1. Introduction
The smart living concept embodies a technology-driven lifestyle to elevate life quality, increase efficiency, and reduce waste. Academics and researchers have thoroughly investigated this idea, encompassing diverse dimensions such as technology, security, health, and education [
1], among others. It employs state-of-the-art Information and Communication Technology (ICT), advanced sensing technology, pervasive computing, big data analytics, and intelligent decision-making to optimize energy consumption, enhance healthcare, and elevate living standards [
2,
3]. Closely linked to smart cities, smart living encourages citizen traits like awareness, independence, and participation [
1]. It aims to transform life and work through ICT, fostering sustainable economic growth and exceptional quality of life while conserving natural resources via collaborative governance [
4]. The central idea is to generate benefits for citizens, considering their well-being and engagement [
5].
Moreover, smart living technologies empower users to access and analyze information pertinent to their lives, such as personal health and living conditions [
3]. Giffinger et al. [
6] propose a smart city framework comprising six core components: smart economy, smart people, smart governance, smart mobility, smart environment, and smart living. Integrating stakeholders like individuals, machines, devices, and the environment is crucial for realizing smart living, which covers aspects like smart lighting, smart water, smart traffic, smart parking, smart objects, smart buildings, smart industry, location/context-based services, and more [
7]. On the other hand, while intelligent connectivity and immersive information drive smart living, it is essential to emphasize the enhanced living quality facilitated by smart technology under sustainable conditions rather than focusing exclusively on technological innovation [
8]. The important thing is that as smart living definitions evolve with advancements in real-time monitoring systems, adapting smart designs and incorporating smart devices, cutting-edge technology, and sensors become critical for fostering a sustainable and efficient lifestyle for individuals and communities [
7,
9].
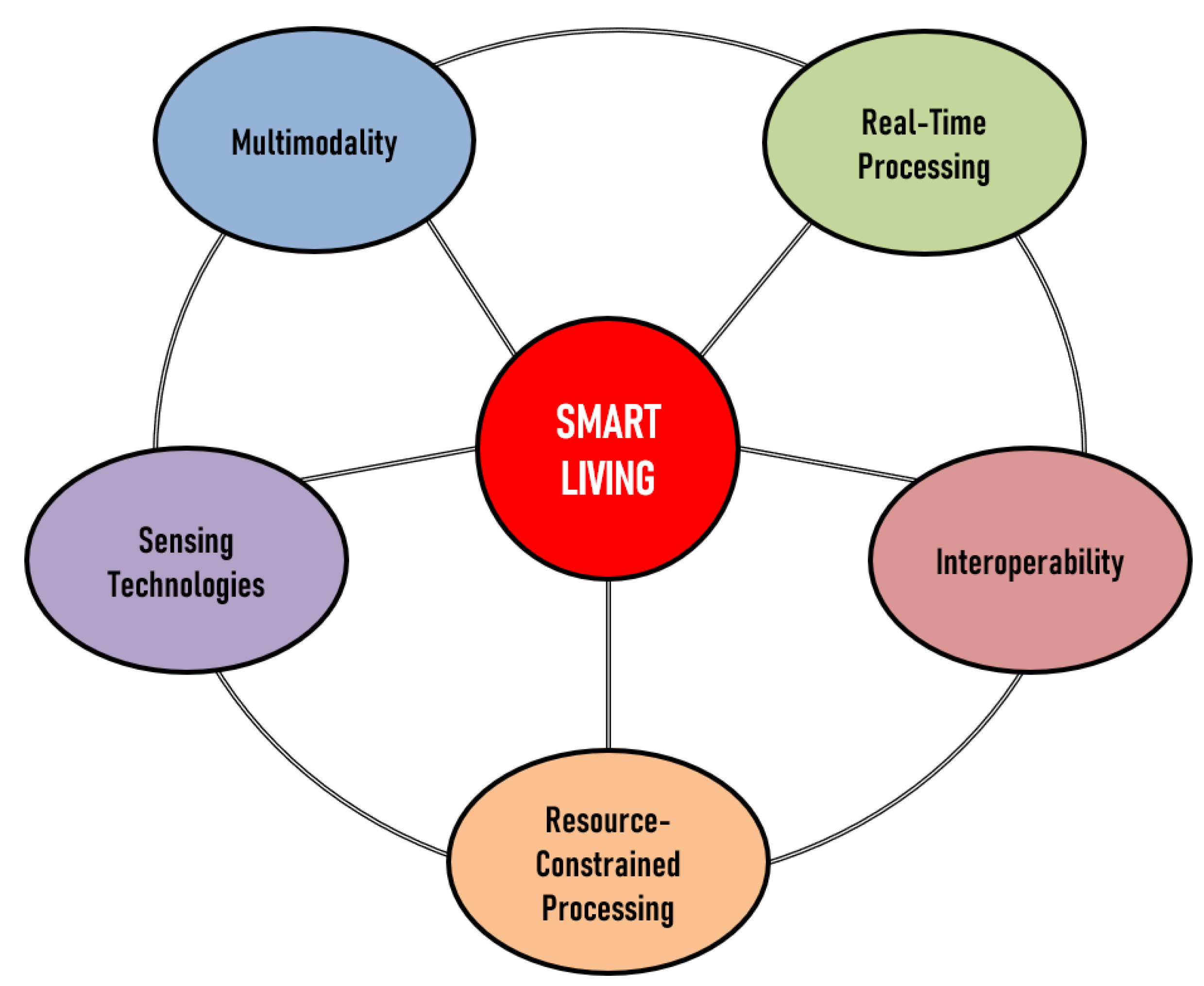
In such a scenario, Human Action Recognition (HAR) plays a significant role in smart living, contributing to various applications such as home automation, healthcare, safety, and security. Accurately identifying and interpreting human actions allows smart living systems to offer real-time responses, delivering personalized support and assistance. In particular, this work emphasizes the domains of Sensing Technology, Multimodality, Real-time Processing, Interoperability, and Resource-Constrained Processing. These elements encapsulate the critical aspects necessary for successfully deploying HAR in smart living environments. Recognizing human actions is essential for effectively implementing smart living solutions, making it a key area of research and development to pursue an enhanced quality of life and more efficient, sustainable living spaces.
1.1. General background on HAR
HAR refers to the process of recognizing and understanding human actions, which is essential for various real-world applications such as assisted living [
10], visual surveillance [
11], autonomous navigation [
12], video retrieval [
13], human-robot interaction [
14,
15], and entertainment [
16]. The concept of HAR encompasses various aspects, including action recognition, intention understanding, and narrative understanding [
17,
18]. Indeed, essentially, HAR involves identifying and interpreting human actions and environmental interactions, particularly whole-body and limb movements. Understanding these actions is crucial for predicting their effects or outcomes and inferring the performer’s intention, goal, and mental status [
19].
Having established the importance and relevance of HAR in various real-world applications and its key aspects, it is crucial to delve deeper into the methodologies and sensing approaches that form the foundation of this field. By examining the diverse techniques and modalities employed in HAR, one can better understand the intricacies of action recognition and the potential for improving and expanding upon existing methods to achieve more accurate and robust recognition of human actions in different contexts.
Primary methodologies for HAR include traditional approaches such as template matching [
20], space-time features [
21], and action grammars [
22], as well as more recent Deep Learning (DL) techniques such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks [
23], to name a few. These methods leverage various sensing modalities such as RGB (Red-Green-Blue) videos, skeleton data, depth data, infrared, thermal, point clouds, audio, binary readings, acceleration, gyroscope, magnetometer, radar, and Wi-Fi. Furthermore, these diverse sensing approaches provide diverse and complementary information about human actions. Visual modalities (e.g., RGB videos, skeleton data, depth data, infrared sequences, point clouds), for example, are more intuitive for representing human actions since they are more similar to the functioning of the human visual system. In contrast, non-visual modalities (e.g., acceleration, gyroscope, magnetometer, radar, and Wi-Fi) can be used for privacy-sensitive scenarios or when visual data are insufficient or unavailable.
Besides the various methodologies and sensing approaches, it is essential to consider how data fusion techniques can further enhance the performance of recognition models. In fact, by combining information from multiple modalities, data fusion can provide a complete understanding of human actions and help address the limitations inherent in individual modalities. Furthermore, action prediction, narrative understanding, and transfer learning advance HAR research significantly and broaden its applicability in diverse real-world situations. More precisely, data fusion plays an important role in HAR as it enhances the accuracy and robustness of the recognition models by combining the information from multiple data modalities [
24]. This can compensate for the limitations of individual modalities and leverage their strengths to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of human actions. Fusion techniques can be applied at various levels, such as feature fusion, decision fusion, or model fusion [
25].
Further aspects relevant to HAR include the investigation of action prediction, where the goal is to anticipate future actions based on observed actions, and narrative understanding, which focuses on identifying the agent’s identity or social role in the context of an action [
26,
27]. Additionally, transfer learning and co-learning across different modalities can improve the robustness and generalizability of HAR models, enabling them to adapt to new scenarios and handle diverse data sources effectively [
28,
29,
30]. In summary, HAR is a complex and multidisciplinary field that aims to understand human actions and their implications in various contexts. Using different methodologies, sensing approaches, and data fusion techniques contributes to advancing HAR research and its applicability in a wide range of real-world applications.
1.2. HAR in Smart Living focusing on Multimodality, Real-time Processing, Interoperability, Resource-Constrained Processing, Sensing Technology
In smart living, HAR plays a crucial role in enabling technology to respond to the occupants’ needs and enhance their quality of life. It involves recognizing human activities and movements within smart living environments using various sensing technologies. HAR aims to provide smart homes and buildings with an understanding of the behaviors and routines of the occupants, allowing for improved automation and personalized services. For example, in a smart home, HAR can be used to recognize and respond to the actions of the occupants, such as opening and closing doors, turning on and off lights, and adjusting the temperature.
In smart healthcare, HAR can be used to monitor the activities of patients and detect any potential health issues. From a broader perspective, HAR can also be applied in smart cities to recognize and respond to the actions of citizens, such as traffic management, public safety, and environmental monitoring. Building on the importance of HAR in smart living, several key domains must be considered to ensure effective implementation and seamless integration within various applications. These domains include Multimodality, Real-time Processing, Interoperability, Resource-Constrained Processing, and Sensing Technologies. By addressing these crucial factors, HAR can contribute to developing intelligent systems capable of adapting to smart living environments’ unique requirements and challenges, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for individuals and communities alike. These aspects, which are distinctive of HAR in smart living contexts, will be addressed in detail later in the following sections, shedding light on their importance and potential impact on the future of HAR in smart living applications.
In
Figure 1, we can observe the representation of the five key domains, interconnected with Smart Living and sharing connections among themselves. The interconnectivity among these domains arises due to the complementary and synergistic nature of their roles in enabling and enhancing Smart Living. Each domain contributes unique capabilities and characteristics that, when combined, result in more efficient, user-centric, and intelligent systems.
Multimodality ensures that various types of sensor data can be processed and interpreted, offering a seamless experience. Real-time Processing allows instantaneous analysis and decision-making, crucial for a responsive and adaptive Smart Living environment. Interoperability guarantees that different devices, systems, and platforms can communicate effectively, fostering collaboration and integration within the ecosystem. Resource-Constrained Processing enables the optimization of computational resources, ensuring that the various components of Smart Living can function efficiently even with limited resources. Finally, Sensing Technologies provide crucial data input, capturing information from the environment and users to allow the system to react and adapt accordingly.
These domains work together to enhance each other’s capabilities and bridge gaps to create a unified, holistic, and efficient Smart Living system. The interconnections between these domains are essential to unlocking their full potential and leveraging their collective strengths to improve the quality of life in our increasingly connected smart environment.
This review paper will comprehensively analyze the current state-of-the-art HAR within smart living. The remainder of the paper is organized as follows: First, we delve into the existing review works in the field, identifying the gaps and motivating the need for this comprehensive study. We then describe the search and inclusion criteria for selecting the relevant literature.
Section 3 presents an overview of the common publicly available datasets used in the studies, followed by a discussion of the widely used performance metrics for evaluating Machine Learning (ML) algorithms in
Section 4.
Section 5 explores various aspects of HAR in smart living through the proposed smart living Temple framework. This framework allows us to examine the interplay between different aspects of HAR and smart living, such as sensing modalities, feature extraction techniques, and classification methods.
Section 6 presents a critical discussion addressing potential concerns and challenges related to the smart living Temple, offering valuable insights for researchers and practitioners. Finally, we conclude the paper in
Section 7, summarizing our findings and providing some closing considerations for future research and development in HAR in smart living applications.
2. Review of Related Works and Rationale for This Comprehensive Study
HAR has gained significant attention as a crucial research area in various application contexts in recent years. This increasing importance has led to the publication of numerous review studies focused on different aspects of the field. Based on a thorough examination of existing literature, it can be concluded that existing survey and review studies predominantly fall into one of the following categories: either they provide a general overview of the field [
31,
32], or they focus on specific aspects such as ML, DL, and hardware architectures [
23,
33,
34,
35], sensing [
36,
37,
38], or computer vision [
39,
40,
41]. To the author’s best knowledge, it is important to note that no studies specifically centered on smart living comprehensively analyze the current literature through the aforementioned key domains essential for smart living solutions. This observation requires a comprehensive literature review on HAR for smart living. Such a review would facilitate a more nuanced understanding of the state-of-the-art in this domain, ultimately fostering the advancement of innovative, effective, and efficient smart living technologies.
For this review, a thorough literature analysis was conducted by examining 511 documents identified using a targeted Scopus query. The query was designed to capture many relevant papers by incorporating specific keywords related to human activity recognition and smart Living. The query utilized the following structure:
TITLE (action OR activity OR activities) AND TITLE (recognition OR classification OR classifying OR recognize OR classified OR classifier OR detector OR detecting OR discriminating OR discrimination) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY ("smart home" OR "smart building" OR "smart environment" OR "smart space" OR "smart living" OR "smart city" OR "smart cities" OR "assisted living" OR "ambient intelligence" OR "smart ambient") AND PUBYEAR > 2019.
The query searched for articles with titles containing terms related to actions or activities and their recognition, classification, or detection. Furthermore, the search was refined to include articles with title-abstract-keywords related to various smart living contexts, such as smart homes, smart buildings, smart environments, smart cities, and ambient intelligence, among others. Additionally, the query focused on publications from 2020 onwards to ensure that the analysis considered recent advancements in the field.
The primary inclusion criterion for selecting a paper in this review was its contribution to one or more of the key domains of smart Living mentioned earlier. This approach allowed for the compilation of a comprehensive and relevant set of literature, which forms the basis for an informed and insightful analysis of human activity recognition in the context of smart living.
5. Recent State-of-the-Art on HAR in Smart Living
This section provides an in-depth analysis of various aspects of HAR within smart living as a cutting-edge field revolutionizing how we interact with our environments. The critical domains of this analysis include Multimodality, Real-time Processing, Interoperability, Resource-Constrained Processing, and Sensing Technologies, which collectively contribute to creating seamless, adaptive, and responsive living spaces.
Each domain represents a crucial aspect of HAR, and together they support the overarching goal of creating seamless, adaptive, and secure living spaces. Through these domains, the suggested framework encapsulates the vital elements contributing to the rapid advancements in HAR. In the following discussion, we will examine each domain of the framework in detail, shedding light on their significance and interconnections, ultimately providing a comprehensive review of HAR literature as an integral aspect of the future of smart living.
5.1. Multimodality
Multimodality is a critical aspect of smart living, encompassing a variety of applications such as health monitoring, human-object interaction, and smart homes. It effectively integrates various sensing modalities, including wearable devices and environmental sensors, to achieve accurate and reliable HAR. Although significant advancements have been made in recent years using CNNs, LSTM networks, transformer networks, and various hybrid models, challenges persist in effectively modeling spatial-temporal dependencies of sensor signals and addressing the distinct contributions of different sensing modalities in complex environments [
89,
90].
To tackle these challenges, Xiao et al. [
91] proposed a self-attention-based Two-stream Transformer Network (TTN). The TTN aims to model the temporal-spatial dependencies for multimodal HAR by introducing an attention block to evaluate the recognition performance of all sensor axis readings. The model incorporates a two-stream structure consisting of temporal and spatial channels, which extract sensor-over-time and time-over-sensor features, respectively. These two-stream features are complementary, as the time-over-reading features can express additional information that cannot be captured directly from sensor signals. To adapt to data heterogeneity caused by the multiple sensor environment, the spatial channel is further enhanced with an attention block that captures the recognition contribution of each sensor axis and assigns attention weights accordingly. While the study by Xiao et al. [
91] primarily focuses on wearable sensing, the concepts and techniques presented can potentially be extended to environmental sensing. A more comprehensive and robust human activity recognition system can be developed by considering various sensing modalities, such as cameras, microphones, and other ambient sensors.
In the paper by Bocus et al. [
24], the authors present a comprehensive multimodal dataset designed for passive HAR and localization techniques using synchronized Radio Frequency (RF) devices and vision-based sensors. The dataset is unique because it incorporates multiple synchronized modalities, including Channel State Information (CSI) from a WiFi Network Interface Card (NIC), passive WiFi radar based on an Software Defined Radio (SDR) platform, Ultra-Wideband (UWB) signals, and vision/infrared data from Kinect sensors. The dataset consists of approximately 8 hours of annotated measurements collected across two rooms from 6 participants performing six daily activities. With over 1 million annotated data points, it is considered comprehensive and well-suited to developing various pattern recognition and DL algorithms for accurately recognizing human activities. The authors highlight that this is the first dataset explicitly aimed at accelerating the development of self-supervised learning techniques, which are known to be data-hungry and typically require larger datasets than traditional supervised learning.
Furthermore, the multiple receivers for each modality can be used in multimodal and multiview data fusion networks, improving performance in concurrent activity recognition and localization tasks. This open-source dataset is relevant to research communities involved in radar, wireless sensing, IoT, and computer vision. The authors have ensured that the dataset adheres to the FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) Data principles of Open Science by making it publicly available for download, providing a clear and in-depth description for each modality, and using standard file types and encoding.
Islam et al. [
92] present a DL-based fusion approach for multimodal HAR in smart healthcare applications. The fusion technique is designed to handle different types of data collected from wearable and stationary devices (i.e., envi-ronmental sensors). The authors utilize CNNs to extract high-level attributes from image data and Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory (ConvLSTM) for capturing significant patterns from multi-sensory data. The extracted features from different modalities are then fused through self-attention mechanisms, which enhance relevant activity data and inhibit superfluous and possibly confusing information by measuring their compatibility. The proposed fusion architecture and two baseline architectures (CNN and ConvLSTM) are evaluated on the UP-Fall detection dataset, which consists of a sizeable multimodal benchmark. The fusion approach demonstrates superior performance compared to the baselines, achieving an accuracy of 97.61%, outperforming other state-of-the-art methods in the HAR literature. The authors attribute the improved classification accuracy to the multimodal sensing and fusion approach, which enables the system to process data from various sources and modalities effectively. This system has potential practical applications in health monitoring, sleep disorder monitoring, eating disorder monitoring, medication intake monitoring, and exercise aid systems.
Alexiadis et al. [
93] presented a sensor-independent fusion method that allows for the design of multimodal methods operating with varying sensors, even when some sensor data are missing. To address the issue of missing sensor data and improve the fusion model’s accuracy, the authors proposed a data augmentation method that creates new observations using all possible subsets of activated sensors. The proposed methods were tested on the ExtraSensory dataset, which contains over 300,000 samples from 60 users and incorporates heterogeneous measurements from various wearable sensors, such as accelerometers, gyroscopes, magnetometers, watch compasses, and audio sensors. The dataset was used to fuse unimodal models for the available sensors. To evaluate the performance of the proposed methods, the researchers devised ex-periments to measure the improvement of the F1-score per class for the entire test set and specific subsets split according to the number of sensors used per observation. The results demonstrated that the sensor-independent fusion method enables the development of fusion models that can operate with fewer data sources than originally intended, as long as the maximum number of sensors is known beforehand. Moreover, the data augmentation method effectively increased the fusion model’s performance when operating with fewer sensor data. It showed an increase in all subsets of the test set.
Dhekane et al. [
94] address the challenge of HAR in unannotated data streams generated by real-world smart home applications. In this context, they propose a real-time annotation framework for HAR based on Change Point Detection (CPD) and develop a novel transfer learning-based CPD algorithm called S-CPD. The al-gorithm calculates a Change Point Index (CPI) for each sensor reading in the data stream using similarities of output probability distributions, allowing for enhanced annotations. The authors emphasize the challenges posed by the multimodal nature of ubiquitous sensor data, which is heterogeneous and often noisy. Incorporating information from different sensor modalities into a single framework remains a prominent challenge in sensor-based HAR. To tackle this, they investigate the components of feature extraction, data augmentation, noise handling, and classification to create an optimal HAR framework for the chosen datasets. The S-CPD algorithm is tested using a new metric called Sensor Distance Error (SDE). It achieves an average SDE of around 1.1 over the four datasets, indicating a minimal error between predicted and actual change points. The annotation framework achieves an average accuracy of 94% across three test cases for the datasets under consideration, outperforming the current state-of-the-art annotation framework by around 14%.
Hiremath et al. [
95] present a novel approach to boot-strapping HAR systems in smart homes. The authors acknowledge that starting an activity recognition system for specific smart homes is challenging due to the highly individualized nature of these spaces and the inhabitants’ unique behaviors. The proposed approach operates in a cold-start scenario, where the HAR system passively observes raw sensor data in the smart home without prior knowledge about the environment or its inhabitants. It then learns representations called action units, which are aggregated into activity models through a motif learning and discovery process that requires minimal supervision. The final HAR system can then recognize relevant and frequent activities in the smart home. The authors use an Active Learning-like procedure to minimize user burden during bootstrapping. Active learning provides annotations for a limited number of relevant and informative data points, reducing the need for large amounts of labeled data. This method is particularly useful in smart homes, where annotating large volumes of data can be time-consuming and expensive. The effectiveness of the bootstrapping procedure is demonstrated through experimental evaluations on CASAS datasets, Aruba and Milan. The authors also provide practical guidelines for practitioners interested in instrumenting smart homes and building activity recognition systems for such environments. One potential application of the knowledge gained from the bootstrapping procedure is the utilization of additional sensor modalities. The authors suggest that the discovered knowledge about movement patterns and subsequences could be used to fine-tune HAR systems for specific tasks and assist smart home residents in their Activities of Daily Living (ADLs).
The works discussed in this section are summarized in
Table 1 and
Table 2.
5.2. Real-Time Processing
In the realm of smart living applications, real-time processing plays a critical role in ensuring the seamless integration of technology into our daily lives. By enabling immediate analysis and response to various sensor inputs, real-time processing facilitates a smooth and intuitive user experience, ultimately improving the overall quality of life. Furthermore, real-time data processing is crucial for applications such as smart homes, healthcare monitoring, and security systems [
96]. It allows for timely decision-making, proactive intervention, and seamless adaptation to changing conditions. Ultimately, the pursuit of real-time processing plays a vital role in unlocking the full potential of smart living technologies and ensuring their successful integration into our everyday lives.
To achieve real-time processing, developers can explore various approaches, including the choice of sensing modality, the implementation of lightweight computational frameworks, and other optimization techniques [
97,
98]. One approach to achieve real-time processing is by selecting an appropriate sensing modality. For example, video stream processing is computationally expensive, but utilizing depth cameras can help mitigate this issue. Depth cameras offer several advantages, such as easing segmentation algorithms, increased independence from lighting conditions, reduced noise, and providing richer spatial information [
99].
Zin et al. [
10] present a real-time action recognition system for older adults using a stereo-depth camera. The proposed system combines feature extraction methods from previous works in a novel combination of action recognition. The system localizes people by extracting different regions of interest from UV-disparity maps. It recognizes actions in long sequences using spatial-temporal and distance-based features fused with the automatic rounding method. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed system can detect various actions in real time with reasonable recognition rates, regardless of the length of the image sequences.
Wearable sensing is an additional modality that reduces processing load. While the complexity of wearable sensor data is typically lower than that of RGB cameras, their proximity to the body enables extensive data gathering, which makes them highly appropriate for HAR [
100]. Another way to pursue real-time processing is by employing lightweight computational frameworks. These frameworks are designed with fewer parameters, low memory occupancy, and faster processing speeds, all contributing to lessening the computational load. Examples of such frameworks include MobileNet [
76], SqueezeNet [
101], and ShuffleNet [
102], which deliver high performance while maintaining low resource requirements. Additionally, implementing model quantization and pruning techniques can further optimize these architectures, leading to more efficient processing.
Hu et al. [
103] address the challenge of real-time activity recognition in health smart homes, focusing on optimizing SVMs (SVM) using genetic algorithms. The authors propose an online real-time activity recognition approach based on the genetic algorithm–optimized SVM classifier. The core of this approach involves a sliding window-based feature representation technique enhanced by the mutual information between sensors, which supports online real-time activity recognition. The authors’ proposed solution has two main aspects. Firstly, they design a sliding window-based feature extraction method that effectively reduces the influence of irrelevant information in a time window of sensor events by incorporating sensor mutual information into the feature vector. This ultimately improves the accuracy of activity recognition. Secondly, they develop a multiclass SVM classification framework based on the feature mentioned above extraction technique for online real-time activity recognition. The genetic algorithm automatically selects optimal hyperparameters for the SVM classifier, reducing recognition inaccuracy caused by over-dependence on the human experience. The authors conduct comprehensive experiments using freely available datasets to validate the effectiveness of their proposed approach. The results show that the macro-F1-scores on the datasets are above 0.9, indicating excellent ability in activity recognition across different datasets. Despite these promising results, the authors acknowledge some limitations in their work. The requirement of many labeled data samples for training an SVM classifier makes manual labeling costly. Additionally, the need for a specific SVM classifier for each smart home prevents sharing a common activity recognition model between different smart environments.
In the paper by Chen et al. [
104], the authors propose a novel approach to HAR by utilizing skeleton extraction and image reconstruction. Traditional methods for HAR directly input source images, which can be affected by various factors such as heights, weights, poses, angles, and occlusions. In contrast, the proposed method uses the OpenPose library to extract 2D positions of human skeleton joints as a preprocessing phase. The skeleton image is then reconstructed from these joints, with coloring used to encode the categories of different human parts. These reconstructed images are input into a CNN structure for classification. The authors focus on four typical activity classes: squat, stand, walk, and work. By employing the proposed method, the complexity of the neural network is reduced, and the recognition accuracy is significantly improved compared to using original complex source images. All images used for training and testing are collected from real public places, and the method achieved a recognition accuracy of 97.3% in experiments. One of the main advantages of the proposed method is its real-time processing capability. The OpenPose library enables the extraction of 2D skeleton joints with lightning speed, allowing the HAR method to be carried out in real time. Furthermore, the authors demonstrate the general significance of using synthesized input to bridge existing technologies, which can be applied to other complex systems, especially neural network systems.
In their excellent work, Yan et al. [
105] address the challenge of accurate and efficient real-time HAR in smart IoT systems by proposing a method that integrates offline and online learning to improve the performance of event-count sliding window techniques on streaming data. The authors use unsupervised learning to learn latent knowledge from explicit-activity window sequences, which helps to enhance the limited information of sliding windows without much domain knowledge. They then derive the probability distribution prediction of activity classes for a given sliding window. The researchers employ two unsupervised feature learning techniques, the enhanced topic-aware Bayesian approach, and the Hidden Markov Model (HMM)-based prediction, to consider activity classes within a window as the latent semantics or states underlying window feature/observation. They then feed the basic feature representation of a sliding window and the high-level feature representation, which is the probability distribution prediction of activity classes, into a classifier model to produce the activity class report for the window. The online activity report is produced once per event by processing the sliding window, which ends on that event. The authors tested their proposed method on five real-world smart home datasets from the CASAS smart home project. The experimental results demonstrated that their method improved the performance of hand-crafted features-based methods by at least 20 percent on average, without requiring significant extra time and effort in the testing stage.
Ramos et al. [
106] present a real-time human activity recognition system for monitoring the daily activities of elderly individuals. The system is developed using a prediction model based on bidirectional LSTM networks, which allows it to recognize real-time activities, a crucial feature for timely intervention in case of anomalies. The model is trained using data from the public CASAS dataset, which contains information from non-intrusive sensors installed in a person’s home. The authors employ data processing and filtering techniques, such as a sliding window method and a stacking and reordering algorithm, to ensure real-time processing and maintain a high accuracy rate. These methods enable the model to handle activities of varying durations and consider the time reference of each activity. The developed model provides an impressive 95.42% accuracy rate, outperforming existing models. One of the main strengths of this system is its ability to make real-time predictions with equispaced time intervals, addressing a limitation in previous approaches that required knowledge of the activity duration for making predictions. Using non-intrusive sensors also respects users’ privacy, essential for maintaining autonomy and security. The real-time nature of this system allows for the swift detection of anomalies or deviations from established patterns, making it a valuable tool for monitoring the well-being of elderly individuals living alone.
The works discussed in this section are summarized in
Table 3 and
Table 4.
5.3. Interoperability
Interoperability, a key aspect of any modern system, refers to the ability of different systems or components to work together in a coordinated manner, exchanging and utilizing information seamlessly. In the context of HAR in smart living, interoperability is crucial as it enables integration with various smart home systems to provide users with a comprehensive and cohesive experience [
107]. Interoperability is essential because it allows organizations to utilize different systems and technologies, saving time and money. Moreover, achieving semantic interoperability ensures that the real meaning of shared data is preserved across systems, applications, and devices, regardless of the vendor. This concept is particularly relevant in healthcare, where data sharing between clinicians, labs, hospitals, and pharmacies is vital for effective patient care. For HAR systems to effectively integrate with smart living environments, non-intrusiveness is vital. This ensures user privacy, comfort, and acceptance, ultimately fostering a sense of dignity and independence for the individuals involved. These systems can effectively monitor and recognize activities without compromising users’ well-being by minimizing disruption to daily routines and maintaining a discreet presence [
113].
Zhang et al. [
108] proposed a knowledge-based approach for multiagent collaboration in smart homes, addressing issues such as device heterogeneity, composite activities recognition, and providing appropriate services. The authors developed a layered architecture of smart homes that combines ontology and multiagent technologies to automatically acquire semantic knowledge and support heterogeneity and interoperability services. This architecture is composed of four layers: the physical layer, the middleware layer, the knowledge management layer, and the service layer. The experimental evaluation of the proposed approach was conducted in a lab setting where eight typical human activities containing a total of 32 actions were selected for testing. Eight participants from the laboratory, unfamiliar with the deployment plans, participated in the experiments. The authors designed experimental and control groups, each divided into three subgroups. The experimental group used a generic inference algorithm based on unordered actions and temporal activity properties for activity recognition. The experimental results showed that the recognition accuracies for human activities were high, with an average accuracy of 99.22%. This demonstrates the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed approach in recognizing human activities in real time.
Interoperability is crucial in integrating various systems, especially in smart homes, where various sensing devices are utilized to monitor and recognize human activities. A seamless exchange of information and understanding between wearable and ambient sensors can lead to more accurate and efficient activity recognition systems. One way to achieve interoperability in such systems is by employing ontologies, which formally represent knowledge and facilitate data sharing among devices. By leveraging ontology-based approaches, fusing data from multiple sensing sources becomes possible, enhancing activity recognition systems’ performance and promoting seamless interoperability between wearable and ambient sensors.
Noor et al. [
110] investigated the fusion of wearable and ambient sensors for recognizing ADLs in a smart home setting using ontology. The study aimed to resolve uncertainties due to missing sensor data by exploiting the advantages of both types of sensing. The authors proposed an ontology-based sensor fusion approach that combines user context provided by wearable sensor-based activity recognition with environmental contexts to handle missing sensor data. The activity recognition system proposed by Noor et al. consists of two phases: knowledge acquisition and ontology reasoning. The approach was evaluated using the Intelligent Environment Laboratory (IELAB) and OPPORTUNITY human activity datasets. The IELAB dataset was collected in the University of Auckland’s laboratory, partitioned into four areas (lounge, toilet, kitchen, and dining), and involved 20 participants performing various activities. The OPPORTUNITY dataset contained wearable, object, and location sensor data recorded in a simulated studio apartment involving four subjects performing five activities. The authors compared the accuracy of activity recognition systems without wearable sensors (AR) and wearable sensors (ARW). For the IELAB dataset, the overall average recognition accuracy was 91.5% when using the ARW system, whereas the OPPORTUNITY dataset achieved an overall recognition accuracy of 90% with the ARW system. This approach demonstrated that the proposed system was more robust in handling uncertainties and could infer additional information about activities, which was impossible only with environment sensing. The system was capable of inferring activities more precisely, including those that did not involve interaction with objects.
Enhancing interoperability among various devices and components in IoT systems is critical in realizing effective HAR in smart living environments, allowing for seamless communication and data exchange between connected appliances and sensors. Under this perspective, Franco et al. [
109] proposed an IoT-based approach for load monitoring and activity recognition in smart homes, focusing on Intrusive Load Monitoring (ILM) techniques. The authors developed an IoT architecture composed of five layers: appliances, perception, communication network, middleware, and application. As part of the application layer, the appliance recognition module is responsible for labeling sensor data to enable the implementation of different home applications, such as activity recognition. The paper tests three different classifier models using real-world data from the UK-DALE dataset: feed-forward neural network (FFNN), LSTM, and SVM. The developed ADLs algorithm maps each ADL to a set of criteria depending on the appliance used. Features are extracted according to the consumption in Watt-hours and the times when appliances are switched on.
Regarding experimental results, the accuracy of the FFNN and LSTM networks was above 0.9, while it was around 0.8 for the SVM network. For the FFNN classifier, the F1-score was above 0.9 for all cases. The authors also performed experiments to evaluate the classifier model using a new test set and conducted a sensitivity analysis to study the impact of group size on classifier accuracy. The results suggest that before the system is fully operational, it might be necessary to retrain the classifier with new data. Additionally, the impact of group size on the ML classifier accuracy varied, with accuracy decreasing or increasing depending on the group size, except for the LSTM model, which showed increased accuracy when the group size was more significant. Moreover, interoperability can be achieved by employing semantic fusion techniques that integrate data from diverse sensors, such as environmental sensors and computer vision systems, enabling a cohesive understanding of human activities in pervasive environments. Stavropoulos et al. [
72] presented a framework that integrates computer vision and heterogeneous sensors for activity recognition in pervasive environments, specifically targeting the application of dementia care. The paper proposed a combination of ambient intelligence, semantic web technologies, computer vision, and Ambient Assisted Living (AAL) to provide real-world healthcare solutions. This integration addressed challenges for realistic applications such as fast, efficient image analysis and ontology-based temporal interpretation models. The authors employed an ontology-based knowledge representation and semantic fusion for activity recognition using OWL as the underlying knowledge representation and reasoning language. The framework architecture included a sensor, analysis, representation, interpretation, service, and application layers, which provided a multidisciplinary approach for integrating various sensors and computer vision techniques. The framework enabled extracting atomic events and observations from different sensors and mapping them to a uniform semantic representation for interoperability. The framework was evaluated at the GAADRD daycare center with a dataset of 98 participant trials. The dataset was collected through a series of semi-directed activities. Participants were given a list of activities to perform in any order, and the activity recognition performance was not affected by repetitions or omissions. The evaluation aimed at combining and assessing the effectiveness of computer vision, ambient sensors, and semantic event fusion in activity recognition. The results presented in the paper showed an average recall and precision for activity recognition of about 82%, except for the activity EstablishAccountBalance which had a significantly lower performance. The framework demonstrated the effectiveness of combining computer vision and ambient sensor data for activity recognition, specifically in dementia care. The proposed semantic fusion of vision and sensor observations proved beneficial, showing this approach’s potential for addressing real-world healthcare scenarios.
In the context of interoperability, Mekruksavanich et al. [
111] propose a framework for Exercise Activity Recogni-tion (EAR) using Surface Electromyography (sEMG) data. This approach is designed to improve recognition accuracy in applications such as AAL, smart healthcare, and smart rehabilitation. Interoperability is essential to this research as it enables integrating sEMG data with various ML algorithms to recognize different exercise activities. The authors indicate that the recognition accuracy can be enhanced using sEMG data from three sensors. This finding suggests that the interoperability of these sensors and ML algorithms has the potential to improve the overall effectiveness of wearable smart devices in HAR. By efficiently integrating sEMG data with ML techniques, the authors’ research contributes to developing versatile solutions for various healthcare and daily life applications.
In their paper, Minarno et al. [
112] explore the performance of various ML algorithms for activity recognition using accelerometer and gyroscope sensor data. Focusing on the interoperability aspect, the authors emphasize the relevance of autonomous systems in various applications, such as fall detection, medical rehabilitation, and smart home systems. These systems significantly improve the quality of life by analyzing human physical activities, categorized into three classes: static, transition, and dynamic. The researchers utilized data acquired from 30 volunteers and evaluated seven different ML algorithms, including Logistic Regression (LR), SVM, Decision Tree (DT), Random Forest, Gradient Boosted, and K-Nearest Neighbor. They found that LR and SVM with a linear kernel achieved 98% accuracy, indicating their potential to be integrated into various autonomous systems for human activity recognition. Interoperability is further highlighted by successfully detecting static activities using LR and SVM algorithms. The high performance of these algorithms demonstrates their suitability for integration into a wide range of applications in health and human-computer interaction domains.
The works discussed in this section are summarized in
Table 5 and
Table 6.
5.4. Resource-Constrained Processing
In the context of smart living and HAR applications, addressing the challenges posed by limited processing resources is essential. These constraints arise due to the demand for affordable, energy-efficient devices seamlessly integrating into home environments. Such devices often rely on mobile or wireless platforms, presenting limitations such as restricted processing power, storage, bandwidth, and power resources. To tackle the issue of limited processing power, low-cost and energy-efficient devices should employ lightweight algorithms, which are both computationally efficient and effective at recognizing human actions. These algorithms should be optimized for mobile or wireless platforms, ensuring the best performance on such devices [
114].
Regarding limited storage resources, utilizing efficient algorithms and data structures to handle large volumes of data generated by HAR applications is crucial. This may involve implementing innovative techniques such as data pruning or feature selection, which help reduce the dataset’s size while preserving its essential information. By doing so, devices can store and process the data effectively, even with limited storage capacity. Addressing limited bandwidth for data transmission is another challenge in smart living and HAR applications. To overcome this hurdle, developing efficient compression and communication techniques is crucial. These methods should minimize the amount of data transmitted between devices while maintaining the quality of shared information. This can be achieved through the use of advanced data compression techniques, as well as optimized protocols for data communication [
115].
Moreover, concerning limited power resources, it is important to design efficient algorithms and power management techniques that ensure long battery life for portable devices. This may involve dynamic power management strategies, such as adaptive duty cycling, which adjusts the device’s power consumption based on its current workload. In addition, energy-aware algorithms can be employed in HAR applications to minimize the power consumption of the devices, prolonging their battery life without compromising their performance.
Zhou et al. [
116] proposed an innovative HAR system based on Improved Bayesian Convolution Network (IBCN) for processing on limited-resource devices. The study’s primary focus was addressing resource-constrained processing in Wearable Internet of Things (W-IoT) devices used for data analysis. The IBCN approach allows each smart system to download data using either traditional RF or low-power back-dispersion communication with cloud assistance. The authors designed a distribution of the model’s latent variable and extracted features using convolution layers, aiming to improve the performance of W-IoT devices. Combining a variable autoencoder with a standard deep net classifier was used to achieve this goal.
Additionally, the Bayesian network was employed to address security issues using an Enhanced Deep Learning (EDL) design with an effective offloading strategy. The experimental results demonstrated that the data collected from the wearable IoT sensor was sensitive to various sources of uncertainty, including aleatoric and epistemic uncertainties. The labscale experimental analysis of the classification accuracy of patient health data showed that the IBCN approach significantly outperformed conventional designs such as Cognitive Radio (CR) learning, Deep Learning-based Sensor Activity Recognition (DL-SAR), and Cloud-assisted Agent-based Smart home Environment (CASE). Regarding numerical results, the proposed IBCN method achieved less power consumption and higher reliability than other methods such as Deep Q-Learning Approach (DQLA), DL-SAR, CASE, and Robot-integrated Smart Home (RiSH). The IBCN algorithm also showed improved performance on public datasets for state of the art, indicating its strong capacity for generalization.
In their research, Chang et al. [
117] focused on developing a low-power, memory-efficient, and high-speed ML algorithm for smart home activity data classification suitable for resource-constrained environments. However, considering the numerous publicly available HAR datasets, the authors’ decision to use the MNIST da-taset [
118] as a substitute for real-world activity data is questionable. While they argue that experimental constraints and similarities between datasets when converted to image form justify their choice, whether the MNIST dataset adequately represents human activity data’s complexity and unique features are debatable. The proposed ML algorithm consists of data preprocessing, training, and classification stages. In data preprocessing, training data with the same label are grouped into detailed clusters. The classification algorithm is based on an enhanced SVM, in which the training process generates hyperplanes by accumulating and thresholding from each cluster of preprocessed data. The classification process classifies input data by calculating the similarity between the input data and each hyperplane using a bitwise-operation-based error function.
The authors implemented the proposed algorithm on Raspberry Pi 3 and STM32 Discovery board embedded systems. The experimental results showed that the proposed algorithm had an overall accuracy of 82.2%, slightly lower than the Linear Support Vector Machine (LSVM) and the CNN models. However, the proposed algorithm exhibited significant improvements in resource consumption. Compared to the LSVM model, the proposed algorithm improved memory usage to 15.41%, power consumption to 41.7%, performance up to 50.4%, and power per accuracy to 39.2%. Compared to the CNN model, the proposed algorithm improved memory usage to 15.41%, power consumption to 61.17%, performance up to 57.6%, and power per accuracy to 55.4%. The authors noted that although the proposed model had fast execution time and efficient memory and power usage, the model’s accuracy and other evaluation metrics were slightly lower than conventional ML/DL approaches. More research is needed to prove the suitability of using the MNIST dataset to represent real-world activities. Future work should optimize the model for real-world activity data to achieve better accuracy while preserving efficient resource consumption.
The paper by Zhu et al. [
119] proposes a lightweight CNN (CNN) architecture named Mobile-RadarNet, for HAR based on micro-Doppler signatures in resource-constrained mobile-edge computing devices. The authors address the issue of computational complexity and model size, which limit the deployment of DL models in mobile devices. The proposed architecture uses 1-D depthwise and pointwise convolutions to build a streamlined and efficient network, which extracts features in each frequency bin and exchanges information between frequency bins. The authors show that the proposed Mobile-RadarNet achieves high classification accuracy while keeping the computational complexity shallow, making it suitable for mobile device deployment. The authors collected data for seven types of human activities using an Infineon Sense2GoL Doppler radar. They used fivefold cross-validation and leave-one-subject-out cross-validation to evaluate the performance of the proposed model. They compared the proposed Mobile-RadarNet with MobileNet, a famous lightweight CNN for computer vision. They showed that the proposed model has similar or even higher accuracy with 15x fewer parameters and 40x fewer floating-point operations. The authors also evaluated the actual inference speed of the proposed models deployed on a mobile phone with an ARM platform. They showed that the proposed models provide a significant acceleration effect compared with other DL models.
The paper by Helmi et al. [
120] proposes a new method for HAR using wearable sensor data. The method integrates DL and swarm intelligence optimization algorithms to build a robust HAR system that addresses the feature selection problem. The authors develop a light feature extraction approach using the Residual Convolutional Network (RCN) and an RNN and propose three variants of the Marine Predator Algorithm (MPA) for feature selection. The MPA variants use two widely-used transfer functions to perform the binarization process, including the V-shaped transfer function for MPA (MPAV). The study employs three public datasets containing complex and compre-hensive activities: Opportunity, PAMAP2, and UniMiB-SHAR. It compares the proposed MPA variants to several optimization algorithms using two classifiers, the SVM classifier, and the Random Forest Classifier (RFC). The evaluation experiments show that the MPAV recorded the best performance compared to other MPA variants and other compared methods. The proposed method significantly improved the classification accuracy for the studied datasets, including a 2.97% increase for the PAMAP2 dataset and a 3.09% increase for the UniMib-SHAR dataset. The proposed method outperformed previous studies using the same datasets. Overall, the study demonstrates that integrating DL and SI optimization algorithms can improve the performance of HAR systems, and the proposed MPAV algorithm can efficiently solve the feature selection problem.
The authors compare HAR models based on complexity and resource usage in the paper by Angerbauer et al. [
121]. The study compares traditional ML models, such as Random Forest Classifier (RFC) and SVM, with more complex DL models, namely CNNs and RNNs. The authors assess the complexity of the models by considering memory consumption, mean prediction time, and the number of trainable parameters. All models are tested on the same publicly available UCI-HAR Smartphone dataset to ensure a fair comparison. The results show that while the DL models perform similarly to the traditional ML models in recognition accuracy, their increased complexity renders them less favorable for practical applications. The RF model is considered the best option for memory-limited use cases, with an F1-Score of 88.34%, memory consumption of only 0.1 MB, and a mean prediction time of 0.22 ms. The overall best model in complexity and performance is the SVM with a linear kernel, achieving an F1-Score of 95.62%, memory consumption of 2 MB, and a mean prediction time of 0.47 ms.
In HAR, smartphones have become a vital tool due to their embedded accelerometers and gyroscopes. These sensors can monitor daily activities, such as elderly care, healthcare, sports, and smart homes. However, the high-dimensional feature vectors generated from smartphone sensor data pose challenges in processing and classification, leading to the "curse of dimensionality" phenomenon. Ahmed et al. [
122] address this issue by proposing a hybrid feature selection model that combines filter and wrapper methods to achieve efficient HAR in resource-constrained environments. The authors employ an Sequential Floating Forward Search (SFFS) technique to extract relevant features fed into a multiclass SVM to create nonlinear classifiers. The proposed system demonstrates satisfactory activity identification even on limited hardware resources by adopting the kernel trick for training and testing purposes. The significance of this research lies in its ability to provide enhanced HAR performance while mitigating the challenges posed by high-dimensional feature vectors. The hybrid feature selection model proposed by the authors enables the development of efficient and accurate HAR systems suitable for applications in various aspects of daily life, with a particular focus on resource-constrained processing.
The works discussed in this section are summarized in
Table 7 and
Table 8.
5.5. Sensing Technologies
Sensors play a central role in developing smart living applications, enabling the recognition of human actions to improve the overall quality of life. These applications, as discussed in the previous sections, aim to provide increased comfort, safety, and energy efficiency by understanding and adapting to the needs and preferences of their users. Sensing technologies are crucial for identifying and interpreting human actions, and their advances directly impact the performance and effectiveness of HAR systems in smart living environments. According to the revised literature, sensors can be categorized based on the sensing principle or their operational position. When classifying sensors according to the sensing principle, we can identify several subcategories:
Mechanical sensors include:
Inertial sensors (accelerometers and gyroscopes) that measure acceleration and angular velocity to detect motion and orientation.
Pressure sensors that measure force per unit area, enabling the detection of physical interactions, such as touch or contact between objects.
Acoustic sensors that capture sound waves to identify events like footsteps, speech, or glass breaking.
Vibration sensors that detect oscillations and vibrations in structures or objects can indicate various activities or events.
Ultrasound sensors that use high-frequency sound waves to measure distance or detect movement are often employed in obstacle detection and proximity sensing.
Contact switch sensors that detect a physical connection’s open or closed state, such as doors or windows.
Electromagnetic sensors include:
Magnetic sensors that detect changes in magnetic fields are often used for tracking the movement or orientation of objects.
-
Visual spectrum sensors, such as cameras, capture images and videos to recognize activities, gestures, and facial expressions.
- -
Infrared or near-infrared sensors, including cameras, Passive Infrared (PIR) sensors, and IR arrays, can detect heat signatures, enabling motion detection and human presence recognition.
- -
RF systems like WiFi and radar utilize wireless signals to sense movement, location, and even breathing patterns.
An alternative approach to categorizing sensors, based on their underlying sensing principles, involves classifying them according to the types of waves they utilize:
Visible spectrum sensors (e.g., cameras) that capture images in the range of wavelengths perceivable by the human eye.
Infrared sensors that detect thermal radiation emitted by objects help identify human presence and motion.
Radio-frequency sensors that employ wireless signals to track movement, proximity, and location.
Mechanical wave/vibration sensors, including audio, sonar, and inertial sensors, that capture sound waves, underwater echoes, or physical oscillations, respectively.
Besides the previous ways to categorize sensors, an efficient approach is to classify them by operational position. By examining sensors through this lens, we consider where sensors are placed, worn on the body, or attached to objects, which is a more practical and application-oriented categorization method. When categorizing sensors by operational position, we can distinguish the following groups:
Environmental sensors, which monitor physical parameters like atmospheric pressure, temperature, humidity [
66], and open/close states of doors or windows, pressure force sensors installed on the floor or chairs to detect people’s presence [
67].
Ambient sensors, including cameras [
68], microphones [
69], radio-frequency (radar, WiFi) [
69], and motion detectors [
70], that capture information about the surrounding environment to identify activities or events [
71].
Object-attached sensors, such as inertial sensors mounted on everyday objects [
72], that track the movement or usage of these objects [
42].
Body-worn sensors, predominantly inertial sensors, that are attached to the human body to monitor activities [
73], gestures [
74], and postures [
75], but also physiological sensors measuring neurovegetative parameters such as heart rate, respiration rate, and blood pressure [
76]. Wearable sensors can also be employed for comprehensive health monitoring, enabling continuous tracking of vital signs [
77].
The type of sensor used in HAR applications significantly impacts the system’s performance and capabilities. For instance, while some sensors provide high accuracy and rich contextual information, they may also require more computational resources or power consumption, making them less suitable for specific applications. On the other hand, some sensors are more energy-efficient and lightweight (e.g., binary sensors), which may be desirable in specific scenarios but may also come at the cost of reduced accuracy or limited contextual information.
Wearable sensors, particularly inertial sensors, are among the most commonly used in HAR applications within the smart living context. Generally, actions detected using wearable sensors tend to be coarse, such as walking, running, sitting, or standing [
78]. While these sensors can accurately recognize basic actions, more complex or nuanced actions may be challenging to detect.
Most studies in this field focus on feature extraction and classification techniques to improve HAR accuracy [
79]. However, more emphasis on system architecture issues often needed, such as low power consumption, lightweight algorithms, and embedded processing [
80]. While real-time processing is frequently addressed, other critical aspects of HAR system design may need more attention [
81].
Body position is a crucial parameter for wearable sensors, as it influences the quality and reliability of the collected data. For example, the accuracy of a sensor can be affected by its position on the body, the orientation of the sensor, and any potential interference caused by clothing or other factors [syed2021hierarchical, syed2020using]. Therefore, wearable sensors are often investigated with environmental sensors, which can provide complementary information to enhance HAR performance [
81].
The acceptability of sensing technologies for HAR in smart living applications largely depends on their perceived intrusiveness. While camera-based solutions can raise privacy concerns, wearable devices may be intrusive regarding user comfort and convenience. RF-sensing (also known as device-less sensing) has emerged as a promising modality in HAR [
83], primarily due to its potential to preserve occupants’ privacy while providing valuable information about their activities. WiFi [
84] and radar sensors [
85] are increasingly being adopted in HAR systems, as they offer the advantage of non-intrusive monitoring without the need for cameras or wearable devices. While RF-sensing techniques have successfully detected coarse actions or main body poses, such as standing, walking, sitting, and lying down, their recognition of fine actions remains limited [
86]. Fine actions often involve intricate movements of the hands, head, and torso and are more challenging to detect using RF-based sensors. Addressing this limitation necessitates significant research and development to enhance the capabilities of RF-sensing technologies. Advancements in signal processing, ML algorithms, and sensor fusion can improve performance detecting fine actions [
87]. Furthermore, leveraging multimodal sensing approaches, such as combining RF data with other non-intrusive sensing techniques, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of human activities.
Besides RF-sensing, researchers have explored various approaches to positioning sensors around smart environments to enhance human activity recognition and individual identification. One notable example is the Triboelectric Nanogenerator (TENG)-based gait sensor system [
88]. The TENG-based gait sensor system utilizes triboelectric nanogenerators to detect mechanical motions through electrical signals, such as human steps. By embedding these sensors into a smart carpet on the floor, this method offers a non-intrusive and reliable means of monitoring human activities and recognizing individual walking patterns, overcoming traditional sensing technologies’ limitations and privacy concerns.
6. Critical Discussion
The analytical framework suggested in this study provides a comprehensive perspective on the main domains of HAR in smart living. However, it is crucial to analyze these domains critically to ensure that the development of smart living environments addresses potential concerns and challenges.
6.1. Multimodality
The increased complexity resulting from the integration of multiple sensing modalities can lead to resource-intensive management. This is evident in the development of deep learning models, such as CNNs, LSTM networks, and transformer networks, that need to effectively model spatial-temporal dependencies of sensor signals and address the distinct contributions of different sensing modalities in complex environments. Researchers have proposed various solutions, such as self-attention-based models and two-stream structures, to tackle these challenges. However, the resource-intensive nature of these solutions may limit their applicability in certain scenarios.
Furthermore, incorporating multiple sensors in multimodal sensing could raise privacy concerns as more user activity data is collected. For example, the comprehensive multimodal dataset presented by Bocus et al. [
24] includes synchronized RF devices, WiFi signals, UWB signals, and vision/infrared data from Kinect sensors. While such datasets accelerate the development of self-supervised learning techniques, they also highlight the need to balance data collection with users’ privacy rights.
The heterogeneity of data collected from various sensors presents additional challenges in multimodal HAR. This heterogeneity may result in missing sensor data or noisy and unreliable measurements. To overcome these challenges, researchers have proposed data augmentation methods, sensor-independent fusion techniques, and transfer learning-based algorithms. However, the practical implementation of these approaches may require further refinements to ensure robustness and adaptability across different real-world scenarios.
Finally, Bootstrapping HAR systems in smart homes can be particularly challenging due to the highly individualized nature of these environments and the unique behaviors of inhabitants. To minimize user burden and reduce the need for large amounts of labeled data, researchers have proposed active learning-like procedures [
95]. These methods may help discover knowledge about movement patterns and sub-sequences to fine-tune HAR systems for specific tasks. However, the effectiveness of these approaches in diverse and complex smart home settings remains an open question.
Remarkably, multimodality offers promising advancements in smart living applications by integrating various sensing modalities for accurate and reliable HAR. Nonetheless, it also presents critical challenges, including increased complexity, privacy concerns, data heterogeneity, and bootstrapping difficulties in smart homes. Addressing these challenges will require ongoing research and development of innovative solutions that balance the benefits of multimodal sensing with the need for resource efficiency, privacy, robustness, and adaptability.
6.2. Real-time Processing
The critical discussion of real-time processing in smart living applications showcases the need for a balance between processing efficiency, accuracy, and the choice of sensing modalities. Drawing from this analysis, we can derive several general indications that are applicable beyond the specific reviewed works. The choice of sensing modality significantly influences the system’s ability to achieve real-time processing. It is essential to select the appropriate sensing technology based on the requirements of the specific application. While certain modalities like depth cameras or wearable sensing can reduce computational complexity and facilitate real-time processing, their effectiveness may vary depending on the environment, type of activities, and data quality requirements. Thus, a thorough assessment of the application’s goals and constraints should guide the selection of sensing modalities to ensure the desired balance between processing speed and data quality.
Leveraging lightweight computational models and optimization techniques is crucial for enabling real-time processing in smart living applications. By employing models with fewer parameters, lower memory occupancy, and faster processing speeds, developers can ensure efficient analysis and response to sensor inputs. Optimization techniques, such as model quantization and pruning, can further enhance processing efficiency while maintaining acceptable levels of accuracy. However, the choice of lightweight models should consider the potential trade-offs in terms of performance and the ability to learn complex representations. In cases where high accuracy and complex modeling are essential, researches may need to explore more advanced optimization techniques.
Incorporating data preprocessing and feature extraction and selection techniques can significantly improve the efficiency and accuracy of real-time processing [
10,
105]. Techniques like sliding window-based feature representation, skeleton extraction, and image reconstruction can help reduce the influence of irrelevant information, enhance data quality, and simplify the input to the models. These methods can lead to improved recognition accuracy and faster processing times. Nevertheless, developers should carefully consider the limitations of these techniques, such as sensitivity to data quality or extraction errors, and evaluate their suitability for the target application.
Real-time processing systems should prioritize user privacy and security, especially in applications involving monitoring and decision-making. The use of non-intrusive sensors and privacy-preserving techniques can help maintain user autonomy and trust in the system. It is vital to ensure that the pursuit of real-time processing does not compromise the privacy and security requirements of the application.
Adaptability and scalability are essential considerations for real-time processing systems. As smart living applications evolve and new technologies emerge, the ability to adapt and scale the system becomes increasingly important. Developers should design systems with the flexibility to incorporate new sensing modalities, computational models, and optimization techniques. This adaptability ensures that the system remains effective and efficient in handling real-time processing tasks as the application requirements and technological landscape evolve.
6.3. Interoperability
It is evident that standardization is crucial for achieving interoperability. With a multitude of devices and systems from different vendors in the market, the lack of common standards can hinder seamless integration and communication. Standardization not only facilitates data exchange but also ensures the compatibility of systems, making it easier for organizations to adopt and implement new technologies. Therefore, it is necessary for stakeholders, including manufacturers, developers, and researchers, to collaborate and develop open standards that promote interoperability.
The use of ontologies and semantic technologies can greatly enhance interoperability across various domains. Ontologies provide a formal representation of knowledge and facilitate the sharing and understanding of data among devices and systems. By adopting ontology-based approaches, organizations can promote the seamless fusion of data from multiple sources, thereby enhancing the overall performance of their systems. Semantic technologies also enable the preservation of the real meaning of shared data across systems, applications, and devices, which is particularly important in fields such as healthcare and AAL where accurate and meaningful data sharing is essential.
Achieving interoperability may require continuous updates and adaptation. As technology evolves and new devices are introduced, systems need to be updated and adapted to maintain accuracy and effectiveness. This may involve retraining classifiers with new data or updating algorithms to accommodate changes in the environment. Organizations should be prepared to invest in the necessary resources and efforts to ensure that their systems remain interoperable and up-to-date.
The integration of various data sources and sensing modalities can lead to more accurate and efficient systems. Interoperability allows for the seamless exchange of information between wearable and ambient sensors, resulting in a comprehensive understanding of human activities and events. This can be particularly beneficial in fields such as healthcare, where the monitoring and recognition of activities are crucial for providing effective patient care. By leveraging diverse sensing technologies and promoting interoperability, organizations can develop more accurate and robust systems that cater to the diverse needs of their users.
Lastly, interoperability fosters innovation and collaboration. When systems and devices can communicate and exchange data seamlessly, it opens new possibilities for the development of innovative solutions that address complex challenges in various domains. By prioritizing interoperability, stakeholders can work together to create more versatile, user-friendly, and adaptive solutions that can be easily integrated into different environments and cater to the diverse needs of users.
6.4. Resource-Constrained Processing
One crucial consideration when dealing with resource-constrained processing is the need for computational efficiency. This is applicable to various areas, such as healthcare, environmental monitoring, and industrial automation, where devices must perform complex tasks with limited resources [
115,
120]. The use of lightweight algorithms and architectures that minimize computational overhead can be instrumental in addressing these challenges. However, it is essential to maintain a balance between computational efficiency and the desired level of accuracy and reliability. Ongoing research and innovation in algorithm design and optimization can help achieve this balance, ensuring that the resulting solutions are both efficient and effective.
Data management is another critical aspect of resource-constrained processing. In many application domains, vast amounts of data are generated, collected, and processed, leading to storage and transmission challenges. Efficient algorithms and data structures for handling large volumes of data can be invaluable in mitigating these issues. Techniques such as data pruning, feature selection, and data compression can be employed to reduce dataset size while preserving essential information. However, the trade-off between data reduction and information integrity must be carefully managed. Additionally, optimizing communication protocols to handle limited bandwidth and ensure reliable data transmission is vital.
Energy efficiency is a fundamental concern in resource-constrained environments, particularly in portable and battery-powered devices. Designing efficient algorithms and power management techniques that ensure long battery life without compromising performance is essential. Dynamic power management strategies and energy-aware algorithms can help strike a balance between energy consumption and device performance. However, continuous research and innovation are necessary to adapt these strategies to varying workloads and energy demands. Moreover, incorporating energy-harvesting technologies and exploring alternative energy sources could also contribute to more sustainable and energy-efficient solutions.
Addressing resource-constrained processing requires a holistic approach that encompasses computational efficiency, data management, and energy efficiency. By continuously researching and innovating in algorithm design, data handling techniques, communication protocols, and energy management strategies, researchers and developers can contribute to more efficient, accessible, and sustainable solutions that cater to various users and environments. To achieve this goal, interdisciplinary collaboration, including computer science, engineering, and domain-specific expertise, is necessary to ensure that the resulting solutions meet the diverse needs and constraints of real-world applications. Additionally, fostering a research culture that prioritizes resource-constrained processing and shares best practices across different domains can help accelerate progress and pave the way for more effective and sustainable technology solutions.
Remark: Despite its great importance in the context of smart living applications, the majority of studies in recent literature need to address the topic of resource-constrained processing adequately. While lightweight algorithms can help tackle the issue of limited processing power, they may only sometimes provide the desired level of accuracy and reliability. Developing effective HAR systems for resource-constrained environments requires continuous research and innovation to ensure computational efficiency and performance. Researchers and developers must prioritize this aspect, exploring new techniques and methodologies to optimize HAR systems for various constraints, such as power consumption, memory usage, and computational resources. By placing greater emphasis on resource-constrained processing, the research community can help pave the way for more sustainable, accessible, and efficient smart living solutions that cater to a wide range of users and environments.
6.5. Sensing Technologies
The critical discussion on sensing technologies reveals the importance of considering not only the individual capabilities of these technologies but also their potential synergies and interactions within a broader HAR system. Developing more effective and user-friendly smart living solutions requires taking a holistic approach that accounts for the diverse range of available sensing technologies and their associated strengths and limitations.
A crucial aspect that emerges from the discussion is the need to balance the trade-offs between various factors such as accuracy, computational resources, power consumption, and user acceptability. Each sensing technology comes with its unique set of advantages and challenges, necessitating a careful evaluation of their suitability for specific applications and contexts. For instance, while high-accuracy sensors might provide rich contextual information, they may also demand more computational power or energy, making them less suitable for certain applications.
One of the key considerations when selecting sensing technologies for HAR systems is their perceived intrusiveness. To ensure user acceptance and adoption, it is essential to address privacy concerns and minimize the invasiveness of the technologies. For example, solutions such as RF-sensing offer the advantage of non-intrusive monitoring without the need for cameras or wearable devices, making them more appealing to users. However, further research and development are required to enhance the capabilities of these technologies in detecting more complex actions and providing a comprehensive understanding of human activities. In addition, it is important to note that the use of RF-sensing also raises concerns regarding Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) in the presence of medical devices such as pacemakers and implanted defibrillators.
Another important aspect is the development of sensor fusion techniques that can effectively combine data from multiple sensing modalities to provide a more accurate and robust HAR system. By leveraging the complementary strengths of different sensing technologies, researchers can address the limitations of individual sensors and enhance the overall performance of the system. Sensor fusion can also lead to more adaptive and context-aware solutions that can cater to the diverse needs of users and their environments.
In addition to focusing on the technical aspects of sensing technologies, it is also essential to consider the broader societal implications of their widespread adoption in smart living environments. The establishment of ethical guidelines and regulations is crucial to ensuring the responsible use of these technologies and protecting users’ rights. As sensing technologies continue to advance and become more pervasive, it is essential to engage in open dialogues and interdisciplinary collaborations that address the ethical, legal, and social implications of their deployment.
Lastly, the critical discussion highlights the importance of fostering an open and collaborative research environment that encourages the sharing of knowledge, resources, and best practices among researchers, developers, and stakeholders. As sensing technologies continue to evolve and advance, interdisciplinary collaborations between experts in fields such as computer science, engineering, ethics, and social sciences can contribute to the development of more responsible, efficient, and user-friendly smart living solutions.
Remark: The critical discussion on sensing technologies underscores the need for a holistic approach that goes beyond the specific capabilities of individual sensors. By considering the synergistic interactions between different sensing modalities, addressing broader systemic aspects of HAR systems, and engaging in interdisciplinary collaborations, researchers can contribute to the development of more robust, efficient, and user-friendly smart living solutions that cater to the diverse needs of users and their environments. This holistic perspective can pave the way for more effective and responsible deployment of sensing technologies in smart living applications, ultimately improving the overall quality of life for users.
6.6. A Short Note on Sensing Modalities
The type of sensor used for HAR significantly impacts the range of detectable human actions. It is important to note that no single sensing modality can address all HAR’s challenges. Each type of sensor has its strengths and limitations, and selecting the appropriate sensors depends on the specific application and the system’s objectives. For instance, while cameras offer a high level of detail and can recognize intricate gestures and facial expressions, they may not be the best choice for applications that require privacy protection.
Similarly, while wearable sensors can detect basic activities like walking or running, they may not be suitable for applications that require the recognition of fine-grained gestures or facial expressions. Therefore, a combination of sensors with different modalities may be required to address the various challenges of HAR. When designing the system, researchers should consider the trade-offs between accuracy, privacy, intrusiveness, and cost. Given these challenges, researchers should consider adopting a multimodal approach, combining data from different sensor types to leverage their strengths and mitigate their shortcomings.
6.7. A Short Note on Wearable Solutions
Positioning sensors on the body plays a critical role in the effectiveness of wearable solutions for HAR. While some studies focus on using a single device placed on the waist or shoulders for low intrusiveness, this approach limits the range of detectable actions to coarse movements, like walking or sitting. This limitation makes it difficult to recognize more complex activities or subtle gestures that may be relevant to the overall system design.
To overcome this challenge, researchers could explore using multiple sensors strategically placed on various body parts, such as wrists, ankles, or the head [
82,
90,
97]. This approach can significantly improve the range of detectable actions and enable the recognition of fine-grained gestures like hand movements or facial expressions. However, this approach may introduce additional complexity to the system design, such as synchronizing data streams from multiple sensors. Moreover, using multiple sensors can lead to a more intrusive solution, which may not be desirable for some users.
Alternatively, researchers could investigate using advanced algorithms that can extract more information from a single sensor, enabling the detection of complex actions even with limited sensor data. This approach can minimize the number of sensors needed, reducing the system’s complexity, cost, and intrusiveness. However, developing such advanced algorithms may require significant computational resources and focus on ML and signal processing techniques. Furthermore, the choice between using multiple sensors or advanced algorithms for HAR depends on factors such as the system’s specific application, cost, power consumption, and processing capabilities. Researchers must carefully evaluate the trade-offs between these factors to develop effective and practical solutions for wearable HAR.
7. Conclusions
This comprehensive review study has shed light on the complex interplay of various critical domains in the field of human activity recognition for smart living applications. The analysis emphasizes the importance of a holistic approach, recognizing that addressing challenges and harnessing opportunities in these domains is vital for the development of effective, sustainable, and user-friendly smart living solutions. A key takeaway from the analysis is the need to balance trade-offs among factors such as accuracy, computational resources, power consumption, user acceptability, and privacy. This requires ongoing research and the development of innovative solutions that not only integrate various sensing modalities and achieve real-time processing but also ensure interoperability and adaptability in resource-constrained environments.
The study also highlights the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration and the sharing of best practices across different domains. By fostering a research culture that prioritizes these critical domains and embraces collaboration, the research community can accelerate progress and pave the way for more versatile, user-friendly, and adaptive solutions that cater to a wide range of users and environments.
Furthermore, the review underscores the need for continuous research and innovation in algorithm design, data handling techniques, communication protocols, and energy management strategies. These efforts will contribute to the development of more efficient, accessible, and sustainable HAR solutions, ensuring their applicability in various real-world scenarios.