Submitted:
19 May 2023
Posted:
22 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of cannabinoids content using HPLC
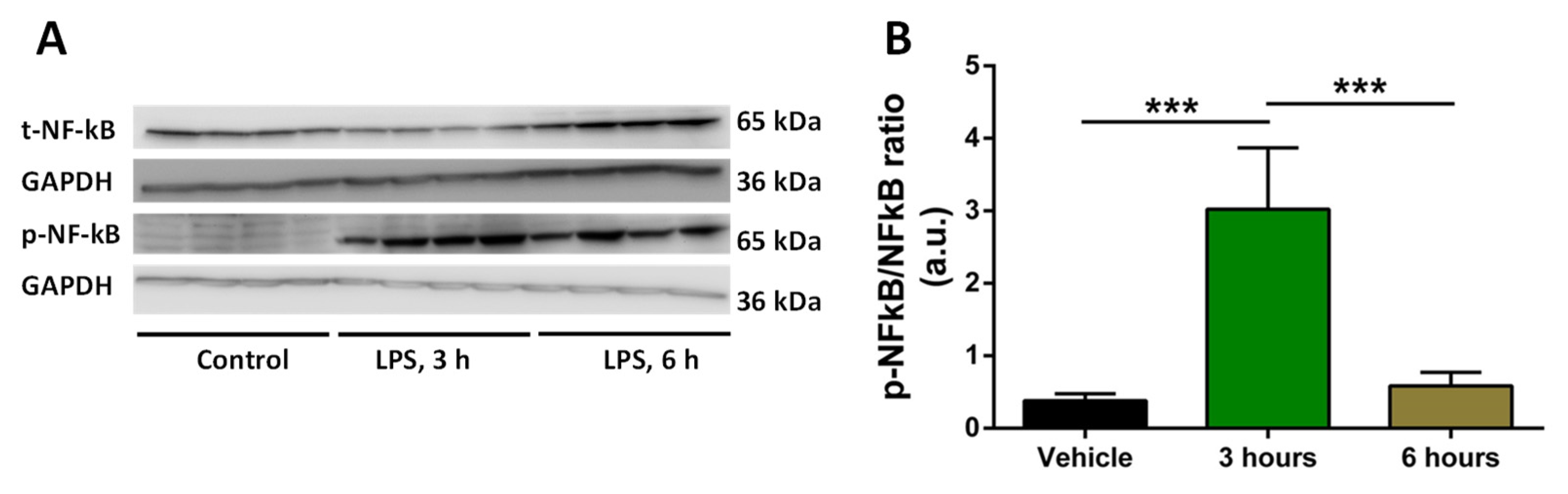
2.2. Analysis of time of induction of inflammation by LPS
2.3. Treatment with selected concentration of LPS, THC, CBD and extracts do not reduce the viability of macrophages
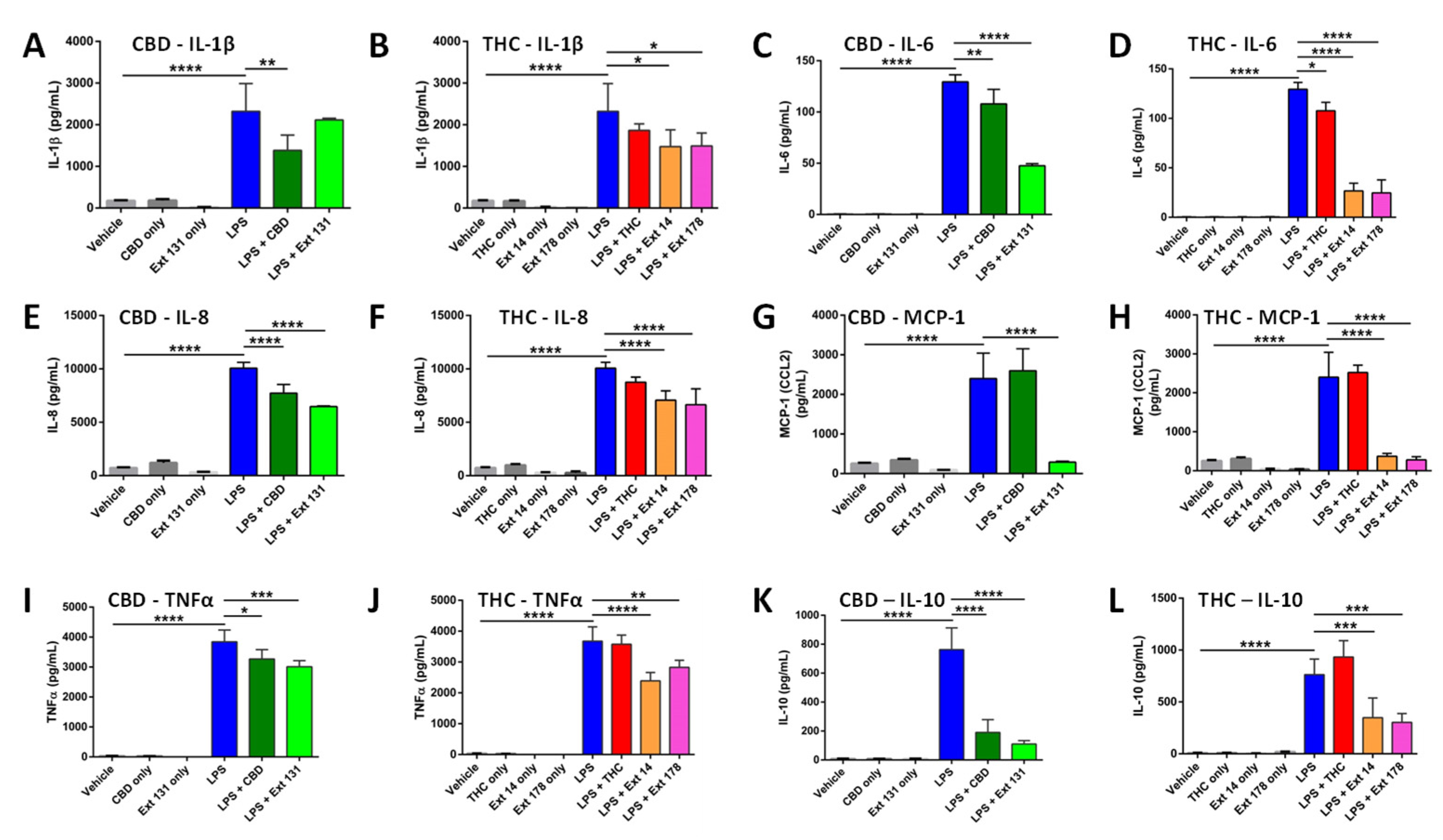
2.4. Cannabis sativa extracts attenuate TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-8, MCP-1, IL-10, and IL-6 production in LPS-stimulated THP-1 macrophages
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Main Reagents
3.2. Plant Growth and Extract Preparation
3.3. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis of Cannabinoids
3.4. Terpene Analysis
3.5. Cell Cultures and Treatments
3.6. Cell viability assay using trypan blue
3.7. Multiplex ELISA
3.8. Statistical analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Limitations of the Study
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Cohen, K.; Weizman, A. and Weinstein, A. Positive and Negative Effects of Cannabis and Cannabinoids on Health. Clin Pharmacol Therapeutics 2019, 105(5), 1139–1147. [CrossRef]
- Cristino, L.; Bisogno, T. and Di Marzo, V. Cannabinoids and the expanded endocannabinoid system in neurological disorders. Nature Rev Neurology 2020, 16(1), 9–29. [CrossRef]
- Russo, E. B. The case for the entourage effect and conventional breeding of clinical cannabis: No ‘Strain,’ no gain”. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Chiurchiù, V. Endocannabinoids and Immunity. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2016, 1(1), 59–66. [CrossRef]
- Galiègue, S.; Mary, S.; Marchand, J.; Dussossoy, D.; Carrière, D.; Carayon, P.; Bouaboula, M.; Shire, D.; Le Fur, G.; Casellas, P. Expression of central and peripheral cannabinoid receptors in human immune tissues and leukocyte subpopulations. Eur J Biochem. 1995, 232(1), 54-61. [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, A.; Foxman, E. F.; Molony, R. D. Early local immune defences in the respiratory tract. Nature Rev. Immunology 2017, 17(1), 7–20. [CrossRef]
- Amarante-Mendes, G. P.; Adjemian, S.; Branco, L. M.; Zanetti, L. C.; Weinlich, R. and Bortoluci, K. R. Pattern recognition receptors and the host cell death molecular machinery. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2379. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9(6), 7204–7218. [CrossRef]
- Tisoncik, J. R.; Korth, M. J.; Simmons, C. P.; Farrar, J.; Martin, T. R.; Katze, M. G. Into the eye of the cytokine storm. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2012, 76(1), 16-32. [CrossRef]
- Deshmane, S. L.; Kremlev, S.; Amini, S. and Sawaya, B. E. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J. Interferon Cytokine Research 2009, 29(6), 313–325. [CrossRef]
- Benakanakere, M. R.; Finoti, L. S.; Tanaka, U.; Grant, G. R.; Scarel-Caminaga, R. M. and Kinane, D. F. Investigation of the functional role of human Interleukin-8 gene haplotypes by CRISPR/Cas9 mediated genome editing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6(1), 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Zelová, H. and Hošek, J. TNF-α signalling and inflammation: Interactions between old acquaintances. Inflammation Research 2013, 62(7), 641–651. [CrossRef]
- Martin-Sanchez, F.; Diamond, C.; Zeitler, M.; Gomez, A.I.; Baroja-Mazo, A.; Bagnall, J.; Spiller, D.; White, M.; Daniels, M.J.D.; Mortellaro, A. et al. Inflammasome-dependent IL-1β release depends upon membrane permeabilisation. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23(7), 1219–1231. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M. and Kishimoto, T. Il-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6(10), 16295–16296. [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S. S. and Cheng, G. Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 32(1), 23–63. [CrossRef]
- Nagarkatti, P.; Pandey, R.; Rieder, S. A.; Hegde, V. L. and Nagarkatti, M. Cannabinoids as novel anti-inflammatory drugs. Future Medicinal Chemistry 2009, 1(7), 1333–1349. [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, W.; Elgendy, N.; Salama, S.; Jawad, M. and Eltoukhy, K. The Effect of Cannabis on the Clinical and Cytokine Profiles in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Int. 2021, 2021, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Kovalchuk, A.; Wang, B.; Li, D.; Rodriguez-Juarez, R.; Ilnytskyy, S.; Kovalchuk, I. and Kovalchuk, O. Fighting the Storm: Could Novel Anti-Tnfá And Anti-Il-6 C. Sativa Cultivars Tame Cytokine Storm in COVID-19? Aging (Albany. NY). 2021, 13(2), 1571–1590. [CrossRef]
- Gallily, R.; Yekhtin, Z. and L. Ondřej Hanuš, L. Overcoming the Bell-Shaped Dose-Response of Cannabidiol by Using Cannabis Extract Enriched in Cannabidiol. Pharmacol. Pharm. 2015, 6, 75–85. [CrossRef]
- Anil, S.M.; Shalev, N.; Vinayaka, A.C.; Nadarajan, S.; Namdar, D.; Belausov, E.; Shoval, I.; Mani, K.A.; Mechrez, G. and Koltai, H. Cannabis compounds exhibit anti-inflammatory activity in vitro in COVID-19-related inflammation in lung epithelial cells and pro-inflammatory activity in macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11(1), 1462. [CrossRef]
- Khuja, I.; Yekhtin, Z.; Or, R. and Almogi-Hazan, O. Cannabinoids Reduce Inflammation but Inhibit Lymphocyte Recovery in Murine Models of Bone Marrow Transplantation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. Artic. 2019, 20(3), 668. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, D.; Fiselier, A.; Kovalchuk, I. and Kovalchuk, O. New AKT-dependent mechanisms of anti-COVID-19 action of high-CBD Cannabis sativa extracts. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 110 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Kovalchuk, A.; Li, D.; Rodriguez-Juarez, R.; Ilnytskyy, Y.; Kovalchuk, I. and Kovalchuk O. In search of preventive strategies: novel high-CBD Cannabis sativa extracts modulate ACE2 expression in COVID-19 gateway tissues. Aging (Albany NY). 2020, 12(22), 22425-22444. [CrossRef]
- Suryavanshi, S.V.; Zaiachuk, M.; Pryimak, N.; Kovalchuk, I.; Kovalchuk, O. Cannabinoids Alleviate the LPS-Induced Cytokine Storm via Attenuating NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling and TYK2-Mediated STAT3 Signaling Pathways In Vitro. Cells 2022, 11, 1391. [CrossRef]
- Chanput, W.; Mes, J. J. and Wichers, H. J. THP-1 cell line: An in vitro cell model for immune modulation approach. International Immunopharmacology 2014, 23(1), 37–45. [CrossRef]
- Gatto, F.; Cagliani, R.; Catelani, T.; Guarnieri, D.; Moglianetti, M.; Pompa, P.P. and Bardi, G. PMA-induced THP-1 macrophage differentiation is not impaired by citrate-coated platinum nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 2017, 7(10), 155. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yin, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Dong, H.; Bai, Y.; Qin, Y.; Li, J.; Feng, S. et al. LPS-induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells and macrophages via NF-κB, STAT3 or AP-1 activation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17(4), 5484–5491. [CrossRef]
- Juknat, A.; Gao, F.; Coppola, G.; Vogel, Z. and Kozela, E. miRNA expression profiles and molecular networks in resting and LPS-activated BV-2 microglia—Effect of cannabinoids. PLoS One 2019, 14(2), p. e0212039. [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C. The P value and statistical significance: Misunderstandings, explanations, challenges, and alternatives. Indian J. Psycholog. Med. 2019, 41(3), 210–215. [CrossRef]
- Harikrishnan, H.; Jantan, I.; Haque, M. A. and E. Kumolosasi. Anti-inflammatory effects of Phyllanthus amarus Schum. & Thonn. through inhibition of NF-κB, MAPK, and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways in LPS-induced human macrophages. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18(1), 224. [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Six, D.A.; Liu, Q.; Gu, L.; Wang, S.; Alamuri, P.; Raetz, C.R.; Curtiss, R. 3rd. Phosphate groups of lipid a are essential for Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium virulence and affect innate and adaptive immunity. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80(9), 3215–3224, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Yang, L.; Dai, F.; Tang, L. and Le, Y. Macrophage differentiation induced by PMA is mediated by activation of RhoA/ROCK signaling. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 42(6), 763-771. [CrossRef]
- Vogel, C.F.; Garcia, J.; Wu, D.; Mitchell, D.C.; Zhang, Y.; Kado, N.Y.; Wong, P.; Trujillo, D.A.; Lollies, A.; Bennet, D. et al. Activation of inflammatory responses in human U937 macrophages by particulate matter collected from dairy farms: an in vitro expression analysis of pro-inflammatory markers. Environ Health. 2012, 11, 17. [CrossRef]
- Sharif, O.; Bolshakov, V.N.; Raines, S.; Newham, P. and Perkins, N.D. Transcriptional profiling of the LPS induced NF-κB response in macrophages. BMC Immunol. 2007, 8, 1. [CrossRef]
- Neustock, P.; Brand, J.M.; Kruse, A. and Kirchner, H. Cytokine production of the human monocytic cell line Mono Mac 6 in comparison to mature monocytes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Immunobiology, 1993, 188(3), 293–302. [CrossRef]
- Hume Underhill, D.A.; Wainwright, B.J.; Aderem, A.; Timothy Ravasi, S.; Wells, C. and Forest, A. Probability of Individual Inducible Genes from Gene-Autonomous Transcriptional System: Macrophage Heterogeneity Arises Generation of Diversity in the Innate Immune. J. Immunol. Ref. 2021, 168, 44–50. [CrossRef]
- Kovalchuk, O. and Kovalchuk, I. Cannabinoids as anticancer therapeutic agents. Cell Cycle, 2020, 19(9), 961–989. [CrossRef]
- Ferber, S.G.; Namdar, D.; Hen-Shoval, D.; Eger, G.; Koltai, H.; Shoval, G.; Shbiro, L.; Weller, A. The ‘Entourage Effect’: Terpenes Coupled with Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Mood Disorders and Anxiety Disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 18(2), 87–96. [CrossRef]
- Martín-Sánchez, F.; Diamond, C.; Zeitler, M.; Gomez, A.I.; Baroja-Mazo, A.; Bagnall, J.; Spiller, D.; White, M.; Daniels, M.J.; Mortellaro, A. et al. Inflammasome-dependent IL-1β release depends upon membrane permeabilisation. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23(7), 1219–1231. [CrossRef]
- Gabay, C. Interleukin-6 and chronic inflammation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8(2), S3. [CrossRef]
- Zelová, H. and Hošek, J. TNF-α signalling and inflammation: Interactions between old acquaintances. Inflammation Research 2013, 62(7), 641–651. [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Castejon, G. and Brough, D. Understanding the mechanism of IL-1β secretion. Cytokine Growth Factor Reviews 2011, 22(4), 189–195. [CrossRef]
- Viedt, C.; Dechend, R.; Fei, J.; Hänsch, G.M.; Kreuzer, J.; Orth, S.R. MCP-1 Induces Inflammatory Activation of Human Tubular Epithelial Cells: Involvement of the Transcription Factors, Nuclear Factor-B and Activating Protein-1. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13(6), 1534-47. [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, W.; Elgendy, N.; Salama, S.; Jawad, M. and Eltoukhy, K. The Effect of Cannabis on the Clinical and Cytokine Profiles in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Int., 2021, 2021, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Aswad, M.; Hamza, H.; Pechkovsky, A.; Zikrach, A.; Popov, T.; Zohar, Y.; Shahar, E.; Louria-Hayon, I. High-CBD Extract (CBD-X) Downregulates Cytokine Storm Systemically and Locally in Inflamed Lungs. Front Immunol., 2022, 13, 875546. [CrossRef]
- Muthumalage, T. and Rahman, I. Cannabidiol differentially regulates basal and LPS-induced inflammatory responses in macrophages, lung epithelial cells, and fibroblasts. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 2019, 382, 114713. [CrossRef]
- Yeisley, D.J.; Arabiyat, A.S.; Hahn, M.S. Cannabidiol-Driven Alterations to Inflammatory Protein Landscape of Lipopolysaccharide-Activated Macrophages In Vitro May Be Mediated by Autophagy and Oxidative Stress. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2021, 6(3), 253-263. [CrossRef]
- Comalada, M.; Ballester, I.; Bailón, E.; Sierra, S.; Xaus, J.; Gálvez, J.; de Medina, F.S.; Zarzuelo, A. Inhibition of pro-inflammatory markers in primary bone marrow-derived mouse macrophages by naturally occurring flavonoids: Analysis of the structure-activity relationship. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006, 72(8), 1010-21. [CrossRef]
- Joffre, J.; Yeh, C.C.; Wong, E.; Thete, M.; Xu, F.; Zlatanova, I.; Lloyd, E.; Kobzik, L.; Legrand, M.; Hellman, J. Activation of CB 1 R Promotes Lipopolysaccharide-Induced IL-10 Secretion by Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressive Cells and Reduces Acute Inflammation and Organ Injury. J. Immunol. 2020, 204(12), 3339–3350. [CrossRef]
- Kozela, E.; Juknat, A.; Health, M.; Kaushansky, N. and Rimmerman, N. Cannabinoids Decrease the Th17 Inflammatory Autoimmune Phenotype Mechanisms of Anti-depressive Treatments View project Cell death induced by delta-aminolevulinic acid in astrocytes View project. Artic. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol., 2013, 8(5), 1265-76. [CrossRef]
- Weiss, L.; Zeira, M.; Reich, S.; Har-Noy, M.; Mechoulam, R.; Slavin, S.; Gallily, R. Cannabidiol lowers incidence of diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice. Autoimmunity, 2006, 39(2), 143–151. [CrossRef]
| Total THC, % | Total CBD, % | THC (μM) | CBD (μM) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #14 | 33.35±2.75 | 2.81±0.23 | 7.42±0.56 | 0.63±0.04 |
| #131 | 2.11±0.19 | 19.65±2.05 | 0.47±0.03 | 4.37±0.33 |
| #178 | 33.98±3.12 | 1.01±0.09 | 7.56±0.64 | 0.22±0.02 |
| Terps in mg/g | #131 | #178 | #14 |
|---|---|---|---|
| α-Pinene | 0.295±0.055 | 0.649±0.12 | 0.048±0.008 |
| β-Pinene | 0.212±0.046 | 0.245±0.042 | 0.068±0.012 |
| β-Myrcene | ND | 0.361±0.064 | 0.124±0.042 |
| Limonene | 0.262±0.052 | 0.003±0.001 | 0.263±0.062 |
| Terpinolene | 0.025±0.005 | 0.008±0.002 | 0.004±0.001 |
| Linalool | 0.058±0.009 | 0.029±0.005 | 0.193±0.062 |
| α-Bisabolol | 0.003±0.001 | 0.244±0.06 | 0.061±0.02 |
| trans-Caryophyllene | 0.04±0.008 | 0.076±0.014 | 0.545±0.08 |
| α-Humulene | ND | 0.04±0.009 | 0.136±0.03 |
| trans-Nerolidol | ND | 0.008±0.002 | 0.187±0.04 |
| cis-Nerolidol | 0.001±0.001 | 0.003±0.001 | ND |
| Camphene | 0.022±0.006 | 0.025±0.001 | 0.015±0.005 |
| β-Ocimene | ND | 0.089±0.016 | ND |
| Fenchone isomers | ND | 0.003±0.001 | 0.004±0.001 |
| δ-3-Carene | 0.506±0.12 | 0.001±0.001 | ND |
| α-Terpinene | 0.006±0.002 | 0.573±0.11 | ND |
| Eucalyptol | 0.002±0.001 | ND | ND |
| γ-Terpinene | ND | 0.001±0.001 | ND |
| β-Cymene | ND | 0.048±0.009 | ND |
| Camphor isomers | ND | 0.118±0.04 | ND |
| isopulegol | 0.01±0.004 | 0.016±0.004 | ND |
| Caryophyllene oxide | 0.017±0.005 | 0.098±0.003 | ND |
| Valencene | ND | 0.01±0.003 | ND |
| Geraniol | 0.005±0.002 | 0.004±0.002 | ND |
| Guaiol | 0.029±0.005 | 0.116±0.04 | ND |
| trans-P-Ocimene | 0.016±0.004 | ND | ND |
| α-Humulene | 0.025±0.006 | ND | 0.136±0.034 |
| Fenchyl Alcohol | ND | ND | 0.036±0.007 |
| Borneol isomers | ND | ND | 0.012±0.003 |
| α -Terpineol | ND | ND | 0.052±0.009 |
| Total Terpene | 1.534± 0.32 | 2.768± 0.46 | 1.75± 0.25 |
| Analyzed cytokines | CBD | THC | #131 | #14 | #178 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | ↓ | = | = | ↓ | ↓ |
| IL-6 | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| IL-8 | ↓ | = | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| IL-10 | ↓ | = | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| MCP-1 | = | = | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| TNF-α | ↓ | = | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





