Submitted:
22 May 2023
Posted:
23 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- For the processing of the data related to the patient’s health profile, that is, for the objective data, different machine learning classification algorithms are considered, working concurrently [1,2,4,5,8,10,11,12], each of which is associated with different AHI threshold levels as in the approach in the first work, and through which it is possible to obtain a set of risk indicators, called Statistical Risks.
- The data relating to the patient’s symptoms, that is, those of a subjective nature, are processed in a similar way to the approach in the second work, using a series of expert systems arranged in a cascade, the output of which determines an indicator, the Symbolic Risk, a common value for the patient, applicable to all AHI levels.
Motivation and conceptual approach
1.1. Wang and Mendel’s method
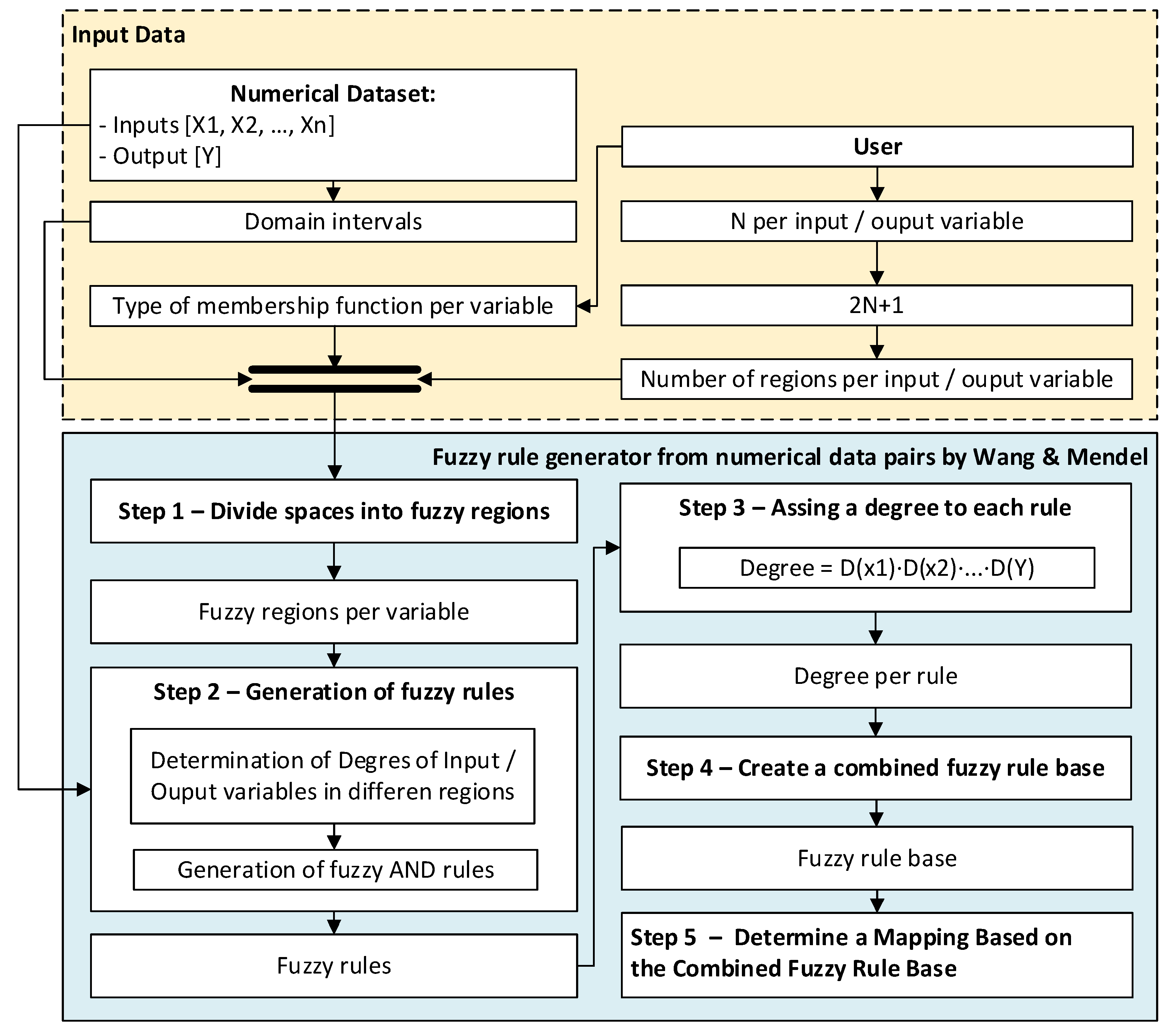
- Stage prior to the application of the method: before applying the Wang–Mendel algorithm, the dataset to be used is prepared by identifying the input and output variables. The range of each variable, that is, their maximum and minimum values, is also determined. The user must also select the type of membership function to use. The original proposal by Wang and Mendel envisaged the use of triangular membership functions. It is also necessary to define the value of N for each variable, which must be an integer greater than or equal to one. This value is used to determine the number of sections for each of the associated membership functions.
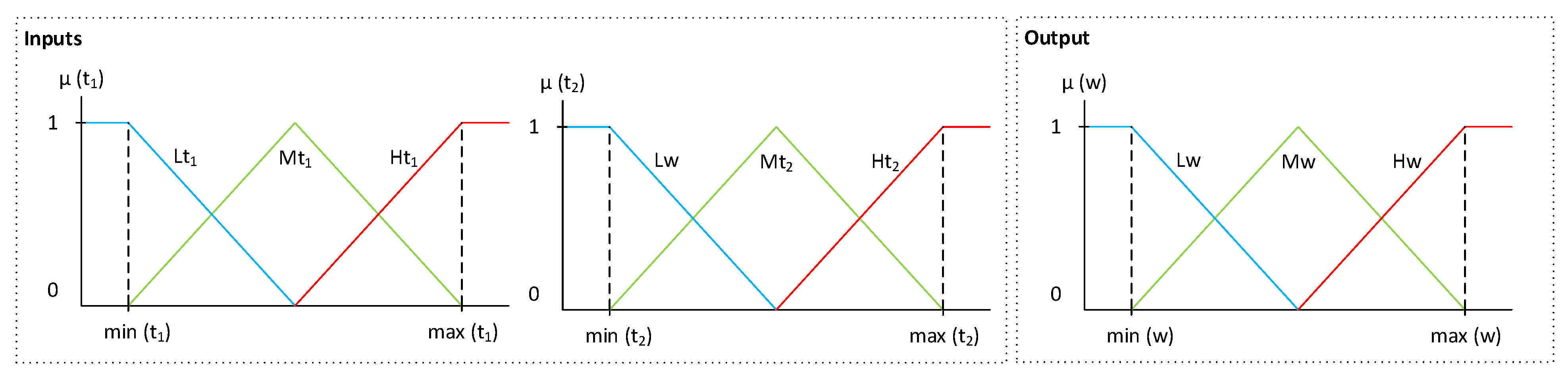
- Stage 1 – Division of the input and output spaces into fuzzy regions: in this stage, for each of the–both input and output–variables considered, the problem domain is divided into 2N + 1 sections, in this case using triangular functions, as originally proposed in the paper of Wang and Mendel [40]. 2N + 1 sections are added, since the goal is to perform a division of the domain of each of the variables in such a way that there is a central or intermediate section. Figure 2 shows an example for N = 1, with three segments of the membership function (L, M and H) for the two input variables (t1,t2) and the output variable (w) of the previous example. As can be seen, and in line with the proposal of the original paper, there is an overlap of the triangles, so that if the top vertex of the central triangle has a maximum degree of membership, at the same point the vertices of the neighboring triangles have minimum degrees of membership.
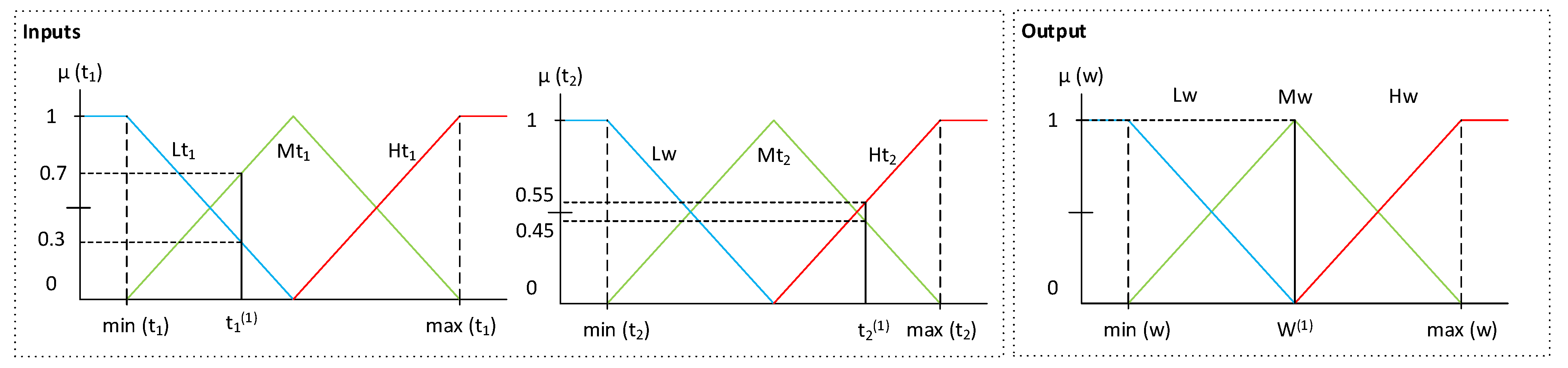
- Stage 2 – Generation of fuzzy rules from the input-output data pairs: once the sections of the membership function associated with each variable have been determined, the rules are to be generated. This is done by first determining the degrees of membership associated with each of the sections of the different functions for each of the different lines of the initial dataset. For this purpose, the variables are fuzzified through their respective membership functions on the basis of the data available in the dataset. For example, in Figure 3 it can be seen that for a given observation of the variable t1, it has a degree of membership of 0.3 to Lt1 and a degree of membership of 0.7 to Mt1. For variable t2, it is observed that it has a degree of membership of 0.45 to Mt2 and a degree of membership of 0.55 to Ht2. In the case of w, it is observed that it has degree of membership 1 to Mw. After that, in each of the rows of the dataset, each variable is assigned to the section with the maximum degree of membership, determining a rule for each row. For the case in Figure 3, taking the maximum degrees of membership, the following would be obtained: (t1(1), t2(1); w(1)) → IF t1 is Mt1 and t2 is Ht2, THEN w is Mw. As mentioned above, this process is carried out for each of the different rows of the dataset, with a rule being determined for each of these rows.
- Stage 3 – Assignation of a degree to each of the rules to solve potential conflicts among the generated rules: the initial numerical set may include observations that, after applying Stage 2, generate rules that could be in conflict, that is, their antecedent part is the same while the consequent part is different. To deal with this problem, Wang and Mendel propose to associate each rule with a degree, in order to select only those rules that have a maximum degree, thus dispensing with a large part of the rules generated in the previous stage. The degree value associated with each rule would be determined as the product of the degrees of membership of the observation that gave rise to the rule, as can be seen in Equation 1, which is particularized in Equation 2 for the case shown in Figure 3. In this case, after carrying out this process for all the rules and selecting those that maximize the coefficient value obtained, the resulting rule base would have the structure shown in Figure 4, with each of the boxes containing a section of the membership function of the consequent, if this combination were possible and present in the initial dataset.
- Stage 4 – Building of the combined fuzzy knowledge base: once the knowledge base has been determined by Wang–Mendel algorithm, the structure of which is shown in Figure 4, this could be enriched by a set of fuzzy rules expressed by the expert team. These rules, which in the case of Wang-Mendel’s definition are called linguistic rules or expert rules, would be incorporated into the knowledge base after being assigned a certain degree of importance by the expert team. In the case of conflict between the rule proposed by the expert and the rule generated by the algorithm in any of the boxes, Wang and Mendel advocate using the one with the maximum degree.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Definition of the system
2.1.1. Database Usage
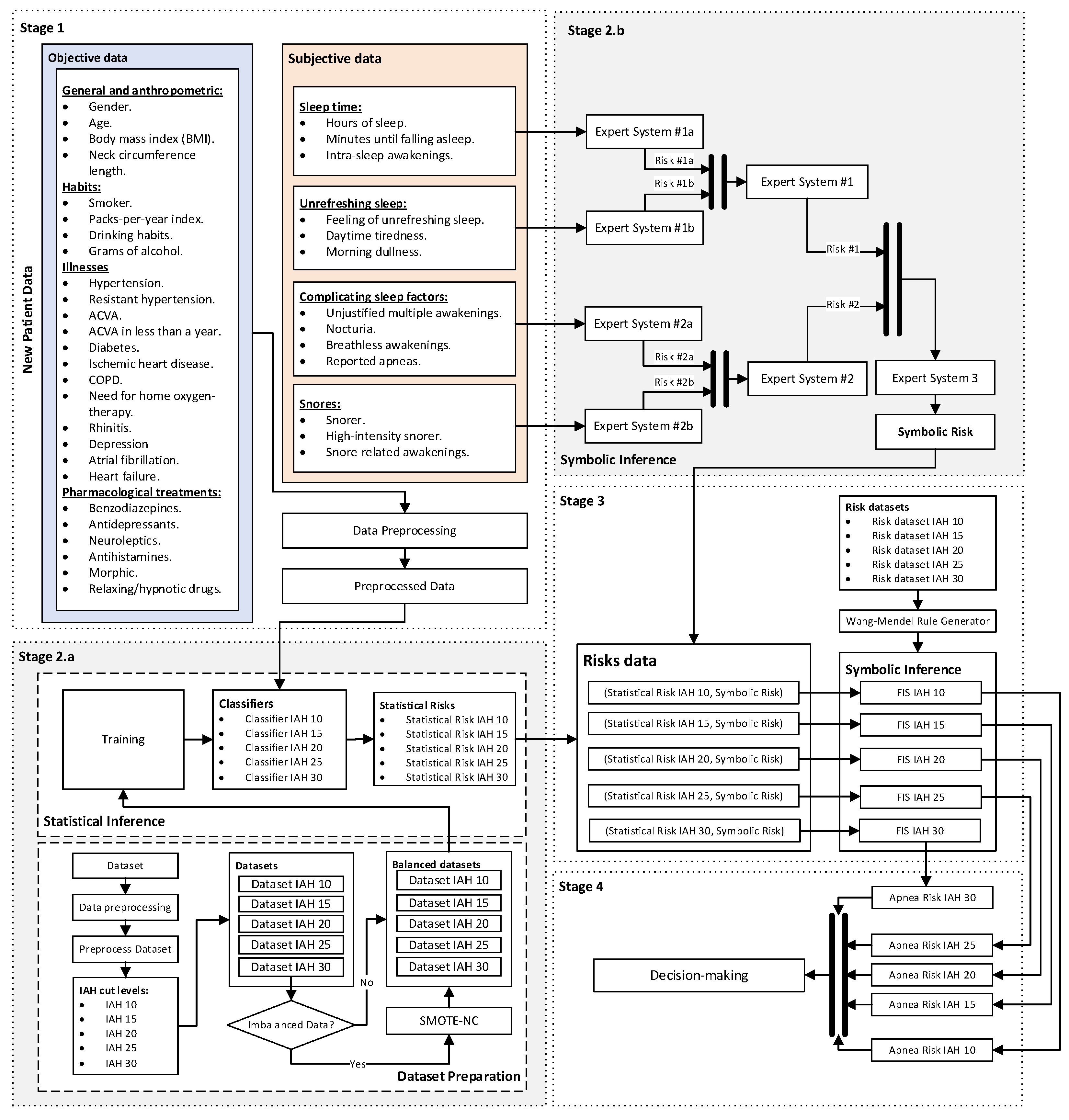
2.1.2. Conceptual Design and Description of the System
Stage 1: Collection of patient information
Stage 2: Determination of the values of Statistical Risk and Symbolic Risk values
Stage 3: Determination of the Apnea Risk level for each AHI threshold level
Stage 4: Generation of alerts and decision-making
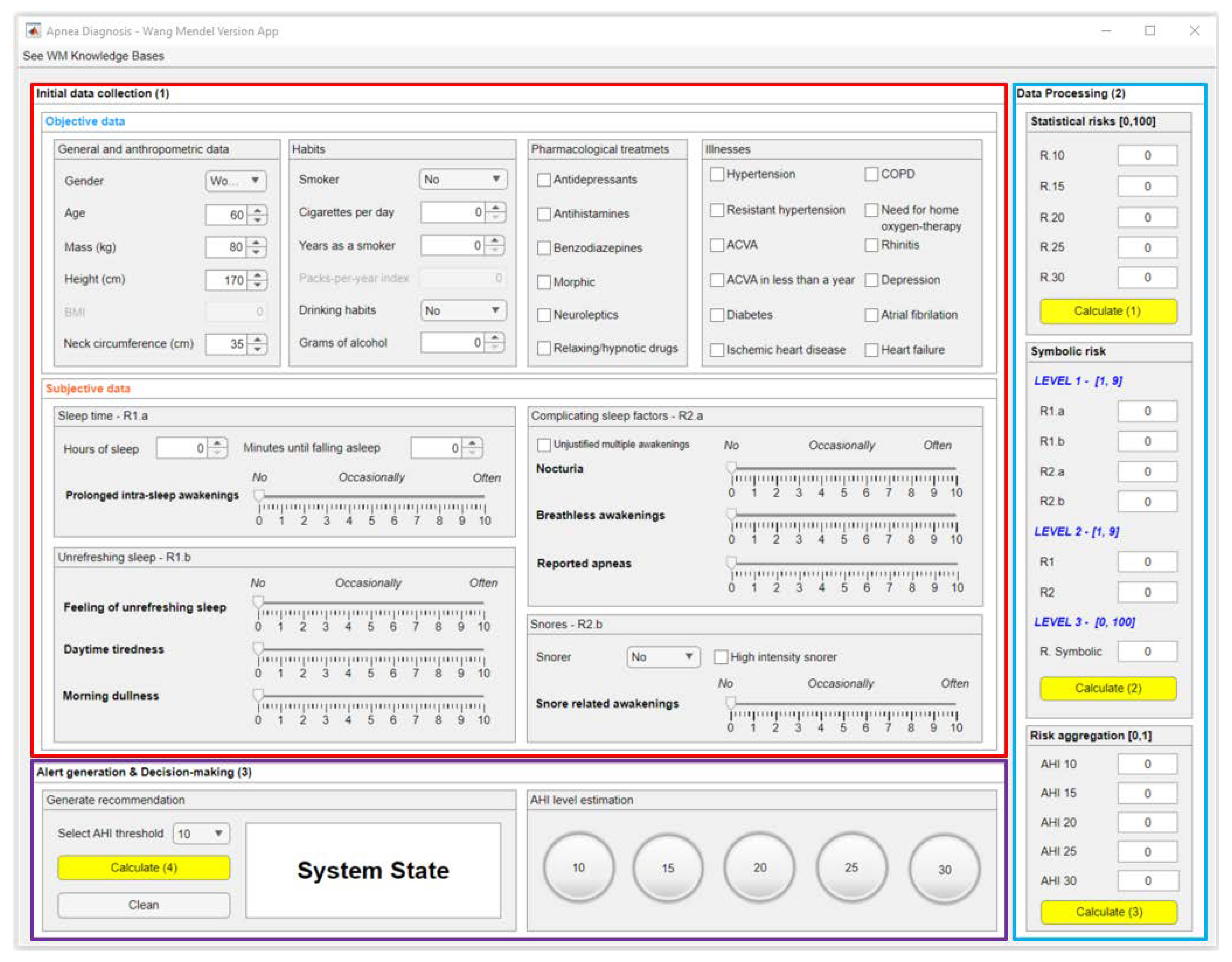
2.2. Implementation of the system
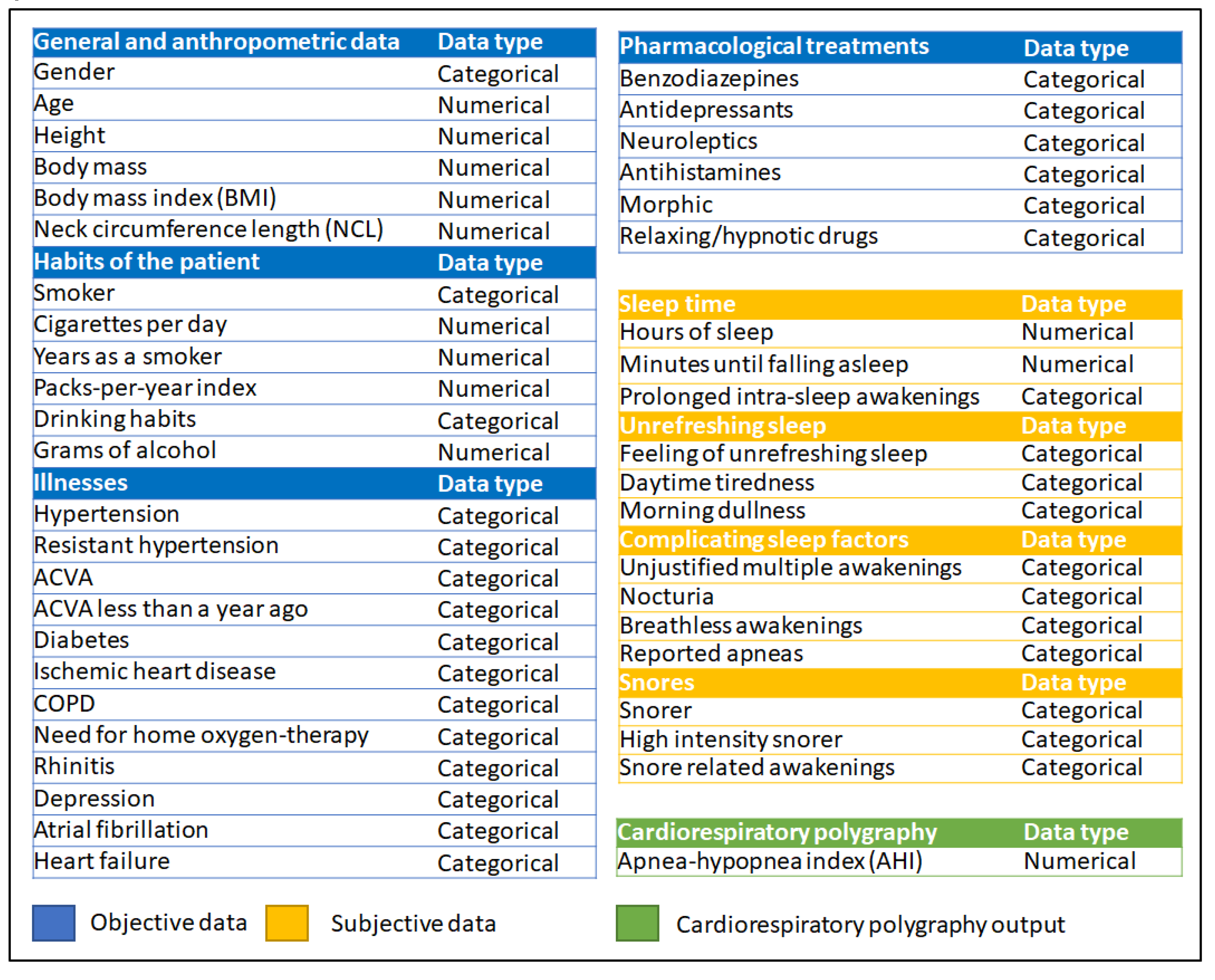
2.2.1. Data collection
2.2.2. Data processing
Machine learning algorithms
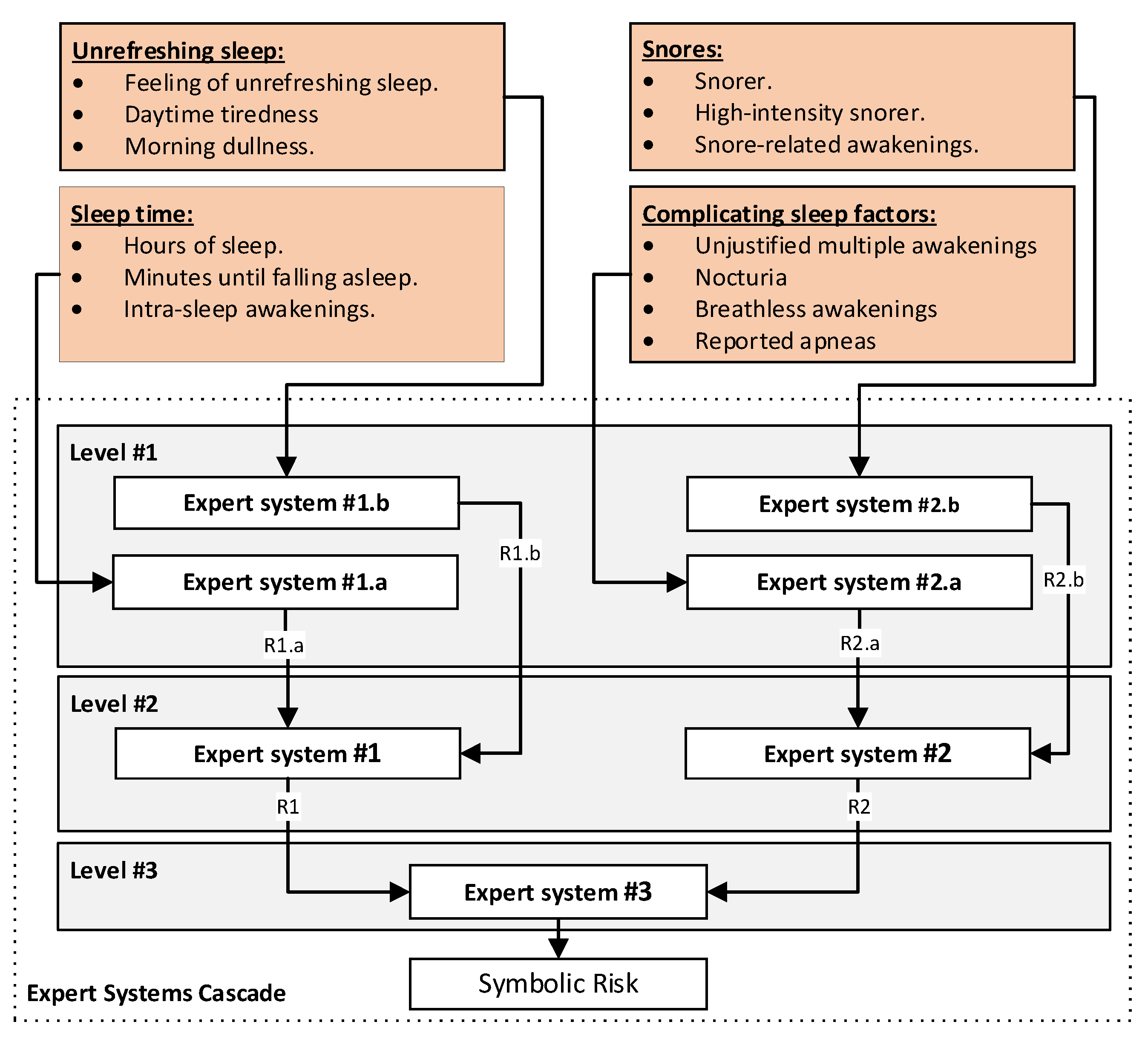
Cascaded Expert Systems
Risk aggregation by means of fuzzy expert systems with an automatically generated knowledge base
Determination of knowledge bases using Wang and Mendel algorithm
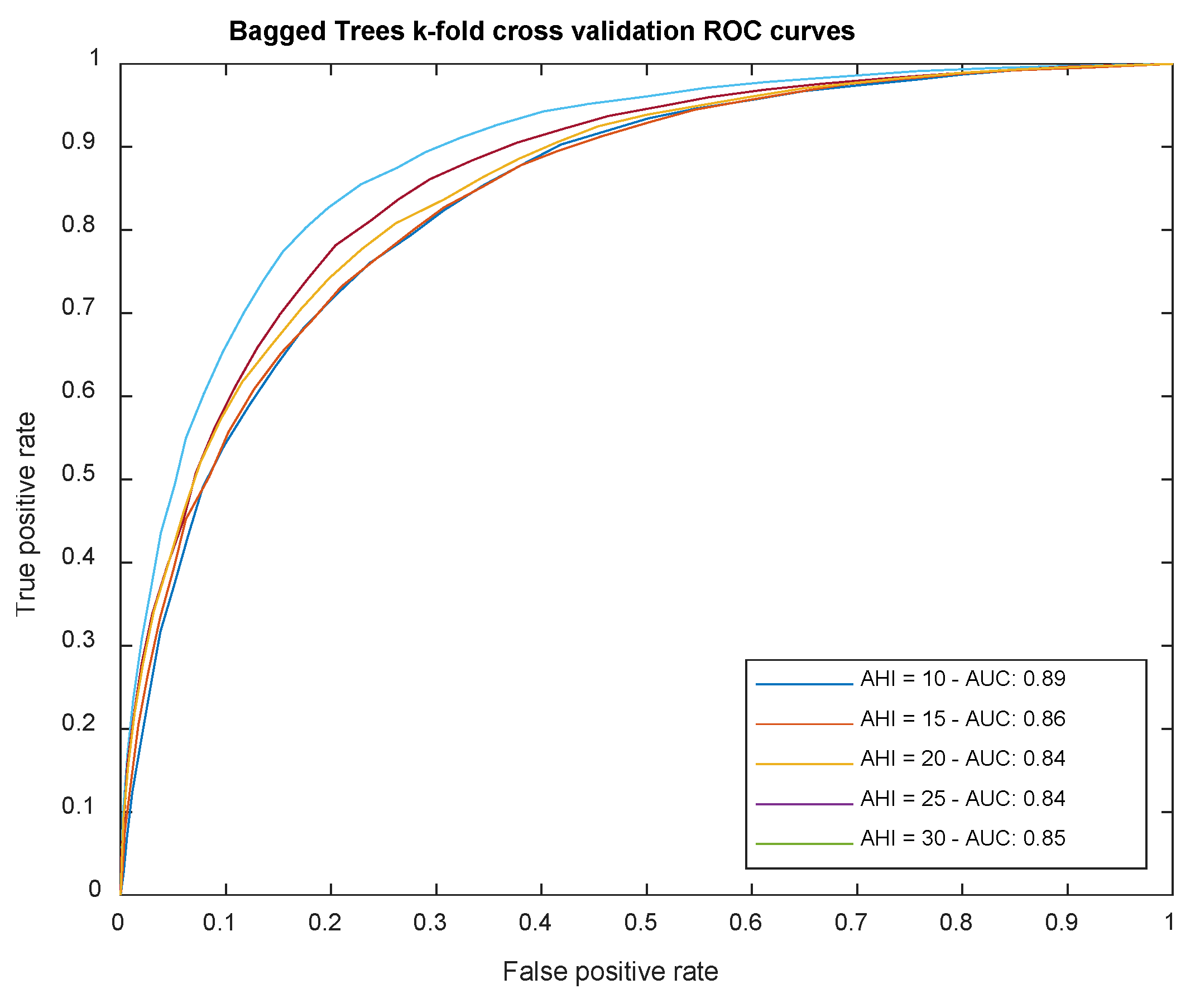
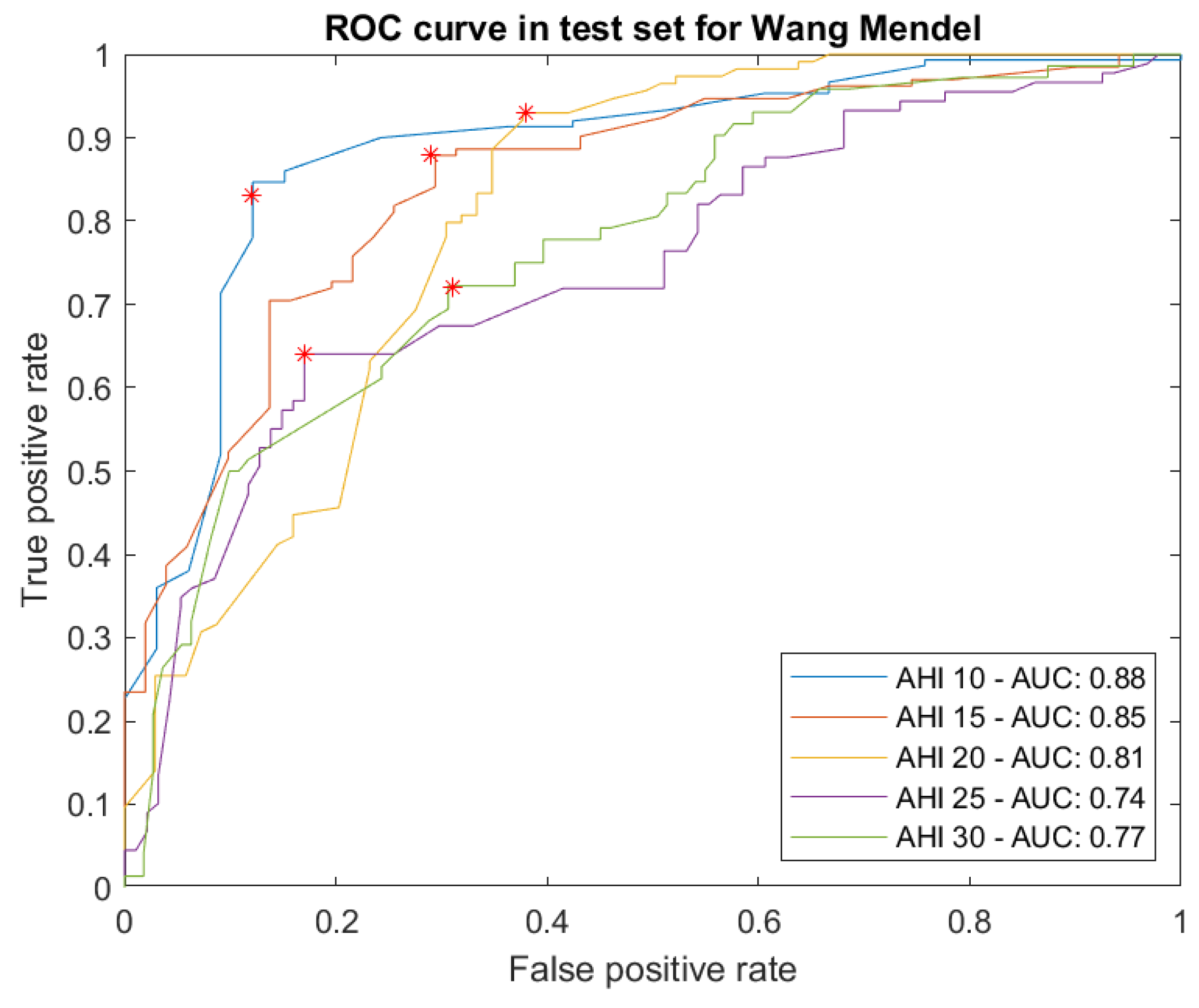
Proof test results
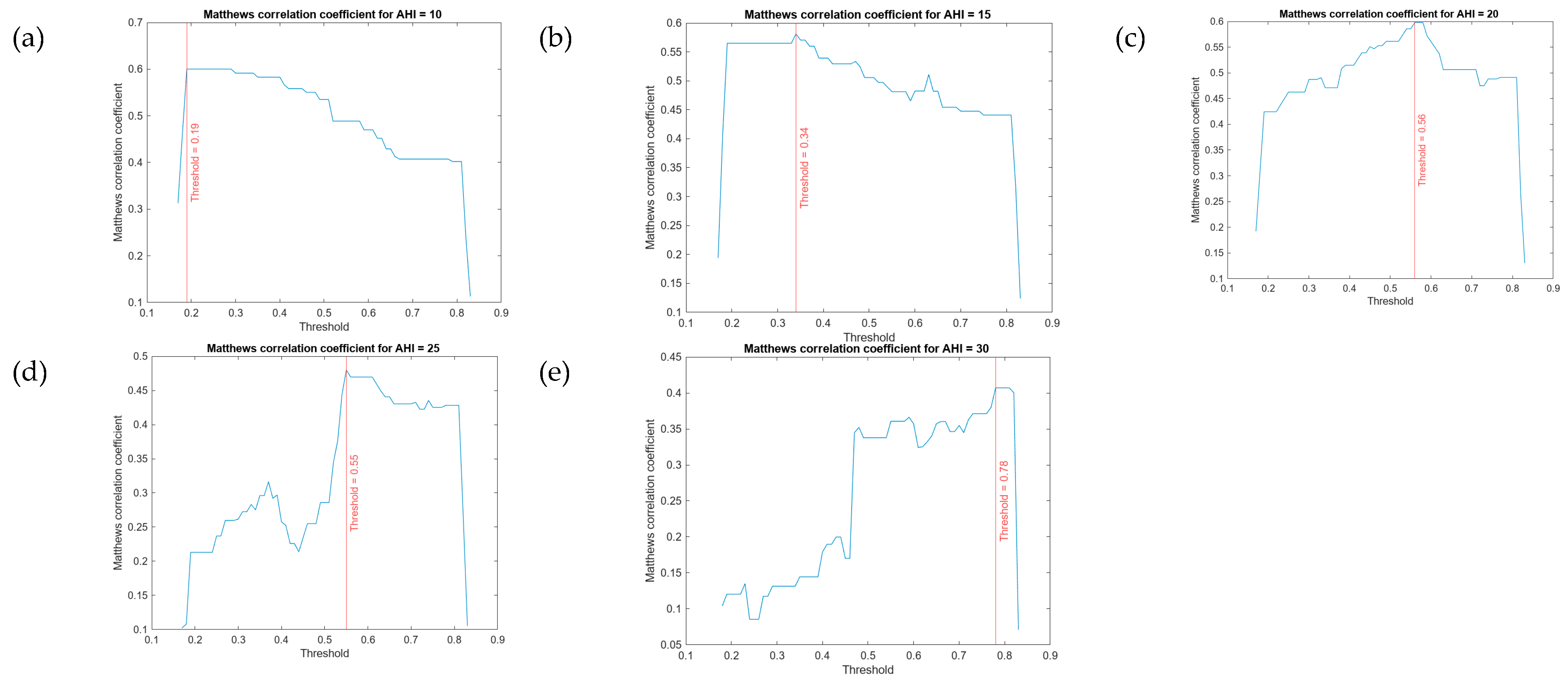
Determination of a threshold level for each AHI level
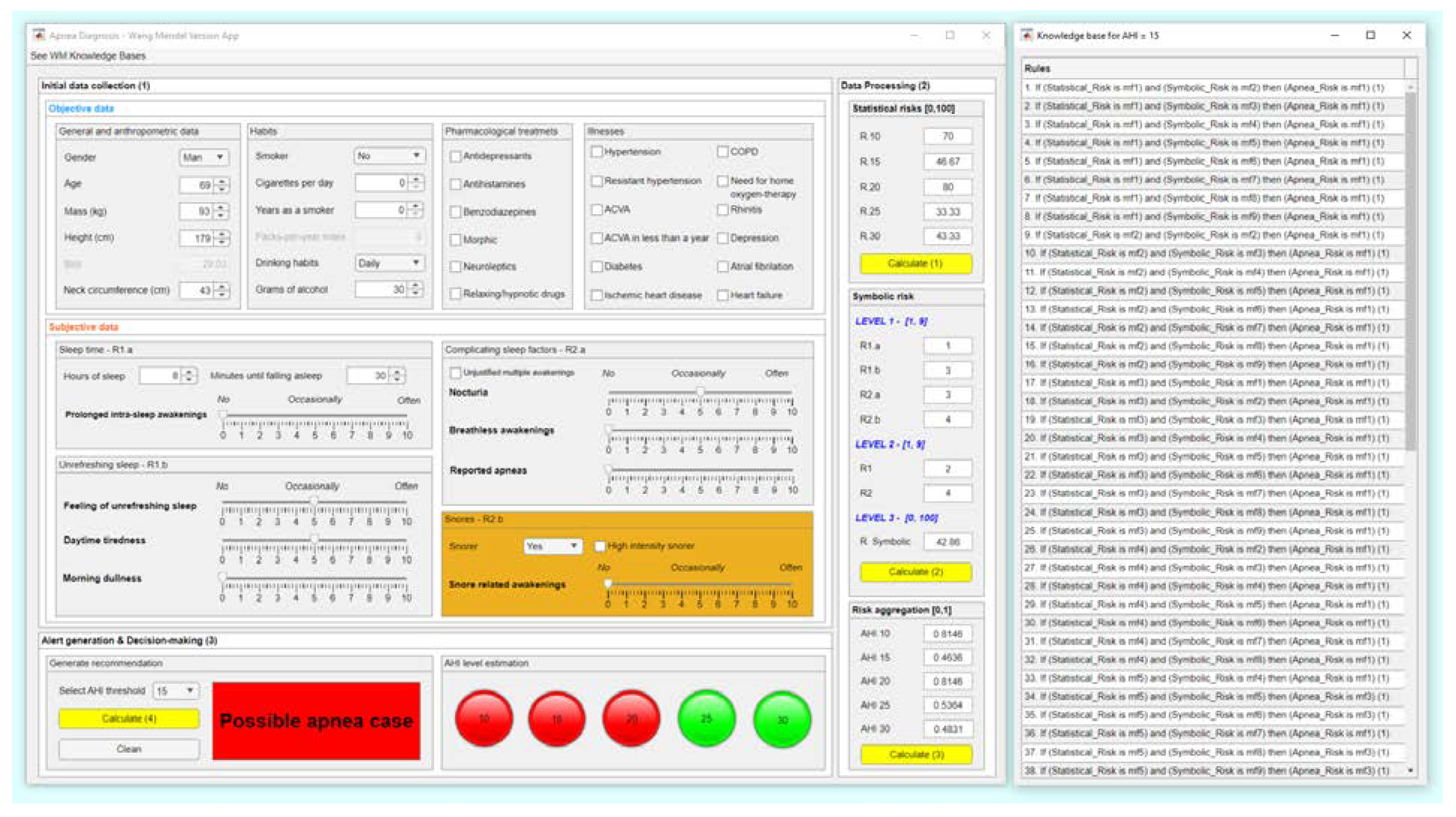
2.2.3. Generation of alerts and decision-making
3. Case study
3.1. Collection of the patient’s information
3.2. Data Processing
3.2.1. Risk aggregation
3.3. Generation of Alerts and Decision-Making
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantages and disadvantages of the aggregation process
- By dealing with the risk values, the algorithm acts indirectly by reducing the enormous dimensionality of the problem by reducing and synthesising the relationships between the initial variables through their representation and influence on the statistical and symbolic risks.
- There is no need to define and find explicit knowledge for risk aggregation. The numerical data representing them, the risks, as well as the labels that complete each line of data, can be interpreted as a non-formal pseudo-logical statement that serves as a basis for establishing a fuzzy rule.
- It is possible to combine the automatically generated rules with others generated by experts, thus completing a knowledge base of more general scope and wider applicability.
- It allows a circumstantial logical formalisation of the knowledge derived from the direct interpretation of numerical data, which is a differential milestone. This incorporates explanatory capabilities into the aggregation model and allows its validation by logical procedures.
- It allows the diversification of the risk aggregation knowledge base in its most basic form. This means that it is possible to understand that the rules form a knowledge base that can be exported to other examples once they have been created and defined.
- It reduces uncertainty in all its variants and interpretations, not only by incorporating fuzzy systems, but also by not introducing aggregation models with optional or optimisable parameters.
- From the different proofs of concept elaborated, of which the case study is an example, it is possible to observe a trend towards finding accurate classifiers in each of the AHI thresholds identified. The AUCs of the ROC curves for each of them extend their area above 0.74 (1 would be a perfect classifier), which in itself would not represent a notable difference with those obtained by other simple or combined machine and deep learning algorithms, if one did not take into account a differentiating factor: explainability.
- Explainability is the fair measure of the differential value of automated fuzzy rule generation from numerical data sets. Although this model, unlike traditional knowledge acquisition models, allows the aggregation of parameters with symbolic inference without the obligation of creating logical knowledge bases, it shares with them the ability to explain -that is, to understand, comprehend and reason- the inference process. However, in order for these new bases to have a permanent, not to say ontological, character, they must be verified by the team of expert pulmonologists.
- The first origin of the rules is the set of objective and subjective, numeric and categorical data from which the initial set of objective and subjective data, represented by its risk measures and class labels, was derived. These data are, by definition, ephemeral and mutable, so the rules derived from them will inherit these characteristics. Therefore, although the result of the application of the algorithm is a set of fuzzy rules, they will necessarily need to be interpreted by the expert team in order to consolidate them into a permanent knowledge base.
- Although the application of the algorithm results in a set of fuzzy rules, it is essential that they are interpreted by a team of experts in order to consolidate them into a permanent knowledge base.
- The logical operators that relate the antecedents must be defined in advance, which implies a prior assumption that may not be true.
- The algorithm classifies and ranks the rules according to a degree value, calculated as the product of the membership values of the set of antecedents and consequents of each rule. In the case of rules having similar antecedents, those with a higher degree are given priority and the others are eliminated. This in fact implies a loss of knowledge due to the operation of the algorithm itself, which will have to be taken into account in due course. In more or less well-known applications where prior knowledge exists, this is not a very significant loss. However, in medical diagnosis it may lead to non-negligible error rates, and therefore in the future it will be necessary to study mechanisms to reduce the loss of knowledge generated by the approach of generating deductive rules on fuzzy sets proposed by Wang and Mendel [40].
4.2. Comparison of systems
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casal-Guisande, M.; Torres-Durán, M.; Mosteiro-Añón, M.; Cerqueiro-Pequeño, J.; Bouza-Rodríguez, J.-B.; Fernández-Villar, A.; Comesaña-Campos, A. Design and Conceptual Proposal of an Intelligent Clinical Decision Support System for the Diagnosis of Suspicious Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients from Health Profile. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2023, Vol. 20, Page 3627 2023, 20, 3627. [CrossRef]
- Casal-Guisande, M.; Ceide-Sandoval, L.; Mosteiro-Añón, M.; Torres-Durán, M.; Cerqueiro-Pequeño, J.; Bouza-Rodríguez, J.-B.; Fernández-Villar, A.; Comesaña-Campos, A. Design and Development of an Intelligent Clinical Decision Support System Applied towards the Diagnosis of Suspected Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients from the Patient’s Health Profile and Symptomatology. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Casal-Guisande, M.; Bouza-Rodríguez, J.B.; Comesaña-Campos, A.; Cerqueiro-Pequeño, J. Proposal and Definition of a Methodology for Remote Detection and Prevention of Hypoxemic Clinical Cases in Patients Susceptible to Respiratory Diseases. Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality 2019, 331–338. [CrossRef]
- Casal-Guisande, M.; Comesaña-Campos, A.; Cerqueiro-Pequeño, J.; Bouza-Rodríguez, J.-B. Design and Development of a Methodology Based on Expert Systems, Applied to the Treatment of Pressure Ulcers. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 614. [CrossRef]
- Casal-Guisande, M.; Comesaña-Campos, A.; Dutra, I.; Cerqueiro-Pequeño, J.; Bouza-Rodríguez, J.-B. Design and Development of an Intelligent Clinical Decision Support System Applied to the Evaluation of Breast Cancer Risk. Journal of Personalized Medicine 2022, Vol. 12, Page 169 2022, 12, 169. [CrossRef]
- Casal-Guisande, M.; Cerqueiro-Pequeño, J.; Comesaña-Campos, A.; Bouza-Rodríguez, J.B. Proposal of a Methodology Based on Expert Systems for the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Condition. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality; ACM: New York, NY, USA, October 21 2020; pp. 491–495.
- Casal-Guisande, M.; Comesaña-Campos, A.; Pereira, A.; Bouza-Rodríguez, J.-B.; Cerqueiro-Pequeño, J. A Decision-Making Methodology Based on Expert Systems Applied to Machining Tools Condition Monitoring. Mathematics 2022, Vol. 10, Page 520 2022, 10, 520. [CrossRef]
- Cerqueiro-Pequeño, J.; Comesaña-Campos, A.; Casal-Guisande, M.; Bouza-Rodríguez, J.-B. Design and Development of a New Methodology Based on Expert Systems Applied to the Prevention of Indoor Radon Gas Exposition Risks. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 18, 269. [CrossRef]
- Cerqueiro-Pequeño, J.; Casal-Guisande, M.; Comesaña-Campos, A.; Bouza-Rodríguez, J.-B. Conceptual Design of a New Methodology Based on Intelligent Systems Applied to the Determination of the User Experience in Ambulances. Ninth International Conference on Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality (TEEM’21) 2021, 290–296. [CrossRef]
- Casal-Guisande, M.; Álvarez-Pazó, A.; Cerqueiro-Pequeño, J.; Bouza-Rodríguez, J.-B.; Peláez-Lourido, G.; Comesaña-Campos, A. Proposal and Definition of an Intelligent Clinical Decision Support System Applied to the Screening and Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, Vol. 15, Page 1711 2023, 15, 1711. [CrossRef]
- Casal-Guisande, M.; Bouza-Rodríguez, J.-B.; Cerqueiro-Pequeño, J.; Comesaña-Campos, A. Design and Conceptual Development of a Novel Hybrid Intelligent Decision Support System Applied towards the Prevention and Early Detection of Forest Fires. Forests 2023, Vol. 14, Page 172 2023, 14, 172. [CrossRef]
- Comesaña-Campos, A.; Casal-Guisande, M.; Cerqueiro-Pequeño, J.; Bouza-Rodríguez, J.B. A Methodology Based on Expert Systems for the Early Detection and Prevention of Hypoxemic Clinical Cases. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17, 1–31. [CrossRef]
- Suthaharan, S. Machine Learning Models and Algorithms for Big Data Classification; Springer US: Boston, MA, 2016; Vol. 36; ISBN 978-1-4899-7640-6.
- Zhou, Z.-H. Machine Learning; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2021; ISBN 978-981-15-1966-6.
- Deo, R.C. Machine Learning in Medicine. Circulation 2015, 132, 1920–1930. [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Huang, J.; Pedrycz, W.; Li, B.; Ren, F. A Fuzzy Clustering Validity Index Induced by Triple Center Relation. IEEE Trans Cybern 2023. [CrossRef]
- Unsupervised Learning Algorithms; Celebi, M.E., Aydin, K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24209-5.
- Raza, K.; Singh, N.K. A Tour of Unsupervised Deep Learning for Medical Image Analysis. Current Medical Imaging Formerly Current Medical Imaging Reviews 2021, 17, 1059–1077. [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, H.K.; Zaman Khan, R. Survey on Development of Expert System from 2010 to 2015. ACM International Conference Proceeding Series 2016, 04-05-March-2016. [CrossRef]
- Sheikhtaheri, A.; Sadoughi, F.; Hashemi Dehaghi, Z. Developing and Using Expert Systems and Neural Networks in Medicine: A Review on Benefits and Challenges. J Med Syst 2014, 38, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Arsene, O.; Dumitrache, I.; Mihu, I. Expert System for Medicine Diagnosis Using Software Agents. Expert Syst Appl 2015, 42, 1825–1834. [CrossRef]
- Masri, R.Y.; Mat Jani, H. Employing Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Mental Health Diagnostic Expert System. 2012 International Conference on Computer and Information Science, ICCIS 2012 - A Conference of World Engineering, Science and Technology Congress, ESTCON 2012 - Conference Proceedings 2012, 1, 495–499. [CrossRef]
- Djam, X.Y.; Wajiga, G.M.; Kimbi, Y.H.; Blamah, N.V. A Fuzzy Expert System for the Management of Malaria. Int J Pure Appl Sci Technol 2011, 5, 84–108.
- Yasnoff, W.A.; Miller, P.L. Decision Support and Expert Systems in Public Health. In; 2014; pp. 449–467.
- Torshizi, A.D.; Zarandi, M.H.F.; Torshizi, G.D.; Eghbali, K. A Hybrid Fuzzy-Ontology Based Intelligent System to Determine Level of Severity and Treatment Recommendation for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2014, 113, 301–313. [CrossRef]
- Benjafield, A. v.; Ayas, N.T.; Eastwood, P.R.; Heinzer, R.; Ip, M.S.M.; Morrell, M.J.; Nunez, C.M.; Patel, S.R.; Penzel, T.; Pépin, J.L.D.; et al. Estimation of the Global Prevalence and Burden of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: A Literature-Based Analysis. Lancet Respir Med 2019, 7, 687–698. [CrossRef]
- Ly, W.K.; Thurnheer, R.; Bloch, K.E.; Laube, I.; Gugger, M.; Heitz, M. Respiratory Polygraphy in Sleep Apnoea Diagnosis. smw.ch.
- Alonso Álvarez, M. de la L.; Terán Santos, J.; Cordero Guevara, J.; Martínez, M.G.; Rodríguez Pascual, L.; Viejo Bañuelos, J.L.; Marañón Cabello, A. Fiabilidad de La Poligrafía Respiratoria Domiciliaria Para El Diagnóstico Del Síndrome de Apneas-Hipopneas Durante El Sueño. Análisis de Costes. Arch Bronconeumol 2008, 44, 22–28. [CrossRef]
- Calleja, J.M.; Esnaola, S.; Rubio, R.; Durán, J. Comparison of a Cardiorespiratory Device versus Polysomnography for Diagnosis of Sleep Apnoea. European Respiratory Journal 2002, 20, 1505–1510. [CrossRef]
- Douglas, N.J.; Thomas, S.; Jan, M.A. Clinical Value of Polysomnography. The Lancet 1992, 339, 347–350. [CrossRef]
- Rundo, J.V.; Downey, R. Polysomnography. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier, 2019; Vol. 160, pp. 381–392.
- Kapur, V.K.; Auckley, D.H.; Chowdhuri, S.; Kuhlmann, D.C.; Mehra, R.; Ramar, K.; Harrod, C.G. Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnostic Testing for Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine 2017, 13, 479–504. [CrossRef]
- Punjabi, N.M. The Epidemiology of Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2008, 5, 136–143. [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, A.; Karuppiah, A. A Survey on Recent Advances in Machine Learning Based Sleep Apnea Detection Systems. Healthcare 2021, Vol. 9, Page 914 2021, 9, 914. [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, S.S.; Mendonça, F.; Ravelo-García, A.G.; Morgado-Dias, F. A Systematic Review of Detecting Sleep Apnea Using Deep Learning. Sensors 2019, Vol. 19, Page 4934 2019, 19, 4934. [CrossRef]
- Denis Bouyssou, T.; Marchant, M.P.; Tsoukiàs, P.V. Evaluation and Decision Models with Multiple Criteria : Stepping Stones for the Analyst; Springer: New York, NY, 2006; ISBN 978-1-4419-4053-7.
- Theil, H. Alternative Approaches to the Aggregation Problem. Studies in Logic and the Foundations of Mathematics 1966, 44, 507–527. [CrossRef]
- Pomerol, J.-C.; Barba-Romero, S. Multicriterion Decision in Management. Principles and Practice.; Springer Science & Business : New York, NY, USA, 2000;
- Allen, B. On the Aggregation of Preferences in Engineering Design. Proceedings of the ASME Design Engineering Technical Conference 2020, 2, 57–67. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.X.; Mendel, J.M. Generating Fuzzy Rules by Learning from Examples. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 1992, 22, 1414–1427. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.M. Machine Learning; McGraw-Hill Education, 1997;
- Neale, I.M. First Generation Expert Systems: A Review of Knowledge Acquisition Methodologies. Knowl Eng Rev 1988, 3, 105–145. [CrossRef]
- Steels, L. Second Generation Expert Systems. Future Generation Computer Systems 1985, 1, 213–221. [CrossRef]
- Rubin, S.H.; Murthy, J.; Ceruti, M.G.; Milanova, M.; Ziegler, Z.C.; Rush Jr., R.J. Third-Generation Expert Systems. In Proceedings of the 2nd International ISCA Conference on Information Reuse and Integration (IRI-2000); Honolulu HI, November 2000; pp. 27–34.
- Mamdani, E.H. Advances in the Linguistic Synthesis of Fuzzy Controllers. Int J Man Mach Stud 1976, 8, 669–678. [CrossRef]
- Mamdani, E.H. Application of Fuzzy Logic to Approximate Reasoning Using Linguistic Synthesis. IEEE Transactions on Computers 1977, C–26, 1182–1191. [CrossRef]
- Mamdani, E.H.; Assilian, S. An Experiment in Linguistic Synthesis with a Fuzzy Logic Controller. Int J Man Mach Stud 1975, 7, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Ross, T.J. Fuzzy Logic with Engineering Applications: Third Edition; Third edit.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: Chichester, UK, 2010; ISBN 9781119994374.
- Boughorbel, S.; Jarray, F.; El-Anbari, M. Optimal Classifier for Imbalanced Data Using Matthews Correlation Coefficient Metric. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0177678. [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Jurman, G. The Advantages of the Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC) over F1 Score and Accuracy in Binary Classification Evaluation. BMC Genomics 2020, 21, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Guilford, J.P. Psychometric Methods; 1954;
- Hevner, A.R.; Chatterjee, S. Design Research in Information Systems: Theory and Practice; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-4419-6107-5.
- Hevner, A.R.; March, S.T.; Park, J.; Ram, S. Design Science in Information Systems Research. MIS Q 2004, 28, 75–105. [CrossRef]
- MATLAB App Designer - MATLAB & Simulink Available online: https://es.mathworks.com/products/matlab/app-designer.html (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- Classification Learner Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/stats/classificationlearner-app.html (accessed on 18 October 2022).
- Fuzzy Logic Toolbox - MATLAB Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/products/fuzzy-logic.html (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Imbalanced-Learn Available online: https://imbalanced-learn.org/dev/index.html (accessed on 18 October 2022).
- Agresti, A. Categorical Data Analysis; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; ISBN 0471360937.
- Powers, D.; Xie, Y. Statistical Methods for Categorical Data Analysis; Emerald Group Publishing, 2008;
- Mohammed, A.J.; Hassan, M.M.; Kadir, D.H. Improving Classification Performance for a Novel Imbalanced Medical Dataset Using Smote Method. International Journal of Advanced Trends in Computer Science and Engineering 2020, 9, 3161–3172. [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N. v.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Technique. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 2002, 16, 321–357. [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.A. The Magical Number Seven, plus or Minus Two: Some Limits on Our Capacity for Processing Information. Psychol Rev 1956, 63, 81–97. [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Srivastava, S. Machine Learning: A Review on Binary Classification. Int J Comput Appl 2017, 160, 11–15. [CrossRef]
- O. Duda, R.; E. Hart, P.; G. Stork, D. Pattern Classification; Wiley: Hoboken, 2000;
- Atacak, I. An Ensemble Approach Based on Fuzzy Logic Using Machine Learning Classifiers for Android Malware Detection. Applied Sciences 2023, Vol. 13, Page 1484 2023, 13, 1484,. [CrossRef]
- Melin, P.; Monica, J.C.; Sanchez, D.; Castillo, O. Multiple Ensemble Neural Network Models with Fuzzy Response Aggregation for Predicting COVID-19 Time Series: The Case of Mexico. Healthcare 2020, Vol. 8, Page 181 2020, 8, 181. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, U.; Issa, G.F.; Khan, M.A.; Aftab, S.; Khan, M.F.; Said, R.A.T.; Ghazal, T.M.; Ahmad, M. Prediction of Diabetes Empowered With Fused Machine Learning. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 8529–8538. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.U.; Abbas, S.; Gollapalli, M.; Ahmed, R.; Aftab, S.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, M.A.; Mosavi, A. Rainfall Prediction System Using Machine Learning Fusion for Smart Cities. Sensors 2022, Vol. 22, Page 3504 2022, 22, 3504. [CrossRef]
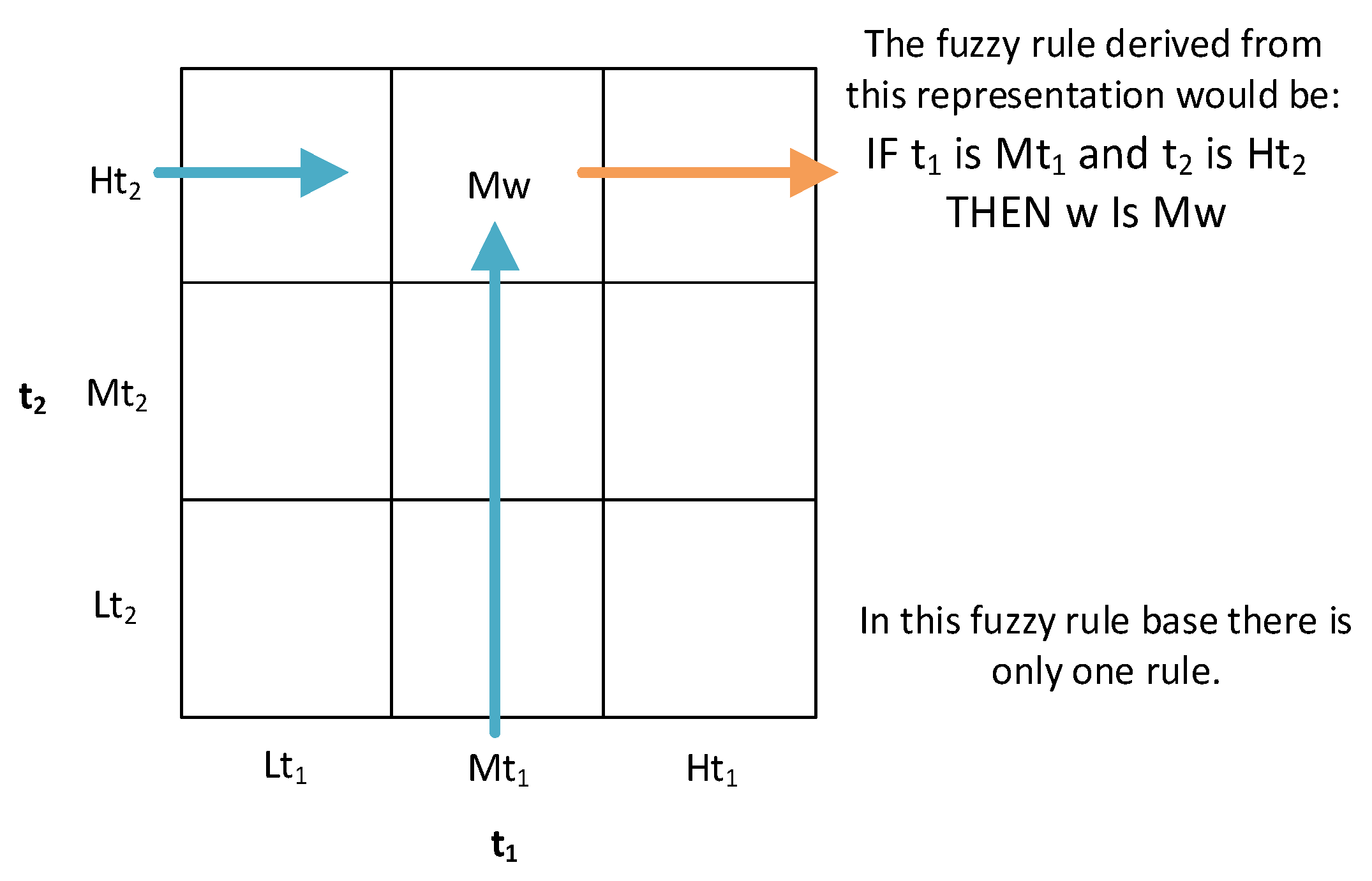
| First proposal [1] | Second proposal [2] | |
|---|---|---|
| Formalization and diversification of knowledge | Incorporates a correcting block based on the use of ANFIS and a specific heuristic algorithm, through which a partial formalization of knowledge is carried out. Considers several AHI threshold levels in the prediction, which facilitates the subsequent prioritization of the patients according to the severity of their condition by different types of health professionals. |
Formalizes knowledge by using of a cascade of expert systems. Considers a single AHI level, which in some way reduces the subsequent performance of the system, and allows only a single threshold to distinguish between patients who suffer from OSA and those who do not. This estimation might be used by the professionals to identify those patients who suffer from the condition. |
|
Uncertainty management |
Performs uncertainty management based on the use of statistical approaches, but without implicit processing of vagueness. | Uses statistical and non-statistical approaches, and therefore performs a more complete management of uncertainty and vagueness. The definition of the method for the union or aggregation of the system risks uses a utility function, which in some way involves increasing the uncertainty associated with the process. |
| MATLAB | |
|---|---|
| Toolbox | Comments |
| App Designer [54] | Facilitates the development of the user graphical interface for the artifact. |
| Classification Learner [55] | Allows to perform the training and massive machine learning classification algorithms test. |
| Fuzzy Logic Toolbox [56] | Makes possible to implement the fuzzy logic-based inferential engines. |
| Python | |
| Package | Comments |
| Imbalanced-learn library [57] | Provides different tools for addressing classification problems when unbalanced datasets are available. In this case, the SMOTE-NC algorithm is used. |
| Threshold | Before SMOTE-NC | After SMOTE-NC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AHI < Threshold | AHI ≥ Threshold | Total | AHI < Threshold | AHI ≥ Threshold | Total | |
| 10 | 1,227 | 3,173 | 4,400 | 4,000 | 4,000 | 8,000 |
| 15 | 1,707 | 2,693 | 4,400 | 4,000 | 4,000 | 8,000 |
| 20 | 1,726 | 2,274 | 4,400 | 4,000 | 4,000 | 8,000 |
| 25 | 2,072 | 1,928 | 4,400 | 4,000 | 4,000 | 8,000 |
| 30 | 2,365 | 1,635 | 4,400 | 4,000 | 4,000 | 8,000 |
| Cascade levels | Observations |
|---|---|
| Level 1 | At the first level, four expert systems are used to process the information related to the symptoms reported by the patient (for more information, see Figure 6 and Figure 7). The first of the expert systems is in charge of processing the set of information related to sleep time and determines the risk indicator R1.a at its output. The second of the expert systems focuses on processing the group of information related to unrefreshing sleep, determining the risk indicator R1.b at its output. The third of the expert systems focuses on the group of information related to complicating sleep factors, determining the risk indicator R2.a at its output. Finally, the fourth of the expert systems focuses on the snores information group, determining the risk indicator R2.b at its output. Each one of the determined risk indicators is related to the group of information used for its determination and represents respectively the hazard level associated with suffering from an OSA case in relation to each group of data. |
| Level 2 | Once the risk indicators have been determined at the first level of the cascade of expert systems, they are aggregated into groups of two (R1.a and R1.b, as well as R2.a and R.2b) using two new expert systems working concurrently [1,2,4,5,8,10,11,12] as can be seen in Figure 6 and Figure 7, and at their output, after the defuzzification process, determine two new indicators, the risks R1 and R2. These new risk indicators represent, respectively, the danger of suffering from OSA in relation to the risk indicators of the previous level, through which it was possible to determine each of the indicator. |
| Level 3 | Finally, at the last level of the cascade, a final expert system aggregates the risk indicators obtained at the second level (R1 and R2), determining at its output an indicator, called Symbolic Risk, related to the conjoint hazard that a patient has of suffering from an OSA case, after contemplating all the symptoms reported by the patient. |
| Fuzzy Structure | Mamdani-type |
|---|---|
| Defuzzification method | Centroid [48] |
| Implication method | Min |
| Aggregation method | Max |
| Inference system associated to the sleep time data group | |||
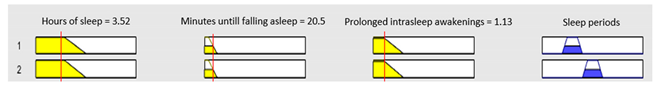
|---|---|---|---|
| Input Data | Range | Output Risk | Range |
| Hours of sleep | 0 – 14 hours | R1.a | 0 – 10 |
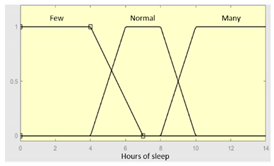 |
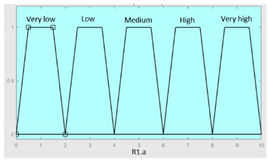 |
||
|
Minutes until falling asleep |
0 – 240 minutes | Initial configuration | |
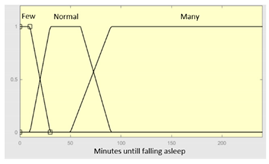 |
Fuzzy structure: Mamdani-type. Membership function type: trapezoidal. Defuzzification method: centroid [48]. Implication method: MIN. Aggregation method: MAX. Number of fuzzy rules: 46 |
||
|
Prolonged intra-sleep awakenings |
0 – 10 | Subset as an example of the 46 fuzzy rules | |
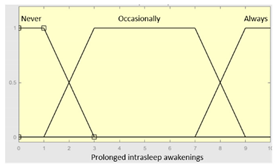 |
1. IF (Hours_of_sleep is Few) AND (Minutes_until_falling_asleep is Few) AND (Prolonged_intra-sleep_awakenings is Never) THEN (R1.a is Low). 2. IF (Hours_of_Sleep is Few) AND (Minutes_until_falling_asleep is Few) AND (Prolonged_intra-sleep_awakenings is Never) THEN (R1.a is Medium). |
||
| Graphical example of fuzzy rules 1 and 2 | |||
 | |||
| Statistical Risk | mfst9 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 |
| mfst8 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | |
| mfst7 | - | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | |
| mfst6 | AR: mf3 | - | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | - | |
| mfst5 | - | - | - | AR: mf1 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf3 | AR: mf3 | |
| mfst4 | - | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | - | |
| mfst3 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | |
| mfst2 | - | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | |
| mfst1 | - | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | AR: mf1 | |
| Apnea Risk (AR) | mfsy1 | mfsy2 | mfsy3 | mfsy4 | mfsy5 | mfsy6 | mfsy7 | mfsy8 | mfsy9 | |
| Symbolic Risk | ||||||||||
| AHI 10 | AHI 15 | AHI 20 | AHI 25 | AHI 30 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of rules | 68 | 71 | 72 | 72 | 71 |
| Generated surface | 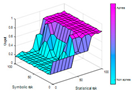 |
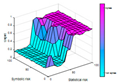 |
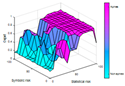 |
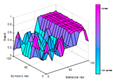 |
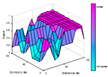 |
| Sensibility | Specificity | |
|---|---|---|
| AHI 10 | 0.83 | 0.88 |
| AHI 15 | 0.88 | 0.71 |
| AHI 20 | 0.93 | 0.62 |
| AHI 25 | 0.64 | 0.83 |
| AHI 30 | 0.72 | 0.69 |
| Data | Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Objective data | Gender | Man | |
| Age | 69 | ||
| Weight | 93 kg | ||
| Size | 179 cm | ||
| BMI | 29.03 | ||
| Neck circumference length | 43 cm | ||
| Habits | Drinking habits: daily, 30g of alcohol |
||
| Drug treatments | - | ||
| Illnesses | - | ||
| Subjective data | Sleep time subgroup | Hours of sleep | 8h |
| Minutes until falling asleep | 30 minutes | ||
| Prolonged intra-sleep awakenings | No | ||
| Unrefreshing sleep subgroup | Feeling of unrefreshing sleep | Occasionally | |
| Daytime tiredness | Occasionally | ||
| Morning dullness | No | ||
| Complicating sleep factors | Unjustified multiple awakenings | No | |
| Nocturia | Occasionally | ||
| Breathless awakenings | No | ||
| Reported apneas | No | ||
| Snores subgroup | Snorer | Yes | |
| High-intensity snorer | No | ||
| Snore-related awakenings | No | ||
| Sleep test | AHI | 23 | |
| Statistical Risk [0,100] | Symbolic Risk [0,100] | |
|---|---|---|
| AHI = 10 | 70 | 42.86 |
| AHI = 15 | 46.67 | 42.86 |
| AHI = 20 | 80 | 42.86 |
| AHI = 25 | 33.33 | 42.86 |
| AHI = 30 | 43.44 | 42.86 |
| Ease of use (Easy / moderate / complex) |
Automated knowledge Acquisition (full / partial) |
Data dependency (full / partial) |
Combination of inference models (yes / no) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ismail Atacak [65]: This paper proposes a malware detection system for the Android operating system. To this end, six classification machine learning algorithms are first used, focusing on the processing of application data. Then, through a voting process, three of the algorithms are selected, whose results are interpreted and aggregated by a Mamdani-type fuzzy inference system, which makes it possible to determine the degree of malware. | Moderate difficulty of use. To use this system, it is essential to define in advance the knowledge base of the fuzzy inference system that will allow the aggregation of the results of the machine learning algorithms. | Partial knowledge acquisition. The system architecture does not have an automatic knowledge acquisition sub-system. The rules of the Mamdani inference system need to be defined manually. | Full data dependency. This is a data dependent approach as it uses supervised machine learning algorithms. | Yes, it consists of the sequential use of a block of machine learning algorithms and a fuzzy inference system, which can be understood as an ensemble, that is, where the fuzzy engine allows the predictions of the preceding algorithms to be aggregated. |
| - | - | = | = | |
| Melin et al. [66]: In this work, aimed at predicting the COVID-19 time series, it is proposed to use jointly a block of neural networks, more specifically nonlinear autoregressive neural networks and function fitting neural networks, and a fuzzy inference system focused on determining the importance of the predictions of the models, which are aggregated through a weighted summation model. | Moderate difficulty of use. To use it, it is essential to first define the knowledge base that will allow the importance of each model’s predictions to be determined on the basis of its prediction error. | Partial knowledge acquisition. The system integrates a module based on the Mamdani inference system. Its rules are defined manually, as it does not include a knowledge acquisition subsystem. | Full data dependency. This is an unavoidably data-dependent approach where it is necessary to train the neural networks used. | Yes, this paper uses together both statistical inferential approaches and symbolic inferential approaches. |
| - | - | = | = | |
| Ahmed et al. [67]: This paper proposes a system for the prediction of diabetes condition. To this end, two machine learning algorithms are used that focus on the processing of initial data, whose predictions are then processed by an inference system based on fuzzy logic of the Mamdani type, which is responsible for determining the final prediction. | Moderate difficulty of use. In order to use this system, it is necessary to first define the knowledge base of the Mamdani inference system, which is essential in determining the prediction of the model. | Partial knowledge acquisition. The knowledge base is manually defined, as the system lacks a knowledge acquisition subsystem. | Full data dependency. As it integrates approaches based on the use of classification machine learning algorithms, the availability of data is essential. | Yes, this system uses both statistical and symbolic inferential approaches in a joint and sequential manner. |
| - | - | = | = | |
| Ragman et al. [68]: This paper proposes a real-time rainfall forecasting system. To achieve this, it uses four classification machine learning algorithms that focus on the processing of sensor data. The predictions of these models are combined by a Mamdani inference system, which is responsible for determining the final prediction. | Moderately difficult to use. In order to use the system, it is essential to define the knowledge base of the fuzzy inference system responsible for aggregating the predictions. | Partial knowledge acquisition. The system does not have a knowledge acquisition subsystem. The knowledge base is manually defined. | Full data dependency. This is a data dependent approach as it incorporates supervised learning approaches into its architecture. | Yes. It uses statistical and symbolic inference approaches. |
| - | - | = | = | |
| Casal-Guisande et al. [2]: This is an intelligent decision support system applied to the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea. Its architecture uses a set of classification machine learning algorithms and a cascade of expert systems, each of which outputs a risk indicator. These indicators are then combined through a utility function that determines a metric associated with suffering from the pathology. | Moderate difficulty of use. In order to use the intelligent system, it is necessary to have defined the knowledge bases of the different expert systems. In this sense, after this milestone, the system could be used without major difficulties other than those related to the revision and improvement of the rules for its use. | Partial knowledge acquisition. The architecture of the intelligent system, more specifically the cascade of expert systems, does not include a specific knowledge acquisition subsystem. This must be manually defined by the expert team. | Full data dependency. The data is required to train the machine learning classification algorithms. | Yes. It uses symbolic and statistical inference approaches in a concurrent mode. Their results are then combined using a specific utility function. |
| - | - | = | = | |
| Casal-Guisande et al. [5]: This is an intelligent decision support system applied to the diagnosis of breast cancer, focusing on the interpretation of information obtained from mammograms. Its sequential architecture uses a cascade of expert systems, whose output is a set of risk indicators. A set of underlying factors that summarise and represent the risks is then obtained by applying factor analysis approaches. These are processed by a classification machine learning algorithm, which makes it possible to determine a risk metric associated with suffering from the pathology. | Moderate difficulty of use. The use of the intelligent system requires the definition of the knowledge bases of the different expert systems. In this sense, after this milestone, the system could be used without major difficulties other than those related to the revision and improvement of the rules. | Partial knowledge acquisition. The architecture of the intelligent system, and more specifically the cascade of expert systems, does not contemplate a specific subsystem for acquiring knowledge. The knowledge bases must be defined manually by the expert team. | Full data dependency. Due to its sequential nature and the use of a machine learning classification algorithm, this approach requires a data set from the beginning. | Yes. It uses symbolic and statistical inferential approaches. |
| - | - | = | = | |
| Casal-Guisande et al. [10]: This paper presents an intelligent system applied to the diagnosis of breast cancer, focusing on the interpretation of the information obtained after performing mammograms. Its architecture uses a set of expert systems and a classification machine learning algorithm working concurrently. The output is a set of risk indicators that are combined using a specific analytical function to obtain a risk indicator. In addition, the system incorporates a corrective approach that allows the weighting of the risk obtained through the opinions of the experts, which is reflected in the BI-RADS indicator. | Moderate difficulty of use. For the use of the intelligent system, it is necessary to define the knowledge bases of the different expert systems. In this sense, after this milestone, the system could be used without major difficulties other than those associated with the revision and improvement of the rules. | Partial knowledge acquisition. There is no subsystem for knowledge acquisition. The knowledge bases of expert systems must be defined manually. | Full data dependency. The system is data dependent due to the use of a classification machine learning algorithm. | Yes, the system integrates various inferential approaches, both symbolic and statistic. |
| - | - | = | = | |
| Our proposal | Very easy to use. Beyond the definition of the knowledge bases of the cascade of expert systems, it is not necessary to define the rules of the Mamdani inference system responsible for risk aggregation. The system can be used from the beginning without major difficulties. | Full and automatic knowledge acquisition. The system integrates an automatic fuzzy rule generation mechanism, the algorithm proposed by Wang and Mendel. | Full data dependency. In addition to defining the classification machine learning algorithms, data is also needed to create the corpus of rules for the aggregation inference system. | Yes, the system integrates a variety of inference approaches, both symbolic and statistical. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





