Submitted:
09 May 2023
Posted:
09 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Deep Learning for Semantic Segmentation
2.2. Convolutional Random Fourier Features Gradient - CRFFg
2.3. Layer-Wise Weighted Class Activation Maps for Semantic Segmentation
- –
- CAM-Dice (): a version of the Dice measure that quantifies mask thickness and how the extracted CAM is densely filled:where holds the Layer-CAM for image n with respect to layer l (see Equation (7)). Additionally, collects a binary mask that identifies the pixel locations associated with the class r.
- –
- CAM-based Cumulative Relevance (): It involves computing the cumulative contribution from each CAM representation to detect class r within the segmented region of interest. This can be expressed as follows:
- –
-
Mask-based Cumulative Relevance (): It assesses the relevance averaged across the class pixel set related to the target mask of interest. Then, each class-based cumulative relevance is computed as follows:The normalized Mask-based Cumulative Relevance can be computed as:
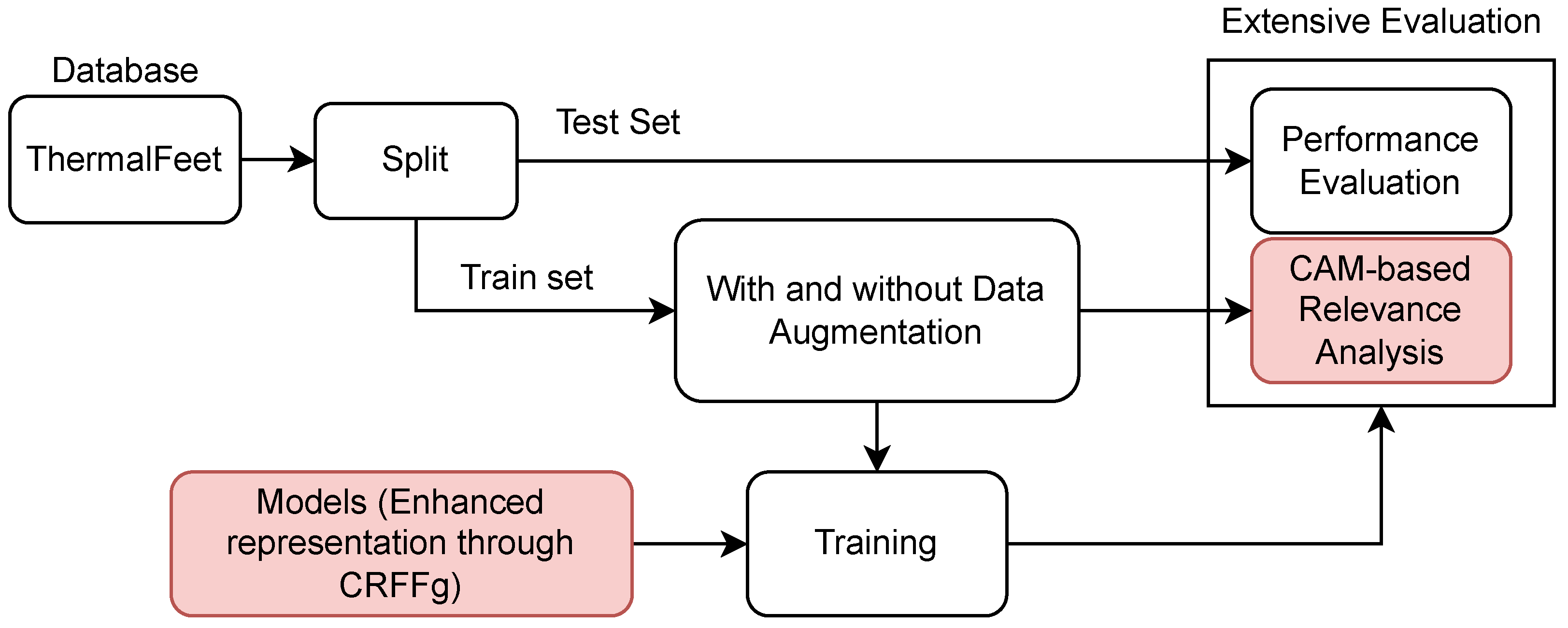
3. Experimental Set-Up
- i)
- Foot Infrared Thermal Data Acquisition and Preprocessing.
- ii)
- Architecture Set-Up of tested Deep models for foot segmentation. Three DL architectures are contrasted using our CRFFg: U-Net, Fully Convolutional Network (FCN), and ResUNet.
- iii)
- Assessment of semantic segmentation accuracy. In this study, we examine how data augmentation affects the performance of tested deep learning algorithms.
- iv)
- Relevance-maps extraction from our Layer-Wise weighted CAMs to provide interpretability.
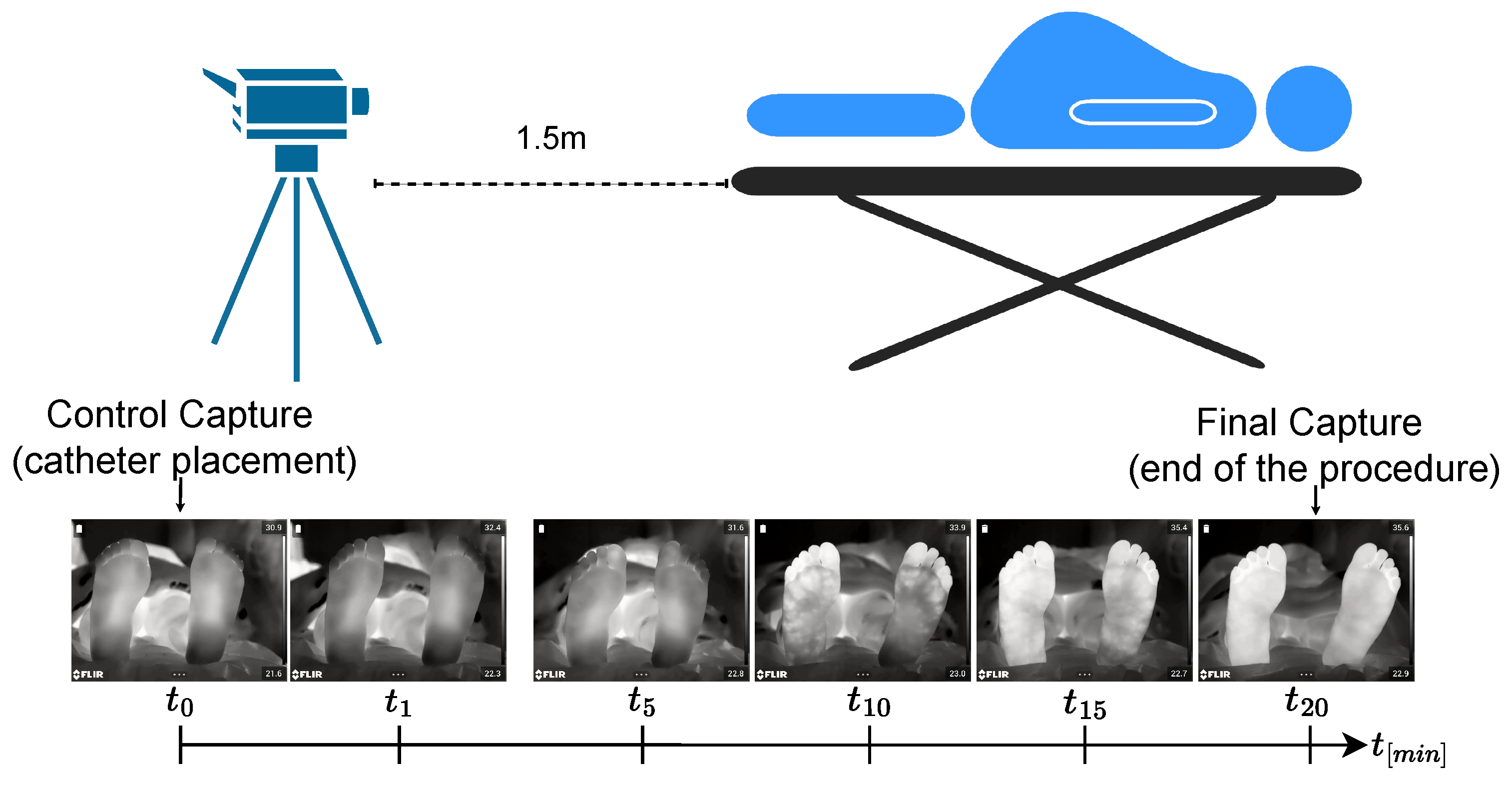
3.1. Protocol for Infrared Thermal Data Acquisition: ThermalFeet Dataset
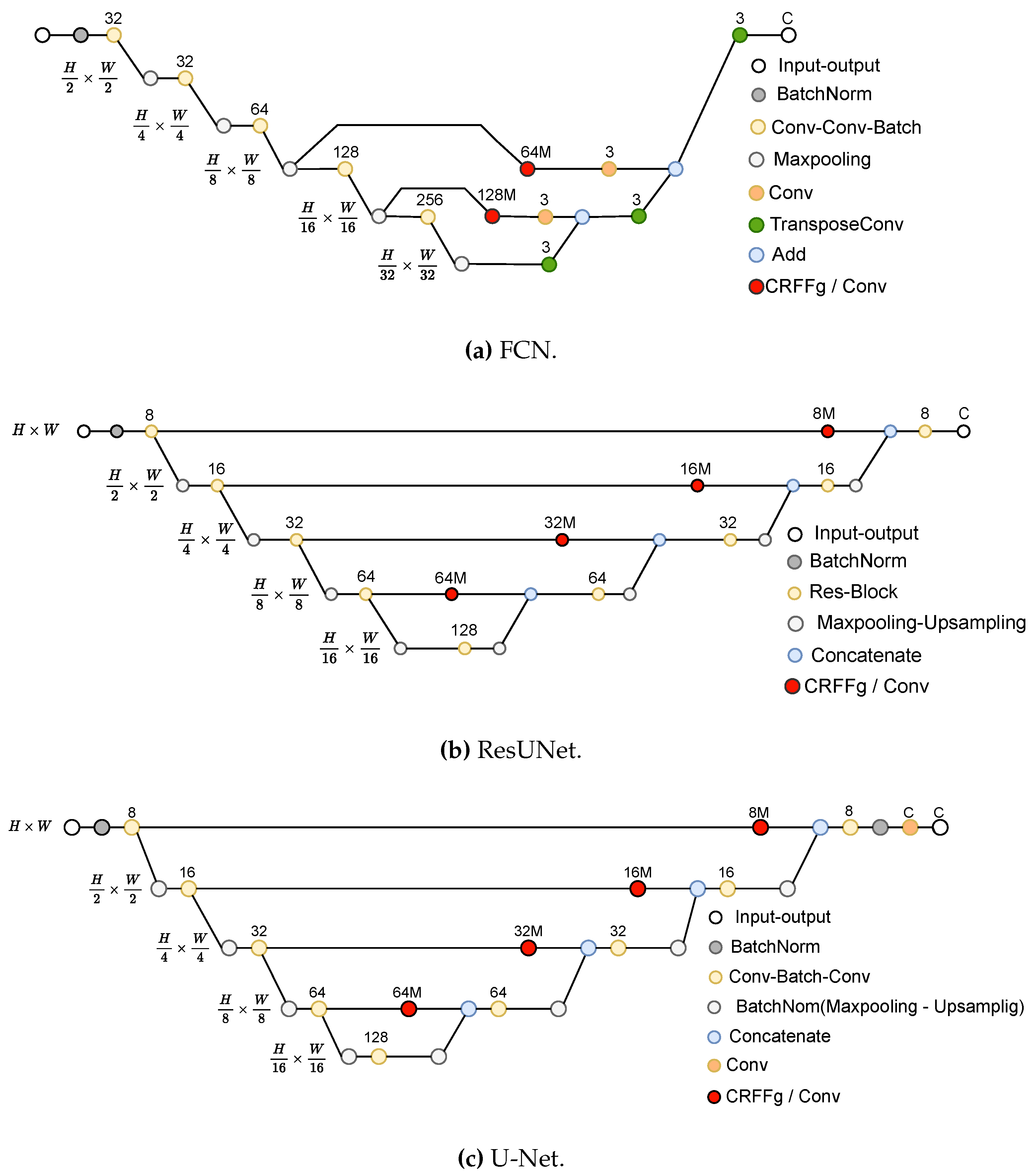
3.2. Set-Up of compared Deep Learning Architectures
- –
- Fully Convolutional Network (FCN) [12]: This architecture is based on the VGG (Very Deep Convolutional Network) [47] model to recognize large-scale images. By using only convolutional layers, FCN models can deliver a segmentation map with pixel-level accuracy while reducing the computational burden.
- –
- U-Net [14]: This architecture unfolds into two parts: The encoder consists of convolutional layers to reduce the spatial image dimensions. The decoder holds layers to upsample the encoded features back to the original image size.
- –
- ResUNet [33]: This model extends the U-Net architecture by incorporating residual connections to improve performance. Deep learning training is improved by residual connections, which allow gradients to flow directly through the network.
3.3. Training Details and Quantitative Assessment
4. Results and Discussion
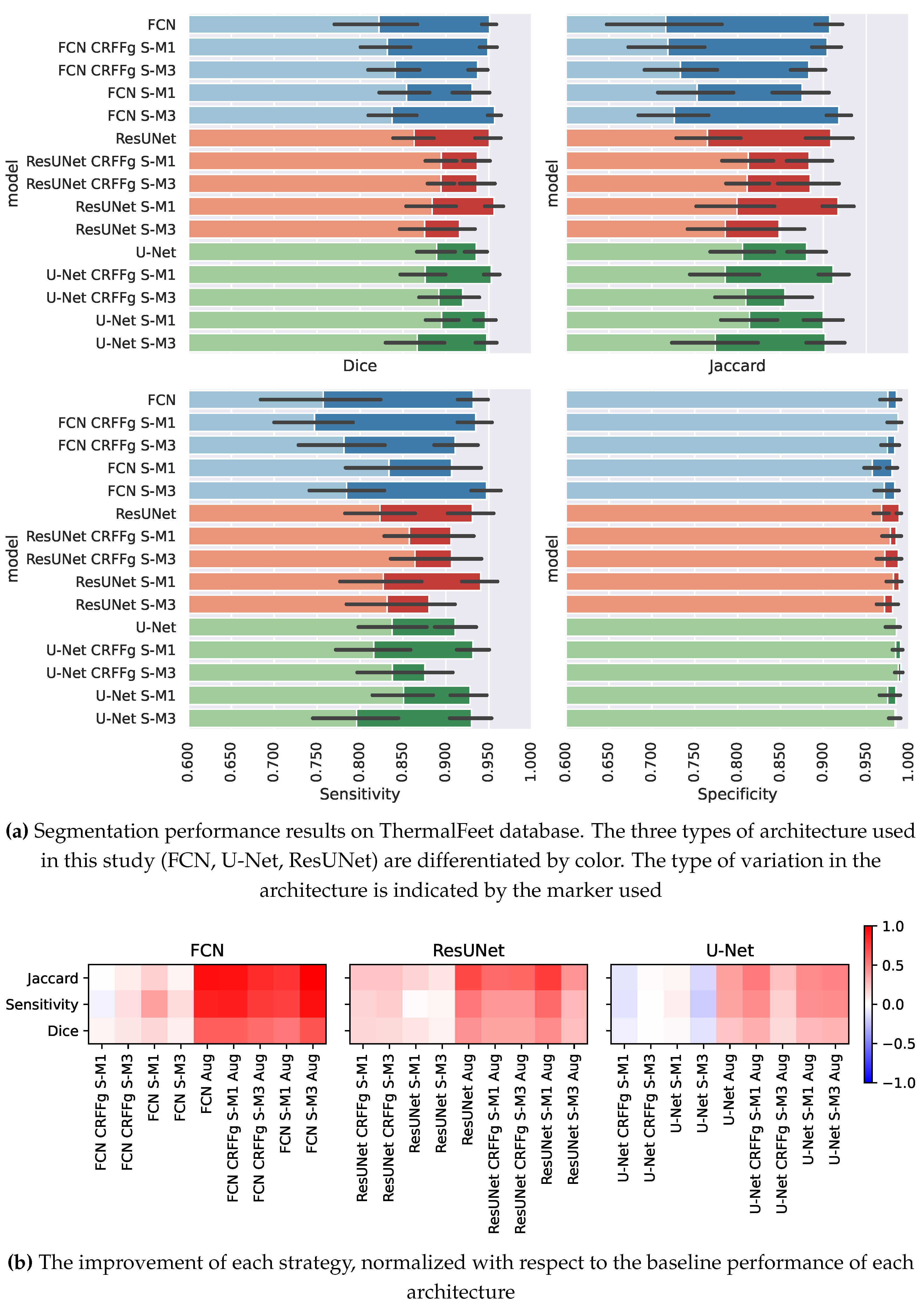
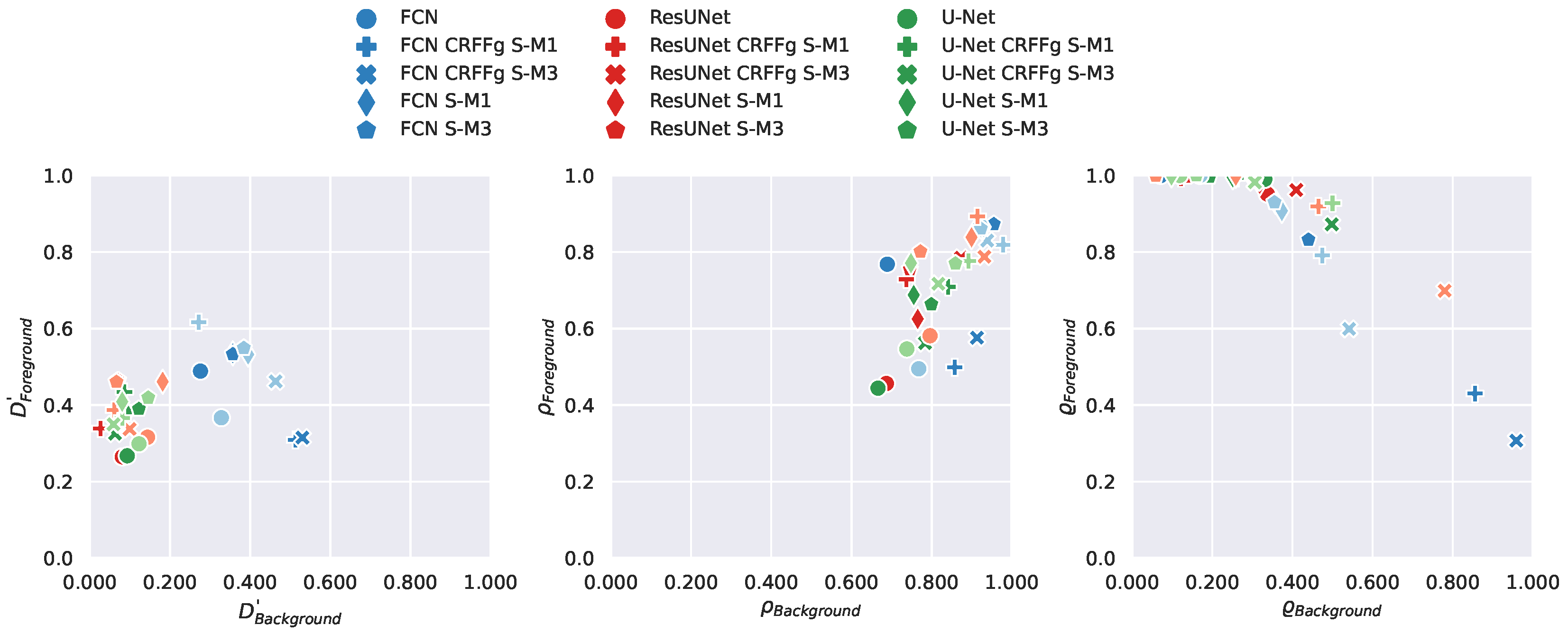
4.1. Method Comparison Results of Semantic Segmentation Performance
4.2. Results of Assessing the Proposed CAM-based Relevance Analysis Measures
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, D.T.; Wildsmith, J.A.W.; Covino, B.G.; Scott, D.B. Effect of Baricity on Spinal Anaesthesia with Amethocaine. BJA: British Journal of Anaesthesia 1980, 52, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCombe, K.; Bogod, D. Regional anaesthesia: risk, consent and complications. Anaesthesia 2021, 76, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, Y.; Park, H.J.; Lee, I.S. Pain modalities in the body and brain: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2022, 139, 104744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curatolo, M.; Petersen-Felix, S.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Assessment of regional analgesia in clinical practice and research. British Medical Bulletin 2005, 71, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruins, A.; Kistemaker, K.; Boom, A.; Klaessens, J.; Verdaasdonk, R.; Boer, C. Thermographic skin temperature measurement compared with cold sensation in predicting the efficacy and distribution of epidural anesthesia. Journal of clinical monitoring and computing 2018, 32, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruins, A.A.; Kistemaker, K.R.J.; Boom, A.; Klaessens, J.; Verdaasdonk, R.; Boer, C. Thermographic skin temperature measurement compared with cold sensation in predicting the efficacy and distribution of epidural anesthesia. Journal of Clinical Monitoring and Computing 2018, 32, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haren, F.; Kadic, L.; Driessen, J. Skin temperature measured by infrared thermography after ultrasound-guided blockade of the sciatic nerve. Acta anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2013, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.F.; Werdehausen, R.; Hermanns, H.; Lipfert, P. Skin temperature during regional anesthesia of the lower extremity. Anesthesia and analgesia 2006, 102, 1247–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdehausen, R.; Braun, S.; Hermanns, H.; Freynhagen, R.; Lipfert, P.; Stevens, M.F. Uniform Distribution of Skin-Temperature Increase After Different Regional-Anesthesia Techniques of the Lower Extremity. Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine 2007, 32, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Nan, Q.; Bian, S.; Liu, T.; Xu, Z. Real-time segmentation method of billet infrared image based on multi-scale feature fusion. Scientific Reports 2022, 12, 6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kütük, Z.; Algan, G. Semantic Segmentation for Thermal Images: A Comparative Survey, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. CoRR, 1411. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, L.; Kim, J.; Kumar, A.; Fulham, M.J.; Feng, D. Stacked fully convolutional networks with multi-channel learning: application to medical image segmentation. The Visual Computer 2017, 33, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. CoRR, 2015; abs/1505.04597. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Webb, J.M.; Gregory, A.; Denis, M.; Meixner, D.D.; Bayat, M.; Whaley, D.H.; Fatemi, M.; Alizad, A. Automated and real-time segmentation of suspicious breast masses using convolutional neural network. PloS one 2018, 13, e0195816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. CoRR, 2018; abs/1807.10165. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. 2016; arXiv:cs.CV/1511.00561].
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. 2018; arXiv:cs.CV/1703.06870].
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. T: R-CNN, 2016; arXiv:cs.CV/1506.01497].
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. 2017; arXiv:cs.CV/1612.01105].
- Arteaga-Marrero, N.; Hernández, A.; Villa, E.; González-Pérez, S.; Luque, C.; Ruiz-Alzola, J. Segmentation Approaches for Diabetic Foot Disorders. Sensors 2021, Vol. 21, Page 934 2021, 21, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting with Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouallal, D.; Bougrine, A.; Douzi, H.; Harba, R.; Canals, R.; Vilcahuaman, L.; Arbanil, H. Segmentation of plantar foot thermal images: Application to diabetic foot diagnosis. International Conference on Systems, Signals, and Image Processing 2020, 2020, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougrine, A.; Harba, R.; Canals, R.; Ledee, R.; Jabloun, M. On the segmentation of plantar foot thermal images with deep learning. European Signal Processing Conference, 2019, 2019-September. [CrossRef]
- Mejia-Zuluaga, R.; Aguirre-Arango, J.C.; Collazos-Huertas, D.; Daza-Castillo, J.; Valencia-Marulanda, N.; Calderón-Marulanda, M.; Aguirre-Ospina, Ó.; Alvarez-Meza, A.; Castellanos-Dominguez, G. Deep Learning Semantic Segmentation of Feet Using Infrared Thermal Images. In Proceedings of the Advances in Artificial Intelligence – IBERAMIA 2022; Bicharra Garcia, A.C.; Ferro, M.; Rodríguez Ribón, J.C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 342–352.
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. CoRR, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. TransUNet: Transformers Make Strong Encoders for Medical Image Segmentation 2021.
- Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q.; Wang, M. Swin-Unet: Unet-like Pure Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation 2021. pp. 205–218. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Hu, Q. TransFuse: Fusing Transformers and CNNs for Medical Image Segmentation. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) 2021, 12901 LNCS, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sui, X.; Luo, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Goh, R. Medical Image Segmentation Using Squeeze-and-Expansion Transformers. IJCAI International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Hu, M.; Song, T.; Wang, G.; Zhang, S. Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation via Cross Teaching between CNN and Transformer 2022. pp. 820–833.
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.Y.; et al. 2023; arXiv:cs.CV/2304.02643].
- Anas, E.M.A.; Nouranian, S.; Mahdavi, S.S.; Spadinger, I.; Morris, W.J.; Salcudean, S.E.; Mousavi, P.; Abolmaesumi, P. Clinical Target-Volume Delineation in Prostate Brachytherapy Using Residual Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention − MICCAI 2017; Descoteaux, M.; Maier-Hein, L.; Franz, A.; Jannin, P.; Collins, D.L.; Duchesne, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2017; pp. 365–373.
- Zhou, B.; Khosla, A.; Lapedriza, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. 2015; arXiv:cs.CV/1512.04150].
- Zhang, A.; Lipton, Z.C.; Li, M.; Smola, A.J. Dive into deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.11342, arXiv:2106.11342 2021.
- Rahimi, A.; Recht, B. Random features for large-scale kernel machines. 2009.
- Rudin, W. .. Fourier analysis on groups; Interscience tracts in pure and applied mathematics ;, Interscience: New York, New York, 1976; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez-Meza, A.M.; Cárdenas-Peña, D.; Castellanos-Dominguez, G. Unsupervised Kernel Function Building Using Maximization of Information Potential Variability. In Proceedings of the Progress in Pattern Recognition, Image Analysis, Computer Vision, and Applications; Bayro-Corrochano, E.; Hancock, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2014; pp. 335–342.
- Bronstein, M.M.; Bruna, J.; Cohen, T.; Velickovic, P. Geometric Deep Learning: Grids, Groups, Graphs, Geodesics, and Gauges. CoRR, 2021; abs/2104.13478. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Khosla, A.; Lapedriza, À.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Learning Deep Features for Discriminative Localization. CoRR, 2015; abs/1512.04150. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, P.T.; Zhang, C.B.; Hou, Q.; Cheng, M.M.; Wei, Y. LayerCAM: Exploring hierarchical class activation maps for localization. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 2021, 30, 5875–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Castaño, C.A.; Álvarez-Meza, A.M.; Aguirre-Ospina, O.D.; Cárdenas-Peña, D.A.; Orozco-Gutiérrez, Á.A. Random fourier features-based deep learning improvement with class activation interpretability for nerve structure segmentation. Sensors 2021, 21, 7741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, E.M.; Niehof, S.; Medina, H.J.; Zijlstra, F.J.; van Bommel, J.; Klein, J.; Verbrugge, S.J.C. Thermographic temperature measurement compared with pinprick and cold sensation in predicting the effectiveness of regional blocks. Anesthesia and analgesia 2006, 102, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chestnut, D.H.; Wong, C.A.; Tsen, L.C.; Kee, W.M.D.N.; Beilin, Y.; Mhyre, J. Chestnut’s Obstetric Anesthesia: Principles and Practice E-Book: Expert Consult-Online and Print 2014.
- ASGHAR, S.; LUNDSTRØM, L.H.; BJERREGAARD, L.S.; LANGE, K.H.W. Ultrasound-guided lateral infraclavicular block evaluated by infrared thermography and distal skin temperature. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2014, 58, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, K.H.; Jansen, T.; Asghar, S.; Kristensen, P.; Skjønnemand, M.; Nørgaard, P. Skin temperature measured by infrared thermography after specific ultrasound-guided blocking of the musculocutaneous, radial, ulnar, and median nerves in the upper extremity. British journal of anaesthesia 2011, 106 6, 887–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Ibtehaz, N.; Rahman, M.S. MultiResUNet: Rethinking the U-Net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation. Neural Networks 2020, 121, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhong, X.; Bai, C.; Huang, X.; Zhao, R.; Xia, M. PaI-Net: A modified U-Net of reducing semantic gap for surgical instrument segmentation. IET Image Processing 2021, 15, 2959–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga-Marrero, N.; Hernández, A.; Villa, E.; González-Pérez, S.; Luque, C.; Ruiz-Alzola, J. Segmentation Approaches for Diabetic Foot Disorders. Sensors 2021, 21, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: Redesigning Skip Connections to Exploit Multiscale Features in Image Segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 2020, 39, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Pappas, N.; Yogatama, D.; Schwartz, R.; Smith, N.A.; Kong, L. Random feature attention. arXiv, 2021; arXiv:2103.02143 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Pham, T.T.; Nguyen, T.; Le, H.; Nguyen, D.; Lam, H.; Nguyen, P.; Fowler, J.; Tran, M.T.; Le, N. EmbryosFormer: Deformable Transformer and Collaborative Encoding-Decoding for Embryos Stage Development Classification. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, 2023, pp.; pp. 1981–1990.
| 1 |


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




