagon, and catecholamines, level of glucose in skeletal muscle is simultaneously monitored by intracellular sensors and its homeostasis is maintained through regulated expression of glucose transporters and activity of metabolic pathways of glucose utilization.[
15,
16]
Another example for homeostasis is the drive to sleep in response to the duration of wakefulness. It is seen that when there is more sleep deprivation happening then as an outcome, periods of deeper sleep are observed. This is because
sleep deprivation requires compensatory rebound sleep. Prolonged sleep deprivation would exhaust energy and interfere with the alertness and ability of physical performance ultimately leading to disturbance in the energy homeostasis.[
17]
Amongst the several brain centers and theories proposed to explain the sleep and energy balance, the most widely accepted is the circadian rhythm.[4-6] The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus is the dominant loci of the mammalian circadian cycle. The SCN is the recipient of dense retino-hypothalamic innervation and functions as part of the larger visual system.[
21]
The SCN, consequently, provides inputs to the hypocretin-producing neurons in the hypothalamus that are primarily relayed via the subparaventricular area and the dorsomedial nucleus.[
22]
These neural innervations are important to the regulation of sleep-wakefulness balance and metabolism as well because the hypocretin-producing neurons target many wake-promoting regions. SIRT1, a member of the sirtuin family, released by the pre-opiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons of the hypothalamus is involved in fine-tuning the balance between the dietary intake and the expenditure of energy especially when a high calorie-diet is administered. It works in close association with the satiety hormone leptin, to prevent obesity development.[
23]
SIRT1 also fortifies neurons and their synaptic functions, thereby playing a neuroprotective role against neurodegenerative disorders, such as PD and AD. In PD it aids in alpha-synuclein clearance and in AD it impedes tau degradation and consequently prevents the formation of neurofibrillary tangles. SIRT1 promotes neurogenesis and increases cellular lifespan by inhibiting inflammatory mechanisms and abating oxidative stress.[
24,
25]
In case of chronic sleep restriction, plenty of food intake occurs due to altered pattern of appetite regulatory hormones which contributes to weight gain.[
17]
Thus, sleep homeostasis is essential to the maintenance of metabolic homeostasis and therefore loss of sleep may lead to dysregulation of myriad pathways.
2.1. Disturbance in homeostasis and obesity
The fundamental reason of obesity is abnormality in the mechanism of energy balance. In other words, obesity basically develops when energy intake is more than energy expenditure and differences in input and output are buffered primarily by changes in the fat stores.[
26] Understanding the fundamental of dynamic monitoring of balance between intake and expenditure is a longstanding challenge in elementary biology. Inadequacy of the intake and the expenditure of food is insufficient to explain obesity; however, a robust, holistic and integrative approach is needed to address this emerging, global issue.
There are two key rules of occurrence of obesity: (1) the intake must be more than the expenditure; (2) higher energy expenditure then the lean subjects which in turn leads to higher average energy intake..[
27] The higher energy expenditure induces additional energy intake which leads to greater body mass. The difficulty in manipulating body mass for longitudinal energy balance studies in humans with precision has been a key reason for the extensive focus on animal models, and specifically on laboratory rodents. Several such models are available, including those in which obesity is induced by dietary manipulation (e.g., high-fat diet, severe vitamin B12 deficient diet), endocrinological administration (e.g., corticosteroid or neuropeptide Y administration), surgery (e.g., lesions of the ventromedial hypothalamus), chemical manipulation (e.g., gold thioglucose administration) or through transgenics (e.g., uncoupling protein 1, 11b-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-1 and melanocortin-4 receptor knockouts).[
28,
29] Several studies have demonstrated the irrefutable association between the dietary intake and obesity. Ghosh et al. showed that severe vitamin B12 deficiency is positively correlated with body fat % and visceral adiposity in the vitamin B12 deficient C57BL/6 mice model.[
28,
29] They also showed that vitamin B12 deficiency increases oxidative stress and alters epigenetic factors.[
30] Sucrose consumption, on the other hand, did not show such a correlation with epigenetic changes (DNA methylation) in neurogenesis-inducing genes.[
31,
32] A calorie-restricted diet increases longevity by decreasing DNA damage and indirectly, helps us understand the crosstalk between obesity and ageing.[
2,
33] The WNIN/Ob is a novel rodent model that was developed recently to elucidate the role of oxidative stress in hastening senescence in obese rats.
[7-11]
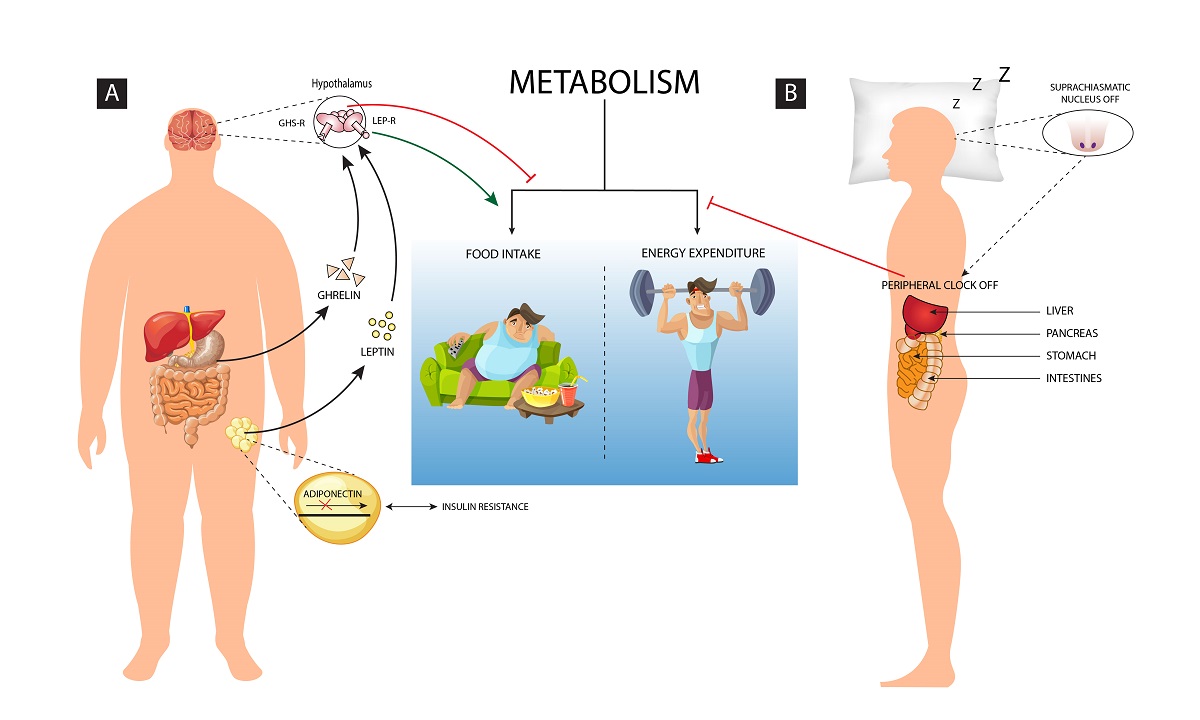
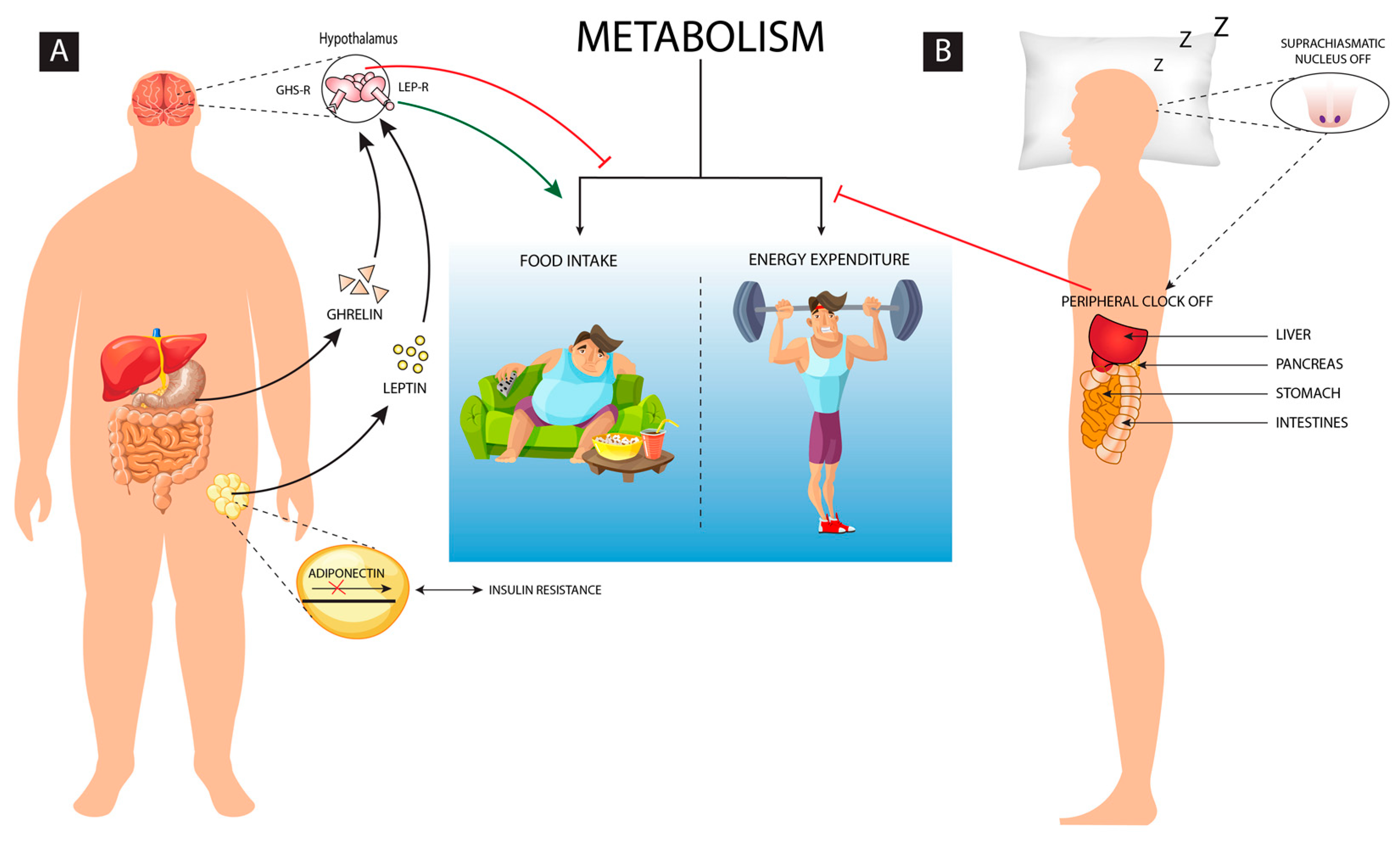
The adipose tissue produces biologically active molecules known as adipocytokines, which are the protein hormones actively involved in the regulation of energy metabolism, hunger, insulin sensitivity, and so on. During obesity, accumulation of fat causes dysregulation of adipokine production, which becomes the major contributing factor for the onset of obesity and its related diseases. Adiponectin was identified by Scherer et al. as 30-kDa adipocyte complement-related protein (Acrp30) and it is produced by the adipocytes.[
39] According to adiponectin hypothesis, high intake of fat diet can cause reduced adiponectin levels, which, can further lead to decreased adiponectin signaling or disruption of adiponectin receptors may serve as an upstream pathway of increased inflammation in white adipose tissue.[
40] Insulin regulates the secretion of adiponectin by enhancing its level. Obesity can lead to hypertrophic adipocytes which can cause obesity-linked insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. The decrease in expression of the adiponectin receptors (AdipoR1/R2) mRNA reduces adiponectin binding capacity, and this leads to an attenuation of the adiponectin effects. Thus, adiponectin resistancealong with insulin resistance forms a vicious cycle which triggers weight gain. Reduced Adiponectin level exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-atherogenic properties by inducing the vascular endothelial nitric oxide production which in turn disturbs thehomeostasis.[
41]
A common neural network regulates the feeding as well as the quantity and quality of sleep, which facilitates adequate adjustment as per the varying environmental conditions. The interaction of genetic, environmental and behavioral factors decides body adiposity and thus energy balance is established and maintained. Human sleep is oppositely altered if the energy balance and the metabolic fuel availability are changed.[
42] Inadequate sleep can influence the energy homeostasis leading to impaired regulation of energy intake and expenditure. Disturbances in sleep modifies metabolic patterns of an individual leading to countering behavioral response by overeating and food storage. Sleep ensures 20–30% reduction in metabolic rate as during sleep less energy is consumed to sustain vital functions of the body and it helps in maintaining energy homeostasis. The homeostasis system gets activated when energy expenditure exceeds the food intake, which may threaten body-stored food. The neuroendocrine, metabolic and behavioral changes in synergy with the lower leptin and higher ghrelin level increases hunger anticipating the loss of body weight. [
43,
44] Sleep deprivation changes the regulation pattern of the energy homeostasis, thus creating a negative energy balance. Furthermore, the signs of negative energy balance with reduced sleep condition and increased appetite is responded by reducing the insulin of anorexigenic and increasing the ghrelin of higher orexigenic level, as well as slowing the sympathetic and metabolic rate to conserve energy.[
45] Thus, sleep homeostasis is essentially linked with metabolic homeostasis to avoid obesity and its related disorders.
Sleep disturbance and obesity are two crucial conditions which may significantly influence homeostasis. The disturbance in sleep-wake behavior and energy homeostasis are reciprocally associated.[
42] In humans, ATP sensitive potassium channel (SUR2), a human gene encoding subunit has been identified which reciprocally links the cellular energy balance and the sleep variability.[
46] As evident in animal models, sufficient food in rodents promotes sleep while food deprivation leads to increased phase of arousal, probably to search for food and reach to the energy balanced state. The hypocretin/orexin neurons are primarily active to facilitate such energy homeostasis states in sleep deprived conditions.[
47] Sleep loss is compensated by high metabolic expenditure as it induces neuroendocrine, metabolic and behavioral equilibrium by enhancing food intake and energy conservation. Spiegel et al. documented that two nights of insufficient sleep and reduced caloric intake of 1500kcal/day for control participants of body weight of 75kg, can lead to reduced plasma leptin and increased ghrelin concentration along with increased appetite.[
48] Thus, sleep deprivation signals for excessive food intake, reduced resting energy expenditure, and limited physical activity, leading to weight gain or obesity.[
42] However, majority of the studies associating sleep disturbance and homeostasis are based on short duration of sleep loss ranging from few hours to few days, which need to be further tested for longer duration of sleep disturbances.
2.2. Lack of exercise leads to disturbed homeostasis and obesity
Maintenance of a stable and constant internal environment by opposing the changes happening outside is called homeostasis. Changes in temperature of the body and concentration of ions, pH and glucose in the blood streams kept in check through homeostasis regulations.[
49] This process happens at many levels, from maintaining acidic pH by the stomach to maintaining ion concentration by each cell of our body. Homeostasis is very crucial for maintaining overall body functions. Homeostasis is maintained through negative feedback loops which resist any cue or stimulus that activates them. During exercise, when muscles produce heat which increases the body temperature, then the negative feedback loop will start functioning and it will bring back the body temperature to the normal set point.[
50] Hence, temperature which is a stimulus perceived by body sensors basically having nerve endings in the skin or the brain which sends the signal to the hypothalamus which is a center of temperature regulation in the brain, as a result effector which is a sweat gland counter the stimulus by decreasing the body temperature. Like these, there are two types of negative feedback loops present in our body to maintain homeostasis, one which activates when the body temperature rises above the set point and other switch on when the body temperature drops below the set point to bring them to the normal. For example, when body temperature falls during winter, blood vessels constrict and shiver, which is an involuntary contraction of muscles that produces heat to warm the body and brings back to the normal body temperature (original set point). Similarly, during excessive exercise, when the body temperature increases, blood vessels dilates and heat loss occurs in the environment and the sweat glands secrete fluids to cool down back to the normal body temperature (original set point) [
50]. Although, body set point is not always fixed, for example, during 24 hours, the body temperature will be highest during afternoon whereas, lowest during night.
In total, homeostasis mechanisms depend heavily on proper functioning of the negative feedback loop. Slight disturbance in the negative feedback mechanism leads to disruption of the homeostasis. In metabolic disease like Diabetes, hormone insulin causes breaking of this negative feedback loop involved in maintaining homeostasis.[
51] As a result, it is impossible to bring back the high blood sugar level to normal in the Diabetes. Similarly, obesity also leads to imbalance in the negative feedback loop. Insulin and leptin resistance in the central nervous system is also an indication of homeostasis dysregulation in obesity.[
52] One of the reasons for being overweight is lack of exercise. In obesity, due to no activity, unused energy gained through food we eat generally stores as fat. Hence, regular exercise keeps high energy outflow and which assists in maintaining energy balance and finally weight loss. Hence, exercise not only activates the sympathetic nervous system, but also helps in homeostasis regulation and due to which high physical activity leads to increased cardiovascular, respiratory and metabolic requirements.
3. Obesity as a disturbance in the physiology
The fundamental mechanism for regulation of obesity is based on appetite, energy expenditure, gene regulation and endocrine factors, which explain the biological basis of obesity. Gower et al. reported the physiologic basis of obesity in African-American (AA) women by stating that insulin sensitivity and glycemic load are the primary cause of obesity.[
53] They further explained that the AA women have high beta-cell responsiveness, low hepatic insulin extraction, and relatively high insulin sensitivity, which lead to high exposure of insulin to tissues and organs. High glycemic diet induces increased insulin secretion which diverts energy production to storage.[
54] Disproportionate insulin secretion to insulin sensitivity was noted in all cases of AA. When the acute insulin response to glucose (AIRG) was plotted across insulin sensitivity, higher AIRG in AA was observed then European American (EA) women at any given level of insulin sensitivity.[
55] Thus, higher insulin secretion among AA women is not simply a compensatory response for insulin resistance, but it also results in a higher tonic level of “insulin action.” Insulin is a highly lipogenic hormone and therefore, hypothesis of ‘higher insulin action could promote fat deposition’ appears reasonable.[
56] Hence, fat cells are beneficial which stores lipid inside. However, if fat cells become insulin resistant, then lipid come out of fat cells and rise in the circulations. Regular exercise and proper sleep can help to stay lipid inside the cells and helps in improvement of physiology in obese patients.
The endocrine control of obesity is also richly documented in the obesity literature.[
57] Eikilis et al. identified a direct correlation between plasma leptin concentration and adiposity in humans.[
58] The function of leptin is to maintain energy balance by regulating food intake and caloric burn rate. An increase in leptin synthesis or decrease in leptin clearance or both could be the reason for the increase in plasma leptin concentration in obesity. Studies are documented which precisely determined the leptin plasma kinetics.[
59] It is commonly agreed that endogenous leptin production rate increases with increase in adiposity.
An increase in size of Adipocytes is reported due to the accumulation of triglyceride which leads to increased synthesis of leptin.[
58,
60]
Leptin's impact on body weight are regulated via hypothalamic centers that control eating behavior and energy expenditure. In the year 1994, the gene responsible for obesity in human (OB Gene) and its product leptin were identified and characterized by Zhang
et al.[
61] Primarily, leptin is secreted from the adipose tissue and it binds through leptin receptors which are expressed at the hypothalamus and the cerebellum.[
62,
63] The adipose tissue releases Leptin into the circulatory system as it crosses through the blood-brain barrier and the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) and reaches the brain and binds to the hypothalamic leptin receptors and signals about the storage of body energy.[
64] This lead to reduced food intake and enhanced energy expenditure to maintain the size of the body fat stores.
[12-16] Similarly, in humans ghrelin, the other hormone, which is actively involved in the regulation of obesity, was primarily obtained from the stomach, however, ghrelin-releasing neurons have also been identified in the pituitary and the hypothalamic regions.
[17-19] Ghrelin binds through growth hormone receptors which are found in the pituitary and the hypothalamus.[
73] The production of ghrelin by the stomach depends on the increase in the level before food intake and its subsequent decrease.[
74,
75] Indeed, impact of Leptin and Ghrelin on energy homeostasis is contrasting in nature. Leptin enhances weight loss by suppressing the diatery intake while ghrelin acts as an appetite stimulator.[
76,
77] Leptin and ghrelin have varying effects on the hypothalamic neurons, producing an opposite effect on the energy balance.[
78] Thus, obesity as a physiological imbalance can be caused due to the disparity between these essential metabolic hormones. Obesity is linked with lack of sleep. Insufficient sleep enhances overeating and unhealthy food choices which leads to abnormal hormone production. Sleep is important in regulation of hormone levels which include leptin and ghrelin hormone levels.
Furthermore, to explain the sympathetic activation during obesity, many mechanisms have been proposed. It has been suggested that increases in sympathetic tone are due to the state of insulin resistance, as it has been documented that high levels of insulin may increase sympathetic nerve traffic in man. Eikelis et al. and others found that renal norepinephrine spillover, indicative of renal sympathetic activity, is approximately doubled, while cardiac sympathetic activity is reduced.[
58,
60,
79] This renal sympathetic activation appears to be a primary pathophysiological mechanism of obesity-related hypertension; that is, the hypertension is ‘neurogenic’ in this case. Even when unaccompanied by elevated blood pressure, human obesity is characterized by sympathetic nervous activation.[
80] The higher renal and lower cardiac sympathetic nerve activity in overweight individuals represents a differentiation of CNS sympathetic outflow, with increased traffic in the renal sympathetic nerves and reduced cardiac sympathetic nerve firing. The hyperleptinemia accompanying human obesity is another candidate for activation of the renal sympathetic outflow, given that administration of leptin in experimental animals increases renal sympathetic activity.[
81] Therefore, a complex interaction occurs amongst neuro-endocrine mechanisms to regulate the physiology and conditions like obesity. Weight gain and obesity is the outcome of insulin resistance due to increased sympathetic output which leads to different sleep disorders.
4. Physiology of sleep
Sleep is an essential physiological phenomenon characterized in evolutionary higher species. Although we are yet to uncover the question as to why we sleep, we know for a fact that sleep conserves energy and adjusts the organism to environmental factors to maintain homeostasis.[
82] Directly or indirectly Sleep directly or indirectly impacts or gets influenced by several physiological processes that are controlled by the brain. Also, sleep is imperative for the maintenance of several other functions like neuroplasticity, memory formation, energy maintenance, neuro-protection, etc. Sleep is not a homogenous phenomenon. Electrophysiologically, sleep has been classified into rapid-eye-movement (REM) sleep and non-REM (NREM) sleep. Rapid movements of the eye, increased brain activity and loss of muscle tone characterize REM sleep. It is known to perform as the housekeeping functions of the brain and thus maintains brain excitability.[
83] It is highest in newborn babies which signifies its importance in brain development, however, the quantity of REM sleep reduces with age but it is never absent in life.[
84,
85] In the context of function, REM sleep is extremely important for brain development. REM sleep facilitates the formation and consolidation of different types of memory through the regulation of neuronal synapses by selective elimination. In addition, REM sleep facilitates cortical plasticity and restoration of aminergic cell/receptor function. Loss of REM sleep is associated with several pathophysiological conditions which include Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, memory loss, schizophrenia, epilepsy, narcolepsy, psychiatric disorders, etc.
[1-3]
There are many chemicals involved in the regulation of REM sleep and one of the key molecules is the neurotransmitter noradrenaline (NA), a catecholamine in chemical nature. The locus coeruleus (LC)-NAergic neurons are mainly responsible for supplying NA throughout the brain.[
86] The NA-ergic neurons in the brainstem are active during wake and inactive during REM sleep. A continuous firing of these neurons is observed during REM sleep loss.[
87] The levels of NA levels are known to increase upon REM sleep loss, which induces several REM sleep loss related sign and symptoms.[
88]
Since the discovery of REM sleep in 1953, by Aserinsky and Kleitman[
89], first time observed the periods of ‘active’ sleep were marked by rapid eye movements in human infants, there have been several attempts to understand the molecular mechanisms, genesis, regulation and functional significance of REM sleep. Methods like sleep deprivation or REM sleep deprivation (REMSD), lesions, brain microinjections, electrical stimulation have been done to gain insights into the significance and regulation of this physiological phenomenon. It was shown that these active REM sleep periods alternate with latent sleep intervals. Kleitman and Dement reported that the rapid eye movements in human adults were associated with specific neural activation patterns of brain and dreams that occurred during rapid eye movements phase of sleep.[
90,
91] Later, Jouvet discovered REM sleep in cats and showed that like humans, cats also experience rapid eye movements which occur in conjunction with lack of muscle tone, muscle twitches and awake-like cortical activity.[
92] In humans, REM sleep constitutes a smaller portion of our sleep and the amounts of daily REM sleep vary across species. It varies due to several external factors like temperature, light and also gets affected by lifestyle, diet, age and changes with environmental and ecological pressure.[
93]
In addition to NA-ergic neurons, it has been observed that cholinergic neurons in LC-alpha, peri-LC-alpha, laterodorsal and pedunculopontine tegmental nuclei help in REM sleep generation.[
94] Among these nuclei, the nucleus pontis oralis is primarily responsible for the generation of active sleep. The ventral nucleus pontis oralis receives cholinergic afferent fibers from rostral peri-LC-alpha, laterodorsal tegmental nuclei, pedunculopontine tegmental nuclei, parabrachial nuclei and gamma-amino butyric acid-ergic fibers from the posterolateral hypothalamus.[
95] These interactions are crucial for the modulation of REM sleep. The ventral portion of the sublaterodorsal nucleus of pons contains spinally projecting neurons that produces motor atonia (natural loss of muscle tone that accompanies REM) during REM sleep.
Sleep centers in the brain also regulate hunger and feeding behavior, which in turn are wakefulness dependent behaviors. The paraventricular nucleus, arcuate nucleus, and dorso- and ventromedial hypothalamus are known to regulate feeding, but the lateral hypothalamus regulates both feeding and sleep-wakefulness cycle.[
96] Furthermore, orexin-ergic neurons synthesize the neurotransmitter orexin located in the perifornical area, in the lateral region of the -posterior hypothalamus, which is active during wakefulness[
97] and essentially regulates appetite[
98]. Vidafar et al. observed that more than half of their subjects that were shift workers reported weight gain after commencing shift work. Higher hedonic appetite correlated with suboptimal sleep quality and duration, propelling the individual towards obesity.[
99] Thus, crucial crosstalk exists between sleep and appetite, which is regulated by the same set of neurons in the brain.
5. Pharmacological tools for the management of sleeping disorders associated with Obesity
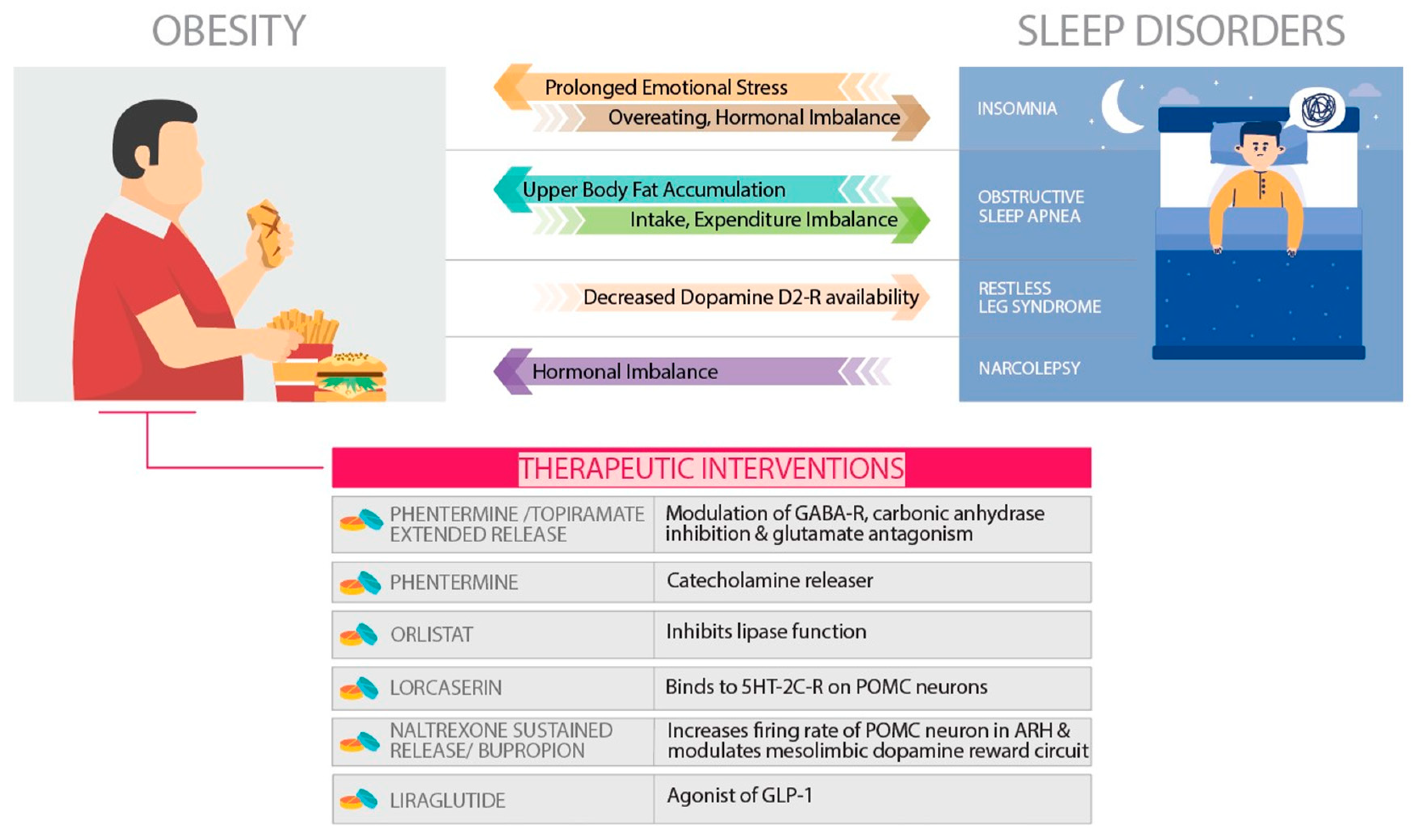
Obesity has emerged as one of the major causal factors for sleep disorder that affects middle-aged men, with a prevalence rate of up to 10-17%.[
100] Several studies have been documented that self-reported sleep of less than 6-7 hours per night can increase the risk of obesity. Most common sleep disorders are insomnia, obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), narcolepsy, and restless leg syndrome (RLS). These sleep disorders will be described here briefly and their relationship with obesity along with their pharmacological interventions will be understood.
5.1. Anti-obesity Pharmacotherapy
Anti-obesity pharmacotherapy is one of the robust strategies to counter the adaptive metabolic changes in response to the lifestyle-based interventions by manipulating the appetite and energy expenditure homeostasis.[
101,
102] The candidacy of pharmacotherapy for obesity is recommended that the body mass index (BMI) be a minimum of 30 kg/m2 or a minimum BMI of 27 kg/m2 for obesity with comorbid conditions such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, type 2 diabetes, or various sleep disorders.[
103,
104] The pharmacotherapy for obesity is recommended for a longer duration to optimize its outcomes.[
105] Phentermine and orlistat were the two drugs that had longer usage history, while recently in 2012, phentermine/topiramate extended-release (ER) and lorcaserin and in 2014, naltrexone sustained-release (SR)/bupropion SR and liraglutide 3.0 mg were approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). In this review, the anti-obesity drugs which are in use since 2010 and approved by the FDA are reviewed.[
106]
5.1.1. Phentermine/Topiramate Extended-Release
Phentermine and topiramate (PHEN/TPM) is a combination drug that contains a catecholamine release (phentermine) and an anticonvulsant (topiramate). Topiramate is currently recommended by the FDA as an anticonvulsant specially for the treatment of epilepsy and the migraine headaches. During clinical trial of Topiramate on Epilepsy, its impact on weight loss was also observed as an unintended side effect. The underlying pharmacotherapeutic mechanism responsible for weight loss in case of PHEN/TPM usage is not clear however, modulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors, inhibition of carbonic anhydrase, and antagonism of glutamate to reduce food intake is widely accepted.[
107] It is developed to minimize the adverse impacts of both agents by constituting acceptable doses in a specified combination formulation. A caution was put forward while approving PHEN/TPM by the FDA, specially during pregnancy as topiramate increases the risk of congenital oral cleft .[
108]
5.1.2. Lorcaserin
This is a well-known selective 5HT-2C receptor agonist, which was approved in 2012 by FDA as a obesity long-term treatment.[
106] It increases satiety and reduces appetite by binding to the 5HT-2C receptors on the anorexigenic POMC neurons of hypothalamus.[
109,
110] The serotonin 2C receptor has selective agonism with lorcaserin and hence it avoids cardiac valvular effects mediated through the 5HT-2B receptors. Research studies show that activation of the serotonin receptor 5-HT2C declines food consumption through the proopiomelanocortin neural system.[
111,
112] Studies involving the nonselective serotonergic agonists fenfluramine and dexfenfluramine (that are known to enhance presynaptic serotonin release and further block its reuptake), validated serotonin receptors to be the pharmacologic targets for significant weight loss.[
113] Nevertheless, usage of such agents enhances the serotonin-associated valvulopathy risk[
114], which is thought to occur through agonism of the 5-HT2b receptors found on cardiac valvular interstitial cells.[
115] It is also known that lorcaserin was devised to selectively activate 5-HT2c receptors in CNS.[
116] Another clinical trial comprising obese individuals, the use of lorcaserin was found to be associated with weight loss in a dose-dependent manner without apparent effects on the heart valves.[
109]
5.1.3. Naltrexone sustained release or Bupropion
In 2014, naltrexone/bupropion had been approved by the FDA for the treatment of obesity.[
106] The two drugs were pre-approved, bupropion is a dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor and it was initially recommended as an antidepressant in 1989 and as a smoking cessation aide in 1997. Naltrexone is an opioid antagonist and it was approved to control opioid dependence in 1984 and alcohol use disorder in 1994. The combination of naltrexone/bupropion influences two different areas of the brain that regulate intake of food.[
108] The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus is the primary region, which regulates appetite. The mesolimbic dopamine reward circuit is the secondary region, by increasing the firing rate of hypothalamic POMC neurons and modulating the dopamine reward circuit, the appetite is reduced.[
117] The POMC neurons in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (ARH; also called the infundibular nucleus) integrate central and peripheral signals related to energy balance and produce a net anorexigenic output[
118] The well-publicized anorectic effect of the hormone leptin is primarily due to the stimulation of POMC cells. POMC cells can become leptin resistant in obesity which may lead to decreased basal activity and a lower anorexigenic drive despite increased adiposity.[
119] Therefore, agents that stimulate POMC signaling are of interest in obesity pharmacotherapy, however efforts employing direct melanocortin agonists are associated with side effects and current clinical experience with monotherapeutic drug approaches has been only modest weight loss which appears to be limited by a therapeutic plateau e.g., bupropion (BUP).[
120]
One of the most important pitfalls of clinical trials investigating pharmacological therapy for sleep disorders is the lack of a consensus on the best variable to use for the classification of OSA severity which can be suitable across age[
121] The apnea/hypopnea index and the oxygen desaturation index (ODI) that are the most common measures for OSA still have limitations to describe its severity.
5.2. Treatment for Sleep disorders
5.2.1. Insomnia and Obesity
Sleep disruption, difficulty in initiation and maintenance of sleep and early rising are the key characteristics of insomnia.[
122] The most acceptable theoretical framework of insomnia on a pathophysiological basis states that hyperarousal and hyperactivity of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) are the main reasons.[
123] Various psychosocially stressful conditions are assumed to be responsible for the initiation of insomnia and it is induced by increased arousal of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis.[
124] The mean secretions of adrenocorticotropic hormone and cortisol are higher during insomnia. Such findings are also supported by positron emission tomography scans in which the cortical regions responsible for awakening utilized more glucose metabolism during the awake period than during night in insomnia patients.[
125,
126]
The literature on obesity suggests that individuals with obesity and insomnia or difficulty of sleep are significantly related.[
127] In obese individuals, history of prolonged emotional stress further influences sleep disturbances, subsequently, the chances of sleep disorders especially insomnia increases. The underlying pathophysiology of insomnia suggests that it induces the overconsumption of energy, which leads to weight gain. Thus, the significance of early identification and intervention of sleep disturbances as a potential approach for obesity management has been identified. Taheri et al. compared compromised sleep duration of 5 hours per night with 8 hours per night and observed that after sleep the leptin level lowered by 15.5% and ghrelin level increased by 14.9%, and based on these observations, concluded that shorter sleep duration could increase appetite which may lead to overeating.[
128] Furthermore, Dallman et al. identified an increased level of glucocorticoids specially cortisol in insomnia that may play a vital role in enhancing the desire of a person to consume a high energy diet.[
129] Therefore, Dallman et al. stated that enhanced levels of glucocorticoid hormones elevate the CRF activity in the central nucleus of the amygdala as it increases stimulus salience, which induces obesity. It also facilitates the metabolic inhibitory feedback that inhibits the catecholamines in the brain and CRF expression. These findings suggest that the hyperactivity occurring in the common pathway of the brain promotes both insomnia as well as the overconsumption of high energy foods which induces abdominal fat deposition leading to obesity.[
129]
5.2.2. Obstructive sleep apnea and Obesity
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common disorder which is caused by periodic partial or complete obstruction of the pharynx during sleep. The prevalence rate of OSA is 2-4% in middle-aged adults and nearly 50% of the obese population. OSA is often associated with several co-morbid conditions such as excessive daytime sleepiness, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, metabolic disorders, and obesity.[
130] The pathogenesis of OSA is multifactorial and complex, thus it is a compelling area of research. One of the major pathophysiological reason of OSA is the upper body obesity, which causes both decreased lung volumes and thus a reduced stabilizing effect on pharyngeal walls as well as lateral fat deposits in the neck. The hypertrophied pharyngeal walls and pharyngeal mucosal edema which narrows the lumen of the pharynx, predispose to OSA.[
131] The collapse of the pharynx leads to recurring hypopnea and apnea associated with arterial oxygen desaturation and arousal from sleep with consequent sleep fragmentation. Till date, there is no clinically established effective pharmacotherapy for OSA. Decoding of the pathogenesis of the disease is essential for successful development of a drug. There are four key pathophysiological mechanisms of OSA: narrowed upper airway, inadequate upper respiratory dilator muscles specially during sleep, lower arousal threshold, and oversensitive ventilatory control. Anatomic predisposition is a crucial pathophysiological factor which triggers OSA and it is accompanied with poor or faulty neuromuscular regulation to compensate adequately for compromised pharyngeal patency during sleep.[
132]
Epidemiological studies suggest OSA and obesity are strongly associated, and based on the BMI status, Malhotra et al. found that more than 70% of people with OSA had co-morbidity of clinically defined obesity.[
133] An association between OSA and obesity has been noted with change impacting the Apnea-Hypopnea Index, a measure of OSA severity.[
130] The explanations of underpinning the connection between obesity and OSA are ever evolving and crosstalk between obesity and OSA exists as both influences each other. Obesity influences the neuromuscular control of the upper respiratory pathway and adipokine production which enhances the development and severity of OSA.[
134] Various vital cytokines related to obesity, especially leptin, restrict the neuromuscular regulation of upper airways leading to compromised respiratory drive.[
135] Accumulation of fat in the thoracic and neck region, can also induce the occurrence of OSA.[
135] Finally, OSA can disrupt the energy intake and expenditure balance thus, leading to an increase in overall body weight.[
134]
5.2.3. Restless leg syndrome (RLS) and obesity
RLS is a sensorimotor disorder with uncontrollable movement of legs triggered by the persistent sensation in the legs, which can interrupt sleep patterns .[
136,
137] The severity of RLS can vary from mild sensation in the legs to severe pain and restriction of movement. RLS at a severe level can impact several activities of daily living.[
138,
139] Besides these, the comorbid conditions along with RLS are delayed sleep onset, interrupted sleep, reduced total sleep time, and compromised slow-wave sleep. The underlying pathophysiology of RLS is not clear. The primary causes of RLS are believed to be dopaminergic and iron metabolism dysfunction as treatment based on these two agents have shown variable success in RLS treatment.[
139]
Several cross-sectional studies have examined the relationship between RLS and obesity.[
140,
141] Thus, establishing a cause-effect relationship between the two is difficult however, a small yet significant relationship between RLS and obesity exists.[
141,
142] Furthermore, a significantly greater BMI in persons with RLS and obesity versus those individuals who were non-obese and have no history of RLS has been observed.[
143] Dopaminergic hypofunction in the central nervous system (CNS) is believed to have a crucial role in disease pathophysiology. Thus, environmental factors, which affect CNS dopaminergic status, may have a role in RLS. Exploring potential associations between these dopamine-related factors and RLS risk could not only improve our understanding of RLS pathogenesis but also provide a practical method for RLS prevention. Obese persons have decreased dopamine D2 receptor availability in the brain and could thus be at increased risk of RLS.[
144] Besides this, those suffering from cardiovascular diseases are at higher risk of both obesity and RLS, based on this it has been suggested that vascular pathology may contribute to RLS.[
127] However, the relationship between obesity and RLS remains uncertain and valid data to assess this hypothesis are limited.
5.2.4. Narcolepsy and Obesity
Narcolepsy refers to an acquired syndrome impacting approximately 1 in 2500 people. It is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, disturbed sleep at night, and REM sleep associated with cataplexy, sleep paralysis, and hallucinations.[
145,
146] Furthermore, , instability of wake-sleep state, impacted onset of REM periods and and disrupted nocturnal sleep are documented.[
147] The neuropeptide hypocretin which is also known as orexin, is critical in promoting wakefulness. Hypocretin-1 is a key modulator of wakefulness, REM sleep and locomotor activity through its actions on aminergic cells including dopamine, norepinephrine, histamine, serotonin, and other neurons.[
148] In humans, low or undetectable levels of hypocretin have been reported in 95% of patients with narcolepsy and cataplexy.[
149] Narcolepsy has been categorized into narcolepsy type I (previously called narcolepsy with cataplexy) and narcolepsy type II (narcolepsy without cataplexy), to incorporate the evolving understanding that the absence of a functional hypocretin system is a fundamental piece of the type I disorder.[
150] Patients with narcolepsy have an increased risk of associated sleep disorders including REM sleep behavior disorder, periodic limb movements, vivid dreams, and nightmares.[
151]
Research work done on narcolepsy infers that insufficient sleep is often linked with obesity. The role of the neuropeptide hypocretin which is also known as orexin, is crucial in inducing wakefulness.[
152] Observational studies,[
150,
151] further suggests the idea that sleep disruption enforces hormonal signals which induce excessive food intake resulting in obesity. Gleadhill et al. observed that a period as short as two weeks of sleep disturbance along with abnormal feeding behavior is sufficient to elicit the ghrelin levels.[
153] The early morning measurement of ghrelin level is associated to be higher in response to even acute sleep disturbance,[
154] however, there are few contrasting findings.[
155] These experimental findings suggest that sleep disruption can induce lower leptin and higher ghrelin level,[
152] as the neuroendocrine response to the restricted energy consumption.[
156]
Weight loss is an effective treatment for sleep disorders; however, there is a high degree of variability in improvements in the nature of sleep disorders.[
106,
157]
Apart from diet therapy, physical exercise, and lifestyle modifications, pharmacotherapy to obesity management is an effective tool.[
101] The sustainability of weight loss achieved through lifestyle modifications alone is often minimal and inconsistent.[
103] Furthermore, restricted caloric intake by modifying the diet and increased energy expenditure through strict physical exercises are countered by metabolic adaptations which increase appetite rather than consuming the stored energy by slowing down the resting metabolism leading to weight gain.[
43,
158]
5.3. Regular exercise and healthy sleep hygiene
Regular exercise not only increases the sleep quality but also leads to the decrease in total body fat, ultimately helping in obesity. Elevated cortisol level and low growth hormones are hallmarks of sleep deprivation which has a relation with obesity. Improper sleep hygiene is also associated with altered metabolism of food which results in gain of weight. New research findings from John Hopkins group proved that change in diet plan alone or proper diet with regular exercise results in better sleep quality and helps in weight loss too. Studies also indicated that 30 minutes of daily exercise aids in significant reduction in weight and also improves sleep hygiene. Sleep hygiene means practicing the habits which help in good sleep. The combination of regular exercise, proper diet plan and good sleep practices (healthy sleep-wake cycle) can be a key for the weight loss in the obese individuals. Hence, in addition to the different pharmacological interventions, these are some organic ways to treat obesity.
6. Conclusion and future perspectives
The cross-sectional nature of the published research makes it difficult to conclude whether it is the sleep disorders contributing to obesity, or obesity contributing to sleep disorders. Further research, with large sample sizes and precise controls for confounding factors are needed. Most concessed explanation isa combination of worsening sleep habits and body adiposity. Reduction in sleep induces energy expenditure, weight regulation and neuroendocrinal and metabolic control. Reduction in sleep quality and duration are observed in healthy individuals across varying age and gender and in patients with medical conditions such as type 1 diabetes. Sleep disturbances and sleep deprivation does appear to have a relationship with the development of or exacerbation of body adiposity or vice versa. There is evidence suggesting regular exercise and modified lifestyle can improve sleep disorders. Maintaining energy homeostasis through a physically active lifestyle can be a long-term and an efficient option for the intervention of obesity and sleep disorders. The randomized controlled trials using longitudinal research will further explore the relationship between obesity and sleep disorders. Co-occurrence of overall and abdominal adiposity can increase the risk of RLS. Further prospective studies are warranted to clarify the causative association between obesity and the risk of developing RLS like sleep disorders. The development, maintenance, and severity of various sleep disorders are induced by obesity. The understanding of the theoretical framework underlying the relationship between obesity and sleep disorders is necessitated to formulate and design the effective interventional options. The weight reductions using various means are considered as a rationalized strategy to control sleep and other related symptoms. Anti-obesity pharmacotherapy is one of the vital strategies to counter the adaptive changes in appetite and energy expenditure in response to the environmental change and there is sufficient evidence for it. However, the plateau in outcome after some interval and undesired side effects are two major challenges. Conclusively, current anti-obesity pharmacotherapies are often underutilized, cumbersome, costly, or associated with residual symptoms.
Combination drugs are one of the recent approaches in anti-obesity pharmacotherapy, which has significant success. In this approach multiple pathways are targeted simultaneously, to have an additive or synergistic effect on body weight. Based on the initial success of phentermine/topiramate ER and naltrexone SR/bupropion SR, other combinations are under investigation for clinical usage, including phentermine/lorcaserin and phentermine/canagliflozin. Stepwise approach is another strategy in which rather than initiating two or more drugs at the same time, another drug is introduced when weight reduction curve reaches to the plateau. Pharmacotherapy along with bariatric surgery has got momentum in recent times; it may also be effective in maintaining body weight post bariatric surgery. It is also assumed that the optimal time for imitation of anti-obesity pharmacotherapy is the time when a person has low weight rather than peak weight. Moreover, the combination of anti-obesity pharmacotherapy along with endoscopic procedures and devices is another area that has withdrawn attention of the researchers and it needs further investigation. Combination therapies has shown encouraging outcomes in the management of chronic diseases[
159], including common conditions such as diabetes and hypertension, and are especially effective for pathologic states where multiple regulatory mechanisms may contribute to the development or maintenance of disease. Moreover, recent advancements in technology based intervention is benefiting comorbid issues along with sleep disturbances.
160, 161
The overall efficacy of the pharmacotherapy approaches needs further investigation to ensure long-term and stable success. There is an evident need for more work from animal models, which specifically aims to describe the pathogenesis of sleep disorders in more detail to define a target for a drug. Drugs need to be developed that specifically address the defined targets e.g., increase the activity of the pharyngeal dilator muscles without disrupting sleep and/or increase inhibitory action of the pharyngeal constrictor mechanism.162,163 The development of such specific drugs is necessary to produce a solid basis for clinical trials in humans with high chances of success.
Research Involving Human Participants or Animals
None.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Author Contributions
VK, SG, RM and JKS conceptualized the hypothesis of this manuscript. SG, PKM and AA performed the review of literature. Manuscript was written by VK, RM, JKS and SG. The critical review and editing were conducted by SG, JKS, PKM, and AA. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgements
Dr. Jitendra Kumar Sinha acknowledges the grant received from International Brain Research Organization (IBRO) and GloNeuro Academy. All the authors acknowledge the kind help of Dr. M. Raghunath, NIN, Hyderabad in reviewing different versions of the manuscript and diagrams, which helped a lot in improving the quality of the present review article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
References
- Vgontzas, A.N.; Bixler, E.O.; Chrousos, G.P.; Pejovic, S. Obesity and sleep disturbances: Meaningful sub-typing of obesity. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 114, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Sinha, J.K.; Raghunath, M. ‘Obesageing’: Linking obesity & ageing. Indian J. Med. Res. 2019, 149, 610. [Google Scholar]
- St-Onge, M.-P. The Role of Sleep Duration in the Regulation of Energy Balance: Effects on Energy Intakes and Expenditure. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2013, 09, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, M.M. Sleep disturbances in Parkinson's disease: The contribution of dopamine in REM sleep regulation. Sleep Med. Rev. 2013, 17, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Alberca, J.M.; Lara, J.P.; Cruz, B.; Garrido, V.; Gris, E.; Barbancho, M. Sleep Disturbances in Alzheimer’s Disease Are Associated With Neuropsychiatric Symptoms and Antidementia Treatment. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2013, 201, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnon, J.-F.; Petit, D.; Latreille, V.; Montplaisir, J. Neurobiology of Sleep Disturbances in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 3430–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, Y.H.C.; Potenza, M.N. Stress and eating behaviors. Minerva Endocrinol. 2013, 38, 255–267. [Google Scholar]
- Prather, A.A.; Gurfein, B.; Moran, P.; Daubenmier, J.; Acree, M.; Bacchetti, P.; Sinclair, E.; Lin, J.; Blackburn, E.; Hecht, F.M.; et al. Tired telomeres: Poor global sleep quality, perceived stress, and telomere length in immune cell subsets in obese men and women. Brain, Behav. Immun. 2015, 47, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marieb, E.N.; Hoehn, K. Human anatomy & physiology; Pearson education: 2007.
- Besnard, V.; Wert, S.E.; Stahlman, M.T.; Postle, A.D.; Xu, Y.; Ikegami, M.; Whitsett, J.A. Deletion of Scap in Alveolar Type II Cells Influences Lung Lipid Homeostasis and Identifies a Compensatory Role for Pulmonary Lipofibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 4018–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotas, M.E.; Medzhitov, R. Homeostasis, inflammation, and disease susceptibility. Cell 2015, 160, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A. Gut feelings: The emerging biology of gut–brain communication. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torday, J.S.; Rehan, V.K. Evolutionary Biology: Cell-Cell Communication, and Complex Disease; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Torday, J.; Powell, F.; Farmer, C.; Orgeig, S.; Nielsen, H.; Hall, A. Leptin integrates vertebrate evolution: From oxygen to the blood–gas barrier. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2010, 173, S37–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, M.A.; Kahn, B.B. Glucose transport and sensing in the maintenance of glucose homeostasis and metabolic harmony. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1767–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.W.Y.; Stange, D.E.; Page, M.E.; Buczacki, S.; Wabik, A.; Itami, S.; van de Wetering, M.; Poulsom, R.; Wright, N.A.; Trotter, M.W.B.; et al. Lrig1 controls intestinal stem-cell homeostasis by negative regulation of ErbB signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanItallie, T.B. Sleep and energy balance: Interactive homeostatic systems. Metabolism 2006, 55, S30–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aton, S.J.; Herzog, E.D. Come together, right… now: Synchronization of rhythms in a mammalian circadian clock. Neuron 2005, 48, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistlberger, R.E. Circadian regulation of sleep in mammals: Role of the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Brain Res. Rev. 2005, 49, 429–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kováčiková, Z.; Sládek, M.; Laurinová, K.; Bendová, Z.; Illnerová, H.; Sumová, A. Ontogenesis of photoperiodic entrainment of the molecular core clockwork in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus. Brain Res. 2005, 1064, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, L.; Allen, C. The circadian visual system, 2005. Brain Res. Rev. 2006, 51, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; McCormack, S.; España, R.A.; Crocker, A.; Scammell, T.E. Afferents to the orexin neurons of the rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 494, 845–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jackson, C.W.; Khoury, N.; Escobar, I.; Perez-Pinzon, M.A. Brain SIRT1 Mediates Metabolic Homeostasis and Neuroprotection. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, P.; Mittal, A.K.; Kalonia, H.; Madan, S.; Ghosh, S.; Sinha, J.K.; Rajput, S.K. SIRT1 Promotes Neuronal Fortification in Neurodegenerative Diseases through Attenuation of Pathological Hallmarks and Enhancement of Cellular Lifespan. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 1019–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Durgvanshi, S.; Agarwal, S.; Raghunath, M.; Sinha, J.K. Current Status of Drug Targets and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies in the Management of Alzheimer's Disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 883–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, E.M.; Mechoulam, R. Tetrahydrocannabinol and endocannabinoids in feeding and appetite. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 95, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trayhurn, P. The biology of obesity. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2005, 64, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Sinha, J.K.; Putcha, U.K.; Raghunath, M. Severe but Not Moderate Vitamin B12 Deficiency Impairs Lipid Profile, Induces Adiposity, and Leads to Adverse Gestational Outcome in Female C57BL/6 Mice. Front. Nutr. 2016, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sinha, J.K.; Muralikrishna, B.; Putcha, U.K.; Raghunath, M. Chronic transgenerational vitamin B12 deficiency of severe and moderate magnitudes modulates adiposity—Probable underlying mechanisms. BioFactors 2017, 43, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sinha, J.K.; Khandelwal, N.; Chakravarty, S.; Kumar, A.; Raghunath, M. Increased stress and altered expression of histone modifying enzymes in brain are associated with aberrant behaviour in vitamin B12 deficient female mice. Nutr. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniam, J.; Antoniadis, C.P.; Youngson, N.A.; Sinha, J.K.; Morris, M.J. Sugar Consumption Produces Effects Similar to Early Life Stress Exposure on Hippocampal Markers of Neurogenesis and Stress Response. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Raghunath, M.; Das, B.C.; Sinha, J.K. High sugar content in baby food: An Indian perspective. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 748–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sinha, J.K.; Raghunath, M. Epigenomic maintenance through dietary intervention can facilitate DNA repair process to slow down the progress of premature aging. IUBMB Life 2016, 68, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, J.; Ghosh, S.; Swain, U.; Giridharan, N.; Raghunath, M. Increased macromolecular damage due to oxidative stress in the neocortex and hippocampus of WNIN/Ob, a novel rat model of premature aging. Neuroscience 2014, 269, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, S.; Fujita, T.; Shimabukuro, M.; Iwaki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Nakayama, O.; Makishima, M.; Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Invest. 2017, 114, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzanetakou, I.P.; Katsilambros, N.L.; Benetos, A.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Perrea, D.N. “Is obesity linked to aging?”: Adipose tissue and the role of telomeres. Ageing Res. Rev. 2012, 11, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, J.K.; Ghosh, S.; Raghunath, M. Progeria: A rare genetic premature ageing disorder. Indian J. Med. Res. 2014, 139, 667–674. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, J.K.; Ghosh, S. Scoring more than ten plus century--antiquity in gerontology? Indian J. Med. Res. 2010, 131, 586–588. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scherer, P.E.; Williams, S.; Fogliano, M.; Baldini, G.; Lodish, H.F. A Novel Serum Protein Similar to C1q, Produced Exclusively in Adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 26746–26749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Iwabu, M.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Kadowaki, T. Adiponectin receptors: A review of their structure, function and how they work. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 28, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Montagnani, M.; Funahashi, T.; Shimomura, I.; Quon, M.J. Adiponectin Stimulates Production of Nitric Oxide in Vascular Endothelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 45021–45026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penev, P.D. Sleep deprivation and energy metabolism: To sleep, perchance to eat? Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2007, 14, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L. Adaptive thermogenesis in humans. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 34, S47–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumithran, P.; Prendergast, L.A.; Delbridge, E.; Purcell, K.; Shulkes, A.; Kriketos, A.; Proietto, J. Long-Term Persistence of Hormonal Adaptations to Weight Loss. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hursel, R.; Rutters, F.; Gonnissen, H.K.; AP Martens, E.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S. Effects of sleep fragmentation in healthy men on energy expenditure, substrate oxidation, physical activity, and exhaustion measured over 48 h in a respiratory chamber. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allebrandt, K.; Amin, N.; Müller-Myhsok, B.; Esko, T.; Teder-Laving, M.; Azevedo, R.; Hayward, C.; Van Mill, J.; Vogelzangs, N.; Green, E. AK ATP channel gene effect on sleep duration: From genome-wide association studies to function in Drosophila. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujino, N.; Sakurai, T. Orexin/Hypocretin: A Neuropeptide at the Interface of Sleep, Energy Homeostasis, and Reward System. Pharmacol. Rev. 2009, 61, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, K.; Tasali, E.; Penev, P.; Van Cauter, E. Brief Communication: Sleep Curtailment in Healthy Young Men Is Associated with Decreased Leptin Levels, Elevated Ghrelin Levels, and Increased Hunger and Appetite. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 141, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.; Rudenski, A.; Naylor, B.; Treacher, D.; Turner, R. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, D.F. Homeostatic theory of obesity. Health Psychol. Open 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, M.B.; Manson, J.E.; Ludwig, D.S.; Colditz, G.A.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Sugar-Sweetened Beverages, Weight Gain, and Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in Young and Middle-Aged Women. JAMA 2004, 292, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.W.; Myers, M.G., Jr. Leptin and the maintenance of elevated body weight. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, B.A.; Fowler, L.A. Obesity in African-Americans: The role of physiology. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 288, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler-Laney, P.C.; Phadke, R.P.; Granger, W.M.; Fernández, J.R.; Muñoz, J.A.; Man, C.D.; Cobelli, C.; Ovalle, F.; Gower, B.A. Age-Related Changes in Insulin Sensitivity and β-Cell Function Among European-American and African-American Women. Obesity 2011, 19, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinini, F.; Polidori, D.C.; Gower, B.A.; Bergman, R.N. Hepatic but Not Extrahepatic Insulin Clearance Is Lower in African American Than in European American Women. Diabetes 2017, 66, 2564–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gower, B.A.; Hunter, G.R.; Chandler-Laney, P.C.; Alvarez, J.A.; Bush, N.C. Glucose Metabolism and Diet Predict Changes in Adiposity and Fat Distribution in Weight-reduced Women. Obesity 2010, 18, 1532–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, M.D.; Jakobsdottir, S.; Drent, M.L. The role of leptin and ghrelin in the regulation of food intake and body weight in humans: A review. Obes. Rev. 2007, 8, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eikelis, N.; Esler, M. The neurobiology of human obesity. Exp. Physiol. 2005, 90, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.D.; Møller, N.; Nair, K.S.; Eisenberg, P.; Landt, M.; Klein, S. Regional leptin kinetics in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdham, D.M.; Zou, M.-X.; Rajapurohitam, V.; Karmazyn, M. Rat heart is a site of leptin production and action. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2004, 287, H2877–H2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Proenca, R.; Maffei, M.; Barone, M.; Leopold, L.; Friedman, J.M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994, 372, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burguera, B.; Couce, M.E.; Long, J.; Lamsam, J.; Laakso, K.; Jensen, M.D.; Parisi, J.E.; Lloyd, R.V. The Long Form of the Leptin Receptor (OB-Rb) Is Widely Expressed in the Human Brain. Neuroendocrinology 2000, 71, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Considine, R.V.; Caro, J.F.; Considine, E.L.; Williams, C.J.; Hyde, T.M. Identification of Incidental Sequence Polymorphisms and Absence of the db/db Mouse and fa/fa Rat Mutations. Diabetes 1996, 45, 992–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigle, D.S.; Duell, P.B.; Connor, W.E.; Steiner, R.A.; Soules, M.R.; Kuijper, J.L. Effect of Fasting, Refeeding, and Dietary Fat Restriction on Plasma Leptin Levels1. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelleymounter, M.A.; Cullen, M.J.; Baker, M.B.; Hecht, R.; Winters, D.; Boone, T.; Collins, F. Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice. Science 1995, 269, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halaas, J.L.; Gajiwala, K.S.; Maffei, M.; Cohen, S.L.; Chait, B.T.; Rabinowitz, D.; Lallone, R.L.; Burley, S.K.; Friedman, J.M. Weight-Reducing Effects of the Plasma Protein Encoded by the obese Gene. Science 1995, 269, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, J.O.; Vahl, N.; Dall, R.; Christiansen, J.S. Resting metabolic rate in healthy adults: Relation to growth hormone status and leptin levels. Metabolism 1998, 47, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqi, I.S.; Keogh, J.M.; Kamath, S.; Jones, S.; Gibson, W.T.; Trussell, R.; Jebb, S.A.; Lip, G.Y.H.; O'Rahilly, S. Partial leptin deficiency and human adiposity. Nature 2001, 414, 34–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.Y.; Steadward, R.D.; Wheeler, G.D.; Bell, G.; McCargar, L.; Harber, V. Intact Sympathetic Nervous System Is Required for Leptin Effects on Resting Metabolic Rate in People with Spinal Cord Injury. Int. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, M.A.; Smith, R.G.; Diano, S.; Tschöp, M.; Pronchuk, N.; Grove, K.L.; Strasburger, C.J.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Esterman, M.; Heiman, M.L.; et al. The Distribution and Mechanism of Action of Ghrelin in the CNS Demonstrates a Novel Hypothalamic Circuit Regulating Energy Homeostasis. Neuron 2003, 37, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin Is a Growth-Hormone-Releasing Acylated Peptide from Stomach. Nature 1999, 402, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbonits, M.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K.; Grossman, A.B. Presence of Ghrelin in Normal and Adenomatous Human Pituitary. Endocrine 2001, 14, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.D.; Feighner, S.D.; Cully, D.F.; Arena, J.P.; Liberator, P.A.; Rosenblum, C.I.; Hamelin, M.; Hreniuk, D.L.; Palyha, O.C.; Anderson, J.; et al. A Receptor in Pituitary and Hypothalamus That Functions in Growth Hormone Release. Science 1996, 273, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariyasu, H.; Takaya, K.; Tagami, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Hosoda, K.; Akamizu, T.; Suda, M.; Koh, T.; Natsui, K.; Toyooka, S.; et al. Stomach Is a Major Source of Circulating Ghrelin, and Feeding State Determines Plasma Ghrelin-Like Immunoreactivity Levels in Humans. Int. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 4753–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschöp, M.; Wawarta, R.; Riepl, R.L.; Friedrich, S.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Landgraf, R.; Folwaczny, C. Post-prandial decrease of circulating human ghrelin levels. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2001, 24, RC19–RC21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kangawa, K.; Nakazato, M. Ghrelin: A gastric peptide that regulates food intake and energy homeostasis. Regul. Pept. 2005, 126, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, D.; Gao, H.-Z.; Muroya, S.; Kikuyama, S.; Yada, T. Ghrelin directly interacts with neuropeptide-Y-containing neurons in the rat arcuate nucleus: Ca2+ signaling via protein kinase A and N-type channel-dependent mechanisms and cross-talk with leptin and orexin. Diabetes 2003, 52, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshinai, K.; Date, Y.; Murakami, N.; Shimada, M.; Mondal, M.S.; Shimbara, T.; Guan, J.-L.; Wang, Q.-P.; Funahashi, H.; Sakurai, T.; et al. Ghrelin-Induced Food Intake Is Mediated via the Orexin Pathway. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 1506–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz, M.; Jennings, G.; Turner, A.; Cox, H.; Lambert, G.; Esler, M. Regional Sympathetic Nervous Activity and Oxygen Consumption in Obese Normotensive Human Subjects. Circ. 1997, 96, 3423–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumantir, M.S.; Vaz, M.; Jennings, G.L.; Collier, G.; Kaye, D.M.; Seals, D.R.; Wiesner, G.H.; Rocca, H.P.B.-L.; Esler, M.D. Neural mechanisms in human obesity-related hypertension. J. Hypertens. 1999, 17, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkiewicz, K.; van de Borne, P.J.H.; Cooley, R.L.; Dyken, M.E.; Somers, V.K. Sympathetic Activity in Obese Subjects With and Without Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Circulation 1998, 98, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, J.M. Sleep viewed as a state of adaptive inactivity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, B.N.; Singh, A. REM sleep loss increases brain excitability: Role of noradrenalin and its mechanism of action. Sleep Med. Rev. 2011, 15, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, M.G.; Heller, H.C. The ontogeny of mammalian sleep: A reappraisal of alternative hypotheses. J. Sleep Res. 2003, 12, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roffwarg, H.P.; Muzio, J.N.; Dement, W.C. Ontogenetic Development of the Human Sleep-Dream Cycle: The prime role of" dreaming sleep" in early life may be in the development of the central nervous system. Science 1966, 152, 604–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallick, B.; Siegel, J.; Fahringer, H. Changes in pontine unit activity with REM sleep deprivation. Brain Res. 1990, 515, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, M.E.; Yizhar, O.; Chikahisa, S.; Nguyen, H.; Adamantidis, A.; Nishino, S.; Deisseroth, K.; de Lecea, L. Tuning arousal with optogenetic modulation of locus coeruleus neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, R.; Singh, S.; Khanday, M.A.; Mallick, B.N. Reciprocal changes in noradrenaline and GABA levels in discrete brain regions upon rapid eye movement sleep deprivation in rats. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 108, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aserinsky, E.; Kleitman, N. Regularly Occurring Periods of Eye Motility, and Concomitant Phenomena, During Sleep. Science 1953, 118, 273–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dement, W.; Kleitman, N. Cyclic variations in EEG during sleep and their relation to eye movements, body motility, and dreaming. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1957, 9, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dement, W.; Kleitman, N. The relation of eye movements during sleep to dream activity: An objective method for the study of dreaming. J. Exp. Psychol. 1957, 53, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouvet, M.; Michel, F. Electromyographic correlations of sleep in the chronic decorticate & mesencephalic cat. C. R. Seances Soc. Biol. Fil. 1959, 153, 422–425. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, R.; Singh, A.; Mallick, B.N. Disciplined sleep for healthy living: Role of noradrenaline. World J. Neurol. 2017, 7, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.; Mallick, B.N. Neural mechanism of rapid eye movement sleep generation with reference to REM-OFF neurons in locus coeruleus. Indian J. Med. Res. 2007, 125, 721–739. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-Q.; Li, R.; Zhang, M.-Q.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, W.-M.; Huang, Z.-L. The Neurobiological Mechanisms and Treatments of REM Sleep Disturbances in Depression. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 13, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworak, M.; Kim, T.; McCarley, R.; Basheer, R. Sleep, brain energy levels, and food intake. Somnologie 2011, 15, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.; Khanday, M.A.; Mallick, B.N. REM sleep loss associated changes in orexin-A levels in discrete brain areas in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 590, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preti, A. Orexins (hypocretins): Their role in appetite and arousal. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2002, 3, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Vidafar, P.; Cain, S.W.; Shechter, A. Relationship between Sleep and Hedonic Appetite in Shift Workers. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silber, M.H.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Bonnet, M.H.; Chokroverty, S.; Grigg-Damberger, M.M.; Hirshkowitz, M.; Kapen, S.; Keenan, S.A.; Kryger, M.H.; Penzel, T.; et al. The Visual Scoring of Sleep in Adults. Sleep Med. 2007, 03, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Manchala, S.; Raghunath, M.; Sharma, G.; Singh, A.K.; Sinha, J.K. Role of Phytomolecules in the Treatment of Obesity: Targets, Mechanisms and Limitations. J. Clin. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenway, F.L. Physiological adaptations to weight loss and factors favouring weight regain. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.D.; Ryan, D.H.; Apovian, C.M.; Ard, J.D.; Comuzzie, A.G.; Donato, K.A.; Hu, F.B.; Hubbard, V.S.; Jakicic, J.M.; Kushner, R.F. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2985–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apovian, C.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Bessesen, D.H.; McDonnell, M.E.; Murad, M.H.; Pagotto, U.; Ryan, D.H.; Still, C.D. Pharmacological Management of Obesity: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 342–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushner, R.F. Weight Loss Strategies for Treatment of Obesity. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 56, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, K.H.; Umashanker, D.; Igel, L.I.; Kumar, R.B.; Aronne, L.J. Obesity Pharmacotherapy. Med Clin. North Am. 2018, 102, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shechter, A.; Foster, G.D.; Lang, W.; Reboussin, D.M.; St-Onge, M.; Zammit, G.; Newman, A.B.; Millman, R.P.; Wadden, T.A.; Jakicic, J.M.; et al. Effects of a lifestyle intervention on REM sleep-related OSA severity in obese individuals with type 2 diabetes. J. Sleep Res. 2017, 26, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenway, F.L.; Whitehouse, M.; Guttadauria, M.; Anderson, J.W.; Atkinson, R.L.; Fujioka, K.; Gadde, K.M.; Gupta, A.K.; O'Neil, P.; Schumacher, D.; et al. Rational Design of a Combination Medication for the Treatment of Obesity. Obesity 2009, 17, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.R.; Weissman, N.J.; Anderson, C.M.; Sanchez, M.; Chuang, E.; Stubbe, S.; Bays, H.; Shanahan, W.R. Multicenter, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Lorcaserin for Weight Management. New Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.R.; Garvey, W.T.; Greenway, F.L.; Zhou, S.; Fain, R.; Pilson, R.; Fujioka, K.; Aronne, L.J. Coadministration of lorcaserin and phentermine for weight management: A 12-week, randomized, pilot safety study. Obesity 2017, 25, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, D.D.; Przydzial, M.J.; Ridley, S.H.; Yeo, G.S.H.; Rochford, J.J.; O’rahilly, S.; Heisler, L.K. Serotonin 5-HT2C Receptor Agonist Promotes Hypophagia via Downstream Activation of Melanocortin 4 Receptors. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jones, J.E.; Kohno, D.; Williams, K.W.; Lee, C.E.; Choi, M.J.; Anderson, J.G.; Heisler, L.K.; Zigman, J.M.; Lowell, B.B.; et al. 5-HT2CRs Expressed by Pro-Opiomelanocortin Neurons Regulate Energy Homeostasis. Neuron 2008, 60, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothman, R.B.; Baumann, M.H. Therapeutic and adverse actions of serotonin transporter substrates. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 95, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, H.M.; Crary, J.L.; McGoon, M.D.; Hensrud, D.D.; Edwards, B.S.; Edwards, W.D.; Schaff, H.V. Valvular Heart Disease Associated with Fenfluramine–Phentermine. New Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, L.W.; Burn, T.C.; Brown, B.S.; Patterson, J.P.; Corjay, M.H.; Valentine, P.A.; Sun, J.H.; Link, J.R.; Abbaszade, I.; Hollis, J.M.; et al. Possible role of valvular serotonin 5-HT(2B) receptors in the cardiopathy associated with fenfluramine. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, W.J.; Grottick, A.J.; Menzaghi, F.; Reyes-Saldana, H.; Espitia, S.; Yuskin, D.; Whelan, K.; Martin, M.; Morgan, M.; Chen, W.; et al. Lorcaserin, a Novel Selective Human 5-Hydroxytryptamine2C Agonist: In Vitro and in Vivo Pharmacological Characterization. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 325, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D'Agostino, R.B.; Massaro, J.; Kwan, H.; Cabral, H. Strategies for Dealing with Multiple Treatment Comparisons in Confirmatory Clinical Trials. Drug Inf. J. 1993, 27, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cone, R.D. Anatomy and regulation of the central melanocortin system. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enriori, P.J.; Evans, A.E.; Sinnayah, P.; Jobst, E.E.; Tonelli-Lemos, L.; Billes, S.K.; Glavas, M.M.; Grayson, B.E.; Perello, M.; Nillni, E.A.; et al. Diet-Induced Obesity Causes Severe but Reversible Leptin Resistance in Arcuate Melanocortin Neurons. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, N.; Bosch, M.A.; Smart, J.L.; Qiu, J.; Rubinstein, M.; Rønnekleiv, O.K.; Low, M.J.; Kelly, M.J. Hypothalamic proopiomelanocortin neurons are glucose responsive and express KATP channels. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; Wang, H.; Ascherio, A. Obesity and restless legs syndrome in men and women. Neurology 2009, 72, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edinger, J.D.; Bonnet, M.H.; Bootzin, R.R.; Doghramji, K.; Dorsey, C.M.; Espie, C.A.; Jamieson, A.O.; McCall, W.V.; Morin, C.M.; Stepanski, E.J. Derivation of Research Diagnostic Criteria for Insomnia: Report of an American Academy of Sleep Medicine Work Group. Sleep 2004, 27, 1567–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemann, D.; Kloepfer, C.; Berger, M. Functional and structural brain alterations in insomnia: Implications for pathophysiology. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vgontzas, A.N.; Bixler, E.O.; Lin, H.-M.; Prolo, P.; Mastorakos, G.; Vela-Bueno, A.; Kales, A.; Chrousos, G.P. Chronic Insomnia Is Associated with Nyctohemeral Activation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis: Clinical Implications. Int. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 3787–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofzinger, E.A.; Nissen, C.; Germain, A.; Moul, D.; Hall, M.; Price, J.C.; Miewald, J.M.; Buysse, D.J. Regional Cerebral Metabolic Correlates of WASO During NREM Sleep in Insomnia. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2006, 02, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vgontzas, A.N.; Lin, H.-M.; Papaliaga, M.; Calhoun, S.; Vela-Bueno, A.; Chrousos, G.P.; Bixler, E.O. Short sleep duration and obesity: The role of emotional stress and sleep disturbances. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singareddy, R.; Vgontzas, A.N.; Fernandez-Mendoza, J.; Liao, D.; Calhoun, S.; Shaffer, M.L.; Bixler, E.O. Risk factors for incident chronic insomnia: A general population prospective study. Sleep Med. 2012, 13, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.; Lin, L.; Austin, D.; Young, T.; Mignot, E. Short Sleep Duration Is Associated with Reduced Leptin, Elevated Ghrelin, and Increased Body Mass Index. PLOS Med. 2004, 1, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallman, M.F.; Pecoraro, N.; Akana, S.F.; La Fleur, S.E.; Gomez, F.; Houshyar, H.; Bell, M.; Bhatnagar, S.; Laugero, K.D.; Manalo, S. Chronic stress and obesity: A new view of “comfort food”. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2003, 100, 11696–11701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargens, T.A.; Kaleth, A.S.; Edwards, E.S.; Butner, K.L. Association between sleep disorders, obesity, and exercise: A review. Nat Sci Sleep 2013, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.; Palta, M.; Dempsey, J.; Skatrud, J.; Weber, S.; Badr, S. The Occurrence of Sleep-Disordered Breathing among Middle-Aged Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.R.; Blackwell, T.; Redline, S.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Cauley, J.A.; Hillier, T.A.; Lewis, C.E.; Orwoll, E.S.; Stefanick, M.L.; Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Research Group; et al. The association between sleep duration and obesity in older adults. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, A.; White, D.P. Obstructive sleep apnoea. Lancet 2002, 360, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.W.; O’driscoll, D.M.; Truby, H.; Naughton, M.T.; Hamilton, G.S. The reciprocal interaction between obesity and obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Med. Rev. 2013, 17, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, K.; Neovius, M.; Lagerros, Y.T.; Harlid, R.; Rössner, S.; Granath, F.; Hemmingsson, E. Effect of a very low energy diet on moderate and severe obstructive sleep apnoea in obese men: A randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2009, 339, b4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, R.P.; Walters, A.S.; Montplaisir, J.; Hening, W.; Myers, A.; Bell, T.J.; Ferini-Strambi, L. Restless legs syndrome prevalence and impact: REST general population study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reese, J.P.; Stiasny-Kolster, K.; Oertel, W.H.; Dodel, R.C. Health-related quality of life and economic burden in patients with restless legs syndrome. Expert Rev. Pharmacoeconomics Outcomes Res. 2007, 7, 503–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, B.R. Restless Legs Syndrome and Periodic Movements of Sleep. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1990, 65, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, J.; Schroeder, C. Iron, brain and restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. Rev. 2001, 5, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alattar, M.; Harrington, J.J.; Mitchell, C.M.; Sloane, P. Sleep Problems in Primary Care: A North Carolina Family Practice Research Network (NC-FP-RN) Study. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 2007, 20, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallon, L.; Broman, J.E.; Hetta, J. Restless legs symptoms with sleepiness in relation to mortality: 20-year follow-up study of a middle-aged Swedish population. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 62, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamer, A.; Delaney, M.; Young, L.R. An expert system for fault management assistance on a space sleep experiment. Arch. Ital. Biol. 2002, 140, 303–313. [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger, I.; Erikh, I.; Avizohar, O.; Sprecher, E.; Yarnitsky, D. Cardiovascular risk factors in restless legs syndrome. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punjabi, N.M.; Shahar, E.; Redline, S.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Givelber, R.; Resnick, H.E. Sleep-Disordered Breathing, Glucose Intolerance, and Insulin Resistance: The Sleep Heart Health Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 160, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohayon, M.M.; Priest, R.G.; Zulley, J.; Smirne, S.; Paiva, T. Prevalence of narcolepsy symptomatology and diagnosis in the European general population. Neurology 2002, 58, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overeem, S.; Mignot, E.; GertvanDijk, J.; Lammers, G.J. Narcolepsy: Clinical features, new pathophysiologic insights, and future perspectives. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2001, 18, 78–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauvilliers, Y.; Arnulf, I.; Mignot, E. Narcolepsy with cataplexy. Lancet 2007, 369, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagan, J.J.; Leslie, R.A.; Patel, S.; Evans, M.L.; Wattam, T.A.; Holmes, S.; Benham, C.D.; Taylor, S.G.; Routledge, C.; Hemmati, P.; et al. Orexin A activates locus coeruleus cell firing and increases arousal in the rat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 10911–10916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, S.; Ripley, B.; Overeem, S.; Lammers, G.J.; Mignot, E. Hypocretin (orexin) deficiency in human narcolepsy. Lancet 2000, 355, 39–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sateia, M.J. International Classification of Sleep Disorders-Third Edition. Chest 2014, 146, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinnell, T.; Wozniak, D. Unmet needs of patients with narcolepsy: Perspectives on emerging treatment options. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2015, 7, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liblau, R.S.; Vassalli, A.; Seifinejad, A.; Tafti, M. Hypocretin (orexin) biology and the pathophysiology of narcolepsy with cataplexy. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleadhill, I.C.; Schwartz, A.R.; Schubert, N.; Wise, R.A.; Permutt, S.; Smith, P.L. Upper Airway Collapsibility in Snorers and in Patients with Obstructive Hypopnea and Apnea. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1991, 143, 1300–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, J.E.; Hull, S.G.; Tiller, J.; Yang, R.; Harsh, J.R. The Long-Term Tolerability and Efficacy of Armodafinil in Patients with Excessive Sleepiness Associated with Treated Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Shift Work Disorder, or Narcolepsy: An Open-Label Extension Study. J Clin Sleep Med 2010, 6, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; Fowler, J.S.; Logan, J.; Alexoff, D.; Zhu, W.; Telang, F.; Wang, G.-J.; Jayne, M.; Hooker, J.M.; Wong, C. Effects of modafinil on dopamine and dopamine transporters in the male human brain: Clinical implications. JAMA 2009, 301, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iftikhar, I.H.; Khan, M.F.; Das, A.; Magalang, U.J. Meta-analysis: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Improves Insulin Resistance in Patients with Sleep Apnea without Diabetes. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2013, 10, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulos, M.S.; Berkowitz, R.I.; Tapia, I.E. Effects of obesity therapies on sleep disorders. Metabolism 2018, 84, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fothergill, E.; Guo, J.; Howard, L.; Kerns, J.C.; Knuth, N.D.; Brychta, R.; Chen, K.Y.; Skarulis, M.C.; Walter, M.; Walter, P.J. Persistent metabolic adaptation 6 years after “The Biggest Loser” competition. Obesity 2016, 24, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sinha, J.K.; Khan, T.; Devaraju, K.S.; Singh, P.; Vaibhav, K.; Gaur, P. Pharmacological and Therapeutic Approaches in the Treatment of Epilepsy. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, J.K.; Vashisth, K.; Ghosh, S. The importance of sleep studies in improving the health indices of a nation. Sleep Med. X 2022, 4, 100049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, J.K.; Vashisth, K.; Ghosh, S. Epidemiological studies on sleep quality can help in improving public mental health initiatives and development of better sleep technologies. Sleep Epidemiology 2022, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, B.; Sachdeva, P.; Negi, A.; Ghosh, S.; Han, S.; Dewanjee, S.; Jha, S.K.; Bhaskar, R.; Sinha, J.K.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; et al. Chitosan Nanoparticles-Based Cancer Drug Delivery: Application and Challenges. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, P.; Ji, S.; Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, S.; Raghunath, M.; Kim, H.; Bhaskar, R.; Sinha, J.K.; Han, S.S. Plausible Role of Stem Cell Types for Treating and Understanding the Pathophysiology of Depression. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).