1. Introduction
Thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR), originally designed for the treatment of degenerative aneurysms, has become the standard treatment for blunt thoracic aortic injury (BTAI), resulting in significantly lower mortality rates and post-operative complications such as paraplegia, and stroke, comparing to open aortic repair [
1,
2].
For a successful TEVAR procedure, accurate measurement of the aortic size, meticulous case planning, and careful selection and placement of the appropriate device are crucial. It is important to assess the intended landing zones for both proximal and distal seals as part of this process. The success of the intervention depends on choosing an endograft with the right size for the measured aortic diameter within the landing zone. Inaccurate sizing of the endograft for TEVAR can have detrimental consequences. Oversizing beyond the recommended range may result in complications such as endoleaks, device infolding, and endograft collapse. Conversely, undersizing the endograft can also lead to endoleaks and endograft migrations [
2,
3,
4].
A 10% to 15% oversizing of the endograft is recommended to ensure sufficient radial force and aortic apposition for a successful seal for the treatment of thoracic aortic aneurysm, while no oversizing is recommended for the treatment of thoracic aorta dissection [
1,
5]. Oversizing indications for TEVAR for the treatment of BTAI are lacking. Patients with these injuries are typically young and have minimal aortic disease and normal aortic diameters. Despite the rapid acceptance of TEVAR, the long-term impact of endovascular grafts on this population is unknown, with some reports suggesting increased aortic diameters and altered morphology during follow-up [
6,
7,
8]. Studies have shown that the changes in the structure of the aorta that occur naturally as a person ages, as well as the forces exerted by the stent graft used in TEVAR treatment, play crucial roles in determining how effective and long-lasting the treatment will be. In other words, understanding the impact of these factors on the durability of TEVAR treatment is essential for developing effective treatment strategies [
6,
7,
8].
Another challenge is that aortic sizing and planning for BTAI is often done in hypotensive and hypovolemic conditions, which can lead to underestimating the true aortic diameter, especially in young patients such as BTAI patients, in which the aorta is more compliant. This underestimating of aortic diameter might lead to choosing an undersized endograft [
9,
10]. Hence several studies have tried to examine immediate aortic diameter changes post-TEVAR intervention.
Few observational clinical studies have tried to define the aortic geometrical changes post-TEVAR in patients with BTAI. However, due to the rarity of the condition, these studies had small-sized groups. The presented study aimed to provide an updated, systematic review of the literature and, by combining the results in a meta-analysis of the various individual studies, to provide evidence on the degree of aortic diameters changes both immediate and long-term following TEVAR for the treatment of BTAI.
2. Materials and Methods
The systematic literature search, inclusion criteria, data synthesis, and analysis (qualitative and quantitative), were prespecified in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [
11].
Eligibility criteria for inclusion were defined as clinical or observational studies (excluding case series, case control, or cohort studies) with the following criteria: (1) included patients with BTAI who underwent standard TEVAR (2) a study sample of more than 15 patients, (3) reported data of morphological features of the aorta on computed tomography angiography (CTA) or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) before and after treatment.
The study was carried out by searching Medline (PubMed), Embase, and The Cochrane Library for articles published in the English language from inception until March 1st, 2023. There were no limitations on study types applied to the search. The first search was conducted in March 2023. Medical subject headings (MeSH) for Medline and The Cochrane Library and EMTREE terms for Embase were used to select keywords. The key-words were " thoracic aortic trauma sizing," and " blunt thoracic traumatic endovascular repair". Titles and abstracts of potentially useful articles were selected. Two researchers independently screened titles, abstracts, and full text of search results. Data from all included studies were independently extracted, and in case of discrepancies in articles or data extraction, a third researcher was consulted to raise the final consensus. References of all identified relevant studies were used to perform a recursive search of the literature. To obtain full-text articles for eligible titles and abstracts, Metalib® (University of Milan, Milan, Italy), SBBL (Lombard Biomedical Librarian System), and personal journal subscriptions were used. Articles presenting the use of TEVAR for BTAIs were primarily included, and those investigating the role of TEVAR only for the treatment of chronic aortic lesions were excluded. Abstract and/or case reports or case series with less than 15 patients, studies that did not provide any data that could be useful for outcomes analysis, studies focused only on open repair or non-operative management, and company-sponsored trials were also excluded. If there were successive publications from the same group, only the most recent article or the one that included the largest number of patients was incorporated. Conversely, studies on both urgent and delayed treatment were considered eligible. Further articles were identified by examining the references cited in the studies that were initially identified through electronic means.
To evaluate the quality of the studies included in this review, the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI) for Quality Assessment Tool for Before-After (Pre-Post) Studies with No Control Group was employed. This quantitative tool assesses each study based on twelve items. A rating system is used in the NHLBI scale, with a maximum of twelve scores. Studies that received a rating of nine or more scores were deemed to be of superior quality, studies that received a rating of three to nine were deemed to be of moderate quality, and studies that received less than 3 were deemed to be of low quality [
12].
3. Results
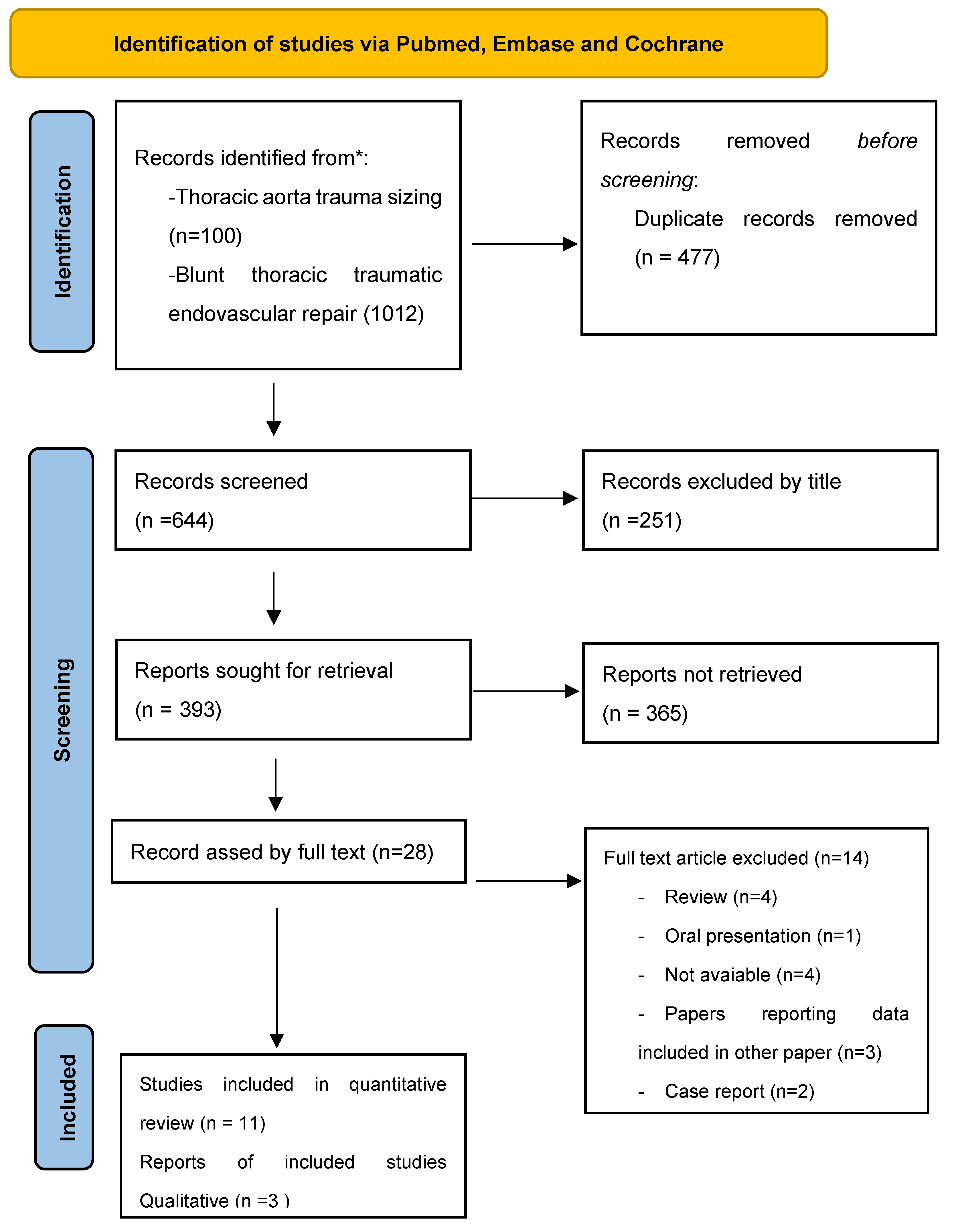
During the screening process, the search identified 644 potentially relevant articles. After a thorough evaluation of the titles and abstracts, 28 full-text articles were assessed for eligibility. Of these, 14 studies met the inclusion criteria and were included in the review. 11 studies were eligible for quantitative review (
Figure 1 summarized the selection process). Out of these 11 studies, two different meta-analyses were conducted; the first included 3 studies comparing pre-intervention with post-intervention aortic proximal and distal necks diameters. The second compared immediate post-intervention with distance follow-up aortic diameters, including 4 studies for the proximal neck and 3 for the distal neck. In all analyzed studies aortic diameters were measured with CT or MRI.
It is important to note that while the treatment and follow-up protocols in the studies varied, the patients' demographics did not vary greatly. A total of 353 patients were included in this systematic review, with 77% of them being males and with a mean age of 43 years old. The ethnic backgrounds of the patients were not reported. In addition, different follow-up times and endograft oversizing protocols were used in the different studies.
Table 1 summarized studies included in the quantitative analysis, with their basic population demographics, endograft oversizing reported in these studies, and NHLBI quality assessment score.
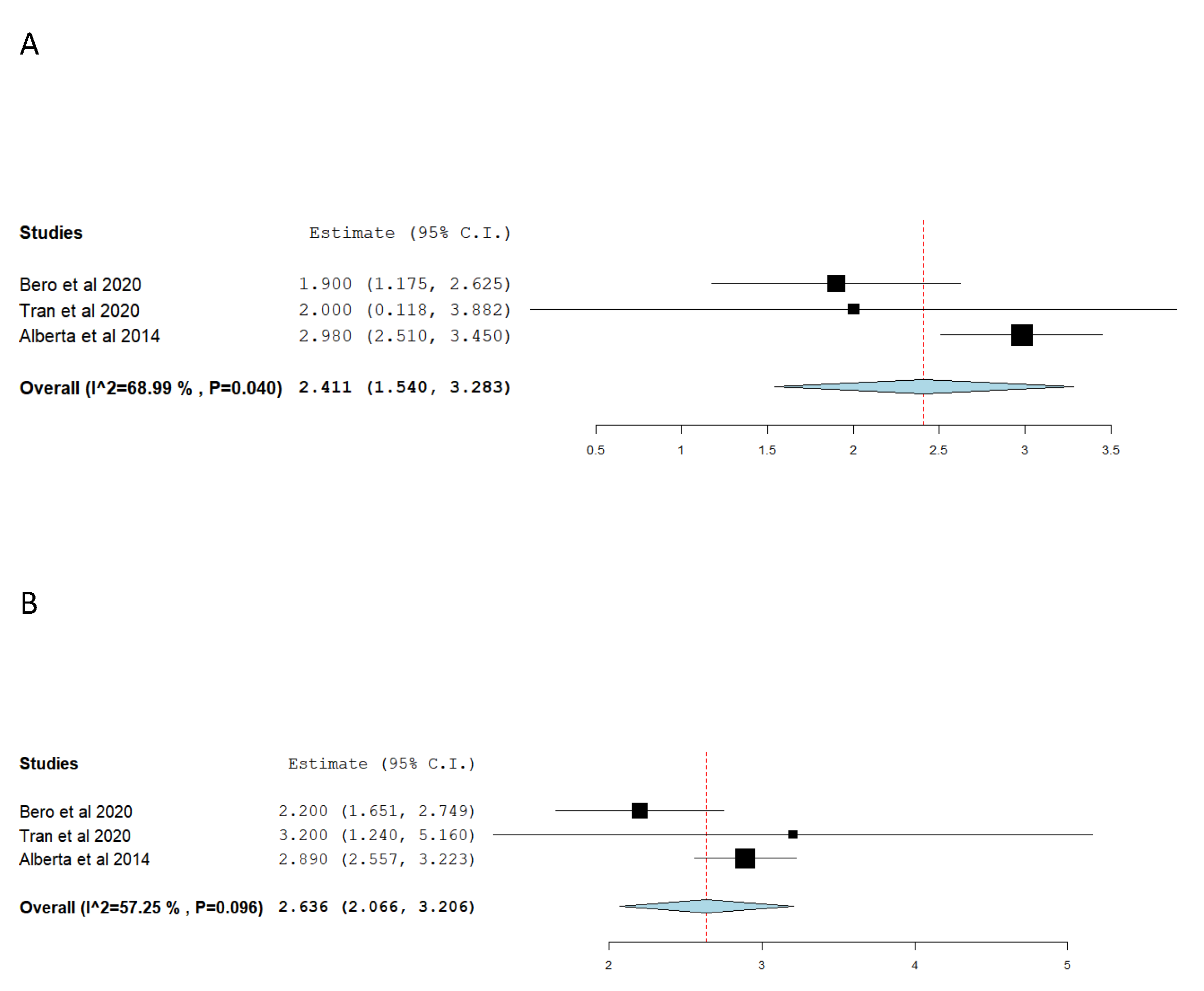
Table 2 report included studies evaluating immediate post-TEVAR aortic diameters change, it summarized proximal and distal aortic neck diameter changes from pre-to-post-TEVAR. As well as reported aortic diameters change proximally and distally to the endograft, (i.e. non-stented aorta diameter change). For convenience purposes, if multiple segments of non-stented aortic measurements were reported by the studies, only the measurement of the non-stented-segment most closed to the aortic neck was reported. Due to variability in aortic diameter measurements, studies methodology, and data reporting, only three studies were included in the final meta-analysis comparing pre and post-intervention aortic necks’ diameters change (
Figure 2A,B) [
8,
9,
13]. Our meta-analysis (including 133 patients) suggests that post-TEVAR for BTAI patients, the aortic diameter at the level of proximal and distal aortic necks increased by 2.41 mm and 2.63 mm, respectively. The meta-analyses conducted found statistically significant results for the proximal neck diameter change, as well as high heterogeneity. The quality of evidence was rated as high. Notably, out of the studies that investigated immediate post-TEVAR aortic diameter changes, a statistical correlation between aortic diameter changes and hypotension was established only by Bae et al [
16]. While Alberta et al found a statistical correlation between endograft oversizing and immediate post-intervention aortic diameter changes [
9].
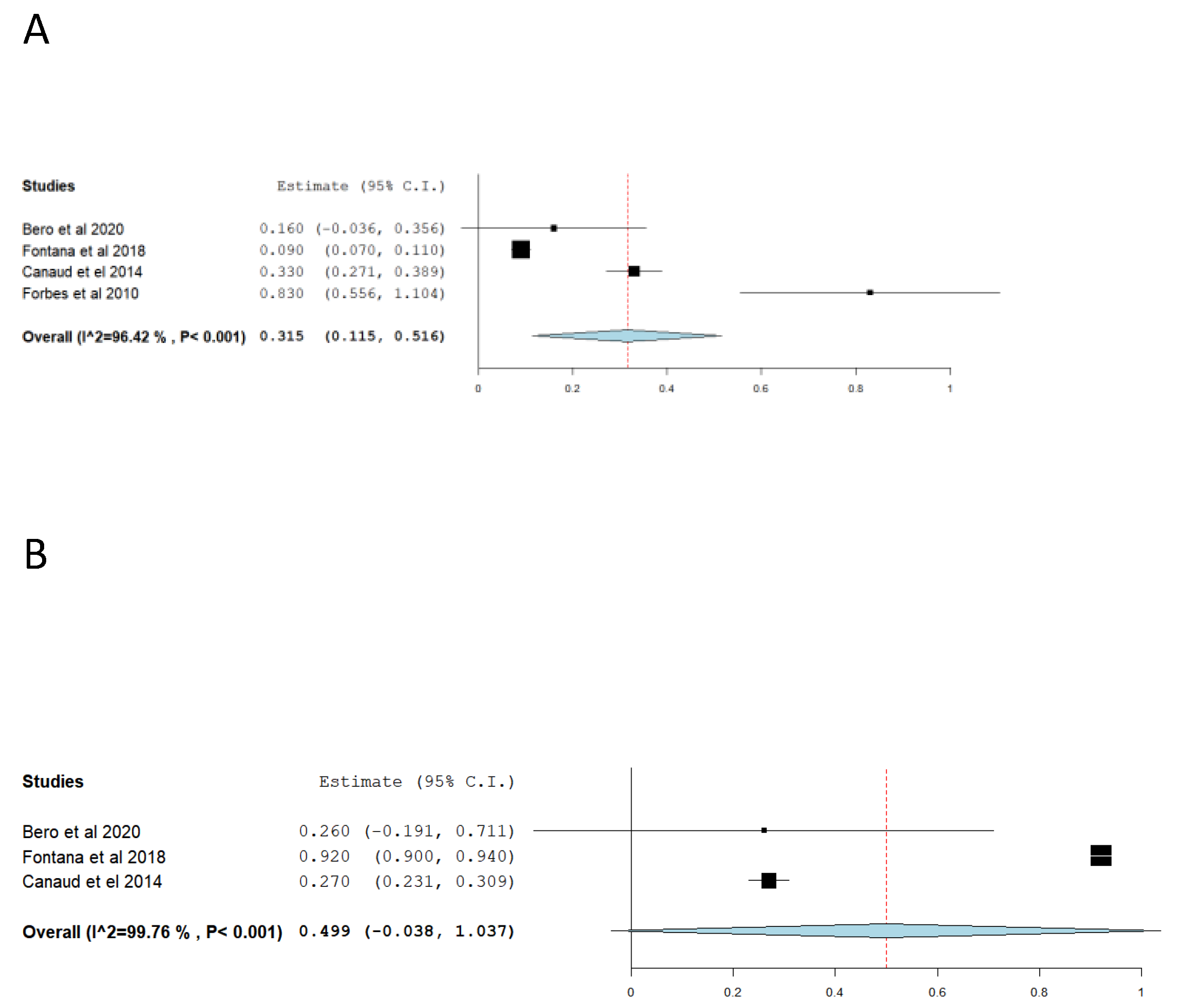
In regards to long-term aortic remodeling post-TEVAR, Table 3 summarized the result of studies that aortic proximal and distal necks diameters change during follow-up (i.e. the difference in aortic diameter between post-TEVAR and the most recent post-intervention surveillance CT/MRI scan follow-up), as well as reported proximal and distal non-stent aortic segment diameters changes. Similarly, to aortic diameters changes immediately post-TEVAR, the methodology of the studies comparing long-term post-TEVAR aortic diameter changes, varied among studies. Nevertheless, it is evident that the aorta continues to dilate post-TEVAR, not only in the stented part but also in the non-stented part (i.e., proximal and distal to the endograft). Our meta-analysis, which included 4 studies for the proximal neck [
6,
12,
17,
19] and 3 for the distal neck [
6,
12,
17,
19] diameter changes demonstrated that the dilation of the proximal neck occurred at a rate of 0.35 mm/year and the dilation of the distal neck at a rate of 0.49 mm/year (
Figure 3A
,B). Gennai et al found a correlation between aortic long-term remodeling (i.e. increased diameter) and oversizing above 10% as well as placement of proximal endograft sealing zone over the left subclavian ostium with increased aortic diameter following the intervention [
7].
Table 3.
Table 3, summarized the result of studies evaluating long-term post-TEVAR aortic diameters changes. *Mean and standard deviation, between post-intervention imaging and most recent follow-up imaging **Mean or median values are reported, when available. Otherwise, the minimum time is reported. *** mm/year.
Table 3.
Table 3, summarized the result of studies evaluating long-term post-TEVAR aortic diameters changes. *Mean and standard deviation, between post-intervention imaging and most recent follow-up imaging **Mean or median values are reported, when available. Otherwise, the minimum time is reported. *** mm/year.
| |
Proximal Neck diameter change* |
Distal Neck diameter change* |
Aortic segment proximal/distal to endograft diameter change* |
Time from post-TEVAR imaging to Followup imaging ** |
| Bero et al[8] |
0.5 ± 1.8mm |
0.8± 4.1mm |
0.2/NR |
1.5 years |
| Fontana et al[19] |
0,5 ± 0,3mm |
0,5 ± 0,4mm |
0.7/0.5mm |
5,4 years |
| Canaud et el[6] |
3.3 ± 1.5mm |
2.7 ± 1 mm |
NR/NR |
10 years |
| Forbes et al[17] |
0.83*** |
x |
0.74/0.63 *** r |
>`1 years |
| Gennai et al*[7] |
4,3mm |
3,4mm |
NR/NR |
10 years |
| Tran et al[13] |
x |
0,67mm/y |
NR/0 |
5 years |
| Mufty et al[15] |
0,58mm |
x |
- 0.23mm/ -0.39mm |
7.5 years |
4. Discussion
BTAI is a rare, yet life-threatening condition caused by, most commonly, high deceleration forces, leading to a tear in the aortic wall. It is estimated to occur in 0.1-0.5% of all trauma patients and has a high mortality rate of 75-90% if left untreated. BTAI predominantly affects young males between the ages of 25-45 years and is often accompanied by concomitant injuries. Prompt diagnosis and treatment of BTAI are vital for improving patient outcomes. Clinical suspicion should be high in cases of trauma involving the chest, and a prompt evaluation with CT angiography or transesophageal echocardiography should be performed to confirm the diagnosis. Delay in diagnosis and treatment can lead to progressive aortic rupture, traumatic cardiac arrest, and death [
1,
2,
3,
19,
20,
21]
Treatment options for BTAI include both operative and non-operative management, depending on the extent and location of the injury, the patient's overall condition, and the presence of associated injuries. However, operative repair, either via open or endovascular approach, has become the preferred method for treating BTAI, with a survival rate of approximately 80% in appropriately selected patients [
1,
2,
3]
Although TEVAR has become the treatment of choice for BTAI, endograft sizing and planning are still debated, with no consensus regarding the degree of endograft oversizing for BTAI [
1,
14]. TEVAR endograft undersizing might lead to endoleaks, and endograft migrations, while excessive oversizing could lead to fatal complication as device infoldings, endoleaks, and endograft collapse, [
2,
3]. In addition, the small aortic arch diameter of young patients with BTAI, with respect to degenerative aortic pathologies, might lead to angulation between the proximal endograft edge and the aortic wall which is called “bird’s beak’’ deformity, and of itself, can lead to graft migration, collapse, and endoleaks [
4,
22,
23,
24,
25]. Similarly, some aortic segments in specific arch configurations, such zone 2 and 3 of Ischimaru classification in type III aortic arch and bovine arch variant, demonstrated a higher risk of proximal endograft failure [
22,
26].
Another challenge of endograft sizing and fitting in BTAI is pre-operative hypotension. It has been suggested that due to hypotension, the true aortic diameter of BTAI patients is underestimated. Hoffman et al attempt to evaluate the effect of hypovolemia on aortic diameter in patients with BTAI, by examining aortic diameter changes accounted for resuscitation (i.e., aortic diameter before and after resuscitation). They found an increase in aortic diameter of 1.9mm and 1.4mm, proximally and distally [
10]. To better evaluate the aortic size in BTAI patients, some authors suggested using intravascular ultrasounds (IVUS) adjacent to CT scans to surrogate better aortic dimensions in BTAI patients. They demonstrated that IVUS in combination with CT scan better assesses aortic diameter than CT scans alone, and eliminated the need to repeat post-resuscitation CT scan [
27,
28].
Endografts used in TEVAR exert radial forces on the aorta. This essential force for endografts anchoring in place, also alters aortic morphology. This is particularly important in patients for BTAI patients since they tend to be young, without comorbidities, and once they overcome the traumatic event, they expect to have a longer life expectancy compared to patients treated with TEVAR for degenerative disease (as it was originally designed for). Hence, they are expected to be under the influence of the radial forces exerted by the aortic endograft for more years, with consequently more detrimental effects. However, Due to the rarity of this pathology, data on aortic morphological changes in patients treated with TEVAR for BTAI is scarce. To date, only a few observational small sample-sized studies investigated these aortic changes. Therefore, we aim to conduct a comprehensive and up-to-date systematic review of the existing literature. By synthesizing the findings through a meta-analysis of individual studies, we aimed to gather evidence on the extent of aortic diameter changes, both in the short and long term, following TEVAR in the management of BTAI
Our metanalysis demonstrated that the proximal neck and distal neck diameter overall, changes by around 2.5mm, comparing pre and post-intervention imaging. This corresponded with a 10% increase in the proximal aortic neck with respect to normal aortic diameter in the same group of age [
29]. Even though these studies reported an intended oversized greater than 10%. This discrepancy might be correlated to the aortic elastic force acting against endograft radial force, as well as possibly underestimated aortic diameter in hypotensive patients [
8,
9,
13]. Moreover, the non-stented proximal ad distal aortic segment seemed to dilate but to a lesser degree [
8,
13,
14,
16,
18].
Over time, the diameter of the native aorta gradually increased. This phenomenon was observed by Endicott et al, who found that the aortic diameter increased by 0.1 mm/year in adults from 20 years age to 80 years of age [
29]. It appears that post-TEVAR in patients with previously healthy aorta this process is accelerated. Our analysis indicates an increase of 0.35mm and 0.49 mm per year for proximal and distal necks respectively. The rate of dilatation depends on the balance produced by the endograft and flaring of endograft edges and the recoil force of the aorta. Moreover, the radial forces produced by the endoprosthesis doesn’t only dilate the stented aorta but the whole thoracic aorta. It appears that the proximal and distal aortic non-stented area also experienced accelerated dilation with the years. However, due to studies measurement and methodology variation, we weren’t being able to quantify these processes [
8,
13,
15,
17,
19]. Moreover, comparing patients who underwent TEVAR for BTAI to healthy patients also showed statistically significant dilation of the non-stented aorta [
30].
When comparing these results with results of aortic diameter change pre and post-TEVAR for degenerative pathologies such as aneurysms and dissection, it appears that dilation has a somehow similar accelerated progression rate; Yauel al conducted a review of CT scans from 87 patients with type B aortic dissection or aneurysms, demonstrated a gradual increase in the proximal aortic neck of 0.9mm 1.4mm and 4.5mm in the first, second and third year, and proximal to that in the non-stented aorta a gradual increase of 0.6mm 0.3mm 3mm, respectively[
31]. Meanwhile, Berkarda et al. conducted a study on aortic remodeling after TEVAR for acute type B aortic dissection. Their study included 101 patients, revealing a median total growth of 4 mm in proximal and distal landing zones [
32]. However, the degree of oversizing reported by these studies was smaller (or practically no oversizing in dissected aorta), than the degree of oversizing in the treatment of BTAI [
6,
7,
8,
13,
15,
17,
19].
In terms of pre-intervention planning and sizing effect on aortic long-term remodeling, none of the reviewed studies demonstrated clear evidence that one type of endograft is more prone than another to cause aortic dilation. Several studies have compared the dilation rates of various types of endograft, but none have definitively demonstrated a statistically significant difference in dilation rates between these groups [
6,
7,
8,
13,
15,
17,
19]. Moreover, only the study conducted by Gennai et al. found a correlation between oversizing and proximal stent location with long-term aortic remodeling. The study reported that oversizing of the endograft by more than 10% and placement of the proximal endograft sealing zone over the left subclavian ostium were associated with an increased aortic diameter dilation following the intervention [
7].
A systematic review and meta-analysis of proximal aortic neck dilatation after infrarenal endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair conducted by Chatzelas et al. demonstrated a continuous aortic neck dilation that seems to evolve in two phases: an immediate post-implantation period that is strongly associated with the percentage of oversizing, and a subsequent period that is not correlated with oversizing. Adverse events of aortic neck dilation after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair include type Ia endoleak, stent graft migration, and consequently increased reinterventions rate [
32]. A scoping review by Mezzetto et al from 2023, demonstrated that the suprarenal or thoracic aorta is less prone to dilation over time, with respect to infrarenal. This review also supports the hypothesis that increasing device oversizing and larger preoperative aortic seal diameter were predictors of future neck dilation, and does not seem to be associated with any particular type of endograft [
34].
However, not only ‘vascular’ consequences, but also flow-dynamic, consequences of aortic long-term morphological alteration post TEVAR, play a crucial role in BTAI patients. New technologies such as cardiovascular magnetic resonance 4D flow, as well as transoesophageal echocardiography, demonstrated increased aortic stiffness, and increase cardiac mass, in BTAI patients post-TEVAR. Similarly, a higher incidence of pathological high blood pressure was found in these patients. All represent an established risk factor for cardiovascular and target organ damage via various mechanisms. These findings underline the need for specific attention to younger patients who have fewer comorbidities and fewer cardiovascular risk factors but might be affected more by the adverse effects of TEVAR on the cardiovascular system and target organs [
30,
35].
Despite variation in treatment and follow-up protocols in the studies analyzed, this systemic review and meta-analysis found statistically significant changes in aortic diameter post-TEVAR. The findings in our study align with previously established results regarding aortic morphological post-TEVAR for the treatment of degenerative disease as well as, aortic morphological post-EVAR [
31,
32,
33]. This suggests that the procedure may have a long-term impact on aortic morphology. These morphological changes should be further studied to unveil their clinical importance in terms of long-term vascular complications, such as the development of endoleaks and migration, as well as long-term cardiac morbidities. Future research should aim to address the limitations of the current study, such research would provide valuable insights into the long-term effects of TEVAR and could help to guide clinical practice and improve patient outcomes.
5. Limitations
While our search strategy involved thorough screening of prominent databases, it is important to note that our search was limited to English-language journals. As a result, studies published in non-English journals, particularly small-scale studies, may not have been included in our analysis. Additionally, as of the time of writing, no randomized controlled trials were found addressing this specific topic. The majority of the included studies were retrospective, originating from a single center, and featured relatively modest sample sizes.
The lack of randomization in the endograft selection, as well as the lack of patient population ethnic background reporting in all studies evaluated, should also be noted. The difference in endograft oversizing and pre-operative planning, as well as the difference in follow-up protocols, must also be acknowledged.
The heterogeneity of the studies included in this systemic review presented some challenges in comparing the results. Variability in reporting methods for aortic diameter measurements made it difficult to establish a standard for measuring the effects of TEVAR on the aorta.
6. Conclusions
14 articles, including 353 patients, were included in the systemic review. The meta-analysis demonstrated an immediate post-intervention dilation 2.41 mm and 2.63 mm of the proximal and distal aortic necks’, respectively, as well as continuous dilation of the respective regions at a rate of 0.35 mm/year and 0.49 mm/year. The review had some limitations, including a low number of studies and studies with diverse treatment protocols, measurement, and reporting methodology. Nevertheless, this study's findings provide important insights into the long-term outcomes of TEVAR in BTAI and may assist in clinical decision-making. Further, well-designed studies are required to confirm these results and to determine the optimal treatment strategy for BTAI.
Author Contributions
D.A.: Conceptualization, methodology, data collection, data analysis, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review, editing critical revision, final approval P.R.: Conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review, editing critical revision, final approval; D.M.: writing—review and editing, critical revision, final approval; M.G: data collection, data analalysus, critical revision, final approval; G.N.: critical revision, final approval. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors disclose no interests that could inappropriately influence or bias their work, nor any other conflict of interest.
References
- Grabenwöger M, Alfonso F, Bachet J, et al. Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair (TEVAR) for the treatment of aortic diseases: a position statement from the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) and the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), in collaboration with the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI). European Heart Journal. 2012;33(13):1558–1563. [CrossRef]
- Kim SH, Huh U, Song S, et al. Open repair versus thoracic endovascular aortic repair for treating traumatic aortic injury. Asian journal of surgery. 2022;45(11):2224–2230. [CrossRef]
- Mazzaccaro D, Righini P, Fancoli F, Giannetta M, Modafferi A, Malacrida G, Nano G. Blunt Thoracic Aortic Injury. J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 17;12(8):2903.
- García Reyes ME, Gonçalves Martins G, Fernández Valenzuela V, Domínguez González JM, Maeso Lebrun J, Bellmunt Montoya S. Long-Term Outcomes of Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair Focused on Bird Beak and Oversizing in Blunt Traumatic Thoracic Aortic Injury. Annals of vascular surgery. 2018;50:140–147.
- Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Aortic Disease: A Report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022;146(24):e334-e482. [CrossRef]
- Canaud L, Marty-Ané C, Ziza V, Branchereau P, Alric P. Minimum 10-year follow-up of endovascular repair for acute traumatic transection of the thoracic aorta. The Journal of thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. 2015;149(3):825–829. [CrossRef]
- Gennai S, Leone N, Andreoli F, et al. Influence of Thoracic Endovascular Repair on Aortic Morphology in Patients Treated for Blunt Traumatic Aortic Injuries: Long Term Outcomes in a Multicentre Study. European journal of vascular and endovascular surgery : the official journal of the European Society for Vascular Surgery. 2020;59(3):428–436. [CrossRef]
- Bero EH, Nguyen-Ho CT, Patel PJ, Foley WD, Lee CJ. Aortic Remodeling and Clinical Outcomes Following Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair for Blunt Thoracic Aortic Injury. The Journal of surgical research. 2020;255:124–129. [CrossRef]
- Alberta HB, Secor JL, Smits TC, et al. Comparison of thoracic aortic diameter changes after endograft placement in patients with traumatic and aneurysmal disease. Journal of vascular surgery. 2014;59(5):1241–1246. [CrossRef]
- Hoffman JRH, Chowdhury R, Johnson LS, et al. Posttraumatic Resuscitation Affects Stent Graft Sizing in Patients with Blunt Thoracic Aortic Injury. The American surgeon. 2016;82(1):75–78. [CrossRef]
- Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ (Clinical research ed.). 2015;350:g7647. [CrossRef]
- Study Quality Assessment Tools. [(accessed on 21 January 2022)]. Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools.
- Tran K, Li M, Stern JR, Lee JT. Thoracic Aortic Dilation after Endovascular Repair of Blunt Traumatic Aortic Injury. Annals of vascular surgery. 2021;70:101–108. [CrossRef]
- Jonker FHW, Verhagen HJM, Mojibian H, Davis KA, Moll FL, Muhs BE. Aortic endograft sizing in trauma patients with hemodynamic instability. Journal of vascular surgery. 2010;52(1):39–44. [CrossRef]
- Mufty H, Maleux G, Houthoofd S, et al. The effect of TEVAR for blunt traumatic thoracic aortic injury on maximal aortic diameter: Mid- and long-term outcome. Vascular. 2019;27(4):411–416. [CrossRef]
- Bae M, Jeon CH. Optimal Sizing of Aortic Stent Graft for Blunt Thoracic Aortic Injury Considering Hypotension-Related Decrease in Aortic Diameter. Journal of endovascular therapy : an official journal of the International Society of Endovascular Specialists. 2022:15266028221134894. [CrossRef]
- Forbes TL, Harris JR, Lawlor DK, Derose G. Aortic dilatation after endovascular repair of blunt traumatic thoracic aortic injuries. Journal of vascular surgery. 2010;52(1):45–48.
- Berger T, Voetsch A, Alaloh D, et al. Diameter Changes in Traumatic Aortic Injury: Implications for Stent-Graft Sizing. The Thoracic and cardiovascular surgeon. 2022;70(4):333–338. [CrossRef]
- Fontana F, Macchi E, Piacentino F, et al. The Evaluation of Aortic Diameter Changes During Long-Term Follow-Up After Endovascular Treatment of Acute Blunt Traumatic Thoracic Aortic Injuries. Vascular and endovascular surgery. 2018;52(5):335–343. [CrossRef]
- Grigorian A, Spencer D, Donayre C, et al. National trends of thoracic endovascular aortic repair versus open repair in blunt thoracic aortic injury. Ann Vasc Surg. 2018;52:72–78. [CrossRef]
- Parmley LF, Mattingly TW, Manion WC, Jahnke EJ., Jr. Nonpenetrating traumatic injury of the aorta. Circulation. 1958;17(6):1086– 1101. [CrossRef]
- Marrocco-Trischitta M.M., Spampinato B., Mazzeo G., Mazzaccaro D., Milani V., Alaidroos M., Ambrogi F., Nano G. Impact of the Bird-Beak Configuration on Postoperative Outcome after Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair: A Meta-analysis. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2019;26:771–778. [CrossRef]
- Marrocco-Trischitta MM, de Beauforta HW, Piffaretti G, Bonardelli S, Gargiulo M, Antonello M , van Herwaarden JA, Boveri S, Bellosta R, Trimarchi S, on behalf of the MALAN Collaborators. The Modified Arch Landing Areas Nomenclature predicts proximal endograft failure after thoracic endovascular aortic repair. EJCTS 58 (2020) 309–318. [CrossRef]
- Nano G., Mazzaccaro D., Malacrida G., Occhiuto M.T., Stegher S., Tealdi D.G. Delayed endovascular treatment of descending aorta stent graft collapse in a patient treated for post- traumatic aortic rupture: A case report. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2011;6:76. [CrossRef]
- D'Alessio I, Domanin M, Bissacco D, Rimoldi P, Palmieri B, Piffaretti G, Trimarchi S. Thoracic endovascular aortic repair for traumatic aortic injuries: insight from literature and practical recommendations. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2020 Dec;61(6):681-696. [CrossRef]
- Marrocco-Trischitta MM, Alaidroos M,. Romarowski RM, Secchi F, Righini P, Glauber M, Nano G. Geometric Pattern of Proximal Landing Zones for Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair in the Bovine Arch Variant. EJVES (2020) 59, 808e816.
- Shi Y, Tsai PI, Wall MJ, Gilani R. Intravascular ultrasound enhanced aortic sizing for endovascular treatment of blunt aortic injury. The journal of trauma and acute care surgery. 2015;79(5):817–821. [CrossRef]
- Wallace GA, Starnes BW, Hatsukami TS, Sobel M, Singh N, Tran NT. Intravascular ultrasound is a critical tool for accurate endograft sizing in the management of blunt thoracic aortic injury. Journal of vascular surgery. 2015;61(3):630–635. [CrossRef]
- Endicott KM, Tolaymat B, Farhat-Sabet A, et al. Healthy Thoracic Aorta Diameter Growth Slows by Age 60 Years With Persistent Age-Dependent Centerline Elongation Throughout Life. Journal of vascular surgery. 2020;72(1):e90-e91. [CrossRef]
- Gil-Sala D, Guala A, Garcia Reyes ME, et al. Geometric, Biomechanic and Haemodynamic Aortic Abnormalities Assessed by 4D Flow Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Patients Treated by TEVAR Following Blunt Traumatic Thoracic Aortic Injury. European journal of vascular and endovascular surgery: the official journal of the European Society for Vascular Surgery. 2021;62(5):797–807. [CrossRef]
- Yau P, Lipsitz EC, Friedmann P, Indes J, Aldailami H. Aortic Neck Dilatation Following Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair. Annals of vascular surgery. 2021;76:104–113. [CrossRef]
- Berkarda Z, Kondov S, Kreibich M, Czerny M, Beyersdorf F, Rylski B. Landing Zone Remodelling after Endovascular Repair of Dissected Descending Aorta. European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery. 2020;59(6):939–945. [CrossRef]
- Chatzelas DA, Loutradis CN, Pitoulias AG, Kalogirou TE, Pitoulias GA. A systematic review and meta-analysis of proximal aortic neck dilatation after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2023 Mar;77(3):941-956.e1. [CrossRef]
- Mezzetto L, D'Oria M, Lepidi S, et al. A Scoping Review on the Incidence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Proximal Neck Dilatation after Standard and Complex Endovascular Repair for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Journal of clinical medicine. 2023;12(6). [CrossRef]
- Mandigers TJ, Bissacco D, Domanin M, et al. Cardiac and Aortic Modifications After Endovascular Repair for Blunt Thoracic Aortic Injury: A Systematic Review. European journal of vascular and endovascular surgery: the official journal of the European Society for Vascular Surgery. 2022;64(2-3):176–187.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).