1. Introduction
Diabetes Mellitus is metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia which due to the disorder action of insulin on the target organ or its secretion from pancreatic β-cell. Hyperglycemia induces oxidative stress, which contributes to diabetic complications such as retinopathy, nephropathy, neurophaty, atherosclerosis, stroke and cardia cell damage [
1,
2].
This condition of oxidative stress results from ROS (O
2-, OH
- and H
2O
2) overproduction and decreasing the antioxidant enzyme (SOD, GPx, Catalase) formation which has an important role in diabetes complications. [
3,
4]. ROS are chemical molecules containing one or more unpaired electrons that can interfere with the normal signaling process. These ROS cause cellular damage through their unpaired electron by triggering the oxidant of the molecule and cellular components such as cell membrane, protein and DNA which accelerate occurring diabetic complications such as diabetic cardiopathy. In normal physiological processes will produce ROS which has a role in cell signaling and tissue homeostasis. However, excessive production ROS will oxidize lipids, protein, and DNA that are detrimental to cell component so that they cause necrosis and apoptosis. Overproduction ROS will activate the process of lipid peroxidation in polyunsaturated fats (PUFA) of cell membrane which produce lipid peroxide or MDA. High levels of MDA indicate elevated ROS production which causes cardiac cells damage [
8,
9,
10]. MDA can be used to assess ROS in diabetes melitus.
In addition, oxidative stress can inhibit Nrf2 from Keap1 and inactivates the antioxidant response element (ARE). This will further decrease the production of antioxidative enzymes, such as SOD, GPx and Catalase. Nrf2 expression and activity are the primary transcription factor that control the production of endogenic antioxidative enzymes for maintaining cellular redox homeostasis [
5,
6,
7].
The use of STZ in a diabetic rat model causes cardiac cell damage, which can increase level of CK-MB and LDH in the serum. Therefore level of CK-MB and LDH in serum can be used as marker of cardiac function disorder [
11,
12,
13]. Administration of STZ also can increase MDA levels, and decrease Nrf2 expression, SOD and GPx levels.
Previous research showed the benefits and potential of some medicinal herbal in dealing with antioxidant in both the treatment of diabetes and its complication. Referring to the world ethnobotany reports, about 800 medicinal herbal, including
S. macrophylla, are used as traditional treatment for diabetes, since they are considered to have better efficacy with fever side effects, and are affordable. S. macrophylla has become of great interest and has been used as traditional diabetes treatment and its complication. Moreover, hypoglycemic and antioxidant activity of
S. macrophylla are supported by evidence from experimental studies [
14,
15]. Herbal medicine antioxidants are widely used as an alternative exogenous antioxidant to protect cardiac cell in diabetic rats [
16,
17,
18].
S. macrophylla is an herbal medicine that has a strong antioxidant effect, and can scavenge ROS so that it can inhibit oxidative stress. The phytochemical analysis of S. macrophylla seeds showed the presence of alkaloids, flavonoid, saponin, tannins and phenolic compounds which may the active compounds [
19,
20]. Furthermore, typical phenolic that possess antioxidant activity are mainly phenolic acid, flavonoid and tannins, which is able to neutralize free radicals.
S. macrophylla also has several pharmacological effects, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral, antifungal, antibacterial, immunomodulatory, and antidiabetes [
21,
22,
23].
Common problem in natural product antioxidants are bioavailability, solubility, absorpsion and distribution it. To overcome this problem is conducted the development of nanotechnology to make dosage nanoparticles of natural product antioxidant. Nanobiotechnology is a technology where substance particles are made on the nanosize 10-1000 nm [
24,
25,
26,
27]. The use nanotechnology is expected can increase therapeutic effects and reduce the toxicity of natural product antioxidant. Considering the anti-diabetes properties and antioxidant activities of
S. macrophylla, therefore in the current study was conducted to prove the antioxidant activity of
S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles as a protector against STZ-induced cardiac cell damage.
2. Results
2.1. Qualitative Phytochemicals Analysis of S. macrophylla Extract Nanoparticles
The qualitative phytochemical testing of bioactive compounds for the
S. macrophylla Nanoparticles were presented in
Table 1. The finding showed that the phytochemical compounds of
S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles contained Saponin, Flavonoids, alkaloids, phenolics, and tannins. The data reveals that the strong positive results were found for alkaloids, flavonoids and phenolics.
2.2. Quantitative Phytochemicals Analysis of S. macrophylla Extract Nanoparticles
Determination of the quantity of total phenols, flavonoids, alkaloids of S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles has been undertaken as per methods reported in literature. The results showed that the S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles had a total phenolic content (59.23 ± 2.41 mg GAE/g extract), flavonoids (41.75 ± 3.42 mg QE/extract) and alkaloids ( 22.61 ± 1.97 mg CoE/g extract) respectively.
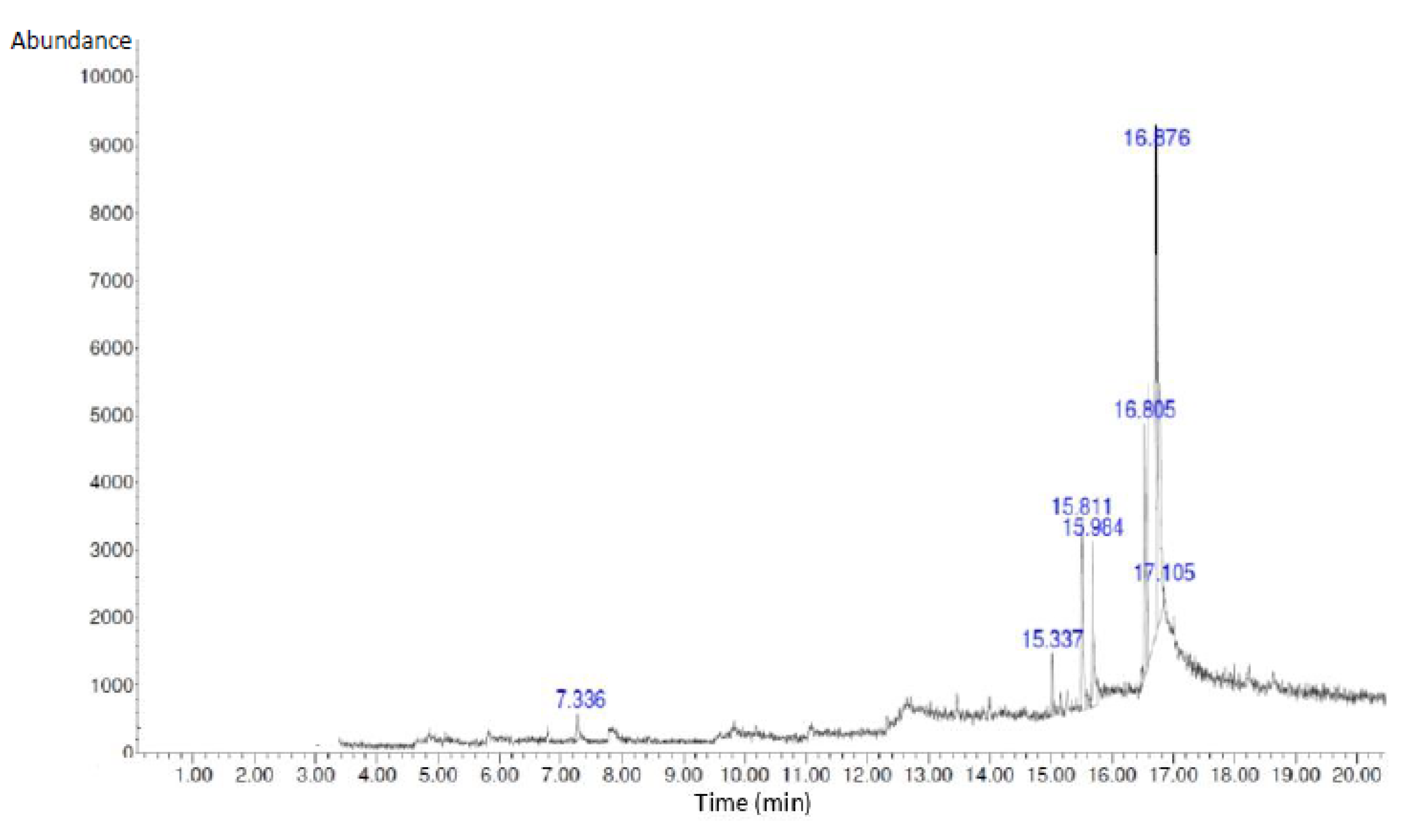
2.3. GC-MS Analysis of Bioactive Compounds in S. macrophylla Extract Nanoparticles
GC-MS analysis was performed for bioactive compounds profiling in
S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles were presented in
Figure 1 and
Table 2. Seven compounds were characterized in the S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles by GC-MS namely 1-Heptanol,4-methyl, Dihexylsulfide, Phenol,2,4-bis(1,1-dimethyl), imidazole-4,5-d2, Piperidine, 7-Hexadecene, and 1-Heptadecanol respectively
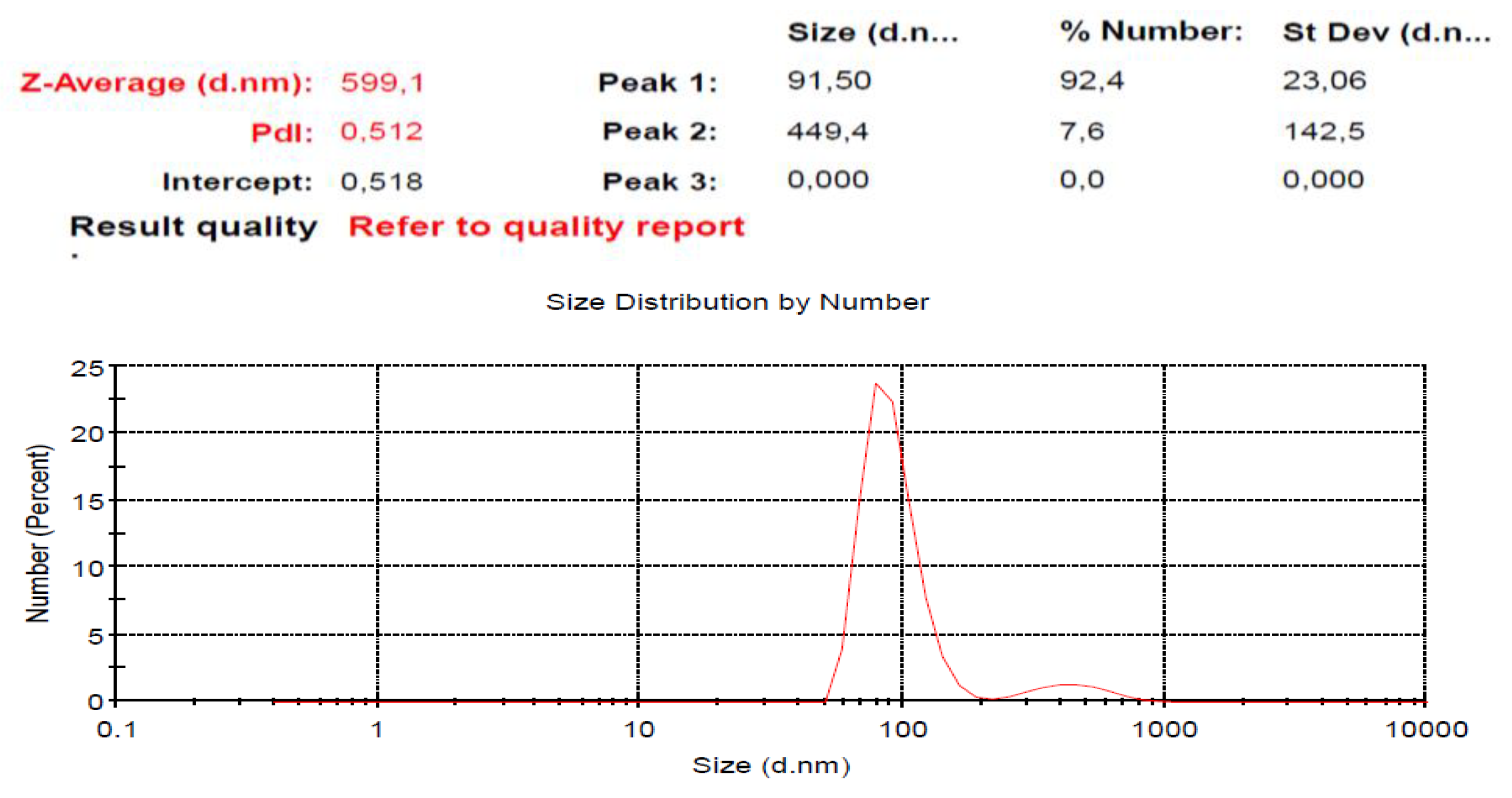
2.4. The Size Distribution of S. macrophylla Extract Nanoparticles
This research was designed to investigate the protective mechanism pathway of
S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles against STZ-induced cardiac tissue damage in rats. Characterization by DLS showed that the distribution of the
S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles size is 91.50 ± 23.06, as seen in
Figure 2.
2.5. S. macrophylla Extract Nanoparticles Effect on Level of CK-MB and LDH in Serum of Diabetic Rats
The serum CK-MB and LDH levels can be used to identify dysfunction and cardiac cell damage.
S. microphylla nanoparticles effect on the level of CK-MB and LDH in the serum of diabetic rats is shown in
Table 3. The intraperitoneally injection of STZ significantly increase the level of CK-MB and LDH in serum when compared with the control rats (p<0.05). However, the administration of
S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles dose-dependent reduced the level of CK-MB and LDH in serum, and only at a dose of 300 mg/kg BW can decrease significantly compared with the diabetic group (p<0.05). These results suggest that
S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles prevent dysfunction and cardiac cell injury in diabetic rats.
2.6. S.macrophylla Extract Nanoparticles Effect on Cardiac Tissue of MDA Levels in Diabetic Rat
The levels of MDA are used as an indicator of cardiac damage due to oxidative stress, which was caused by increased ROS production.
Table 4 showed that the efficacy of
S. macrophylla nanoparticles on MDA levels in cardiac tissue. Rats that were injected with streptozotocin significantly increased cardiac MDA levels compared with control rats (p<0.05). Whereas
S. microphylla nanoparticles administered, dose-dependent significantly reduced MDA levels in cardiac tissue.
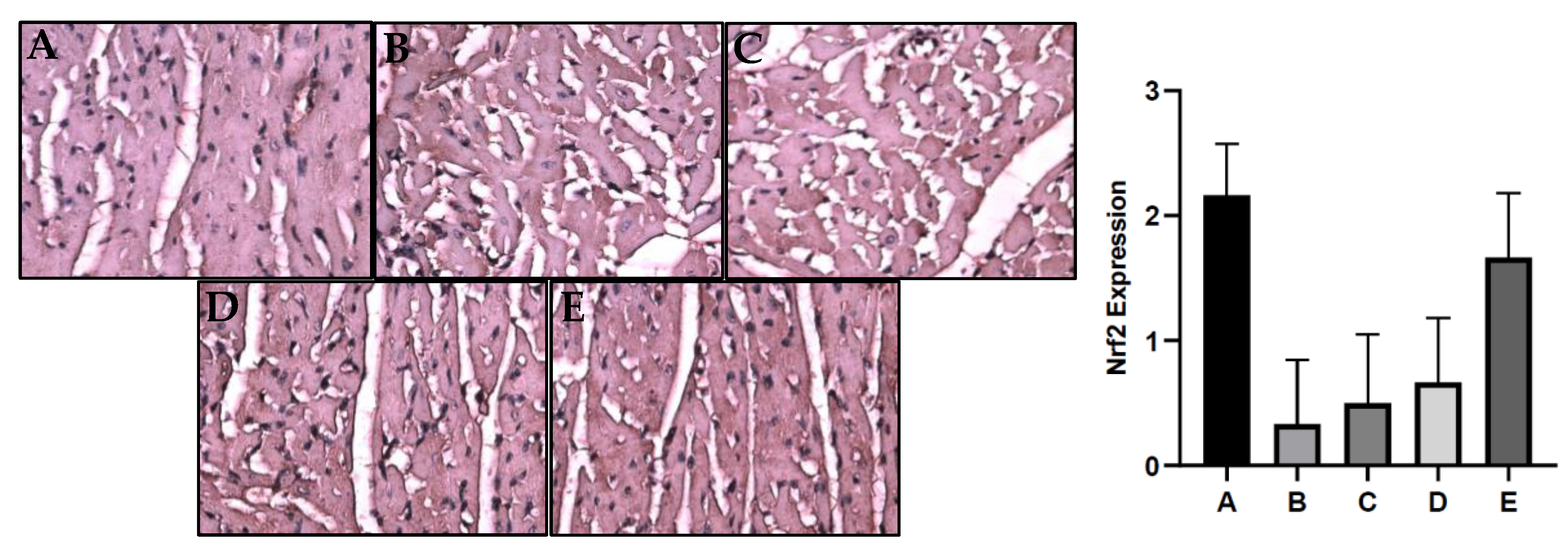
2.7. S. macrophylla Extract Nanoparticles Effect on Cardiac Tissue of Nrf2 Expression on Diabetic Rats
Nrf2 is an important regulator of cellular protection against oxidants. The expression of Nrf2 in the cardiac tissue was evaluated by immunohistochemistry and can be seen in
Figure 3. The gene expression of Nrf2 in diabetic group was significantly reduced cmpared to the control group (p<0.05), Administration of
S. macrophyla extract nanoparticles dose-dependent increases expression of Nrf2 in cardiac tissue, and only at a dose of 300 mg/kg BW significantly increasesNrf2 expression compared to the diabetic groups.
2.8. S macrophylla Extract Nanoparticles effect on Cardiac Tissue of SOD and GPx Levels in Diabetic Rat
SOD is a first-line antioxidant that catalyzes the dismutation of Superoxide Anion (O
2) to Hydrogen Peroxide (H
2O
2), furthermore, in turn, is reduced to oxygen and water by GPx. The level of SOD and GPx in tissue of heart can be seen in
Table 5. Rats that were injected intraperitoneally with STZ could reduce levels of SOD and GPx in the tissue of the heart significantly when compared with control rats (p<0.05). Meanwhile, pretreatment with
S. macrophylla nanoparticles increased dose-dependent SOD and GPx levels, but only a dose of 300 mg/kg significantly increase SOD and GPx levels in cardiac tissue when compared to diabetic rats (p<0.05).
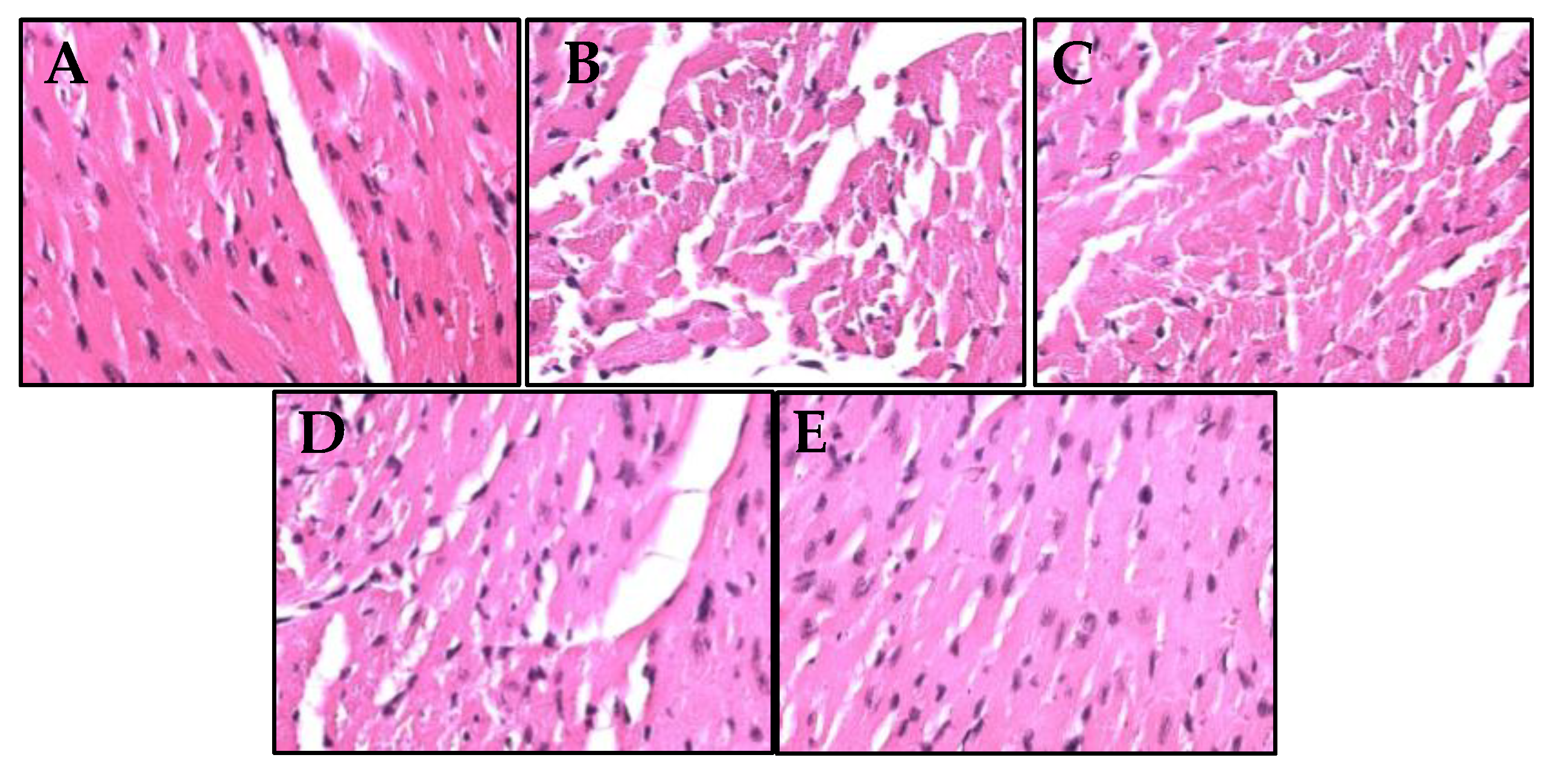
2.9. S. macrophylla Extract Nanoparticles Effect on the Structural Change of Diabetic Rats Cardiac Tissue
Histopathological observations were used to investigate changes in the cardiac cells structure of rat diabetics, as seen in
Figure 4. On examination with light microscopy, the control rats showed that the cardiac cell structure was normal, while the rats that were given STZ showed irregular morphology, necrosis of cardiac cell. Administration of
S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles can protect normal structures and inhibit necrosis of cardiac cells.
3. Discussion
Hyperglycemia is a sign of DM that can increase ROS production and can accelerate cardiac cell damage in diabetics [
28,
29,
30]. This study aims to prove the anti-ROS effect of S. macrophylla nanoparticles in protecting cardiac cell damage in STZ-induced rats. Many studies have used STZ to model diabetes cardiomyopathy in rats [
15,
16,
17]. In this diabetic cardiomyopathy rat model can occur elevating ROS is presented with higher MDA levels, and decreased antioxidant such as SOD, GPx and Nrf2 expression, and then induced cardiac cell damage [
1,
5,
7].
Our result in this research showed that injection with STZ intraperitoneally can increase the level of MDA, and decrease the level of SOD, GPx and Nrf2 expression in cardiac tissue significantly when compared with control rats. An increase in MDA indicates an increase in ROS production. Increased ROS in diabetes will oxidize lipids, proteins, and DNA, which can cause damage to cell membranes, disruption of protein function, and DNA fragmentation which results in increased levels of MDA, cell necrosis, and apoptosis [
2,
6,
9]. STZ also induced hyperglycemia that can inhibit antioxidant activity via the inhibition of scavenging, interaction glucose with protein, formation of AGE, and block receptors so resulting in oxidative cell injury. Streptozotocin can affect the released of insulin from beta cells of langerhans islet which can decrease insulin levels so occur increase blood glucose and induce diabetic complications such as cardiomyopathy. Another study showed that
oxidative stress due to STZ can inhibit Nrf2 from Keap1 and inactivates the antioxidant response element (ARE). This can decrease antioxidant enzyme production such as SOD, GPx and Catalase. Nfr2 is an essential transcription factor that controls the response of antioxidants for maintenance in homeostasis on cellular redox [
5,
12,
13]
.
Nanobiotechnology can be utilized to increase the solubility, absorption, distribution, bioavailability, effectiveness, and reduce the toxicity of antioxidant materials [
25,
26,
27]. To prepare S. macrophylla nanoparticles, a grinding process was carried out using the ball milling method. This result of the research shows that the manufacture of S. macrophylla extract has a nanozise was 91.50 ± 23.06 nm.
Our results indicate that pretreatment with S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles only at a dose of 300 mg/kg BW significantly decrease MDA levels, and increment SOD, GPx levels and Nrf2 expression in the cardiac tissue of diabetic rats compared with diabetic rat group. These results suggest that dose-dependent administration of S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles can balance endogenous antioxidants and oxidants so that they can inhibit oxidative stress. Phytochemical screening and GC-MS showed that S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles contain active compounds such as flavonoid, phenolic, piperidine, imidazole, hexadecene have strong antioxidant activity, which suppresses oxidative stress by combating ROS as well as maintaining redox homeostasis.
Increasing the formation of antioxidants and reducing the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can prevent oxidation in polyunsaturated fatty acids on cell membranes and then can decrease MDA levels which can be used as a marker occurring inhibit cardiac tissue damage. This can also be achieved through an activated Nrf2 by S. macrophylla by increasing the antioxidants response element (ARE) which can stimulate the gene transcription that codes endogenic antioxidants enzymes, further, SOD and GPx levels increase.
It has been reported that in vivo and in vitro research shows that
S. macrophylla scavenging ROS so can prevent Lipid Oxidation, furthermore reducing MDA levels, and elevating SOD and GPx levels so resulting protective effect in oxidative damage cells [
21,
22,
23]. The administration of natural product antioxidants has been proven can decrease oxidative stress. A recent study shows that Nrf2 has a crucial role in the protection of cardiac cell damage and death caused by oxidative stress in diabetic complications [
5,
6,
7,
9].
Injected with STZ intraperitoneally in rats significantly can increment CK-MB and LDH levels compared with control rats. The increasing serum CK-MB and LDH levels can be used as indicators of impaired cardiac function and cell damage. Whereas, dose-dependent administration of
S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles, significantly decreased levels of serum CK-MB and LDH in diabetic rats. This result shows that the pretreatment with
S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles as an antioxidant capable prevent cardiac cell damage in diabetic rats. ROS in higher levels in diabetes accelerates cardiac injury which induces the increase CK-MB and LDH serum. Oxidative stress in diabetic have an important role in the progress of cardiac cell damage which is associated with increased CK-MB, and LDH levels. In the same result, exogenous antioxidants can reduce ROS production and can prevent cardiac cell damage by reducing of serum CK-MB and LDH levels [
1,
2,
12].
Histological observations clearly showed that the presence of necrosis of rat cardiac cells induced by STZ, conversely administration of S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles had a cardioprotective effect by inhibiting necrosis of cardiac cells through antioxidant activity. The same results were also shown by several researchers, administration of STZ can cause necrosis in cardiac cells, and administration of exogenous antioxidants can prevent necrosis of cardiac cells due to STZ. Therefore, S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles which have strong antioxidant effects, are expected to be utilized as protector on diabetes complications, which one of cardiomyopathy.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of S. macrophylla Extract
The S. macrophylla seed was collected from The Purwodadi Botanical Garden, Indonesia and identified by a botanist in The Program Study of Pharmacy, Faculty of Medicine, Hang Tuah University, Surabaya, Indonesia. Dried S. macrophylla leaves are powdered using a blender. 500 g of powder leaves were macerated with 96 %, 2 liters for 3 days, and then filtered through the Whatman filter. Filtrate was collected and concentrated in a rotary evaporator at 50 oC. The concentrated extract was dried under open air and stored under refrigeration until further use.
4.2. The Manufacturing of S. macrophylla Extract Nanoparticles
The high-energy ball milling method is used to make S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles according to the instructions of the nanomachine manufacturer. And then the results of S. macrophylla extract nanoparticle were characterized by Dynamic Light Scattering (Horiba LA 900, Japan)
4.3. Qualitative Phytochemical Screening of S. macrophylla Extract Nanoparticles
The phytochemicals contained in S. macrophylla extract nanoparticle can be investigated qualitatively using standard phytochemical screening procedures. Discoloration or the presence of foam can be used as an indicator of the presence or absence of certain phytochemical compounds.
4.3.1. Test for Alkaloids
2 g of S. macrophylla extract nanoparticle was added to 10 ml of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid, warm in a water bath (50 oC) for 5 minutes, and filtered trough Whatman filter paper No 1. After cooling, 3 drops of Dragendorff’s reagent were added and mixed. The appearance of reddish-brown color is a positive indication of the presence of alkaloids in the sample
4.3.2. Test for Flavonoids
2 ml of S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles and 5 drops of concentrated hydrochloric acid were added. The formation of a red colour indicates the presence of flavonoids.
4.3.3. Test for Phenols
0.5 g of S. macrophylla extract nanoparticle was boiled in 5 ml of 70 % ethanol in a waterbath for 5 minutes and then filtered through Whatman filter paper No 1. After cooling, 5 drops of 5 % ferric chloride were added and mixed. The appearance of a green precipitate indicates the presence of phenol in the sample
4.3.4. Test for Saponin
2 g of S. macrophylla extract nanoparticle dissolved in 5 ml of distilled water. Thereafter, aliquots of 2 ml were taken from S.macrophylla extract nanoparticle solution, stirred for 30 seconds, and briskly agitated. The setups were allowed to settle for 15 minutes. The presence of frothing, which persists for over 15 minutes, is an indication of the presence of saponinin the tested sample.
4.3.5. Test for Terpenoids
100. mg of S.macrophylla extract nanoparticles was dissolved in 10 ml water. Furthermore, 2 ml of the S. macrophylla was taken and then added with 3 drops of concentrated HCl and 1 drop of concentrated H2SO4. A positive result is indicated by the formation of a red or purple color
4.3.6. Test for Tanin
40 mg of the S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles was dissolved with 4 ml water, then 2 ml was taken and then added 1 ml of 10 % Fe Cl3. A positive reaction is indicated by the formation of a dark blue or greenish black color.
4.4. Quantitative Phytochemical of S. macrophylla Extract Nanoparticles
The quantitative estimation of phenol, alkaloids, flavonoids and tannin contents in the S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles were analyzed by methods reported in the literature.
4.4.1. Total Phenols
Total phenols were investigated by the Folin-Ciocalteu methods (Diouf et al., 200). Approximately 0.5 ml of an ethanol solution of the S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles (0.25 mg/ml) was mixed and incubated for 2 minutes with 2.5 ml of the folin Ciocalteu reagent (10 times dilution). Furthermore, 2 ml of 7.5 % aqueous sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) was added to the solution, and the mixture was allowed to stand for 30 minutes at room temperature. The absorbance of the sample was read at 765 nm and the results were expressed as gallic acid equivalent (mg GAE/g based on dry extract weight)
4.4.2. Total Flavonoids
The AlCl3 methods is used to determine the total flavonoids (Brighente at al., 2007). 2 ml of the S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles at 1 mg /ml concentration was added to 2 % AlCl3.6H2O solution and stood after 1 h incubation at 20 oC. After that. the absorbance was read at 415 nm, the results expressed in quercetin equivalent (mg QE/g extract)
4.4.3. Total Alkaloids
5 ml of pH4.7 phosphate buffer and 5 ml of BCG ( Bromocresolgreen) solution were added to 1 ml of S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles. The mixture was then vigorously shaken with chloroform before being collected in a 10 ml volumetric flask and diluted with chloroform. In the same manner, as previously described, a set of colchicine reference standard solutions was prepared. A UV-visble spectrophotometer was used to measure the absorbance of test and standard solutioan against the reagent blank at 470 nm. The total alkaloid content was measured in milligram of colchicine equivalent per gram (mg CoE/g)
4.5. GC-MS Analysis of Bioactive Compounds in S. macrophylla Extract Nanoparticles
S. macrophylla solution of 1 μL was injected into GC-MS-QP2010SE, which had a capillary column with a length of 30 mm, a diameter of 0.25 mm, and a thickness of 0.25 μm. Helium carrier gas at a flow rate of 1 mL/min with a split ratio 1 :50. The pre programmed oven temperature was 150 oC and stored isothermal for five minutes, the rate of increase was 10 oC/minute, and the temperature was increased to 250 oC for five minutes. Compound identification of the GC-MS mass spectrum was performed using the National Institute Sandard and Technology (NIST) database. The spectrum components compare to NIST data library. The identification of chemical compounds was confirmed based on the peak area and retention time.
4.6. Experimental of Animal
Wistar rats with body weights 200-250 g were purchased from LPPT, Universitas Gadjah Mada Indonesia. Rats were kept in plastic cages on a 12 h day/night cycle at a temperature of 26 ±2 oC and acclimatized for one week before the research. All rats were given food and water ad libitum.
4.7. Model of Diabetic Rat
Diabetes was induced by a single injection of STZ intraperitoneally at a dose 55 mg/kg BW which was dissolved in 0.1 M citrate buffer (pH 4.5). After 3 days of STZ injection, all rats were checked for blood glucose levels with an Accu-check glucometer (Roche Diagnostic). Rats with blood glucose level > 200 mg/dl were considered as diabetic
4.8. Experimental Design
The study utilize rats randomly divided into five group with eight rats in each groups. Control group (rats were given aqua dest); STZ group (rats were injected with a single dose intraperitoneally STZ 55 mg/kg BW); S. macrophylla group (Rats were injected single dose intraperitoneally with STZ 55 mg/kg BW, and then after 3 days, rats were given S. macrophylla at dose 75, 150, 300 mg/kg BW respectively for 72 days). Rats were euthanized on day 75 with intraperitoneally injection of ketamine (60 mg/kg) an xylazine (7.5 mg/ kg BW). Then the heart is taken to investigate the MDA levels, SOD and GPx expression. Histopathological examination of the heart is also performed by Hematoxylin Eosin staining.
4.9. Biochemical Estimation of Serum CM-KB and LDH
The serum CM-KB and LDH levels were carried out using commercially available test kits (sigma-Aldrich Corp.,MO, USA) and according to the manufacturer’s instructions
4.10. Assessment of Cardiac tissue MDA Levels
The Thiobarbituric Acid (TBA) method is utilized to measure MDA in cardiac tissues, which can assess MDA formation by TBARS assay kit (Chemical by using a TBARS Assay Kit (Company of Cayman Chemical USA). The MDA-TBA complex coefficient was measured with absorbance at 532 nm with the reader of the microplate for assessing MDA levels. The MDA levels is expressed in nm/mg tissue.
4.11. Immunohistochemical Staining of Nrf2 Expression in Cardiac Tissue
Heart section (4 μm in thickness) were incubated in 3 % H2O2 for15 minute at temperature room to inhibit endogenous peroxidase activity. Furthermore the section were inhibited with normal goat serum for 1 h and then incubated overnight at 4 oC with rabbit polyclonal antibodies specific for Nrf2 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, USA), diluted 1:200 in PBS, 0.01 M, pH 7.2. Control section were incubated with blocking serum alone. After that, we washed three time with PBS and incubated with a secondary antibody from the Ultra Vision Quanto Detection system HRP DAB (Therma Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) for 30 minutes at room temperature, and with 3 3’ diaminobenzidine (DAB) color reagent. All slides were scored, for each slide ten microscopic viewing fields were examined at 400x magnification which were scored as follows: no immunopositive cells were given a score of 0; there are between 1 and 25% of immunopositive cells given a score of 1; there are between 26 and 50% immunopositive cells given a score of 2; there are between 51 and 75% immunopositive cells given a score of 3, and more than 75% immunopositive cells given a score of 4.
4.12. Assessment of Cardiac Tissue SOD and GPx Expression
To assess the SOD enzymatic activity in rat cardiac tissue, protein from the cardiac was extracted and assessed according to the procedure of the Bradford. SOD inhibiton decreased Nitro Blue Tetrazolium (NBT) (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) in each sample was determined by Spectrophotometry at 560 nm. SOD levels are shown as U/mg protein.
To assess the levels of GPx, the samples were incubated with NaN3 and H2O2. The homogenate 0.1 ml of cardiac tissue was incubated with ethylene diamine tetraacetate 0.2 ml, Sodium Azide, and H2O2 mixe with Phosphate Buffer. The mixture was centrifuged at 200 rpm and adding stopping reagent TCA. The supernatant was mixed with Disodium Hydrogen Phosphate and DTNB. The absorbance was measured at 412 nm after the color was formed. The level of GPx are shown as U/mg protein.
4.13. Histopathological Observations
At the end of the study, all rat heart were fixed in buffer formalin 10 % and embedded with paraffin. The section of the heart tissue was 4 μm stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin. Histopathological observation of the heart was carried out with a light microscope to determine the presence of kidney cell damage such as degeneration and necrosis.
4.14. Statistical Analysis
The results are showed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) and were analyzed by one-way analysis if variance (ANOVA) followed by the Duncan multiple multiple comparison test using SPSS 21. Differences in means were considered significant at p<0.05.
5. Conclusions
The mechanism pathways of S. macrophylla nanoparticles as cardioprotection in diabetic rats via an antioxidant effect by inhibiting MDA production, and elevating expression Nrf2, SOD and GPx levels in heart tissue. In addition, S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles also reduce serum CK-MB and LDH in diabetic rats. S. macrophylla extract nanoparticles also contain active compounds such as flavonoid, phenolic, piperidine, imidazole, hexadecene have strong antioxidant activity, which suppresses oxidative stress by combating ROS as well as maintaining redox homeostasis
Author Contributions
R.K, M.R.M. and S.A.S. involved conceptualization and experimental design. R.K and G.W involved in methodology and interpretation data. S.A.S and M.R.M review and editing. R.K involved in project administration, S.A.S. involved in funding acquisition. All author have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Airlamgga University, Surabaya, Indonesia in conducting this research work Grants Mandat No 1408/UN3/2019.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The research treatment on rats has been approved by
Airlangga University and the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine by the Animal Care and Ethics Committee
(Approval number: No : 1.KEH.115.09.2022). All research is in accordance with the Association
for Assessment and Accreditation of Animal Care International Laboratory.
Data Availability Statement
Data are presented within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dare, A.; Elrashedy, A.A.; Channa, M.L.; Nadar, A. Cardioprotective effects and in-silico antioxidant mechanism of L-Ergothioneine in experimental type 2 diabetic rats. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents, Med. Chem. 2022, 20, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjalil, S.; Pillai, N.; Soumya, P.; Modal, S.; Mini, S. Cardioprotective effect of Ferulic acid in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Bioact. Compd. Health. Dis. 2022, 5, 149–159. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, M.; Varghese, A.; Gaviraju, V.K.; Talwar, S.N.; Malini, S.S. Impact of hyperglycemia on molecular marker of oxidative stress and antioxidants in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cli. Diabetol. 2019, 8, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi-Dehnoo, M.; Amini-Khoei, H.; Lorigooini, Z.; Rafieian-Kopaei, m. Oxidative stress and antioxidants in diabetes mellitus. Asian. Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2020, 13, 431–438. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, H.; He, D.; Rao, C.; Xu, B. Cardioprotective effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum against streptozotocin induced cardiac toxicity in rats via alteration of AMPK.Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. J. Oleo. Sci. 2022, 71, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardani, G.; Nugraha, J.; Mustafa, M.R.; Sudjarwo. S.A. Antioxidative stress and ant-inflamatory activity of fucoidan nanoparticles against nephropathy of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Evid-Based complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, Z.; Li, F mulberry granules protect against diabetic cardiomyopathy through the AMPK. Nrf2 pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, T.; Wu, X.; Nice, E.C.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Y. Oxidative stress and diabetes: antioxidative strategies. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardani, G.; Nugraha, J.; Kurnijasanti, R.; Mustafa, M.R.; Sudjarwo, S.A. Molecular mechanism of fucoidan nanoparticles as protector on endothelial cell dysfunction in diabetic rats aorta. Nutrients 2023, 15, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, C.M.O.; Villar-Delfino, P.H.; dos Anjos, P.M.F.; Nogueira-Machado, J.A. Cellular death, reactive oxygen species and diabetic complications. Cell. Death. Dis. 2018, 9, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abukhalil, M.H.; Althunibat, O.Y.; Aladaileh, S.H.; Algrfare, A.I.; Al-Swailmi. l Mahmoud, A.M. Galangin Attenuate diabetic cardiomyopathy through modulating oaxidative stress, inflammation in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Prasad, S.; Sitasawad, S.L. Multiple Antioxidants improve cardiac complications and inhibit cardiac cell death in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Plos One 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Wang, P.; Dong, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Pei, H. Oxidative stress signalling mediated pathogenesis of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Birah,A. ; Selvaraj,S.; Holla,S.R.; De, S. Extraction and characterization of total phenolic and flavonoid contents from bark od Swietenia macrophylla and their antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. Arabian. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coello, F.P.; Azuaje, D.R.; Catari, I.P.; Marrero, M.P.; Vargas, C.O. Evaluation of the antioxidant activity of aqueous extracts of leaves and seeds of Swietenia macrophylla King by chemical and biological methods. J. Drugs. Res.Dev. 2020, 6, 106. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.Y.; Shi, W.L.; Guo, G.X. Cardioprotective role of gingerol along with prominent ati-diabetic cardiomyopathy action in a streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats model. Cell. J. 2017, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Darenskaya, M.A.; Kolesnikova, L.I.; Kolesnikov, S.I. Pathogenetic role in diabetes mellitus and its complications and therapeutic approach to correction. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 171, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, JC.; Ho, F.; Dan, C.; Jandeleit-Dahm, K. A causal link between oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiovascular and renal complication of diabetes. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 1811–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falah, S.; Safithri, M.; Katayama, T.; Suzuki, T. Hypoglycemic Effect of Mahogany (Swietenia macrophylla King) Bark Extracts in Alloxan-induced Diabetic Rats. Wood. Res. J. 2010, 11, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, S.B.; Azharin, N.H.; Mashitah, Y.M.; Abdurahman, N.H.; Mazza, A.S. In vitro antimicrobial activity and GC-MS analysis of medicinal plant Swietenia macrophylla King. J. Cehem. Pharma. Res. 2015, 7, 519–524. [Google Scholar]
- Masendra. ; Arisandi, R.; Purba, B.A.V.; Sumantri, F.; Ihda, F.V.; Wati, F.Z.; Lukmandaru, G. Extractives contributing to the color of Swieteniamacrophylla Bark. Wood Res. J. 2020, 11, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Hajra, S.; Mehta, A.; Pandey, P. Phenolic compound and antioxidant activity of Swietenia macrophylla seeds. Int. J. Pharm, Pharma Sci. 2011, 3, 43–434. [Google Scholar]
- Eid, A.M.M.; Elmarzugi, N.A.; EL-enshasy. A review in the phytopharmacological effect of Swietenia macrophylla. Int. J. Pharm. Pharma. Sci. 2013, 5, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, S.; Wong, N.K. Nanotechnology and its use in imaging and drugs delivery. Biomed. Rep. 2021, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, T.; Ratre, Y.K.; Chauhan, S.; Bhaskar, L.V.K.S.; Nair, M.P.; Verma, H.K. Nanotechnology based drug delivery system: Current strategies and emerging therapeutic potential for medical science. J. Drugs. Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shen, H.; He, Q.; Wu, Z.; Liao, W.; Yuan, M. Application of the nano-drug delvery system in treatment of cardiovascular Disease. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 7, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Eskandarany, M.S.; Al-Hazza, A.; Al-Hajji, L.A.; Ali, N.; Al-Duweesh, A.A.; Banyan, M.; Al-Ajmi, F. Mechanical Milling: A superior Nanothecnological tool for fabrication of nanocrystalline and nanocomposite materials. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighodaro, O.M. ; Molecular pathways associated with oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifuentes-Franco, S.; Padilla-Tejeda, S.; Carillo-Ibarra, S.; Miranda-Dia, A.G. Oaxidative stress, apoptosis, and mitochondrial function in diabetic nephropathy. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 1875870. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, N.; Omagari, D.; Ushikhosi-Nakayama, R.; Yamazaki, T.; Inoue, H.; Saito, I. Hyperglycemia induces generation of reactive oxygen species and accelerates apoptotic cell death in salivary gland cells. Pathobiol. 2021, 88, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).