1. Introduction
Worldwide prevalence of obesity and metabolic syndrome is continuously increasing [1-3]. Metabolic syndrome is one of the main risk factors for cardiovascular diseases [
4] that are the number one cause of death in public health statistics [
5]. The underlying complex interactions have not been fully elucidated until now. In particular, chronic low-grade inflammatory state, adipose inflammation and metaflammation in obesity are assumed to play a crucial role in the development of local and systemic insulin resistance, cardiovascular diseases, and in impaired immune responses [
4]. Recently published data argue for a role of adipose tissue innate immunity in regulating the molecular interface of metabolism and inflammation [
6,
7].
Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) represents an immunomodulatory peptide mainly secreted by immune cells such as monocytes, macrophages, and lymphocytes [
8] with a crucial role in the innate immune system. CAMP enhances monocyte [
9] and granulocyte [
10] infiltration at sites of local inflammation by chemoattractant action and alters the immune response in the course of infection via toll-like receptor (TLR) modulation [
11]. In bacteria, CAMP causes a loss of membrane integrity by increased permeability, leading to the death of microbial cells [
12].
In 2015, Zhang et al. described CAMP to be produced by adipocytes for the first time [
13], thereby introducing CAMP as a novel adipokine. During subcutaneous Gram-positive infection with Staphylococcus aureus, CAMP secreted by adipocytes inhibits bacterial growth and is an important protective component of subdermal adipose tissue against bacterial infection [
13]. In mice, diet-induced obesity results in the loss of a dermal pool of preadipocytes and thus inhibits the capacity to initiate reactive adipogenesis and to express CAMP [
14]. In humans, CAMP gene expression is higher in subcutaneous than in visceral adipose tissues [
15]. However, further data on the precise function and regulation of CAMP in adipocytes is sparse.
In 2021, we elucidated regulatory mechanisms of CAMP expression in murine 3T3-L1 adipocytes [
16]. Activation of TLR2 and TLR4 by specific ligands (MALP2, lipopolysaccharides (LPS)) up-regulates adipocyte CAMP expression involving classical signal transduction elements such as NF-ĸB, PI3K or STAT3 [
16]. This TLR-mediated proinflammatory activation of CAMP expression can be modified by immunomodulatory adipokines such as C1q/TNF-related protein-3 (CTRP-3) [
17]. Furthermore, immuno-metabolic factors such as bile acids, glucose, insulin, and incretins are able to modulate CAMP expression in adipocytes in vitro [
15].
TLR9 is a well-characterized intracellular receptor [
18] recognizing non-methylated CpG DNA motifs derived from bacteria [
19], viral double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) [
20], and cell-free nucleic acids (cfDNA) as a signal for severe tissue damage inside the organism [
21]. Activation of TLR9 leads to an increased production of proinflammatory cytokines [
22] and TLR9 signaling in macrophages is involved in obesity-induced insulin resistance [
23]. In obesity, death of adipocytes leads to an increase of cfDNA in adipose tissue and plasma [
21] and adipose tissue-resident macrophages are involved in the recognition of these elevated cfDNA levels via TLR9 [
21].
Of note, Nakagawa et al. demonstrated that CAMP is required for normal TLR9 function in dendritic cells and macrophages [
24]. Whether CAMP plays an additional role in TLR9 modulation of adipocytes has not been elucidated so far. A possible interaction between CAMP expression and TLR9 in adipocytes and adipose tissues might provide a novel molecular interface to obesity-related inflammation with adipocyte function.
Therefore, the primary aim of the present study was to investigate
1. the potential effects of both, TLR9 activation and inhibition on CAMP gene expression in murine 3T3-L1 adipocytes,
2. the underlying mechanisms involved in TLR9-mediated regulation of CAMP expression, with respect to components of established proinflammatory pathways as well as to the action of agonistic and inhibitory oligonucleotides, and
3. circulating CAMP concentrations as well as local CAMP gene expression in adipose tissue of TLR9 knockout mice compared to wildtype mice.
2. Results
2.1. CAMP Gene Expression is Induced During Differentiation in Murine 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and in Human SGBS Cells
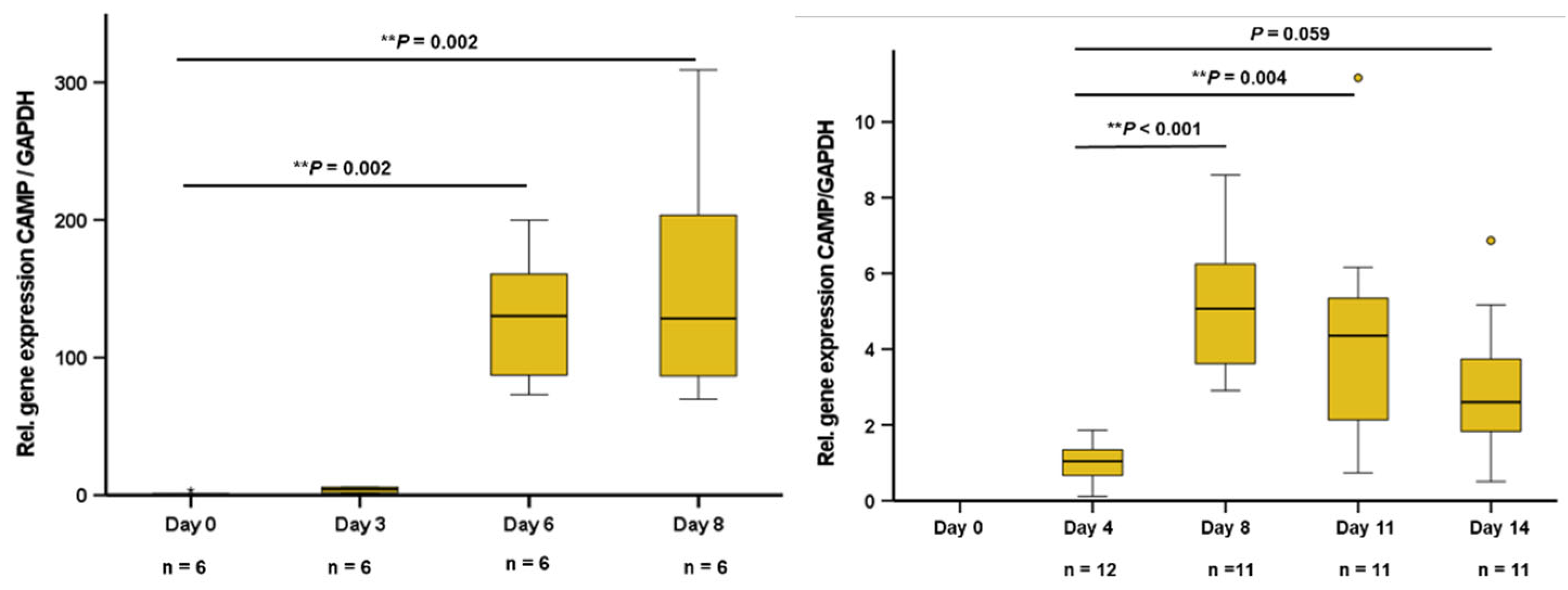
During the differentiation process, 3T3-L1 adipocytes phenotypically turn from fibroblastic preadipocytes into mature adipocytes with multiple lipid vacuoles within 8 days. The pattern of adipokine expression and secretion varies depending on the stage of differentiation. In early stage 3T3-L1 preadipocytes at days 0 and 3 of differentiation, no significant CAMP gene expression was detected. In later stages at day 6 and in mature adipocytes (day 8), a strong and significant increase of CAMP expression was observed (
Figure 1A). Human SGBS preadipocytes were differentiated over 14 days into mature adipocytes. In early preadipocytes, there was no significant CAMP expression. During differentiation, CAMP expression increased strongly until day 8, remaining on an elevated level during final adipocyte maturation (
Figure 1B).
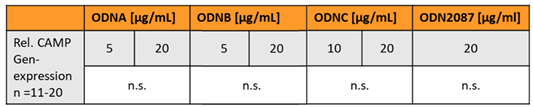
2.2. Synthetic TLR9 Ligands do not Modify CAMP Gene Expression in Murine or Human Adipocytes
Generally, activation of TLR9 leads to an increased production of proinflammatory cytokines [
22]. Oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs) are established synthetic ligands of TLR9 [
36]: ODN2087 is a commonly used TLR7/TLR9 inhibitor, whereas ODNA, ODNB, and ODNC represent agonists inducing TLR9 activity [
37]. Therefore, we investigated if ODNA, ODNB, ODNC, and ODN2087 are able to modify basal CAMP gene expression in murine or human adipocytes in vitro (
Table 1). Doses of 5 µg/mL and 20 µg/mL ODNA, 5 µg/mL, 20 µg/mL ODNB, 10 µg/mL and 20 µg/mL ODN C, and 20 µg/mL ODN2087 were applied in murine 3T3L-1 adipocytes. None of the tested ODNs significantly affected adipocyte CAMP gene expression (
Table 1).
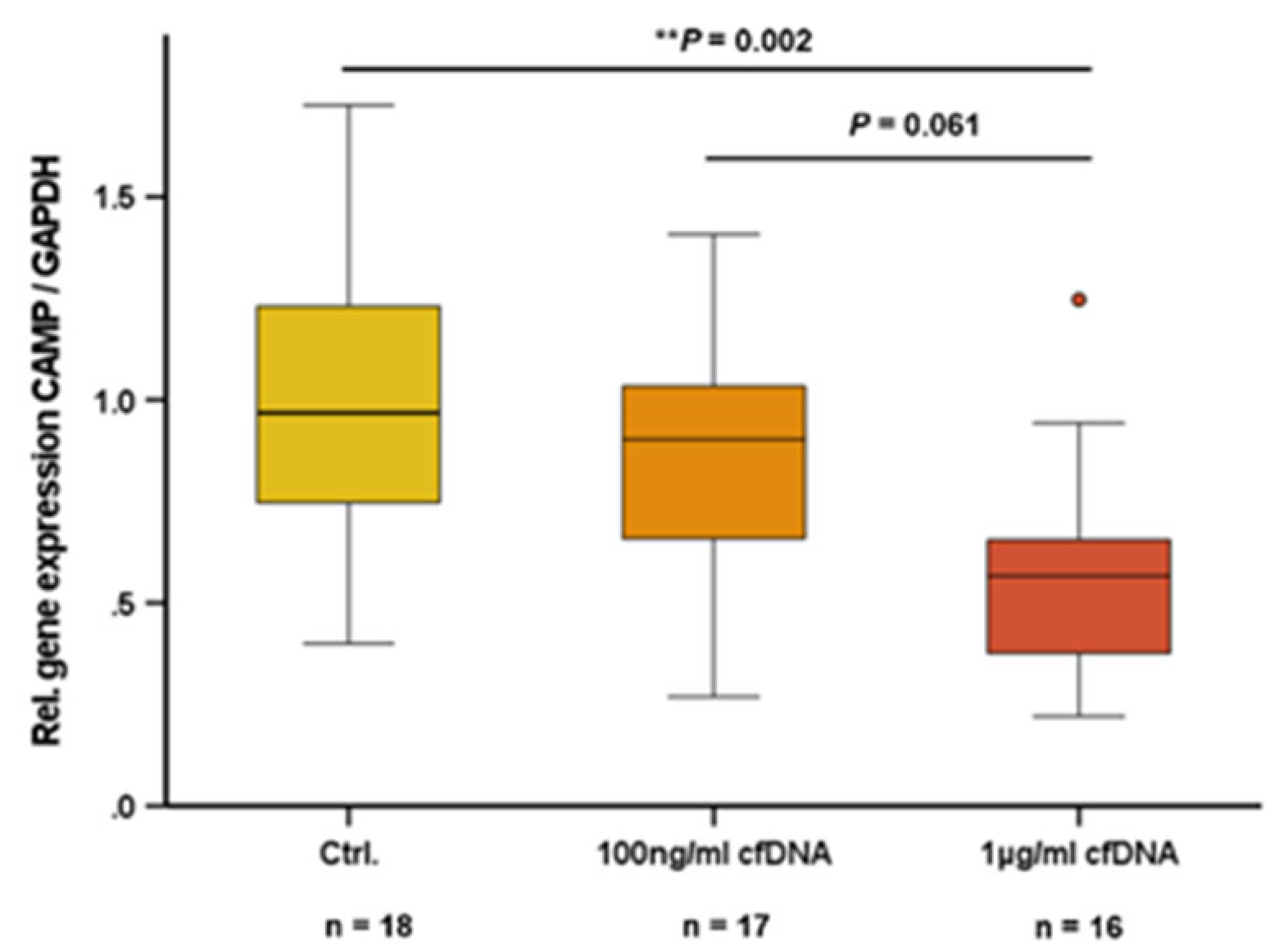
2.3. Cell-Free Nucleic Acids (cfDNA) Impair CAMP Expression in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
Adipocytes release cfDNA as a response to inflammatory stress [
21] and cfDNA acts as an endogenous ligand for TLR9 in immune cells [
38]. In the present study, we investigated whether cfDNA from adipocytes has an impact on CAMP expression in adipocytes. In 3T3-L1 adipocytes, cfDNA dose-dependently reduced CAMP expression with an effective dosage of 1 µg/ml cfDNA (
P=0.002) (
Figure 2).
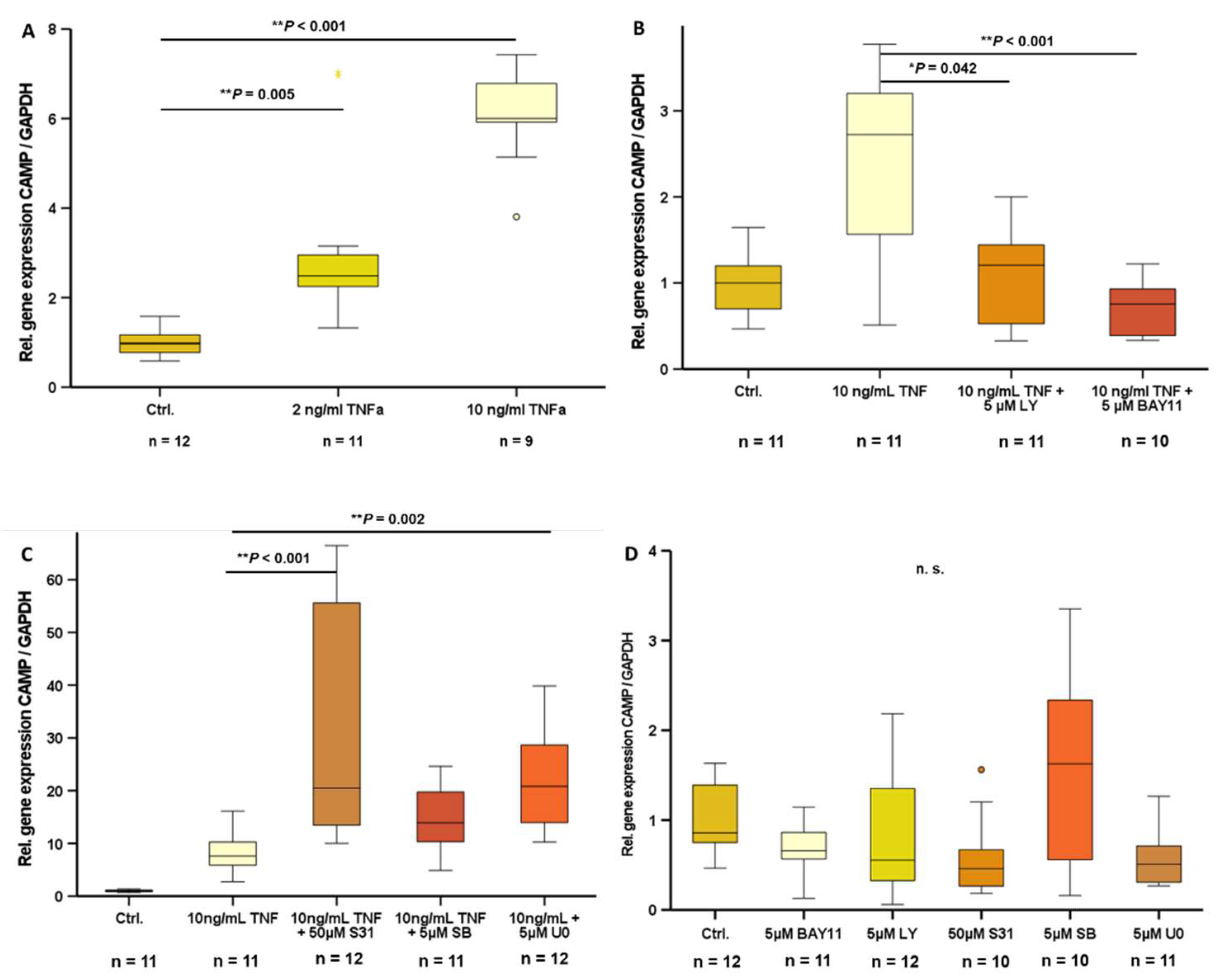
2.4. TNFα-Induced CAMP Gene Expression Can Be Antagonized by Inhibitors of Intracellular Signal Transduction Pathways
In 3T3-L1 adipocytes, a state of inflammation was induced by stimulation with TNFα. Treatment with doses of 2 ng/ml TNFα (
P=0.005) and 10 ng/ml TNFα (
P<0.001) significantly increased CAMP gene expression (
Figure 3A). Inhibition of PI3K (LY294002) (
P=0.042) and NF-ᴋB (BAY11-7085) (
P<0.001) signal transduction pathways effectively antagonized TNFα-induced CAMP gene expression (
Figure 3B), whereas inhibition of STAT3 (S3I-201), MAPK (SB239063), or MEK-1/2 (U0126) signal transduction pathways did not inhibit TNFα-induced CAMP expression (
Figure 3C). Basal CAMP mRNA levels were not affected by inhibition of any of these signal transduction pathways (
Figure 3D).
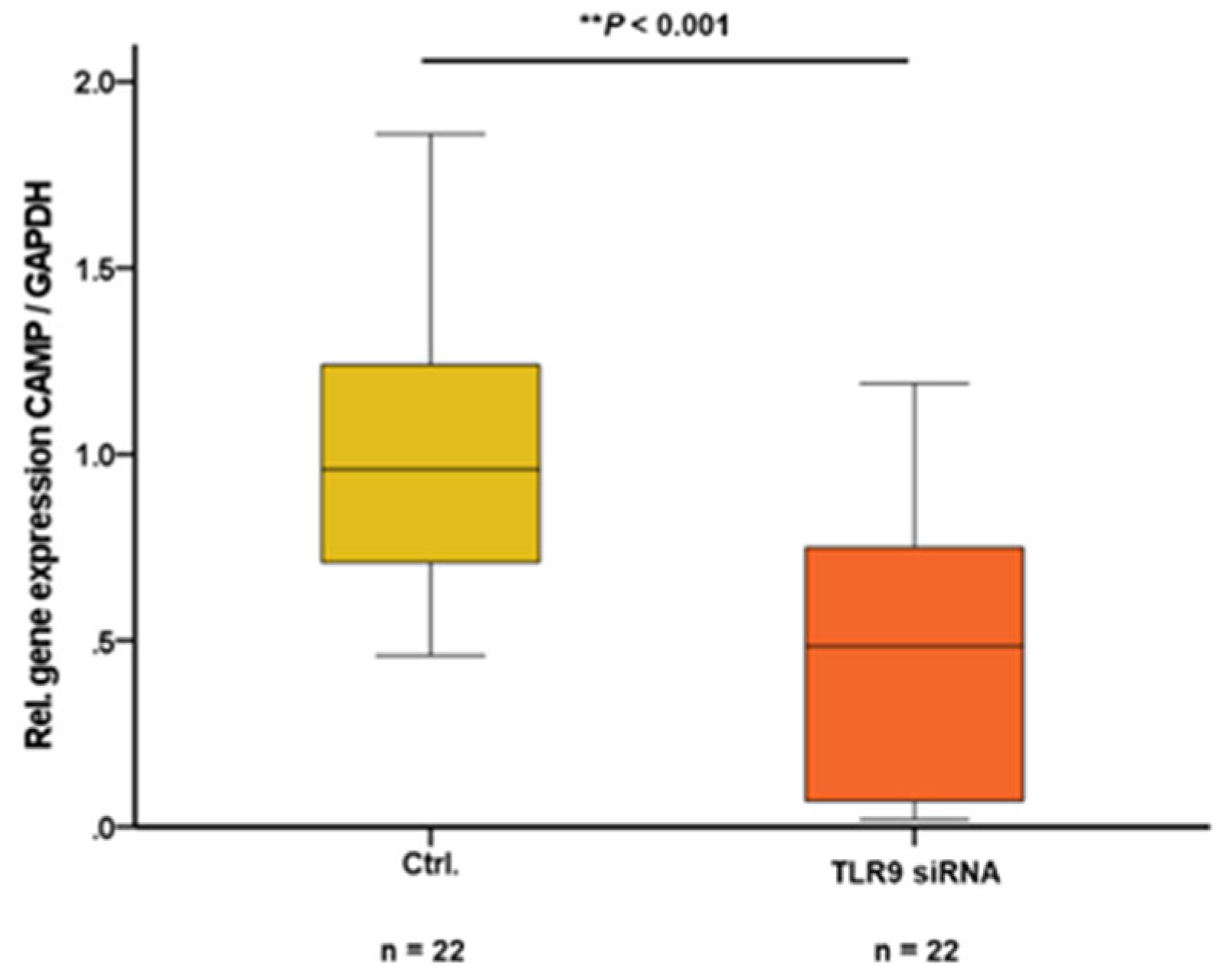
2.5. siRNA-Mediated Knockdown of TLR9 Reduces CAMP Expression in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
Since TLR9 expression and activity can be efficiently inhibited via siRNA-mediated cellular knockdown [
39], we aimed to investigate potential concomitant effects of TLR9 downregulation on CAMP expression in adipocytes. In mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes, cellular knockdown of TLR9 – being maintained during the entire adipocyte differentiation progress – resulted in significantly decreased levels of CAMP gene expression (
P<0.001) (
Figure 4).
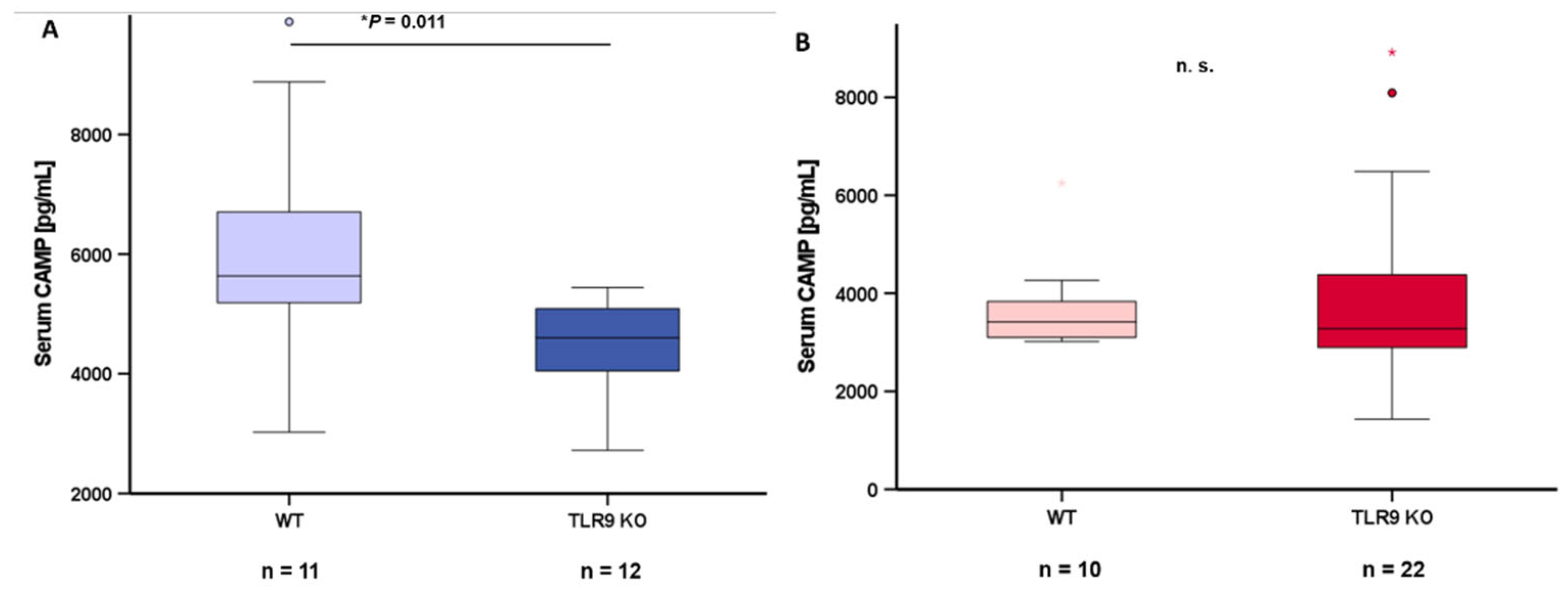
2.6. TLR9 Deficiency is Associated with Reduced Systemic CAMP Serum Concentrations in Male Mice
Blood serum samples from wildtype mice and TLR9 KO mice were collected at the age of 5-8 months and circulating CAMP levels were quantified via ELISA. CAMP serum concentrations were significantly lower (
P=0.011) in male TLR9 KO mice when compared to wildtype mice (
Figure 5A). This difference between genotypes was not observed in female mice (
Figure 5B).
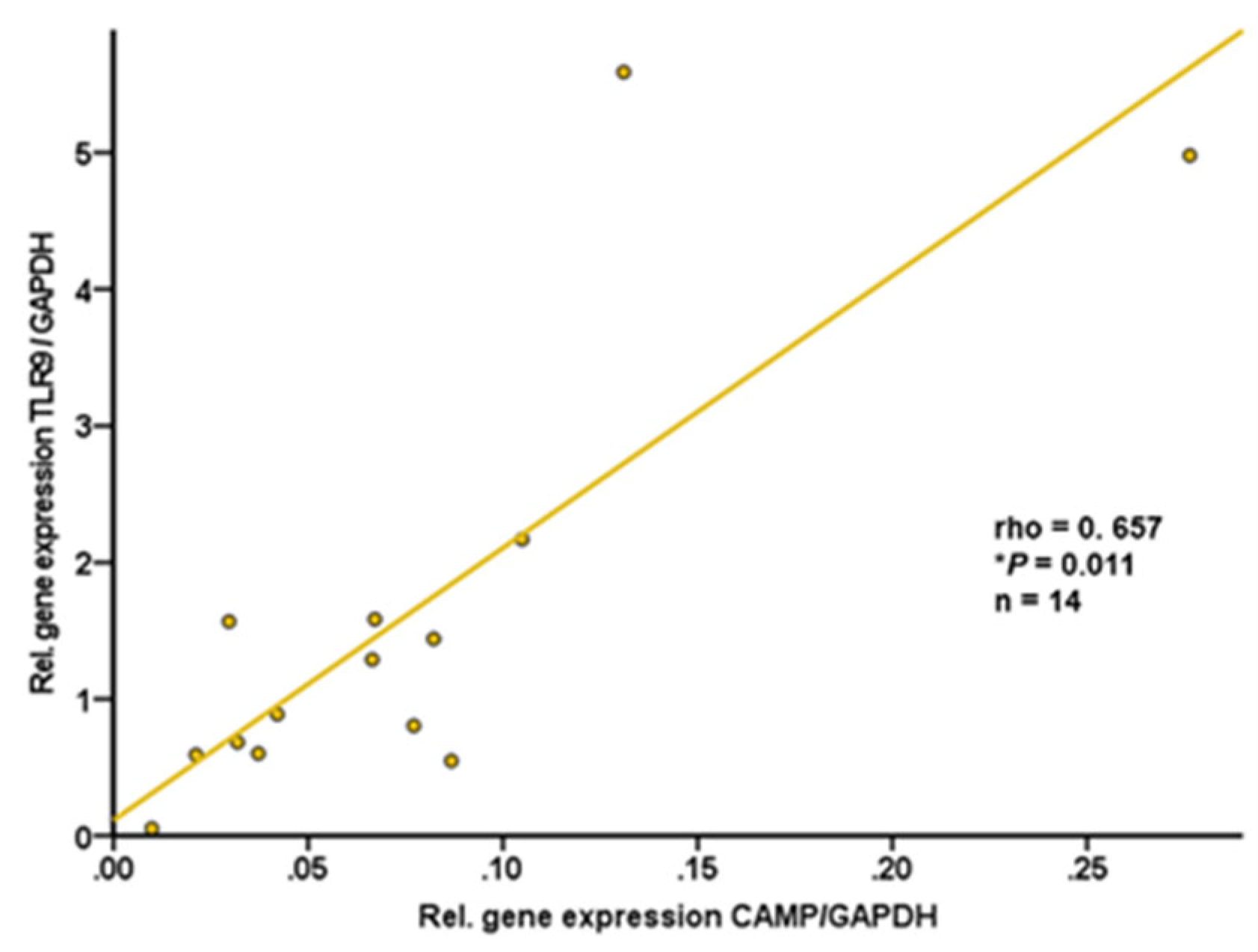
2.7. CAMP and TLR9 Gene Expression Levels are Positively Correlated in Murine Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue
It is well known that subcutaneous and gonadal/intra-abdominal adipose tissues differ in the numerical ratio of adipocytes to stromal vascular cells as well as in functional characteristics [
40]. Therefore, we investigated both adipose tissue compartments separately. Subcutaneous and gonadal adipose tissue specimens were resected from wildtype C57BL/6J mice. CAMP and TLR9 gene expression levels in subcutaneous adipose tissue were found to be positively correlated (rho=+0.657; P=0.011; n=14) (
Figure 6). In contrast, there was no significant correlation of TLR9 and CAMP mRNA levels in intra-abdominal adipose tissue (rho=-0.178; P=0.543; n=14; data not shown).
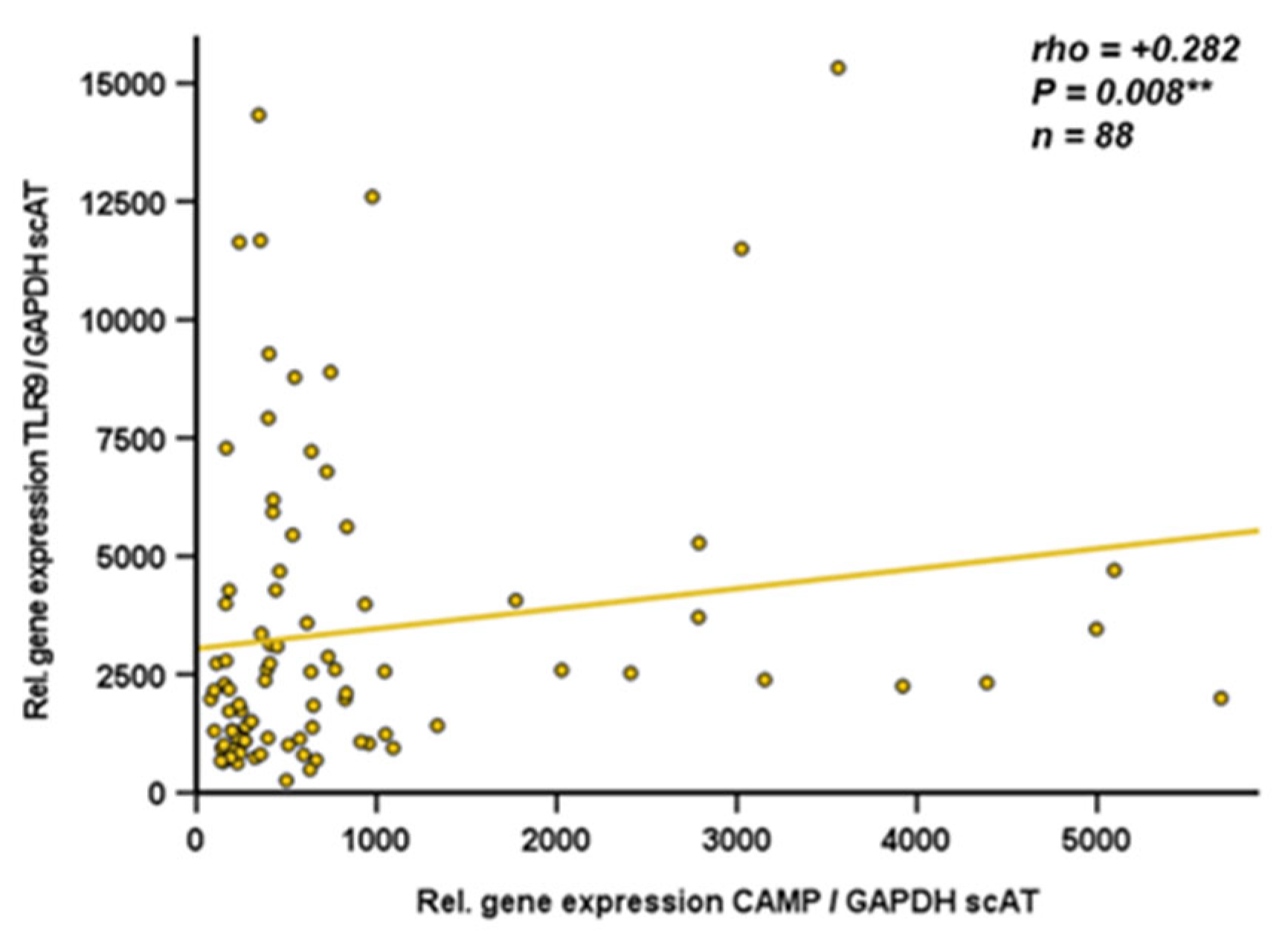
2.8. CAMP and TLR9 mRNA Levels are Positively Correlated in Human Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue
Since data on CAMP gene expression in human adipose tissue compartments are sparse, we analyzed gene expression of CAMP and TLR9 by quantitative real-time PCR in subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue specimens obtained from obese individuals undergoing bariatric surgery. TLR9 and CAMP gene expression levels in subcutaneous adipose tissue were positively correlated (rho=+0.282; p=0.008; n=88) (
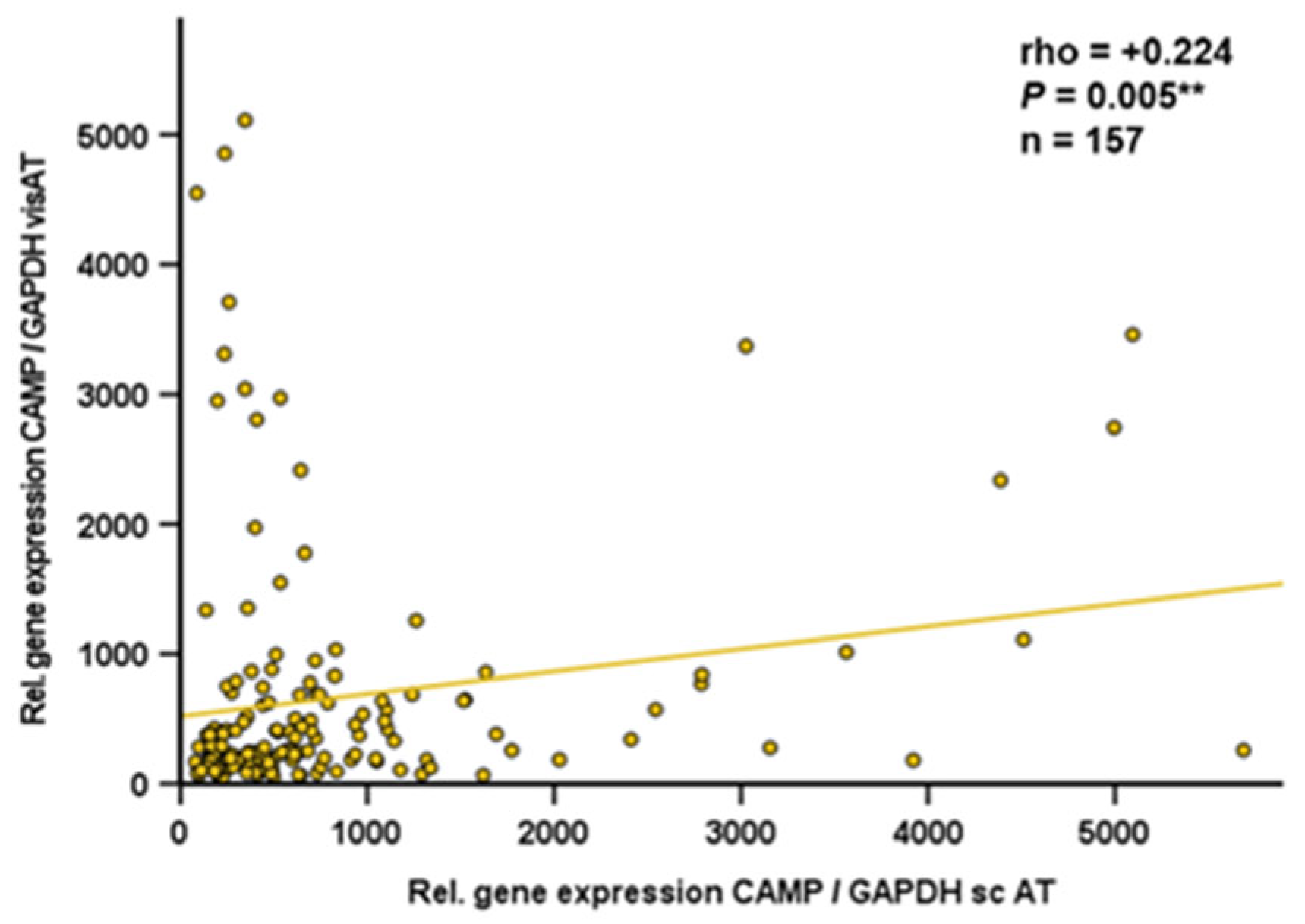
Figure 7). In human visceral adipose tissue, there was no correlation of TLR9 and CAMP expression (rho=+0.034; P=0.747; n=90; data not shown). Furthermore, CAMP mRNA quantities in human visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissues correlated positively (rho=+0.224; p=0.005; n=157) (
Figure 8).
3. Discussion
The present study investigates the interrelation of Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) and Toll-like receptor (TLR) 9 as a potential mechanism of innate immune processes in adipocytes and adipose tissues.
CAMP gene expression in adipocytes was described for the first time in 2015 [
13], identifying a crucial role of adipocyte-derived CAMP in local host defense of subcutaneous adipose tissue [
13]. The capacity of host defense in subcutaneous bacterial infection depends on metabolic factors, which is demonstrated by impaired host defense in obesity [
14]. CAMP is required for normal TLR9 function in dendritic cells and macrophages [
24]. Our group demonstrated previously that there is significant and functional TLR9 expression in adipocytes [
35]. Activation or inhibition of TLR9 activity affects the pattern of adipokine secretion in 3T3-L1 adipocytes in vitro [
35]. In the present study, we aimed to investigate if adipocyte CAMP gene expression is modulated by TLR9 activity.
During adipocyte differentiation, expression and secretion of various adipokines increase [
41]. Zhang et al. reported that CAMP gene expression in mature murine 3T3-L1 adipocytes is increased when compared to preadipocytes [
13], which was confirmed by our group [
42]. In the experiments presented now, we could further demonstrate a strong and persistent induction of CAMP gene expression during differentiation of human SGBS preadipocytes into mature adipocytes, a finding comparable to the expression of CAMP during in vitro differentiation of primary human preadipocytes [
13]. SGBS adipocytes [
33] therefore might represent an applicable cell culture model for the analysis of CAMP regulation in human adipocytes, improving the translational potential of in vitro findings for future clinical and therapeutical application.
Adipocytes and adipose tissues represent an important part of the innate immune system [
43]. Adipose tissue is composed of adipocytes and the stroma-vascular cell fraction, the latter including various immune cell-types [
44]. Depending on metabolic parameters, adipose tissue composition significantly varies between subcutaneous and visceral/gonadal adipose tissues [
44]. Currently, data on the regulation of CAMP by TLR9 in the context of adipose inflammation is sparse. Therefore, we investigated CAMP regulation via TLR9 ligands in vitro and in TLR9 knockout models in vivo.
In obesity, an increased quantity of visceral adipose tissue and adipocyte hypertrophy are associated with systemic low-grade inflammation, representing a key aspect of the metabolic syndrome [
6]. Macrophage infiltration into visceral adipose tissue induces local inflammatory stress in adipocytes [
21]. Subsequent adipocyte degeneration results in the release of nucleic acids (cell-free DNA, cfDNA) [
21], presumably exerting paracrine effects on adipocytes [
37]. Local cfDNA acts as an endogenous ligand of TLR9 on immune cells leading to an increased recruitment of immune cells to the site of inflammation [
38]. In obesity, levels of cfDNA in circulating blood are increased and positively correlated with the quantity of visceral adipose tissue [
21]. Representing well-established TLR9 ligands, the oligodeoxynucleotides ODN1585 (ODNA), ODN1826 (ODNB), ODN2395 (ODNC) [
45] and ODN2087 [
37] are known to modify immune responses by modulating TLR9 activity. Here we investigated the effects of TLR9 ligands in adipocytes on CAMP gene expression in vitro. CAMP gene expression was not affected by ODNA, ODNB, ODNC, nor by ODN2087 in adipocytes. Interestingly, stimulation with cfDNA significantly reduced CAMP gene expression, suggesting that cfDNA represents an yet unknown paracrine factor in adipose tissue inhibiting CAMP expression in adipocytes.
As an antimicrobial peptide, CAMP represents a part of the innate immune system. Regulation of CAMP in adipocytes by factors of the innate immune system (such as TNFα) is unknown so far. The proinflammatory cytokine TNFα is expressed in adipose tissue and affects insulin sensitivity as well as adipose tissue resident macrophage activation [
46]. In the present study, we found TNFα to significantly induce CAMP gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. This inflammatory elevation of CAMP expression was antagonized by inhibition of PI3K- and NF-ᴋB-, but not STAT3-, MAPK- or MEK-1/2-signaling. Basal, non-stimulated CAMP gene expression levels were not affected by inhibition of these signal transduction pathways, suggesting a specific TNFα-/inflammation-related mechanism.
Cellular knockdown mediated by siRNA is an established method in order to decrease TLR9 expression and activity in macrophages [
47] and adipocytes [
35]. As reported previously, siRNA-mediated TLR9 knockdown in adipocytes during adipocyte differentiation results in reduced adiponectin mRNA expression [
35]. Here, we demonstrate that reduced TLR9 activity also significantly impairs CAMP gene expression in mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Therefore, TLR9 activity might be relevant for CAMP regulation in adipocytes. However, since TLR9 knockdown was induced during adipocyte differentiation, the effect of reduced CAMP expression might also be caused by impaired adipocyte differentiation. Further studies need to clarify this effect.
Of note, siRNA mediated knockdown reduces TLR9 expression, but presumably does not abolish TLR9 entirely. Therefore, further investigations of CAMP regulation in a TLR9 knockout experimental approach were necessary. Thus, CAMP serum levels were measured in C57BL/6J wildtype and TLR9 knockout mice. Consistent with our findings in knockdown assays in adipocytes in vitro, systemic CAMP concentrations were significantly lower in TLR9 deficient mice when compared to wildtype animals. Of note, this difference between genotypes was exclusively observed in male but not in female mice. This unexpected sexual dimorphism needs to be further elucidated, bearing in mind that testosterone or estradiol did not exert a significant impact on CAMP expression in adipocytes in previous experiments in vitro [
15]. In accordance with the present findings in mice, human male individuals exhibited higher serum concentrations and subcutaneous adipose tissue mRNA levels of CAMP when compared to women in this previous study [
15]. Taken together, these data strongly argue for a sexual dimorphism in CAMP expression. With the underlying regulatory processes yet remaining to be elucidated, future studies should address this important issue on the molecular level of sexual hormones potentially affecting transcriptional and / or secretory regulation of CAMP in more detail.
Considering the differing cellular composition and function of subcutaneous and intra-abdominal adipose tissues, we comparatively investigated these compartments in mice and in human individuals. In subcutaneous adipose tissue of wildtype mice, TLR9 and CAMP expression were positively correlated, whereas no significant correlation of these parameters was observed in intra-abdominal adipose tissue. Consistent with these findings, TLR9 and CAMP expression were positively correlated in human subcutaneous but not in visceral adipose tissue. Additionally, CAMP expression showed a significant positive correlation between subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue. In this context, it is important to consider that visceral adipose tissue in obesity generally exhibits a higher proportion of immune cells in the stroma-vascular cell fraction than subcutaneous adipose tissue [
40]. Thus, in obesity, infiltration of macrophages is increased in visceral adipose tissue [
48]. In addition, macrophages are activated and produce predominantly proinflammatory cytokines, leading to an proinflammatory environment [
49].
4. Materials and Methods
3. T3-L1 Cell Culture And Stimulation Experiments
Murine 3T3-L1 fibroblasts [
25] were cultured and differentiated into mature adipocytes as described previously [
26]. Briefly, cells were cultured at 37 °C and 5 % CO2 in Dulbecco´s Modified Eagle Medium (Biochrom AG, Berlin, Germany) supplemented with 10 % newborn calf serum (Sigma-Aldrich, Deisenhofen, Germany) and were differentiated into adipocytes in DMEM/F12/glutamate medium (Lonza, Basel, Switzerland) supplemented with 20 µM 3-isobutyl-methyl-xanthine (Serva, Heidelberg, Germany), 1 µM corticosterone, 100 nM insulin, 200 µM ascorbate, 2 µg/mL transferrin, 5 % fetal calf serum (FCS, Sigma-Aldrich, Deisenhofen, Germany), 1 µM biotin, 17 µM pantothenic acid (all from Sigma Aldrich, Deisenhofen Germany), and 300 µg/mL Pedersen-fetuin (MP Biomedicals, Illkirch, France) [
27,
28]. A differentiation protocol reported in the literature [25,29-32] was used with slight modifications. Visual control of the cellular phenotype and of lipid accumulation by light-microscopy was done during all stages of the differentiation process.
Mature adipocytes were incubated under serum-free conditions prior to stimulation experiments. TLR9 agonistic oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) ODN1585 (referred to as ODNA), ODN1826 (ODNB), ODN2395 (ODNC) and inhibitory ODN2087 were purchased from Invivogen (San Diego, CA, USA) and were dissolved in H2O under sterile conditions. ODNA (5µg/ml, 20µg/ml), ODNB (5µg/ml, 20µg/ml), ODNC (10µg/ml, 20µg/ml) and ODN2087 (20 µg/mL) were applied in two separate overnight (18 h) stimulation experiments. Cell-free nucleic acids (referred to as cfDNA) were isolated from 3T3-L1 adipocytes as described below and were applied in doses of 100 ng/mL and 1 µg/mL. As an inflammatory stimulus, TNFα was applied at a dosage of 2 ng/mL and 10 ng/mL. Furthermore, co-stimulation experiments were performed with 10 ng/mL TNFα and inhibitors of different signal transduction pathways (NF-ᴋB inhibitor BAY-11 (5 mM), STAT3 inhibitor S3I-201 (50 mM), selective MAPK inhibitor SB239063 (5 mM), MEK-1/-2 inhibitor U0126 (5 mM), and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor LY294002 (5 mM), all purchased from Merck). Dosage was applied as described in our previous study [
16].
All applied stimulatory doses were within the concentration range recommended by the manufacturer and had been determined either by preliminary tests or previous experiments in adipocyte culture with respect to dose effects and cell viability. Furthermore, LDH (lactate dehydrogenase) concentration was measured in the cell supernatants (Cytotoxicity Detection Kit, Roche, Mannheim, Germany) of all experiments in order to exclude any unintended cytotoxic effects.
SGBS Cell Culture
The Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome (SGBS) preadipocyte cell strain represents primary human cells originated from adipose tissue specimens of a patient suffering from SGBS [
33]. They were kindly provided by Prof. Martin Wabitsch (University of Ulm, Germany). The cells were differentiated into mature adipocytes within 14 days of culture following the provider’s established protocol [
33]. SGBS preadipocytes were cultured in DMEM/F12 (1:1) (Invitrogen, Darmstadt, Germany) supplemented with 10 % FCS (all purchased from Invitrogen, Darmstadt, Germany). Differentiation into mature adipocytes was induced at confluence. After 3 washing steps with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), cells were cultured in serum-free medium supplemented with 0.01 g/ml transferrin, 20 nM insulin, 0.2 nM triiodothyronine, and 100 nM cortisol (all purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Deisenhofen, Germany). During the initial 4 days of differentiation, 2 μM rosiglitazone (BRL 49653) (Cayman, Tallinn, Estonia), 250 μM isobutylmethylxanthine (IBMX), and 25 nM dexamethasone (all purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Deisenhofen, Germany) were additionally added to the medium. The culture medium was replaced every third or fourth day. Adipocyte differentiation was completed after 14 days. The characteristic adipocyte morphology was visually controlled by light microscopy.
Preparation of Cell-Free Nucleic Acids from 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
Prior to isolation of cell-free nucleic acids (cfDNA) using the QIAamp® DNA Micro Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), murine 3T3-L1 adipocytes were exposed to inflammatory stress induced by stimulation with 50 ng/mL tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) (Biomol, Hamburg, Germany). After 18 h, adipocytes were harvested and cfDNA was isolated from cell lysates. Differing doses of cfDNA (100ng/ml; 1µg/ml) were applied for overnight (18 h) stimulation experiments in 3T3-L1 while treatment with solvent control containing no cfDNA served as a control setting.
Cellular TLR9 Knockdown in Adipocytes
For siRNA mediated knockdown of TLR9 expression, 3T3-L1 cells were repeatedly transfected with TLR9 siRNA during hormonally induced adipocyte differentiation at days 0, 3, 6, 8 for 3 h each, applying X-tremeGENE siRNA Transfection Reagent (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Penzberg, Germany). A pool of 3 distinct TLR9 siRNA molecules (# 175054, 175055, 175056, Ambion Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) with a final concentration of 100 nM was used (# 175054: sense: 5’-GCUAUAAUGGUAUCACCAACtt-3’; # 175055: sense: 5’-GCUCUCUCCAUACACUGAAtt-3’; # 175056: sense: 5’-GCGAGAACUUUCUCUAUGAtt-3’). Control cells were transfected with 100 nM non-targeting (nt) siRNA (Silencer® Select Negative Control siRNA #1, Ambion Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA).
Quantification of CAMP Concentrations in Murine Blood Serum
Healthy C57BL/6J (WT) and C57BL/6J-Tlr9M7Btlr/Mmjax mice (TLR9-KO) were bred under standard conditions and were fed a chow diet ad libitum until euthanasia for organ and tissue resection and blood serum collection. Concentrations of CAMP in blood serum from C57BL/6J-Tlr9M7Btlr/Mmjax mice (TLR9-KO) and wildtype C57BL/6J mice (WT) (age 5-8 months) were measured in technical duplicates by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (Kit purchased from Abbexa Ltd, Cambridge, UK) and are expressed as means ± standard deviation in the text and displayed as box plots in the figures. The test range of the applied ELISA Kit was 1.56–100 ng/mL. All measurements exceeding an intra-duplicate variance of 20 % were repeated. Animal experiments were performed at the University of Giessen, Germany, and all animal studies were approved by the local government agency.
Quantification of CAMP Gene Expression in Visceral and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue
Human adipose tissue specimens were obtained from the ROBS (Research in Obesity and Bariatric Surgery) study [
34], an open-label, non-randomized, monocentric, prospective and observational study of patients undergoing either bariatric surgery or dietary intervention at the University Hospital of Giessen, Germany. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue were obtained intra-surgically from patients receiving bariatric surgery (gastric sleeve or Roux-en-Y gastric bypass). Detailed information about the ROBS study cohort was published previously and can be drawn from the literature [
34]. The study was approved by the local ethical committee at the University of Giessen, Germany (file: AZ 101/14). All patients gave informed consent for their participation in the study. Data anonymization and privacy policy were accurately applied.
Isolation of mRNA and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis of CAMP Gene Expression in Murine Adipocytes and in Murine and Human Adipose Tissue
Intra-abdominal/gonadal and subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments were resected from C57BL/6J-Tlr9M7Btlr/Mmjax mice (TLR9-KO) [
35] and wildtype C57BL/6J mice (WT) that were bred under standard conditions and fed a normal chow (age 5-8 months). Animals were euthanized for serum samples conformably to the German animal protection law (§4 Abs. 3 Tierschutzgesetz). A specific announcement was made at the local ethical committee (Regierungspraesidium Giessen; internal registration number: 710_M) that was approved subsequently.
Subcutaneous adipose tissue was digested with 0.225 U/mL of collagenase NB 6 (#17458, SERVA Electrophoresis; Heidelberg, Germany) and adipocytes were separated from stromal vascular cells (SVC) via centrifugation (300 rcf, 10 min, 4°C).
Total mRNA was isolated from frozen human and murine total adipose tissues, from isolated murine mature adipocytes and SVC, and from cultured 3T3-L1 adipocytes as described previously [
26]. Briefly, tissues were homogenized in TRIzol®-Reagent (Life Technologies GmbH, Darmstadt, Germany) in combination with gentleMACS dissociator and M-tubes (Miltenyi Biotec GmbH, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany) for dissociation and RNA was isolated applying RNeasy® Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) including DNase (RNase-Free DNase Set, Qiagen, Hilden, Germany).
For gene expression analysis, reverse transcription of RNA (QuantiTect Reverse Transcription Kit from Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) was performed in order to generate corresponding cDNA for real-time PCR (RT-PCR) (iTaq Universal SYBR Green Supermix, CFX Connect RT-PCR system; Bio-Rad, Munich, Germany). Expression levels of the target gene CAMP were normalized to the gene expression of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) as a house-keeping gene applying the ΔΔCT method. The following primer-pairs were used:
Murine CAMP: 5’-ACATGTGGCTGAGATTGCTGG-3’ / 5‘-CCTTTGCTCTGTGATTCCATGTAG-3‘
Murine GAPDH: 5´ TGTCCGTCGTGGATCTGAC-3´ / 5´- AGGGAGATGCTCAGTGTTGG-3´
Human CAMP: 5’-TAGATGGCATCAACCAGCGG-3’ / 5’-CTGGGTCCCCATCCATCGT-3’
Human GAPDH: 5´-GAGTCCACTGGCGTCTTCAC-3´ / 5´-CCAGGGGTGCTAAGCAGTT-3´
All oligonucleotides used were purchased from Metabion, Martinsried, Germany.
Statistical Analysis
For explorative data analysis, a statistical software package (SPSS 28.0) was used. Non-parametric numerical parameters were analyzed by Mann-Whitney U-test (for 2 unrelated samples) or Kruskal-Wallis test (> 2 unrelated samples). Correlation analysis was performed by using the Spearman-rho test. P values below 0.05 (two-tailed) were considered as statistically significant. In the figures, the data are presented as box plots, with the box representing the second and third quartile of values, the whiskers giving the inter quartile range, and statistical outliers outside inter quartile range being indicated by dots and stars.
5. Conclusions
As a part of the innate immune system, adipocytes as well as adipose tissue as a whole organ play a crucial role in immune-metabolism (“metaflammation”, “adipose inflammation”) [
50]. Here we investigate and discuss a novel aspect of TLR9-mediated regulation of CAMP in adipocytes and adipose tissues. Our results implicate that TLR9 expression and activity are substantially involved in CAMP regulation in adipocytes in vitro and in adipose tissues in vivo. Further studies are necessary in order to investigate the molecular mechanisms and functional consequences of this novel relation within innate immunity and metaflammation in more detail. TLR9, CAMP and adipose tissue-derived cell-free nucleic acids might provide potential molecular targets in future anti-inflammatory drug therapies addressing metabolic inflammation and concomitant morbidities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.H., T.K., A.S. (Andreas Schmid) and A.S. (Andreas Schäffler); methodology, A.H., T.K. and A.S. (Andreas Schmid); validation, A.H. and A.S. (Andreas Schmid); formal analysis, A.H., T.K. and A.S. (Andreas Schmid); investigation, L.S., M.P., A.W. and A.S. (Andreas Schmid); resources, A.H. and T.K.; data curation, A.H. and A.S. (Andreas Schmid); writing—original draft preparation, A.H. and A.S. (Andreas Schmid); writing—review and editing, T.K., L.S., M.P., A.W. and A.S. (Andreas Schäffler); visualization, A.H. and A.S. (Andreas Schmid); supervision, T.K. and A.S. (Andreas Schäffler); project administration, T.K. and A.S. (Andreas Schäffler); funding acquisition, A.H. and T.K.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded by DEUTSCHE FORSCHUNGSGEMEINSCHAFT (to A. Höpfinger, grant number HO 6929/2-1, and to T. Karrasch, grant number KA 1846/4-2) and from UKGM GIESSEN (to A. Höpfinger, grant number 3/2022 GI).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the local Institutional Ethics Committee of Giessen University Hospital, Germany (Ethik-Kommission am Fachbereich Medizin, 12.06.2014, identification code: 101/14). Animal experiments were performed at the University of Giessen, Germany, and all sampling of animal tissue was conducted according to an announcement made at the local Ethical Committee (Regierungspräsidium Giessen) conformable to §4 Abs. 3 Tierschutzgesetz on 12 March 2019. Internal project identification code 710_M was assigned to the project at the University of Giessen. The study did not comprise any animal experiments subject to approval by the Ethics Committee.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on reasonable requestfrom the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The excellent administrative and technical support of the ROBS study consortium is highly appreciated. We thank Kathrin Ebeling, Lisa Knüpfer, Nicole Odenthal, Melina Gwiazdowski, and Veronika Eckert for excellent technical assistance during in vitro experiments and sample acquisition.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Engin: A. The Definition and Prevalence of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 960, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48382-5_1. [CrossRef]
- Übergewicht und Adipositas | Statista. Available online: https://de.statista.com/statistik/studie/id/14790/dokument/uebergewicht-und-adipositas-statista-dossier/ (accessed on 24 July 2022).
- Jokinen, E. Obesity and cardiovascular disease. Minerva Pediatr. 2015, 67, 25–32.
- Silveira Rossi, J.L.; Barbalho, S.M.; Reverete de Araujo, R.; Bechara, M.D.; Sloan, K.P.; Sloan, L.A. Metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases: Going beyond traditional risk factors. Diabetes. Metab. Res. Rev. 2022, 38, e3502. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.3502. [CrossRef]
- Mathers, C.D.; Loncar, D. Projections of global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e442. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0030442. [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375-C391. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00379.2020. [CrossRef]
- Suganami, T.; Ogawa, Y. Role of chronic inflammation in adipose tissue in the pathophysiology of obesity. Nihon Rinsho 2013, 71, 225–230.
- Agerberth, B.; Charo, J.; Werr, J.; Olsson, B.; Idali, F.; Lindbom, L.; Kiessling, R.; Jörnvall, H.; Wigzell, H.; Gudmundsson, G.H. The human antimicrobial and chemotactic peptides LL-37 and alpha-defensins are expressed by specific lymphocyte and monocyte populations. Blood 2000, 96, 3086–3093.
- de Yang; Chen, Q.; Schmidt, A.P.; Anderson, G.M.; Wang, J.M.; Wooters, J.; Oppenheim, J.J.; Chertov, O. LL-37, the neutrophil granule- and epithelial cell-derived cathelicidin, utilizes formyl peptide receptor-like 1 (FPRL1) as a receptor to chemoattract human peripheral blood neutrophils, monocytes, and T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1069–1074. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.192.7.1069. [CrossRef]
- Tjabringa, G.S.; Ninaber, D.K.; Drijfhout, J.W.; Rabe, K.F.; Hiemstra, P.S. Human cathelicidin LL-37 is a chemoattractant for eosinophils and neutrophils that acts via formyl-peptide receptors. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2006, 140, 103–112. https://doi.org/10.1159/000092305. [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Lee, M.W.; Wong, G.C.L. Modulation of toll-like receptor signaling by antimicrobial peptides. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 88, 173–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.02.002. [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Xing, L.; Qu, P.; Tan, T.; Yang, N.; Li, D.; Chen, H.; Feng, X. Identification of a novel cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide from ducks and determination of its functional activity and antibacterial mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17260. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17260. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-J.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Hata, T.; Bapat, S.P.; Ramos, R.; Plikus, M.V.; Gallo, R.L. Innate immunity. Dermal adipocytes protect against invasive Staphylococcus aureus skin infection. Science 2015, 347, 67–71. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1260972. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-J.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Chen, S.X.; Zhang, X.; Yin, M.; Li, F.; Wu, S.; Chen, J.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; et al. Diet-induced obesity promotes infection by impairment of the innate antimicrobial defense function of dermal adipocyte progenitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.abb5280. [CrossRef]
- Hochberg, A.; Patz, M.; Karrasch, T.; Schäffler, A.; Schmid, A. Serum Levels and Adipose Tissue Gene Expression of Cathelicidin Antimicrobial Peptide (CAMP) in Obesity and During Weight Loss. Horm. Metab. Res. 2021, 53, 169–177. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1323-3050. [CrossRef]
- Höpfinger, A.; Karrasch, T.; Schäffler, A.; Schmid, A. Regulation of CAMP (cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide) expression in adipocytes by TLR 2 and 4. Innate Immun. 2021, 27, 184–191. https://doi.org/10.1177/1753425920988167. [CrossRef]
- Karrasch, T.; Höpfinger, A.; Schäffler, A.; Schmid, A. The adipokine C1q/TNF-related protein-3 (CTRP-3) inhibits Toll-like receptor (TLR)-induced expression of Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) in adipocytes. Cytokine 2021, 148, 155663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155663. [CrossRef]
- Blasius, A.L.; Beutler, B. Intracellular toll-like receptors. Immunity 2010, 32, 305–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2010.03.012. [CrossRef]
- Hemmi, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Kawai, T.; Kaisho, T.; Sato, S.; Sanjo, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Hoshino, K.; Wagner, H.; Takeda, K.; et al. A Toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature 2000, 408, 740–745. https://doi.org/10.1038/35047123. [CrossRef]
- Krug, A.; French, A.R.; Barchet, W.; Fischer, J.A.A.; Dzionek, A.; Pingel, J.T.; Orihuela, M.M.; Akira, S.; Yokoyama, W.M.; Colonna, M. TLR9-dependent recognition of MCMV by IPC and DC generates coordinated cytokine responses that activate antiviral NK cell function. Immunity 2004, 21, 107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2004.06.007. [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, S.; Fukuda, D.; Higashikuni, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Hirata, Y.; Murata, C.; Kim-Kaneyama, J.-R.; Sato, F.; Bando, M.; Yagi, S.; et al. Obesity-induced DNA released from adipocytes stimulates chronic adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501332. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1501332. [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity 2011, 34, 637–650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2011.05.006. [CrossRef]
- Revelo, X.S.; Ghazarian, M.; Chng, M.H.Y.; Luck, H.; Kim, J.H.; Zeng, K.; Shi, S.Y.; Tsai, S.; Lei, H.; Kenkel, J.; et al. Nucleic Acid-Targeting Pathways Promote Inflammation in Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 717–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.06.024. [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Gallo, R.L. Endogenous intracellular cathelicidin enhances TLR9 activation in dendritic cells and macrophages. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 1274–1284. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1402388. [CrossRef]
- Green, H.; Kehinde, O. An established preadipose cell line and its differentiation in culture II. Factors affecting the adipose conversion. Cell 1975, 5, 19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(75)90087-2. [CrossRef]
- Schmid, A.; Hochberg, A.; Kreiß, A.F.; Gehl, J.; Patz, M.; Thomalla, M.; Hanses, F.; Karrasch, T.; Schäffler, A. Role of progranulin in adipose tissue innate immunity. Cytokine 2019, 125, 154796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154796. [CrossRef]
- Zaitsu, H.; Serrero, G. Pedersen fetuin contains three adipogenic factors with distinct biochemical characteristics. J. Cell. Physiol. 1990, 144, 485–491. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.1041440316. [CrossRef]
- Bachmeier, M.; Löffler, G. Adipogenic activities in commercial preparations of fetuin. Horm. Metab. Res. 1994, 26, 92–96. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-1000780. [CrossRef]
- Green, H.; Kehinde, O. Formation of normally differentiated subcutaneous fat pads by an established preadipose cell line. J. Cell. Physiol. 1979, 101, 169–171. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.1041010119. [CrossRef]
- Green, H.; Meuth, M. An established pre-adipose cell line and its differentiation in culture. Cell 1974, 3, 127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(74)90116-0. [CrossRef]
- MacDougald, O.A. Transcriptional Regulation of Gene Expression During Adipocyte Differentiation. Annual Review of Biochemistry 1995, 64, 345–373. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.64.1.345. [CrossRef]
- Cornelius, P. Regulation of Adipocyte Development. Annual Review of Nutrition 1994, 14, 99–129. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.nutr.14.1.99. [CrossRef]
- Wabitsch, M.; Brenner, R.E.; Melzner, I.; Braun, M.; Möller, P.; Heinze, E.; Debatin, K.M.; Hauner, H. Characterization of a human preadipocyte cell strain with high capacity for adipose differentiation. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2001, 25, 8–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801520. [CrossRef]
- Brock, J.; Schmid, A.; Karrasch, T.; Pfefferle, P.; Schlegel, J.; Busse, I.; Hauenschild, A.; Schmidt, B.; Koukou, M.; Arapogianni, E.; et al. Progranulin serum levels and gene expression in subcutaneous vs visceral adipose tissue of severely obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf) 2019, 91, 400–410. https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.14040. [CrossRef]
- Thomalla, M.; Schmid, A.; Neumann, E.; Pfefferle, P.I.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Schäffler, A.; Karrasch, T. Evidence of an anti-inflammatory toll-like receptor 9 (TLR 9) pathway in adipocytes. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 240, 325–343. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-18-0326. [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, F.; Gursel, I.; Ishii, K.J.; Suzuki, K.; Gursel, M.; Klinman, D.M. Signal transduction pathways mediated by the interaction of CpG DNA with Toll-like receptor 9. Semin. Immunol. 2004, 16, 17–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2003.10.009. [CrossRef]
- Thomalla, M.; Schmid, A.; Hehner, J.; Koehler, S.; Neumann, E.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Schäffler, A.; Karrasch, T. Toll-like Receptor 7 (TLR7) Is Expressed in Adipocytes and the Pharmacological TLR7 Agonist Imiquimod and Adipocyte-Derived Cell-Free Nucleic Acids (cfDNA) Regulate Adipocyte Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158475. [CrossRef]
- Guillerey, C.; Mouriès, J.; Polo, G.; Doyen, N.; Law, H.K.W.; Chan, S.; Kastner, P.; Leclerc, C.; Dadaglio, G. Pivotal role of plasmacytoid dendritic cells in inflammation and NK-cell responses after TLR9 triggering in mice. Blood 2012, 120, 90–99. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-02-410936. [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Li, B.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, S. Specific siRNA downregulated TLR9 and altered cytokine expression pattern in macrophage after CpG DNA stimulation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2005, 2, 130–135.
- Ibrahim, M.M. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: structural and functional differences. Obes. Rev. 2010, 11, 11–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2009.00623.x. [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Tucci, J.; Malvar, J.; Mittelman, S.D. Adipocyte differentiation is affected by media height above the cell layer. Int. J. Obes. (Lond) 2014, 38, 315–320. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2013.96. [CrossRef]
- Schmid, A.; Karrasch, T.; Thomalla, M.; Schlegel, J.; Salzberger, B.; Schäffler, A.; Hanses, F. Innate Immunity of Adipose Tissue in Rodent Models of Local and Systemic Staphylococcus aureus Infection. Mediators Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 5315602. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5315602. [CrossRef]
- Blaszczak, A.M.; Jalilvand, A.; Hsueh, W.A. Adipocytes, Innate Immunity and Obesity: A Mini-Review. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 650768. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.650768. [CrossRef]
- Crewe, C.; An, Y.A.; Scherer, P.E. The ominous triad of adipose tissue dysfunction: inflammation, fibrosis, and impaired angiogenesis. J. Clin. Invest. 2017, 127, 74–82. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI88883. [CrossRef]
- Becker, Y. CpG ODNs treatments of HIV-1 infected patients may cause the decline of transmission in high risk populations - a review, hypothesis and implications. Virus Genes 2005, 30, 251–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-004-5632-2. [CrossRef]
- Tzanavari, T.; Giannogonas, P.; Karalis, K.P. TNF-alpha and obesity. Curr. Dir. Autoimmun. 2010, 11, 145–156. https://doi.org/10.1159/000289203. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Choe, J.-Y.; Park, K.-Y. Activation of CpG-ODN-Induced TLR9 Signaling Inhibited by Interleukin-37 in U937 Human Macrophages. Yonsei Med. J. 2021, 62, 1023–1031. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2021.62.11.1023. [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2921. [CrossRef]
- Engin, A.B. Adipocyte-Macrophage Cross-Talk in Obesity. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 960, 327–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48382-5_14. [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature 2017, 542, 177–185. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21363. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
CAMP gene expression is induced during differentiation in murine 3T3-L1 adipocytes and in human SGBS cells: In preadipocytes, no significant CAMP expression is detectable. At day 6 and in mature adipocytes, a considerable increase of CAMP mRNA levels is observed (1A). CAMP expression significantly increases during differentiation of SGBS cells (1B). CAMP expression was investigated by quantitative real-time PCR. The Kruskal–Wallis test was applied for calculation of P values and statistical significance (P<0.05). N=6–12 wells were investigated per experimental setting.
Figure 1.
CAMP gene expression is induced during differentiation in murine 3T3-L1 adipocytes and in human SGBS cells: In preadipocytes, no significant CAMP expression is detectable. At day 6 and in mature adipocytes, a considerable increase of CAMP mRNA levels is observed (1A). CAMP expression significantly increases during differentiation of SGBS cells (1B). CAMP expression was investigated by quantitative real-time PCR. The Kruskal–Wallis test was applied for calculation of P values and statistical significance (P<0.05). N=6–12 wells were investigated per experimental setting.
Figure 2.
Adipocytic Cell-free nucleic acids (cfDNA) impair CAMP expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: cfDNA reduces CAMP mRNA levels in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. CAMP expression was investigated by quantitative real-time PCR. Kruskal–Wallis test was applied for calculation of P values and statistical significance (P<0.05). N=16–18 wells were investigated per experimental setting.
Figure 2.
Adipocytic Cell-free nucleic acids (cfDNA) impair CAMP expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: cfDNA reduces CAMP mRNA levels in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. CAMP expression was investigated by quantitative real-time PCR. Kruskal–Wallis test was applied for calculation of P values and statistical significance (P<0.05). N=16–18 wells were investigated per experimental setting.
Figure 3.
TNFα-induced CAMP gene expression is antagonized by inhibitors of NF-ᴋB- and PI3K signaling: TNFα induces CAMP expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes (A). Inhibition of NF-ᴋB (BAY11-7085)- and PI3K (LY294002)-pathway antagonize TNFα induced CAMP expression (B). Inhibition of STAT3 (S3I-201)-, MAPK (SB239063)-, MEK-1/-2 (U0126)-pathway do not alter TNFα induced CAMP expression (C). Basal CAMP expression is not modified by inhibition of classical signal transduction pathways (D) (*P<0.05, ** P<0.01). n=9-12 samples were investigated.
Figure 3.
TNFα-induced CAMP gene expression is antagonized by inhibitors of NF-ᴋB- and PI3K signaling: TNFα induces CAMP expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes (A). Inhibition of NF-ᴋB (BAY11-7085)- and PI3K (LY294002)-pathway antagonize TNFα induced CAMP expression (B). Inhibition of STAT3 (S3I-201)-, MAPK (SB239063)-, MEK-1/-2 (U0126)-pathway do not alter TNFα induced CAMP expression (C). Basal CAMP expression is not modified by inhibition of classical signal transduction pathways (D) (*P<0.05, ** P<0.01). n=9-12 samples were investigated.
Figure 4.
siRNA mediated knockdown of TLR9 reduces CAMP expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: CAMP gene expression levels in 3T3-L1 adipocytes are significantly decreased after cellular knockdown of TLR9 (**P<0.001). CAMP expression was investigated by quantitative real-time PCR and Mann-Whitney U-test was applied for calculation of statistical significance (P<0.05). N=22 wells were investigated per experimental setting.
Figure 4.
siRNA mediated knockdown of TLR9 reduces CAMP expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: CAMP gene expression levels in 3T3-L1 adipocytes are significantly decreased after cellular knockdown of TLR9 (**P<0.001). CAMP expression was investigated by quantitative real-time PCR and Mann-Whitney U-test was applied for calculation of statistical significance (P<0.05). N=22 wells were investigated per experimental setting.
Figure 5.
TLR9 KO is associated with reduced systemic CAMP concentrations in male mice: CAMP concentration in blood serum is significantly lower (*P=0.011) in male TLR9 KO mice than in wildtype mice (5A) whereas this difference was not observed in female animals (5B). Blood serum samples from wildtype and TLR9 KO mice were collected at the age of 5-8 months. Blood serum CAMP concentrations were measured by ELISA and Mann-Whitney U-test was applied for calculation of statistical significance (P<0.05). Samples from n=10-22 animals per group were investigated.
Figure 5.
TLR9 KO is associated with reduced systemic CAMP concentrations in male mice: CAMP concentration in blood serum is significantly lower (*P=0.011) in male TLR9 KO mice than in wildtype mice (5A) whereas this difference was not observed in female animals (5B). Blood serum samples from wildtype and TLR9 KO mice were collected at the age of 5-8 months. Blood serum CAMP concentrations were measured by ELISA and Mann-Whitney U-test was applied for calculation of statistical significance (P<0.05). Samples from n=10-22 animals per group were investigated.
Figure 6.
CAMP and TLR9 gene expression levels are positively correlated in murine subcutaneous adipose tissue: TLR9 expression in subcutaneous adipose tissue is positively correlated with CAMP expression in subcutaneous adipose tissue of wildtype mice. Samples of subcutaneous adipose tissue from wildtype mice were collected at the age of 12 months. CAMP and TLR9 expression were investigated by quantitative real-time PCR. The Spearman-rho test was applied for calculation of correlation coefficient and statistical significance (*P<0.05). N=14 samples were investigated.
Figure 6.
CAMP and TLR9 gene expression levels are positively correlated in murine subcutaneous adipose tissue: TLR9 expression in subcutaneous adipose tissue is positively correlated with CAMP expression in subcutaneous adipose tissue of wildtype mice. Samples of subcutaneous adipose tissue from wildtype mice were collected at the age of 12 months. CAMP and TLR9 expression were investigated by quantitative real-time PCR. The Spearman-rho test was applied for calculation of correlation coefficient and statistical significance (*P<0.05). N=14 samples were investigated.
Figure 7.
CAMP and TLR9 mRNA levels are positively correlated in human subcutaneous adipose tissue: TLR9 expression in subcutaneous adipose tissue is positively correlated with CAMP expression in subcutaneous human adipose tissue. Specimens of human subcutaneous adipose tissue were collected during bariatric surgery. CAMP and TLR9 expression were investigated by quantitative real-time PCR and Spearman-rho test was applied for calculation of correlation coefficient and statistical significance (*P<0.05). N=88 samples were investigated.
Figure 7.
CAMP and TLR9 mRNA levels are positively correlated in human subcutaneous adipose tissue: TLR9 expression in subcutaneous adipose tissue is positively correlated with CAMP expression in subcutaneous human adipose tissue. Specimens of human subcutaneous adipose tissue were collected during bariatric surgery. CAMP and TLR9 expression were investigated by quantitative real-time PCR and Spearman-rho test was applied for calculation of correlation coefficient and statistical significance (*P<0.05). N=88 samples were investigated.
Figure 8.
CAMP mRNA levels are positively correlated in human subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: CAMP gene expression levels in subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue are positively correlated. Specimens of human subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue were collected during bariatric surgery. CAMP and TLR9 expression were investigated by quantitative real-time PCR and Spearman-rho test was applied for calculation of correlation coefficient and statistical significance (*P<0.05). N=157 samples were investigated.
Figure 8.
CAMP mRNA levels are positively correlated in human subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: CAMP gene expression levels in subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue are positively correlated. Specimens of human subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue were collected during bariatric surgery. CAMP and TLR9 expression were investigated by quantitative real-time PCR and Spearman-rho test was applied for calculation of correlation coefficient and statistical significance (*P<0.05). N=157 samples were investigated.
Table 1.
Synthetic TLR9 ligands do not modify CAMP gene expression in murine adipocytes: Stimulation of murine 3T3‐L1 adipocytes with various doses of ODNA, ODNB, ODNC, and ODN2087 does not significantly affect CAMP gene expression. CAMP expression was investigated by quantitative real‐time PCR. The Kruskal–Wallis test was applied for calculation of P values and statistical significance (P<0.05). N=11–20 wells were investigated per experimental setting.
Table 1.
Synthetic TLR9 ligands do not modify CAMP gene expression in murine adipocytes: Stimulation of murine 3T3‐L1 adipocytes with various doses of ODNA, ODNB, ODNC, and ODN2087 does not significantly affect CAMP gene expression. CAMP expression was investigated by quantitative real‐time PCR. The Kruskal–Wallis test was applied for calculation of P values and statistical significance (P<0.05). N=11–20 wells were investigated per experimental setting.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).