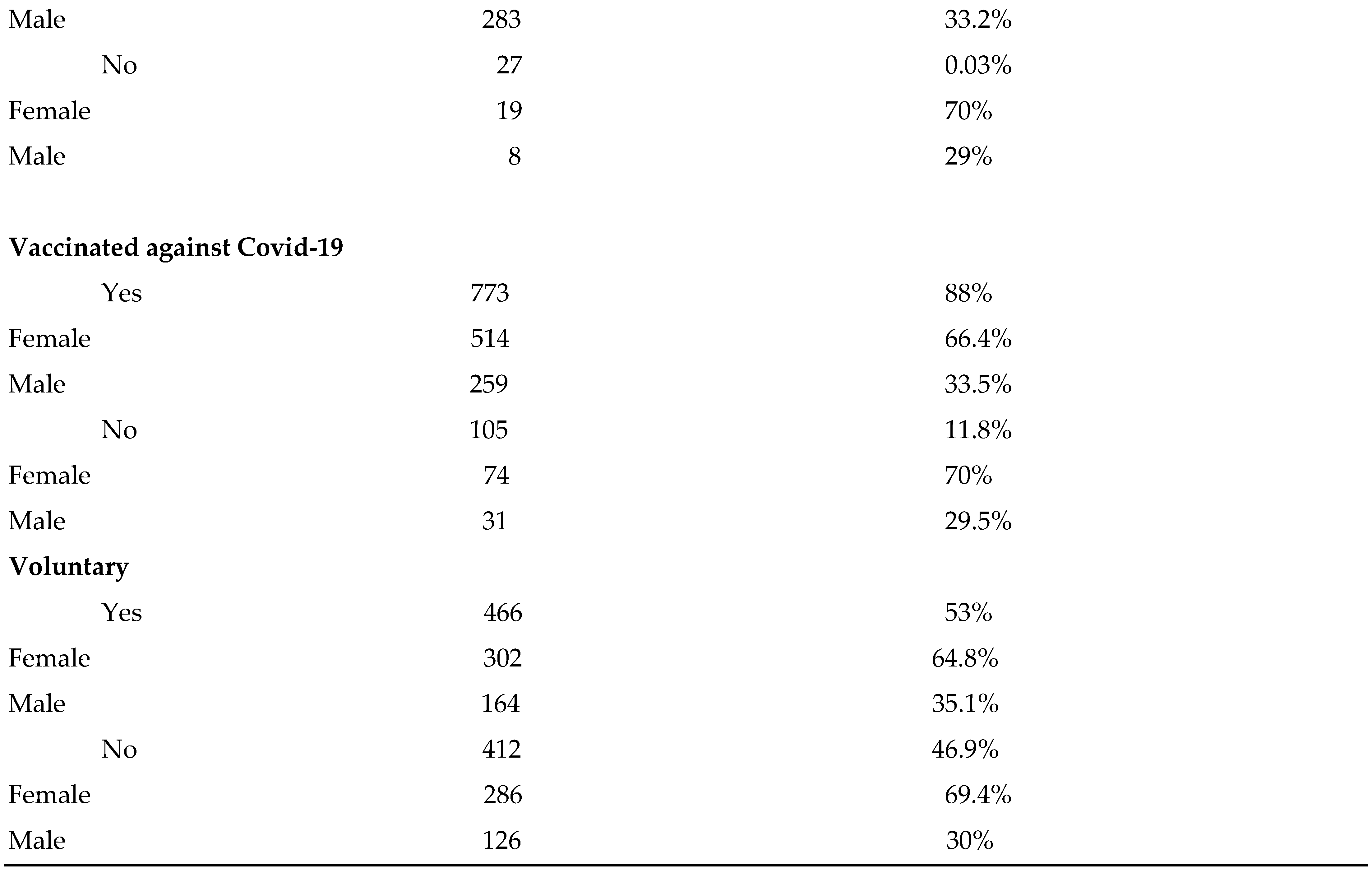1. Introduction
Covid-19 faced the world with serious health and socioeconomic issues. At the very beginning of the pandemic, the vaccine was considered by health authorities and the medical community the only way the only way to curb the spread of the virus. Efforts to enable the vaccine was documented by WHO, counting on April 26 seven candidate vaccines in the clinical evaluation phase [
1]. Regardless the crucial role vaccination plays in preventing infectious diseases, vaccine hesitancy (VH) that “refers to delay in acceptance or refusal of vaccination despite availability of vaccination services” was recognized by WHO as “one of the top-ten threats for global health” [
2]. Hence, although a vaccine was not available, researchers worldwide started evaluating the rate of VH and VA (vaccine acceptance) for the possible Covid-19 vaccine [
3,
4,
5]. Almost in accordance, besides evaluating different target groups, safety-related fear, lack of adequate information and conspiracy, were acknowledged as vaccination hindering factors [
6,
7,
8].
For many reasons related to disease severity, crucial role in preventing spread of infection [
9] previous vaccine hesitancy [
10,
11], many studies focused on students. The overall rate of COVID-19 VH among 31,948 college/university students around the world was 22% with contributing factors like general population i.e. safety related fear and misinformation [
12].
Even the field of study, especially medicine related was taken into consideration as a factor toward vaccination attitude [
13,
14,
15]. Bearing in mind that those students are future medical personnel, which with their attitude may impact people’s vaccination [
7], the study of this target group becomes even more important. In this context, the reported data on vaccination of healthcare students seems to provide optimistic results [
16,
17]. Regardless, higher expectations, VH were reported in medicine related students. The 22.5% VH rate among dental students worldwide was related with socioeconomic factors, social media and insufficient knowledge [
18]. In another review, 25.8% VH rate was reported among healthcare students concerned about side effects [
19].
The recognition of vaccine hesitancy posed a barrier to the successful implementation of vaccination, hence mandatory policy were included among measures to increase vaccination. Mills[
20] suggested that mandatory certification could be one mechanism to increase uptake among younger people and certain groups such as men and those from low socioeconomic backgrounds to reach population-level immunity and protect the broader population. Graeber [
21] stated that a mandatory vaccination would almost certainly achieve herd immunity against Covid-19 since all those for whom there is no medical contraindication would also get vaccinated.
On March 9,2020 the day of confirmed first case infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Albania, Universities among other education institutions were closed initially for two weeks but this restrictive measure was extended so that the second semester of the 2019-2020 academic year was concluded by means of online lecture. Regarding the academic year 2020-2021, health authorities considered that reopening of the Universities would increase Covid-19 transmission so the whole year was concluded online. Vaccination in Albania began on December 2020 with a target group of healthcare workers. In August 2021, in Albania 23.6% of population had received at least one dose of Covid-19 vaccine [
22] hence mandatory vaccination was announced for all healthcare workers, teachers and students over 18, and facilities were adopted to better assist students [
23]. The announcement regarding the mandatory policy was not supported by the students [
24].
There is a lack of information for Albanian Students’ attitudes toward Covid-19 vaccination. In the study performed by Patelarou [
25] assessing nursing students from 7 countries, 32.6% Albanian students including Albania among 313 students responded positively to vaccination and was considered among the lowers. Understanding factors that contribute to vaccine acceptance and hesitancy could help in improving vaccination campaigns. The purpose of this study was to compare determinants of voluntary and mandatory vaccination students of Albanian University.
2. Materials and Methods
This cross-sectional study was conducted among students of Albanian University (AU), Tirana, Albania during the last week of the winter semester from 7 to 14 Feb 2022. AU is a private University with 3849 students (2471females and 1378 males), attending three Faculties: Faculty of Medical Science (MS) which includes (dentistry, pharmacy, nursery, dental technician) 2150 (1568 females, 582 males) students, Faculty of Applied Sccience and Economics (ASE) 1092 (433 females, 659 males), and Faculty of Social Science (SS) 607 (470 females, 137 males) students.
The questionnaire was developed according to WHO [
26] guidelines and after an extensive literature review [
13,
14,
27,
28]
It consisted of 25 close-ended questions addressing: 1) demographic (gender, age, study program); 2) Covid-19 related health experiences, fear at the beginning of pandemics, fear of life if affected, observance of protective measures, infected with Covid-19, severity of illness experienced in the family, major source of information. 3) Attitude toward vaccination. Vaccinated or not against Covid-19, did they vaccinate voluntary or they were vaccinated because the mandatory policy, influence from classmates, intention to recommend vaccination to others, encouragement from academic staff, hesitation over unsafe and ineffective vaccine. No particular vaccine name was included.
A Microsoft Form Link containing the questionnaire was emailed to a total of 3849 students enrolled in the academic year 2021-2022. To be enrolled in any study program offered from AU was the only inclusion criteria for the study. The email containing the link had also information regarding the study and students were asked to fill the form only once. The form was designated to accept answers from 7-14 February 2022 the last week of winter semester. Postponement was also foreseen if there were not enough answers. During the week, the form was active, 3 email remainders were sent. By the end of the week 934 returned forms was considered optimal so there was no need to postpone acceptance.
The statistical analyses were evaluated by SPSS 26. The mean and standard deviation were used for the description of the continuous variables taken in the study and frequencies for categorical variables. Statistical method used hypothesis testing for the equality of proportion using the standard values methods. The level of significance alfa 5%.
Ethical Issues
The study was conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethic Committee of Albanian University ref No 66, date 31.01.2022.
Participation was voluntary and return of the questionnaire were accepted as a form of individual consent to participate in the survey. Students were informed of the withdrawing possibility, with no other consequences on their status or grades. No incentives were offered for taking part in this study.
3. Results
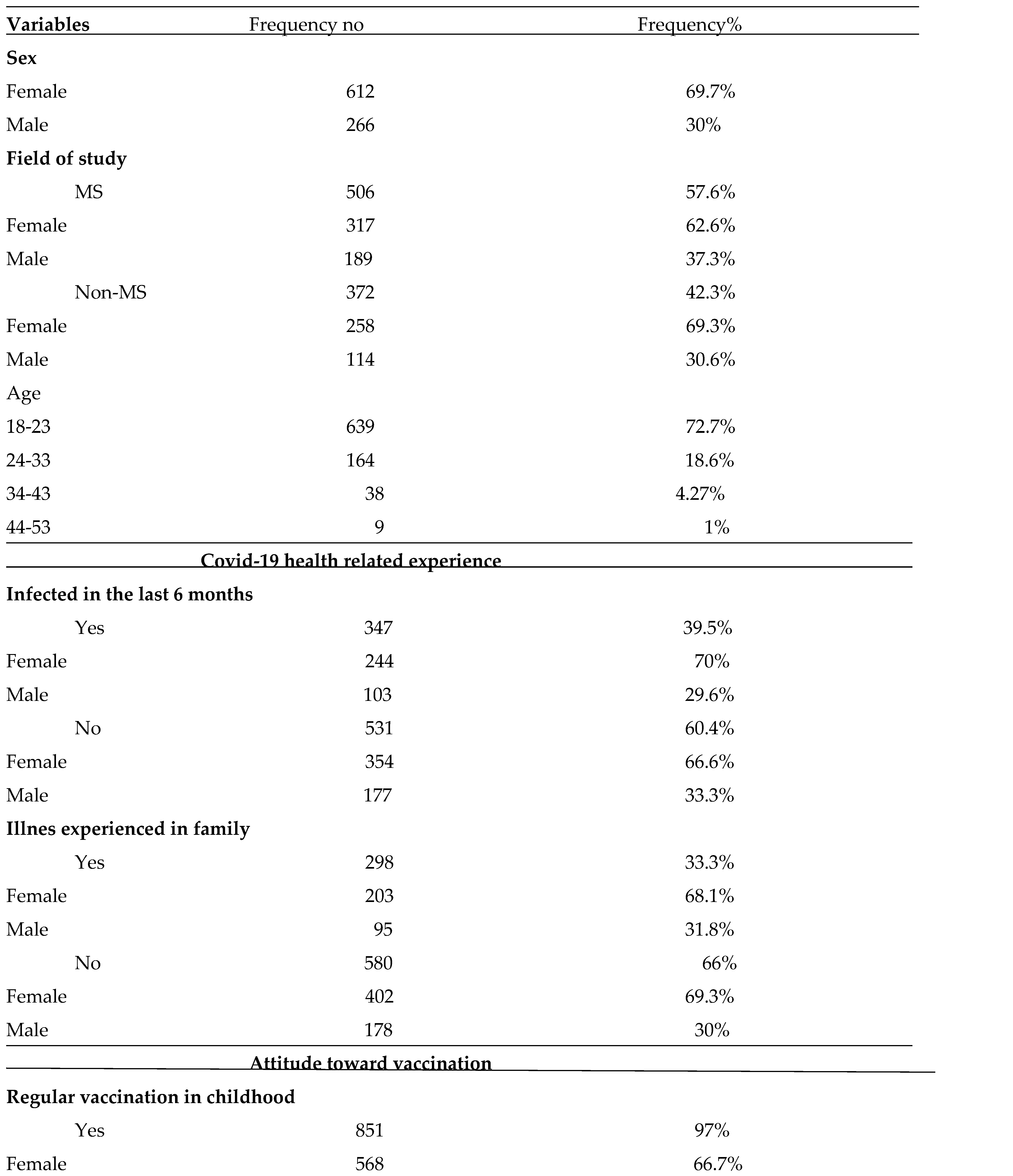
From the 934 questionnaires received (56 were not considered eligible since 45 had incomplete answers, 11 did not report sex) 878 was included in the study. Among them 612 (68.8%) were females, 266 (29.2%) were male students. The average age included in the study is 22.76 years with a minimum of 18 years and a maximum of 29 years, with a standard deviation of 5.336 years. The majority 72.89% belonged to 18-23years. According to the study field 506 (57.6%) of the participants were enrolled in MS (Medical Sciences students enrolled in one of the study program of Faculty of Medical Science), 372 (42.3%) were Non-Ms (Non-Medical Science students enrolled in one of study program of Faculty of Applied and Economic Science and Social Science).
Covid-19 related health experiences are shown in
Table 1. 347(37.8%) students were infected in the last 6 months. 298(33.3%) stated that they have experienced SarsCov2 disease in the family.
With regard to attitude toward vaccination result as shown in
Table 1, 851 (97%) had regular vaccination in childhood. 773 (86.8%) were vaccinated against Covid-19, 105 (11.8%) were not vaccinated. Based on the definition of VH the sample was divided in two groups those that declared mandatory vaccination VH group 412 (46.9%), while those vaccinated voluntary VA group 466 (53%). To compare attitude toward vaccination according the study field, students of VH and VA group were divided in MS and Non-Ms. subgroups.
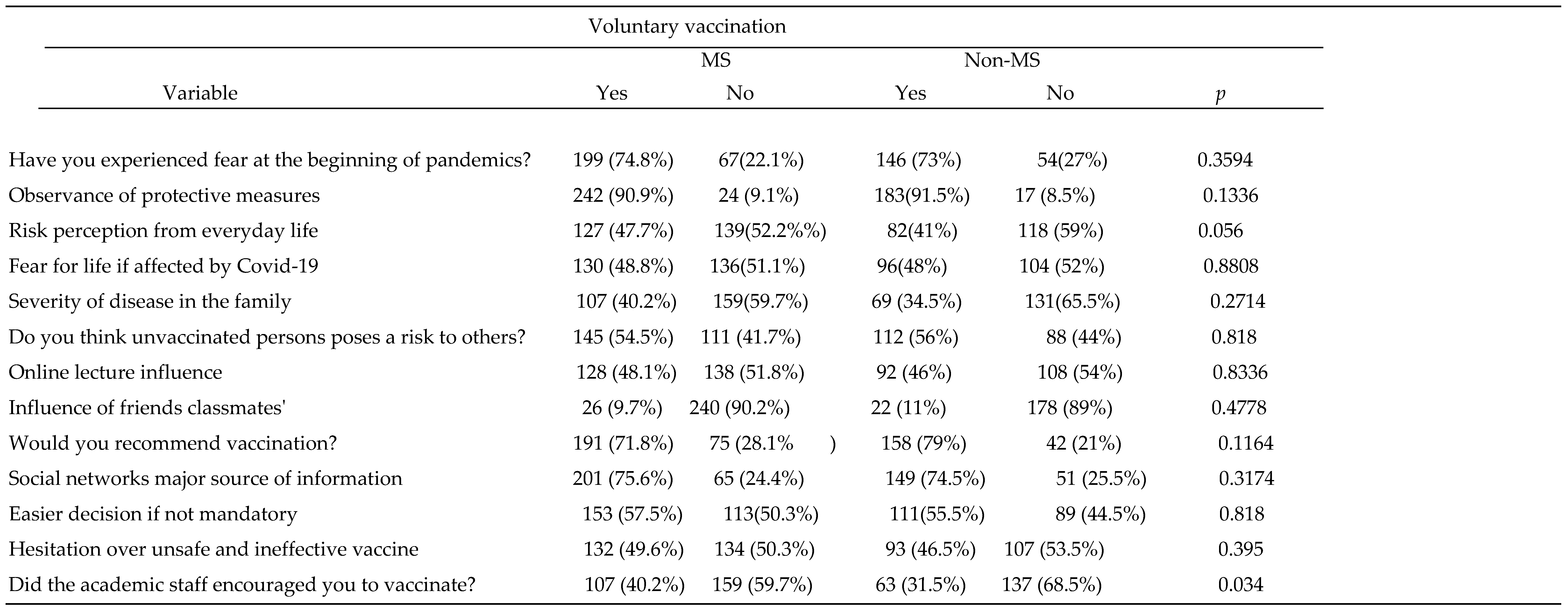
In
Table 2 we present results obtained after comparison of determinants of VA according to the field of study as MS and Non-Ms 466(53%) reported voluntary vaccination. 302(64.8%) were females, 266(57%) were form MS group. 207(77.8%) of MS students versus 146(73%) from Non-Ms group declared experiencing fear at the beginning of pandemics. With regard to observance of protective measures, the results of positive answer almost at the same level 242(90.9%) and 183(91.5%). When asked about fear of life if affected and disease severity of family members. To the question of risk from unvaccinated persons respectively 145 (54.5%) from MS and 112 (56%) from Non-Ms responded yes. When asked about the influence of friends or classmates on their vaccination decision 240 (90.2%) MS and 178 (89%) of Non-Ms responded no perceived influence. More than half students from both groups expressed their intention to recommend vaccination to friends or family members. A slight but not significant difference were observed regarded the non-vaccination of family members (p =0.3628). Interestingly almost the same results were obtained regarding the social networks as major source of information with 201(75.6%) MS and 149 (74.5%) Non-MS. Similar results also with no significant difference were observed with regard to unsafe and ineffective vaccine (p=0.395). The only significant change (p=0.034) between the groups was with regard to encouragement from the academic staff.
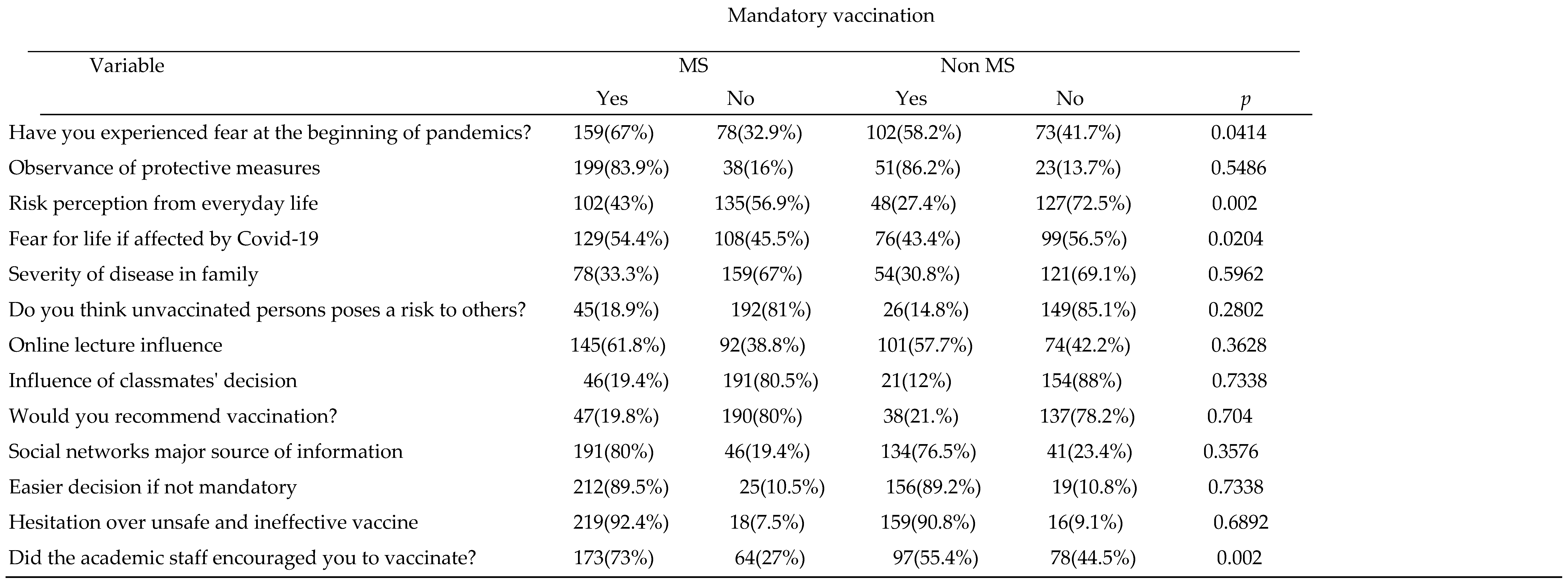
Results obtained after comparing groups if mandatory vaccination are shown in
Table 3. From 878 students that participated this study 412(46.9%) declared mandatory vaccination. 286 (69.4%) were females 126(30%) were males. As according to the study field 237(57.5%) were MS students, 175(42.4%) were Non-MS. A significant change was observed regarding fear experienced at the beginning of pandemic. 159(67%) from MS and a102(58.2%) from Non-MS answered yes. With regard to observance of protective measures MS and Non-Ms students had similar attitude reporting high levels 199 (83.9%) and 151(86.2%). MS students perceived more risk perception from everyday life p=0.002. A significant change (p=0.0204) were observed to fear of life if affected by Covid-19 more than half of Non-Ms group 99(56.5%) answered negatively, while 129(54.4%) from MS positively. 78(33.4%) from MS and 54(30.8) from Non-Ms had familiars severely affected from Covid-19. Although students from MS group 47(19.8%) versus 21(12%) Non-Ms reported a slight influence from classmates the change was not significant (p=0.7338). To the question if the decision to vaccinate would have been easier if not mandatory no significant change was observed (p=0.7338) as 212(89.5%) from MS and 156(89.2%) from Non-Ms answered yes. Similarly, there was no significant change regarding social network as major source of information (p=0.3576). From the results obtained it is obvious that students from both groups are equally hesitant over unsafe and ineffective vaccine (p=0.6892). A significant change was observed with regard to the academic staff encouragement (p=0.002) as 173(73%) students from MS group answered yes.
4. Discussion
This survey study conducted among students of Albanian University aimed to explore the factors related to mandatory and voluntary COVID-19 vaccination. Beside the mandatory policy 53% of participants of this study reported voluntary vaccination. In the majority of studies performed before the start of vaccination campaigns worldwide and large availability of vaccines students showed VA range from 52.8%, 58%, 60%, 69.3%,73.3% ,80% to 91% [
5,
13,
14,
15,
29,
30]. At the time this study was performed (Feb 2022) in Albania 44.3% of population was vaccinated [
31]. Regarding students from AU 1095 (28.4%) was vaccinated. In a previous study among Bulgarian students 61.8% of students were vaccinated while country vaccination rate was 30.2%. According to the author the reasons for the increased vaccination among students in particular MS students was the requirement of “EU Digital Certificate” and better information about benefits of vaccination [
16]. In the framework of above mentioned, 28.4% vaccination rate of AU students constitutes a serious concern.
Available literature with similar sample composition as in the current study reported rates 73.3%, 77.81% [
16,
32]. In our study 266(57%) of VA were form MS group. Meanwhile, in previous studies the field of study related to health science was linked with increased VA [
14,
15,
17,
18]. In this study a significant change related to the field of study was found in VH group (p= 0.0414) indicating that MS students perceived more fear at the beginning of pandemics and risk perception on everyday life. This may be related to differences in level of knowledge as related to study field. The perceived fear and risk according to [
17,
33] were not influential factors of vaccination and was related with younger age and the large availability of vaccines at the time the study was performed. Although the results obtained from VA did not show significant change, since students in this group were vaccinated voluntary similar to [
25,
34] that considered fear experienced at the beginning of pandemics, disease severity we also can consider as factors contributing in VA.
Observance of protective measures during the pandemic period was among the questions included in this survey. Regardless of whether they were vaccinated voluntary or mandatory, the small difference shows that overall, there was a very good attitude toward observance of protective measures. In this context, our findings are not in line with Gallè et al [
34] that in a study among Albanian undergraduates found that more one third did not consider either facial masks or the disinfection of surfaces to be effective protective measures
. It is expected for students in branches related to medicine to have a more positive attitude towards infection control as they receive higher knowledge of risk factors. Results of our study show a similar observance of protective measures among MS and Non-Ms students concerning vaccination attitude either voluntary or mandatory. It was found from [
30] that VH students considered personal protection as substitute of vaccination. Furthermore, in her study among French students Tavolacci [
14] observed that negative vaccine intentions were significantly less likely engaged in the COVID-19 prevention behaviors of wearing masks and social distancing.
Concerning online lecture, a measure adopted worldwide at the beginning of pandemics, previous studies among Albanian university students the authors [
25,
35] reported that online learning was not considered by the majority of students to adequately replace in class learning and were not satisfied. Additionally, the desire to return to classroom teaching was considered as “an important driver for increased uptake of vaccine in this population” [
28]. If we take into consideration the field of study related to medicine, online learning hinders the possibility of clinical and laboratory practices, which are essential part of medical education [
36]. It is worth remembering that for the entire academic year 2020-2021 there was only online learning. Unlike expectations, more than half of MS in VA group did not consider that vaccination would enable in class learning. Interestingly, VH students, expressed more conviction that vaccination would enable the return to classroom learning.
At the beginning of the pandemic, misinformation and conspiracy theories focused on the way the virus spread and protective measures undertaken. As soon as the first vaccines began to be tested, were surrounded by misinformation and conspiracy theories. With this regard the result of this study in the VH group are in line with [
37] that apart from studying general adults’ population or students seems to agree on attributing to social media the role of misinformation about preventive attitudes and behaviors and Covid-19 vaccines. Interestingly the findings from VA both groups showed similar trend of using social networks as major information source seems to be supported from [
17] that found a positive association between social media trust and vaccination.
Surprisingly, among VH group both MS and Non-Ms students showed similar levels of knowledge in the protection offered from vaccination since almost a quarter of them declined the risk from non-vaccinated individuals. Similarly, they were not willing to recommend vaccination to family or friends. On the other side, among students that vaccinated voluntary, this study did not find a significant change related to the field of study in neither knowledge related protection nor in willingness to recommend vaccination [
38].
Students that reported voluntary vaccination had almost the same attitude, their positive and negative answers were almost divided in half to the question if the decision would have been easier if not mandatory. In their studies [
21,
39] found an agreement with the mandatory policy among those willing to get the vaccine and who would get vaccinated voluntary. 46.9% of our sample reported mandatory vaccination. As we considered this group as VH respondents the positive answer to the same question by majority of both subgroups (89.5%, 89.2%) clearly express their disagreement with the mandatory policy.
As it results from existing literature, hesitation over unsafe and ineffective vaccine was among factors contributing in VH [
3,
5,
17,
30]. In this study, contrary to [
19,
30,
39] studies where the most reported barrier safety-related was found among non-vaccinated students, hesitation over unsafe and ineffective vaccine was found among voluntary vaccinated students of both subgroups. Additionally, no significant changes were observed related to the field study thus similar to [
38]
The results of this study showed that, although MS students from VH perceived encouragment from academic staff, they still did not embrace themselves toward voluntary vaccination [
28]. The significant change in VA group as regards perceived encouragement from academic staff is supported by [
5,
7,
33] attribuiting medical academic staff a crucial role in increasing VA.
This study has its limitations. As with all similar studies, self-reporting data may report bias. It was impossible to have an equally distributed sample with regard to sex and study program, which in turn may lead to selection bias. To not oversize the questionnaire, we did not include questions about socioeconomic status, place of living. This could have generated enlarged conclusions. In our opininion, another limitation is related with the missing data from our country regarding VH and VA among general population, that’s shrinks the conclusions. Besides its limitation, we strongly believe that this study provides important information regarding factors that affect student’s decision to vaccinate, especially considering the lack of such information in our country.
5. Conclusions
This survey study conducted among Albanian University students provides valuable knowledge about the factors related to vaccination against COVID-19.
Vaccine safety and efficacy were hindering factors of vaccination. Also, based on the results of this study, the students felt encouraged to vaccinate by the academic staff. This clearly demonstrates that the staff does not lack the skills to enhance students' knowledge about the risk of infectious diseases and the importance of vaccination. Therefore, to influence as much as possible students’ attitude toward vaccination, comprehensive educational programs including modification of existing curricula should be considered.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.E and SH.K.; methodology, X.S.; software, V.U and M.E validation, K.E., D.A. and S.Y.; formal analysis, K.E.; investigation, K.E.; resources, SH.K.; data curation, SH.K writing—original draft preparation, K.E.; writing—review and editing, X.S.; visualization, S.Y.; supervision, K.E.
Funding
“This research received no external funding”.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all the students that participated, and Administrative Bord for the support.
Conflicts of Interest
“The authors declare no conflict of interest.”.
References
- World Health Organization (WHO): Draft of the landscape of COVID-19 candidate vaccines. Available online: https: //www.who.int (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- MacDonald, Noni E, and SAGE Working Group on Vaccine Hesitancy. “Vaccine hesitancy: Definition, scope and determinants.” Vaccine 2015, 33,34: 4161-4. [CrossRef]
- Dror AA, Eisenbach N, Taiber S, et al Vaccine hesitancy: the next challenge in the fight against COVID-19Eur J Epidemiol 2020, 35:775-779. [CrossRef]
- Reiter PL, Pennell ML, Katz ML Acceptability of a COVID- 19 vaccine among adults in the United States: how many people would get vaccinated? Vaccine 2020, 38:6500-6507. [CrossRef]
- Mant M, Aslemand A, Prine A, Jaagumägi Holland A University students' perspectives, planned uptake, and hesitancy regarding the COVID-19 vaccine: A multi-methods study. PLoS One 2021, 3;16: e0255447. [CrossRef]
- Kuhn SAK, Lieb R, Freeman D, Andreou C, Zander- Schellenberg T Coronavirus conspiracy beliefs in the German-speaking general population: endorsement rates and links to reasoning biases and paranoia. Psychol Med 2021, 16;1–15. [CrossRef]
- Dowdle, Travis S., et al "Intention to Receive COVID-19 Vaccine by US Health Sciences University Employees. Journal of Primary Care & Community Health 2021. 12; 21501327211036611. [CrossRef]
- Sallam, Malik. "COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy worldwide: a concise systematic review of vaccine acceptance rates." Vaccines 9.2 2021: 160. [CrossRef]
- Boehmer TK, DeVies J, Caruso E, et al. Changing Age Distribution of the COVID-19 Pandemic- United States, May-August 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep; 69:1404-1409. [CrossRef]
- Dubé E, Vivion M, MacDonald NE Vaccine hesitancy, vaccine refusal and the anti-vaccine movement: influence, impact and implications. Expert Rev Vaccines 2015, 14:99-117. [CrossRef]
- Barnard, M., George, P., Perryman, M. L., & Wolff, L. A. (2017) Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine knowledge, attitudes, and uptake in college students: Implications from the Precaution Adoption Process Model. PLoS ONE, 8;12: e0182266. [CrossRef]
- Khubchandani, Jagdish, et al "COVID-19 vaccination refusal among college students: global trends and action priorities." Brain Behav Immun 2022, 99: 218-222. [CrossRef]
- Barello, Serena, et al "‘Vaccine hesitancy’ among university students in Italy during the COVID-19 pandemic." European journal of epidemiology 2020, 8; 35:781-783. [CrossRef]
- Tavolacci, M.P.; Dechelotte, P.; Ladner, J COVID-19 Vaccine Acceptance, Hesitancy, and Resistancy among University Students in France. Vaccines 2021,5; 9:654. [CrossRef]
- Taye BT, Amogne FK, Demisse TL, Zerihun MS, Kitaw TM, Tiguh AE, Mihret MS, Kebede AA Coronavirus disease (2019) vaccine acceptance and perceived barriers among university students in northeast Ethiopia: A cross-sectional study. Clin Epidemiol Glob Health 2021, 12:100848. [CrossRef]
- Moskova, M.; Zasheva, A.;Kunchev, M.; Popivanov, I.; Dimov,D.; Vaseva, V.; Kundurzhiev, T.;Tsachev, I.; Baymakova, M. Students’Attitudes toward COVID-19 Vaccination: An Inter-University Study from Bulgaria. Int. J. Environ.Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9779. [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, M., Stark, B., Werner, A.M. et al. Determinants of university students’ COVID-19 vaccination intentions and behavior. Sci Rep 2022, 12:18067. [CrossRef]
- Riad, A.; Abdulqader, H.; Morgado, M.; Domnori, S.; Košcík, M.; Mendes, J.J.; Klugar, M.; Kateeb, E.; on behalf of IADS-SCORE. GlobalPrevalence and Drivers of Dental Students’ COVID-19 VaccineHesitancy. Vaccines 2021, 9, 566. [CrossRef]
- Patwary, Muhammad Mainuddin, et al. "COVID-19 vaccine acceptance rate and its factors among healthcare students: A systematic review with meta-analysis." Vaccines 2022: 10.5 806. [CrossRef]
- Mills MC, Rüttenauer T The effect of mandatory COVID-19 certificates on vaccine uptake: synthetic-control modelling of six countries Lancet Public Health 2022, 1: e15-e22. [CrossRef]
- Graeber D, Schmidt-Petri C, Schröder C Attitudes on voluntary and mandatory vaccination against COVID-19: Evidence from Germany. PLoS ONE 2021, 16(5): e0248372. [CrossRef]
- Global Change Data Lab. Coronavirus (Covid-19) Vaccinations. Available online https://ourworldindata.org/covid vaccinations (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Exit. Vaccination centres to be set up at Albanian universities. Available online https://exit.al/en (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Exit. Survey reveals majority of Albanian university students against mandatory vaccines Available online https://exit.al/en (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Patelarou E, Galanis P, Mechili EA, Argyriadi A, Argyriadis A, Asimakopoulou E, Brokaj S, Bucaj J, Carmona-Torres JM, Cobo-Cuenca AI, Doležel J, Finotto S, Jarošová D, Kalokairinou A, Mecugni D, Pulomenaj V, Saliaj A, Sopjani I, Zahaj M, Patelarou Factors influencing nursing students' intention to accept COVID-19 vaccination: A pooled analysis of seven European countries. Nurse Educ Today 2021, 9; 104:105010. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO) Survey tool and guidance: rapid, simple, flexible behavioral insights on COVID-19. Available online: https: //www.who.int (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Larson, H. J., Jarrett, C., Schulz, W. S., Chaudhuri, M., Zhou, Y., Dube, E., Schuster, M., MacDonald, N. E., Wilson, R., & SAGE Working Group on Vaccine Hesitancy Measuring vaccine hesitancy: The development of a survey tool. Vaccine 2015. 33(34), 4165–4175. [CrossRef]
- Kecojevic A, Basch CH, Sullivan M, Chen YT, Davi NK COVID-19 Vaccination and Intention to Vaccinate Among a Sample of College Students in New Jersey J Community Health 2021, 46:1059-1068. [CrossRef]
- Riad, A.; Pokorná, A;Antalová, N.; Krobot, M.; Zviadadze,N.; Serdiuk, I.; Košˇcík, M.; Klugar, M.Prevalence and Drivers of COVID-19Vaccine Hesitancy among CzechUniversity Students: NationalCross-Sectional Study Vaccines 2021, 9, 948. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Dean J, Yin Y, Wang D, Sun Y, Zhao Z, Wang J. Determinants of COVID-19 Vaccine Acceptance and Hesitancy: A Health Care Student-Based Online Survey in Northwest China. Front Public Health 2022, 6; 9:777565. [CrossRef]
- Global Change Data Lab. Coronavirus (Covid-19) Vaccinations. Available online https://ourworldindata.org/covid vaccinations (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Hilverda, Femke, and Manja Vollmann. "The role of risk perception in students’ COVID-19 vaccine uptake: a longitudinal study." Vaccines 2021: 10.1:22. [CrossRef]
- Dafogianni C, Kourti FE, Koutelekos I, et al. Association of University Students' COVID-19 Vaccination Intention with Behaviors toward Protection and Perceptions Regarding the Pandemic. Medicina (Kaunas)2022;58(10):1438. [CrossRef]
- Gallè, F.; Veshi, A.; Sabella, E.A.; Çitozi, M.; Da Molin, G.; Ferracuti, S.; Liguori, G.; Orsi, G.B.; Napoli, C.; Napoli C 8Awareness and Behaviors Regarding COVID-19 among Albanian Undergraduates. Behav. Sci 2021. 31:11-45. [CrossRef]
- Xhelili, Paola, et al. "Adaptation and perception of online learning during COVID-19 pandemic by Albanian university students." International Journal on Studies in Education 202: 3.2 103-111. [CrossRef]
- Antoniadou, Maria, Christos Rahiotis, and Afrodite Kakaboura. "Sustainable Distance Online Educational Process for Dental Students during COVID-19 Pandemic." International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022: 19.15 :9470. [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Zeballos Rivas DR, Lopez Jaldin ML, Nina Canaviri B, Portugal Escalante LF, Alanes Fernández AMC, Aguilar Ticona JP. Social media exposure, risk perception, preventive behaviors and attitudes during the COVID-19 epidemic in La Paz, Bolivia: A cross sectional study. PLoS One. 2021 Jan 22;16(1): e0245859. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Liyan, et al. "Medical and non-medical students’ knowledge, attitude and willingness towards the COVID-19 vaccine in China: a cross-sectional online survey." Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics 2022: 18.5 2073757. [CrossRef]
- Lucia, Victoria C., Arati Kelekar, and Nelia M. Afonso. "COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among medical students." Journal of public health 2021,3: 445-449. [CrossRef]
Table 1.
General description of the sample, COVID 19 related health experience and attitude toward vaccination.
Table 1.
General description of the sample, COVID 19 related health experience and attitude toward vaccination.
Table 2.
Comparison between MS and Non-Ms in VA group.
Table 2.
Comparison between MS and Non-Ms in VA group.
Table 3.
Comparison between MS and Non-Ms in VH group.
Table 3.
Comparison between MS and Non-Ms in VH group.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).