Submitted:
18 May 2023
Posted:
19 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
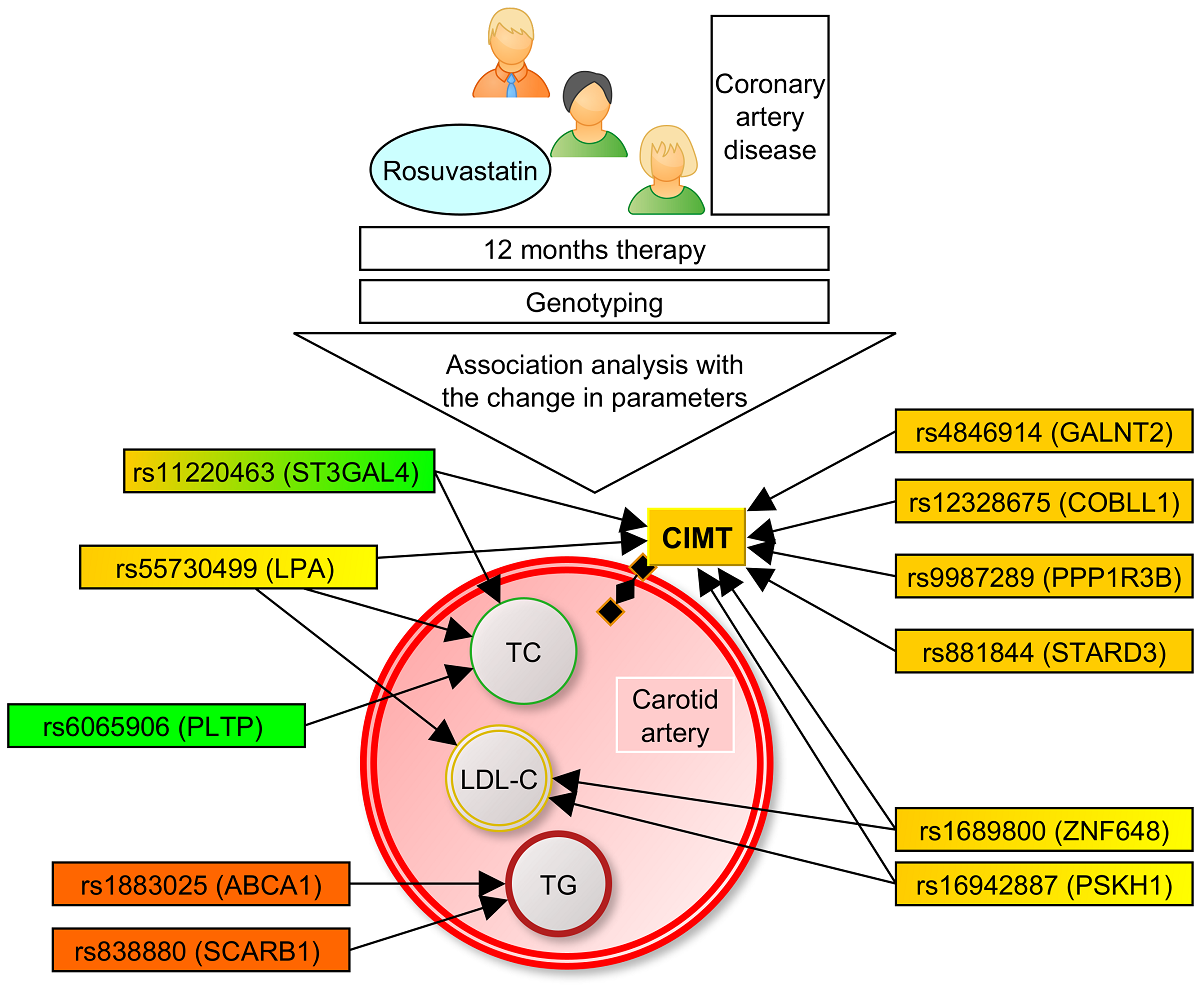
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Associations of the SNPs with lipid and CIMT reduction during the 6-month therapy by rosuvastatin.
3.2. Associations of SNPs with lipid and CIMT reduction during 12-month therapy by rosuvastatin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, RM; Schnitzler, G; Fang, S; Lee-Kim, VS; Barry, A. Multiomic Analysis and CRISPR Perturbation Screens Identify Endothelial Cell Programs and Novel Therapeutic Targets for Coronary Artery Disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, H. Invited commentary: 30-year perspective on the seven countries study. Am J Epidemiol. 2017, 185, 1143–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, R; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A. Genetics of Coronary Artery Disease. Circ Res. 2016, 118, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churilin, M.I.; Kononov, S.I.; Mal, G.S.; Polonikov, A.V.; Lazarenko, V.A. Lipid metabolism genes and predisposition to ischemic heart disease. Medical News of North Caucasus, 2019, 14, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, AS; Duffy, J; Wang, MC. Lipid metabolism and lipid signals in aging and longevity. Dev Cell. 2021, 56, 1394–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, R.; Jurgens, S.J.; Erdmann, J. , Bezzina, C.R. Genome-wide association studies of cardiovascular disease. Physiol Rev. [CrossRef]
- Willer, C.J.; Schmidt, E.M.; Sengupta, S.; Peloso, G.M.; Gustafsson, S.; Kanoni, S.; Ganna, A.; Chen, J.; Buchkovich, M.L.; Mora, S.; et al. Discovery and refinement of loci associated with lipid levels. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Nikpay, M.; Goel, A.; Won, H.H.; Hall, L.M.; Willenborg, C.; Kanoni, S.; Saleheen, D.; Kyriakou, T.; Nelson, C.P.; Hopewell, J.C.; et al. A comprehensive 1000 Genomes–based genome-wide association meta-analysis of coronary artery disease. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Teslovich, T.M.; Musunuru, K.; Smith, A.V.; Edmondson, A.C.; Stylianou, I.M.; Koseki, M.; Pirruccello, J.P.; Ripatti, S.; Chasman, D.I.; Willer, C.J.; et al. Biological, clinical and population relevance of 95 loci for blood lipids. Nature. 2010, 466, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathiresan, S.; Melander, O.; Guiducci, C.; Surti, A.; Burtt, N.P.; Rieder, M.J.; Cooper, G.M.; Roos, C.; Voight, B.F.; Havulinna, A.S.; et al. Six new loci associated with blood low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol or triglycerides in humans. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, S.; Coassin, S.; Rueedi, R.; Yousri, N.A.; Seppälä, I.; Gieger, C.; Schönherr, S.; Forer, L.; Erhart, G.; Marques-Vidal, P.; et al. A genome-wide association meta-analysis on lipoprotein (a) concentrations adjusted for apolipoprotein (a) isoforms. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gan, W.; Tian, C.; Li, H.; Lin, X.; Chen, Y. Association of PPP1R3B polymorphisms with blood lipid and C-reactive protein levels in a Chinese population. J. Diabetes. 2013, 5, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postmus, I; Trompet, S; Deshmukh, H. A.; Arsenault B.J.; Avery C.L.; Bis J.C.; Chasman D.I.; de Keyser C.E.; Deshmukh H.A.; Evans D.S.; et al. Pharmacogenetic meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of LDL cholesterol response to statins. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chasman, D.I.; Giulianini, F.; MacFadyen, J. , Barratt B.J., Nyberg F., Ridker P.M. Genetic determinants of statin-induced low-density lipoprotein cholesterol reduction: the Justification for the Use of Statins in Prevention: an Intervention Trial Evaluating Rosuvastatin (JUPITER) trial. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2012, 5, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chasman, D.I. , Giulianini, F., Demler, O.V., Udler, M.S. Pleiotropy-Based Decomposition of Genetic Risk Scores: Association and Interaction Analysis for Type 2 Diabetes and CAD. Am J Hum Genet. 2020, 106, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouse, J.R. 3rd, Raichlen, J.S., Riley, W.A.; Evans G.W.; Palmer M.K.;, O'Leary D.H.; Grobbee D.E.; Bots M.L.; METEOR Study Group. Effect of rosuvastatin on progression of carotid intima-media thickness in low-risk individuals with subclinical atherosclerosis: the METEOR Trial. JAMA. 2007, 297, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nezu, T; Hosomi, N; Aoki, S; Matsumoto M. Carotid Intima-Media Thickness for Atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2016, 23, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S; Casas, J. P., Drenos, F.; Whittaker, J.; Deanfield, J.; Swerdlow, D.I.; Holmes, M.V.; Kivimaki, M.; Langenberg, C.; Wareham, N.; et al. Causal relevance of blood lipid fractions in the development of carotid atherosclerosis: mendelian randomization analysis. Circ. Cardiovasc Genet. 2013, 6, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, JD; Manichaikul, A; Wang, X. Q.; Rich, S.S.; Rotter, J.I.; Post, W.S.; Polak, J.F.; Budoff, M.J., Bluemke, D.A. Detailed analysis of association between common single nucleotide polymorphisms and subclinical atherosclerosis: The Multi-ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Data Brief. 2016, 7, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaricci, A.I.; Arcadi, T.; Brunetti, ND; Maffei, E. ; Montrone, D.; Martini, C.; De Luca, M.; De Rosa, F.; Cocco, D.; Midiri, M.; et al. Carotid intima media thickness and coronary atherosclerosis linkage in symptomatic intermediate risk patients evaluated by coronary computed tomography angiography. Int J Cardiol. 2014, 176, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.; Montorsi, P.; Ravani, P. , et al. Carotid intima-media thickness by B-mode ultrasound as surrogate of coronary atherosclerosis: correlation with quantitative coronary angiography and coronary intravascular ultrasound findings. Eur Heart J. 2007, 28, 2094–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graner M, Varpula M, Kahri J et al. Association of carotid intima-media thickness with angiographic severity and extent of coronary artery disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 97, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushima Y, Kawano H, Koide Y, Baba T, Toda G, Seto S, Yano K. Relationship of carotid intima-media thickness, pulse wave velocity, and ankle brachial index to the severity of coronary artery atherosclerosis. Clin Cardiol. 2004, 27, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne CM, Raichlen JS, Nicholls SJ et al. Effect of rosuvastatin therapy on coronary artery stenoses assessed by quantitative coronary angiography: a study to evaluate the effect of rosuvastatin on intravascular ultrasound-derived coronary atheroma burden. Circulation 2008, 117, 2458–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri R, Libby P, Nissen SE et al. Long-term effects of maximally intensive statin therapy on changes in coronary atheroma composition: insights from SATURN. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging. 2014, 15, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumyantsev NA, Kukes VG, Kazakov RE, Rumyantsev AA, Sychev DA. Ispol'zovanie farmakogeneticheskogo testirovaniia dlia predotvrashcheniia nezhelatel'nykh lekarstvennykh reaktsiĭ pri terapii statinami [Use of pharmacogenetic testing to prevent adverse drug reactions during statin therapy]. Ter Arkh. 2017, 89, 82–87. Russian. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soko ND, Masimirembwa C, Dandara C. Pharmacogenomics of Rosuvastatin: A Glocal (Global + Local) African Perspective and Expert Review on a Statin Drug. OMICS 2016, 20, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonsi JE, Hegele RA, Gryn SE. Pharmacogenetics of lipid-lowering agents: precision or indecision medicine? Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2016, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churilin, M.I. , Kononov, S.I., Luneva, Y.V.,...Solodilova, M.A., Polonikov, A.V. Polymorphisms of Intracellular Cholesterol Transporters Genes: Relationship to Blood Lipid Levels, Carotid Intima-Media Thickness, and the Development of Coronary Heart Disease. Russian Journal of Genetics 2020, 56, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churilin, M.I. , Kononov, S.I., Luneva, Y.V.,...Polonikov, A.V., Kazanov, V.A. Apolipoprotein E gene polymorphisms: A relationship with the risk of coronary artery disease and the effectiveness of lipid-lowering therapy with rosuvastatin. Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention (Russian Federation), 2020b, 19, pp. 17–23.
- Kononov S, Mal G, Azarova I, Klyosova E, Bykanova M, Churnosov M, Polonikov A. Pharmacogenetic loci for rosuvastatin are associated with intima-media thickness change and coronary artery disease risk. Pharmacogenomics. 2022 Jan;23, 15-34. [CrossRef]
- Lazarenko V, Churilin M, Azarova I, Klyosova E, Bykanova M, Ob'edkova N, Churnosov M, Bushueva O, Mal G, Povetkin S, Kononov S, Luneva Y, Zhabin S, Polonikova A, Gavrilenko A, Saraev I, Solodilova M, Polonikov A. Comprehensive Statistical and Bioinformatics Analysis in the Deciphering of Putative Mechanisms by Which Lipid-Associated GWAS Loci Contribute to Coronary Artery Disease. Biomedicines. 2022 Jan 25;10, 259. [CrossRef]
- Pignoli P, Tremoli E, Poli A, Oreste P, Paoletti R. Intimal plus medial thickness of the arterial wall: a direct measurement with ultrasound imaging. Circulation 74, 1399–1406 (1986).
- Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, de Bakker PI, Daly MJ, Sham PC. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet. 2007 Sep;81, 559–575. [CrossRef]
- Gaudet P, Livstone MS, Lewis SE, Thomas PD. Phylogenetic-based propagation of functional annotations within the Gene Ontology consortium. Brief Bioinform. 2011 Sep;12, 449–462. [CrossRef]
- Shahid SU, Shabana, Humphries S. The SNP rs10911021 is associated with oxidative stress in coronary heart disease patients from Pakistan. Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Jan 5;17, 6. [CrossRef]
- Khetarpal SA, Schjoldager KT, Christoffersen C, Raghavan A, Edmondson AC, Reutter HM, Ahmed B, Ouazzani R, et al. Loss of Function of GALNT2 Lowers High-Density Lipoproteins in Humans, Nonhuman Primates, and Rodents. Cell Metab. 2016 Aug 9;24, 234–245. [CrossRef]
- Zilmer M, Edmondson AC, Khetarpal SA, Alesi V, Zaki MS, Rostasy K, Madsen CG, et al. Novel congenital disorder of O-linked glycosylation caused by GALNT2 loss of function. Brain. 2020 Apr 1;143, 1114-1126. [CrossRef]
- Chen J, Guan L, Liu H, Liu Q, Fan P, Bai H. GALNT2 Gene Variant rs4846914 Is Associated with Insulin and Insulin Resistance Depending on BMI in PCOS Patients: a Case-Control Study. Reprod Sci. 2021 Apr;28, 1122-1132. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, Zhao H, Zhang J, Han D, Zheng Y, Guo X, He D, Guo J, Wang Y. Gene environment interaction of GALNT2 and APOE gene with hypertension in the Chinese Han Population. Biomed Mater Eng. 2015;26 Suppl 1:S1977-83. [CrossRef]
- Guo Z, Neilson LJ, Zhong H, Murray PS, Zanivan S, Zaidel-Bar R. E-cadherin interactome complexity and robustness resolved by quantitative proteomics. Sci Signal. 2014 Dec 2;7, rs7. [CrossRef]
- Churilin, MI. Association of RS12328675 COBLL1 polymorphism with coronary heart disease and intermediate phenotypes of atherosclerosis: validation study in Central Russia. Research Results in Biomedicine. 2020;6, 209-218. Russian. [CrossRef]
- Sakaue S, Kanai M, Tanigawa Y, Karjalainen J, Kurki M, Koshiba S, Narita A, Konuma T, Yamamoto K, Akiyama M, Ishigaki K, Suzuki A, Suzuki K, Obara W, Yamaji K, Takahashi K, Asai S, et al. A cross-population atlas of genetic associations for 220 human phenotypes. Nat Genet. 2021 Oct;53, 1415-1424. [CrossRef]
- Mishra A, Malik R, Hachiya T, Jürgenson T, Namba S, Posner DC, Kamanu FK, Koido M, Le Grand Q, Shi M, He Y, Georgakis MK, Caro I, Krebs K, Liaw YC, Vaura FC, Lin K, et al. Stroke genetics informs drug discovery and risk prediction across ancestries. Nature. 2022 Nov;611, 115-123. Erratum in: Nature 2022, 612, E7. [CrossRef]
- Wojcik GL, Graff M, Nishimura KK, Tao R, Haessler J, Gignoux CR, Highland HM, Patel YM, Sorokin EP, Avery CL, Belbin GM, Bien SA, Cheng I, et al. Genetic analyses of diverse populations improves discovery for complex traits. Nature. 2019 Jun;570, 514-518. [CrossRef]
- Sethwala AM, Goh I, Amerena JV. Combating Inflammation in Cardiovascular Disease. Heart Lung Circ. 2021 Feb;30, 197-206. [CrossRef]
- Lind, L. Genome-Wide Association Study of the Metabolic Syndrome in UK Biobank. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2019 Dec;17, 505-511. [CrossRef]
- Chen J, Spracklen CN, Marenne G, Varshney A, Corbin LJ, Luan J, Willems SM, Wu Y, Zhang X, Horikoshi M, Boutin TS, Mägi R, Waage J, Li-Gao R, Chan KHK, Yao J, Anasanti MD, Chu AY, et al. The trans-ancestral genomic architecture of glycemic traits. Nat Genet. 2021 Jun;53, 840-860. [CrossRef]
- Meza CA, La Favor JD, Kim DH, Hickner RC. Endothelial Dysfunction: Is There a Hyperglycemia-Induced Imbalance of NOX and NOS? Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 2;20, 3775. [CrossRef]
- Clyne, AM. Endothelial response to glucose: dysfunction, metabolism, and transport. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Feb 26;49, 313-325. [CrossRef]
- Krimbou L, Denis M, Haidar B, Carrier M, Marcil M, Genest J Jr. Molecular interactions between apoE and ABCA1: impact on apoE lipidation. J Lipid Res. 2004 May;45, 839–848. [CrossRef]
- Huang QQ, Sallah N, Dunca D, Trivedi B, Hunt KA, Hodgson S, Lambert SA, Arciero E, Wright J, Griffiths C, Trembath RC, Hemingway H, et al. Transferability of genetic loci and polygenic scores for cardiometabolic traits in British Pakistani and Bangladeshi individuals. Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 9;13, 4664. [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann TJ, Theusch E, Haldar T, Ranatunga DK, Jorgenson E, Medina MW, Kvale MN, Kwok PY, Schaefer C, Krauss RM, Iribarren C, Risch N. A large electronic-health-record-based genome-wide study of serum lipids. Nat Genet. 2018 Mar;50, 401-413. [CrossRef]
- Wu Y, Byrne EM, Zheng Z, Kemper KE, Yengo L, Mallett AJ, Yang J, Visscher PM, Wray NR. Genome-wide association study of medication-use and associated disease in the UK Biobank. Nat Commun. 2019 Apr 23;10, 1891. [CrossRef]
- Mondal N, Buffone A Jr, Stolfa G, Antonopoulos A, Lau JT, Haslam SM, Dell A, Neelamegham S. ST3Gal-4 is the primary sialyltransferase regulating the synthesis of E-, P-, and L-selectin ligands on human myeloid leukocytes. Blood. 2015 Jan 22;125, 687–696. [CrossRef]
- Ligthart S, Vaez A, Hsu YH; Inflammation Working Group of the CHARGE Consortium; PMI-WG-XCP; LifeLines Cohort Study; Stolk R, Uitterlinden AG, Hofman A, Alizadeh BZ, Franco OH, Dehghan A. Bivariate genome-wide association study identifies novel pleiotropic loci for lipids and inflammation. BMC Genomics. 2016 Jun 10;17:443. [CrossRef]
- Ozbeyaz NB, Gokalp G, Algul E, Kilic P, Saricam O, Aydinyilmaz F, Guliyev I. Could Systemic Inflammation in Healthy Individuals With Obesity Indicate Subclinical Atherosclerosis? Angiology. 2022 Apr 28:33197221089375. [CrossRef]
- Kivimäki M, Lawlor DA, Smith GD, Kumari M, Donald A, Britton A, Casas JP, Shah T, Brunner E, Timpson NJ, Halcox JP, Miller MA, Humphries SE, Deanfield J, Marmot MG, Hingorani AD. Does high C-reactive protein concentration increase atherosclerosis? The Whitehall II Study. PLoS One. 2008 Aug 20;3, e3013. [CrossRef]
- Moran CA, Sheth AN, Mehta CC, Hanna DB, Gustafson DR, Plankey MW, Mack WJ, Tien PC, French AL, Golub ET, Quyyumi A, Kaplan RC, Ofotokun I. The association of C-reactive protein with subclinical cardiovascular disease in HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected women. AIDS. 2018 ;32, 999-1006. 15 May. [CrossRef]
- Brede G, Solheim J, Prydz H. PSKH1, a novel splice factor compartment-associated serine kinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Dec 1;30, 5301–5309. [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm LP, Wendling C, Védie B, Kobayashi T, Chenard MP, Tomasetto C, Drin G, Alpy F. STARD3 mediates endoplasmic reticulum-to-endosome cholesterol transport at membrane contact sites. EMBO J. 2017 ;36, 1412-1433. 15 May. [CrossRef]
- Li L, Liu Y, Liu X, Zheng N, Gu Y, Song Y, Wang X. Regulatory roles of external cholesterol in human airway epithelial mitochondrial function through STARD3 signalling. Clin Transl Med. 2022 Jun;12, e902. [CrossRef]
- Zhang M, Zhai X, Li J, Albers JJ, Vuletic S, Ren G. Structural basis of the lipid transfer mechanism of phospholipid transfer protein (PLTP). Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2018 Sep;1863, 1082-1094. [CrossRef]
- Albers JJ, Vuletic S, Cheung MC. Role of plasma phospholipid transfer protein in lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Mar;1821, 345–357. [CrossRef]


| Chr | Gene (SNP ID) | Effect allele | EAF | N | Total cholesterol | LDL-C | CIMT, maximum | CIMT, mean | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta* | Pperm# | Beta* | Pperm# | Beta* | Pperm# | Beta* | Pperm# | |||||
| 1 | ZNF648 (rs1689800) | G | 0.392 | 115 | 0.020 | 0.1786 | 0.046 | 0.0493A | -0.084 | 0.0234R | -0.021 | 0.2308 |
| 1 | GALNT2 (rs4846914) | G | 0.388 | 115 | 0.004 | 0.7778 | -0.005 | 0.8571 | -0.045 | 0.0133A | -0.038 | 0.0344A |
| 2 | COBLL1 (rs12328675) | C | 0.170 | 111 | -0.003 | 0.8571 | -0.003 | 1.0000 | 0.035 | 0.2647 | 0.041 | 0.1000 |
| 6 | LPA (rs55730499) | T | 0.056 | 115 | 0.323 | 0.0022R | 0.504 | 0.0224R | -0.010 | 0.8571 | 0.028 | 0.8571 |
| 7 | NPC1L1 (rs217406) | G | 0.203 | 115 | 0.017 | 0.2308 | 0.033 | 0.3556 | -0.001 | 1.0000 | -0.003 | 1.0000 |
| 8 | PPP1R3B (rs9987289) | A | 0.086 | 115 | 0.019 | 0.3404 | -0.013 | 0.8571 | 0.041 | 0.3404 | 0.051 | 0.1550 |
| 9 | ABCA1 (rs1883025) | T | 0.263 | 115 | 0.001 | 1.0000 | -0.004 | 0.8571 | -0.024 | 0.2982 | -0.025 | 0.2535 |
| 11 | F2 (rs3136441) | C | 0.180 | 102 | 0.011 | 0.6429 | 0.025 | 0.7778 | 0.021 | 0.6923 | 0.023 | 0.2982 |
| 11 | ST3GAL4 (rs11220463) | T | 0.190 | 115 | -0.031 | 0.1280 | -0.068 | 0.0803 | 0.066 | 0.0159D | 0.061 | 0.0243A |
| 12 | SCARB1 (rs838880) | C | 0.336 | 115 | 0.002 | 1.0000 | 0.005 | 1.0000 | -0.014 | 0.7273 | -0.015 | 0.6923 |
| 16 | CETP (rs3764261) | A | 0.147 | 115 | 0.007 | 0.6250 | 0.027 | 0.8571 | -0.045 | 0.2466 | -0.042 | 0.1900 |
| 16 | PSKH1 (rs16942887) | A | 0.116 | 115 | 0.009 | 0.6429 | 0.025 | 0.4643 | 0.066 | 0.0421D | 0.068 | 0.0483D |
| 17 | STARD3 (rs881844) | C | 0.310 | 115 | 0.003 | 0.8571 | -0.038 | 0.1667 | 0.048 | 0.0086A | 0.057 | 0.0033A |
| 19 | LILRA3 (rs386000) | C | 0.203 | 115 | 0.006 | 0.5455 | -0.001 | 1.0000 | 0.015 | 0.7778 | 0.003 | 0.8571 |
| 20 | PLTP (rs6065906) | C | 0.160 | 115 | 0.140 | 0.0135R | -0.008 | 1.0000 | -0.022 | 0.6923 | -0.022 | 0.5455 |
| Chr, chromosome; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; EAF, effect allele frequency; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; CIMT, carotid intima-media thickness. *Beta for difference between the natural log-transformed on- and off-treatment values adjusted for natural log-transformed off-treatment level. The beta reflects the fraction of differential lipid- or CIMT-lowering effect in carriers versus non-carriers of the minor allele (for additive model), in carriers of the genotype according to the model (dominant, recessive) versus the carriers of alternative genotypes; a negative beta indicates a better statin response (stronger lipid or CIMT reduction), a positive beta – a worse statin response. Betas were generated using linear regression analysis with age, sex, body mass index, and rosuvastatin dose as covariates. #p-values were generated using the permutation procedure. Superscript indicates genetic model: R, recessive; A, additive; D, dominant. | ||||||||||||
| Chr | Gene (SNP ID) | Effect allele | EAF | N | 6-month period | 12-month period | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta* | Pperm# | Beta* | Pperm# | |||||
| 1 | ZNF648 (rs1689800) | G | 0.392 | 114 | -0.6495 | 0.1148 | -0.1946 | 0.4643 |
| 1 | GALNT2 (rs4846914) | G | 0.388 | 114 | 0.4816 | 0.1919 | 0.05046 | 0.7778 |
| 2 | COBLL1 (rs12328675) | C | 0.170 | 110 | -0.2948 | 0.6250 | -0.1431 | 0.7778 |
| 6 | LPA (rs55730499) | T | 0.056 | 114 | -0.5923 | 0.4242 | 0.1825 | 0.6923 |
| 7 | NPC1L1 (rs217406) | G | 0.203 | 114 | 0.4106 | 0.4118 | -0.1208 | 0.6429 |
| 8 | PPP1R3B (rs9987289) | A | 0.086 | 114 | -0.9197 | 0.1887 | -0.7977 | 0.0756 |
| 9 | ABCA1 (rs1883025) | T | 0.263 | 114 | -0.177 | 0.5789 | -0.7246 | 0.0160D |
| 11 | F2 (rs3136441) | C | 0.180 | 101 | -0.185 | 0.5789 | 0.02512 | 1.0000 |
| 11 | ST3GAL4 (rs11220463) | T | 0.190 | 114 | -0.774 | 0.1587 | 3.624 | 0.0503R |
| 12 | SCARB1 (rs838880) | C | 0.336 | 114 | 1.736 | 0.0478R | 0.1063 | 0.6429 |
| 16 | CETP (rs3764261) | A | 0.147 | 114 | 0.695 | 0.2931 | 0.02338 | 1.0000 |
| 16 | PSKH1 (rs16942887) | A | 0.116 | 114 | -0.6306 | 0.1439 | -0.2626 | 0.3947 |
| 17 | STARD3 (rs881844) | C | 0.310 | 114 | 0.4075 | 0.4815 | -0.2337 | 0.2647 |
| 19 | LILRA3 (rs386000) | C | 0.203 | 114 | -0.1847 | 0.8571 | -0.1448 | 0.6923 |
| 20 | PLTP (rs6065906) | C | 0.160 | 114 | -0.4654 | 0.5789 | -0.0718 | 0.8571 |
| Chr, chromosome; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; EAF, effect allele frequency. *Beta for difference between the natural log-transformed on- and off-treatment values adjusted for natural log-transformed off-treatment level. Betas were generated using linear regression analysis with age, sex, body mass index, and rosuvastatin dose as covariates. #p-values were generated using the permutation procedure. Superscript indicates genetic model: R, recessive; A, additive; D, dominant. | ||||||||
| Chr | Gene (SNP ID) | Effect allele | EAF | N | Total cholesterol | LDL-C | CIMT, maximum | CIMT, mean | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta* | Pperm# | Beta* | Pperm# | Beta* | Pperm# | Beta* | Pperm# | |||||
| 1 | ZNF648 (rs1689800) | G | 0.392 | 113 | 0.010 | 0.3091 | 0.024 | 0.2043 | -0.093 | 0.0105R | -0.036 | 0.0282A |
| 1 | GALNT2 (rs4846914) | G | 0.388 | 113 | -0.004 | 0.7273 | -0.016 | 0.4118 | 0.002 | 0.8571 | -0.002 | 0.8571 |
| 2 | COBLL1 (rs12328675) | C | 0.170 | 109 | -0.011 | 0.4643 | -0.018 | 0.4643 | 0.059 | 0.0213A | 0.075 | 0.0056D |
| 6 | LPA (rs55730499) | T | 0.056 | 113 | 0.364 | 0.0001R | 0.367 | 0.0415R | 0.018 | 0.8571 | 0.414 | 0.0146R |
| 7 | NPC1L1 (rs217406) | G | 0.203 | 113 | -0.002 | 1.0000 | 0.003 | 0.2043 | 0.019 | 0.3636 | 0.018 | 0.4516 |
| 8 | PPP1R3B (rs9987289) | A | 0.086 | 113 | 0.004 | 0.8571 | -0.068 | 0.4118 | 0.072 | 0.0359D | 0.079 | 0.0109D |
| 9 | ABCA1 (rs1883025) | T | 0.263 | 113 | 0.010 | 0.3148 | 0.001 | 0.4643 | 0.011 | 0.8571 | 0.019 | 0.2687 |
| 11 | F2 (rs3136441) | C | 0.180 | 100 | 0.013 | 0.3478 | 0.018 | 0.2043 | -0.011 | 0.6429 | -0.005 | 1.0000 |
| 11 | ST3GAL4 (rs11220463) | T | 0.190 | 113 | -0.181 | 0.0273R | -0.027 | 0.4118 | 0.001 | 1.0000 | 0.032 | 0.1709 |
| 12 | SCARB1 (rs838880) | C | 0.336 | 113 | -0.001 | 1.0000 | -0.005 | 0.4643 | -0.003 | 1.0000 | -0.004 | 1.0000 |
| 16 | CETP (rs3764261) | A | 0.147 | 113 | 0.017 | 0.3478 | 0.021 | 0.2043 | -0.053 | 0.0833 | -0.043 | 0.0880 |
| 16 | PSKH1 (rs16942887) | A | 0.116 | 113 | 0.006 | 0.5789 | 0.086 | 0.0175D | -0.011 | 0.5217 | -0.004 | 0.7778 |
| 17 | STARD3 (rs881844) | C | 0.310 | 113 | 0.009 | 0.4375 | 0.010 | 0.8571 | 0.028 | 0.1852 | 0.040 | 0.0223A |
| 19 | LILRA3 (rs386000) | C | 0.203 | 113 | 0.019 | 0.2400 | 0.015 | 0.5200 | 0.026 | 0.2982 | 0.010 | 0.7778 |
| 20 | PLTP (rs6065906) | C | 0.160 | 113 | 0.013 | 0.4815 | 0.031 | 0.2571 | -0.029 | 0.3478 | -0.006 | 1.0000 |
| Chr, chromosome; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; EAF, effect allele frequency; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; CIMT, carotid intima-media thickness. *Beta for difference between the natural log-transformed on- and off-treatment values adjusted for natural log-transformed off-treatment level. The beta reflects the fraction of differential lipid- or CIMT-lowering effect in carriers versus non-carriers of the minor allele (for additive model), in carriers of the genotype according to the model (dominant, recessive) versus the carriers of alternative genotypes; a negative beta indicates a better statin response (stronger lipid or CIMT reduction), a positive beta – a worse statin response. Betas were generated using linear regression analysis with age, sex, body mass index, and rosuvastatin dose as covariates. #p-values were generated using the permutation procedure. Superscript indicates genetic model: R, recessive; A, additive; D, dominant. | ||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





