Submitted:
06 May 2023
Posted:
08 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The study population
2.2. Ethical approval
2.3. Food Frequency Questionnaire
2.4. Estimation of Macronutrients Intake
2.5. Anthropometric Measurements
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
| Nutrients | *RDARecommendations | SD | %Below recommended RDA intake | %Within recommended RDA intake | % Above recommended RDA intake |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Calories (kcal/day) | Male: 2200-2420 Female: 1760-2200 |
2232±509.96 2290±425.46 |
32.09 6.17 |
9.89 2.47 |
28.39 20.99 |
| Total Proteins (g/day) |
Male: 63-65 Female: 52-53 |
66.76±36.36 65.35±11.70 |
2.47 6.17 |
27.16 12.35 |
40.74 11.11 |
| Total lipids (g/day) | Male: 49-54 Female: 39-49 |
36.36±10.92 37.04±7.74 |
9.87 8.64 |
2.47 1.23 |
58.03 19.76 |
| Total carbohydrates (g/day) | Male: 250-300 Female: 190-250 |
364.04±73.46 333.18±87.68 |
0.00 0.00 |
0.00 0.00 |
70.37 29.63 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suttajit, M. Advances in Nutrition Support for Quality of Life in HIV/AIDS. Asia Pac. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 16, 318–322. [Google Scholar]
- Enwereji, E.E.; Ezeama, M.C.; Onyemachi, P.E. Basic Principles of Nutrition, HIV and AIDS: Making Improvements in Diet to Enhance Health. In Nutrition and HIV/AIDS-Implication for Treatment, Prevention and Cure. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Scrimshaw, N.S.; SanGiovanni, J. P; Synergism of Nutrition, Infection, and Immunity: an Overview. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 66, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colecraft, E. HIV/AIDS: Nutritional Implications and Impact on Human Development. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2008, 67, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scrimshaw, N.S.; SanGiovanni, J.P. Synergism of Nutrition, Infection, and Immunity: an Overview. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 66, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.D.; Quinn, T.C.; Strober, W.; Janoff, E.N.; Masur, H. Gastrointestinal Infections in AIDS. Ann. Intern. Med. 1992, 116, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Süttmann, U.; Ockenga, J.; Selberg, O.; Hoogestraat, L.; Deicher, H.; Müller, M.J. Incidence and Prognostic Value of Malnutrition and Wasting in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-infected Outpatients. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes and Human Retrovirology: Official Publication of the International Retrovirology Association 1995, 8, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duggal, S.; Chugh, T.D.; Duggal, A.K. HIV and Malnutrition: Effects on Immune System. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 8, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiébaut, R.; Daucourt, V.; Mercié, P.; Ekouévi, D.K.; Malvya, D.; Morlat, P.; Dabis, F. Lipodystrophy, Metabolic Disorders, and Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection: Aquitaine Cohort, France. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 1482–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, K.V.; Hogg, R.S.; Chan, K.J.; Harris, M.; Montessori, V.; O'Shaughnessy, M.V.; Montaner, J.S. Lipodystrophy-associated Morphological, Cholesterol and Triglyceride Abnormalities in a Population-Based HIV/AIDS Treatment Database. AIDS 2001, 15, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, M.E.; Bencomo, J.F.; Perez, L.E.; Torrez, O.; Barrera, O. Influence of HIV/AIDS Infection on Some Biochemical Indicators of the Nutritional Status. Biomed. : J. Natl. Inst. Health 2002, 22, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.; Kelly, P. Interactions of Malnutrition and Immune Impairment, With Specific Reference to Immunity Against Parasites. Parasite Immunol. 2006, 28, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, R.S.; Tendeiro, R.; Foxall, R.B.; Baptista, A.P.; Cavaleiro, R.; Gomes, P.; Camacho, R.; Valadas, E.; Doroana, M.; Lucas, M.; Antunes, F.; Victorino, R.M.M.; Sousa, A.E. Cell-associated Viral Burden Provides Evidence of Ongoing Viral Replication in aviremic HIV-2-infected Patients. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2429–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicotte, M.; Bemeur, C.; Diouf, A.; Zunzunegui, M.V.; Nguyen, V.K. Nutritional Status of HIV-infected Patients During the First Year HAART in Two West African cohorts. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2015, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuppal, S.V.; Jun, S.; Cowan, A.; Bailey, R.L. The Nutritional Status of HIV-infected US Adults. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2017, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, C.; Devarajan, S.; Gersbach, H. The Long-run Economic Costs of AIDS: A Model with an Application to South Africa. World Bank Econ. Rev. 2006, 20, 55–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivers, L.C.; Cullen, K.A.; Freedberg, K.A.; Block, S.; Coates, J.; Webb, P.; Mayer, K.H. HIV/AIDS, Undernutrition, and Food Insecurity. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hailemariam, S.; Bune, G.T.; Ayele, H.T. Malnutrition: Prevalence and its Associated Factors in People Living with HIV/AIDS, in Dilla University Referral Hospital. Arch. Public Health 2013, 71, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuh, B.; Tate, J.; Butt, A.A.; Crothers, K.; Freiberg, M.; Leaf, D.; Justice, A.C. Weight Change After Antiretroviral Therapy and Mortality. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1852–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, W. Monographs in Epidemiology and Biostatistics: Nutritional Epidemiology Vol. 40 3rd Ed. Oxford university press 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mulberry Soft. Health & Fitness: Diet Controller (2.1.0) 2021. /: Available online: http.
- WHO: World Health Organization. Nutrient Requirements for People Living with HIV 2004. Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/42853/9241591196.
- Byrd-Bredbenner, C.; Moe, G.; Berning, J.; Kelley, D. Wardlaw's Perspectives in Nutrition (pp. 187-219). McGraw-Hill Higher Education 2013.
- Dietz, W.H.; Bellizzi, M. C. Introduction: the use of body mass index to assess obesity in children. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 70, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, C.B.; Jan, A. BMI Classification Percentile and Cut Off Points. State Pearls Publishing, Treasure Island Florida 2019; 3108-2114.
- Width, M.; Reinhard, T. The Essential Pocket Guide for Clinical Nutrition (2nd Ed). Wolters Kluwer 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tinarwo, P.; Zewotir, T.; North, D. Trends and Adaptive Optimal Set Points of CD4+ Count Clinical Covariates at Each Phase of the HIV Disease Progression. AIDS Res. Treat. 2020, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzekri, N.A.; Sambou, J.; Diaw, B.; Sall, E.H.I.; Sall, F.; Niang, A.; Gottlieb, G.S. High Prevalence of Severe Food Insecurity and Malnutrition Among HIV-infected Adults in Senegal, West Africa. Public Libr. Sci. One 2015, 10, 141819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dannhauser, A.; Van Staden, A.M.; Van der Ryst, E.; Nel, M.; Marais, N.; Erasmus, L.; Roux, G.D. Nutritional Status of HIV-1 Seropositive Patients in the Free State Province of South Africa: Anthropometric and Dietary Profile. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nti, C.A.; Hayford, J.; Opare-Obisaw, C. Nutrition knowledge, Diet Quality and Nutritional Status of People Living with HIV (PLHIV) in Ghana. Food Public Health.
- Mutisya, M.; Kandala, N.B.; Ngware, M.W.; Kabiru, C.W. Household Food (in) Security and Nutritional Status of Urban Poor Children Aged 6 to 23 Months in Kenya. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremichael, D.Y.; Hadush, K.T.; Kebede, E.M.; Zegeye, R.T. Food Insecurity, Nutritional Status, and Factors Associated with Malnutrition Among People Living with HIV/AIDS Attending Antiretroviral Therapy at Public Health Facilities in West Shewa Zone, Central Ethiopia. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 9, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorosa, V.; Synnestvedt, M.; Gross, R.; Friedman, H.; MacGregor, R.; Gudonis, D.; Tebas, P.A. Tale of 2 Epidemics: The Intersection Between Obesity and HIV Infection in Philadelphia. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2005, 39, 557–561. [Google Scholar]
- Takarinda, K.C.; Mutasa-Apollo, T.; Madzima, B.; Nkomo, B.; Chigumira, A.; Banda, M.; Mugurungi, O. Malnutrition Status and Associated Factors Among HIV-positive Patients Enrolled in ART Clinics in Zimbabwe. Boston Med. Cent. Nutr. 2017, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Ji, C. Nutritional Status, Psychological Well-being, and the Quality of Life of AIDS Orphans in Rural Henan Province, China. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2007, 12, 1180–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Cañavate, R.; Sonego, M.; Sagrado, M. J.; Escobar, G.; Rivas, E.; Ayala, S.; Custodio, E. Dietary patterns and Nutritional Status of HIV-infected Children and Adolescents in El Salvador: A cross-sectional Study. Public Libr. Sci. Open J. 2018, 13, 13,196–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyango, A.C.; Walingo, M.K.; Mbagaya, G.; Kakai, R. Assessing Nutrient Intake and Nutrient Status of HIV Seropositive Patients Attending Clinic at Chulaimbo Sub-District Hospital, Kenya. J. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villamor, E.; Saathoff, E.; Manji, K.; Msamanga, G.; Hunter, D. J.; Fawzi, W. Vitamin Supplements, Socioeconomic Status, and Morbidity Events as Predictors of Wasting in HIV-infected women from Tanzania. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, A.D.; Silveira, E.A.; Falco, M.D.; Nery, M.W.; Turchi, M.D. Overweight and Abdominal Obesity in Adults Living with HIV/AIDS. , J. Braz. Med. Assoc. 2016, 62, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri, S.; Amatya, A.; Shrestha, B. Nutritional Status and the Associated Factors Among People Living with HIV: An Evidence from Cross-Sectional Survey in Hospital Based Antiretroviral Therapy Site in Kathmandu, Nepal. Boston Med. Cent. Nutr. 2020, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stambullian, M.; Feliu, S.; Slobodianik, N. H. Nutritional Status in Patients with HIV infection and AIDS. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 98, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obirikorang, C.; Yeboah, F.A. Blood Haemoglobin Measurement as a Predictive Indicator for the Progression of HIV/AIDS in Resource-limited Setting. J. Biomed. Sci. 2009, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.C.O. D.; Almeida, A.M.R. Nutritional status and CD4 Cell Count in Patients with HIV/AIDS Receiving Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Braz. Soc. Trop. Med. 2013, 46, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, J.A.; Fausto, M.A.; Carneiro, M.; Tubinambás, U. Prevalence of Hypoalbuminemia in Outpatients with HIV/AIDS. J. Braz. Soc. Trop. Med. 2018, 51, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurpibul, L.; Namwongprom, S.; Sudjaritruk, T.; Ounjaijean, S. Metabolic Syndrome, Biochemical Markers, and Body Composition in Youth Living with Perinatal HIV Infection on Antiretroviral Treatment. Public Libr. Sci. One 2020, 15, 230–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagoe, D.N.A.; Asantewaa, E. Profiling Haematological Changes in HIV Patients Attending Fevers Clinic at the Central Regional Hospital in Cape Coast, Ghana: A case-control Study. Arch. Appl. Sci. Res. 2011, 3, 326–331. [Google Scholar]
- Ositadinma, I.M.; Ikponmwosa, O.S.; Okechukwu, O.C. Haemorheology and Red Cell indices in HIV Positive Individuals on Antiretroviral Therapy in Delta State, Nigeria. Int. J. Curr. Res. Rev. 2015, 7, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Lumbanraja, S.N.; Siregar, D.I.S. Association Between Red Blood Cell Indices and CD4 count in HIV-positive Reproductive Women. Institute of Physics Conference Series: Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 125, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, L.I.; Holmberg, S.D.; Williamson, J.M.; Szczech, L.A.; Carpenter, C.C.; Rompalo, A.M. HIV Epidemiology Research Study Group. Development of Proteinuria or Elevated Serum Creatinine and Mortality in HIV-infected Women. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2003, 32, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adedeji, T.A.; Adedeji, N.O.; Adebisi, S.A.; Idowu, A. A.; Fawale, M. B.; Jimoh, K. A. Prevalence and Pattern of Chronic kidney Disease in Antiretroviral patients with HIV/AIDS. J. Int. Assoc. Provid. AIDS Care 2015, 14, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patients’ characteristics | N % |
|---|---|
| Age range (year) | 22-85 |
|
Gender Male Female |
248 (80.51%) 52 (16.88%) |
|
Nationality Bahraini |
308 |
| Education | |
| Primary | 14 (17.28%) |
| Intermediate | 13 (16.04%) |
| Secondary | 32 (39.50%) |
| Diploma/ B.Sc. | 21 (25.92%) |
| Higher education | 1 (1.23%) |
| Selected food | Count (n) | % Responses |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrate | ||
| White bread | 73 | 90.12% |
| White rice | 64 | 79.01% |
| Potatoes | 15 | 18.51% |
| Protein | ||
| Eggs | 45 | 55.55% |
| Yogurt | 31 | 38.27% |
| Beans | 6 | 7.40% |
| Caffeinated drinks | ||
| Tea | 75 | 92.59% |
| Coffee | 56 | 69.13% |
| Soft drinks | 5 | 6.17% |
| Vegetables | ||
| Arugula (rocket) | 45 | 55.55% |
| Onions | 39 | 48.14% |
| Tomatoes | 25 | 30.86% |
| Fruits | ||
| Apples | 51 | 62.96% |
| Oranges | 32 | 39.50% |
| *BMI Classification | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal (n) 18.5-24.9 |
Overweight (n) 25-29.9 |
Obese class I (n) 30-34.9 |
Obese class II (n) 35-39.9 |
Obese class III (n) ≥ 40 |
|
| Classification n of participant | 31 | 30 | 15 | 4 | 1 |
| % | 38.27 | 37.03 | 18.51 | 4.93 | 1.23 |
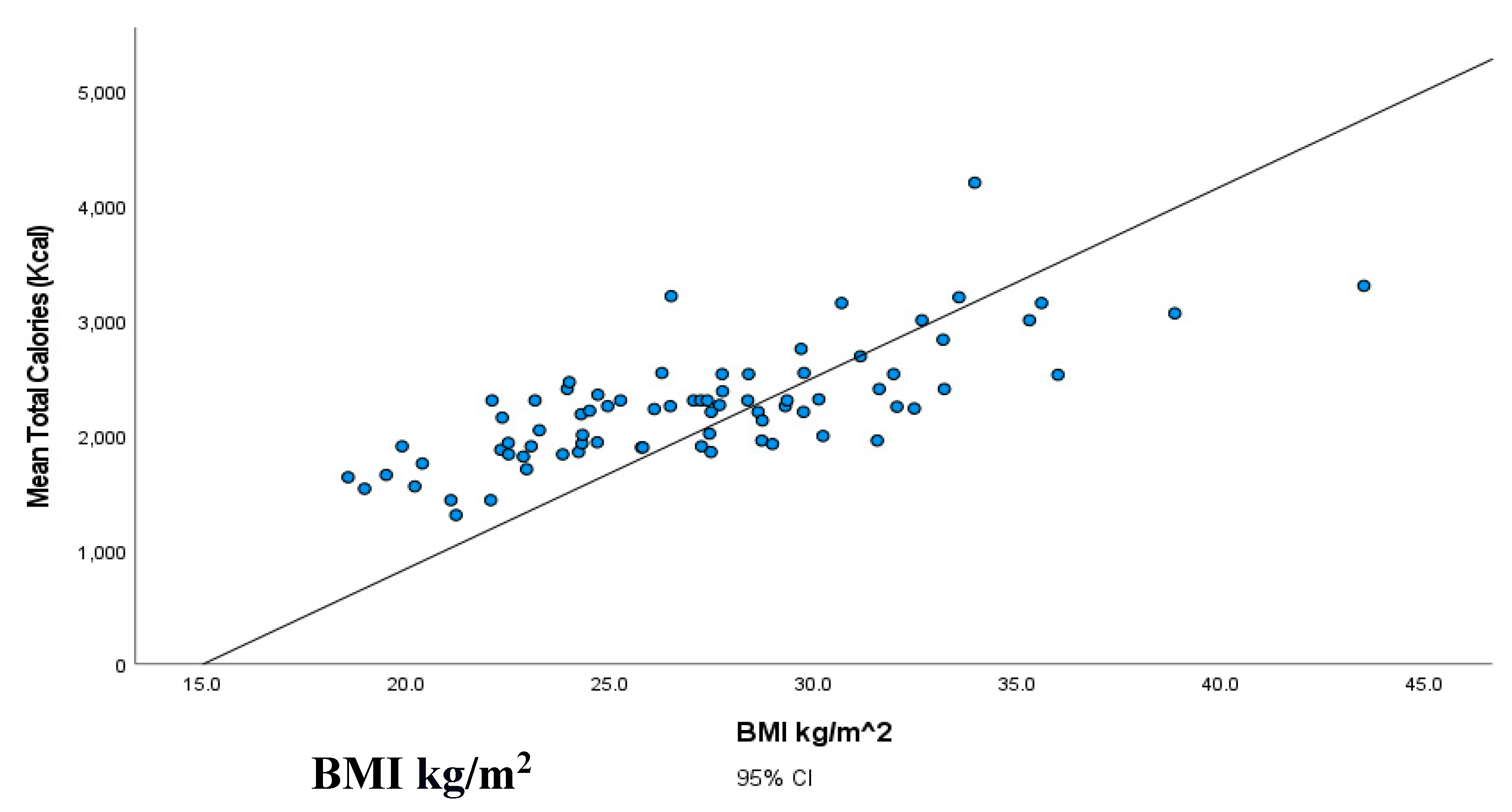
| BMI kg/m2 | Total calories (kcal/day) | Total carbohydrates (g/dL) | Total lipids (g/dL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total calories (kcal/day) | Correlation | 0.740** | |||
| p-value | 0.000 | ||||
| Total carbohydrates (g/dL) | Correlation | 0.744* | 0.907* | ||
| p-value | 0.000 | 0.000 | |||
| Total lipids (g/dL) | Correlation | 0.701* | 0.862* | 0.867* | |
| p-value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| Total proteins (g/day) | Correlation | 0.715* | .814* | 0.746* | 0.695* |
| p-value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
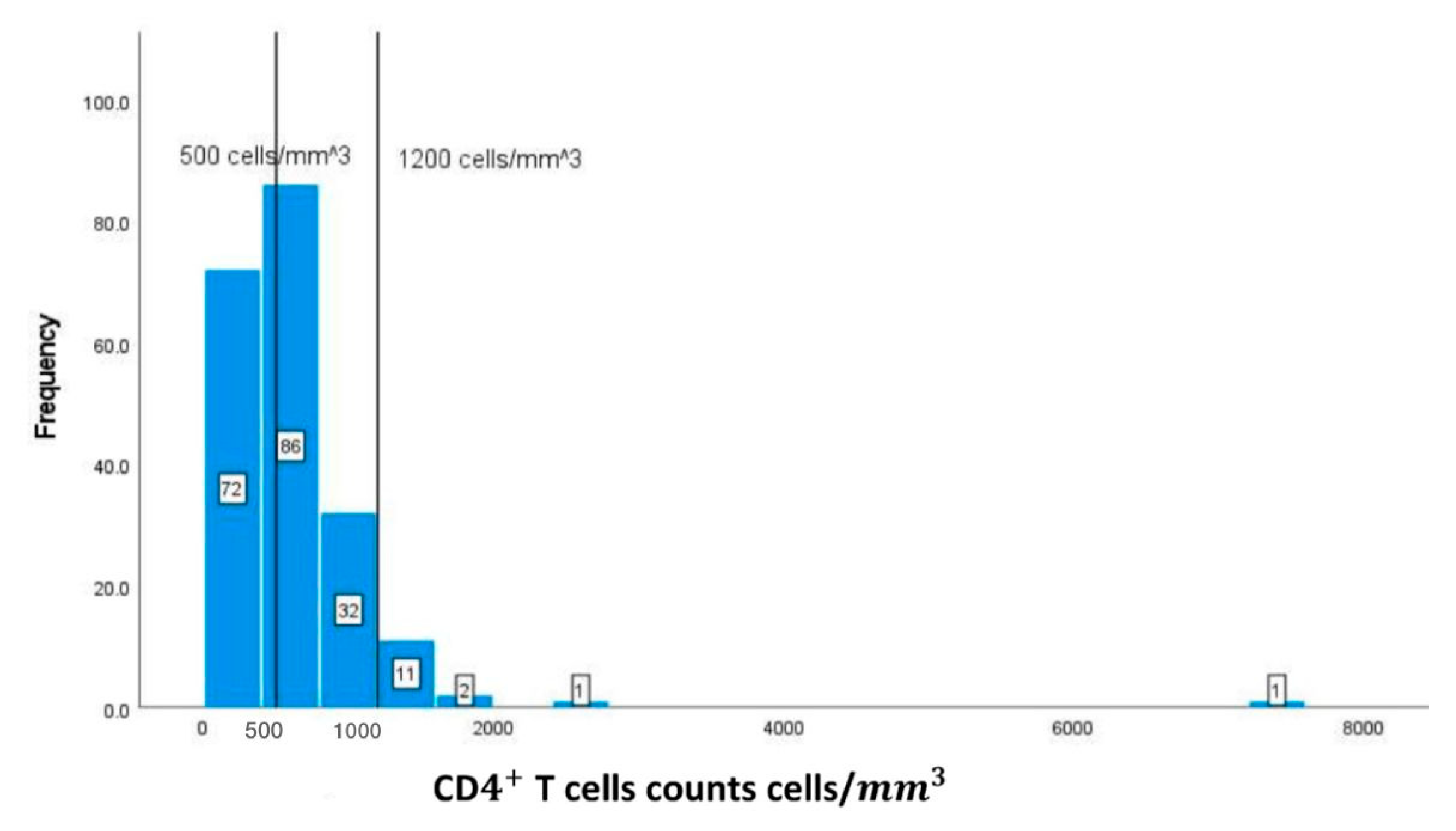
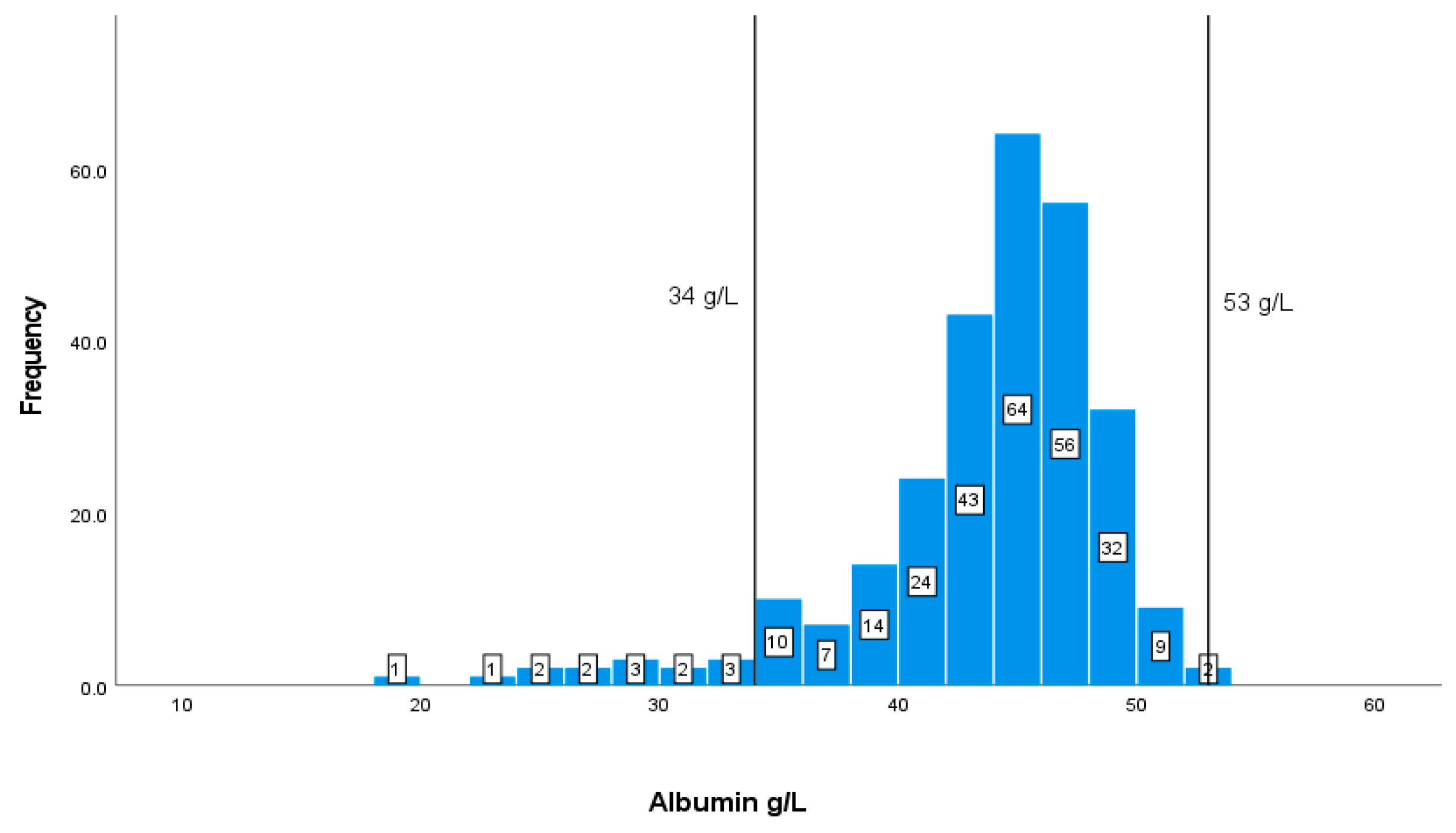
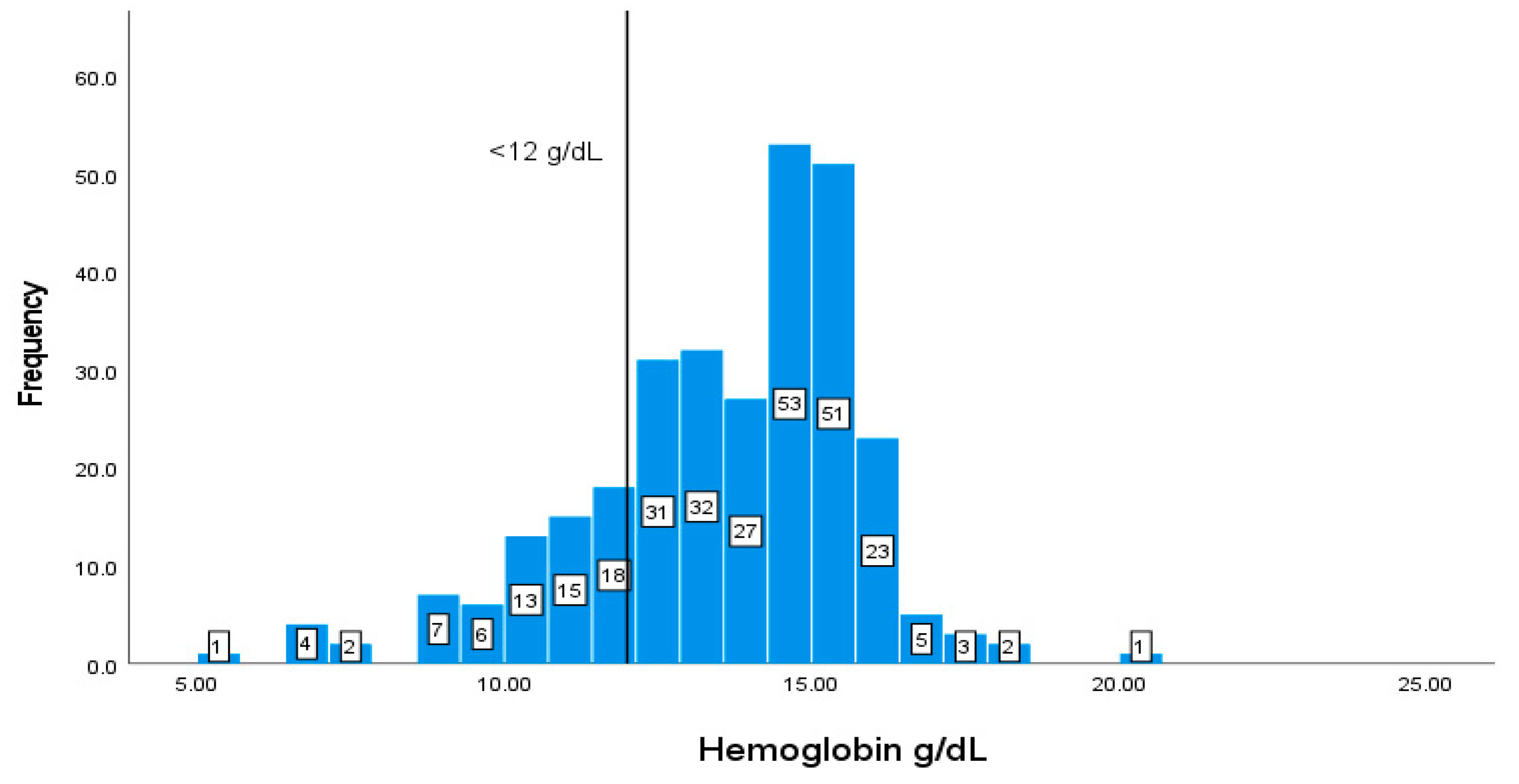
| Markers | *Reference range | SD |
|---|---|---|
| CDT cells counts | (500-1200 cells/) | 620.91673.40 |
| Albumin | (35-53 g/L) | 42.775.62 |
| Hb | Male: (14-18 g/L)Female: (12-16 g/L) | 13.512.31 |
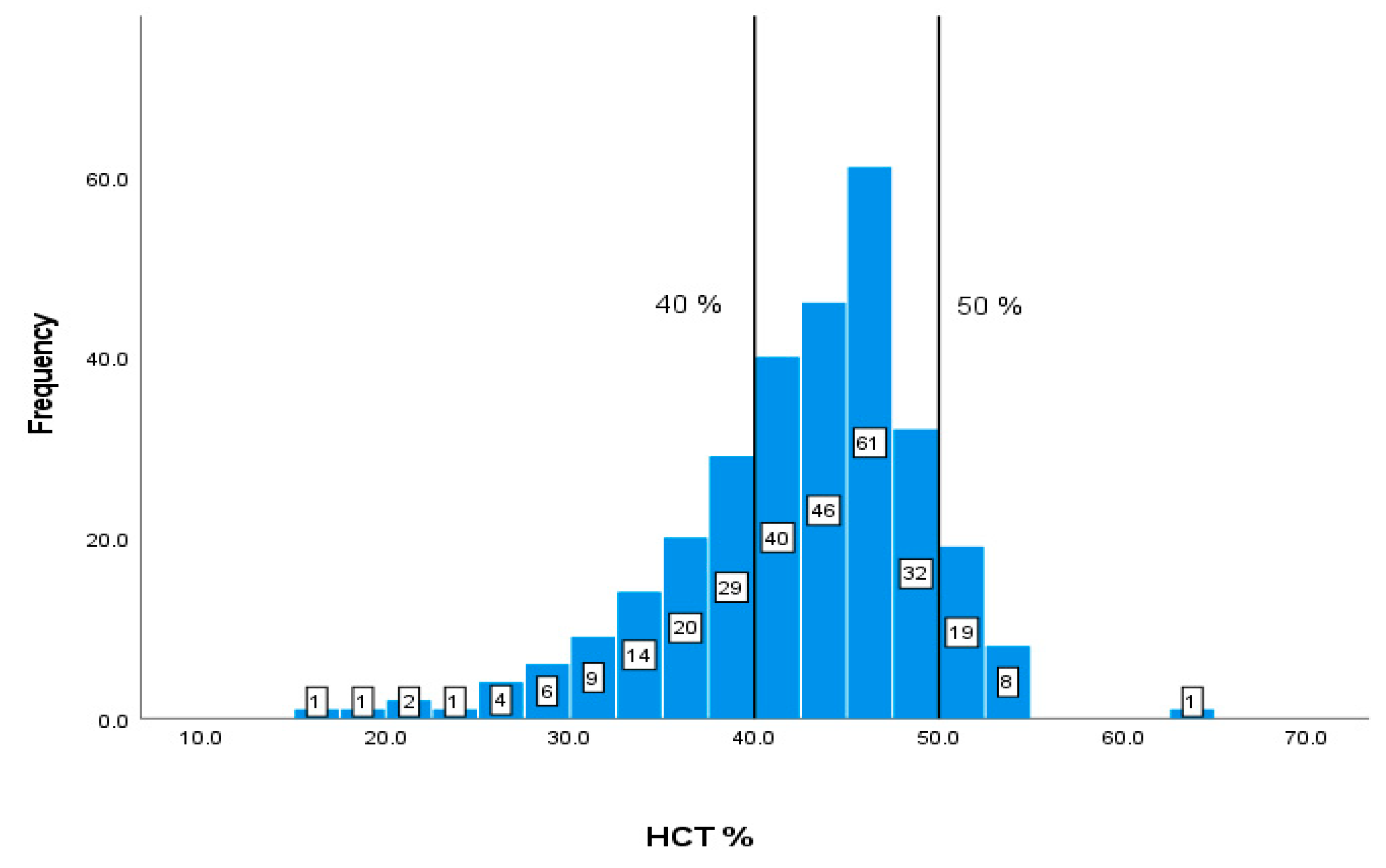
| HCT | 40-50 % | 42.15 7.03 |
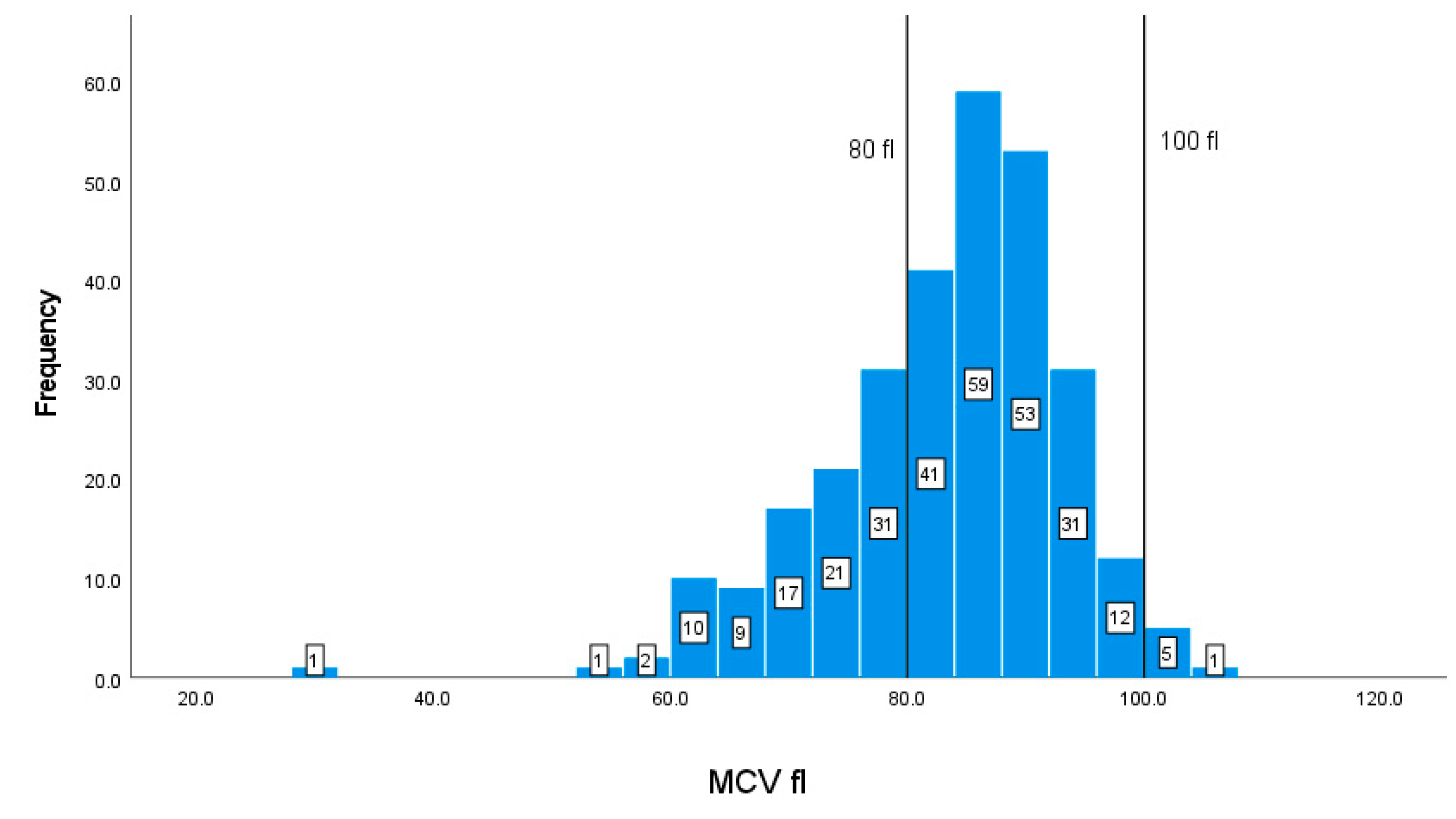
| MCV | 80-100 fl | 83.1310.28 |
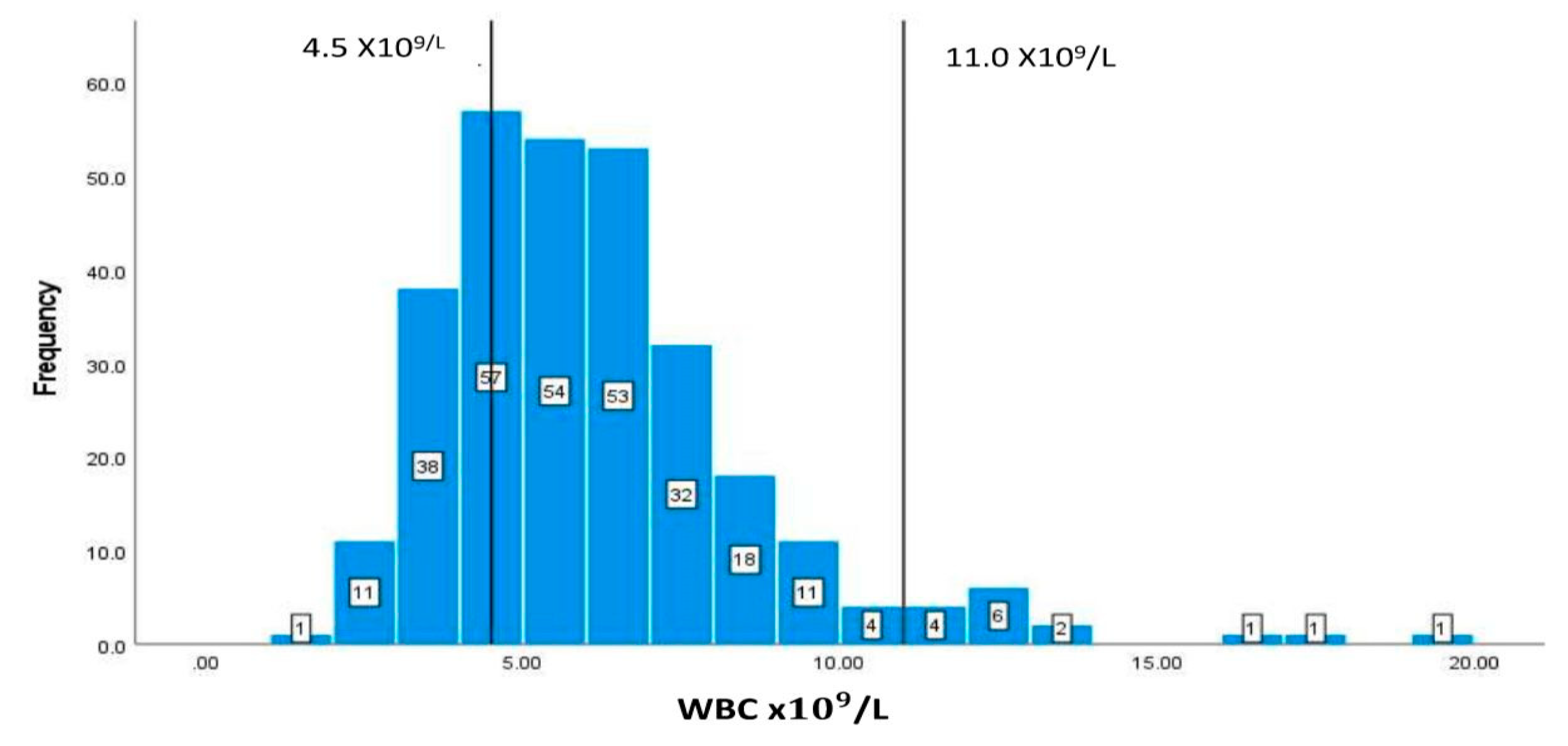
| WBC | 4.5-11/L | 6.162.59 |
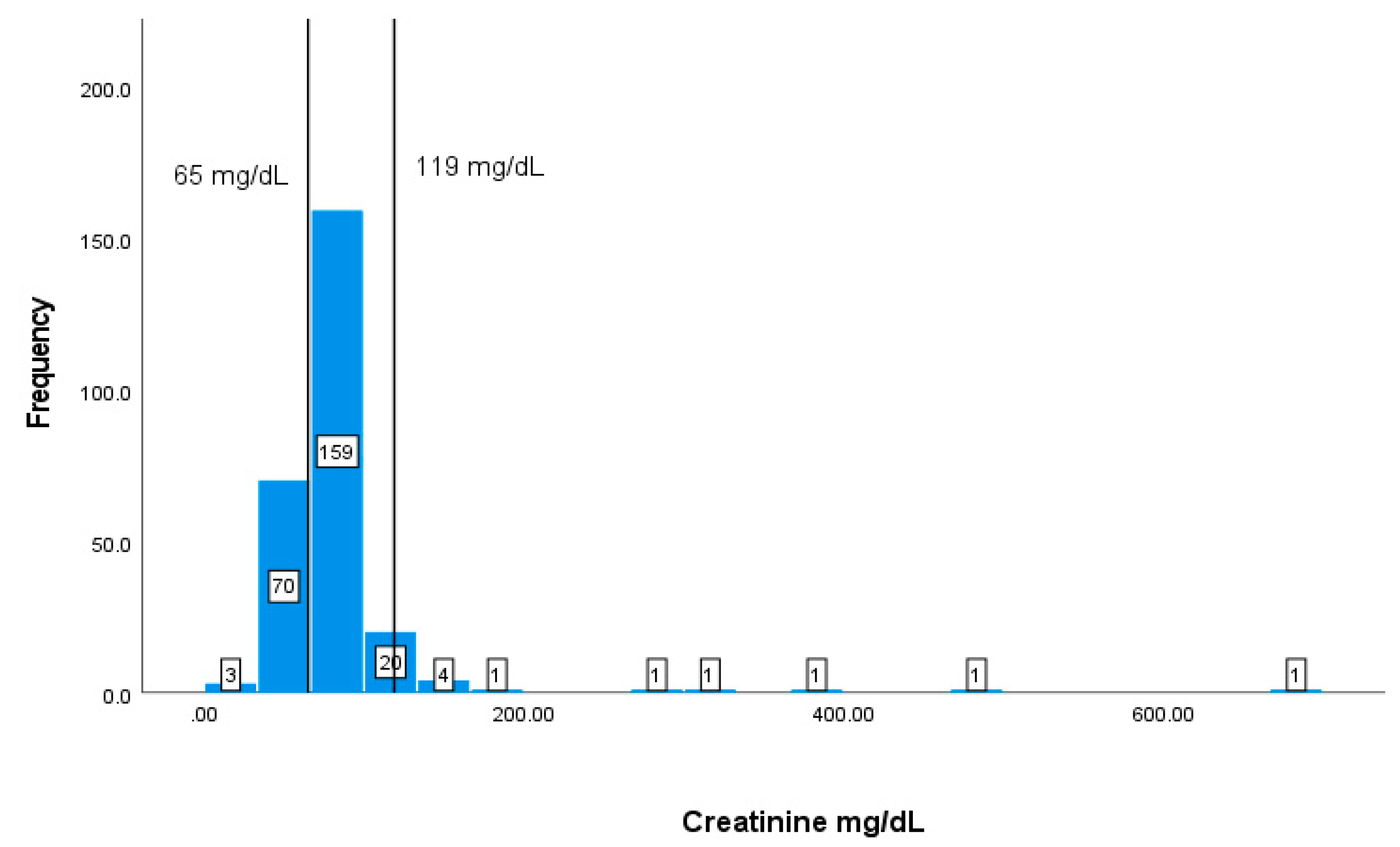
| Creatinine | 65-119 mg/dL | 84.1957.28 |
| Albumin | Cr | Hb | HCT | WBC | MCV | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Creatinine | Correlation coefficient | -0.136 | |||||
| p-value | 0.069 | ||||||
| Hb | Correlation coefficient | .619** | 0.104 | ||||
| p-value | 0 | 0.148 | |||||
| HCT | Correlation coefficient | .612** | 0.081 | .933** | |||
| p-value | 0 | 0.255 | 0 | ||||
| WBC | Correlation coefficient | -0.016 | 0.068 | -0.026 | -0.008 | ||
| p-value | 0.821 | 0.342 | 0.706 | 0.911 | |||
| MCV | Correlation coefficient | 0.091 | 0.046 | .374** | .349** | 0.071 | |
| p-value | 0.2 | 0.52 | 0 | 0 | 0.293 | ||
| CD4+T cells | Correlation coefficient | .271** | -0.02 | 0.161 | .183* | .165* | -0.041 |
| p-value | 0.002 | 0.817 | 0.053 | 0.027 | 0.047 | 0.627 | |
| Model | Coefficients | t | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Std. Error | |||
| (Constant) | -801.898 | 782.798 | -1.024 | 0.308 |
| Albumin | 39.275 | 16.353 | 2.402 | 0.018 |
| Creatinine | -0.049 | 1.013 | -0.048 | 0.961 |
| Hb | -34.312 | 104.535 | -0.328 | 0.743 |
| HCT | 19.406 | 35.736 | 0.543 | 0.588 |
| WBC | 46.563 | 27.002 | 1.724 | 0.087 |
| MCV | -11.122 | 6.903 | -1.611 | 0.110 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





