Submitted:
29 April 2023
Posted:
30 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Review of the literature
1.2. State of the art benchmarks
1.3. Novelties presented
- The best tracking (mean) error performance (best efficacy against overshoot and settling) is achieved using full modal compensation of the first three flexible modes plus a bandpass filter of the fourth flexible mode’s anti–resonance.
- The best tracking error deviation was achieved with merely compensation of the rigid body mode plus bandpass filtering of the first flexible mode’s anti–resonance.
- The lowest control cost was achieved by the same method listed in item #2: merely compensation of the rigid body mode plus bandpass filtering of the first flexible mode’s resonance.
1.4. Highlighting controversial and diverging hypotheses
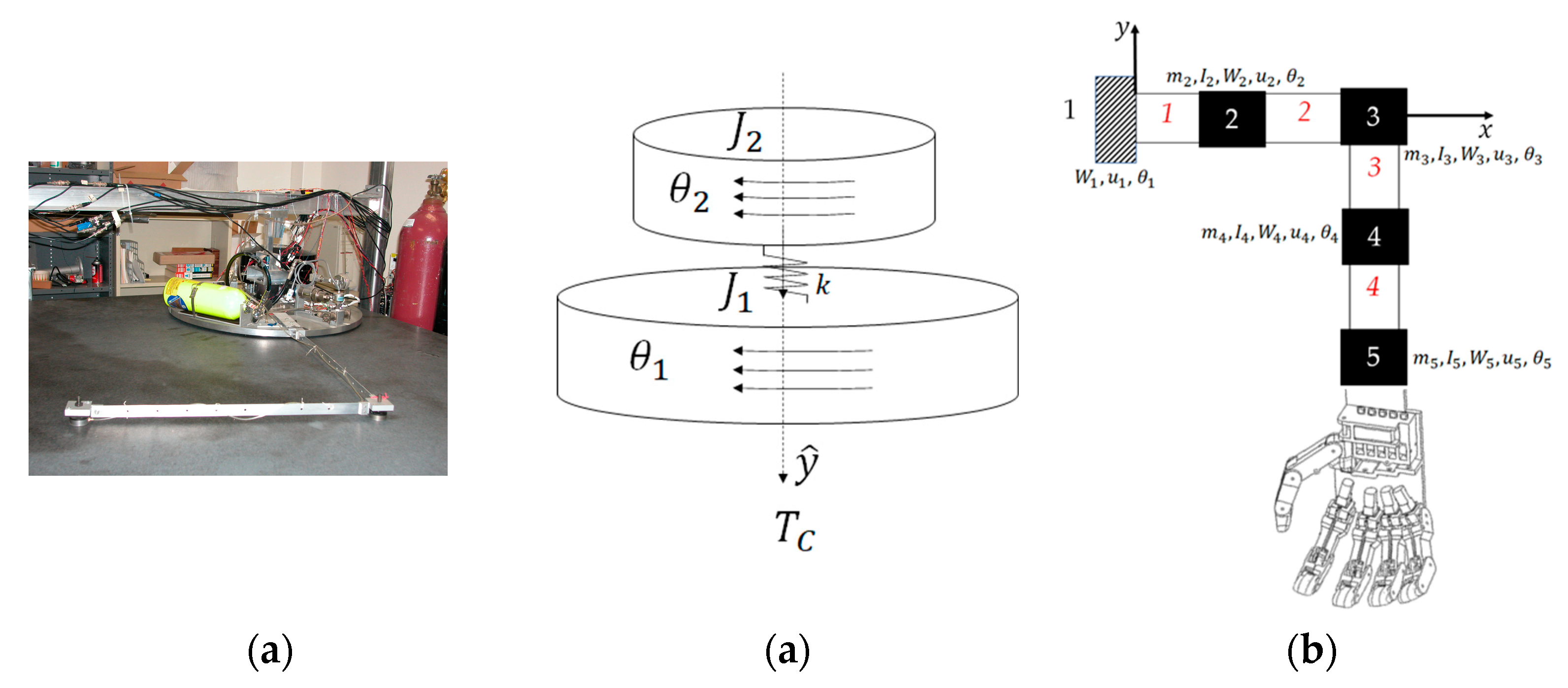
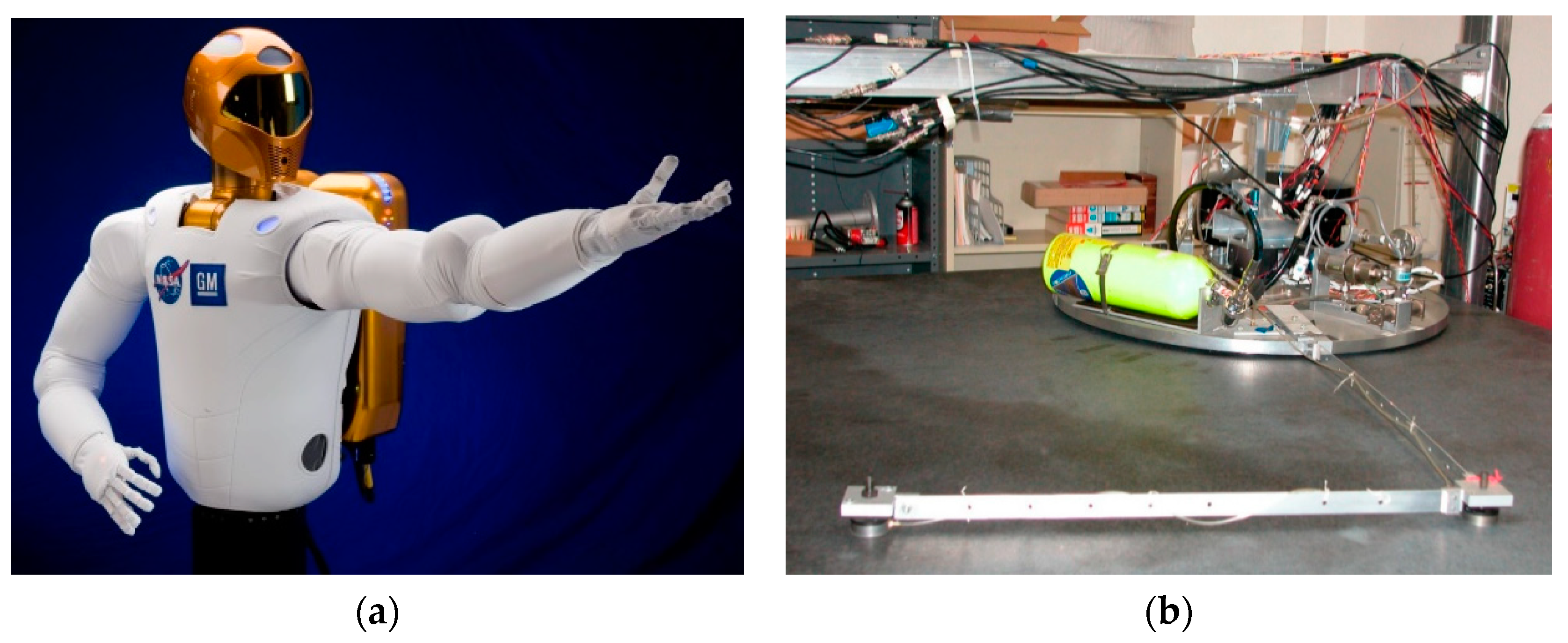
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rigid Body Dynamics
| Variable / acronym |
Definition | Variable / acronym |
Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| F | Vector sum of external forces | Vector sum of external torque | |
| J |
Moments of inertia Velocity relative to reference frame |
|
Position relative to the reference frame Angular velocity |
| Variable/acronym | Definition | Variable/acronym | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hamiltonian | Lagrangian |
2.2. Flexible Body Dynamics
2.3. Modal System Identification
| Variable/ acronym |
Definition | Variable/ acronym |
Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass matrix | Stiffness matrix | ||
| Acceleration in generalized displacement coordinates | Principal moment of inertia with respect to z-axis | ||
| Force vector | Coupling term for rigid-elastic |
2.4. Classical Second–Order Structural Filtering
| Variable/acronym | Definition | Variable/acronym | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active damping | Active stiffness | ||
| Feedforward | |||
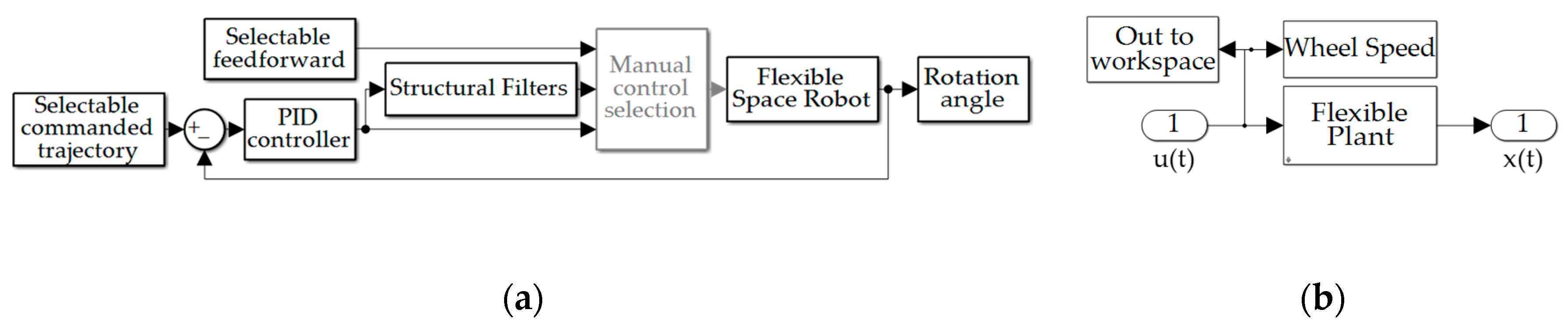
2.5. Simulation Parameters
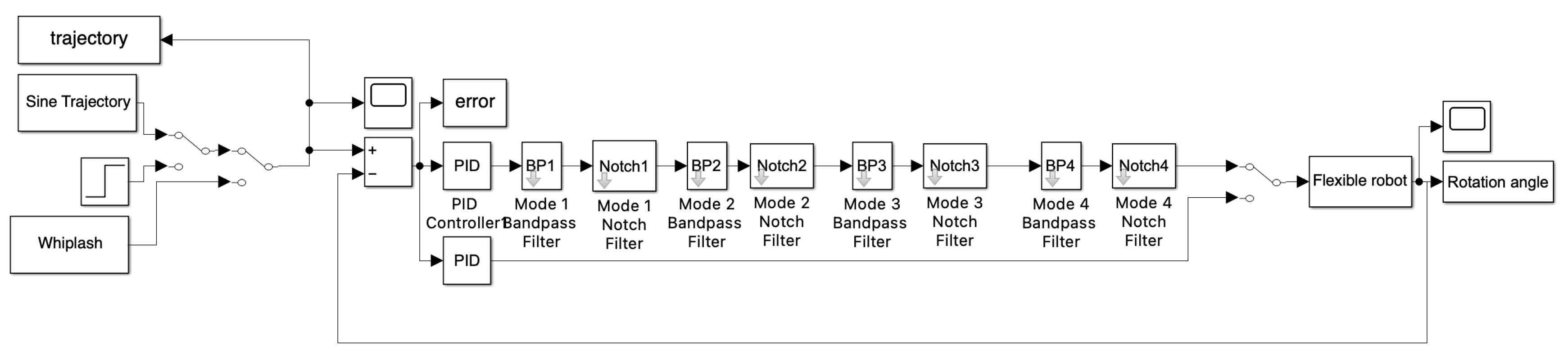
3. Results
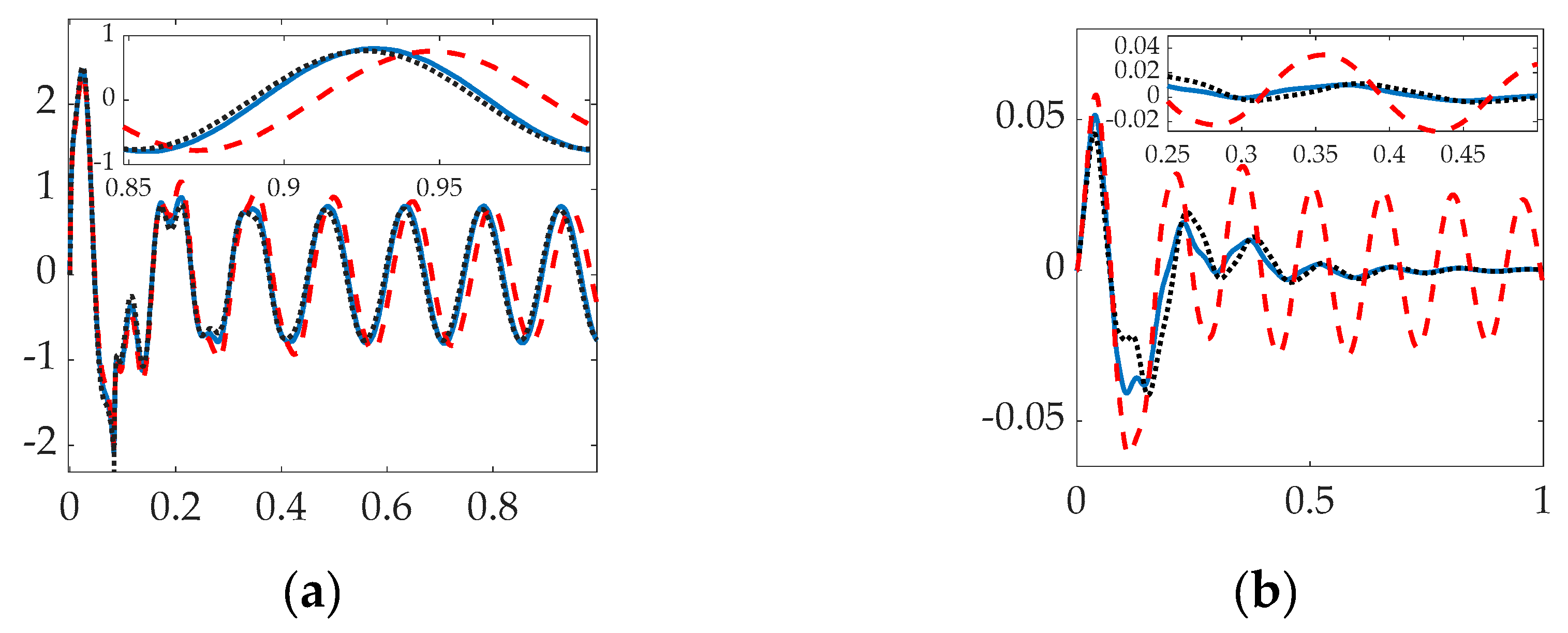
3.1. Simulation results with structural filters (bandpass & notch) for the first flexible mode.
3.2. Simulation results with structural filter (bandpass & notch) for the first four flexible modes.
3.3. Simulation with Structural Filter (Bandpass and Notch) for the First Three Flexible Modes and First Four Bandpass.
4. Discussion
| Recommendation: Use the bandpass filter at the first anti-resonance in first flexible mode with step input to compensate the flexible space robots. |
Recommended future research
References
- Nile, R.; First Humanoid Robot In Space Receives NASA Government Invention of the Year. 17 June 2015. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/research/news/invention_of_the_year (accessed on 17 February 2023).
- NASA. NASA Image Use Policy. 2022. Available online: https://gpm.nasa.gov/image-use-policy (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- Naval Postgraduate School, Flexible Spacecraft Simulator Laboratory. Available online: https://nps.edu/web/srdc/laboratories (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Use of Department of Defense Imagery. Available online: https://www.defense.gov/Help-Center/Article/Article/2762906/use-of-department-of-defense-imagery/#:~:text=Department%20of%20Defense%20photographs%20and,use%2C%20subject%20to%20specific%20guidelines (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- Defense Imagery Management Operations Center. Public Use Notice of Limitations. Available online: https://www.dimoc.mil/resources/limitations/ (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- Marshall Spaceflight Center, Advanced Space Transportation Program: Paving the Highway to Space. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/centers/marshall/news/background/facts/astp.html (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Curiosity Bot, Advantages and disadvantages of using Robots instead of Astronauts. Available online: https://mycuriositybot.wordpress.com/2019/02/18/advantages–and–disadvantages–of–using–robots–instead–of–astronauts/ (accessed on 18 February 2019).
- Armanini, C.; Boyer, F.; Mathew, A.T.; Duriez, C.; Renda, F. Soft Robots Modeling: A Structured Overview. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2023, 39, 1728–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encyclopaedia Britannica, Britannica, Euclidean Space. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/science/Euclidean–space (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Sands, T. Comparison and Interpretation Methods for Predictive Control of Mechanics. Algorithms 2019, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, I. Principia, Jussu Societatis Regiæ ac Typis Joseph Streater; Cambridge University Library: London, UK, 1687. [Google Scholar]
- Mazalov, V.; Parilina, E. The Euler-Equation Approach in Average-Oriented Opinion Dynamics. Mathematics 2020, 8, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A.C.M. Operations, What–Are–the–6–Degrees–of–Freedom, Industrial Inspection & Analysis (IIA). Available online: https://industrial–ia.com/what–are–the–6–degrees–of–freedom–6dof–explained/ (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- Doyle, J.; Francis, A.; Tannenbaum, A. Feedback Control Theory; Dover: Mineola, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, R.; Robertsson, A.; Nilsson, K.; Verhaegen, M. State-space system identification of robot manipulator dynamics. Mechatronics 2000, 10, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corke, P, “High–performance visual closed–loop robot control,” thesis.
- Li, Y.; Ang, K.H.; Chong, G. PID control system analysis and design. IEEE Control. Syst. 2006, 26, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bemporad, A.; Morari, M.; Dua, V.; Pistikopoulos, E. The explicit linear quadratic regulator for constrained systems. Automatica 2002, 38, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K; Kosut, R; Aral, G, “Learning feedforward control,” Proceedings of 1994 American Control Conference –ACC ’94.
- Chang, T.C.; Seufert, C.; Eminaga, O.; Shkolyar, E.; Hu, J.C.; Liao, J.C. Current Trends in Artificial Intelligence Application for Endourology and Robotic Surgery. Urol. Clin. North Am. 2020, 48, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S; Bhavsar, P, “Robotic Arm Control based on internet of things,” 2019 IEEE Long Island Systems, Applications and Technology Conference (LISAT), 2019.
- Sands, T. Inducing Performance of Commercial Surgical Robots in Space. Sensors 2023, 23, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikdar, S.; Rahman, M.H.; Siddaiah, A.; Menezes, P.L. Gecko–Inspired Adhesive Mechanisms and Adhesives for Robots—A Review. Robotics 2022, 11, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, J.M.; Ahern, D.P.; Doinn, T.; Gibbons, D.; Rodrigues, K.N.; Birch, N.; Butler, J.S. Surgeon proficiency in robot-assisted spine surgery. Bone Jt. J. 2020, 102-B, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremeskel, M.; Shafiq, B.; Uneri, A.; Sheth, N.; Simmerer, C.; Zbijewski, W.; Siewerdsen, J.H.; Cleary, K.; Li, G. Quantification of manipulation forces needed for robot-assisted reduction of the ankle syndesmosis: an initial cadaveric study. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2022, 17, 2263–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogowski, A. Scenario–Based Programming of Voice–Controlled Medical Robotic Systems. Sensors 2022, 22, 9520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stauffer, T.P.; Kim, B.I.; Grant, C.; Adams, S.B.; Anastasio, A.T. Robotic Technology in Foot and Ankle Surgery: A Comprehensive Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sühn, T.; Esmaeili, N.; Mattepu, S.Y.; Spiller, M.; Boese, A.; Urrutia, R.; Poblete, V.; Hansen, C.; Lohmann, C.H.; Illanes, A.; Friebe, M. Vibro–Acoustic Sensing of Instrument Interactions as a Potential Source of Texture–Related Information in Robotic Palpation. Sensors 2023, 23, 3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.; Kim, Y.; Oh, C.K.; Kim, J. Robotic palpation and mechanical property characterization for abnormal tissue localization. Med Biol. Eng. Comput. 2012, 50, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Yu, M.; Hou, Y. Design, Fabrication, and Performance Test of a New Type of Soft–Robotic Gripper for Grasping. Sensors 2022, 22, 5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Liu, W.; Zhao, J.; Hou, Y.; Hong, X.; Zhang, H. Modeling and Analysis of a Composite Structure–Based Soft Pneumatic Actuators for Soft–Robotic Gripper. Sensors 2022, 22, 4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Han, J. Active Model–Based Hysteresis Compensation and Tracking Control of Pneumatic Artificial Muscle. Sensors 2022, 22, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Sameoto, D. A Review of Electrically Driven Soft Actuators for Soft Robotics. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, P.; Melchiorre, M.; Mauro, S. Design of a Lightweight and Deployable Soft Robotic Arm. Robotics 2022, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herron, C.W.; Fuge, Z.J.; Kogelis, M.; Tremaroli, N.J.; Kalita, B.; Leonessa, A. Design and Validation of a Low–Level Controller for Hierarchically Controlled Exoskeletons. Sensors 2023, 23, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chellal, A.A.; Lima, J.; Gonçalves, J.; Fernandes, F.P.; Pacheco, F.; Monteiro, F.; Brito, T.; Soares, S. Robot–Assisted Rehabilitation Architecture Supported by a Distributed Data Acquisition System. Sensors 2022, 22, 9532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H. –S.; Yoon, H.–S.; Lee, S.; Hong, C.–K.; Yi, B.–J. Surgical Navigation System for Transsphenoidal Pituitary Surgery Applying U–Net–Based Automatic Segmentation and Bendable Devices. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Kokubu, S.; Qin, R.; Tortós Vinocour, P.E.; Yu, W. Neural Network–Based Active Load–Sensing Scheme and Stiffness Adjustment for Pneumatic Soft Actuators for Minimally Invasive Surgery Support. Sensors 2023, 23, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, F.; Ribeiro, T.; Lopes, G.; Ribeiro, A.F. Large–Scale Tactile Detection System Based on Supervised Learning for Service Robots Human Interaction. Sensors 2023, 23, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Li, K.; Xu, D.; Tan, W. Design of a Laparoscopic Robot System Based on Spherical Magnetic Field. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Wang, T. Multi–Agent Reinforcement Learning with Optimal Equivalent Action of Neighborhood. Actuators 2022, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, T. Optimization Provenance of Whiplash Compensation for Flexible Space Robotics. Aerospace 2019, 6, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, T. Virtual Sensoring of Motion Using Pontryagin’s Treatment of Hamiltonian Systems. Sensors 2021, 21, 4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dai, X.; Huang, Q.; Wu, Q. AILC for Rigid–Flexible Coupled Manipulator System in Three–Dimensional Space with Time–Varying Disturbances and Input Constraints. Actuators 2022, 11, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Shao, G.; Yang, Q.; Yu, L.; Yao, Y.; Tu, S. Adaptive Robust Tracking Control for Near Space Vehicles with Multi–Source Disturbances and Input–Output Constraints. Actuators 2022, 11, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, T. Flattening the Curve of Flexible Space Robotics. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Sands, T. Novel Learning for Control of Nonlinear Spacecraft Dynamics. J. AppliedMath 2023, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeresky, B.; Rizzo, A.; Sands, T. Optimal Learning and Self-Awareness Versus PDI. Algorithms 2020, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

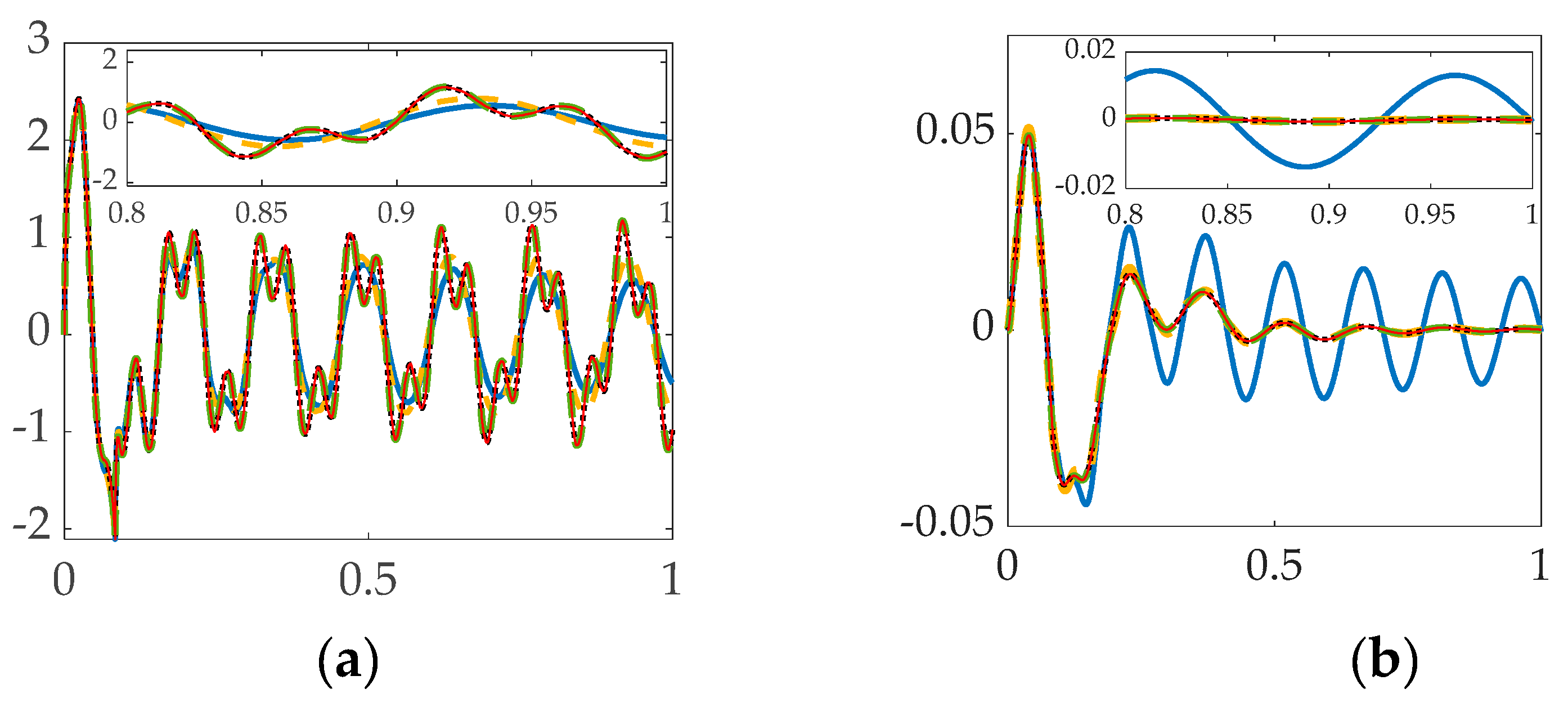
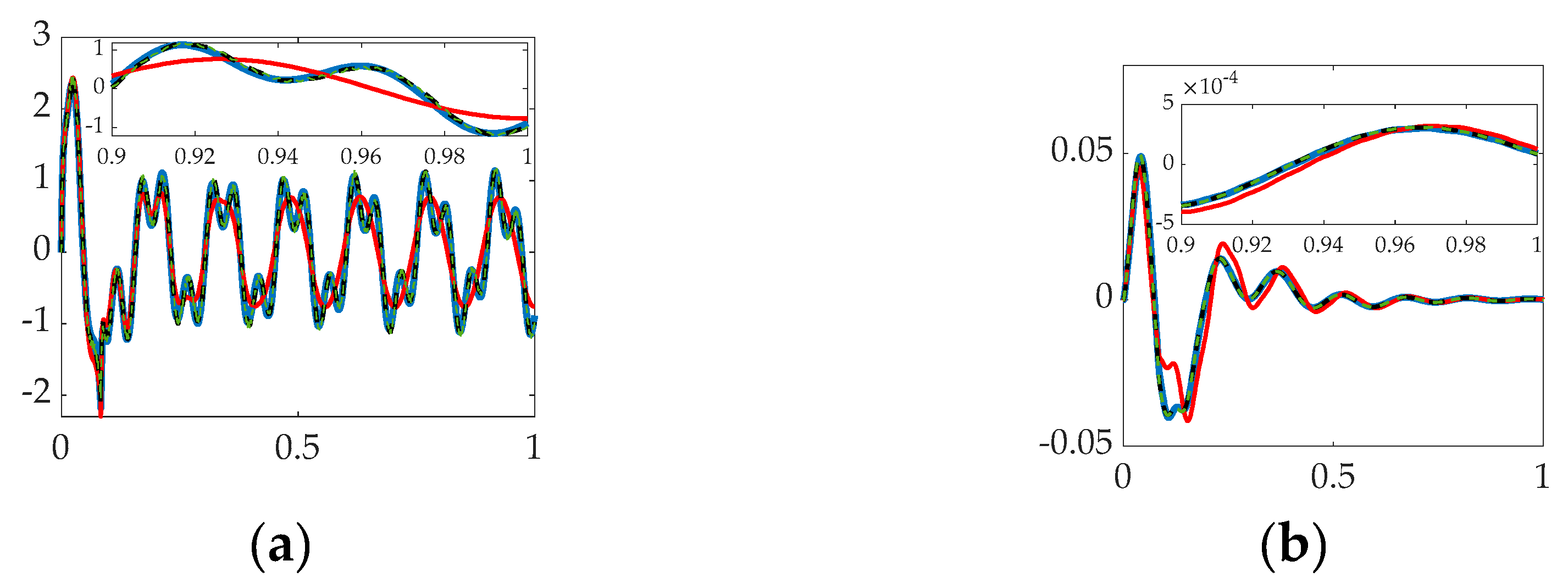
| System | Cost | Tracking error mean |
Tracking Error deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| PID + Bandpass | 8.06 | 0.00014406 | 0.014064 |
| PID + Notch PID + Bandpass + Notch |
8.9353 8.4414 |
0.000714 0.00019857 |
0.025414 0.015501 |
| System | Cost | Tracking error mean |
Tracking Error deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| PID controlled | 7.3167 | 0.00050164 | 0.018844 |
| PID + Mode 1 PID + Mode 1–2 PID + Mode 1–3 PID +Mode 1–4 |
8.4414 9.9155 9.906 9.9054 |
0.00019857 0.00020995 –0.00026647 –0.00031746 |
0.015501 0.015452 0.014086 0.014496 |
| System | Cost | Tracking error mean |
Tracking Error deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| PID + bandpass 1 | 8.06 | 0.00014406 | 0014064 |
| PID + Mode 1 + bandpass 2 PID + Mode 1–2 + bandpass 3 PID + Mode 1–3 + bandpass 4 |
9.7423 9.8582 9.8914 |
0.00019832 0.00017655 0.000013948 |
0.015269 0.01524 0.01414 |
| System | Cost | Tracking Error | Tracking Error deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| PID only PID + bandpass1 PID + notch1 PID + Mode 1 PID + Mode 1–2 PID + Mode 1–3 PID +Mode 1–4 |
– 10.16% 22.12% 15.37% 35.52% 35.38% 35.38% |
– –71.28% 42.33% –60.42% –58.15% –46.88% –36.72% |
– –23.22% 37.01% –15.60% –15.86% –23.11% –20.93% |
| PID + Mode 1 + bandpass 2 PID + Mode 1–2 + bandpass 3 PID + Mode 1–3 + bandpass 4 |
33.15% 34.74% 35.18% |
–60.47% –64.81% –97.22% |
–16.83% –16.98% –22.82% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





