1. Introduction
Thermoregulation is a strictly regulated physiologic response to maintain the homeostasis of our body. However, anesthesia can easily break such response and lead to hypothermia [
1]. Perioperative hypothermia can cause some problems associated with wound infection, such as lengthened hospital stay [
2], prolonged postanesthetic recovery [
3], coagulopathy [
4], and myocardial events [
5]. Consequently, it is recommended to maintain the core body temperature above 36℃ which is the cut off value of perioperative hypothermia during anesthesia [
6,
7].
Appropriate body temperature measurement sites and methods are various depending on their availability, invasiveness, accuracy, and reliability. The gold standard core body temperature measurement method is a pulmonary artery catheter. However, its use is limited because it is a very invasive method. Thus, the esophageal distal region, nasopharynx, tympanic membrane, and bladder have been considered places to measure core body temperature [
1]. These core body temperature measurement locations clearly have disadvantages as they are invasive or could not be monitored continuously. As an alternative, the zero-heat-flux (ZHF) technique introduced in 1971 could be used as a non-invasive way to measure brain temperature continuously [
8]. However, it has not been widely used due to its disadvantages of taking about 20 minutes of temperature equilibrium and requiring additional heater. Recently, by compensating for these shortcomings, SpotOn
® thermometer (3M
®, St. Paul, Minnesota, USA) has been developed using the ZHF technology with a short equilibrium time of 3 minutes and a disposable probe [
9]. Its research and clinical application are increasing. When measuring body temperature using ZHF technology, it is known that the core body temperature of brain tissue can be measured simply by attaching a probe to the forehead without pain or discomfort. Several studies have evaluated the accuracy of body temperature using 3M SpotOn
® compared with conventional body temperature measurement methods [
10]. However, such studies on elderly patients over 80 years of age have not been reported yet.
With age, not only the ability to sense cold and produce a corresponding physiological response, but also the efficiency of thermoregulation for normal body temperature will gradually decrease [11. 12]. The cold environment of an operating room and anesthesia inevitability exacerbate the vulnerable body temperature homeostasis of the elderly. Therefore, proper core body temperature monitoring during surgery is very important in the elderly. Among methods used for core body temperature monitoring mentioned above, 3M SpotOn® sensor is a non-invasive and continuous measurement method. The aim of this study was to examine the accuracy and feasibility of using of 3M SpotOn® sensor in the elderly undergoing a lower extremity orthopedic surgery by comparing 3M SpotOn® sensor with other two reliable methods, a tympanic membrane thermometer and a bladder thermometer.
2. Materials and Methods
The Institutional Review Board of CHA Bundang Medical Center approved this observational study (2019-05-005-003). The study protocol was registered at the Clinical Research Information Service (CRIS) clinical trials registry (KCT0004107). This study was performed from July 2019 to April 2020. All patients were given information about this study. They all provided written informed consent. This study was performed following the ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and all of its subsequent revisions (revised 2013).
This study enrolled 45 patients over 80 years old with an American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status of I-III who were scheduled to undergo a lower extremity surgery (total knee arthroplasty or hip surgery). Patients were excluded if they could not be measured with a tympanic thermometer, had renal failure in which urine output was not maintained, or were in a state in which a thermometer could not be attached to the forehead.
Patients were transferred from the ward to the operating room, covered with a single cotton sheet. Standardized monitoring and two types of anesthesia protocol (general or neuraxial anesthesia) were adopted for all patients according to their conditions. General anesthesia was induced with remifentanil, propofol, and rocuronium. Patients were intubated. General anesthesia was maintained with sevoflurane with infusing remifentanil. Neuraxial anesthesia patients received spinal anesthesia by 25-gauge quincke spinal needle at intervertebral space of lumbar 3-4 with 0.5% heavy bupivacaine 10~15 mg to obtain sensory block level T8~T10. During anesthesia induction, patient’s skin exposure to ambient air was minimized. After induction of anesthesia, depending on the type of operation, supine or lateral position was taken and an upper body forced-air warmer (3M®, St. Paul, Minnesota, USA) was applied until the end of the surgery.
For all patients, body temperature was recorded every 10 minutes after induction of anesthesia using a SpotOn® sensor (attached avoiding the center of the forehead), a tympanic membrane thermometer (Braun®, Kronberg, Germany), and a bladder thermometer (Sewoon Medical, Cheonan, South Korea). To reduce measurement errors, the tympanic membrane temperature was measured by a single physician.
Agreements between SpotOn® sensor and the other two methods were assessed using Bland and Altman plots for repeated measures adjusted for unequal numbers of measurements per patient. We estimated the mean and standard deviation of differences and concordance limits with a 95% confidence interval (CI). In addition, ratios at which the absolute difference between ZHF and the other two core temperature measurement methods were measured to be 0.3℃, 0.5℃, and 0.8℃ or less were expressed in numbers and percentages.
Time-series differences between ZHF and the other two body temperature measurement methods were compared using either paired Student’s t-test or the Wilcoxon rank-sum test after checking for normality with the Shapiro-Wilk test. A P-value of less than 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. Categorical data are expressed as number (n) and percentage. Quantitative data are reported as mean values and standard deviation (SD). All statistical analyses were performed using R Studio software (2022.07.1+554 “Spotted Wakerobin” Release for macOS).
3. Results
3.1. Participant Charicteristics
Between July 2019 and April 2020, 45 patients were enrolled in this study. For all patients, core body temperature was measured with all three methods. There was no missing case due to dropout or data omission. General characteristics of patients are shown in
Table 1.
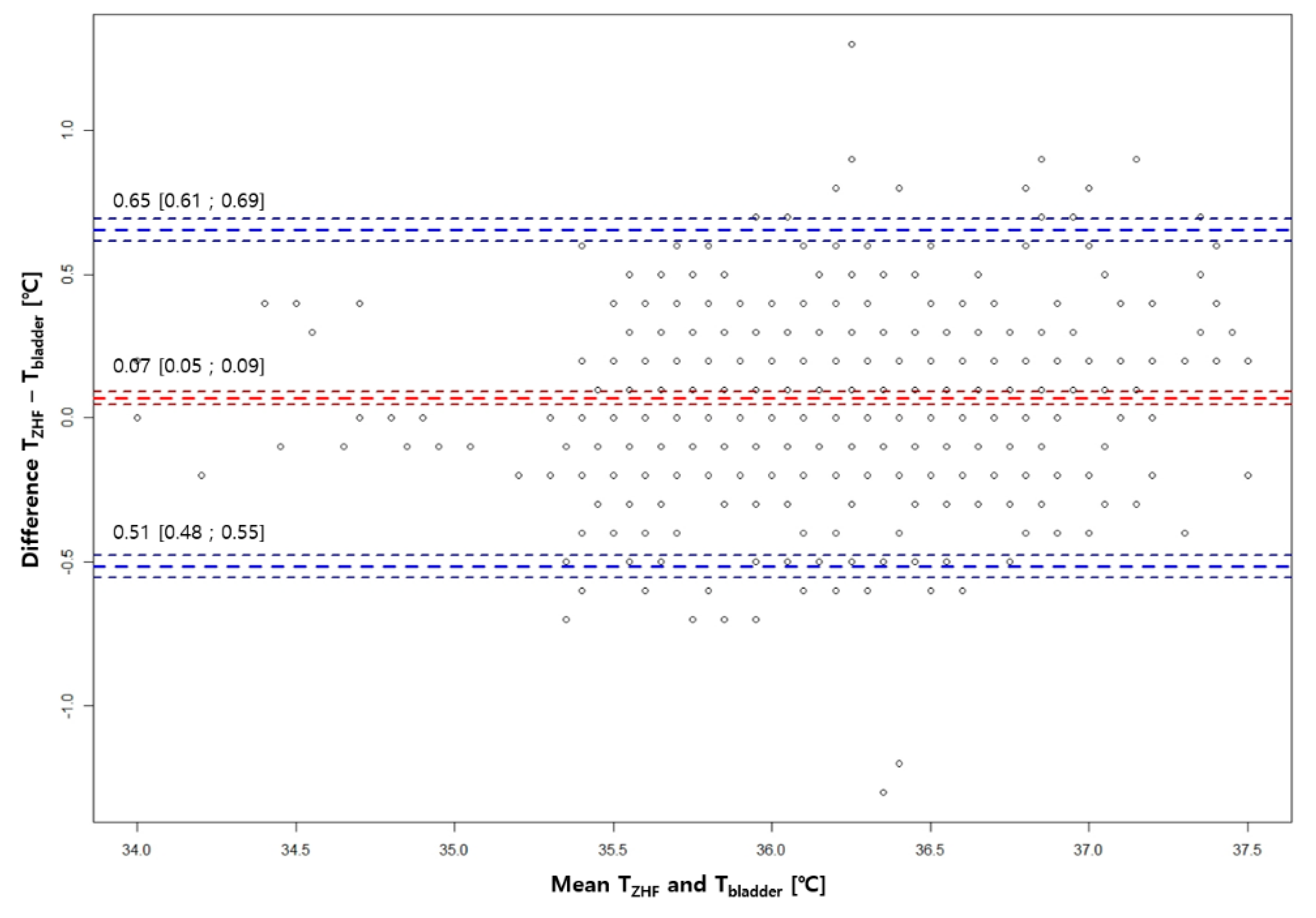
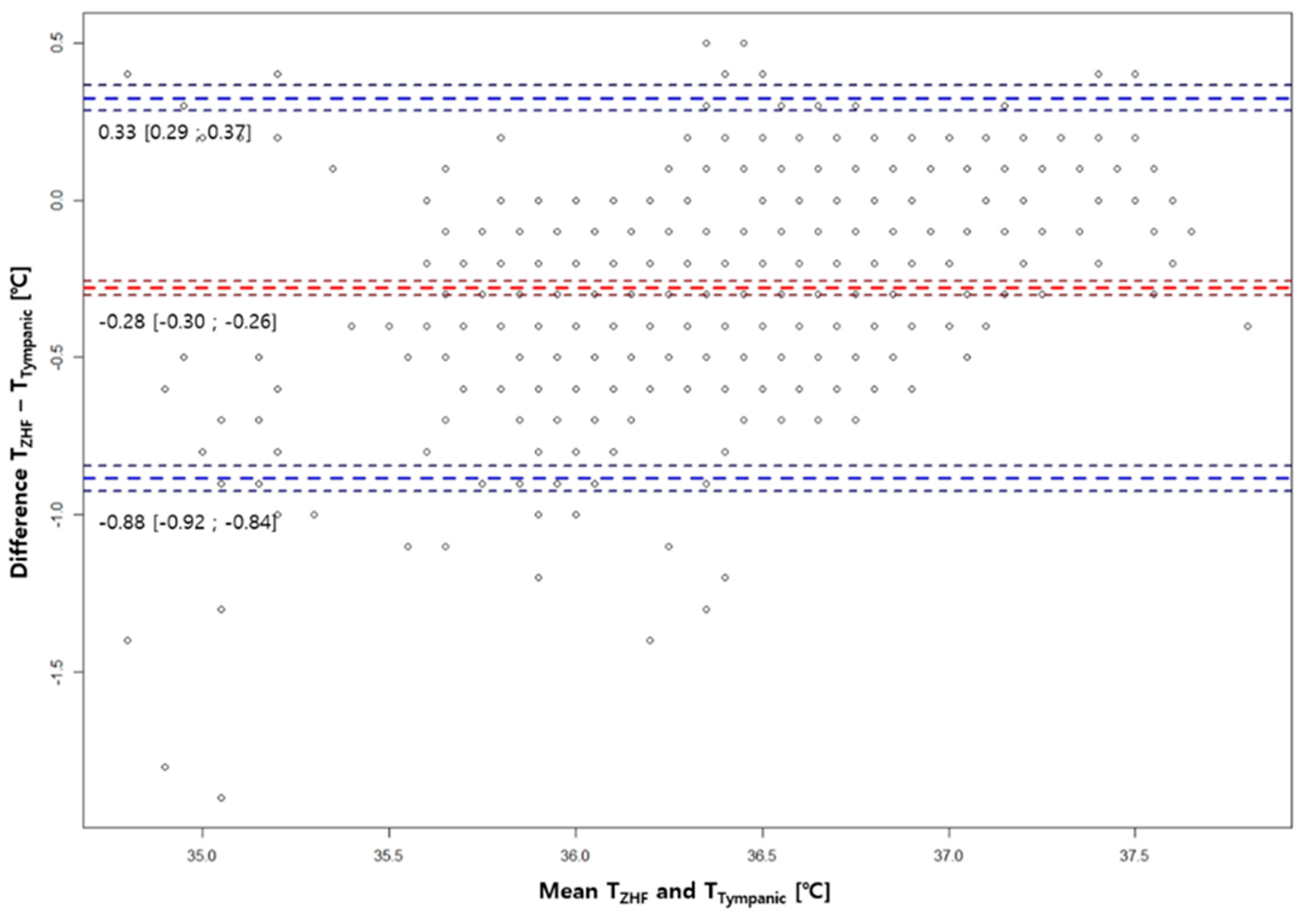
3.2. Bland-Altman Analysis Between ZHF(SpotOn®) Sensor and the Other Two Methods
A total of 679 pairs of ZHF, bladder, and tympanic membrane temperatures were measured for 45 patients ranging from 33.9℃ to 38℃. Compared with Temp
Bladder, bias and limits of agreement for Temp
ZHF were 0.07℃ ± 0.58℃ (
Figure 1). Compared with Temp
Tympanic, bias and limits of agreement for Temp
ZHF were -0.28℃ ± 0.61℃ (
Figure 2).
3.3. Absolute Differences Between ZHF(SpotOn®) Sensor and the Other Two Methods
Table 2 shows the number of pairs showing an absolute difference of 0.3℃, 0.5℃, and 0.8℃, or less between ZHF and the other two core body temperature measurement methods. Ratios of absolute differences between ZHF and bladder temperatures within 0.3°C, 0.5°C, and 0.7°C were all higher than those between ZHF and tympanic membrane temperatures.
3.4. Sensitivity to detect hypothermia during lower extremity orthopedic surgery over aged 80 years
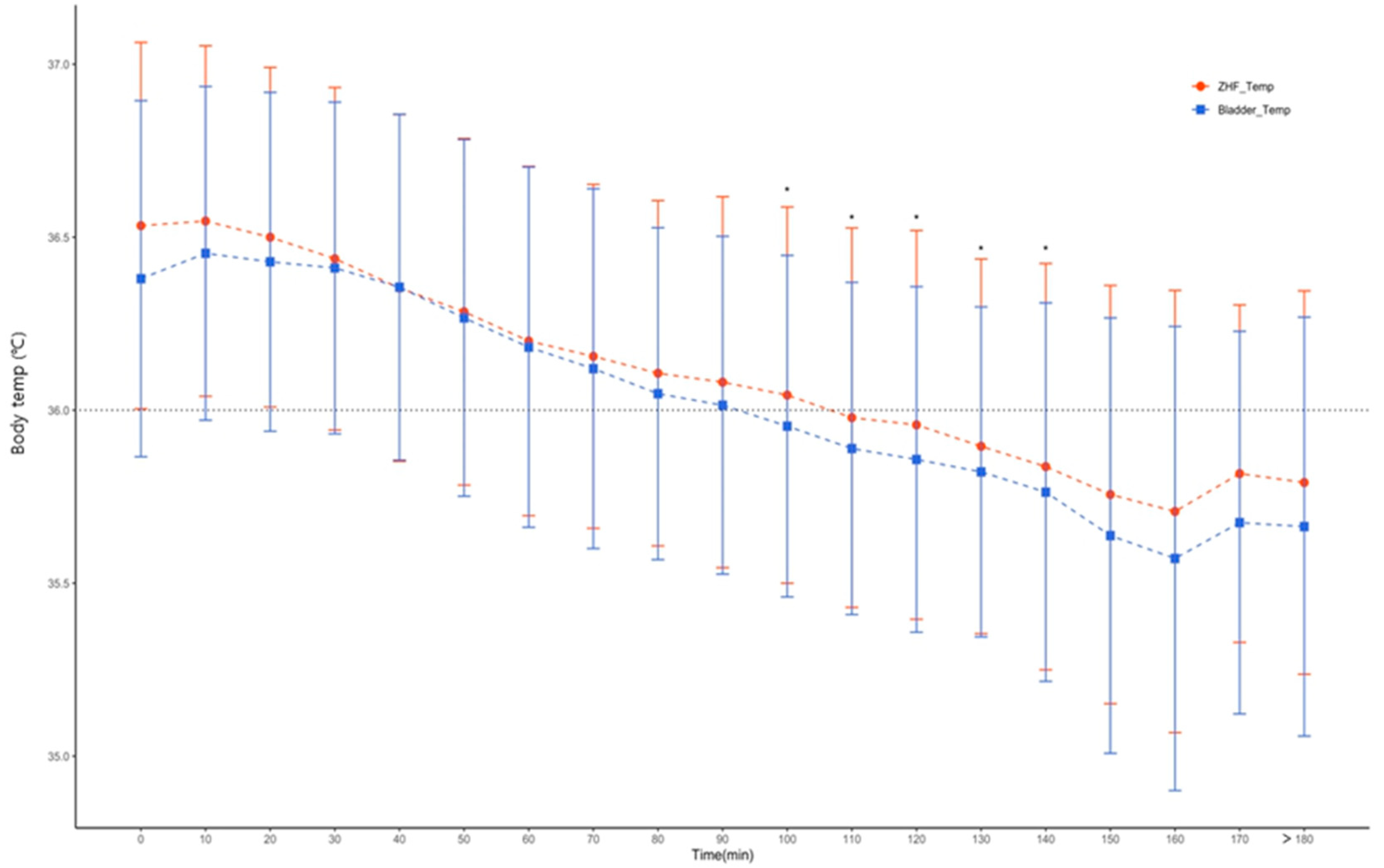
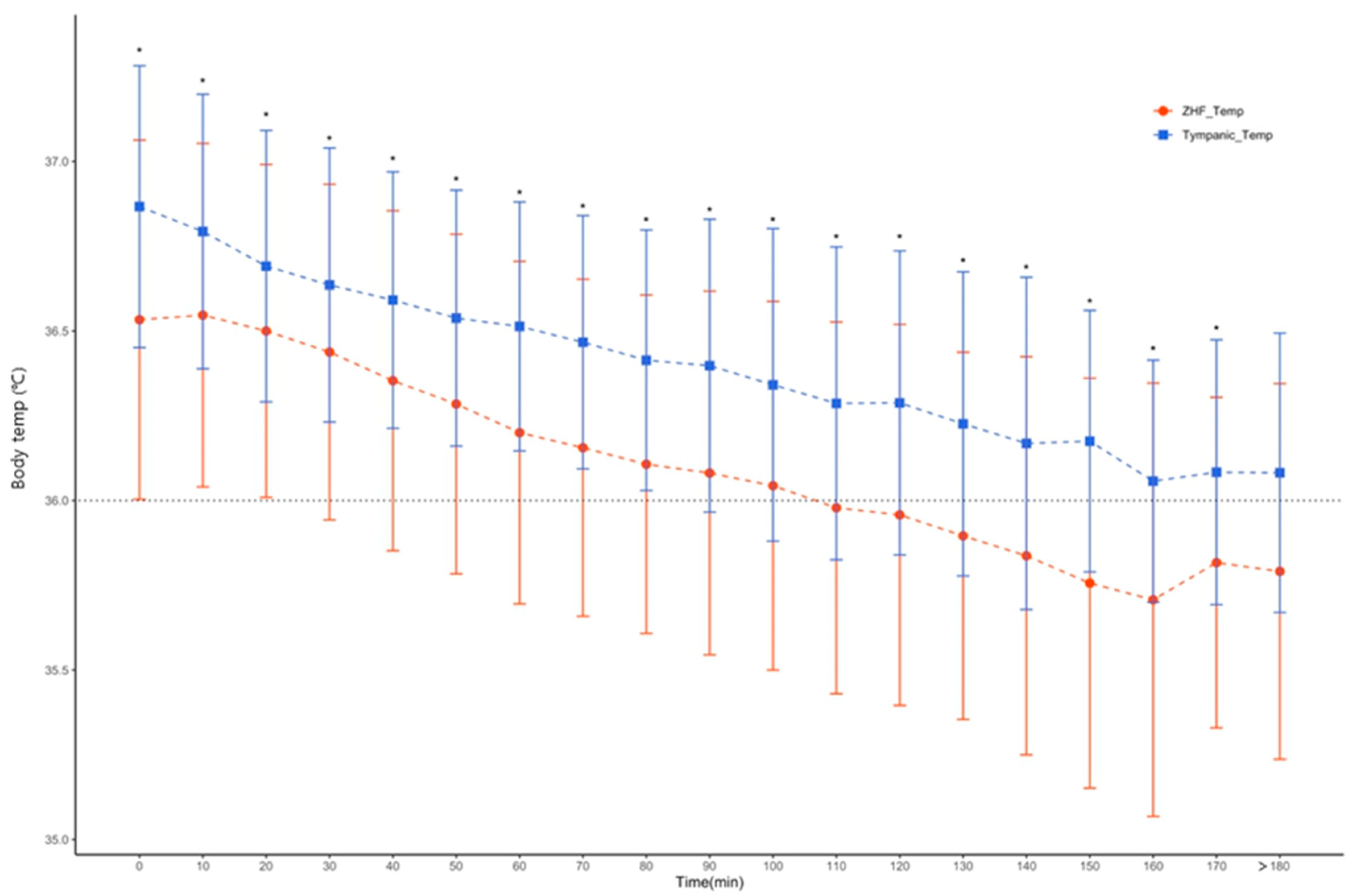
Additionally, we plotted a graph of sensitivity to detect hypothermia below 36°C during surgery.
Figure 3 and
Figure 4 show changes in mean and standard deviation of the core body temperature for each time period of the three core temperature measurement methods. Based on the mean value, the tympanic membrane temperature did not drop below 36°C during the operation. However, hypothermia of less than 36°C was observed in bladder temperature and ZHF, respectively, from 100 and 110 minutes after the start of the operation. Also, between ZHF and bladder body temperature, core body temperature showed a good correlation for each time period. There was a statistically significant difference only between 110 and 140 minutes of operation time (
Figure 3) On the other hand, there was a statistically significant difference between ZHF and tympanic membrane body temperature at all times (
Figure 4).
4. Discussion
In this study, we compared and analyzed three the least invasive methods of measuring core body temperature by applying them to patients aged over 80 years undergoing a lower extremity surgery. Bladder body temperature is traditionally known to reflect core body temperature well. It has been used as a standard core body temperature measurement tool in various situations [
13,
14,
15]. The tympanic membrane temperature also shows a good correlation with the core body temperature measured with a pulmonary artery catheter. It is known to reflect the core body temperature [
1,
16].
Meanwhile, the accuracy of core body temperature of 3M SpotOn
®, a newly designed ZHF system, has been elucidated in many studies [
10]. Each study has measured the accuracy of core body temperature for specific patients, including healthy adults [
9], abdominal surgery patients [
17,
18], cardiac surgery patients [
19], and intensive care unit patients [
14,
20]. The present study not only investigated the accuracy of ZHF acknowledged in previous studies, but also determine the accuracy and feasibility of using ZHF to measure core body temperature for orthopedic lower extremity surgery in the elderly known to be particularly vulnerable to heat control.
In this study, the mean bias between Temp
ZHF and Temp
Bladder was 0.07℃, indicating that the difference in bias was smaller than that between Temp
ZHF and Temp
Tympanic. Sang et al. have also reported a good correlation between esophageal temperature and ZHF bias of 0.07℃ in children [
21]. In addition, Pesonen et al. [
22] have compared ZHF and bladder temperatures in patients undergoing craniotomy. Results of the present study (bias and limits of agreement of 0.07℃ ± 0.58℃) were slightly better than those of Pesonen et al. who observed a bias of -0.14°C and wider limits of agreement of ± 0.66°C between Temp
ZHF and bladder temperature [
22]. The proportion of differences within ±0.5°C of Temp
Bladder was 93.5% in the present study, which was better than that (88.5%) in the study of Pesonen et al. [
22]. In one meta-analysis study [
10], 16 studies comparing ZHF and other core body temperature measurement methods were analyzed. The pooled estimate for the mean bias and limits of agreement between ZHF and other core body temperature measurement methods was 0.03 °C ± 0.98 °C. Compared with the present study, the mean bias showed a difference of 0.04°C from the meta-analysis result. However, limits of agreement in the present study were narrower than those in the meta-analysis [
10]. Therefore, according to results of this study, core body temperature measurement using ZHF for patients aged over 80 years undergoing a lower extremity surgery showed a fairly accurate measurement value.
However, the bias and limits of agreement between Temp
ZHF and Temp
Tympanic were -0.28℃ ± 0.61℃, which showed a greater difference than that with Temp
Bladder. In a meta-analysis, Niven et al.[
23] have compared peripheral (tympanic membrane, temporal artery, axillary, or oral) thermometers and central (pulmonary artery catheter, urinary bladder, esophageal, or rectal) thermometers. They found that compared with central thermometers, peripheral thermometers were outside the pre-defined clinically acceptable range (± 0.5 °C), particularly among patients with fever (-1.44 °C to 1.46 °C) and hypothermia (-2.07 °C to 1.90 °C) [
23]. This result might explain why the mean bias between Temp
ZHF and Temp
Tympanic was larger than that with Temp
Bladder in the present study. Another conceivable reason was the application of a forced air blanket over the patient’s upper body. The constant warm air supplied from the forced-air warmer might have affected the eardrum as well as the external auditory meatus to some extent. On the other hand, it was presumed that ZHF was not affected by forced-air warmer even though it was attached to the forehead due to the insulated characteristic of the sensor.
Applying these results, how sensitively a clinician detects hypothermia below 36°C and provides appropriate management is another issue, especially for elderly patients who are very vulnerable to thermal homeostasis. As shown in
Figure 3, Temp
ZHF and Temp
Bladder dropped to below 36°C from 100 and 110 minutes after initiation of surgery. However, in the Temp
Tympanic, hypothermia below the average core body temperature of 36°C was not observed at any time (
Figure 4.) Judging from these results, hypothermia might occur in elderly patients despite the application of forced air warming of the upper body. It suggests that bladder body temperature and ZHF are methods for measuring core body temperature sensitively reflecting hypothermia. The time gap between bladder body temperature and ZHF detecting hypothermia was only 10 minutes, which was not considered to be a clinically critical. However, the Temp
Tympanic did not reflect such changes well. Thus, if intraoperative management is performed based on the tympanic temperature, an active management to hypothermia may be insufficient.
This study has several limitations. First, the pulmonary artery catheter, the gold standard for measuring core body temperature, was not included in this study. It is unreasonable to insert an invasive pulmonary artery catheter in all patients undergoing an orthopedic surgery. It is even more unsuitable for patients undergoing spinal anesthesia. Thus, pulmonary artery catheter was not applied in this study. However, a recent study comparing pulmonary artery catheter with ZHF, nasopharyngeal, bladder, and rectal body temperatures during cardiac surgery reported that the mean difference between pulmonary artery catheter and ZHF temperatures was smaller than that of other thermometers [
24]. This could serve as a basis for overcoming limitations of this study that did not include a pulmonary artery catheter. Second, this study specified a group of elderly patients undergoing a lower extremity orthopedic surgery without differentiating between patients under general anesthesia and regional anesthesia. As there have been previous studies showing that regional anesthesia and general anesthesia have the same core body temperature profile with similar risk of falling into hypothermia [
25,
26], limitations of this study design are supplemented.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, according to results of this study, a 3M SpotOn® sensor is a non-invasive method of measuring body temperature that can not only reliably measure core body temperature, but also sensitively reflect changes in hypothermia in elderly patients undergoing lower extremities orthopedic surgery.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Chunghyun Park and Yun-Sic Bang; methodology, Chunghuyn Park, Soojeong Oh; software, Taeyeon Kim, Chunghyun Park; validation, Yun-Sic Bang; formal analysis, Chunghyun Park and Taeyeon Kim; investigation, Chunghyun Park and Soojeong Oh; resources, Yun-Sic Bang; data curation, Chunghyun Park and Yun-Sic Bang; writing—original draft preparation, Chunghyun Park and Yun-Sic Bang; writing—review and editing, Yun-Sic Bang; visualization, Taeyeon Kim; supervision,Yun-Sic Bang; project administration, Chunghyun Park; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of CHA Bundang Medical Center approved this observational study (2019-05-005-003).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request due to restrictions, e.g., privacy or ethical concerns.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest..
References
- Sessler, D.I. Perioperative thermoregulation and heat balance. Lancet. 2016, 387, 2655–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurz, A.; Sessler, D.I.; Lenhardt, R. Perioperative normothermia to reduce the incidence of surgical-wound infection and shorten hospitalization. Study of Wound Infection and Temperature Group. N Engl J Med. 1996, 334, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenhardt, R.; Marker, E.; Goll, V.; Tschernich, H.; Kurz, A.; Sessler, D.I.; Narzt, E.; Lackner, F. Mild intraoperative hypothermia prolongs postanesthetic recovery. Anesthesiology. 1997, 87, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, S.; Mascha, E.; Na, J.; Sessler, D.I. The effects of mild perioperative hypothermia on blood loss and transfusion requirement. Anesthesiology. 2008, 108, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, S.M.; Fleisher, L.A.; Breslow, M.J.; Higgins, M.S.; Olson, K.F.; Kelly, S.; Beattie, C. Perioperative maintenance of normothermia reduces the incidence of morbid cardiac events. A randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 1997, 277, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, Shawn S.; Eskicioglu, Cagia.; Nathens, Avery B.; Fenech, Darlene S.; Laflamme, Claude; McLean, Richard F.; McLeod, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Robin, S.; Best Practice in General Surgery Committee, University of Toronto. Evidence-based guidelines for prevention of perioperative hypothermia. J Am Coll Surg. 2009, 209, 492–503.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn EP,; Torossian A. [Prevention of perioperative hypothermia]. Anasthesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther. 2010, 45, 160–167. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, R.H.; Solman, A.J.; Isaacs, R.; Fry, A.J.; MacDonald, I.C. A new method for monitoring deep body temperature from the skin surface. Clin Sci. 1973, 44, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, L.P.; Klewer, J.; de Haan, A.; de Koning, J.J.; Daanen, H.A. Non-invasive continuous core temperature measurement by zero heat flux. Physiol Meas. 2011, 32, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, A.; Bittner, M.; Phan, D.; Chang, K.; Kamboj, N.; Tipton, E.; Parotto, M. Accuracy and precision of zero-heat-flux temperature measurements with the 3M™ Bair Hugger™ Temperature Monitoring System: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Monit Comput. 2021, 35, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Nakao, M.; Araki, T.; Ueda, H. Thermoregulatory responses of young and older men to cold exposure. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1992, 65, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, A.J. Hypothermia in the aged: a study of the role of cold-sensitivity. Environ Res. 1972, 5, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bone, M.E.; Feneck, R.O. Bladder temperature as an estimate of body temperature during cardiopulmonary bypass. Anaesthesia. 1988, 43, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bräuer, A.; Fazliu, A.; Perl, T.; Heise, D.; Meissner, K.; Brandes, I.F. Accuracy of zero-heat-flux thermometry and bladder temperature measurement in critically ill patients. Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 21746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallis, W.M. Monitoring bladder temperatures in the OR. Aorn j 2002, 76, 467–476, 81-6, 88-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, D.G.; Mitchell, C.; Petrinec, A.; Monroe, M.K.; Oblak, M.; Ross, B.; Youngblut, J.M. A comparison of pulmonary artery, rectal, and tympanic membrane temperature measurement in the ICU. Heart Lung. 1993, 22, 435–441. [Google Scholar]
- Boisson, M.; Alaux, A.; Kerforne, T.; Mimoz, O.; Debaene, B.; Dahyot-Fizelier, C.; Frasca, D. Intra-operative cutaneous temperature monitoring with zero-heat-flux technique (3M SpotOn) in comparison with oesophageal and arterial temperature: A prospective observational study. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2018, 35, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmann Camaiora, A.; Brogly, N.; Alsina, E.; de Celis, I.; Huercio, I.; Gilsanz, F. Validation of the Zero-Heat-Flux thermometer (SpotOn®) in major gynecological surgery to monitor intraoperative core temperature: a comparative study with esophageal core temperature. Minerva Anestesiol. 2019, 85, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshraghi, Y.; Nasr, V.; Parra-Sanchez, I.; Van Duren, A.; Botham, M.; Santoscoy, T.; Sessler, D.I. An evaluation of a zero-heat-flux cutaneous thermometer in cardiac surgical patients. Anesth Analg. 2014, 119, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahyot-Fizelier, C.; Lamarche, S.; Kerforne, T.; Bénard, T.; Giraud, B.; Bellier, R.; Carise, E.; Frasca, D.; Mimoz, O. Accuracy of Zero-Heat-Flux Cutaneous Temperature in Intensive Care Adults. Crit Care Med. 2017, 45, e715–e717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, B.H.; Lee, C.; Lee, D.Y. Prospective comparative analysis of noninvasive body temperature monitoring using zero heat flux technology (SpotOn sensor) compared with esophageal temperature monitoring during pediatric surgery. PLoS One. 2022, 17, e0272720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesonen, E.; Silvasti-Lundell, M.; Niemi, T.T.; Kivisaari, R.; Hernesniemi, J.; Mäkinen, M.T. The focus of temperature monitoring with zero-heat-flux technology (3M Bair-Hugger): a clinical study with patients undergoing craniotomy. J Clin Monit Comput. 2019, 33, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niven, D.J.; Gaudet, J.E.; Laupland, K.B.; Mrklas, K.J.; Roberts, D.J.; Stelfox, H.T. Accuracy of peripheral thermometers for estimating temperature: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2015, 163, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheyden, C.; Neyrinck, A.; Laenen, A.; Rex, S.; Van Gerven, E. Clinical evaluation of a cutaneous zero-heat-flux thermometer during cardiac surgery. J Clin Monit Comput. 2022, 36, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, C.G.; Frank, S.M.; Hesel, T.W.; El-Rahmany, H.K.; Kim, L.J.; Tran, K.M. The accuracy and precision of body temperature monitoring methods during regional and general anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2000, 90, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.M.; Shir, Y.; Raja, S.N.; Fleisher, L.A.; Beattie, C. Core hypothermia and skin-surface temperature gradients. Epidural versus general anesthesia and the effects of age. Anesthesiology. 1994, 80, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).