2. Materials and Methods
The study includes 489 patients from the University Hospital Erlangen, Germany, with advanced rectal cancer treated with neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy. The data were collected between May 2010 and March 2022, March 2020 to March 2022 being the COVID-19 time. The questionnaires QLQ-C30 and QLQ-CR38 by the European Organization for Research Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) were used for the survey. They consist of 68 questions in total, item response options ranging from (1) (“not at all”) to (4) (“very much”) for all items except two ((1) (“very poor”) to (7) (“excellent”)). 49 of these questions can be answered by all patients, meanwhile the 19 other questions refer to different subgroups (males/females and patients with/without a stoma). All the answers were converted to 27 different scores, each score containing one to seven items. Out of those 27 scores, there are 17 functional scores and 10 symptom scores, both are recalculated as percentages (0 – 100 %). Regarding functional scores a higher percentage score is more desirable, whereas for symptom scores a lower percentage score represents a better QOL. As some questions can only be answered by a subgroup and/or include private sexual questions, thus resulting in not enough data, only 23 of the scores have been used in this study. Patients were asked to fill out the questionnaires in the beginning (day 0; questionnaire 1), during (day 14; week 2; questionnaire 2) and at the end (day 35; week 5; questionnaire 3) of radiotherapy and right before surgery (day 70; week 10; questionnaire 4). Additionally, four yearly follow-ups were surveyed, one year (435 days; questionnaire 5), two years (800 days; questionnaire 6), three years (1165 days; questionnaire 7) and four years (1530 days; questionnaire 8) after surgery.
Out of the 489 surveyed patients, 343 were males and 146 females. All questionnaires were divided to a Non-COVID-19 and a COVID-19 group, separated by the beginning of March. Therefore, each survey, not patient, was assigned to a group, resulting in some patients changing from the Non-COVID-19 to the COVID-19 group over time. This in conjunction with varying and also declining response rates led to different sample sizes for each questionnaire before COVID-19 (87 to 328 patients) and during COVID-19 (28 to 63 patients). The different characteristics of all patients, including sex, grading and TNM- as well as UICC-stages are shown in the table below (
Table 1). Each patient was assigned to the “Non-COVID-19”, “COVID-19” or for reasons of clarity specifically created “Varying Non-COVID-19/COVID-19” column. The latter includes all patients, who changed groups over time and completed surveys before and during COVID-19.
All patients received their questionnaire either in person during radiotherapy or via mail after completion of treatment. The answers were digitized in Excel 2016 using a written code in Visual Basic for Applications (VBA). The COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 groups were formed by using Excel 2016. Sample sizes were unequal because of the specific time limit of the COVID-19 pandemic. All data analyses, including p-values, means, standard deviations, medians and percentiles were conducted using GraphPad Prism 9.0.2, where p-values < 0.05 as well as a difference of 10 or more percentage points (pp) were considered as statistically significant. Comparisons between Non-COVID-19 and COVID-19 groups were achieved by making use of the Kolmogorov-Smirnov normality test, the Welch’s unequal variances t-test and graphically plotted via GraphPad Prism 9.0.2.
3. Results
A total of 489 advanced rectal cancer patients treated with radiochemotherapy were surveyed at eight different time points prior and during the COVID-19 time, the latter one being from March 2020 to March 2022. Results were compared to analyse the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the patients’ QOL. The first four questionnaires were completed during immediate treatment, questionnaire one before (day 0), the second during (day 14), the third after (day 35) radiotherapy and the fourth right before surgery (day 70). The latter four surveys served as annual follow-ups: at day 435 number 5, day 800 number 6, day 1165 number 7, and day 1530 number 8. As part of the patient sample used in this paper with data extending to June 2021 was examined by another study for the time points one to four [
13], we will focus on the annual follow-ups, developments throughout all questionnaires - including by sex and age - and the QOL dependent on the clinical T-stage of the cancer. There are functional scores, where higher values equal better QOL, and opposing symptom scores with lower percentage scores being more desirable.
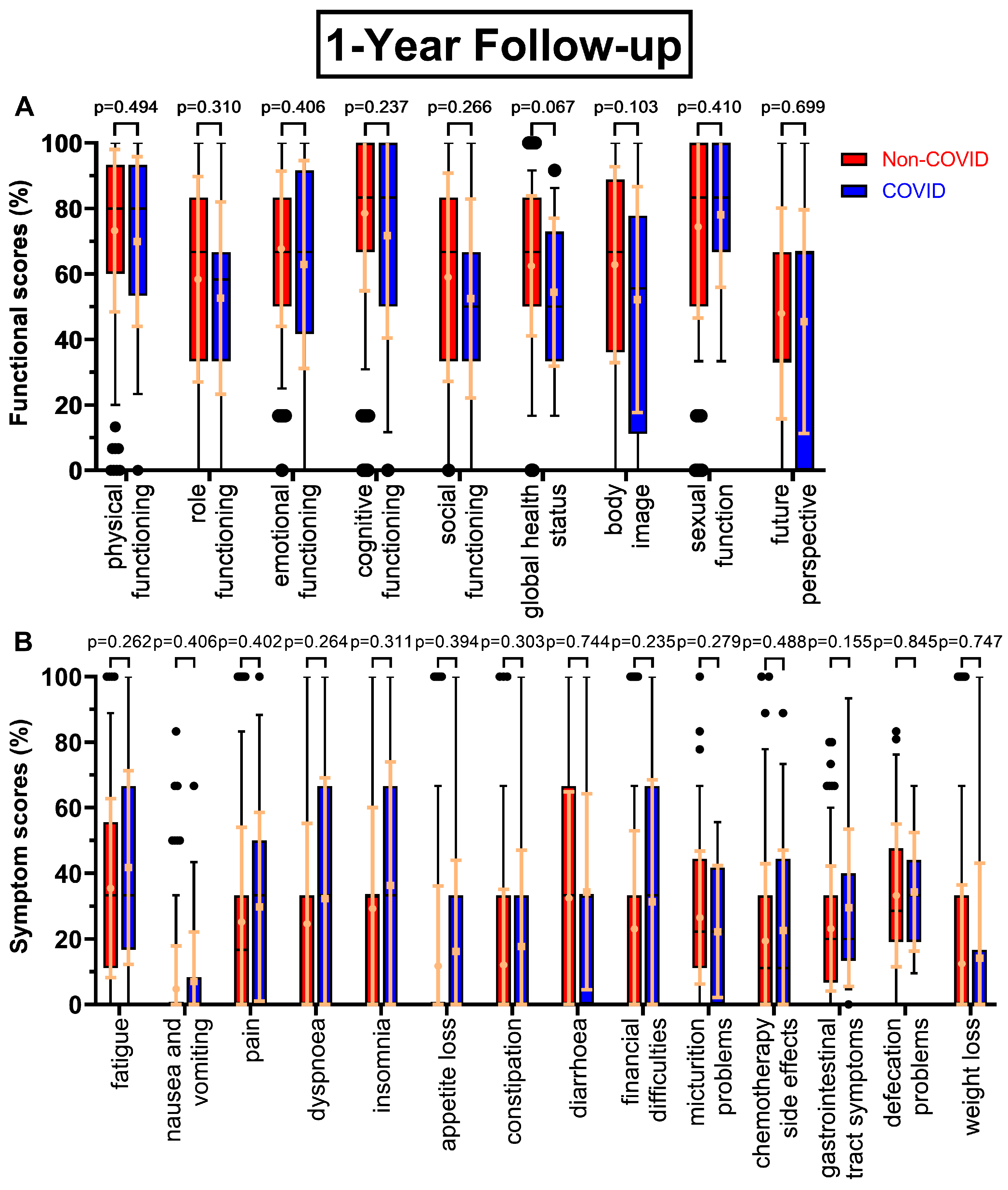
All functional scores decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic at the first annual follow-up (
Figure 1A) except sexual function (+3.7 pp), body image falling the most (-10.6 pp), followed by global health status (-8.1 pp, p=0.067), cognitive functioning (-6.9 pp) and role functioning (-5.8 pp). Future perspective remained the worst rated score (47.9 % to 45.5 %), meanwhile sexual function (74.4 % to 78.1 %) replaced cognitive functioning (78.6 % to 71.7 %) as the highest rated score. Similarly, symptom scores tended to rise during the COVID-19 pandemic (
Figure 1B), where every score except micturition problems (-4.3 pp) increased. Especially gastrointestinal tract symptoms (23.1 % to 29.5 %, p=0.155), financial difficulties (+8.2 pp), dyspnoea (+7.6 pp) and insomnia (+7.1 pp) were rising. Fatigue remained the highest score (35.5 % to 41.8 %).
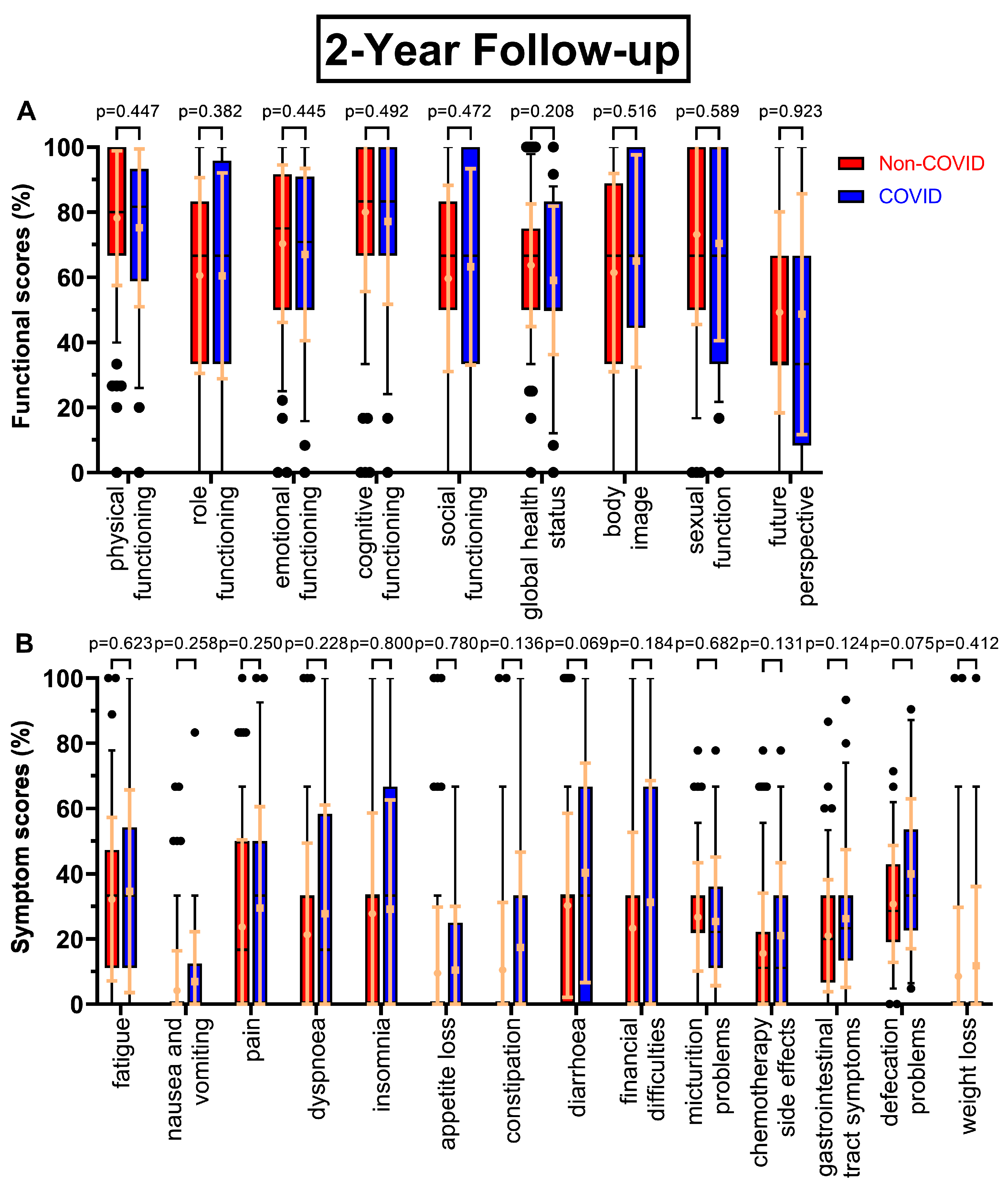
There were few changes in functional scores at the two-year follow-up at day 800 (
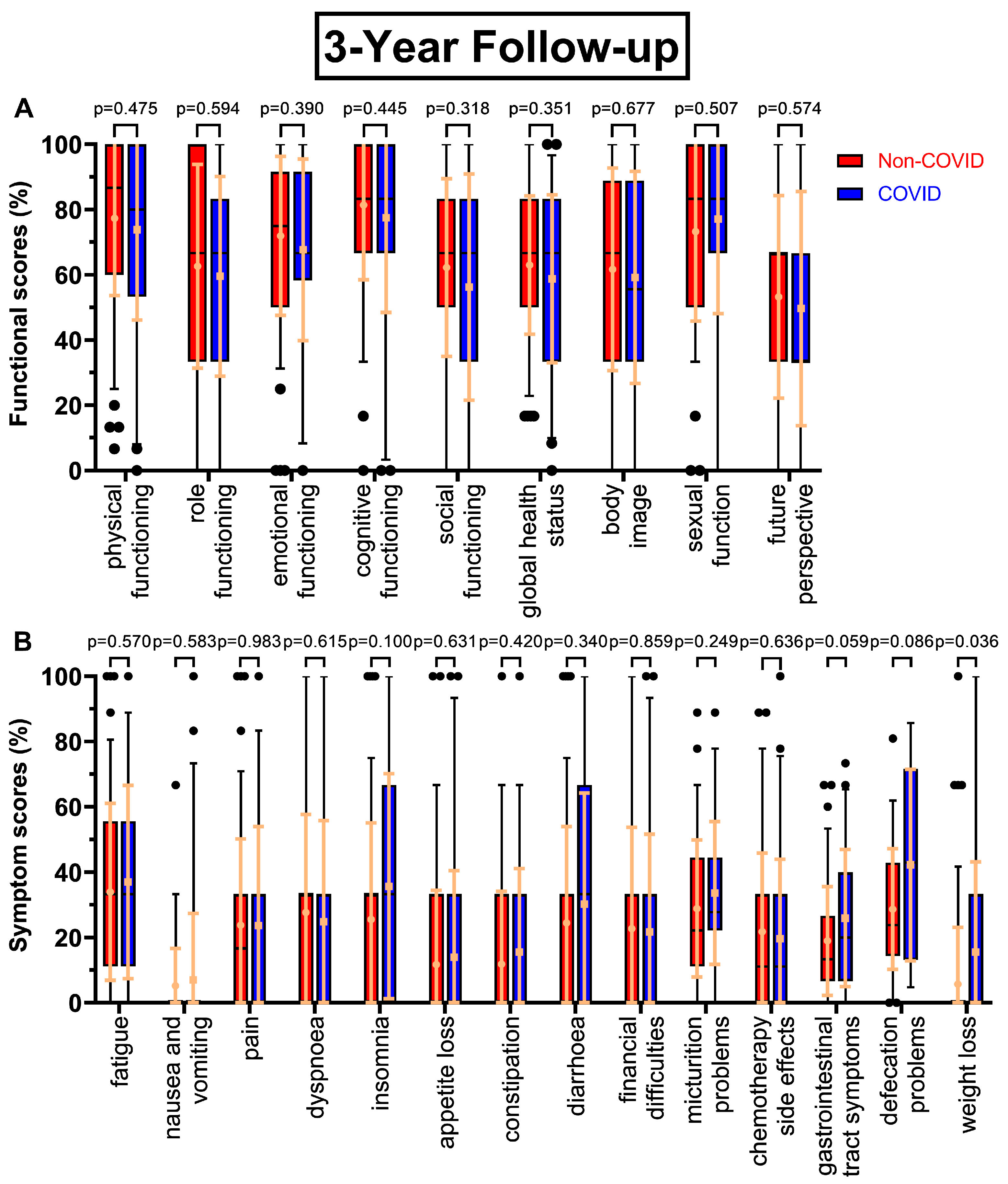
Figure 2A), except global health status (63.7 % to 59.0 %, p=0.208) and in contrast to the first follow-up small increases in social functioning (+3.6 pp) and body image (+3.6 pp), whereas sexual function decreased slightly (-2.7 pp). The trend of decreasing scores continued, with p-values ranging from 0.318 to 0.677, as questionnaire seven (
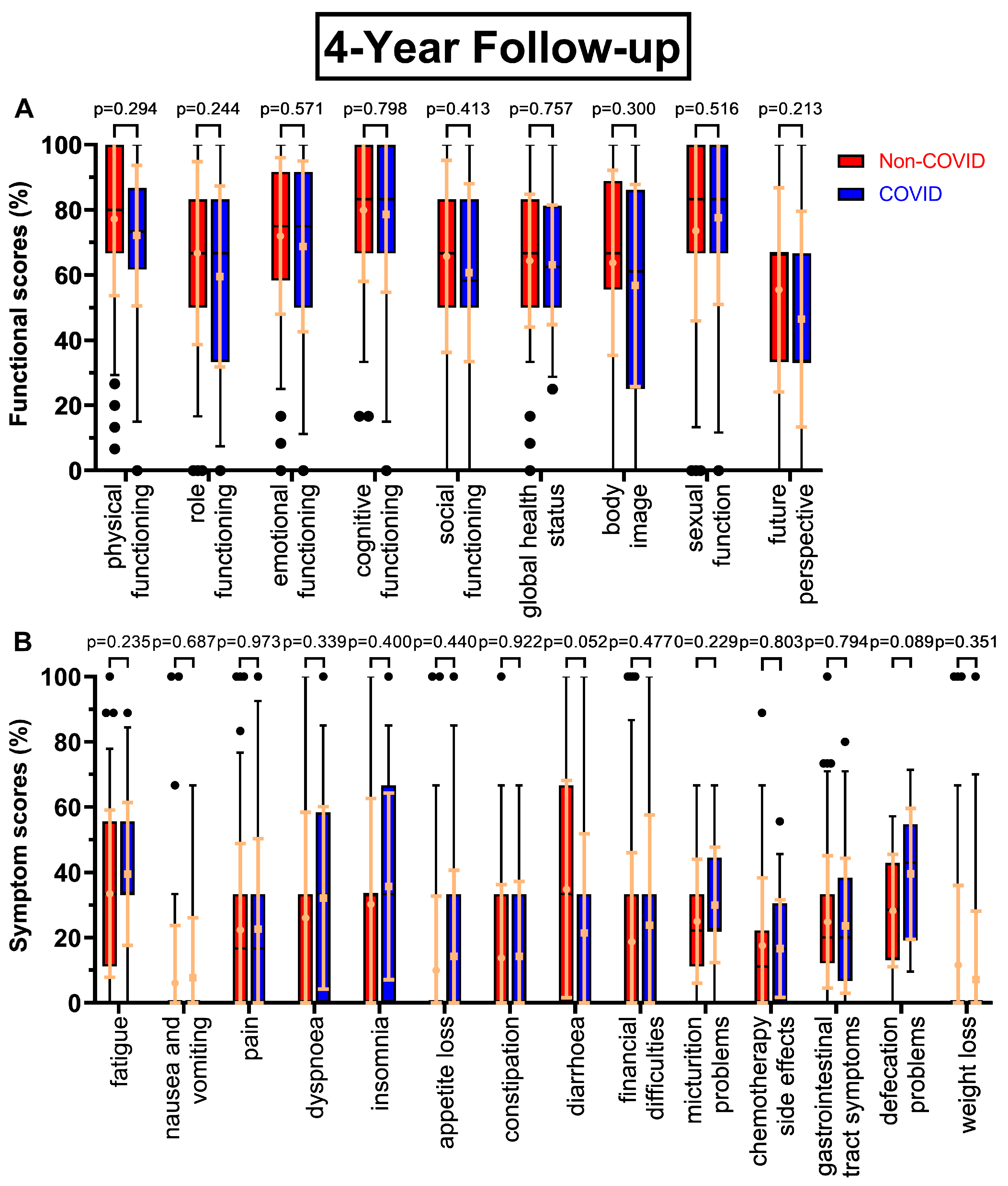
Figure 3A) had small but consistently worsening functional scores before and during COVID-19. One exception was sexual function and the biggest difference was found for social functioning (-6.0 pp). After four years (
Figure 4A) the most pronounced declines were in future perspective (-9.0 pp), role functioning (-7.2 pp) and body image (-7.0 pp). Throughout all follow-ups the difference in global health status became gradually smaller (8.1 pp -> 4.7 pp -> 4.2 pp -> 1.3 pp).
Symptom scores for the follow-ups mostly rose in the COVID-19 cohort. Most prominent examples for the second follow-up (
Figure 2B) being diarrhoea (+10.0 pp), financial difficulties (+8.0 pp) as well as constipation (10.5 % to 17.4 %, p=0.136), gastrointestinal tract symptoms (21.0 % to 26.2 %, p=0.124), chemotherapy side effects (15.5 % to 21.0 %, p=0.131) and defecation problems (30.7 % to 40.0 %, p=0.075). At the third annual survey (
Figure 3B) patients reported highest changing values for defecation problems (+13.5 pp, p=0.086), insomnia (+ 10.2 pp), weight loss (+9.8 pp, p=0.036) and gastrointestinal tract symptoms (18.9 % to 25.9 %, p=0.059). Other scores like pain and dyspnoea remained unchanged or even slightly deteriorated. For follow-up number four (
Figure 4B) diarrhoea improved during COVID (-13.5 pp), whereas defecation problems appeared to get significantly worse (28.3 % to 39.6 %, p=0.089).
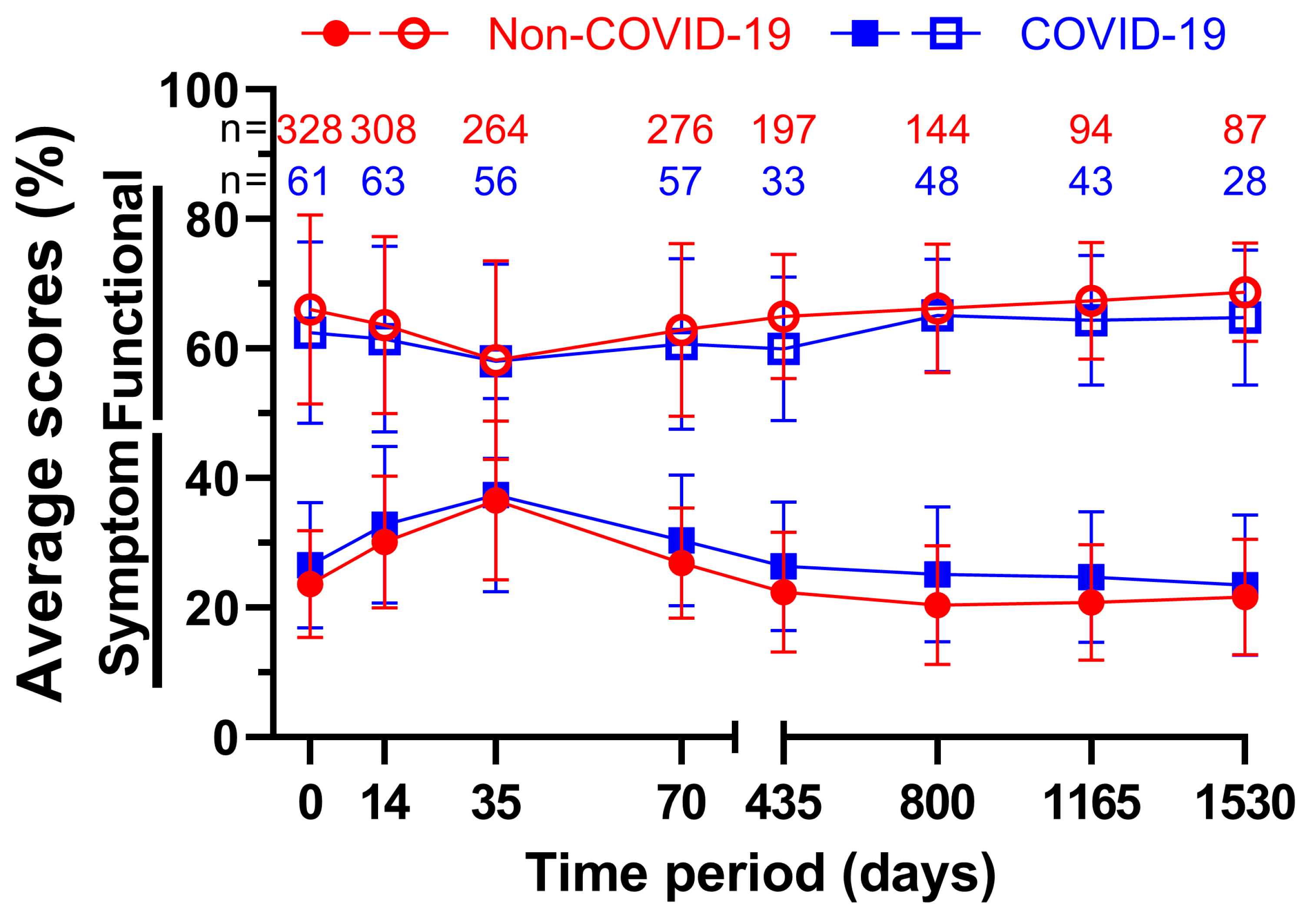
Changes in all surveys over time were recorded and summarized in the following figure (
Figure 5). The averages of all nine functional and fourteen symptom scores were each combined and the time before March 2020 was compared with the time until March 2022. Note that due to varying and declining response rates as well as patients’ deaths sample sizes tend to get smaller over time. In total, every single functional score during COVID performed worse than the Non-COVID counterpart, whereas every symptom score rose during COVID-19, meaning all average scores worsened after March 2020. The average functional score was lowest at 58.2 % on day 35 both prior and at 58.1 % after the beginning of the pandemic, the difference of 0.1 pp being the smallest out of all averages. The highest point was reached at the fourth annual follow-up, where the scores reached their peak at 68.7 % before and at 64.8 % during COVID-19, which was only topped by 65.1 % on day 800 during COVID-19. On day 435 there was a difference of 5.0 pp between the two measurements. This was the largest deviation. The results were the opposite for the symptom scores, but with similar meanings for the scores. At five weeks, the highest scores for both groups were 36.6 % before and 37.4 % during COVID-19. The scores of day 35 were also the closest, with a difference of only 0.8 pp. Prior to the pandemic the second follow-up on day 800 scored the lowest at 20.4 %, while throughout COVID-19 it was follow-up four at 23.5 %. The largest difference was 4.7 pp at follow-up two.
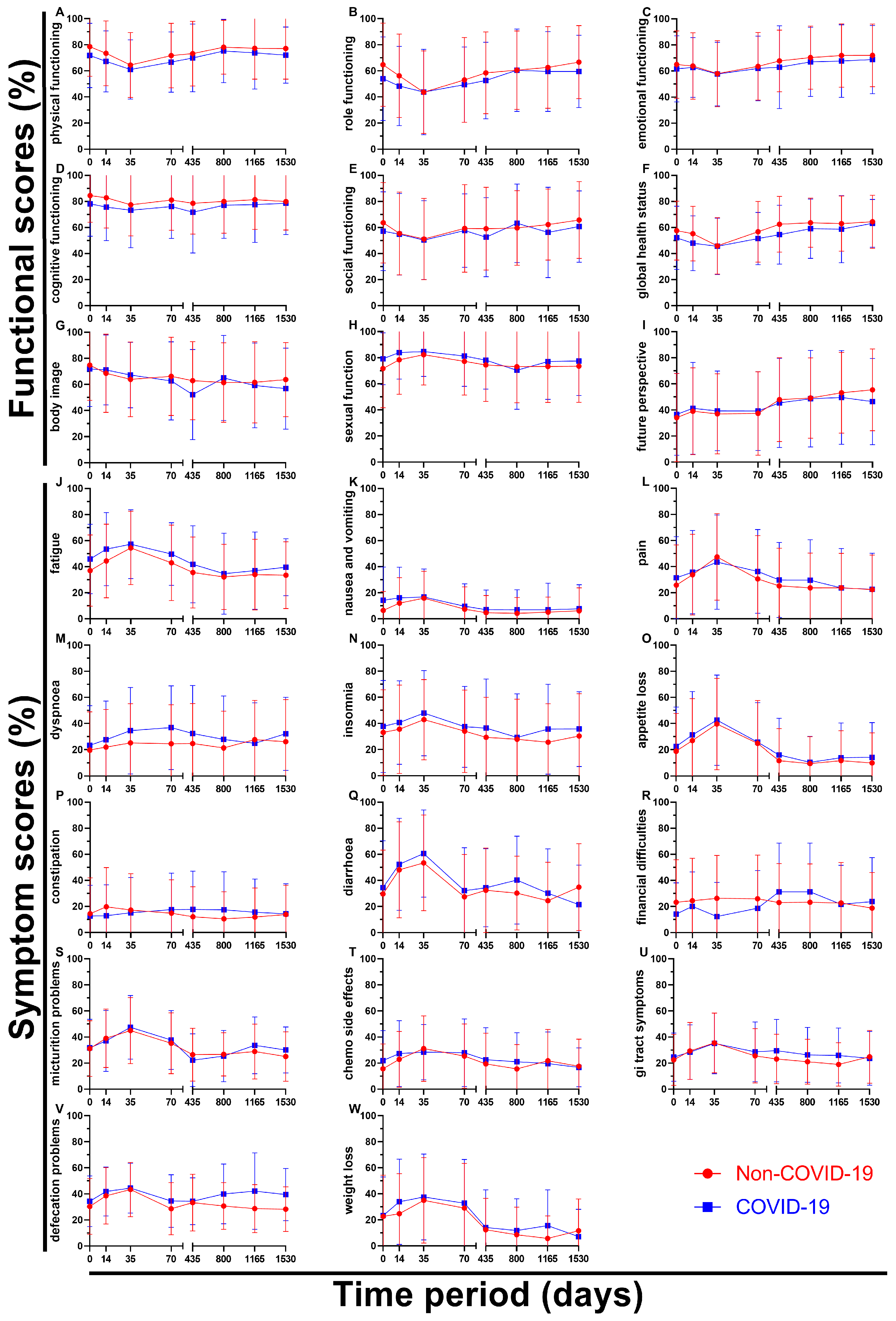
By breaking down the results of the questionnaires over time all nine functional scores and all fourteen symptom scores can be analysed individually (
Figure 6). Regarding functional scores role functioning (B) showed a significant difference at day 0 (10.7 pp), followed by the Non-COVID graph approaching the COVID graph (day 35 and 800) and again ending with a greater gap in between on day 1530 (7.2 pp). Body image (G) showed a huge drop from questionnaire four (62.7 %) to questionnaire five (52.2 %) during the pandemic bouncing right back (65.0 %, questionnaire six) even surpassing the Non-COVID score (61.4 %), marking an outlier in the data. Sexual function (H) was the only score to perform slightly better after March 2020 (except for day 800), score differences changing between 2.4 pp and 7.5 pp. Questionnaires one to six were very even for future perspective (I), the two graphs being separated by 2.4 pp at most, however the last two surveys showed an continued increase (49.2 % -> 53.2 % -> 55.4 %) before the pandemic compared to stagnating values during COVID (48.6 % -> 49.6 % -> 46.4 %) resulting in a difference of 9.0 pp at day 1530.
Symptom scores on the other hand tended to rise for the first three surveys reaching their peak at day 35 and then descending again. Pain (L) was found to be similar or higher during the pandemic except for said climax on questionnaire three (3.9 pp lower). The gaps in between scores for dyspnoea (M) were large, especially at the end of radiotherapy (9.3 pp) and before surgery (12.3 pp). Values for constipation (P) seemed to be mirrored, day 14 offering the highest (Non-COVID: 19.7 %) and second lowest (COVID: 12.9 %) score, meanwhile day 435 showed the third lowest (Non-COVID: 12.0 %) and highest (COVID: 17.7 %) scores. Financial difficulties (R) in the Non-COVID-19 group were reported to only differ to some degree (18.8 % to 26.3 %, 7.5 pp) over time, whereas in the COVID-19 group compared to the Non-COVID group the first four scores were lower by a margin of 4.4 to 13.9 pp, questionnaire five and six rapidly rising to 31.3 % (8.0 and 8.2 pp higher) and then dropping back to 21.7 % and 23.8 % for surveys seven and eight, offering a huge variety of values. Defecation problems (V) differed by 1.1 to 5.8 pp for the first five surveys, while the last three surveys showed larger differences of 9.3 to 13.5 pp.
In addition to analysing the impact of the pandemic on all patients we attempted to divide the patient sample size based by sex (
Figure 7) and age (
Figure 8). Combined means of all nine functional and fourteen symptom scores before and during COVID-19 were compared across all eight questionnaires. For females (
Figure 7A), the first four functional scores differed by a margin of only -0.2 (= COVID-19 score better by 0.2 pp) to 1.0 pp, while the annual follow-ups differed by at least 4.2 pp. Day 435 with 62.1 % and 45.3 % (16.8 pp) and day 1530 with 66.0 % and 54.1 % (11.9 pp) showed the largest gaps. The lowest functional score before COVID-19 was 52.0 % at week 5 and 45.3 % at day 435 during COVID-19, the highest at the fourth annual follow-up before the pandemic (66.0 %) and at the second annual follow-up during the pandemic (60.1 %). On the other hand, slightly larger gaps were found for symptom scores during the first ten weeks (0.2 to 4.5 pp) and slightly smaller gaps at day 435 with 16.4 pp and at day 1535 with 9.4 pp. The highest and lowest symptom scores were at day 35 and 800 respectively, 42.2 % and 23.8 % before COVID-19 and 42.9 % and 29.3 % during COVID-19. In general, functional and symptom score trends were similar.
The functional score results for males (
Figure 7B) didn’t show such large differences, they were between -1.2 and 4.0 pp. During COVID-19, days 35, 435 and 800 all outperformed their Non-COVID-19 counterparts. The highest scores were surveyed at annual follow-up number four with 70.0 % prior to COVID-19 and at annual follow-up number two with 67.7 % during COVID-19, whereas lowest scores were surveyed at day 35 (60.5 % before and 61.5 % during the pandemic). Symptom scores during COVID-19 were slightly lower at day 35 (0.2 pp) and at day 435 (2.4 pp). The largest difference of 3.8 pp was found at day 800. Pre-pandemic scores ranged from 19.1 % on day 1530 to 34.5 % on day 35, while scores during the pandemic ranged from 19.4 % on day 435 to 34.3 % on day 35. Women reported lower quality of life than men in all surveys, regardless of the pandemic.
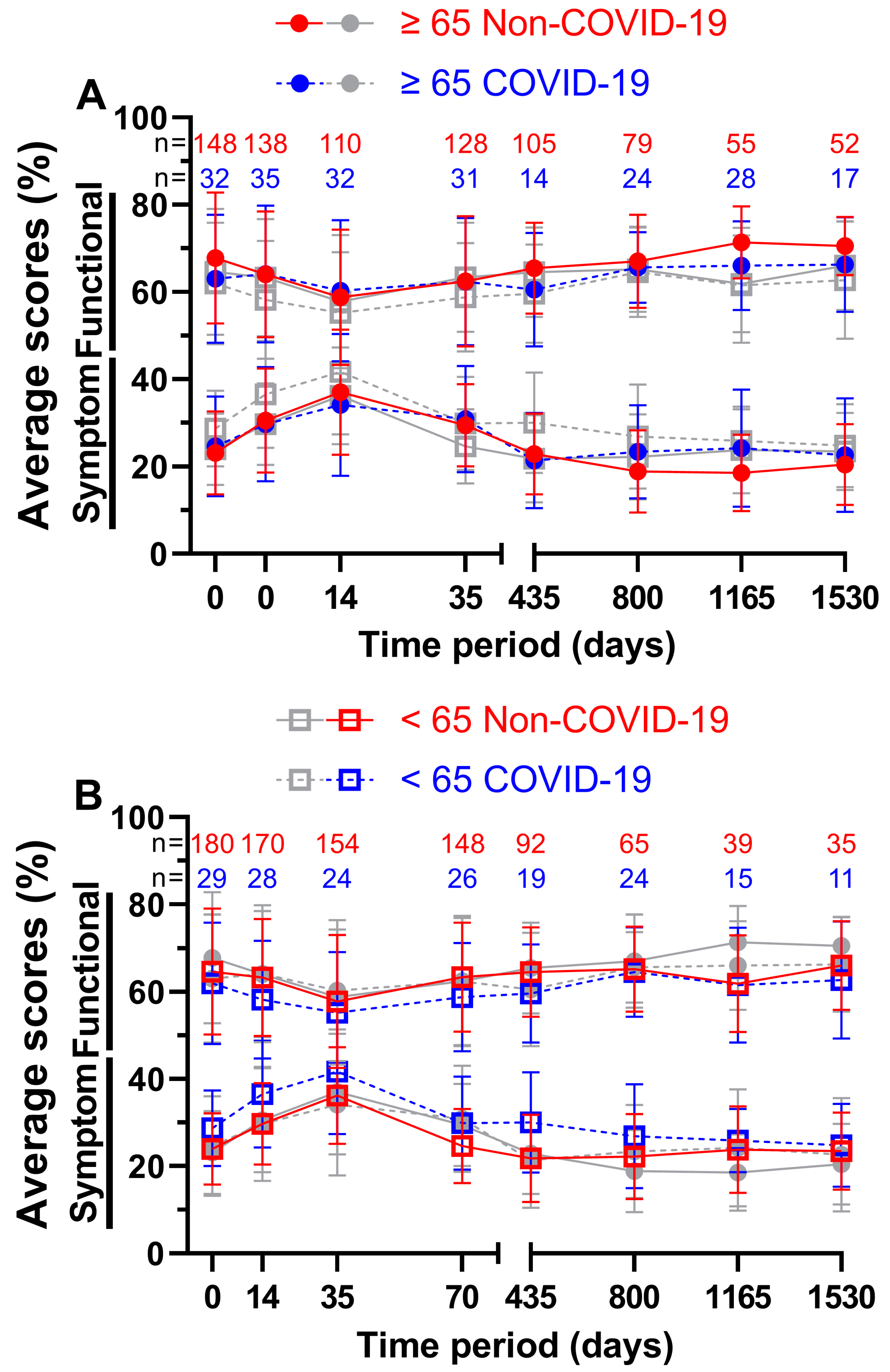
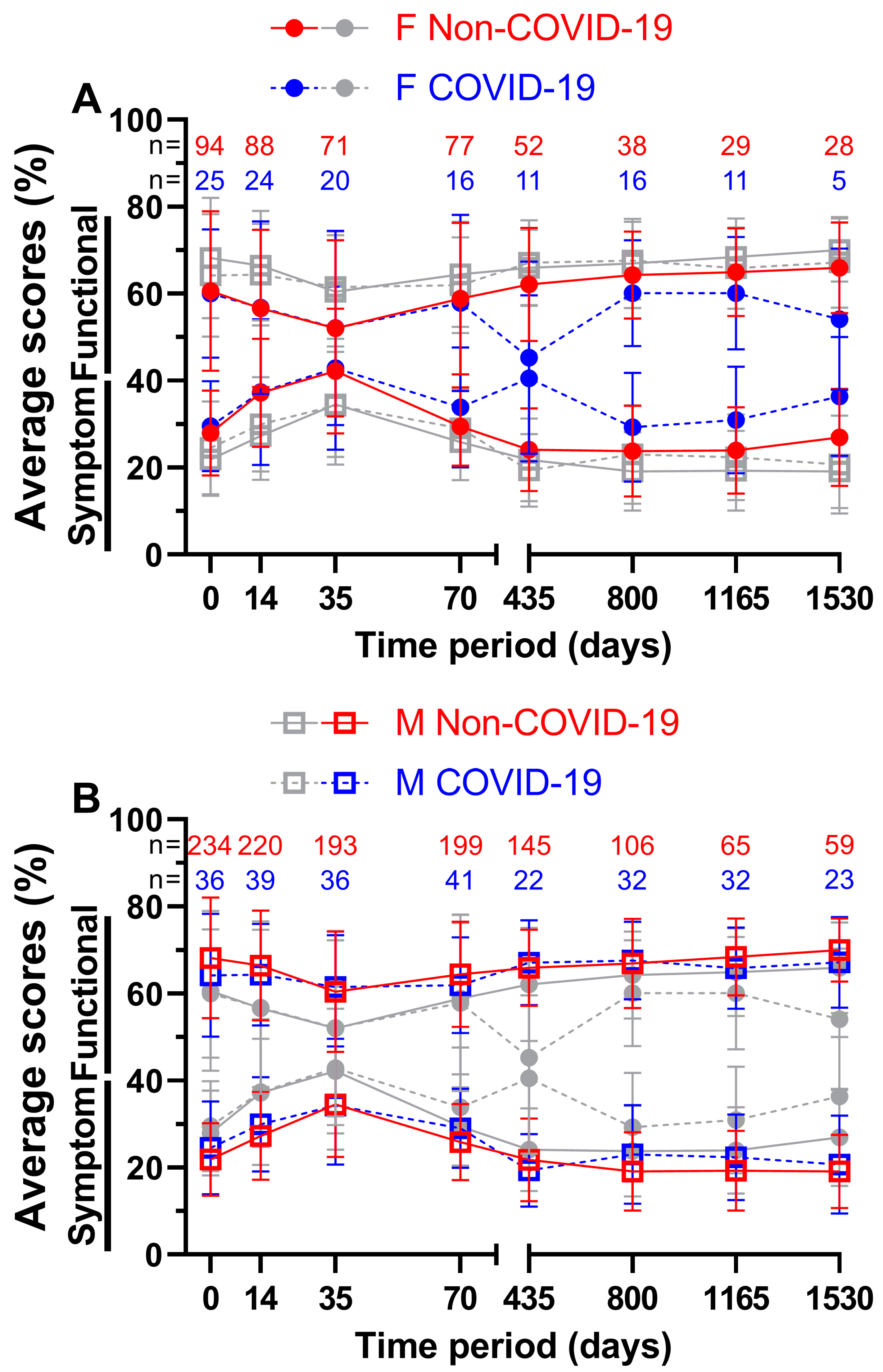
For patients aged 65 years or older (
Figure 8A) the functional score at week 5 during COVID-19 was better by a margin of 1.5 pp, all other scores were outperformed by the Non-COVID-19 time, the largest margin being 5.3 pp on day 1165. 58.8 % and 60.3 % on day 35 both appeared to be the worst scores across all eight questionnaires, resulting to day 35 before COVID-19 being the lowest of all functional scores for patients aged 65 years or older. Peak scores were reached on day 1165 with 71.4 % prior to the pandemic and on day 1530 with 66.3 % during the pandemic. Meanwhile, during COVID-19, symptom scores performed better on days 14, 35 and 435. All ranges were between -2.9 and 5.6 pp. The lowest symptom score before COVID-19 was 18.6 % at the third annual follow-up and 21.4 % during COVID-19 at the first annual follow-up. The highest symptom scores were surveyed at the third questionnaire (37.0 % before and 34.1 % during the pandemic).
In contrast, patients aged younger than 65 years (
Figure 8B) showed greater differences in QOL in the first four surveys, ranging from 2.6 to 5.1 pp for functional scores and from 4.7 to 6.9 pp for symptom scores. Between functional scores, the largest difference was 5.1 pp on day 35 and between symptom scores, it was 8.2 pp on day 435. 66.0 % four years after treatment before the pandemic and 64.6 % two years after treatment during the pandemic outperformed all other functional scores, while day 35 was the lowest at 57.8 % before and at 55.2 % during COVID-19. Correspondingly, symptom scores peaked at day 35 (36.2 % prior to and 41.7 % during COVID-19). The lowest symptom scores were 21.8 % at the first follow-up and 24.8 % at the fourth follow-up respectively.
Figure 8.
Means and error bars of nine functional and fourteen symptom scores combined, by age and with sample sizes. Prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic over the course of eight time points: Before (day 0), during (day 14) and at the end (day 35) of radiotherapy, right before surgery (day 70) and at yearly intervals after surgery (days 435, 800, 1165 and 1530). Patients aged ≥ 65 years are highlighted (grey symbols in the background indicate patients aged < 65 years) in (A), patients aged < 65 years (grey symbols in the background indicate patients aged ≥ 65 years) in (B). Solid lines are Non-COVID and stripped lines are COVID scores.
Figure 8.
Means and error bars of nine functional and fourteen symptom scores combined, by age and with sample sizes. Prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic over the course of eight time points: Before (day 0), during (day 14) and at the end (day 35) of radiotherapy, right before surgery (day 70) and at yearly intervals after surgery (days 435, 800, 1165 and 1530). Patients aged ≥ 65 years are highlighted (grey symbols in the background indicate patients aged < 65 years) in (A), patients aged < 65 years (grey symbols in the background indicate patients aged ≥ 65 years) in (B). Solid lines are Non-COVID and stripped lines are COVID scores.
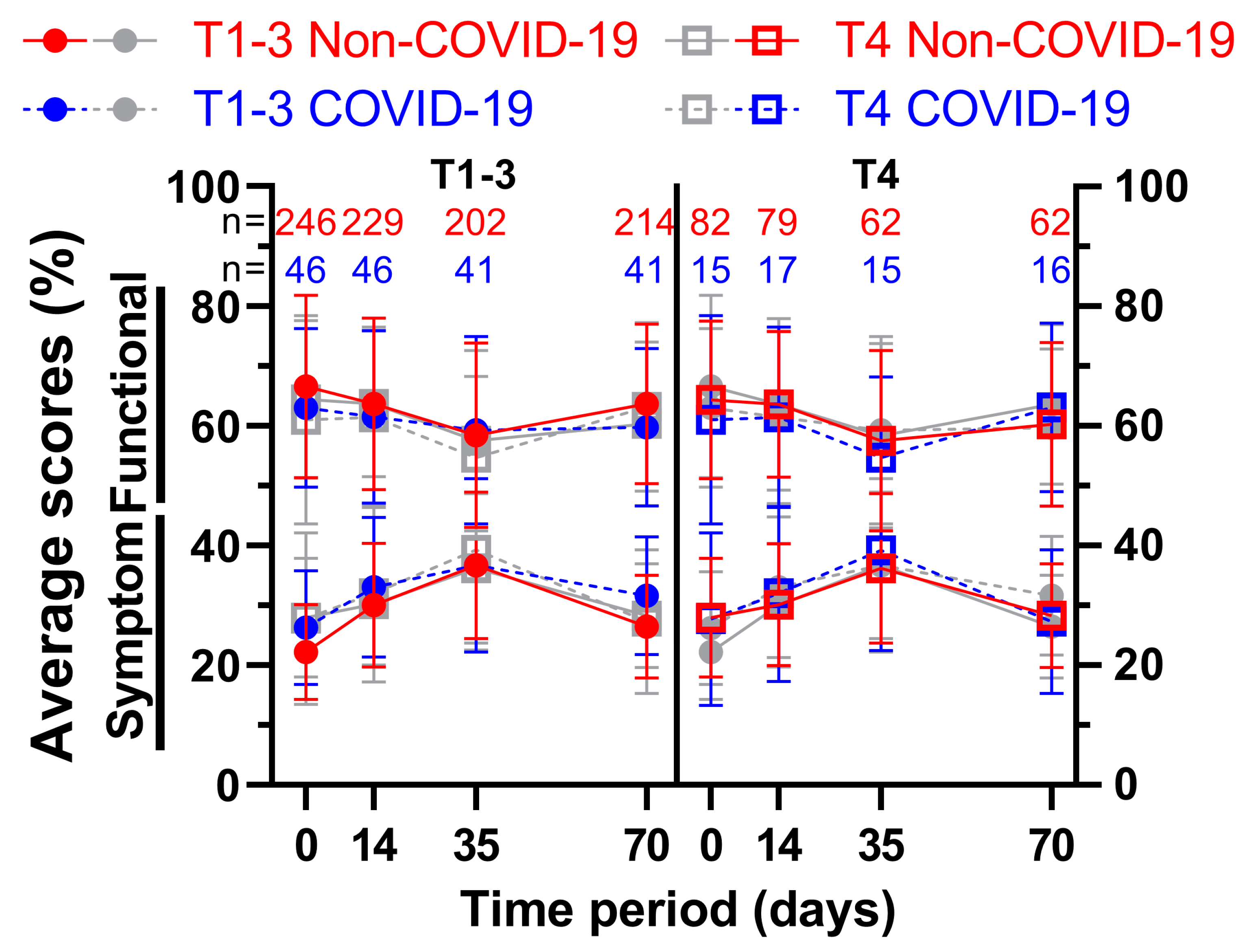
We attempted to divide the patient sample size based on the clinical T stage of their rectal cancer, thus creating one subgroup containing less advanced cancer (cT1 – cT3; subgroup 1) and one containing more advanced cancer (cT4; subgroup 2) (
Figure 9 and
Figure 10). As the first subgroup includes mostly cT3 stage cancer, less advanced has to be seen in relative terms. Again, all nine functional and fourteen symptom scores were plotted over the course of 70 days, including four questionnaires. The first score, physical functioning (A), decreased similarly (between 5.7 and 8.8 pp) for the less advanced rectal cancer patients, whereas the cT4-subgroup decreased slightly (2.3 and 2.6 pp) followed by higher increases (4.0 and 6.4 pp) for the third and fourth survey. This development was similar for role functioning (B). Emotional functioning (C) was just slightly affected by the pandemic irrespective of cancer stage (up to 3.5 pp, one outlier on day 35 with 5.6 pp). Cognitive (D) and social (E) functioning showed significant differences at the end of radiotherapy (10.2 and 10.0 pp) for the higher cT-stage subgroup, in contrast to small differences for the lower cT-stage group (difference of 2.5 pp and less). While body image dropped during COVID for subgroup 2, there was a small rise during (5.3 pp) and after (5.4 pp) radiotherapy for subgroup 1. Sexual function (H) for cT4- stage cancer patients rose significantly before (15.8 pp to 90.3 %) and during (11.6 pp to 90.5 %) radiotherapy, topping the increases of subgroup 1 by a margin. The highest score regarding future perspective (I) was obtained in the second survey for subgroup 2 regardless of COVID, exceeding all other COVID-19 patient scores by at least 6 pp.
There was a significant difference of 10.6 pp for fatigue (J) for subgroup 1 on day 0, and a huge gap of 9.1 pp and 8.7 pp on day 14 throughout all cancer stages. Nausea and vomiting (K) had opposing tendencies: while all COVID-scores got higher for the cT1-3 patient cohort (day 0: 6.3 % to 16.3 %), the cT4 pandemic scores showed lower results except for day 0 (+0.9 pp). Flattened score developments for pain (L) were surveyed during COVID-19, where the pre-COVID peak of 47.3 % and 47.6 % was missed by 3.4 pp and 5.4 pp on week 5. Dyspnoea (M) displayed differences of 8.6 pp and above for all scores for subgroup 1, the jump from 24.4 % to 40.7 % on day 70 being the largest. The T4 subgroup on the other hand revealed significant gaps in both directions (26.8 % to 15.6 % on day 0, 26.2 % to 37.8 % on day 35). Whereas results regarding appetite loss (O) for subgroup 1 differed by 4.4 pp or less, subgroup 2 offered significantly higher results on day 0 (10.8 pp) and day 35 (11.4 pp). Diarrhoea (Q) showed increased results for all scores, day 0 of subgroup 2 being significant (11.5 pp). Contrary to that, scores for financial difficulties (R) were all lower, with four significant differences (subgroup 1: day 35 -13.7 pp; subgroup 2: day 0 -10.7 pp, day 35 -15.6 pp and day 70 -13.9 pp). Micturition problems (S) differed by 9.4 and 9.6 pp on days 14 and 35 for subgroup 2. The pandemic had a greater effect on defecation problems (V) in subgroup 2, with differences ranging from 4.2 to 6.6 pp, whereas in subgroup 1 the differences ranged from -0.3 to 3.7 pp, except on day 70, when it was higher (6.3 pp). Weight loss (W) for more advanced cancer patients was affected by COVID-19 remarkably, with scores rising between 10.7 pp and 13.7 pp, however the less advanced cohort showed fewer differences ranging from -3.7 pp to +7.9 pp.
4. Discussion
During the COVID-19 pandemic rectal cancer patients’ QOL declined, functional scores such as role functioning and body image were impaired. This in addition with the rising perception of symptoms as insomnia, defecation problems and weight loss led to the results. At one to four follow-up years, few clear differences were found, but most scores worsened, indicating a negative impact of COVID-19 on QOL. This trend was also evident when all functional and symptom scores were combined and compared. At the end of radiochemotherapy, when QOL was most affected, the differences between COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 were the smallest. Individual scores were very diverse, some diverging during radiochemotherapy (dyspnoea), even years after therapy (future perspective) or contrarily improving (sexual function). Sex had an impact, as females reported worse QOL than males in all surveys before and during COVID-19. So did age, as patients younger than 65 were more affected by the pandemic during radiochemotherapy than their older counterparts. Scores for TNM-stages cT1-3 and cT4 didn’t change uniformly, however weight loss was significantly higher during COVID-19 for the latter group.
A clear limitation is that the results were only compared between rectal cancer patients and not with the general population. Physical distancing, stay-at-home orders and other lockdown restrictions caused mental health impairments among vulnerable adult groups [
11,
14]. The additional significance of the rectal cancer diagnosis therefor remains unclear. Countering actions for all adults should be applied on rectal cancer patients too, in consequence reducing the need for specific measures.
As voluntary questionnaires can get declined by patients at any stage, there is a selection bias in the study group. As our surveys were all delivered by post, COVID-19 might have contributed leading to former participants not completing surveys. Excessively anxious patients not taking part would create biased and embellished results. Alternatives as digital questionnaires might be used in the future, eliminating some COVID-concerns, however adding boundaries for digital immigrants, as around 70 is the median age at rectal cancer diagnosis in developed countries [
15]. Another limiting concern is the length of our study. The COVID-19 group included patients over a time course of two years and varying restrictions. A total of fifteen Bavarian Infection Protection Measures Ordinances, not including amendments, had been in force in that time span. COVID-19 vaccines were available since December 2020. This supposedly led to QOL-changes, which wasn’t included in the study design. We decided against a shorter time span as a sample size of roughly 30 patients for each yearly follow-up seemed appropriate. Nonetheless comparisons for the first four questionnaires were published by us for a briefer time period (March 2020 – June 2021) [
13].
The decline of nearly all functional scores one to four years after radiotherapy revealed that long term rectal cancer patients’ QOL suffered. Physical activities decreased during COVID-19 [
16] which can have an impact on overall physical functioning and QOL in older adults [
17], explaining the worsening in all follow-ups. As everyday life changed during the pandemic, remote work emerged and outdoor activities were limited, which provides an explanation for diminished role functioning scores. With each follow-up year the gap between the two global health status scores was reduced implying a smaller effect of the pandemic on general QOL and health over time. However, thoughts regarding the future perspective diverged more over time. Possibly due to still facing the COVID-19 global health crisis patients with a medical history of rectal cancer didn’t report increased scores unlike their pre-pandemic counterparts. The risk of getting infected with COVID-19 and being more vulnerable to it because of said medical history could be the reason for this. The drop in body image might be a result of patients not being able to feel what their bodies are capable of, having to stay at home and the fear of gaining weight. Though this doesn’t explain why the pandemic group had higher scores for follow-up two after plummeting in year one, both seeming to be outliners. Sexual function was an exception to the decreasing scores, as it increased in three out of four follow-ups. As a consequence of stay-at-home orders during the pandemic, outside activities were limited and the time spent at home rose. This might have led to more situations craving and actually engaging in sexual activities, thus leading to higher sexual function.
Out of all symptom scores dyspnoea offered the most apparent changes. As it is also a symptom of COVID-19, an infection during answering the questionnaire might have led to higher scores besides also sensitizing patients to the symptom itself without them getting sick. Feeling weaker during radiochemotherapy may contribute to this, music therapy could be a countermeasure [
18]. Worries about the pandemic led to higher rates of insomnia in the general population [
19], which is also clearly evident in our study. Diarrhoea and gastrointestinal tract symptoms are common symptoms after surgery for colon cancer [
20], but can also be caused by COVID-19. Thus, elevated scores are likely due to infection or higher symptom awareness. The differences of diarrhoea after four years in favour of the COVID-19 group however contradict this. Financial difficulties in the first ten weeks of treatment might have been lower as patients were more concerned about their health, just having received a cancer diagnosis hence being more susceptible to SARS-CoV-2. Constant contact to mask-wearing health care workers due to daily radiotherapy may have contributed to those thoughts resulting in financial difficulties not being a primary concern, although financial distress is common among cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy [
21]. Few years after treatment, getting used to the diagnosis as well as not visiting hospitals regularly could lead to more present financial thoughts before adapting to that. Given that patients stayed more at home during the pandemic, defecation problems could have been more apparent for cancer patients in general as well as a consequence of a SARS-CoV-2 infection. Staying at home and less physical activity may lead to increase in weight, yet patients reported weight loss. Long term patients might have skipped follow-up examinations and hence not detected tumour recurrences. Other reasons might be increased anxiety and COVID-19 infections [
22].
Both before and during COVID, QOL-scores were reported to be lowest and closest after radiochemotherapy (day 35). This may be because patients’ already compromised QOL is more stable to external factors such as the pandemic, as their main focus is on their disease and the immediate side effects of radiochemotherapy [
3,
4], superseding possible threats from COVID-19.
Regardless of the pandemic, females had lower QOL than males in all surveys, which is supported by our findings from March 2020 to June 2021 for the first ten weeks of treatment [
13]. During treatment, females receive slightly higher deposited energies per weight of ionizing radiation, which could explain the differences in QOL [
23]. In addition, increased chemotherapy-induced toxicity in women could worsen QOL [
24]. The annual follow-ups of females stuck out, as their QOL decreased by a great margin during the pandemic. Sex-related factors are important, as females who are pregnant, have had a miscarriage, are postpartum or experience physical abuse are at greater risk of mental health impairments [
25]. However, this doesn’t explain the huge differences in QOL years after treatment. Though it should be noted that the follow-ups were completed by only five to sixteen females, limiting the findings.
Patients younger than 65 years of age were more affected by the COVID-19 pandemic during radiochemotherapy than patients aged 65 years or older. As some studies pointed out that the impact of radiochemotherapy on QOL decreases with increasing age [
26,
27], the COVID-19 pandemic or other external factors may be an additional high burden for younger patients during treatment, while older patients are less affected by it. Another study found that increasing age is a protective factor for mental health during COVID-19, as it is associated with less stress and fewer psychological problems [
28]. This may be due to life reflection, adaptive use of personal memory and generativity [
29], and highlights the resilience of older patients.
cT4-staged rectal cancer patients lost more weight as their cT1-3 counterparts, which is directly linked to higher appetite loss. COVID-19 infections and worries could have contributed to that as well as delayed search for medical treatment, leading to larger carcinomas.
Research using the QLQ-C30 questionnaire and comparing QOL prior and during the pandemic revealed different results: A study observing Danish cancer patients [
30] showed comparable results, though lower QOL and the fear of getting infected with COVID-19 were correlated. Another survey from Denmark investigating hematologic cancer patients indicated lower QOL during the pandemic [
31]. Among Italian head and neck cancer survivors a significant deterioration in physical (p=0.028), role (p=0.030) and emotional functioning (p=0.041) was found [
32]. Significantly worse insomnia (p<0.0001), fatigue (p=0.003), loss of appetite (p=0.006), financial difficulties (p<0.0001) and cognitive (p<0.0001) as well as social functioning (p<0.0001) scores were found for stage III/IV cancer patients in Poland [
33]. However, one should be cautious transferring results to this study. Besides either including other or different types of cancer and covering shorter time periods, countries in Europe showed varying COVID-19 developments [
34]. A study done by us regarding an overlapping rectal cancer patient sample for the first four questionnaires from March 2020 to June 2021 showed more significances between the COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 group. Particularly day 0 stood out with five functional (physical, role, cognitive, social functioning, global health status) and four symptom scores (fatigue, pain, nausea and vomiting, weight loss) changing significantly, though the divergences decreased gradually over the next time points [
13].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Daniel Blasko, Rainer Fietkau and Luitpold Valentin Distel; Data curation, Daniel Blasko, Tim Fitz, Christoph Schröter, Christopher Sörgel and Luitpold Valentin Distel; Formal analysis, Daniel Blasko; Investigation, Daniel Blasko, Tim Fitz, Christoph Schröter, Christopher Sörgel and Annett Kallies; Methodology, Daniel Blasko, Claudia Schweizer and Luitpold Valentin Distel; Project administration, Rainer Fietkau and Luitpold Valentin Distel; Resources, Rainer Fietkau and Luitpold Valentin Distel; Software, Daniel Blasko and Luitpold Valentin Distel; Supervision, Daniel Blasko, Rainer Fietkau and Luitpold Valentin Distel; Validation, Daniel Blasko, Claudia Schweizer, Rainer Fietkau and Luitpold Valentin Distel; Visualization, Daniel Blasko and Luitpold Valentin Distel; Writing – original draft, Daniel Blasko; Writing – review & editing, Daniel Blasko, Claudia Schweizer and Luitpold Valentin Distel. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Figure 1.
Boxplots of functional and symptom scores prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic with whiskers defined as the 5th and 95th percentile and points marking outliers. Means and standard deviations are shown over the boxplots in yellow ochre. Scores were collected one year after surgery. Functional scores can be seen in (A), symptom scores in (B).
Figure 1.
Boxplots of functional and symptom scores prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic with whiskers defined as the 5th and 95th percentile and points marking outliers. Means and standard deviations are shown over the boxplots in yellow ochre. Scores were collected one year after surgery. Functional scores can be seen in (A), symptom scores in (B).
Figure 2.
Boxplots of functional and symptom scores prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic with whiskers defined as the 5th and 95th percentile and points marking outliers. Means and standard deviations are shown over the boxplots in yellow ochre. Scores were collected two years after surgery. Functional scores can be seen in (A), symptom scores in (B).
Figure 2.
Boxplots of functional and symptom scores prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic with whiskers defined as the 5th and 95th percentile and points marking outliers. Means and standard deviations are shown over the boxplots in yellow ochre. Scores were collected two years after surgery. Functional scores can be seen in (A), symptom scores in (B).
Figure 3.
Boxplots of functional and symptom scores prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic with whiskers defined as the 5th and 95th percentile and points marking outliers. Means and standard deviations are shown over the boxplots in yellow ochre. Scores were collected three years after surgery. Functional scores can be seen in (A), symptom scores in (B).
Figure 3.
Boxplots of functional and symptom scores prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic with whiskers defined as the 5th and 95th percentile and points marking outliers. Means and standard deviations are shown over the boxplots in yellow ochre. Scores were collected three years after surgery. Functional scores can be seen in (A), symptom scores in (B).
Figure 4.
Boxplots of functional and symptom scores prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic with whiskers defined as the 5th and 95th percentile and points marking outliers. Means and standard deviations are shown over the boxplots in yellow ochre. Scores were collected four years after surgery. Functional scores can be seen in (A), symptom scores in (B).
Figure 4.
Boxplots of functional and symptom scores prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic with whiskers defined as the 5th and 95th percentile and points marking outliers. Means and standard deviations are shown over the boxplots in yellow ochre. Scores were collected four years after surgery. Functional scores can be seen in (A), symptom scores in (B).
Figure 5.
Means and error bars of nine functional and fourteen symptom scores combined, with sample sizes. Functional scores have open symbols and symptom scores have filled symbols. Prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic over the course of eight time points: Before (day 0), during (day 14) and at the end (day 35) of radiotherapy, right before surgery (day 70) and at yearly intervals after surgery (days 435, 800, 1165 and 1530).
Figure 5.
Means and error bars of nine functional and fourteen symptom scores combined, with sample sizes. Functional scores have open symbols and symptom scores have filled symbols. Prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic over the course of eight time points: Before (day 0), during (day 14) and at the end (day 35) of radiotherapy, right before surgery (day 70) and at yearly intervals after surgery (days 435, 800, 1165 and 1530).
Figure 6.
Means and error bars of nine functional and fourteen symptom scores. Prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic over the course of eight time points: Before (day 0), during (day 14) and at the end (day 35) of radiotherapy, right before surgery (day 70) and at yearly intervals after surgery (days 435, 800, 1165 and 1530).
Figure 6.
Means and error bars of nine functional and fourteen symptom scores. Prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic over the course of eight time points: Before (day 0), during (day 14) and at the end (day 35) of radiotherapy, right before surgery (day 70) and at yearly intervals after surgery (days 435, 800, 1165 and 1530).
Figure 7.
Means and error bars of nine functional and fourteen symptom scores combined, by sex and with sample sizes. Prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic over the course of eight time points: Before (day 0), during (day 14) and at the end (day 35) of radiotherapy, right before surgery (day 70) and at yearly intervals after surgery (days 435, 800, 1165 and 1530). Females are highlighted (grey symbols in the background indicate males) in (A), males (grey symbols in the background indicate females) in (B). Solid lines are Non-COVID and stripped lines are COVID scores.
Figure 7.
Means and error bars of nine functional and fourteen symptom scores combined, by sex and with sample sizes. Prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic over the course of eight time points: Before (day 0), during (day 14) and at the end (day 35) of radiotherapy, right before surgery (day 70) and at yearly intervals after surgery (days 435, 800, 1165 and 1530). Females are highlighted (grey symbols in the background indicate males) in (A), males (grey symbols in the background indicate females) in (B). Solid lines are Non-COVID and stripped lines are COVID scores.
Figure 9.
Means and error bars of nine functional and fourteen symptom scores combined, by cT-stage and with sample sizes. Prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic. Each side shows four graphs with the same four data sets, the left side putting emphasis on (= colouring) less advanced cancers (TNM cT1-3), the right side on more advanced cancers (TNM cT4). The data is plotted over the course of four time points: Before (day 0), during (day 14) and at the end (day 35) of radiotherapy and right before surgery (day 70). Solid lines are Non-COVID and stripped lines are COVID scores.
Figure 9.
Means and error bars of nine functional and fourteen symptom scores combined, by cT-stage and with sample sizes. Prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic. Each side shows four graphs with the same four data sets, the left side putting emphasis on (= colouring) less advanced cancers (TNM cT1-3), the right side on more advanced cancers (TNM cT4). The data is plotted over the course of four time points: Before (day 0), during (day 14) and at the end (day 35) of radiotherapy and right before surgery (day 70). Solid lines are Non-COVID and stripped lines are COVID scores.
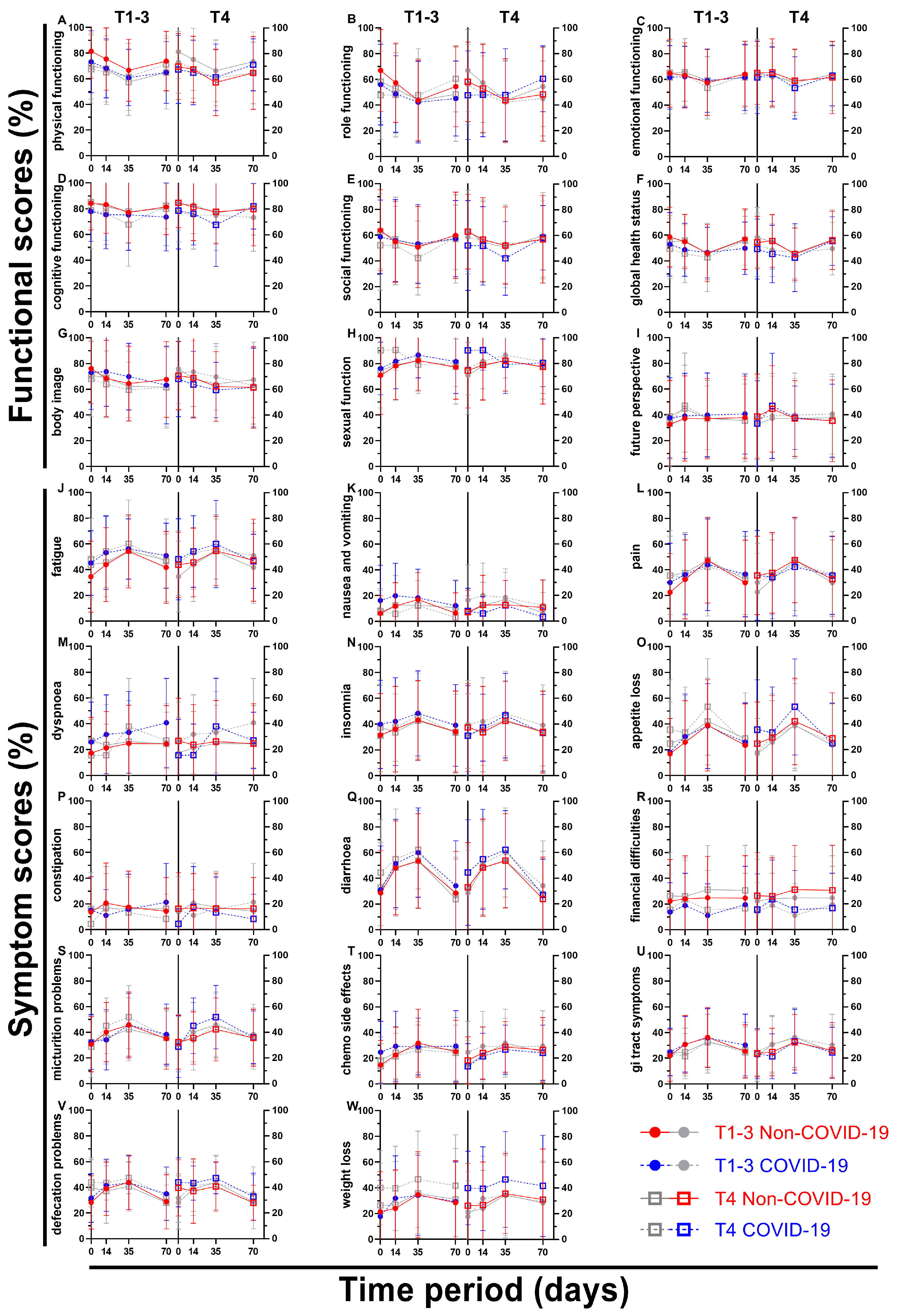
Figure 10.
Means and error bars of nine functional and fourteen symptom scores. Prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic. Each letter shows two graphs with the same four data sets, the left side putting emphasis on (= colouring) less advanced cancers (TNM cT1-3), the right side on more advanced cancers (TNM cT4). The data is plotted over the course of four time points: Before (day 0), during (day 14) and at the end (day 35) of radiotherapy and right before surgery (day 70).
Figure 10.
Means and error bars of nine functional and fourteen symptom scores. Prior (Non-COVID) compared to during (COVID) the COVID-19 pandemic. Each letter shows two graphs with the same four data sets, the left side putting emphasis on (= colouring) less advanced cancers (TNM cT1-3), the right side on more advanced cancers (TNM cT4). The data is plotted over the course of four time points: Before (day 0), during (day 14) and at the end (day 35) of radiotherapy and right before surgery (day 70).
Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of the surveyed group of patients.
Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of the surveyed group of patients.
| |
|
Non-COVID-19 |
Varying Non-COVID-19/COVID-19 |
COVID-19 |
Rectal cancer
patients |
244 (49.9 %) |
169 (34.6 %) |
76 (15.5 %) |
| Sex |
|
male: 174 (71.3%) |
|
female: 70 (28.7 %) |
male: 122 (72.2 %) |
|
female: 47 (27.8 %) |
male: 47 (61.8 %) |
|
female: 29 (38.2 %) |
| |
|
0 (%) |
1 (%) |
2 (%) |
3 (%) |
4 (%) |
0 (%) |
1 (%) |
2 (%) |
3 (%) |
4 (%) |
0 (%) |
1 (%) |
2 (%) |
3 (%) |
4 (%) |
| |
cT |
- |
1 (0.4) |
25 (10.2) |
153 (62.7) |
65 (26.6) |
- |
4 (2.4) |
12 (7.1) |
113 (66.9) |
40 (23.7) |
- |
2 (2.6) |
10 (13.2) |
45 (59.2) |
19 (25.0) |
| |
pT |
26 (10.6) |
18 (7.3) |
71 (29.0) |
106 (43.5) |
24 (9.7) |
30 (17.5) |
15 (9.1) |
39 (23.1) |
72 (42.7) |
13 (7.7) |
8 (10.5) |
7 (8.8) |
20 (26.3) |
39 (50.9) |
3 (3.5) |
| |
cN |
62 (25.2) |
128 (52.5) |
54 (22.3) |
- |
- |
40 (23.6) |
71 (41.9) |
58 (34.5) |
- |
- |
17 (22.9) |
31 (41.4) |
27 (35.7) |
- |
- |
| Stage |
pN |
152 (62.3) |
58 (23.7) |
34 (14.0) |
- |
- |
130 (76.9) |
31 (18.2) |
8 (4.9) |
- |
- |
57 (75.4) |
15 (19.3) |
4 (5.3) |
- |
- |
| |
cM |
190 (78.0) |
54 (22.0) |
- |
- |
- |
149 (87.9) |
20 (12.1) |
- |
- |
- |
58 (76.7) |
18 (23.3) |
- |
- |
- |
| |
cUICC |
- |
10 (4.0) |
43 (17.7) |
136 (55.6) |
55 (22.7) |
- |
8 (4.9) |
28 (16.8) |
111 (65.7) |
21 (12.6) |
- |
4 (5.6) |
10 (12.5) |
44 (58.3) |
18 (23.6) |
| |
pUICC |
- |
60 (24.6) |
74 (30.2) |
72 (29.6) |
38 (15.6) |
- |
58 (34.2) |
58 (34.2) |
35 (20.5) |
19 (11.1) |
- |
21 (27.8) |
24 (31.5) |
14 (18.5) |
17 (22.2) |
| |
Grading |
- |
9 (3.6) |
194 (79.6) |
41 (16.9) |
- |
- |
9 (5.2) |
137 (81.2) |
23 (13.6) |
- |
- |
2 (2.8) |
62 (81.7) |
12 (15.5) |
- |