Submitted:
16 May 2023
Posted:
17 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study design
2.2. PBMCs isolation
2.3. Multiparametric flow cytometry
2.4. t-SNE analysis
2.5. Trajectory analysis
2.6. B-cell ELISpot
2.7. ELISA and ACE2/RBD inhibition assay
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
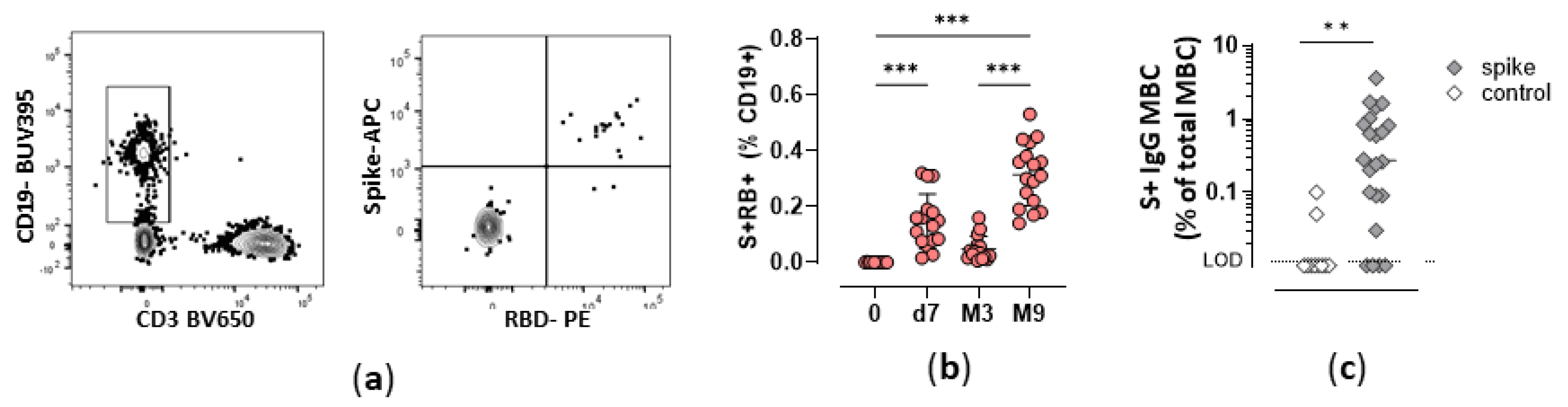
3.1. Durability of Spike-specific memory B cells overtime
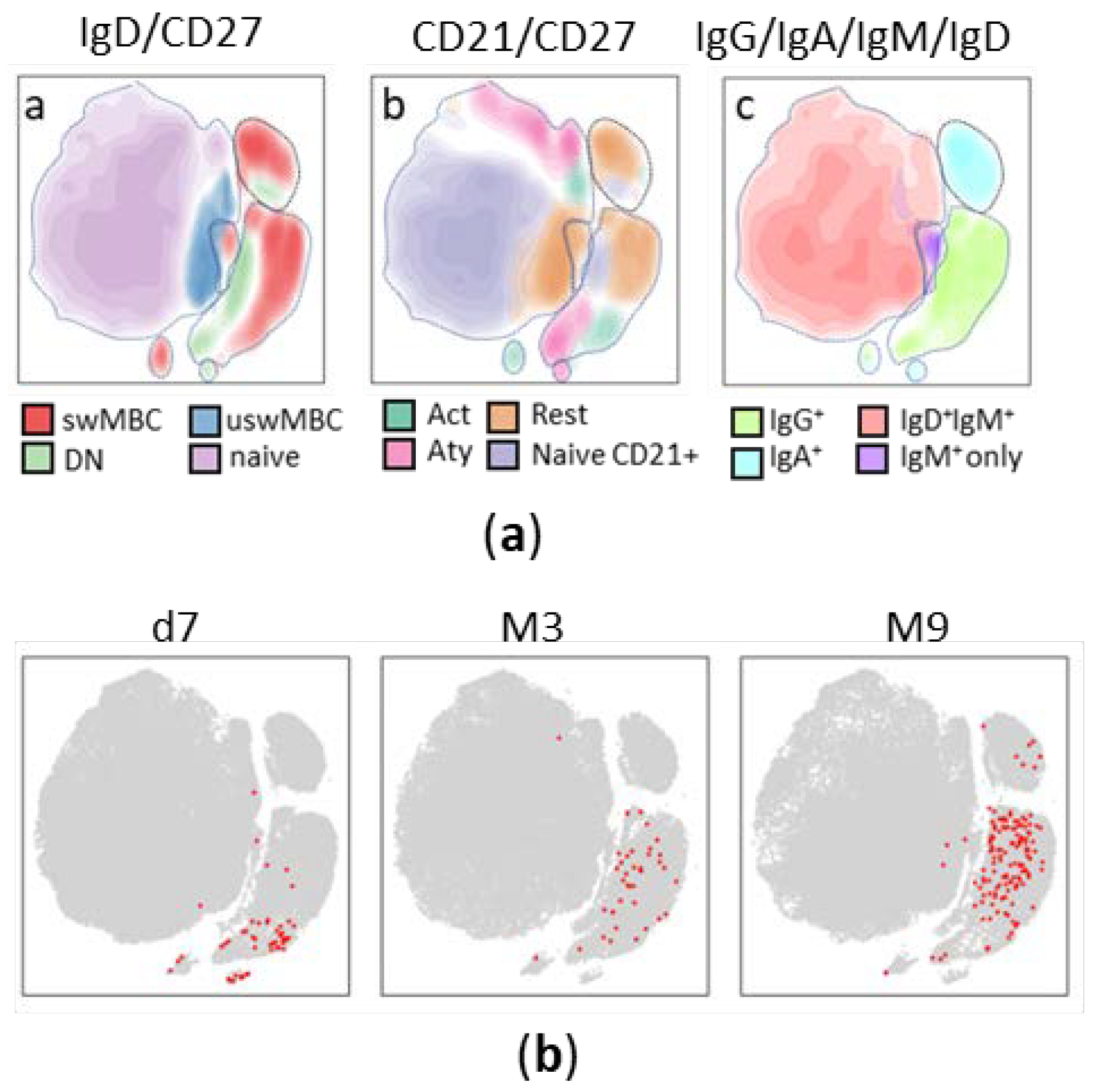
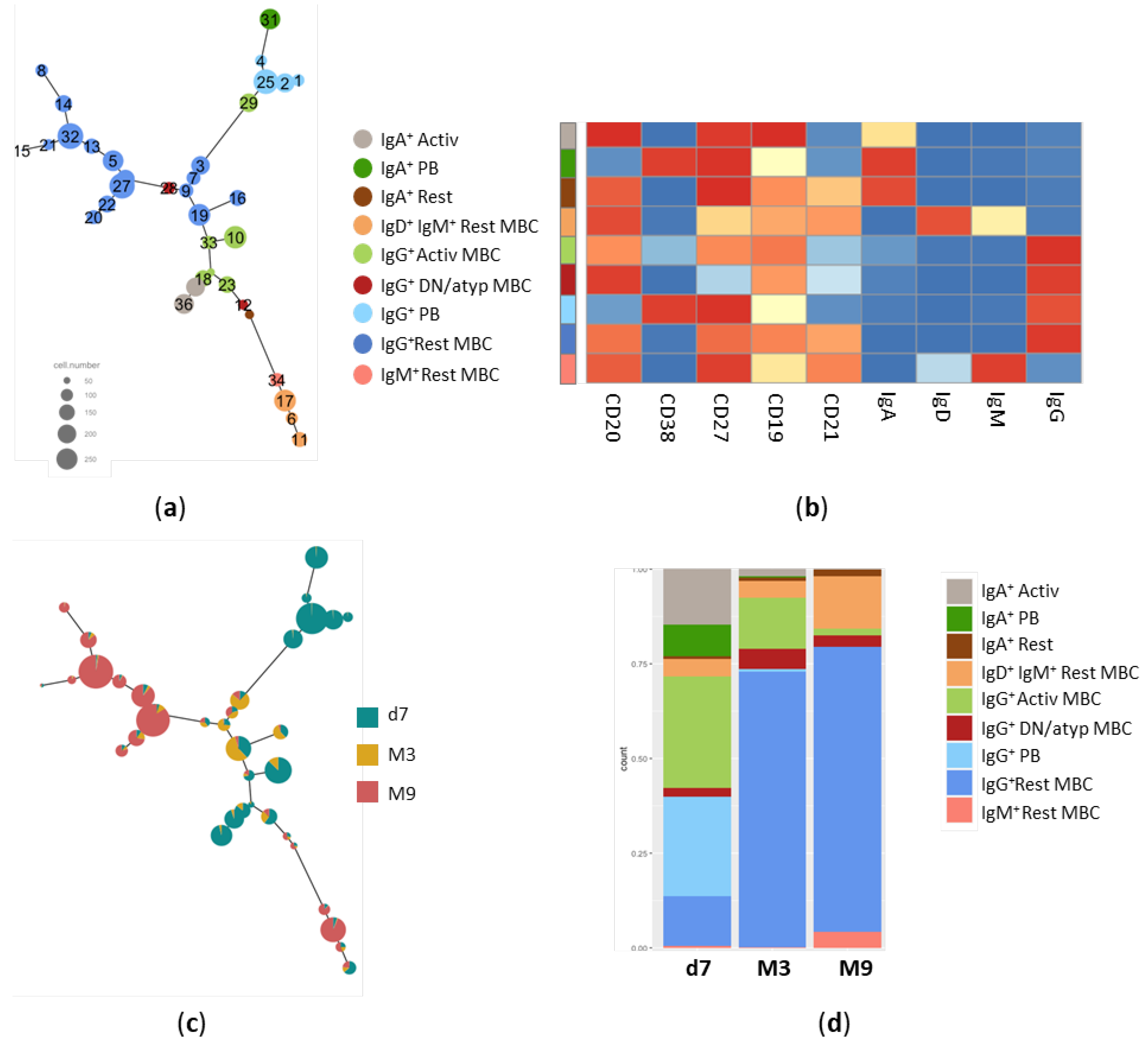
3.2. Trajectory analysis of Spike-specific B cells at different time points
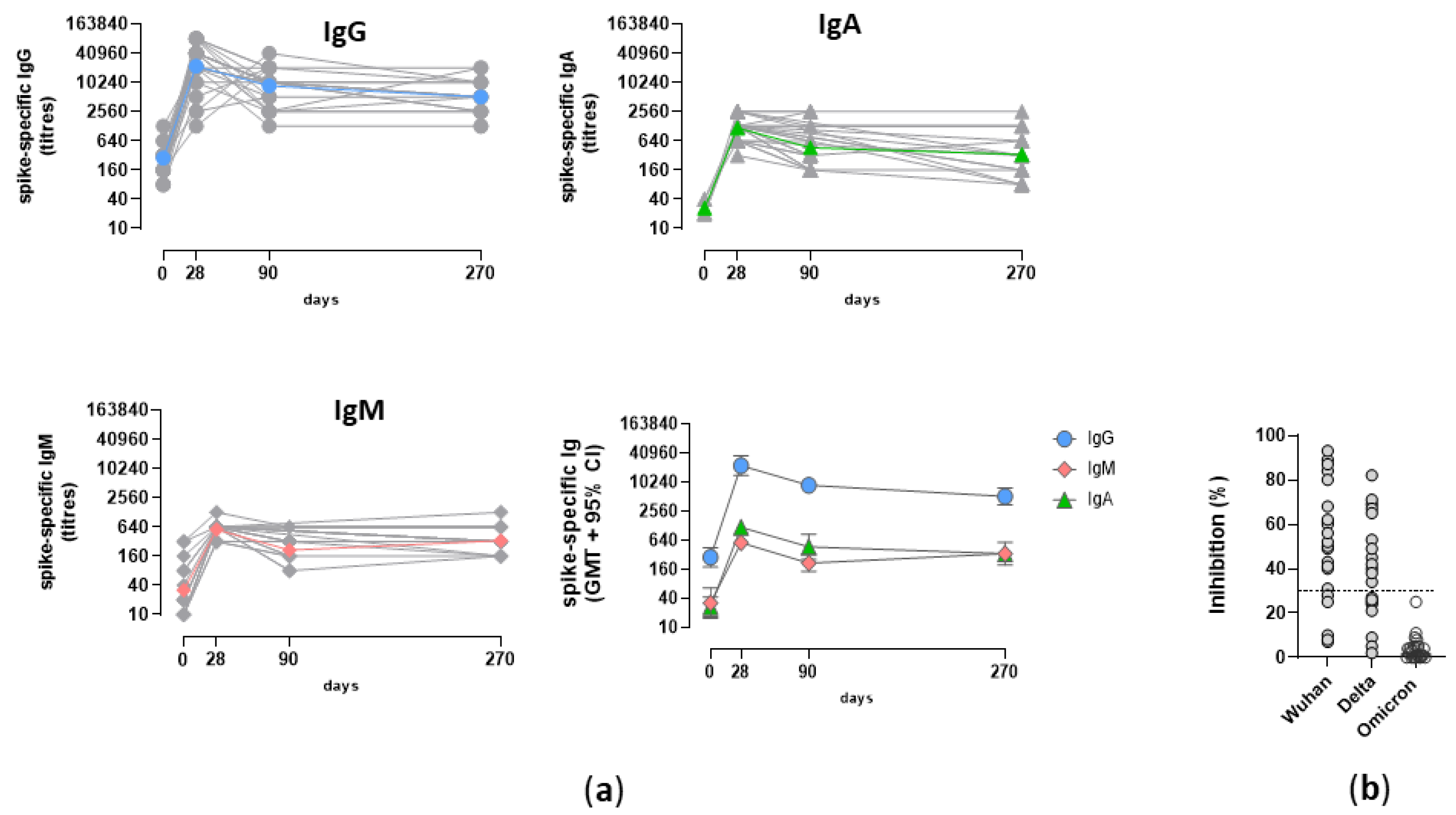
3.3. Analysis of the Spike-specific IgG response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDonald, I.; Murray, S.M.; Reynolds, C.J.; Altmann, D.M.; Boyton, R.J. Comparative Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Reactogenicity, Immunogenicity and Efficacy of Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. npj Vaccines 2021, 6, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, M.T. An MRNA Universal Vaccine for Influenza. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2023, 22, 98–98. [CrossRef]
- NIH Launches Clinical Trial of Three MRNA HIV Vaccines | National Institutes of Health (NIH). Available online: https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/nih-launches-clinical-trial-three-mrna-hiv-vaccines (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Flemming, A. MRNA Vaccine Shows Promise in Autoimmunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2021, 21, 72–72. [CrossRef]
- Rzymski, P.; Szuster-Ciesielska, A.; Dzieciątkowski, T.; Gwenzi, W.; Fal, A. MRNA Vaccines: The Future of Prevention of Viral Infections? Journal of Medical Virology 2023, 95, e28572. [CrossRef]
- Feikin, D.R.; Higdon, M.M.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Andrews, N.; Araos, R.; Goldberg, Y.; Groome, M.J.; Huppert, A.; O’Brien, K.L.; Smith, P.G.; et al. Duration of Effectiveness of Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Disease: Results of a Systematic Review and Meta-Regression. The Lancet 2022, 399, 924–944. [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Sung, H.; Kim, S.-H. Covid-19 Breakthrough Infections in Vaccinated Health Care Workers. N Engl J Med 2021, 385, 1629–1630. [CrossRef]
- Interim Statement on the Use of Additional Booster Doses of Emergency Use Listed MRNA Vaccines against COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/17-05-2022-interim-statement-on-the-use-of-additional-booster-doses-of-emergency-use-listed-mrna-vaccines-against-covid-19 (accessed on 16 November 2022).
- Ciabattini, A.; Garagnani, P.; Santoro, F.; Rappuoli, R.; Franceschi, C.; Medaglini, D. Shelter from the Cytokine Storm: Pitfalls and Prospects in the Development of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines for an Elderly Population. Semin Immunopathol 2020, 42, 619–634. [CrossRef]
- Ciabattini, A.; Nardini, C.; Santoro, F.; Garagnani, P.; Franceschi, C.; Medaglini, D. Vaccination in the Elderly: The Challenge of Immune Changes with Aging. Semin Immunol 2018, 40, 83–94. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, M.; Fuentes, L.R.; Thwin, O.; Grobe, N.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Kotanko, P. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Response after Three Doses of MRNA1273 Vaccine and COVID-19 in Hemodialysis Patients. Frontiers in Nephrology 2022, 2.
- Alidjinou, E.K.; Demaret, J.; Corroyer-Simovic, B.; Labreuche, J.; Goffard, A.; Trauet, J.; Lupau, D.; Miczek, S.; Vuotto, F.; Dendooven, A.; et al. Immunogenicity of BNT162b2 Vaccine Booster against SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron Variants in Nursing Home Residents: A Prospective Observational Study in Older Adults Aged from 68 to 98 Years. Lancet Reg Health Eur 2022, 17, 100385. [CrossRef]
- Corradini, P.; Agrati, C.; Apolone, G.; Mantovani, A.; Giannarelli, D.; Marasco, V.; Bordoni, V.; Sacchi, A.; Matusali, G.; Salvarani, C.; et al. Humoral and T-Cell Immune Response after Three Doses of MRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Fragile Patients: The Italian VAX4FRAIL Study 2022, 2022.01.12.22269133.
- Fiorino, F.; Ciabattini, A.; Sicuranza, A.; Pastore, G.; Santoni, A.; Simoncelli, M.; Polvere, J.; Galimberti, S.; Baratè, C.; Sammartano, V.; et al. The Third Dose of MRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines Enhances the Spike-Specific Antibody and Memory B Cell Response in Myelofibrosis Patients. Frontiers in Immunology 2022, 13.
- Pettini, E.; Ciabattini, A.; Pastore, G.; Polvere, J.; Lucchesi, S.; Fiorino, F.; Montagnani, F.; Bucalossi, A.; Tozzi, M.; Marotta, G.; et al. A Third Dose of MRNA-1273 Vaccine Improves SARS-CoV-2 Immunity in HCT Recipients with Low Antibody Response after 2 Doses. Blood Adv 2022, bloodadvances.2021006599. [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Yakushijin, K.; Funakoshi, Y.; Ohji, G.; Ichikawa, H.; Sakai, H.; Hojo, W.; Saeki, M.; Hirakawa, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; et al. A Third Dose COVID-19 Vaccination in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Patients. Vaccines (Basel) 2022, 10, 1830. [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Ferreira, V.H.; Kothari, S.; Pasic, I.; Mattsson, J.I.; Kulasingam, V.; Humar, A.; Mah, A.; Delisle, J.-S.; Ierullo, M.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity After a Three-Dose SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Schedule in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Transplant Cell Ther 2022, 28, 706.e1-706.e10. [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, G.; Magrì, D.; Gioria, S.; Medaglini, D.; Calzolai, L. Characterization of Nanoparticles-Based Vaccines for COVID-19. Nat Nanotechnol 2022, 17, 570–576. [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi Nejad, M.-M.; Shobeiri, P.; Dehghanbanadaki, H.; Tabary, M.; Aryannejad, A.; Haji Ghadery, A.; Shabani, M.; Moosaie, F.; SeyedAlinaghi, S.; Rezaei, N. Seroconversion Following the First, Second, and Third Dose of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Immunocompromised Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Virol J 2022, 19, 132. [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.; Koch, M.; Wu, K.; Chu, L.; Ma, L.; Hill, A.; Nunna, N.; Huang, W.; Oestreicher, J.; Colpitts, T.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Variant MRNA Vaccine Boosters in Healthy Adults: An Interim Analysis. Nat Med 2021, 27, 2025–2031. [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.R.; Painter, M.M.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Mathew, D.; Meng, W.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; Lundgreen, K.A.; Reynaldi, A.; Khoury, D.S.; Pattekar, A.; et al. MRNA Vaccines Induce Durable Immune Memory to SARS-CoV-2 and Variants of Concern. Science 2021, 374, abm0829. [CrossRef]
- Pettini, E.; Medaglini, D.; Ciabattini, A. Profiling the B Cell Immune Response Elicited by Vaccination against the Respiratory Virus SARS-CoV-2. Frontiers in Immunology 2022, 13.
- Terreri, S.; Piano Mortari, E.; Vinci, M.R.; Russo, C.; Alteri, C.; Albano, C.; Colavita, F.; Gramigna, G.; Agrati, C.; Linardos, G.; et al. Persistent B Cell Memory after SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination Is Functional during Breakthrough Infections. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 400-408.e4. [CrossRef]
- Kotaki, R.; Adachi, Y.; Moriyama, S.; Onodera, T.; Fukushi, S.; Nagakura, T.; Tonouchi, K.; Terahara, K.; Sun, L.; Takano, T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron-Neutralizing Memory B Cells Are Elicited by Two Doses of BNT162b2 MRNA Vaccine. Science Immunology 2022, 7, eabn8590. [CrossRef]
- Andreano, E.; Paciello, I.; Piccini, G.; Manganaro, N.; Pileri, P.; Hyseni, I.; Leonardi, M.; Pantano, E.; Abbiento, V.; Benincasa, L.; et al. Hybrid Immunity Improves B Cells and Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Nature 2021, 600, 530–535. [CrossRef]
- Hui, D.S. Hybrid Immunity and Strategies for COVID-19 Vaccination. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2022, 0. [CrossRef]
- Akkaya, M.; Kwak, K.; Pierce, S.K. B Cell Memory: Building Two Walls of Protection against Pathogens. Nat Rev Immunol 2020, 20, 229–238. [CrossRef]
- Palm, A.-K.E.; Henry, C. Remembrance of Things Past: Long-Term B Cell Memory After Infection and Vaccination. Frontiers in Immunology 2019, 10.
- Papadopoulou, A.; Stavridou, F.; Giannaki, M.; Paschoudi, K.; Chatzopoulou, F.; Gavriilaki, E.; Georgolopoulos, G.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Yannaki, E. Robust SARS-COV-2-Specific T-Cell Immune Memory Persists Long-Term in Immunocompetent Individuals Post BNT162b2 Double Shot. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09863. [CrossRef]
- Tarke, A.; Coelho, C.H.; Zhang, Z.; Dan, J.M.; Yu, E.D.; Methot, N.; Bloom, N.I.; Goodwin, B.; Phillips, E.; Mallal, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination Induces Immunological T Cell Memory Able to Cross-Recognize Variants from Alpha to Omicron. Cell 2022, 185, 847-859.e11. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Mateus, J.; Coelho, C.H.; Dan, J.M.; Moderbacher, C.R.; Gálvez, R.I.; Cortes, F.H.; Grifoni, A.; Tarke, A.; Chang, J.; et al. Humoral and Cellular Immune Memory to Four COVID-19 Vaccines. Cell 2022, 185, 2434-2451.e17. [CrossRef]
- Pušnik, J.; König, J.; Mai, K.; Richter, E.; Zorn, J.; Proksch, H.; Schulte, B.; Alter, G.; Streeck, H. Persistent Maintenance of Intermediate Memory B Cells Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Vaccination Recall Response. J Virol 96, e00760-22. [CrossRef]
- Sette, A.; Crotty, S. Immunological Memory to SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Vaccines. Immunological Reviews 2022, 310, 27–46. [CrossRef]
- Sokal, A.; Chappert, P.; Barba-Spaeth, G.; Roeser, A.; Fourati, S.; Azzaoui, I.; Vandenberghe, A.; Fernandez, I.; Meola, A.; Bouvier-Alias, M.; et al. Maturation and Persistence of the Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Memory B Cell Response. Cell 2021, 184, 1201-1213.e14. [CrossRef]
- Ciabattini, A.; Pastore, G.; Fiorino, F.; Polvere, J.; Lucchesi, S.; Pettini, E.; Auddino, S.; Rancan, I.; Durante, M.; Miscia, M.; et al. Evidence of SARS-Cov-2-Specific Memory B Cells Six Months after Vaccination with BNT162b2 MRNA Vaccine; 2021; p. 2021.07.12.21259864;
- Kim, W.; Zhou, J.Q.; Horvath, S.C.; Schmitz, A.J.; Sturtz, A.J.; Lei, T.; Liu, Z.; Kalaidina, E.; Thapa, M.; Alsoussi, W.B.; et al. Germinal Centre-Driven Maturation of B Cell Response to MRNA Vaccination. Nature 2022, 604, 141–145. [CrossRef]
- Polvere, J.; Fabbiani, M.; Pastore, G.; Rancan, I.; Rossetti, B.; Durante, M.; Zirpoli, S.; Morelli, E.; Pettini, E.; Lucchesi, S.; et al. B Cell Response Six Months after SARS-CoV-2 MRNA Vaccination in People Living with HIV under Antiretroviral Therapy 2022, 2022.07.01.22277132.
- Hahne, F.; LeMeur, N.; Brinkman, R.R.; Ellis, B.; Haaland, P.; Sarkar, D.; Spidlen, J.; Strain, E.; Gentleman, R. FlowCore: A Bioconductor Package for High Throughput Flow Cytometry. BMC Bioinformatics 2009, 10, 106. [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.R.; Roederer, M.; Moore, W.A. A New “Logicle” Display Method Avoids Deceptive Effects of Logarithmic Scaling for Low Signals and Compensated Data. Cytometry Part A 2006, 69A, 541–551. [CrossRef]
- van der Maaten, L.; Hinton, G. Viualizing Data Using T-SNE. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2008, 9, 2579–2605.
- Van Gassen, S.; Callebaut, B.; Van Helden, M.J.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Demeester, P.; Dhaene, T.; Saeys, Y. FlowSOM: Using Self-Organizing Maps for Visualization and Interpretation of Cytometry Data. Cytometry A 2015, 87, 636–645. [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Xu, A.; Li, J.; Wu, L.; Yu, S.; Chen, J.; Zhao, W.; Sun, X.-J.; Huang, J. CytoTree: An R/Bioconductor Package for Analysis and Visualization of Flow and Mass Cytometry Data. BMC Bioinformatics 2021, 22, 138. [CrossRef]
- Leek, J.T.; Johnson, W.E.; Parker, H.S.; Jaffe, A.E.; Storey, J.D. The Sva Package for Removing Batch Effects and Other Unwanted Variation in High-Throughput Experiments. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 882–883. [CrossRef]
- Malek, M.; Taghiyar, M.J.; Chong, L.; Finak, G.; Gottardo, R.; Brinkman, R.R. FlowDensity: Reproducing Manual Gating of Flow Cytometry Data by Automated Density-Based Cell Population Identification. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 606–607. [CrossRef]
- Lucchesi, S.; Furini, S.; Medaglini, D.; Ciabattini, A. From Bivariate to Multivariate Analysis of Cytometric Data: Overview of Computational Methods and Their Application in Vaccination Studies. Vaccines (Basel) 2020, 8. [CrossRef]
- Lucchesi, S.; Nolfi, E.; Pettini, E.; Pastore, G.; Fiorino, F.; Pozzi, G.; Medaglini, D.; Ciabattini, A. Computational Analysis of Multiparametric Flow Cytometric Data to Dissect B Cell Subsets in Vaccine Studies. Cytometry A 2020, 97, 259–267. [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.W.; Chia, W.N.; Qin, X.; Liu, P.; Chen, M.I.-C.; Tiu, C.; Hu, Z.; Chen, V.C.-W.; Young, B.E.; Sia, W.R.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 Surrogate Virus Neutralization Test Based on Antibody-Mediated Blockage of ACE2–Spike Protein–Protein Interaction. Nat Biotechnol 2020, 38, 1073–1078. [CrossRef]
- Sallusto, F.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Araki, K.; Ahmed, R. From Vaccines to Memory and Back. Immunity 2010, 33, 451–463. [CrossRef]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing Antibody Levels Are Highly Predictive of Immune Protection from Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nat Med 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F. A Correlate of Protection for SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines Is Urgently Needed. Nat Med 2021, 27, 1147–1148. [CrossRef]
- Buckner, C.M.; Kardava, L.; Merhebi, O.E.; Narpala, S.R.; Serebryannyy, L.; Lin, B.C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Assis, F.L. de; Kelly, S.E.M.; et al. Interval between Prior SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Booster Vaccination Impacts Magnitude and Quality of Antibody and B Cell Responses. Cell 2022, 185, 4333-4346.e14. [CrossRef]
- Rodda, L.B.; Morawski, P.A.; Pruner, K.B.; Fahning, M.L.; Howard, C.A.; Franko, N.; Logue, J.; Eggenberger, J.; Stokes, C.; Golez, I.; et al. Imprinted SARS-CoV-2-Specific Memory Lymphocytes Define Hybrid Immunity. Cell 2022, 185, 1588-1601.e14. [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.F.; Chambers, M.J.; Schramm, C.A.; Plyler, J.; Raab, J.E.; Kanekiyo, M.; Gillespie, R.A.; Ransier, A.; Darko, S.; Hu, J.; et al. Activation Dynamics and Immunoglobulin Evolution of Pre-Existing and Newly Generated Human Memory B Cell Responses to Influenza Hemagglutinin. Immunity 2019, 51, 398-410.e5. [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Anolik, J.; Cappione, A.; Zheng, B.; Pugh-Bernard, A.; Brooks, J.; Lee, E.-H.; Milner, E.C.B.; Sanz, I. A New Population of Cells Lacking Expression of CD27 Represents a Notable Component of the B Cell Memory Compartment in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J Immunol 2007, 178, 6624–6633. [CrossRef]
- Moir, S.; Ho, J.; Malaspina, A.; Wang, W.; DiPoto, A.C.; O’Shea, M.A.; Roby, G.; Kottilil, S.; Arthos, J.; Proschan, M.A.; et al. Evidence for HIV-Associated B Cell Exhaustion in a Dysfunctional Memory B Cell Compartment in HIV-Infected Viremic Individuals. Journal of Experimental Medicine 2008, 205, 1797–1805. [CrossRef]
- Weiss, G.E.; Crompton, P.D.; Li, S.; Walsh, L.A.; Moir, S.; Traore, B.; Kayentao, K.; Ongoiba, A.; Doumbo, O.K.; Pierce, S.K. Atypical Memory B Cells Are Greatly Expanded in Individuals Living in a Malaria-Endemic Area. The Journal of Immunology 2009, 183, 2176–2182. [CrossRef]
- Colonna-Romano, G.; Bulati, M.; Aquino, A.; Pellicanò, M.; Vitello, S.; Lio, D.; Candore, G.; Caruso, C. A Double-Negative (IgD-CD27-) B Cell Population Is Increased in the Peripheral Blood of Elderly People. Mech Ageing Dev 2009, 130, 681–690. [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt, G.R.A.; Hsu, J.T.; Gartland, L.; Leu, C.-M.; Zhang, S.; Davis, R.S.; Cooper, M.D. Expression of the Immunoregulatory Molecule FcRH4 Defines a Distinctive Tissue-Based Population of Memory B Cells. Journal of Experimental Medicine 2005, 202, 783–791. [CrossRef]
- Sutton, H.J.; Aye, R.; Idris, A.H.; Vistein, R.; Nduati, E.; Kai, O.; Mwacharo, J.; Li, X.; Gao, X.; Andrews, T.D.; et al. Atypical B Cells Are Part of an Alternative Lineage of B Cells That Participates in Responses to Vaccination and Infection in Humans. Cell Reports 2021, 34. [CrossRef]
- Fiorino, F.; Sicuranza, A.; Ciabattini, A.; Santoni, A.; Pastore, G.; Simoncelli, M.; Polvere, J.; Galimberti, S.; Auddino, S.; Baratè, C.; et al. The Slower Antibody Response in Myelofibrosis Patients after Two Doses of MRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Calls for a Third Dose. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1480. [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, E.M.; Nelli, F.; Giannarelli, D.; Fabbri, A.; Giron Berrios, J.R.; Virtuoso, A.; Marrucci, E.; Mazzotta, M.; Schirripa, M.; Signorelli, C.; et al. Dynamic Changes in Peripheral Lymphocytes and Antibody Response Following a Third Dose of SARS-CoV-2 MRNA-BNT162b2 Vaccine in Cancer Patients. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 21908. [CrossRef]
- Notarte, K.I.; Guerrero-Arguero, I.; Velasco, J.V.; Ver, A.T.; Santos de Oliveira, M.H.; Catahay, J.A.; Khan, M.S.R.; Pastrana, A.; Juszczyk, G.; Torrelles, J.B.; et al. Characterization of the Significant Decline in Humoral Immune Response Six Months Post-SARS-CoV-2 MRNA Vaccination: A Systematic Review. J Med Virol 2022, 94, 2939–2961. [CrossRef]
- Sokal, A.; Broketa, M.; Barba-Spaeth, G.; Meola, A.; Fernández, I.; Fourati, S.; Azzaoui, I.; Selle, A. de L.; Vandenberghe, A.; Roeser, A.; et al. Analysis of MRNA Vaccination-Elicited RBD-Specific Memory B Cells Reveals Strong but Incomplete Immune Escape of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant. Immunity 2022, 55, 1096-1104.e4. [CrossRef]
- Munro, A.P.S.; Janani, L.; Cornelius, V.; Aley, P.K.; Babbage, G.; Baxter, D.; Bula, M.; Cathie, K.; Chatterjee, K.; Dodd, K.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of Seven COVID-19 Vaccines as a Third Dose (Booster) Following Two Doses of ChAdOx1 NCov-19 or BNT162b2 in the UK (COV-BOOST): A Blinded, Multicentre, Randomised, Controlled, Phase 2 Trial. The Lancet 2021, 398, 2258–2276. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; St Denis, K.J.; Hoelzemer, A.; Lam, E.C.; Nitido, A.D.; Sheehan, M.L.; Berrios, C.; Ofoman, O.; Chang, C.C.; Hauser, B.M.; et al. MRNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccine Boosters Induce Neutralizing Immunity against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant. Cell 2022, 185, 457-466.e4. [CrossRef]
- Muik, A.; Lui, B.G.; Wallisch, A.-K.; Bacher, M.; Mühl, J.; Reinholz, J.; Ozhelvaci, O.; Beckmann, N.; Güimil Garcia, R. de la C.; Poran, A.; et al. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron by BNT162b2 MRNA Vaccine-Elicited Human Sera. Science 2022, 375, 678–680. [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.R.; Painter, M.M.; Lundgreen, K.A.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Baxter, A.E.; Giles, J.R.; Mathew, D.; Pattekar, A.; Reynaldi, A.; Khoury, D.S.; et al. Efficient Recall of Omicron-Reactive B Cell Memory after a Third Dose of SARS-CoV-2 MRNA Vaccine. Cell 2022, 185, 1875-1887.e8. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




