Submitted:
07 May 2023
Posted:
08 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
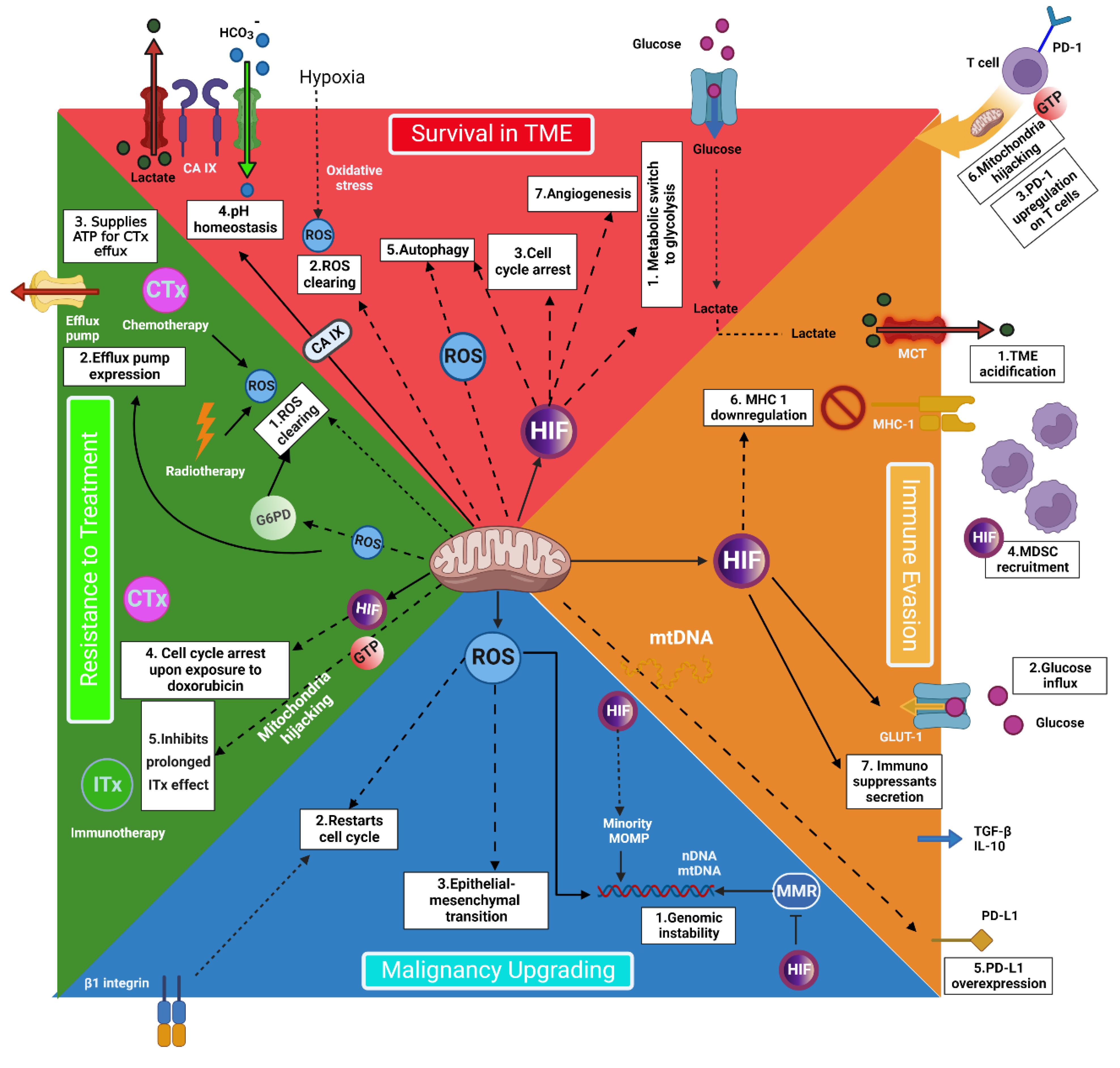
2. The Pivotal Role of Mitochondria in Cancer Cells’ Metabolism
3. Mitochondria Individualized Role in Cancer Metastasis
4. Targeting Mitochondria: A Practical Strategy for Personalized Cancer Treatment
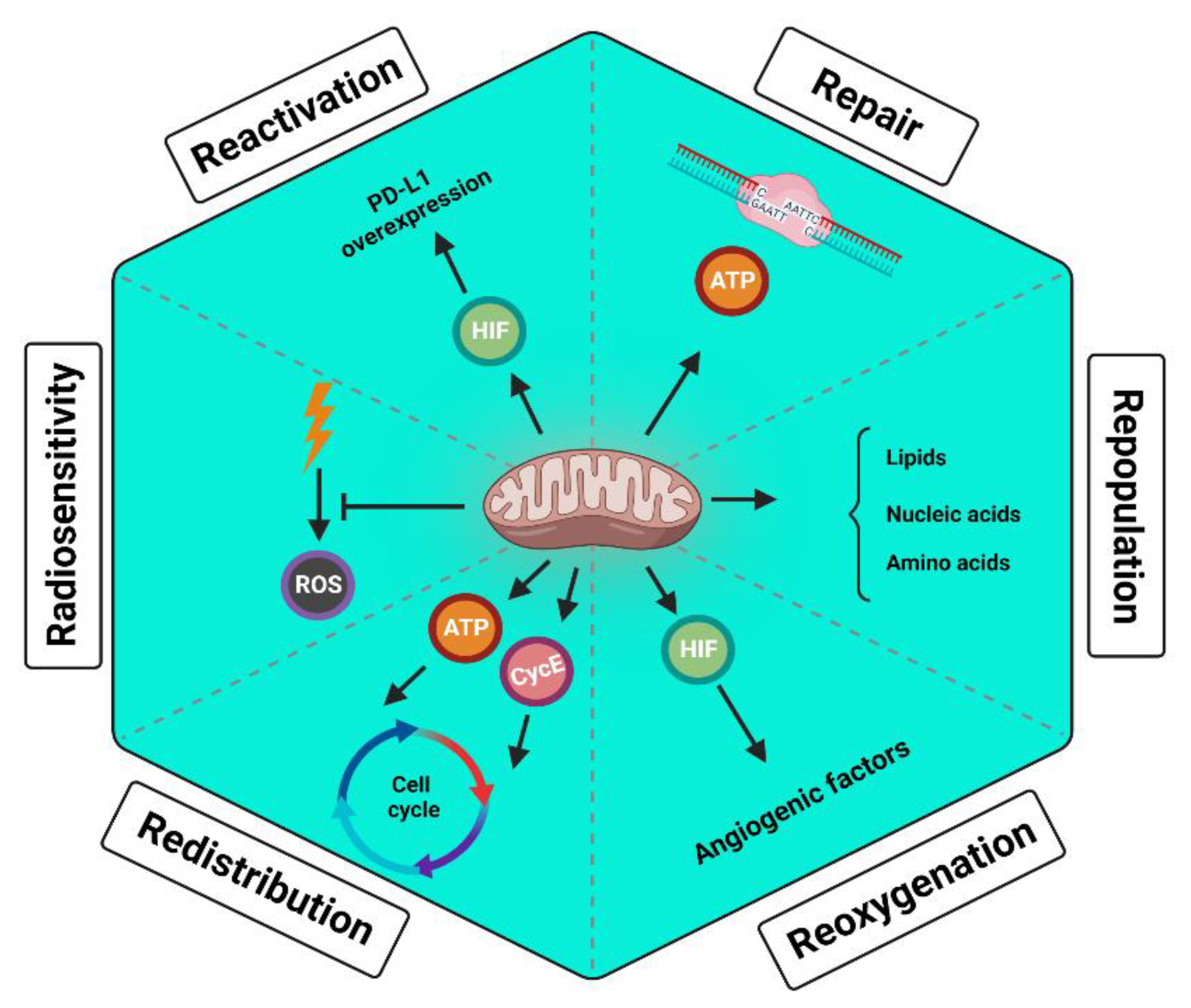
5. Enhancing the Normal Cells’ Mitochondria Reduces the Radiotherapy Toxicity
6. Immune Cells’ Mitochondria: A Chance to Improve Treatment Results
7. Heteroplasmy Provides Unique Profiles in Cancer
8. Conclusions
References
- Trapani, D.; Franzoi, M.A.; Burstein, H.J.; Carey, L.A.; Delaloge, S.; Harbeck, N.; Hayes, D.F.; Kalinsky, K.; Pusztai, L.; Regan, M.M.; et al. Risk-adapted modulation through de-intensification of cancer treatments: an ESMO classification. Ann Oncol 2022, 33, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, T.; Dash, C.; Jayabalan, R.; Khiste, S.; Kulkarni, A.; Kurmi, K.; Mondal, J.; Majumder, P.K.; Bardia, A.; Jang, H.L.; et al. Intercellular nanotubes mediate mitochondrial trafficking between cancer and immune cells. Nat Nanotechnol 2022, 17, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Heredia, J.M.; Carnero, A. Role of Mitochondria in Cancer Stem Cell Resistance. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaney, G.; Jacob, S.; Featherstone, C.; Barton, M. The role of radiotherapy in cancer treatment: estimating optimal utilization from a review of evidence-based clinical guidelines. Cancer 2005, 104, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overgaard, J.; Aznar, M.C.; Bacchus, C.; Coppes, R.P.; Deutsch, E.; Georg, D.; Haustermans, K.; Hoskin, P.; Krause, M.; Lartigau, E.F.; et al. Personalised radiation therapy taking both the tumour and patient into consideration. Radiother Oncol 2022, 166, A1–a5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelkarem, O.A.I.; Choudhury, A.; Burnet, N.G.; Summersgill, H.R.; West, C.M.L. Effect of Race and Ethnicity on Risk of Radiotherapy Toxicity and Implications for Radiogenomics. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 2022, 34, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghizadeh-Hesary, F.; Akbari, H.; Bahadori, M.; Behnam, B. Targeted Anti-Mitochondrial Therapy: The Future of Oncology. Genes 2022, 13, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, H.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F.; Bahadori, M. Mitochondria determine response to anti-programmed cell death protein-1 (anti-PD-1) immunotherapy: An evidence-based hypothesis. Mitochondrion 2022, 62, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V. Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Tumor Metastasis. Annu Rev Pathol 2018, 13, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazilaty, H.; Gardaneh, M.; Akbari, P.; Zekri, A.; Behnam, B. SLUG and SOX9 Cooperatively Regulate Tumor Initiating Niche Factors in Breast Cancer. Cancer Microenviron 2016, 9, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazilaty, H.; Gardaneh, M.; Bahrami, T.; Salmaninejad, A.; Behnam, B. Crosstalk between breast cancer stem cells and metastatic niche: emerging molecular metastasis pathway? Tumour Biol 2013, 34, 2019–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, V.; Tuli, H.S.; Varol, A.; Thakral, F.; Yerer, M.B.; Sak, K.; Varol, M.; Jain, A.; Khan, M.A.; Sethi, G. Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Cancer Progression: Molecular Mechanisms and Recent Advancements. Biomolecules 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Jang, K.; Miller, P.; Picon-Ruiz, M.; Yeasky, T.M.; El-Ashry, D.; Slingerland, J.M. VEGFA links self-renewal and metastasis by inducing Sox2 to repress miR-452, driving Slug. Oncogene 2017, 36, 5199–5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erler, J.T.; Bennewith, K.L.; Nicolau, M.; Dornhöfer, N.; Kong, C.; Le, Q.T.; Chi, J.T.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Giaccia, A.J. Lysyl oxidase is essential for hypoxia-induced metastasis. Nature 2006, 440, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amendola, P.G.; Reuten, R.; Erler, J.T. Interplay Between LOX Enzymes and Integrins in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gisbergen, M.W.; Offermans, K.; Voets, A.M.; Lieuwes, N.G.; Biemans, R.; Hoffmann, R.F.; Dubois, L.J.; Lambin, P. Mitochondrial Dysfunction Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced HIF-1α Stabilization and Expression of Its Downstream Targets. Front Oncol 2020, 10, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paupe, V.; Prudent, J. New insights into the role of mitochondrial calcium homeostasis in cell migration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2018, 500, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, E.; O'Sullivan, J.; Marcone, S. Targeting cancer-cell mitochondria and metabolism to improve radiotherapy response. Transl Oncol 2021, 14, 100905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houshyari, M.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. Is Mitochondrial Metabolism a New Predictive Biomarker for Antiprogrammed Cell Death Protein-1 Immunotherapy? JCO Oncol Pract 2022, Op2200733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Hesary, F.; Houshyari, M.; Farhadi, M. Mitochondrial metabolism: a predictive biomarker of radiotherapy efficacy and toxicity. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentle, M.S.; Reinicke, K.E.; Bey, E.A.; Spitz, D.R.; Boothman, D.A. Calcium-dependent modulation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 alters cellular metabolism and DNA repair. J Biol Chem 2006, 281, 33684–33696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lévy, N.; Martz, A.; Bresson, A.; Spenlehauer, C.; de Murcia, G.; Ménissier-de Murcia, J. XRCC1 is phosphorylated by DNA-dependent protein kinase in response to DNA damage. Nucleic Acids Res 2006, 34, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlov, S.; Gueven, N.; Keating, K.; Ramsay, J.; Lavin, M.F. ATP activates ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) in vitro. Importance of autophosphorylation. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 9309–9317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellenberger, T.; Tomkinson, A.E. Eukaryotic DNA ligases: structural and functional insights. Annu Rev Biochem 2008, 77, 313–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaupel, P.; Multhoff, G. Revisiting the Warburg effect: historical dogma versus current understanding. J Physiol 2021, 599, 1745–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotomalala, A.; Escande, A.; Furlan, A.; Meignan, S.; Lartigau, E. Hypoxia in Solid Tumors: How Low Oxygenation Impacts the "Six Rs" of Radiotherapy. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2021, 12, 742215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Esteban, L.C.; Fajas, L. Cell cycle regulators in cancer cell metabolism. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease 2020, 1866, 165715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syljuåsen, R.G. Cell cycle effects in radiation oncology. Radiation Oncology; Wentz, F., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Salazar-Roa, M.; Malumbres, M. Fueling the Cell Division Cycle. Trends Cell Biol 2017, 27, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwa, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Nam, J.-M.; Harada, H. Tumor microenvironment and radioresistance. Experimental & Molecular Medicine 2021, 53, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoum, I.B.; Smallwood, C.A.; Siemens, D.R.; Graham, C.H. A mechanism of hypoxia-mediated escape from adaptive immunity in cancer cells. Cancer Res 2014, 74, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Yu, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, S. Relationship between p53 status and the bioeffect of ionizing radiation. Oncol Lett 2021, 22, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ericson, N.G.; Kulawiec, M.; Vermulst, M.; Sheahan, K.; O'Sullivan, J.; Salk, J.J.; Bielas, J.H. Decreased mitochondrial DNA mutagenesis in human colorectal cancer. PLoS Genet 2012, 8, e1002689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Yu, B.; Xue, Y.; Guo, R.; Su, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L. p53/PGC-1α-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction promotes PC3 prostate cancer cell apoptosis. Mol Med Rep 2020, 22, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Jarvis, I.W.H.; Bottai, M.; Dreij, K.; Stenius, U. TGF beta promotes repair of bulky DNA damage through increased ERCC1/XPF and ERCC1/XPA interaction. Carcinogenesis 2018, 40, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Yang, J.; Deng, S.; Xu, H.; Wu, D.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, S.; Hu, T.; Wu, F.; Zhou, H. TGF-β signaling in the tumor metabolic microenvironment and targeted therapies. Journal of Hematology & Oncology 2022, 15, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.W.; Sun, P.; Zhang, D.X.; Xiong, W.J.; Mi, J. Hexokinase 2 regulates G1/S checkpoint through CDK2 in cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Signal 2014, 26, 2210–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydström, J. Mitochondrial NADPH, transhydrogenase and disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics 2006, 1757, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.-Q.; Lin, J.-F.; Tian, T.; Xie, D.; Xu, R.-H. NADPH homeostasis in cancer: functions, mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2020, 5, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.N.; Lai, A.; Li, S.; Pope, W.B.; Teixeira, S.; Harris, R.J.; Woodworth, D.C.; Nghiemphu, P.L.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Ellingson, B.M. Increased sensitivity to radiochemotherapy in IDH1 mutant glioblastoma as demonstrated by serial quantitative MR volumetry. Neuro Oncol 2014, 16, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuani, L.; Sabatier, M.; Saland, E.; Cognet, G.; Poupin, N.; Bosc, C.; Castelli, F.A.; Gales, L.; Turtoi, E.; Montersino, C.; et al. Mitochondrial metabolism supports resistance to IDH mutant inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia. J Exp Med 2021, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sun, C.; Gu, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, F.; Hu, P.; Liang, W.; Cao, K.; et al. Mutation of IDH1 aggravates the fatty acid-induced oxidative stress in HCT116 cells by affecting the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Mol Med Rep 2019, 19, 2509–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlante, A.; Calissano, P.; Bobba, A.; Azzariti, A.; Marra, E.; Passarella, S. Cytochrome c is released from mitochondria in a reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent fashion and can operate as a ROS scavenger and as a respiratory substrate in cerebellar neurons undergoing excitotoxic death. J Biol Chem 2000, 275, 37159–37166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, M.; Burgess, J.T.; O’Byrne, K.; Richard, D.J.; Bolderson, E. PARP Inhibitors: Clinical Relevance, Mechanisms of Action and Tumor Resistance. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillot, C.; Favaudon, V.; Herceg, Z.; Sagne, C.; Sauvaigo, S.; Merle, P.; Hall, J.; Chemin, I. PARP inhibition and the radiosensitizing effects of the PARP inhibitor ABT-888 in in vitrohepatocellular carcinoma models. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.D.; Parveen, A.; Yadav, D.K. Role of PARP in TNBC: Mechanism of Inhibition, Clinical Applications, and Resistance. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbini, A.A.; Guerra, F.; Greco, M.; Marra, E.; Gandee, L.; Xiao, G.; Lotan, Y.; Gasparre, G.; Hsieh, J.T.; Moro, L. Mitochondrial DNA depletion sensitizes cancer cells to PARP inhibitors by translational and post-translational repression of BRCA2. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Graham, P.H.; Hao, J.; Ni, J.; Bucci, J.; Cozzi, P.J.; Kearsley, J.H.; Li, Y. PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitors enhance radiosensitivity in radioresistant prostate cancer cells through inducing apoptosis, reducing autophagy, suppressing NHEJ and HR repair pathways. Cell Death Dis 2014, 5, e1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Cruz López, K.G.; Toledo Guzmán, M.E.; Sánchez, E.O.; García Carrancá, A. mTORC1 as a Regulator of Mitochondrial Functions and a Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Frontiers in Oncology 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yi, J.; Tao, L.; Huang, G.; Chu, X.; Song, H.; Chen, L. Wnt signaling induces radioresistance through upregulating HMGB1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 2018, 9, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Kang, R.; Livesey, K.M.; Kroemer, G.; Billiar, T.R.; Van Houten, B.; Zeh, H.J., 3rd; Lotze, M.T. High-mobility group box 1 is essential for mitochondrial quality control. Cell Metab 2011, 13, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.P.; Zheng, C.C.; Huang, Y.N.; He, M.L.; Xu, W.W.; Li, B. Molecular mechanisms of chemo- and radiotherapy resistance and the potential implications for cancer treatment. MedComm (2020) 2021, 2, 315–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albensi, B.C. What Is Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB) Doing in and to the Mitochondrion? Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pour Khavari, A.; Liu, Y.; He, E.; Skog, S.; Haghdoost, S. Serum 8-Oxo-dG as a Predictor of Sensitivity and Outcome of Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy of Upper Gastrointestinal Tumours. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018, 2018, 4153574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Sun, M.; Li, G.H.; Wu, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.; Jin, F.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, D.L. Activation of the phosphorylation of ATM contributes to radioresistance of glioma stem cells. Oncol Rep 2013, 30, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, J.S.; Lin, Z.P.; Sartorelli, A.C.; Bonawitz, N.D.; Shadel, G.S. Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated kinase regulates ribonucleotide reductase and mitochondrial homeostasis. J Clin Invest 2007, 117, 2723–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, A.; Feldman, C.H.; Niedernhofer, L.J. ERCC1 and XRCC1 as biomarkers for lung and head and neck cancer. Pharmgenomics Pers Med 2011, 4, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Xu, J.; Ji, G.; Liu, Q.; Shao, W.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J.; Weng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Deficiency of X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1 in primordial germ cells contributes to male infertility. The FASEB Journal 2019, 33, 7427–7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, S.; Pang, J.; Yin, J.; Zhang, J.; Mu, D.; Tang, S.; Li, L.; Bao, H.; Wu, X. Genomic Profiling Reveals Novel Predictive Biomarkers for Chemo-Radiotherapy Toxicity and Efficacy in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics 2021, 111, e437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Zhuang, J.; Zhou, P.; Liu, X.; Luo, Y. MicroRNA-34a promotes mitochondrial dysfunction-induced apoptosis in human lens epithelial cells by targeting Notch2. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 110209–110220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, K.; Ye, P.; Matsumiya, T.; Tanji, K.; Ozaki, T. Emerging functional cross-talk between the Keap1-Nrf2 system and mitochondria. J Clin Biochem Nutr 2015, 56, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A.; Choubey, V.; Gupta, R.; Kuum, M.; Safiulina, D.; Vaarmann, A.; Gogichaishvili, N.; Liiv, M.; Ilves, I.; Tämm, K.; et al. A novel role of KEAP1/PGAM5 complex: ROS sensor for inducing mitophagy. Redox Biology 2021, 48, 102186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitosugi, T.; Fan, J.; Chung, T.-W.; Lythgoe, K.; Wang, X.; Xie, J.; Ge, Q.; Gu, T.-L.; Polakiewicz, Roberto D. ; Roesel, Johannes L.; et al. Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Mitochondrial Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 1 Is Important for Cancer Metabolism. Molecular Cell 2011, 44, 864–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Xiao, H.; Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, C.; Jin, Y.; Li, H.; Cui, M.; Fan, S. LncRNA HOTAIR enhances breast cancer radioresistance through facilitating HSPA1A expression via sequestering miR-449b-5p. Thoracic Cancer 2020, 11, 1801–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, P.; Xiong, Q.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Fleming, J.; Gao, D.; Bi, L.; Ge, F. Quantitative Proteomics Analysis Reveals Novel Insights into Mechanisms of Action of Long Noncoding RNA Hox Transcript Antisense Intergenic RNA (HOTAIR) in HeLa Cells. Mol Cell Proteomics 2015, 14, 1447–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Zhou, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, P.; Liu, S.; Sun, S.; Ren, Y.; Mei, M. Targeting HOTAIR induces mitochondria related apoptosis and inhibits tumor growth in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Current Molecular Medicine 2015, 15, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, T.; Urushihara, Y.; Murata, Y.; Fujishima, Y.; Hosoi, Y. AMPK increases expression of ATM through transcriptional factor Sp1 and induces radioresistance under severe hypoxia in glioblastoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2022, 590, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzig, S.; Shaw, R.J. AMPK: guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2018, 19, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, H.; Anne Adanma Obara, E.; Elbæk, K.J.; Vitting-Serup, K.; Hamerlik, P. Replication Protein A (RPA) Mediates Radio-Resistance of Glioblastoma Cancer Stem-Like Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shan, G. Mitochondria Encoded Non-coding RNAs in Cell Physiology. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Yin, Z.; Ren, J.; Huang, K.; Liu, L.; Yang, K.; et al. β-Trcp ubiquitin ligase and RSK2 kinase-mediated degradation of FOXN2 promotes tumorigenesis and radioresistance in lung cancer. Cell Death Differ 2018, 25, 1473–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozowski, RM. Targeting the Ser/Thr protein kinase RSK to reduce breast cancer metastasis, : Vanderbilt University; 2015.
- Chu, C.; Niu, X.; Ou, X.; Hu, C. LAPTM4B knockdown increases the radiosensitivity of EGFR-overexpressing radioresistant nasopharyngeal cancer cells by inhibiting autophagy. Onco Targets Ther 2019, 12, 5661–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milkereit, R.; Persaud, A.; Vanoaica, L.; Guetg, A.; Verrey, F.; Rotin, D. LAPTM4b recruits the LAT1-4F2hc Leu transporter to lysosomes and promotes mTORC1 activation. Nature Communications 2015, 6, 7250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Yadav, P.; Sainis, K.B.; Shankar, B.S. TNF-α and IGF-1 differentially modulate ionizing radiation responses of lung cancer cell lines. Cytokine 2018, 101, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, A.; Jung, H.; Lee, H.; Singh, K.; Roy, M.; Gohel, D.; Kim, H.B.; Mane, M.; Vasiyani, H.; Currim, F.; et al. TNF-α differentially modulates subunit levels of respiratory electron transport complexes of ER/PR +ve/−ve breast cancer cells to regulate mitochondrial complex activity and tumorigenic potential. Cancer & Metabolism 2021, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, N.S. Mitochondrial complex III: an essential component of universal oxygen sensing machinery? Respir Physiol Neurobiol 2010, 174, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dörr, W. Radiobiology of tissue reactions. Ann ICRP 2015, 44, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolatou-Galitis, O.; Bossi, P.; Orlandi, E.; René-Jean, B. The role of benzydamine in prevention and treatment of chemoradiotherapy-induced mucositis. Support Care Cancer 2021, 29, 5701–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holley, A.K.; Miao, L.; St Clair, D.K.; St Clair, W.H. Redox-modulated phenomena and radiation therapy: the central role of superoxide dismutases. Antioxid Redox Signal 2014, 20, 1567–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobin, K.; Marczyk, M.; Halle, M.; Danielsson, D.; Papiez, A.; Sangsuwan, T.; Bendes, A.; Hong, M.G.; Qundos, U.; Harms-Ringdahl, M.; et al. Molecular Profiling for Predictors of Radiosensitivity in Patients with Breast or Head-and-Neck Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, N.; Groenendyk, J.; Michalak, M. Binding Proteins | Ca2+ Binding/Buffering Proteins: ER Luminal Proteins☆. In Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry III (Third Edition), Jez, J., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, 2021; pp. 534–546. [Google Scholar]
- Henke, N.; Albrecht, P.; Pfeiffer, A.; Toutzaris, D.; Zanger, K.; Methner, A. Stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) is involved in the regulation of mitochondrial shape and bioenergetics and plays a role in oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 2012, 287, 42042–42052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewson, G. Bax to the wall: Bax-and Bak-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in apoptosis. Trends in Biochemical Sciences 2001, 26, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, J.A.; Shyam, R.; Choi, M.; Ogando, D.G. The H(+) Transporter SLC4A11: Roles in Metabolism, Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Uncoupling. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprung, C.N.; Forrester, H.B.; Siva, S.; Martin, O.A. Immunological markers that predict radiation toxicity. Cancer Lett 2015, 368, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Hwang, S.C.; Choi, K.S.; Yoon, G. TGF beta1 induces prolonged mitochondrial ROS generation through decreased complex IV activity with senescent arrest in Mv1Lu cells. Oncogene 2005, 24, 1895–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.A.; Larner, A.C. Toward a new STATe: the role of STATs in mitochondrial function. Semin Immunol 2014, 26, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, L.; Terradas, M.; Camps, J.; Martín, M.; Tusell, L.; Genescà, A. Aging and radiation: bad companions. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S. The Mitochondrial Basis of Aging and Age-Related Disorders. Genes (Basel) 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, J.M.; Demaree, S.R. Relationship between NADP-specific isocitrate dehydrogenase and glutathione peroxidase in aging rat skeletal muscle. Mech Ageing Dev 2001, 122, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Tepper, J.E. Radiation therapy-associated toxicity: Etiology, management, and prevention. CA Cancer J Clin 2021, 71, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, A.; Alack, K.; Richter, M.J.; Krüger, K. Immune-regulating effects of exercise on cigarette smoke-induced inflammation. J Inflamm Res 2018, 11, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, J.M.; New, J.; Hamilton, C.D.; Lominska, C.; Shnayder, Y.; Thomas, S.M. Radiation-induced fibrosis: mechanisms and implications for therapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2015, 141, 1985–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willenborg, S.; Sanin, D.E.; Jais, A.; Ding, X.; Ulas, T.; Nüchel, J.; Popović, M.; MacVicar, T.; Langer, T.; Schultze, J.L.; et al. Mitochondrial metabolism coordinates stage-specific repair processes in macrophages during wound healing. Cell Metabolism 2021, 33, 2398–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratson, C.L.; Larkins, M.C.; Karimian, B.H.; Curtis, C.M.; Lepera, P.A.; Brodish, B.N.; Ju, A.W. The Impact of Smoking, Alcohol Use, Recurrent Disease, and Age on the Development of Neck Fibrosis in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Following Radiation Therapy. Frontiers in Oncology 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoek, J.B.; Cahill, A.; Pastorino, J.G. Alcohol and mitochondria: a dysfunctional relationship. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 2049–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memme, J.M.; Erlich, A.T.; Phukan, G.; Hood, D.A. Exercise and mitochondrial health. J Physiol 2021, 599, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luoma, R.L.; Butler, M.W.; Stahlschmidt, Z.R. Plasticity of immunity in response to eating. J Exp Biol 2016, 219, 1965–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Antona, G.; Ragni, M.; Cardile, A.; Tedesco, L.; Dossena, M.; Bruttini, F.; Caliaro, F.; Corsetti, G.; Bottinelli, R.; Carruba, M.O.; et al. Branched-Chain Amino Acid Supplementation Promotes Survival and Supports Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Middle-Aged Mice. Cell Metabolism 2010, 12, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Shanmugam, H.; Abdallah, H.; John Britto, J.S.; Galerati, I.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Frühbeck, G.; Portincasa, P. The Potential of the Mediterranean Diet to Improve Mitochondrial Function in Experimental Models of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, N.R.; Macedo, G.E.; Martins, I.K.; Gomes, K.K.; de Carvalho, N.R.; Posser, T.; Franco, J.L. Short-term sleep deprivation with exposure to nocturnal light alters mitochondrial bioenergetics in Drosophila. Free Radic Biol Med 2018, 120, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, A.H.; Costa, A.B.; Engel, J.D.G.; Rezin, G.T. Mitochondrial dysfunction in obesity. Life Sci 2018, 192, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.A.; Singal, A.K. Mitochondrial dysfunction and alcohol-associated liver disease: a novel pathway and therapeutic target. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2020, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malińska, D.; Więckowski, M.R.; Michalska, B.; Drabik, K.; Prill, M.; Patalas-Krawczyk, P.; Walczak, J.; Szymański, J.; Mathis, C.; Van der Toorn, M.; et al. Mitochondria as a possible target for nicotine action. J Bioenerg Biomembr 2019, 51, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoto, K.; Chowdhury, P.S.; Kumar, A.; Sonomura, K.; Matsuda, F.; Fagarasan, S.; Honjo, T. Mitochondrial activation chemicals synergize with surface receptor PD-1 blockade for T cell-dependent antitumor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017, 114, E761–e770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzorno, J. Mitochondria-Fundamental to Life and Health. Integr Med (Encinitas) 2014, 13, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burtscher, J.; Romani, M.; Bernardo, G.; Popa, T.; Ziviani, E.; Hummel, F.C.; Sorrentino, V.; Millet, G.P. Boosting mitochondrial health to counteract neurodegeneration. Progress in Neurobiology 2022, 215, 102289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendt, L.; Fazzini, F.; Weissensteiner, H.; Bruckmoser, E.; Schönherr, S.; Schäfer, G.; Losso, J.L.; Streiter, G.A.; Lamina, C.; Rasse, M.; et al. Profiling of Mitochondrial DNA Heteroplasmy in a Prospective Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Study. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, J.F.; Sabelnykova, V.Y.; Weischenfeldt, J.; Simon, R.; Aguiar, J.A.; Alkallas, R.; Heisler, L.E.; Zhang, J.; Watson, J.D.; Chua, M.L.K.; et al. Mitochondrial mutations drive prostate cancer aggression. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloss-Brandstätter, A.; Schäfer, G.; Erhart, G.; Hüttenhofer, A.; Coassin, S.; Seifarth, C.; Summerer, M.; Bektic, J.; Klocker, H.; Kronenberg, F. Somatic mutations throughout the entire mitochondrial genome are associated with elevated PSA levels in prostate cancer patients. Am J Hum Genet 2010, 87, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, S.; LaFramboise, T. Mutational patterns in the breast cancer mitochondrial genome, with clinical correlates. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Yao, A.; Yang, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, F. Heteroplasmy of mutant mitochondrial DNA A10398G and analysis of its prognostic value in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett 2016, 12, 3081–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.; Bankier, A.T.; Barrell, B.G.; de Bruijn, M.H.; Coulson, A.R.; Drouin, J.; Eperon, I.C.; Nierlich, D.P.; Roe, B.A.; Sanger, F.; et al. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature 1981, 290, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandon, M.; Baldi, P.; Wallace, D.C. Mitochondrial mutations in cancer. Oncogene 2006, 25, 4647–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.-S.; Wang, H.-S.; Mugaka, B.P.; Yang, G.-J.; Ding, Y. Mitochondria: promising organelle targets for cancer diagnosis and treatment. Biomaterials Science 2018, 6, 2786–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.R.; Han, J. Mitochondrial Nucleoid: Shield and Switch of the Mitochondrial Genome. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017, 2017, 8060949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Gong, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, S.; Luo, Y. Mitochondrial DNA genomes revealed different patterns of high-altitude adaptation in high-altitude Tajiks compared with Tibetans and Sherpas. Scientific Reports 2020, 10, 10592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Wong, L.J.; Mims, M.P. Mitochondrial inheritance and cancer. Transl Res 2018, 202, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, D.; Zampieri, L.X.; Capelôa, T.; Van de Velde, J.A.; Sonveaux, P. Mitochondria in cancer. Cell Stress 2020, 4, 114–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajbner, Z.; Pnini, R.; Camus, M.F.; Miller, J.; Dowling, D.K. Experimental evidence that thermal selection shapes mitochondrial genome evolution. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 9500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Fu, Q.; Xu, B.; Zhou, H.; Gao, J.; Shao, X.; Xiong, J.; Gu, Q.; Wen, S.; Li, F.; et al. Breast cancer-associated mitochondrial DNA haplogroup promotes neoplastic growth via ROS-mediated AKT activation. Int J Cancer 2018, 142, 1786–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoi, M.; Nishimura, T.; Egashira, Y.; Kishida, F.; Watanuki, S. Relationship between mitochondrial haplogroup and physiological responses to hypobaric hypoxia. J Physiol Anthropol 2016, 35, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toncheva, D.; Serbezov, D.; Karachanak-Yankova, S.; Nesheva, D. Ancient mitochondrial DNA pathogenic variants putatively associated with mitochondrial disease. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0233666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Fang, H.; Lyu, J.; Shen, L. Association between mitochondrial DNA haplogroup variation and coronary artery disease. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2020, 30, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wu, J.; Dressman, D.C.; Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.; Markowitz, S.D.; Velculescu, V.E.; Diaz, L.A., Jr.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; Papadopoulos, N. Heteroplasmic mitochondrial DNA mutations in normal and tumour cells. Nature 2010, 464, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechuga-Vieco, A.V.; Latorre-Pellicer, A.; Johnston, I.G.; Prota, G.; Gileadi, U.; Justo-Méndez, R.; Acín-Pérez, R.; Martínez-de-Mena, R.; Fernández-Toro, J.M.; Jimenez-Blasco, D.; et al. Cell identity and nucleo-mitochondrial genetic context modulate OXPHOS performance and determine somatic heteroplasmy dynamics. Sci Adv 2020, 6, eaba5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooks, D.R.; Maio, N.; Lang, M.; Ricketts, C.J.; Vocke, C.D.; Gurram, S.; Turan, S.; Kim, Y.Y.; Cawthon, G.M.; Sohelian, F.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA alterations underlie an irreversible shift to aerobic glycolysis in fumarate hydratase-deficient renal cancer. Sci Signal 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.K.; Keum, D.Y. Nuclear and mitochondrial DNAs microsatellite instability and mitochondrial DNA copy number in adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of lung: a pilot study. Apmis 2015, 123, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.; Ru, G.; Mao, Z.; Wang, C.; Nie, Z.; Li, Q.; Huang-Yang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Liang, X.; Yu, J.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA depletion, mitochondrial mutations and high TFAM expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 84373–84383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wan, J.; Song, R.; Zhao, H. Peripheral blood mitochondrial DNA copy number, length heteroplasmy and breast cancer risk: a replication study. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Alvarez, M.I.; Zorzano, A. Mitochondrial Dynamics and Liver Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K.S.; Mukherjee, S. Mitophagy in Carcinogenesis and Tumour Progression- A New Paradigm with Emerging Importance. Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry 2021, 21, 2130–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.S.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Gerstung, M.; Martincorena, I.; Nik-Zainal, S.; Ramakrishna, M.; Davies, H.R.; Papaemmanuil, E.; Gundem, G.; Shlien, A.; et al. Origins and functional consequences of somatic mitochondrial DNA mutations in human cancer. Elife 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marlein, C.R.; Zaitseva, L.; Piddock, R.E.; Robinson, S.D.; Edwards, D.R.; Shafat, M.S.; Zhou, Z.; Lawes, M.; Bowles, K.M.; Rushworth, S.A. NADPH oxidase-2 derived superoxide drives mitochondrial transfer from bone marrow stromal cells to leukemic blasts. Blood 2017, 130, 1649–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampieri, L.X.; Silva-Almeida, C.; Rondeau, J.D.; Sonveaux, P. Mitochondrial Transfer in Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Amado, C.J.; Bazan-Cordoba, A.; Hidalgo-Miranda, A.; Jiménez-Morales, S. Mitochondrial Heteroplasmy Shifting as a Potential Biomarker of Cancer Progression. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickerson, T.; Jauregui, C.E.; Teng, Y. Friend or foe? Mitochondria as a pharmacological target in cancer treatment. Future Med Chem 2017, 9, 2197–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filograna, R.; Mennuni, M.; Alsina, D.; Larsson, N.G. Mitochondrial DNA copy number in human disease: the more the better? FEBS Lett 2021, 595, 976–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frattaruolo, L.; Brindisi, M.; Curcio, R.; Marra, F.; Dolce, V.; Cappello, A.R. Targeting the Mitochondrial Metabolic Network: A Promising Strategy in Cancer Treatment. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factors | Cancer | Ref. | Interaction with mitochondria | Ref. |
| Increasing radioresistance | ||||
| Mutated P53 | Various | [32] | - Mutated p53 preserves mtDNA integrity - Mutated p53 improves mt capacity (PGC1α-mediated) - More functional mt scavenge more RT-induced ROS |
[33] [34] [7] |
| TGF-β | HCC | [35] | - TGF-β signalling in CAFs mediates reverse Warburg effect - CAFs’ lactate and pyruvate feed cancer cells’ mt OxPhos - Activated OxPhos helps to restore NADPH - NADPH supports the antioxidant defense system |
[36] [37] [38] [39] |
| IDH1 | Glioblastoma | [40] | - Mutated IDH1 enhances mt OxPhos (ROS generation) - Mutated IDH1 downregulates cytochrome c - Cytochrome c can nullify ROS - Thus, IDH1 mutation disrupts the ROS balance |
[41] [42] [43] |
| PARP | Breast Ovarian Prostate Pancreatic HCC |
[44] [45] |
- PARP requires RAD51 for HR - BRCA2 regulates RAD51 function - BRCA2 requires mt support - Thus, functional mt improves radioresistance by mediating HR |
[46] [46] [47] |
| PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway | Prostate | [48] | - mTOR upregulates mt proteins responsible for mt metabolism - More functional mt scavenge more RT-induced ROS |
[49] [7] |
| Wnt/β-catenin pathway | Esophageal SCC | [50] | - Wnt upregulates HMGB1 - HMGB1 activates mitochondria - More functional mt scavenge more RT-induced ROS |
[50] [51] [7] |
| NF-κB pathway | Breast Glioma HCC Melanoma NSCLC |
[52] | - Enhances mt respiration - Regulates mt dynamics - Regulates mt gene expression |
[53] |
| 8-oxo-dG | Esophageal Gastric |
[54] | - Serum 8-oxo-DG level represents cellular ROS - Cellular ROS is dependent on mt metabolism |
[54] [7] |
| ATM | Glioma | [55] | - Preserves mtDNA | [56] |
| XRCC1 | NSCLC HNC |
[57] | - Preserves mt respiratory chain | [58] |
| NOTCH2 | NSCLC | [59] | - Regulates mitochondrial function | [60] |
| KEAP1 | NSCLC | [59] | - Regulates mitochondrial function - Regulates mitophagy |
[61] [62] |
| FGFR1/3 | NSCLC | [59] | - Regulates mitochondrial energy metabolism | [63] |
| HOTAIR | Breast | [64] | - Regulates mitochondrial function | [65], [66] |
| AMPK | Glioblastoma | [67] | - Preserves mt biogenesis upon energy stress | [68] |
| RPA1 | Glioblastoma | [69] | - Preserves mtDNA | [70] |
| RSK2 | NSCLC | [71] | - Stimulates mt OxPhos | [72] |
| LAPTM4B | NPC | [73] | - Activates mTOR - mTOR upregulates mt proteins responsible for mt metabolism - More functional mt scavenge more RT-induced ROS |
[74] [49] [7] |
| Decreasing radioresistance | ||||
| TNFα | NSCLC | [75] | - Impairs mt complex I and III - Complex III is essential for NADPH activity - Thus, reduces mt capacity to scavenge RT-induced ROS |
[76] [77] |
| Note: This table is retrieved from Taghizadeh-Hesary et al. study [20]. Abbreviations:8-oxo-dG, 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine; Akt, protein kinase B; AMPK, serine/threonine kinase AMP-activated protein kinase; ATM, ataxia-telangiectasia mutated; BRCA2, breast cancer gene 2; CAF, cancer-associated fibroblasts; FGFR1/3, fibroblast growth factor 1/3; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HMGB1, high mobility group box 1; HOTAIR, HOX transcript antisense RNA; HR, homologous recombination; IDH1, Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1; KEAP1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein; LAPTM4B, lysosome-associated transmembrane protein 4B; mt, mitochondrial; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; NOTCH2, neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 2; NPC, nasopharyngeal carcinoma; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; OxPhos, oxidative phosphorylation; PARP, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1α; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinases; ROS, reactive oxygen species; RPA1, replication protein A1; RSK2, ribosomal S6 kinase; RT, radiotherapy; SCC, squamous cell carcinoma; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; XRCC1, X-ray repair cross complementing 1. | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




