1. Introduction
Machine learning algorithms have been used in the last ten years in almost all fields where the problems associated with the data classification, pattern recognition, non-linear regression, etc., have to be solved. Application of such algorithms has also intensified in the field of queueing theory. While the first steps in the successful application of machine learning to evaluate the performance characteristics of simple and complex queueing systems have already been taken, the total number of works on this topic still remains modest. As for reviews, we can only refer to recent paper by Vishnevskiy and Gorbunova [
32] which proposes a systematic introduction to the use of machine learning in the study of queueing systems and networks. Thus, we would also like to make a small contribution to the popularisation of the topic by briefly describing existing works. In Stintzing and Norrman [
29], the artificial neural network was used for predicting the number of busy servers in the
queueing system. The papers of Nii et al. [
23] and Sherzer et al. [
26] have answered positively the question, whether the machines could be useful for solving the problems in general queueing systems. They have used neural network to estimate the mean performance measures of the multi-server queues
based on the first two moments of the inter-arrival and service time distributions. A machine learning approach was used in Kyritsis and Deriaz [
20] to predict the waiting time in queueing scenarios. The combination of a simulation and a machine learning techniques for assessing the performance characteristics have been illustrated in Vishnevsky et al. [
31] on a queueing system
with
K priority classes. Markovian queues were simulated using artificial neural networks in Sivakami et al. [
27]. The neural networks were used also in Efrosinin and Stepanova [
9] to estimate the optimal threshold policy in a heterogeneous
queueing system. The combination of the Markov decision problem and the neural network for the heterogeneous queueing model with a process sharing was studied by Efrosinin et al. [
10]. The performance parameters of the closed queueing network by means of a neural network were evaluated in Gorbunova and Vishnevskiy [
13]. The main conclusion to be drawn from the results already obtained by application of the machine learning to models of the queueing theory is that the neural networks cannot be treated as a replacement for classical methods for system performance analysis, but rather complement the capabilities of such analysis.
This paper proposes a fairly universal method for solving the problem of optimal dynamic scheduling or allocation in queueing systems of the general type, i.e. where the times between events are arbitrarily distributed, and in queueing systems with correlated inter-arrival and service times. It can provide also the performance analysis of complex controlled systems described by multidimensional random processes, for which finding analytical, approximate or heuristic solutions is a difficult task. The method is exemplified by some version of a well-known queueing model consisting of several parallel queues and one server which serve the queues according to some control policy. The system is assumed to have heterogeneous arrival and service attributes, i.e. unequal arrival and service rates, as well as holding and switching costs. Such systems are known also as polling systems which have found wide application in various fields such as computer networks, telecommunications systems, control in manufacturing and road traffic. For analytic and numerical results in various types of polling systems with applications to the broadband wireless Wi-Fi and Wi-MAX networks, we refer interested readers to the textbook by Vishnevsky and Semenova [
33] and the references therein. The same authors in [
34] developed their research on polling systems to systems with correlated arrival flows such as
,
, and the group Poisson arrivals. In Vishnevskiy et al. [
35] it was shown that the results obtained by a neural network are close enough to the results of analytical or simulation calculations for the
and
-type polling systems with cyclic polling.
A Markovian analog of such a model has been investigated by a number of authors. The two queue homogeneous model with equal service rates and holding costs has been studied in Horfi and Ross [
15], where it was shown that the queues must be serviced exhaustively according to the optimal policy. In Liu et al. [
21] it was shown that the scheduling policy that routes the server with respect to the LQF (Longest Queue First) policy is optimal when all queue lengths are known and that the cyclic scheduling policy is optimal in the case that the only information available is the previous decisions. The systems with multiple heterogeneous queues, also known as asymmetric polling systems, in different settings have been studied intensively for the case of no switching costs in Buyukkoc et al. [
4], Cox and Smith [
5], where the optimality of the static
-rule was proved. This policy schedules a server first to the queue
i with a maximum weight
consisting of the holding cost and service rate. In Koole [
19], the problem of optimal control in a two-queue system was analysed by means of the continuous-time Markov decision process and dynamic programming approach. The author has found numerically that the optimal policy which minimizes the average cost per unit of time could be quite complex if there are both holding and switching costs. The threshold-based policy for such a queueing system was applied by Avram and Gómez-Corral [
3], where the expressions for the long-run expected average cost of holding units and switching actions of the server were given. The queueing system with general service times and set-up costs which effect on instantaneous switch from one queue to another was studied in Duenyas and Van Oyen [
6]. The authors proposed a simple heuristic scheduling policy for the system with multiple queues. A rather similar model is described in Matsumoto [
22], where the optimal scheduling problem is solved in a system with arbitrary time distributions. Here, instead of switching costs, the corresponding set-up time intervals required for switching are used. The system is controlled by the Learning Vector Quantization (LVQ) network, see for details Kohonen [
18], which classifies the system state by the closest codebook vector of a certain class in terms of the Euclidean metric. The problem with this approach is the large number of parameters associated with the codebook vectors, normally it is required several vectors per class, which must be estimated for a given control policy using computationally quite expensive recurrent algorithm.
It is assumed in our model that the queue currently being served by the server is serviced exhaustively. The next queue to be served by the server is selected according to a dynamic scheduling policy based on the queue state information, i.e. on the number of customers waiting in each of parallel queues. It is expected that the changing of the serviced queue involves the switching costs. The holding of a customer in the system is also linked to the corresponding cost. Obviously, even with some fixed scheduling control policy, calculating any characteristics of the proposed queueing system with arbitrary inter-arrival and service time distributions in explicit form is not a trivial task. It is also difficult to fix the dynamic control policy defining the scheduling in large systems in a standard way, e.g. through a control matrix that would contain for all possible states of the system the corresponding control action. Therefore, in such a case we consider it justified to solve the problem of finding the optimal scheduling policy with the aim to minimize the average cost per unit of time by combining the simulation as a tool to calculate the performance characteristics of the system with a machine learning paradigm, where the neural network will be responsible for the dynamic control. By training a neural network for some initial control policy, we obtain characteristics of the network in form of a matrix of weights and a vector of biases. Then the process of solving the optimal scheduling problem is reduced to a discrete parametric optimization. The parameters of the neural network must be optimized in such a way that this network by generating control actions at decision epochs can guarantee the minimal values of the average cost functional. For this purpose we have chosen one of the random search methods, such as simulated annealing, see e.g. in Aarts and Korst [
1], Ahmed [
2]. It is a heuristic method based on a concept of heating and controlled cooling in metallurgy and it is normally used for global optimization problems in a large search space without any assumption on the form of the objective function. Specially for the probabilistic scheduling problem this algorithm was implemented by Gallo and Capozzi [
12]. The algorithm will be adapted for a non-explicitly defined parametric function with a large number of variables defined on a discrete domain. To verify the quality of the calculated optimal parameters of the neural network, the values of the average cost functional for the markovian version of the queueing system are compared with the results obtained by solving the Markov decision problem (MDP). The general theory on MDP models is discussed in Puterman [
25] and Tijms [
30]. The details on application of MDP to controlled queueing systems with heterogeneous servers can be found in Efrosinin [
8]. The optimal control policy and the corresponding objective function are calculated in the paper by a policy-iteration algorithm proposed in Howard [
16] for an arbitrary finite-state Markov decision process. According to the MDP, the router in our system has to find an optimal control action in the state visited at a decision epoch with the aim to minimize the long-run average cost. Note that for our queueing model under general assumptions the semi-markov decision problem (SMDP) can be formulated. The SMDP is more powerful model than the MDP since by calculating the objective function the time spent by the system in each state before a transition is taken into account. The objective function must be calculated here also by means of a simulation. In this case the reinforcement learning algorithm, e.g.
Q-
P-Learning, can be applied. The main problem of this approach consists in the fact that for deterministic control policy many pairs of state and action can remain non-observable and as a result the control actions in such states can not be optimized. However, in our opinion, neural networks could also be used to solve this problem which is a potential task for further research. The SMDP topic is outside the scope of this article but we refer the readers to book by Gosavi [
14], where one can find very interesting overview on reinforcement learning and a well-designed classification of simulated-based optimization algorithms.
Summarising our research in this paper we can highlight the following main contributions: (a) We proposed a new controlled single-server system with parallel queues where the router uses a trained multi-level neural network to perform a scheduling control; (b) a simulated annealing method was adapted to optimize the weights and the biases of the neural network with the aim to minimize the average cost function which can be calculated only by a simulation; (c) the quality of the resulting optimal scheduling policy was verified solving a Markov decision problem for the markovian analog of the queueing system; (d) we provide detailed numerical analysis of the optimal scheduling policy and discuss its sensitivity to the shape of the inter-arrival and service time distributions; (e) the distinctive feature of our paper is the presence of algorithms used in the paper in form of pseudocodes with detailed descriptions of relevant steps.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 presents the formal description of the queueing system and optimization problem.
Section 3 describes the Markov decision problem and the policy-iteration algorithm used to calculate optimal scheduling policy. In
Section 4, the event based simulation procedure of the proposed queueing system is discussed. The neural network architecture, parametrization and training algorithm are summarized in
Section 5.
Section 6 presents simulated annealing optimization algorithm. Numerical analysis is shown in
Section 7 and we conclude the paper in
Section 8.
The following notations are introduced for use in sequel. Let denote the vector of appropriate dimension with 1 in the jth position beginning from 0th and 0 elsewhere, denote the indicator function which takes the value 1 if the event A occurs and 0 otherwise. The notations and mean the minimum and maximum of the values that a can assume, and , denote the element index associated respectively with the minimum and maximum value.
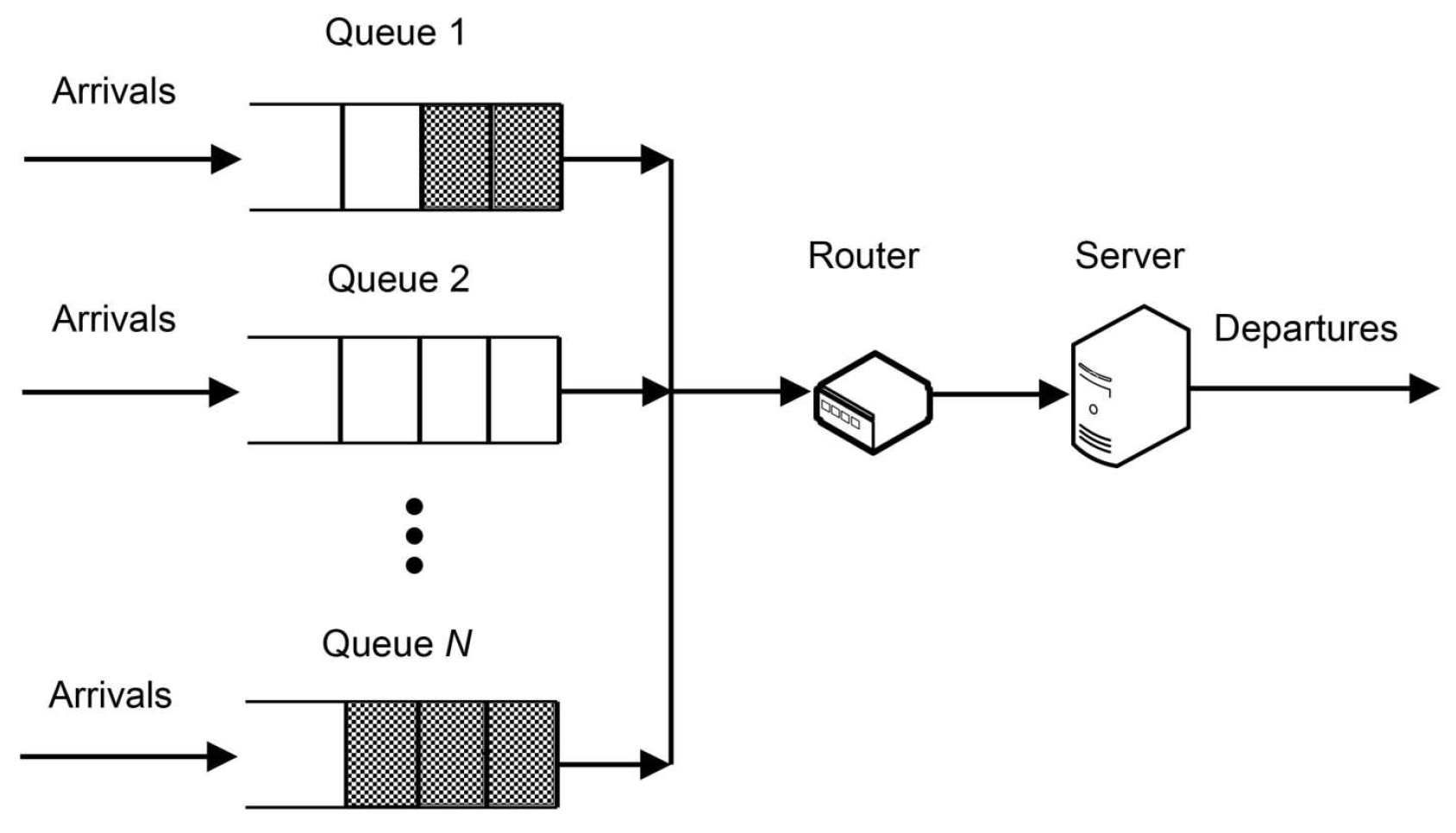
2. Single-server system with parallel queues
Consider a single-server system with
N parallel heterogeneous queues of the type
and router for scheduling of one server between the queues. Heterogeneity here refers to unequal attributes associated with the arrival and service of customers, as well as unequal holding and switching costs. If a queue starts to be serviced, it is serviced exhaustively. Denote by
the queue index set. The proposed queueing system is shown schematically in
Figure 1.
Denote by
,
, the time instants of arrivals to queue
i and by
,
, the sequence of mutually independent and identically distributed inter-arrival times with a CDF
,
. Further denote by
,
, the service time of the
nth customer in the
ith queue. These random variables are also assumed to be mutually independent and generally distributed with CDF
,
. We assume that introduced random variables have at least two first finite moments
The squared coefficients of variation are defined then respectively by
The last characteristic will be required to provide a comparison analysis of the optimal scheduling policy for different types of inter-arrival and service time distributions. From now it is assumed that the ergodicity condition is fulfilled, i.e. the traffic load
.
Let
indicates the sequence number of the queue currently being serviced by the server at time
t and
denote the number of customers in the
ith queue at time
t, where
. The states of the system at time
t are then given by a multidimensional random process
with a state space
Further in this section, the notations
and
will be used to identify the corresponding components of the vector state
. The cost structure consists of the holding cost
per unit of time the customer spends in queue
i and the switching cost
to switch the server from queue
i to queue
j.
It is assumed that the system states
are constantly monitored by the router which defines which queue must be serviced next after a current queue becomes empty. In initial state, when the total system is empty, a server is randomly scheduled to some queue. If the
ith queue to be served becomes empty, such a moment we call a decision epoch, the router decides by means of the neural network, whether it must leave the server at the current queue or dispatch it to another queue according to a specified scheduling control policy. The routing to an idle queue is also possible. We remind that the server allocated by the router to a certain queue serves it exhaustively, i.e. it is only possible to change the queue if it becomes empty. Denote by
an action space with elements
, where
a indicates the sequence number of the queue to be served next after the current queue has been emptied. The subsets
of control actions in state
with
coincide with the action space
A. In all other states
x from
the subsets
includes only a fictitious control action 0 which has no influence on the system’s behavior.
The router can operate according to some heuristic control policies. It could be for example a Longest Queue First (LQF) policy which is a dynamic one and it prescribes at decision epochs to serve the next queue with the highest number of customers. If there are more than one queue with the same maximal number of customers, the queue number is selected randomly. Alternatively, the static
-rule, which needs only the information if a certain queue in non-empty, can be used as an initial policy. According to this policy the queue
i with the highest factor
, which is the product of the holding cost and the service intensity, must be serviced next. In the system with totally symmetric queues the former policy is according to [
21] optimal. The latter control policy is optimal due to [
4] if there is no switching costs, i.e.
. Otherwise, in case of positive switching costs and asymmetric queues such policies are not optimal with respect to minimization of the average cost per unit of time.
The main idea of an optimal scheduling in a such general model is as follows. We will equip the router with a trained neural network which will inform it on the sequence number of the next queue to which the server should be routed with the aim to reach formulated optimization aims. Obviously, we can only train the neural network based on the available data, i.e. on some heuristic control policy, and then we will need to optimize the network parameters to solve the problem of finding the optimal scheduling policy. In the average cost criterion the limit of the expected average cost over finite time intervals is minimized in a set of admissible policies. The control policy
is a stationary policy which prescribes the usage of a control action
whenever at a decision epoch the system state is
. The decision epochs arise whenever after serving any queue that queue becomes empty. For studied controllable queueing system operating under a control policy
f the average cost per unit of time for the ergodic system is of the form
Here
is the random number of switches from queue
i to queue
j in time interval
. Expectation
must be calculated with respect to the control policy
f. The policy
is said to be optimal when for any admissible policy
f,
For our purposes in case of a general model, we combine simulation modelling and neural networks. To verify the results of solving the optimization problem (
4), we formulate an appropriate Markov decision problem, for which we compute using a policy iteration algorithm, see e.g. in Howard [
16], Puterman [
25], Tijms [
30], the optimal control policy and the corresponding minimum average cost
.
3. Markov decision problem formulation
Assume that the inter-arrival and service times are exponentially distributed, i.e.
and
,
. Under markovian assumption the process (
1) is a continuous-time Markov chain with a state space
E. The MDP associated with this Markov process is represented as a five-tuple:
where state space
E, action spaces
A and
have been already defined in the previous section.
- –
is a transition intensity to go from state
x to state
y by choosing a control action
a are defined as
where
.
- –
-
is an immediate cost in state
by selecting an action
a,
Here the first summand denotes the total holding cost of customers in all parallel queues in state x which is independent of a control action. Let and if , , we get the number of customers in state x. The second summand includes the fixed cost for switching the server from the current queue j to the next queue numbered by a.
The optimal control policy
and the corresponding average cost
are the solutions of the system of Bellman optimality equations,
where
B is a dynamic programming operator acting on value function
.
Proposition 1.
The dynamic programming operator B is defined as
Proof. From the Markov decision theory, e.g. [
25,
30], it is known that for Markov chain with continuous time the operator
B is defined as
. This equality for the proposed system can be obviously rewritten in form (
8). In this equation, the first term
represents the immediate holding cost of customers in state
x. The second term by
describes the changes in value function due to new arrivals to the system. The third term by
for
stands for the value function by service completion in the queue
j where there are customers waiting for service. The last term by
for
describes also a service completion which leads now to the state with an empty queue when a control action must be performed. Hence only the last term occurs with a min operator. □
Note that the state space of the Markov decision model is countable infinite and the immediate costs
are unbounded. The existence of the optimal stationary policy and convergence of the policy iteration algorithm can be verified for the system under study in a similar way as in Özkan and Kharoufeh [
24], where first, the convergence of the value iteration algorithm for the equivalent discounted model is proved, and then, using the criteria proposed in Sennott [
28], this result is extended to the policy iteration algorithm for the average cost criterion.
To solve equations (
8) in the policy iteration algorithm which calculates the optimal control policy, we convert the multidimensional state space into a one-dimensional space by mapping
. Thus, the state
can be rewritten in the following form:
where
with
. The notation
will be used for the inverse function. In one-dimensional case the state transitions can be expressed as
To calculate the optimal policy the buffer sizes must be truncated, i.e.
. In this case the set of states
E is finite with a cardinality
. To start the algorithm an initial policy is required. The LQF policy is used as initial policy in algorithm 1 which consists of two main steps: Policy evaluation and policy improvement. In first step for the given initial control policy the system of linear equations with constant coefficients must be solved, and the value function
for one of the states can be assumed to be an arbitrary constant, e.g.
with
and
. In this case we obtain from the optimality equation (
7) the equality
. The remaining equations can be solved numerically. As a solution we get the
values for the function
and the current value of the average cost
g. In the next policy improvement step, a control action
a that minimizes the test value in the right-hand side of equation (
7) must be evaluated. The algorithm generates a sequence of control policies that converges to the optimum one. The convergence of the algorithm requires that the control actions in two adjacent iterations coincide in each state. To avoid policy improvement bouncing between equally good control actions in a given state, one can simply keep the previous control action unchanged if the corresponding test function is at least as large as for any other policy in determining the new policy. Also, in order to fix the convergence of the algorithm, one can use the values of average costs, the variation of which should be for example less than a given some small value.
|
Algorithm 1: Policy iteration algorithm |
 |
Example 1. Consider the queueing system with
queues. The buffer sizes are equal to
,
. At these settings the number of states already reaches large values,
, which confirms one of significant restrictions on application of dynamic programming for this type of control problems. The switching costs are defined as
, so that it costs more to switch to queues with a higher service rate. The values of system parameters
,
,
and
are summarized in
Table 1.
These values correspond to the system load that is the system is stable. This value is enough small to ensure on the one hand that the system is sufficiently loaded so that states appear where all queues are not empty, and on the other hand to minimise the probability of losing an arriving customer for given rather small buffer sizes. The solution of the large system of optimality equations is carried out numerically. The optimized average cost .
Using the Algorithm 1 we calculate the optimal scheduling policy. For some of states with fixed number of customers in the third and fourth queues and varied number of customers in the first two queues the control actions are listed in
Table 2. The first row of the table contains the values of the number of customers
and
in the second or first queue when a decision is made respectively when the first or second queue is emptied. The first column contains some selected states of the system for the fixed levels
and
of the third and fourth queues. As we can see, the optimal scheduling policy has a complex structure with a large number of thresholds, making it difficult to obtain any acceptable heuristic solution explicitly. The
-rule as expected is not optimal here,
that is almost two and a half times more than the value of the average cost under the optimal policy. When the values
and
are small, the router directs the server to serve the queues with low service rates, in this case the switching costs are low as well. According to the optimal scheduling the initiative to route a server to the queue with a higher service rate and switching costs increases as the length of the first two queues increases.
Example 2. In this example we increase the arrival rates
as given in
Table 3. The other parameters are fixed at the same values as in the previous example. The load factor now is
, and the corresponding optimized average cost is
and
.
The table of scheduling policy shows that as the system load increases the router switches the server to queue 2 or to queue 1 with a higher service rates at almost all queue lengths and respectively.
4. Event based simulation for the general model
To simulate the proposed queueing system we use an event based simulation. This technique is suitable for random process evaluation where it is sufficient to have the information about the time instants when changes in states occur. Such changes will refer as events. Note that although simulation modelling is extensively used in queueing theory, many papers lacks explicitly described algorithms that readers can use for independent research. For more information on simulation methods with applications to single- and multi-server queueing systems we can recommend Ebert et al. [
7] and Franzl [
11]. In this regard, it will not be certainly superfluous, if we preset and discuss here an algorithm for the system simulation which is not difficult to adapt for other similar systems.
In our case the events are the arrivals to one of N parallel queues and the departures of customers from the queue d currently being served by the server. The present time is selected as a global time reference.
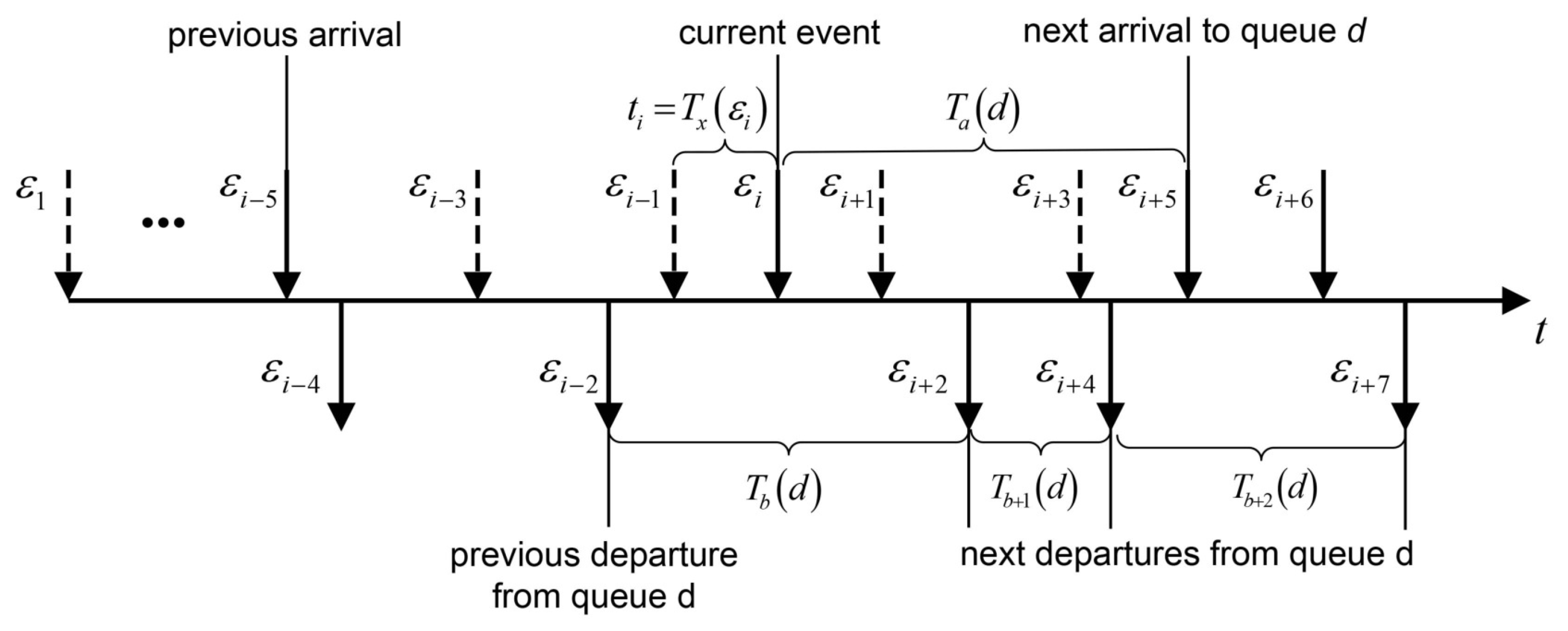
In
Figure 2, on the time axis we mark the moments of arrival of new applications and the moments of their service in a fixed queue with number
d by means of arrows above and below the axis respectively. The dotted arrows indicate the arrival of new applications in other queues. The successive events are denoted by
and the corresponding time moments by
. In the proposed queue simulation algorithm 2 all the times are referred to the present time. Suppose that at the present moment of time there is a new arrival to the queue with the number
d, which is serviced by the server, i.e.
. Denote by
the holding time of the system in state
x up to the occurrence of the event
. According to the time schema the holding time in a previous state is defined as
, where
is a remaining inter-arrival time to the queue
d,
stands for the generated service time after the event
of the previously occurred departure and the dots replace the time intervals associated with arrivals of customers in other queues. The next event is determined then by subtracting the holding time
from the all event time intervals. In this case the current event is a new arrival. Thus the holding time
in state up to the event
of an arrival to some other queue which not equal to
d is of the form
. The subsequent holding times are calculated as follows,
, i.e. the event
is then the next departure from queue
d,
, where
is the next generated service time,
and
is a remaining inter-arrival time for the next arrival to the queue
d. Continuing the process in a similar manner, all holding times of the system in the corresponding states are evaluated. By summing up the times
we obtain the total simulation running time of the system
. The average cost per unit of time is then obtained by division of the accumulated cost by the time
.
The time instants of arrival events to the queue
are stored in vector variable
and the departure events in the queue with a number
q in
. The algorithm 2 contains the pseudo-code of the main elements of the event based simulation procedure.
|
Algorithm 2: Queue simulation algorithm |
 |
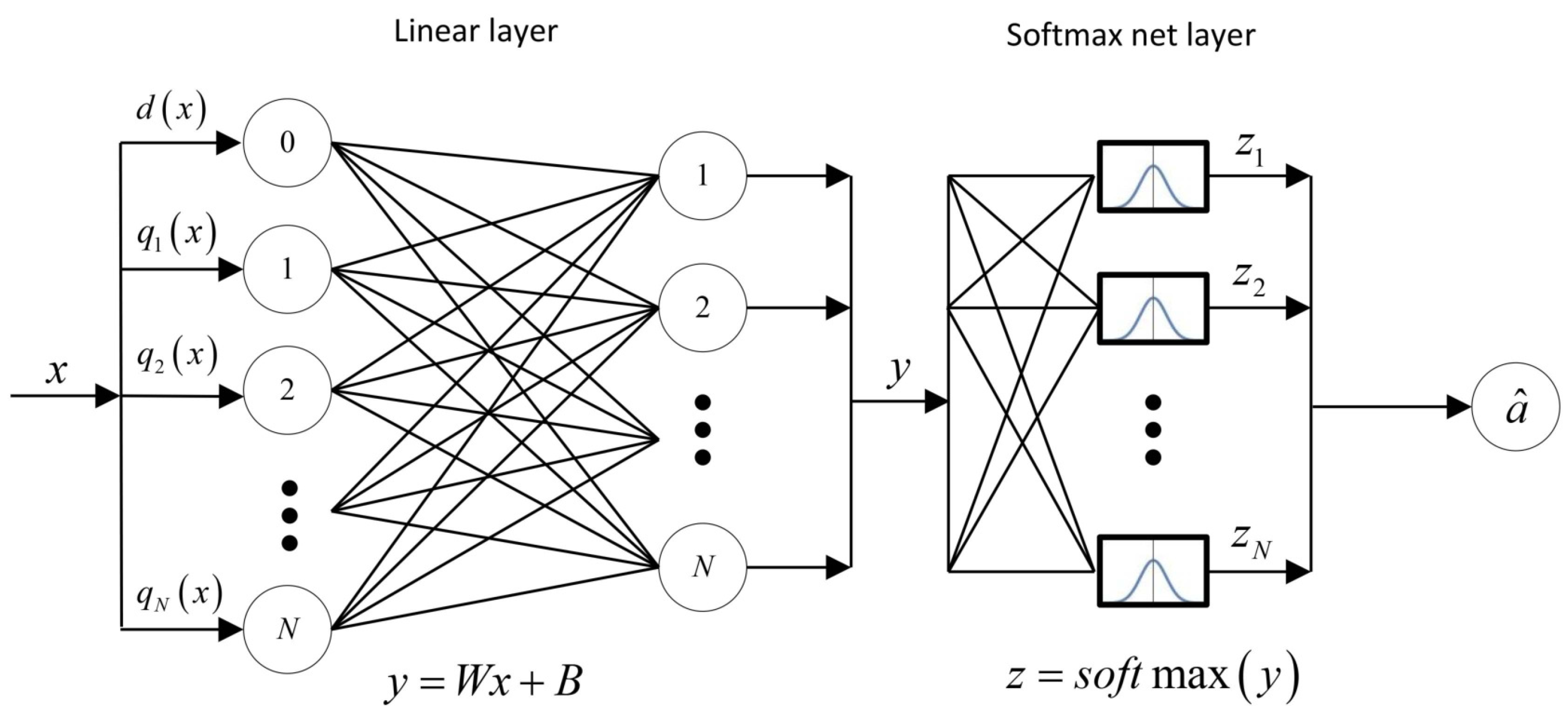
5. Neural network architecture
In our model, we propose to equip the router with a trained neural network. This network will determine a sequence number of the queue that the server will serve next based on the information about the system state at a decision epoch when the server finishes service of a certain queue. We have chosen a simple architecture for the neural network consisting of only two layers in such a way that, on the one hand, it would have a small number of parameters for further optimization and, on the other hand, that the quality of correct classification of some fixed initial control policy would be equal at least 95%. The proposed neural network has one linear layer which represents an affine transformation and softmax normalization layer as illustrated in
Figure 3.
The input includes
neurons according to the system state
, where
. The neuron 0 gets the information on
, the
ith neuron for
gets the information on the state of
ith queue. When the server finishes service at the queue
d, then the neural network classifies this state to one of
N classes which defines a current control action
for the state
x. The hidden linear layer consists of
N neurons
which are connected with an input neurons via the system of linear equations
or in matrix form
with
and
, where
with
are respectively the matrix of weights and the vector of biases of the given neural network which must be estimated by means of the training set. The softmax layer
is a final layer of the multiclass classification. The softmax layer generates as an output the vector of
N estimated probabilities of the input sample
, where the
ith entry is the likelihood that
x belongs to class
i. The vector
y is normalized by the transformation
The class number is then defined as
. Hence, the output
z is a mapping of the form
, where
is the parameter vector of the neural network which includes all entries of the weight matrix
and the bias vector
, i.e.
The values of the parameter vector
of the initial control policy, which in the next section will be used as a starting solution for optimization procedure, are obtained by training the neural network on some known heuristic control policy. In our case this policy is the LQF. In the training phase the following optimization problem must be solved given the training set
,
where a non-negative loss function
with
takes the value 0 only if the class of the
kth element of a sample is
i, i.e.
. The problem (
12) can be solved in a usual way by the stochastic gradient descent method, where a single learning rate
to update all parameters is maintained. The corresponding iterative expression is given below,
where
is a Nabla-operator defining the gradient of the function relative to the parameter vector
. In our calculations we use the adaptive moment estimation algorithm (ADAM) to solve the problem (
12). It updates iteratively the parameters of the neural network based on training data. The ADAM calculates independent adaptive learning rates for the elements of
by evaluating the first-moment and second moment estimation of the gradient. The method is simple to implement, computationally efficient, requires little memory and is invariant to diagonal changes in gradients. The further detailed information regarding ADAM algorithm can be found in Kingma and Ba [
17]. Despite of fact that the ADAM algorithm can be found in various sources, we have also chosen to cite it in this article. The main steps required for the iterative updating the parameter vector
are summarized in the algorithm 3.
|
Algorithm 3: Adaptive moment estimation algorithm |
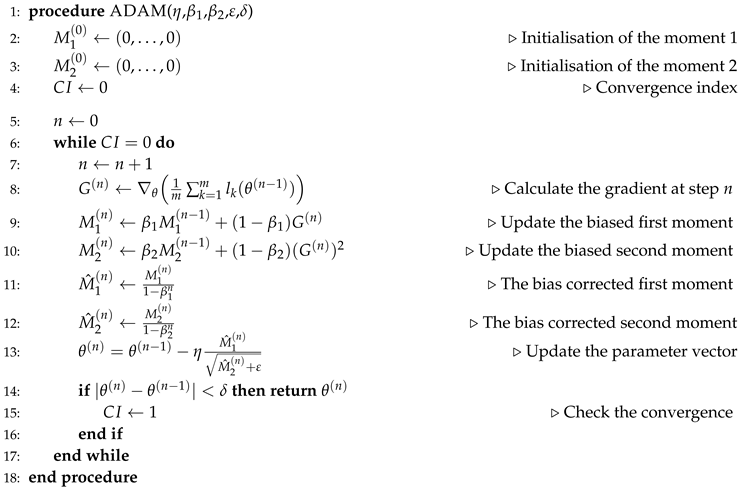 |
The parameters of the algorithm 3 are fixed to , , , and . The classification accuracy of the proposed neural network trained on the LQF policy is over 97%. The test phases of the trained network were conducted on system states with a queue length of up to 100 customers per queue. Thus this starting network can be used to generate control actions of the initial control policy for subsequent parameters’ optimization of this neural network.
6. Optimization of the neural network based allocation policy
Denote by
the known parameter vector of the trained neural network as was defined in (
11). The function
means the average cost for the queueing system where the router chooses an action obtained from the trained neural network with the parameter vector
. We adapt further a simulated annealing method described in algorithm 4 for discrete stochastic optimization of the average cost function
with a multidimensional parameter vector
. This algorithm is quite straightforward. It needs some starting solution and in each iteration the algorithm evaluates for the randomly selected neighbor values of the function parameters the corresponding function value. If the neighbor occurs to be better than the current solution with respect to value of the objective function, algorithms replaces the current solution with a new one. If the neighbor value is worse, the algorithm keeps the current solution with a high probability and chooses a new value with a specified low probability.
|
Algorithm 4: Simulated annealing algorithm |
 |
The simulated annealing requires the finite discrete space for the parameters of the optimized function. It is assumed that all weights and biases of the neural network summarized in the vector take values in the interval with a low bound and an upper bound . Moreover, this interval is quantized in such a way that , , takes only discrete values , , where is a quantization level. Note that the domains for the elements of the parameter vector can be specified separately, and the values of the vector obtained by training the neural network based on the optimal policy of the Markov model will be suitable for determining the possible maximum and minimum bounds. In this case it is possible to achieve faster convergence of algorithm 4 to the optimal value.
Since the average cost function
g can not be calculated analytically, for this purpose a simulation technique is used. As it is shown in algorithm 4, at each iteration at the step where the current solution can be accepted with a given probability we need to calculate the difference between the object functions. Due to the fact that this function can be calculated only numerically, it is necessary to check whether this difference is statistically significant at each iteration of the algorithm. The algorithm is modified in such a way that the
t-test for two samples is used to compare the expected values of two normally distributed samples with unknown but equal variances. Denote by
and
respectively the current and the modified parameter vector and by
two corresponding first empirical moments of the objective function. According to the
t-test the null hypothesis which states that for the modified vector the average cost is statistically smaller then the previous solution is rejected if
where
stands for the
q-quantile of the
t-distribution and statistics
is defined as
with empirical variances
and
.
Below we briefly describe the main steps of the algorithm 4. At the initialisation step of the algorithm, the neural network is trained based on the LQF control policy. The parameter vector is then equal to the initial vector
to be optimized. The simulation algorithm 2 is then used to calculate the initial sample
with
of the average cost function for a given initial parameter vector
and the corresponding first empirical moment
. These values are set as the current solution
and
to the optimization problem (
13). At the perturbation step, a randomly chosen element of the previous parameter vector
must be randomly perturbed on the specified set
of admissible discrete domain. For the new parameter vector
next sample
of average costs must be calculated together with the first empirical moment
. At the acceptance step, a new policy
can be accepted as a current solution with a probability
p defined as
where
is the temperature at the
nth iteration. If a new policy
is accepted, then it is defined together with a corresponding average cost
as a current solution. Otherwise, the last change in the parameter vector
must be reversed, i.e.
and the sample size
m for calculating the first moments is updated. Then the perturbation step must be repeated. For termination of the algorithm the stopping criteria
or
is used.
We note that the classical simulated annealing method generates for some function
a sample
which for the constant temperature
can be interpreted as a realization of a homogeneous Markov chain
with transition probabilities
where
is a uniformly distributed random variable on the interval
. It is easy to show that the modified transition probabilities, where the objective function is calculated numerically, converges to the transition probabilities (
17) which in turn can guarantee the convergence to an optimal solution.
Proposition 2.
The acceptance probability satisfies the limit relation
Proof. The probability
can be obviously rewritten as
where
. Then the following relation holds,
due to the strong law of large numbers and the fact that for
the sample size
and hence
□
7. Numerical analysis
Consider the queueing system with
. We first analyze a Markov model, where the parallel queues are of the type
with
and
,
, the coefficient of variation
. The values of system parameters
and
are fixed as in examples 1 and 2 which will refer to as Case 1 and Case 2. For this model it is possible to compare the optimization results obtained by combining the simulation, trained neural network and simulated annealing algorithm with the results of the policy iteration algorithm. In Cases 1 and 2 the weights and biases of the trained neural network based on PIA take respectively the following values
Based on these values, in the simulation annealing algorithm 4 we can define the domain for each element of the vector
. In our experiments for simplicity we set general boundaries for all elements at values
and
. The length of the increment
implies the quantization level
. Next we set
,
, and
. As an initial value we take the parameter vector obtained for the LQF policy. For the initial control policy one could also choose the policy
obtained by algorithm 1. However, we would like to check the convergence of the algorithm when choosing not the best initial solution, since in general case one usually chooses either some heuristic policy or an arbitrary one. The empiric average cost
for each iteration step is calculated based on sample with a size
. The accumulation of sample data in QSIM algorithm 2 is carried out after 1000 customers have entered the system and is completed after 5000 customers have entered the system.
Application of the algorithm 4 to a Markov model leads to the following optimal solutions:
- Case 1:
Optimal solution is reached at
,
,
- Case 2:
Optimal solution is reached at
,
,
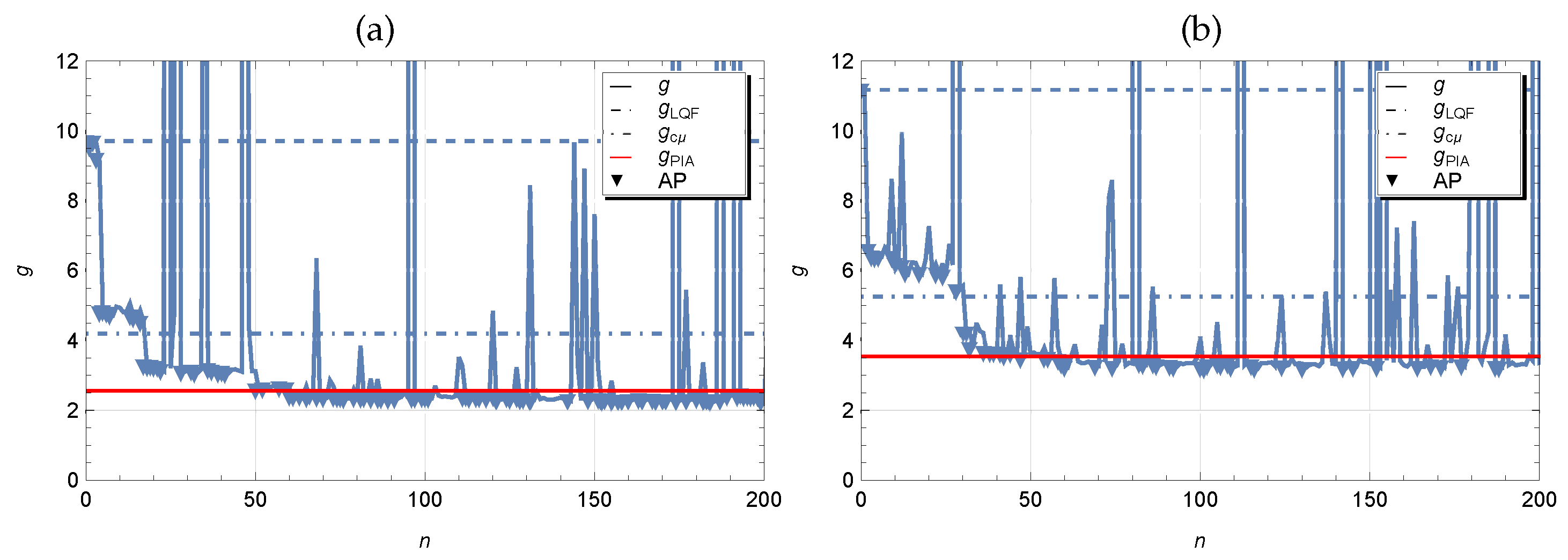
The optimization process of the scheduling policy is illustrated in
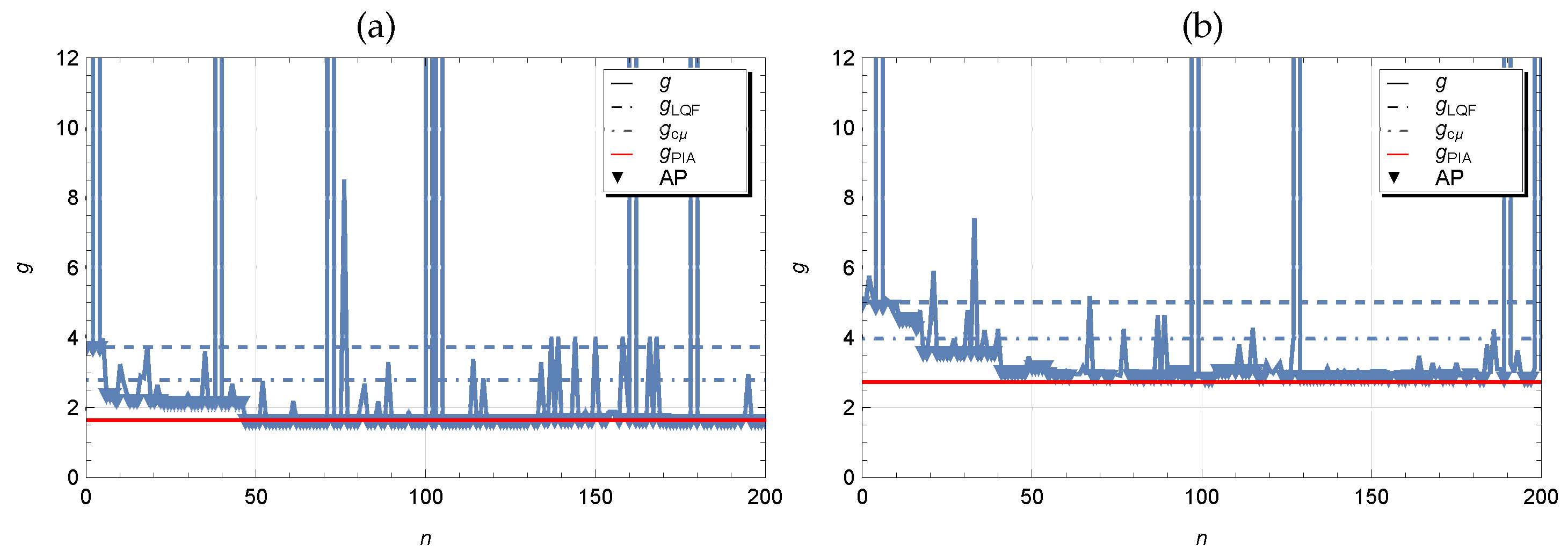
Figure 4. In addition to the numerical results of calculating the average cost at each iteration step of the simulated annealing algorithm, the figures show horizontal dotted and dash-dotted lines respectively at the level of the average cost
and
in figure labeled by (a) and
and
in figure labeled by (b) for the LQF and
heuristic policies. As expected, control policy LQF implies too high average cost. The results look much better for policy
, but still the presence of switching costs significantly worsens the performance of this policy. The red horizontal line indicates the average cost
and
obtained by solving the Markov decision problem using the policy iteration algorithm 1. We can observe that the values are quite close to those obtained by random search. However, some small difference may be due, firstly, to the fact that the simulation is used for the calculations and the results have a certain scattering, and ,secondly, we do not exclude the influence of boundary states in the Markov model, where a buffer size truncation has been used. In the figures, we have also marked with triangles those iteration steps with accepted policy (AC) where the perturbed parameter vector has been accepted. The number of accepted points in Case 1 and 2 is equal respectively to 98 and 110. From above results in case of exponential time distributions we can make the following observations. If the parameter vector
with elements
and
is used for the initial scheduling policy, then one can expect the faster convergence of the simulated annealing algorithm to the optimal solution which was confirmed numerically. If an optimal policy for a controlled Markov process is not available, e.g. when the number of queues is too large, in this case it is reasonable to use the static
-rule as the initial policy.
The
Figure 5 displays experiments realized for the queues of the type
with deterministic inter-arrival and service times which are equal to corresponding mean values
and
of the Markov model. Here the coefficient
. The SA algorithm converges to the values
and
respectively for Case 1 and 2 with the following optimal policies,
- Case 1:
- Case 2:
The average costs for heuristic policies take the values , , and , , .
It is observed that the optimal policy obtained by the SA algorithm is quite close to those obtained by the PIA. Nevertheless, from experiment to experiment certain deviations in the value of the average costs may appear. Therefore it is of interest for us to check whether such differences are statistically significant.
Further we analyse how sensitive is the optimal policy obtained in exponential case by the SA algorithm to the shape of arrival and service time distributions. The following distributions will be used to calculate the optimal control policy in the non-exponential case: gamma
, log-normal
and Pareto
distributions , where two last options belong to a set of heavy tail distributions. The parameters of these distributions are chosen so that the first two moments coincide with the moments of the Markov counterpart. Thus, they need to be represented as functions depending on the corresponding sample moments as in a moment method for the parameter estimation. In the following experiments the first moments of the inter-arrival and service times are fixed at values of Case 2, and the squared coefficient of variation is varied as
and
. Denote by
a sample random variable
Z distributed according to the proposed distributions with two first sample moments
,
and squared empirical coefficient of variation
. Then for the gamma distribution
with a PDF
the parameters
and
satisfy the relations,
In case of the lognormal distribution
with a PDF
the parameters
and
are calculated by
In case of a Pareto distribution
with a PDF
the parameters
and
are calculated by relations
The parameters of the proposed distributions are listed in
Table 5 and
Table 6 respectively for the inter-arrival and service time distributions.
The sensitivity of the optimal control policy to the shape of the distributions is tested by means of a two-sided
t-test for samples with unknown but equal variances. Let
and
are the samples of the average cost values obtained for the optimal control policy in case of exponentially distributed times and for the system with proposed distributions for the inter-arrival and service times. These samples of size
m are associated with the normally distributed random variables
and
, where
and
. The test is defined then as
where statistics
is calculated by (
16). The results of tests in form of the
p-value, the values of the average costs
and
together with their
confidence intervals are summarized in
Table 7 and
Table 8 for the systems with different inter-arrival and service time distributions with the smaller and greater levels of dispersion around the mean, d.h. for
in
Table 7 and
in
Table 8.
From numerical examples it is observed that the shape of distributions has a high level of influence over the value of the average cost functions and . However, an examination of the entries in last two tables reveals that in all experiments the p-value exceeds a significance level . Furthermore, it is worth noting that in most cases this exceeding is significant. In this regard, the statistical test fails to reject null hypothesis at a given signigicance level, in other words, the average cost values are statistically equal and the corresponding optimal control policies are equivalent. Thus, for practical purposes in general queueing systems one can either apply the proposed optimization method, or use the control policy optimized for the exponential model as a suboptimal scheduling policy.