Submitted:
19 May 2023
Posted:
19 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
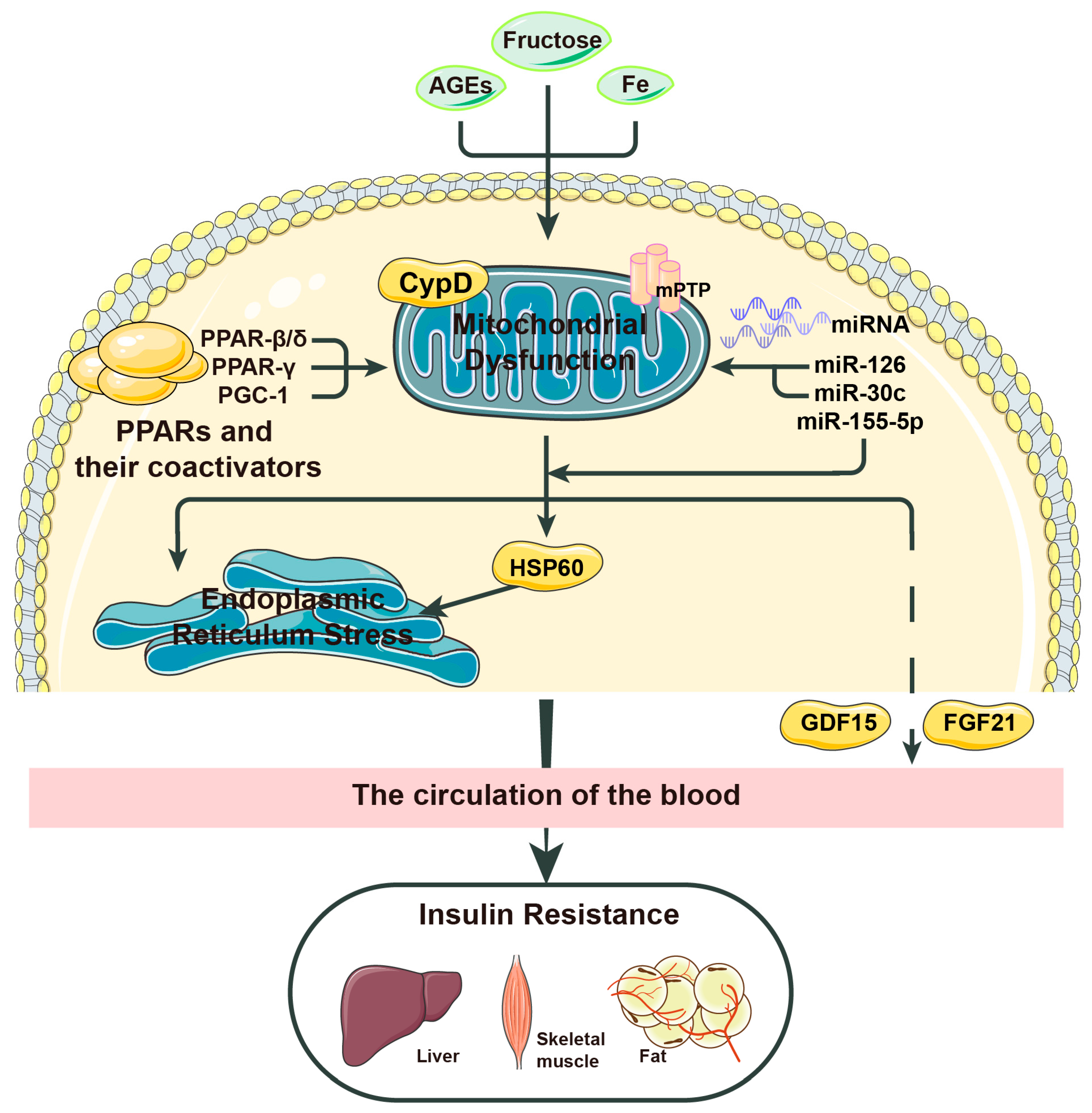
2. Mitochondrial Stress, a Key Inducer of Insulin Resistance
2.1. Major Factors Leading to Mitochondrial Stress
2.2. How does Mitochondrial Stress Affect Insulin Resistance?
2.2.1. HSP60
2.2.2. FGF21
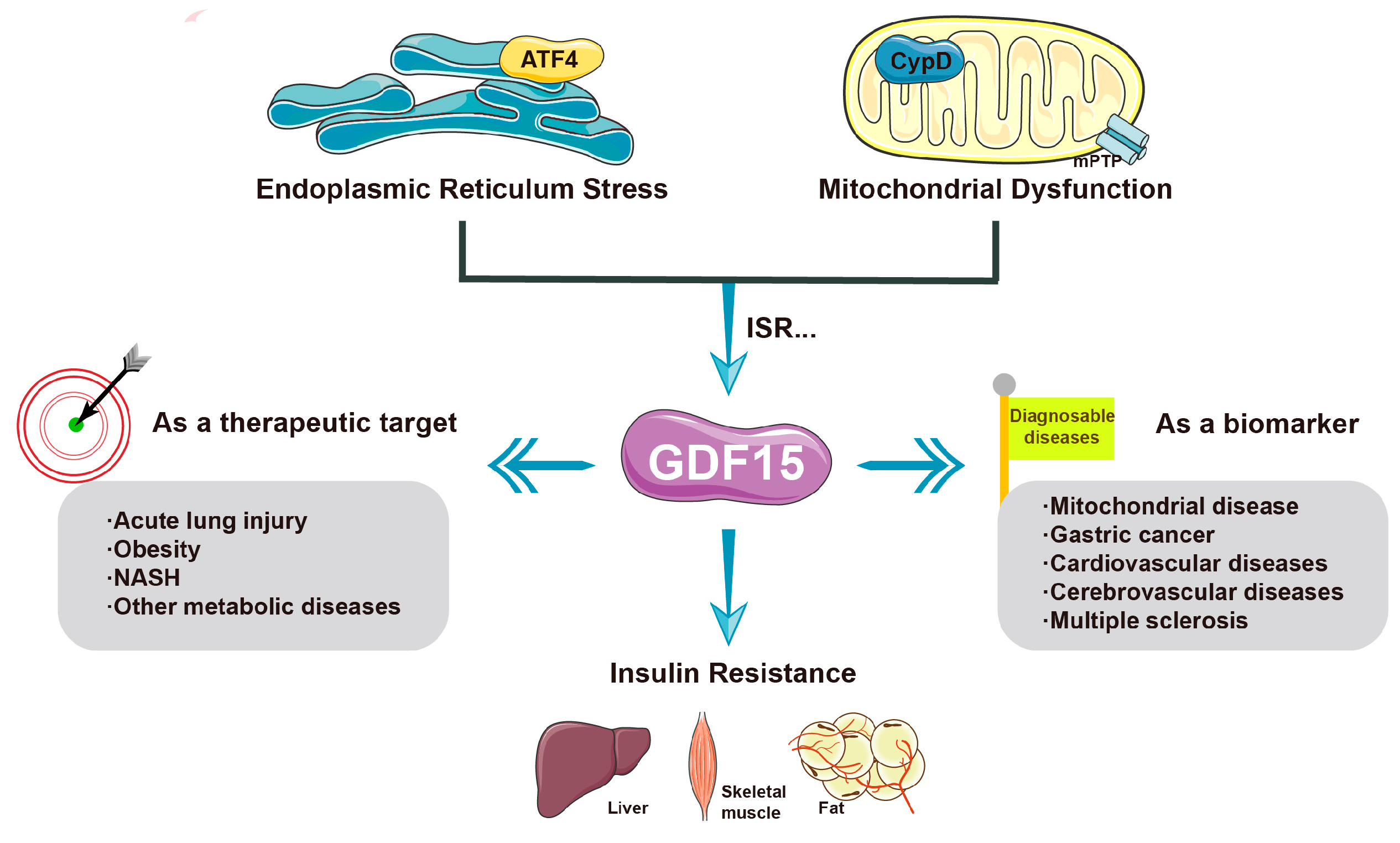
2.2.3. GDF-15
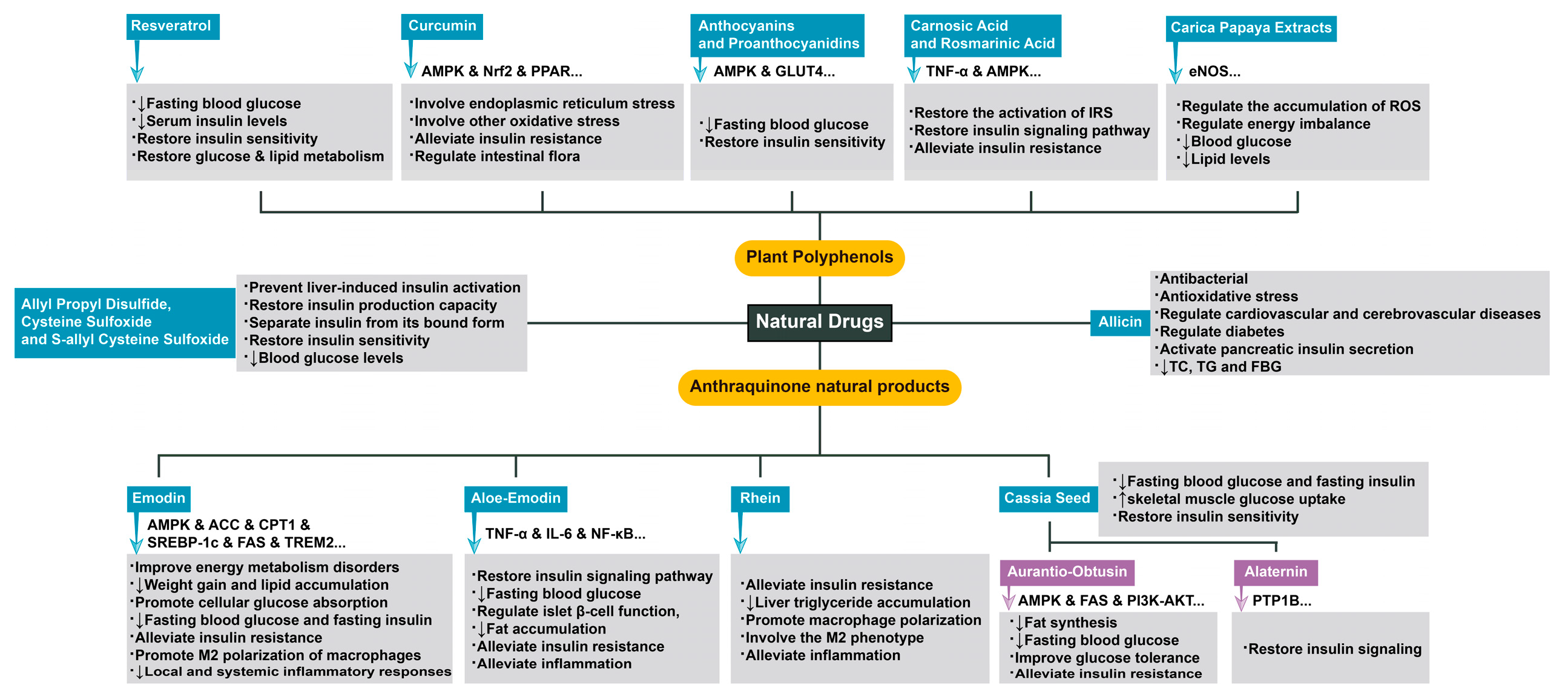
3. Complex Mechanisms of Natural Drugs in the Treatment of Diseases Related to Insulin Resistance
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Sundaram, K.; Mu, J.; Dryden, G.W.; Sriwastva, M.K.; Lei, C.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, X.; Xu, F.; Yan, J.; et al. High-fat diet-induced upregulation of exosomal phosphatidylcholine contributes to insulin resistance. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perseghin, G.; Price, T.B.; Petersen, K.F.; Roden, M.; Cline, G.W.; Gerow, K.; Rothman, D.L.; Shulman, G.I. Increased glucose transport–phosphorylation and muscle glycogen synthesis after exercise training in insulin-resistant subjects. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowotny, K.; Jung, T.; Höhn, A.; Weber, D.; Grune, T. Advanced glycation end products and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 194–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Du, H.; Shao, S.; Bo, T.; Yu, C.; Chen, W.; Zhao, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; et al. Cyclophilin D deficiency attenuates mitochondrial perturbation and ameliorates hepatic steatosis. Hepatology 2018, 68, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassir, F.; Ibdah, J.A. Role of mitochondria in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 8713–8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, C.A.; Lee, H.; Brookes, P.S.; Yoon, Y. Decreasing mitochondrial fission alleviates hepatic steatosis in a murine model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 307, G632–G641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkey, B.F.; Li, X.; Bolognese, L.; Balkan, B.; Mone, M.; Russell, M.; Hughes, T.E.; Wang, P.R. Acute and chronic effects of the incretin enhancer vildagliptin in insulin-resistant rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005, 315, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klymenko, O.; Brecklinghaus, T.; Dille, M.; Springer, C.; de Wendt, C.; Altenhofen, D.; Binsch, C.; Knebel, B.; Scheller, J.; Hardt, C.; et al. Histone deacetylase 5 regulates interleukin 6 secretion and insulin action in skeletal muscle. Mol. Metab. 2020, 42, 101062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, G.R., Jr.; Khazai, N.B.; Bouloux, G.F.; Camalier, C.E.; Lin, Y.; Garneys, L.M.; Siqueira, J.; Peng, L.; Pasquel, F.; Umpierrez, D.; et al. The effects of thiazolidinediones on human bone marrow stromal cell differentiation in vitro and in thiazolidinedione-treated patients with type 2 diabetes. Transl. Res. 2013, 161, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, F.; Scheen, A. Understanding and overcoming metformin gastrointestinal intolerance. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.I.; Blau, J.E.; Rother, K.I.; Beitelshees, A.L. SGLT2 inhibitors as adjunctive therapy for type 1 diabetes: Balancing benefits and risks. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, E.; Um, M.Y.; Choi, M.; Han, T.; Kim, I.H.; Shin, S. Cassia tora seed improves pancreatic mitochondrial function leading to recovery of glucose metabolism. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.R.; Cui, H.X.; Fang, J.L.; Yuan, K.; Guo, Y. Ameliorative effect and mechanism of the purified anthraquinone-glycoside preparation from Rheum palmatum L. on type 2 diabetes mellitus. Molecules 2019, 24, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deora, N.; Sunitha, M.M.; Satyavani, M.; Harishankar, N.; Vijayalakshmi, M.A.; Venkataraman, K.; Venkateshan, V. Alleviation of diabetes mellitus through the restoration of β-cell function and lipid metabolism by Aloe vera (L.) Burm. f. extract in obesogenic WNIN/GR-Ob rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 272, 113921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PAOLISSO, G.D.A.A.; VOLPE, C.; et al. Evidence for a relationship between oxidative stress and insulin action in non-insulin-dependent (type II) diabetic patients. Metabolism 1994, 43, 1426–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.K.S.; Peixoto, C.A. Role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease inflammation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 2951–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Yeon, J.E.; Ko, E.J.; Yoon, E.L.; Suh, S.J.; Kang, K.; Kim, H.R.; Kang, S.H.; Yoo, Y.J.; Je, J.; et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-delta agonist ameliorated inflammasome activation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12787–12799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Montagner, A.; Tan, N.; Wahli, W. Insights into the role of PPARβ/δ in NAFLD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Du, H.; Chai, Q.; jia, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhao, M.; Li, J.; Tang, H.; Chen, W.; Zhao, L.; et al. Blocking mitochondrial cyclophilin D ameliorates TSH-impaired defensive barrier of artery. Redox Biol. 2018, 15, 418–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D. , Hu, F., Mao, Y., Yan, L., Zhang, Y., Zheng, Z., Wu, A., Forouzanfar, T., Pathak, J. L., & Wu, G. Cationic antimicrobial peptide NRC-03 induces oral squamous cell carcinoma cell apoptosis via CypD-mPTP axis-mediated mitochondrial oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2022, 54, 102355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, E.C.; Morales, J.A.; Chapoy-Villanueva, H.; Silva-Platas, C.; Trevino-Saldana, N.; Guerrero-Beltran, C.E.; Bernal-Ramirez, J.; Torres-Quintanilla, A.; Garcia, N.; Youker, K.; et al. Mitochondrial hyperacetylation in the failing hearts of obese patients mediated partly by a reduction in SIRT3: The involvement of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 53, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldogazieva, N.T.; Mokhosoev, I.M.; Mel’nikova, T.I.; Porozov, Y.B.; Terentiev, A.A. Oxidative stress and advanced lipoxidation and glycation end products (ALEs and AGEs) in aging and age-related diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 3085756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C. Y. , Lu, C. H., Wu, C. H., Li, K. J., Kuo, Y. M., Hsieh, S. C., & Yu, C. L. The Development of Maillard Reaction, and Advanced Glycation End Product (AGE)-Receptor for AGE (RAGE) Signaling Inhibitors as Novel Therapeutic Strategies for Patients with AGE-Related Diseases. Molecules 2020, 25, 5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selenscig, D.; Ferreira, M.D.R.; Chicco, A.; Lombardo, Y.B. Dietary fish oil ameliorates adipose tissue dysfunction in insulin-resistant rats fed a sucrose-rich diet improving oxidative stress, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ and uncoupling protein 2. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 2496–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sil, R.; Chakraborti, A.S. Oxidative inactivation of liver mitochondria in high fructose diet-induced metabolic syndrome in rats: Effect of glycyrrhizin treatment. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse-Patin, A.; Léveillé, M.; Oropeza, D.; Nguyen, B.N.; Prat, A.; Estall, J.L. Estrogen signals through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor−γ coactivator 1α to reduce oxidative damage associated with diet-induced fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.M.F.; Klein, D.; Álvarez-Cubela, S.; Domínguez-Bendala, J.; Pastori, R.L. The role of MicroRNAs in diabetes-related oxidative stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, C.; Lal, M.; Binukumar, B.K. Crosstalk between the unfolded protein response, MicroRNAs, and insulin signaling pathways: In search of biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of type 2 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotta, F.; Ventriglia, G.; Snowhite, I.V.; Pugliese, A. MicroRNAs: Markers of beta-cell stress and autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2018, 25, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPierre, M.P.; Stoffel, M. MicroRNAs as stress regulators in pancreatic beta cells and diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 1010–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Wei, Y.; Geißler, C.; Abschlag, K.; Campos, J.C.; Hristov, M.; Möllmann, J.; Lehrke, M.; Karshovska, E.; Schober, A. Hyperlipidemia-induced MicroRNA-155-5p improves β-cell function by targeting Mafb. Diabetes 2017, 66, 3072–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Zhao, Y.; He, M.; Li, H.; Fan, J.; Nie, X.; Yan, M.; Chen, C.; Wang, D.W. MiR-30c/PGC-1β protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy via PPARα. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, T.; Liang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, F.; Meng, W.; Hu, F. Mitochondrial stress protein HSP60 regulates ER stress-induced hepatic lipogenesis. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2020, 64, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juwono, J.; Martinus, R.D. Does Hsp60 provide a link between mitochondrial stress and inflammation in diabetes mellitus? J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 8017571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddeo, E.P.; Alsabeeh, N.; Baghdasarian, S.; Wikstrom, J.D.; Ritou, E.; Sereda, S.; Erion, K.; Li, J.; Stiles, L.; Abdulla, M.; et al. Mitochondrial proton leak regulated by cyclophilin D elevates insulin secretion in islets at nonstimulatory glucose levels. Diabetes 2020, 69, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.S. Effect of mitochondrial stress on systemic metabolism. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1350, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.; Li, J.; Fu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, M.; Wang, C. Hypertrophic adipocyte–derived exosomal miR-802-5p contributes to insulin resistance in cardiac myocytes through targeting HSP60. Obesity 2020, 28, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K. H.; Jeong, Y. T.; Oh, H.; Kim, S. H.; Cho, J. M.; Kim, Y. N.; Kim, S. S.; Kim, D. H.; Hur, K. Y.; Kim, H. K.; et al. Autophagy deficiency leads to protection from obesity and insulin resistance by inducing Fgf21 as a mitokine. Nature medicine 2013, 19, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsström, S.; Jackson, C.B.; Carroll, C.J.; Kuronen, M.; Pirinen, E.; Pradhan, S.; Marmyleva, A.; Auranen, M.; Kleine, I.-M.; Khan, N.A.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 drives dynamics of local and systemic stress responses in mitochondrial myopathy with mtDNA deletions. Cell Metabol. 2019, 30, 1040–1054.e1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtonen, J.M.; Auranen, M.; Darin, N.; Sofou, K.; Bindoff, L.; Hikmat, O.; Uusimaa, J.; Vieira, P.; Tulinius, M.; Lönnqvist, T.; et al. Diagnostic value of serum biomarkers FGF21 and GDF15 compared to muscle sample in mitochondrial disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2021, 44, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Joe, Y.; Ryter, S.W.; Surh, Y.J.; Chung, H.T. Similarities and distinctions in the effects of metformin and carbon monoxide in immunometabolism. Mol. Cells 2019, 42, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.S.; Goeminne, L.J.E.; Kim, J.T.; Tian, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Nga, H.T.; Kang, S.G.; Kang, B.E.; Byun, J.S.; Lee, Y.S.; et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 protects against the aging-mediated systemic inflammatory response in humans and mice. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.J.; Jung, S.B.; Lee, S.E.; Kang, S.G.; Lee, J.H.; Ryu, M.J.; Chung, H.K.; Chang, J.Y.; Kim, Y.K.; Hong, H.J.; et al. An adipocyte-specific defect in oxidative phosphorylation increases systemic energy expenditure and protects against diet-induced obesity in mouse models. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.S. Implications of mitochondrial unfolded protein response and mitokines: A perspective on fatty liver diseases. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 34, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariyanto, T.I.; Kurniawan, A. Appetite problem in cancer patients: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2021, 27, 100336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, B.J.; Hirano, M.; Quinzii, C.M.; Colantuoni, E.; Needham, D.M.; Lederer, D.J.; Baldwin, M.R. Growth differentiation factor-15 as a biomarker of strength and recovery in survivors of acute respiratory failure. Thorax 2019, 74, 1099–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Gonzalez, C.; Badosa, C.; Madruga-Garrido, M.; Martí, I.; Paradas, C.; Ortez, C.; Diaz-Manera, J.; Berardo, A.; Alonso-Pérez, J.; Trifunov, S.; et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 is a potential biomarker of therapeutic response for TK2 deficient myopathy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, N.S.; Madsen, K.L.; Hornsyld, T.M.; Eisum, A.-S.V.; Fornander, F.; Buch, A.E.; Stemmerik, M.G.; Ruiz-Ruiz, C.; Krag, T.O.; Vissing, J. Growth and differentiation factor 15 as a biomarker for mitochondrial myopathy. Mitochondrion 2020, 50, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, R.; Yubero, D.; Villarroya, J.; Henares, D.; Jou, C.; Rodríguez, M.A.; Ramos, F.; Nascimento, A.; Ortez, C.I.; Campistol, J.; et al. GDF-15 is elevated in children with mitochondrial diseases and is induced by mitochondrial dysfunction. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0148709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, I. R.; Weraarpachai, W.; Shoubridge, E. A. Multi-OMICS study of a CHCHD10 variant causing ALS demonstrates metabolic rewiring and activation of endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial unfolded protein responses. Hum Mol Genet 2021, 30, 687–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffen, J.; Ngo, J.; Wang, S. P.; Williams, K.; Kramer, H. F.; Ho, G.; Rodriguez, C.; Yekkala, K.; Amuzie, C.; Bialecki, R.; et al. The mitochondrial fission protein Drp1 in liver is required to mitigate NASH and prevents the activation of the mitochondrial ISR. Mol Metab 2022, 64, 101566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.K.; Ryu, D.; Kim, K.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Kim, Y.K.; Yi, H.-S.; Kang, S.G.; Choi, M.J.; Lee, S.E.; Jung, S.-B.; et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 is a myomitokine governing systemic energy homeostasis. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, Y. Hepatic GDF15 is regulated by CHOP of the unfolded protein response and alleviates NAFLD progression in obese mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 498, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akazawa, S.; Sun, F.; Ito, M.; Kawasaki, E.; Eguchi, K. Efficacy of troglitazone on body fat distribution in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 1067–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ensuring drug safety: Lessons from the thiazolidinediones. Lancet 2007, 370, 1101. [CrossRef]
- Hou, CY.; Tain, YL.; Yu, HR.; Huang, LT. The Effects of Resveratrol in the Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, N.; Cristina Orihuela-Campos, R.; Inagaki, Y.; Fukui, M.; Nagata, T.; Ito, H.-O. Resveratrol improves oxidative stress and prevents the progression of periodontitis via the activation of the Sirt1/AMPK and the Nrf2/antioxidant defense pathways in a rat periodontitis model. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 75, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto, C.; Auwerx, J. Targeting sirtuin 1 to improve metabolism: All you need is NAD(+)? Pharm. Rev. 2012, 64, 166–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, T.M.; Kabisch, S.; Randeva, H.S.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H.; Weickert, M.O. Implications of Resveratrol in Obesity and Insulin Resistance: A State-of-the-Art Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wu, C.H.; Qiu, S.H.; Yuan, X.L.; Li, L. Effects of resveratrol on glucose control and insulin sensitivity in subjects with type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, Z.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Mirmiran, P. Anti-hyperglycemic and insulin sensitizer effects of turmeric and its principle constituent curcumin. Int J Endocrinol Metab 2014, 12, e18081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, L. X.; Zhang, Y. L.; Li, Y.; Liu, L. Y.; Li, R.; Kong, T.; Sun, C. H. Curcumin improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of rats. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2011, 21, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirola, L.; Balcerczyk, A.; Okabe, J.; El-Osta, A. Epigenetic phenomena linked to diabetic complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, L.; Li, D. Curcumin improves insulin sensitivity in high-fat diet-fed mice through gut microbiota. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2022, 19, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Keogh, JB.; Clifton, PM. Polyphenols and Glycemic Control. Nutrients 2016, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirone, A.C.; Huang, C.; Klip, A. Tissue-specific roles of IRS proteins in insulin signaling and glucose transport. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2006, 17, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthy, G. ; Roshana, Devi. V.; Ilango, K.; Subramanian, S.P. Rosmarinic Acid Mediates Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Insulin Resistant Skeletal Muscle Through Activation of AMPK. J Cell Biochem 2017, 118, 1839–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Hartogh, D.J.; Vlavcheski, F.; Tsiani, E. Muscle Cell Insulin Resistance Is Attenuated by Rosmarinic Acid: Elucidating the Mechanisms Involved. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, J.; Inose-Maruyama, A.; Taniuchi, S.; Kosaka, K.; Yoshida, H.; Yamazaki, H.; Kasai, S.; Harada, N.; Kaufman, R. J.; Oyadomari, S.; et al. Concomitant Nrf2- and ATF4-activation by Carnosic Acid Cooperatively Induces Expression of Cytoprotective Genes. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, L.F.; Inada, A.C.; Espirito Santo, B.L.S.D.; Filiú, W.F.O.; Pott, A.; Alves, F.M.; Guimarães, R.C.A.; Freitas, K.C.; Hiane, P.A. Nutraceutical Potential of Carica papaya in Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, R.H.; Kamel, E.M.; Mahmoud, A.M.; El-Bassuony, A.A.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Lamsabhi, A.M.; Ahmed, S.A. Rumex dentatus L. phenolics ameliorate hyperglycemia by modulating hepatic key enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism, oxidative stress and PPARγ in diabetic rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 138, 111202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Kim, J.H.; Ghim, J.; Yoon, J.H.; Lee, A.; Kwon, Y.; Hyun, H.; Moon, H.Y.; Choi, H.S.; Berggren, P.O.; et al. Emodin regulates glucose utilization by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 5732–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Yu, N.; Peng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, F. Emodin inhibits lipid accumulation and inflammation in adipose tissue of high-fat diet-fed mice by inducing M2 polarization of adipose tissue macrophages. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Dang, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, A.; Zhou, X.; Gao, X.; Li, Z. Aloe vera-fermented beverage ameliorates obesity and gut dysbiosis in high-fat-diet mice. Foods 2022, 11, 3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, T.; Mu, F.; Guo, Q.; Guo, C.; Jia, N.; Liu, W.; et al. Aloe-emodin ameliorates renal fibrosis via inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Rejuvenation Res. 2019, 22, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, Y.; Gong, L.; He, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, M.; Cao, Z.; Li, Y.; Peng, C. Aloe emodin induces hepatotoxicity by activating NF-κB inflammatory pathway and P53 apoptosis pathway in zebrafish. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 306, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Régnier, M.; Rastelli, M.; Morissette, A.; Suriano, F.; Le Roy, T.; Pilon, G.; Delzenne, N.M.; Marette, A.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. Rhubarb supplementation prevents diet-induced obesity and diabetes in association with increased Akkermansia muciniphila in mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gao, C.; Vong, C.T.; Tao, H.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Rhein regulates redox-mediated activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes in intestinal inflammation through macrophage-activated crosstalk. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 1978–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genua, M.; Rutella, S.; Correale, C.; Danese, S. The triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells (TREM) in inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Tong, A.H.; Pan, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.D.; Ding, W.Y.; Xiong, W. The effect of cassia seed extract on the regulation of the LKB1-AMPK-GLUT4 signaling pathway in the skeletal muscle of diabetic rats to improve the insulin sensitivity of the skeletal muscle. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 11, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Ding, M.; Gu, Y.; Fan, G.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Sun, R.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Xue, X.; et al. Aurantio-obtusin attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through AMPK-mediated autophagy and fatty acid oxidation pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 826628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.Y.; Liao, W.T.; Qiu, R.J.; Zhou, D.S.; Ni, W.J.; Yu, C.P.; Zeng, Y. Aurantio-obtusin improves obesity and insulin resistance induced by high-fat diet in obese mice. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.A.; Ali, M.Y.; Choi, J.S. Promising inhibitory effects of anthraquinones, naphthopyrone, and naphthalene glycosides, from Cassia obtusifolia on α-glucosidase and human protein tyrosine phosphatases 1B. Molecules 2016, 22, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.K.; Prasad, S.K.; Kumar, R.; Hemalatha, S. An overview on antidiabetic medicinal plants having insulin mimetic property. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, B.; Zhang, C.; Sheng, Y.; Zhao, C.; He, X.; Xu, W.; Huang, K.; Luo, Y. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effect of S-allyl-cysteine sulfoxide (alliin) in DIO mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saber Batiha, G.; Beshbishy, A.M.; Wasef, L.G.; Elewa, Y.H.A.; Al-Sagan, A.A.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Taha, A.E.; Abd-Elhakim, Y.M.; Devkota, H.P. Chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of garlic (Allium sativum L.): A review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faroughi, F.; Charandabi, S.; Javadzadeh, Y.; Mirghafourvand, M. Effects of garlic pill on blood glucose level in borderline gestational diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. Iran. Red Crescent Med. J. 2018, 20, e60675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factor | Mechanism |
|---|---|
| AGEs | Promotes mitochondrial stress by activating NADPH |
| CypD | Promotes mitochondrial stress when the MPTP is open and NEFAs are present |
| PPARs | Inhibit mitochondrial stress by inhibiting IL-6 |
| miR-126 | Inhibits mitochondrial stress by activating SIRT1 and SOD |
| miR-30c | Inhibits mitochondrial stress by activating PGC-1 and PPAR-α |
| HSP60 | Mitochondrial stress causes overexpression of HSP60; HSP60 promotes mTORC1-SREBP1 signal transduction and promotes insulin resistance together with endoplasmic reticulum stress |
| FGF21 | Metformin induces mitochondrial stress through the Perk-eIF2α-ATF4 axis; mitochondrial stress promotes FGF21 expression by activating the comprehensive stress response (ISR); FGF21 improves insulin resistance |
| GDF-15 | GDF-15 improves insulin resistance; CYPD may cause insulin resistance by inhibiting GDF-15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




