1. Introduction
Histoplasma capsulatum is a thermo-dimorphic and geophilic fungus that has a close relationship with environmental factors, adapting favorably in tropical and subtropical regions[
1]. It has a wide geographic distribution, with autochthonous cases detected in more than 60 countries[
1]. However, it has a clear predominance in the Americas, East Asia, Oceania and Sub-Saharan Africa[
2]. In Latin America, histoplasmosis is the most prevalent systemic endemic mycoses[
3].
H. capsulatum infection and the clinical expression of the disease depend on a complex interaction between the pathogen and the host, and at least three conditions are observed in the pathogenesis of this mycosis: immunocompetence of the host, virulence of the infecting strain and the acquired parasite load[
4].
Immunosuppression resulting from the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is closely related to the disseminated form of histoplasmosis and in 1987 it was classified as an AIDS-defining opportunistic infection by the World Health Organization (WHO)[
5] and the Center Disease Control (CDC)[
6], emphasizing it as a potentially fatal disease. In Brazil, however, it was made notifiable in only two of the states, Rio de Janeiro and Goiás, in 2021 [
7].
This study intends to describe the clinical, laboratory and epidemiological characteristics of histoplasmosis cases at Instituto Nacional de Infectologia Evandro Chagas, Fiocruz , Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, from 2000 to 2018, to compare HIV positive (HIV+) and HIV negative (HIV-) patients and finally to outline the associated risk profile in both groups.
2. Materials and Methods
We have carried out a descriptive, retrospective study, by collecting data on histoplasmosis from medical records at the INI Evandro Chagas/Fiocruz, from 2000 to 2018.
Epidemiological, sociodemographic, clinical and laboratory data were extracted from outpatient visits and hospitalizations of HIV+ and HIV- patients, with the completion of a case report form specially designed for this study.
Only definitive cases of histoplasmosis based on clinical diagnosis and laboratory evidence of histoplasmosis were included, that is, positive culture for H. capsulatum, histopathological finding demonstrating fungal elements consistent with H. capsulatum or presence of H and/or M bands by immunodiffusion and/or or Western Blot (WB). At the time of the study, the urinary antigen (galactomannan) test was not approved for use by the Brazilian regulatory agency,ANVISA, and was therefore not available for diagnosis.
We excluded pregnant women, individuals under 18 years of age, suspected cases of histoplasmosis without laboratory confirmation by means of culture, histopathology or immunodiagnostics, as well as confirmed or probable cases with insufficient information in the medical records. Data were collected through the electronic data capture tool for research REDCap (Research Electronic Data Capture), version 12.5.5. hosted at the hospital.
Statistics was performed using the R program version 3.5.1. Exploratory data analysis used absolute and relative frequencies for qualitative variables and summary measures (mean, median, first and third quartiles) for quantitative variables, depending on normality of data. Comparison between qualitative variables according to HIV status was performed using Pearson's chi-square test or Fisher's exact test (when necessary). The comparison between the quantitative variables according to the HIV serostatus was performed by using the Mann-Whitney test or t test (when possible). The tests used a significance level of 5% as a reference (p<0.05). Univariate and multivariate analysis was performed for the outcome death due to histoplasmosis with a binomial model (logit) with the control variables in the multivariate model being age, gender, time of disease progression and HIV status; variables removed by missing data were hypoxemia, albumin, hemoglobin, AST, ALT and LDH.
The project was approved by the INI Research Ethics Committee with the number CAAE: 98094718.4.0000.5262, on December 10, 2018.
3. Results
An active search for histoplasmosis cases was carried out at INI, in the records of the mycology and pathological anatomy laboratories, from 2000 to 2018.
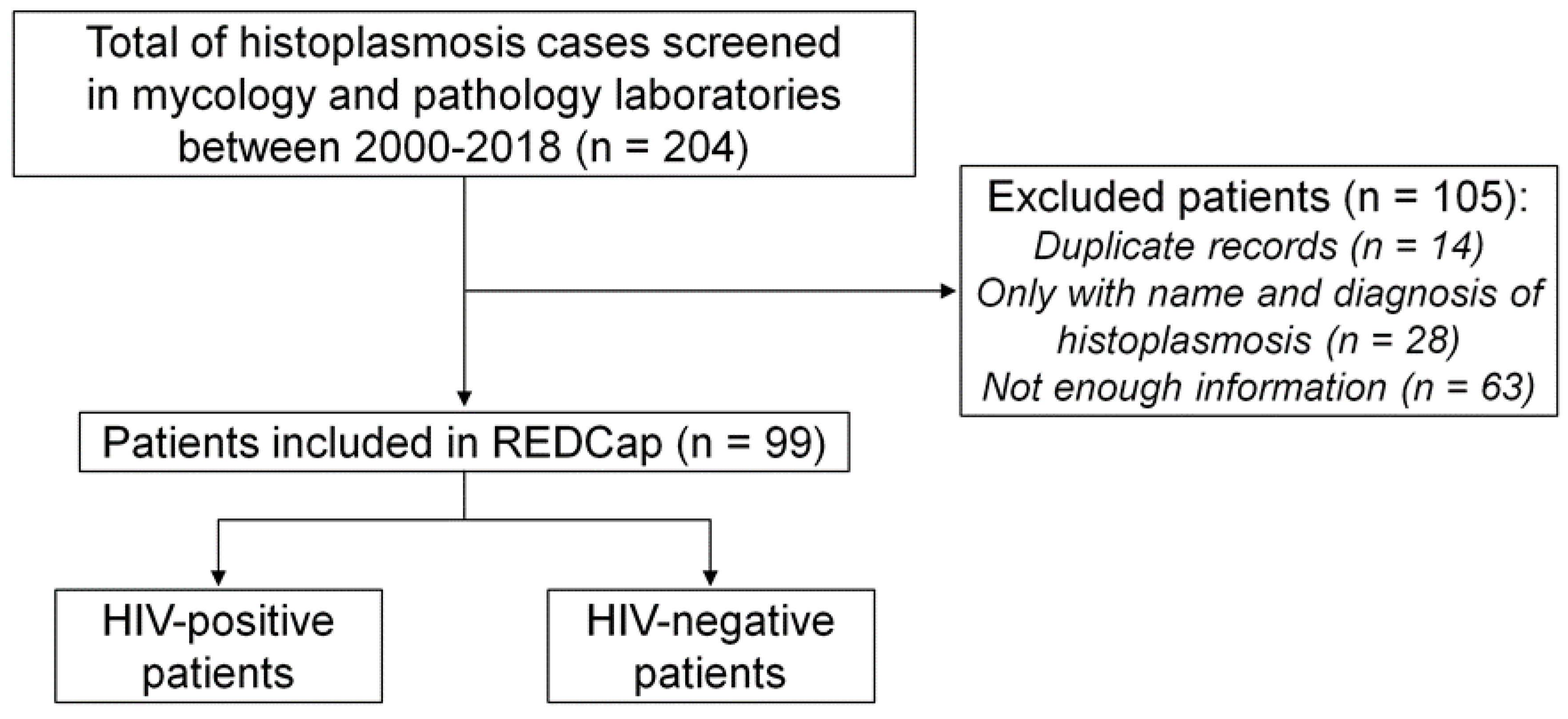
In total, 204 records of patients diagnosed with histoplasmosis were found in both laboratories, but 105 were excluded (Figure 1). Of these, 14 had duplicate numbers; 28 records had only the name of the patient with a positive mycological result; 63 were records with insufficient information in the computerized system (these records basically showed just age, gender and address of the patient).Of these 63 records, 41 were men and 22 were women, with a mean age of 43.20 ± 12.17 years, 13 HIV+ and 50 HIV-. Of those excluded, 9 were empirically treated for histoplasmosis, 3 patients were diagnosed by radiological findings, 5 by histopathology, 1 by blood culture, 1 by bone marrow culture, 8 by ID and 33 concomitantly by WD and ID. Ninety-nine records were then included, of which 65 were HIV+ and 34 were HIV-.
Figure 1.
Flowchart of inclusion of patients with histoplasmosis, INI Evandro Chagas, Fiocruz, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2000-2018.
Figure 1.
Flowchart of inclusion of patients with histoplasmosis, INI Evandro Chagas, Fiocruz, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2000-2018.
There was a predominance of white men in both groups; the mean age was 39.1 ± 11 years for HIV+ and 39.4 ± 16.1 years for HIV-. Just over a third of the patients had elementary education, that is, up to 8 years of schooling (HIV+ n=26/64 or 40%; and HIV- n=12/34 or 35.3%). The majority of patients in both groups came from the city of Rio de Janeiro-RJ (HIV+ n=36/64; 55.4% and HIV- n=18/34; 52.9%).
Use of chemotherapy drugs was reported in 2 HIV+ patients, one of whom had non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma and one had Kaposi's Sarcoma. Among HIV- patients, there were two cases of solid organ transplantation (both were using prednisone and mycophenolate) and two patients had leprosy ( one of which was using prednisone, and the other used thalidomide and had recurrent hospitalizations for pulse therapy with methylprednisolone).
Regarding the epidemiological history, HIV- patients presented, in most cases, exposure factors for the acquisition of histoplasmosis, while these were absent or infrequent in HIV+ patients. It is important to note that no findings on epidemiological history in the medical records were found in 59 (90.8%) of HIV+ vs 19 (55.9%) of HIV-( p<0.001). Comparing HIV+ with HIV-, contact with chickens was reported by 1 (1.5%) vs 2 (5.9%) patients ( p=0.271); contact with bats by 0 vs 6 (17.6%, p=0.001); cleaning of abandoned buildings in the last 6 months by 1 (1.5%) vs 2 (5.9%), p=0.271; contact with dust/soil in the last months by 1 (1.5%) vs 5 (14.7%), p=0.017.
Table 1 shows information on the clinical picture presented by the patients on diagonis. The median time between onset of symptoms and diagnosis was 22 weeks, significantly longer, for HIV+ patients, while it was 8 weeks for HIV- patients (p. =0.047). Most patients had fever, weight loss, and respiratory signs or symptoms. There was statistical significance regarding the frequency of hepatomegaly, splenomegaly and anemia, which were more frequent in HIV+ in relation to HIV- .
As for the ophthalmologic evaluation, thirty HIV+ patients (46%) underwent fundoscopy, and of these, only 1 had a description of an eye lesion resulting from histoplasmosis infection (the report consisted of mouthpiece choroiditis, peripapillary atrophy and choroidal neovascularization). Other results showed 19 fundoscopies without alterations; 4 retinopathies resulting from HIV infection; 2 scar lesions compatible with ocular tuberculosis, 3 cytomegalovirus retinitis and 1 exam described bilateral optic nerve pallor unrelated to infection. None of the HIV- patients underwent fundoscopy.
Table 1.
- Clinical findings and clinical form presented by patients diagnosed with histoplasmosis, INI 2000-2018.
Table 1.
- Clinical findings and clinical form presented by patients diagnosed with histoplasmosis, INI 2000-2018.
| |
Variables |
|
Diagnosis of HIV |
|
| |
|
|
Negative |
Positive |
P-value |
| Onset of symptoms until diagnosis: (in weeks) |
Median (IQR) |
8 (6-18) |
22 (8-44) |
0.047 |
| Signs and symptoms |
Fever |
No |
12 (35.3) |
12 (18.5) |
0.063 |
| Yes |
22 (64.7) |
53 (81.5) |
|
| Weight loss |
No |
16 (47.1) |
20 (30.8) |
0.11 |
| Yes |
18 (52.9) |
45 (69.2) |
|
| Adenomegaly |
No |
29 (85.3) |
44 (67.7) |
0.059 |
| Yes |
5 (14.7) |
21 (32.3) |
|
| Hepatomegaly |
No |
32 (94.1) |
51 (78.5) |
0.044 |
| Yes |
2 (5.9) |
14 (21.5) |
|
| Splenomegaly |
No |
33 (97.1) |
53 (81.5) |
0.032 |
| Yes |
1 (2.9) |
12 (18.5) |
|
| Anaemia |
No |
30 (88.2) |
42 (64.6) |
0.012 |
| Yes |
4 (11.8) |
23 (35.4) |
|
| Jaundice |
No |
34 (100) |
60 (92.3) |
0.162 |
| Yes |
0 (0) |
5 (7.7) |
|
| Diarrhea |
No |
32 (94.1) |
57 (87.7) |
0.487 |
| Yes |
2 (5.9) |
8 (12.3) |
|
| Vomiting |
No |
33 (97.1) |
54 (83.1) |
0.053 |
| Yes |
1 (2.9) |
11 (16.9) |
|
| Abdominal pain |
No |
32 (94.1) |
58 (89.2) |
0.714 |
| Yes |
2 (5.9) |
7 (10.8) |
|
| Respiratory syndrome |
No |
15 (44.1) |
33 (50.8) |
0.529 |
| Yes |
19 (55.9) |
32 (49.2) |
|
| Skin Lesions |
No |
29 (85.3) |
55 (84.6) |
0.929 |
| Yes |
5 (14.7) |
10 (15.4) |
|
| Oral lesions |
No |
31 (91.2) |
62 (95.4) |
0.41 |
| Yes |
3 (8.8) |
3 (4.6) |
|
| Gastrointestinal problems |
No |
34 (100) |
62 (95.4) |
0.549 |
| Yes |
0 (0) |
3 (4.6) |
|
| No symptoms reported |
No |
34 (100) |
61 (93.8) |
0.296 |
| Yes |
0 (0) |
4 (6.2) |
|
| Total |
|
|
34 |
65 |
|
Table 2.
- Results of nonspecific laboratory tests in 99 patients with histoplasmosis stratified by HIV serostatus, INI 2000-2018.
Table 2.
- Results of nonspecific laboratory tests in 99 patients with histoplasmosis stratified by HIV serostatus, INI 2000-2018.
| Variables |
|
Diagnosis of HIV |
|
| |
|
Negative |
Positive |
P-value |
| Hypoxaemia |
No |
23 (67.6) |
39 (60) |
0.041 |
| No data found |
9 (26.4) |
9 (13.8) |
|
| Yes |
2 (5.8) |
16 (24.6) |
|
| Metabolic acidosis |
No |
21 (63.6) |
41 (65.1) |
0.359 |
| No data found |
9 (27.3) |
11 (17.5) |
|
| Yes |
3 (9.1) |
11 (17.5) |
|
| Creatinine(mg/dL) |
Median (IQR) |
0.8 (0.6-1.2) |
1 (0.8-1.3) |
0.091 |
| Urea(mg/dl) |
Median (IQR) |
28.5 (17.5-31.8) |
32 (26-54) |
0.165 |
| Haemoglobin(g/dL) |
Mean (SD) |
12.6 (2.5) |
9.5 (2.1) |
< 0.001 |
| Total Leukocytes(cells/ mm3) |
Median (IQR) |
4,800 (12.4-5810) |
3,410 (10.3-5,647.5) |
0.593 |
| Absolute neutrophil |
Median (IQR) |
1,297 (6.6-4031) |
2,223 (66.6-4001.2) |
0.887 |
| Platelets(x10³/mm³) |
Median (IQR) |
251 (123,877.5) |
227 (117,358.5) |
0.473 |
| ESR (mm) |
Mean (SD) |
21.5 (16.3) |
71.3 (36.9) |
- |
| CRP (mg/dL) |
Median (IQR) |
8.9 (4-15.4) |
9 (6.1-14.1) |
0.912 |
| Lactate(mmol/L) |
Median (IQR) |
- |
1.95 (1.2-4.25) |
- |
| AST (IU/L) |
Median (IQR) |
22 (19-39) |
78 (39-167) |
< 0.001 |
| ALT (IU/L) |
Median (IQR) |
34 (23-51) |
41 (25-74) |
0.244 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (IU/L) |
Median (IQR) |
196.5 (99.8-219.8) |
197 (150-496) |
0.215 |
| LDH(IU/L) |
Median (IQR) |
186 (132.8-616.2) |
618 (309-1304) |
0.048 |
| GGT(IU/L) |
Median (IQR) |
48 (36-94.8) |
161 (81-402.5) |
0.002 |
| Albumin(g/dL) |
Median (IQR) |
3.7 (2.2-4) |
2.5 (2-2.9) |
0.17 |
| INR |
Median (IQR) |
- |
1.345 (1.14-1.54) |
- |
| Total Bb(mg/dL) |
Median (IQR) |
0.6 (0.4-1.1) |
0.6 (0.3-1.2) |
0.936 |
| Direct Bb |
Median (IQR) |
0.1 (0.1-0.5) |
0.2 (0.1-0.7) |
0.066 |
| Indirect Bb |
Median (IQR) |
0.4 (0.3-0.5) |
0.4 (0.2-0.6) |
0.899 |
| Total |
|
34 |
65 |
|
The laboratory variables are shown on Table 2. Comparing HIV+ with HIV-, we observed statistical significance regarding: hypoxemia 24.6% vs 5.8%, (p=0.041); anemia with mean hemoglobin 9.5 (SD 2.1) vs 12.5 (SD 2.5%), p<0.01; oxalacetic glutamic transaminase (AST) 22 (IQR 29 - 39) vs 78 (IQR 39 - 167), p<0.01; lactate dehydrogenase (Lactic Dehydrogenase, LDH) median 186 (IQR 132.8 - 616.2) vs 618 (IQR 309 - 1304), p=0.048; as well as gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT), median of 161 (IQR 81 - 402.5) vs 48 (IQR 36 - 4894.8), p=0.002. As for imaging tests, in HIV+ patients, diffuse infiltrate on plain chest X-ray predominated, and on chest CT, lymphadenopathy and nodular parenchymal lesions.
Tuberculosis was diagnosed in 13/65 (20%) HIV+ patients with histoplasmosis.
In addition to histoplasmosis, other mycological diagnoses were screened such as: cryptococcosis, aspergillosis, paracoccidioidomycosis, sporotrichosis and coccidioidomycosis. No findings were found in the HIV- group, while in the HIV+ group two immunochromatographic tests (Crag) were positive for cryptococcosis in serum and 1 was positive in the cerebrospinal fluid, so cryptococcosis was diagnosed concomitantly with histoplasmosis.
Clinical specimens sent for culture are shown in supplementary table 1. Among the HIV+ group, 39/65 (60%) patients collected specimens for culture, and 28 (71.7%) were culture positive for Hc. In the HIV- group, 20/34 (58.8%) specimens were collected for culture, and a positive result was verified in 5 patients (25%). The only two variables with statistical significance were blood culture positivity: in HIV+ patients, this was 32.3% vs 11.8% in HIV- (p=0.025) and bone marrow culture positivity (this was 36.9% in HIV+ vs 8.8% in HIV-, p=0.003).
The final culture results were available in HIV+ patients in 13.5 days (IQR= 8.8 - 27) and in HIV- patients in 12.5 days (IQR= 7 - 19.5).
Table 3 shows the diagnostic tests used in the group. When comparing data from patients who were culture positive and who underwent serological tests, 7 false negative immunodiagnostics were observed (non-reactive WB and non-reactive ID). All of them had the disseminated form of the disease and required hospitalization. Six of the seven patients were HIV positive, with a median CD4 count of 39 cells/µl, all of whom had abandoned antiretroviral treatment. One of the HIV positive patients was using chemotherapy for non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma, further worsening his immune status. The HIV-negative patient was immunosuppressed due to chronic use of corticosteroids and recent pulse therapies to control leprosy reaction. He did not receive antifungal therapy as histoplasmosis was not suspected ante-mortem and his positive culture became available only after he died.
Table 3.
- Sensitivity of diagnostic tests for histoplasmosis in HIV-positive and negative patients, INI 2000-2018.
Table 3.
- Sensitivity of diagnostic tests for histoplasmosis in HIV-positive and negative patients, INI 2000-2018.
| Variables |
Diagnosis of HIV |
|
|
| |
Negative N =34 |
Positive N = 65 |
Total |
P-value |
| Cultivation |
5/20 (25%) |
28/39 (71.7%) |
33/59 (55.9%) |
<0.01 |
| Histopathology |
7/12 (58.3%) |
18/28 (72%) |
25/40 (65.5%) |
1 |
| Western blot |
29/32 (90.6%) |
54/60 (90%) |
83/92 (90.2%) |
0.6095 |
| Double immunodiffusion |
26/32 (83.8%) |
39/60 (65%) |
65/94 (69.1%) |
0.8924 |
As for treatment, amphotericin B deoxycholate was widely used in the HIV+ group, 32/65 (49.2%) vs 0 in the HIV- group, p<0.01; amphotericin B lipid complex was used in 10/65 (15.4%) of the HIV+ group vs in none of the HIV- group (p=0.014). Itraconazole was the most widely used antifungal in the HIV-group.
Table 4 shows the serious outcomes and deaths of the patients with disseminated forms. More than 70% of HIV+ patients diagnosed with histoplasmosis required hospitalization: among those hospitalized, 35.5% needed to be transferred to the intensive care unit (ICU), and 40% died within approximately 6 days. In the HIV- group, only 4/34 (11.7%) were hospitalized, but 3 needed to be transferred to the ICU, 3/4 needed vasoactive drugs and mechanical ventilation and 2/4 needed hemodialysis.
Table 4.
- Data on hospitalization, severity and outcome in cases of disseminated histoplasmosis, INI 2000-2018.
Table 4.
- Data on hospitalization, severity and outcome in cases of disseminated histoplasmosis, INI 2000-2018.
| Variables |
Diagnosis of HIV |
|
| |
Negative N =34 |
Positive N = 65 |
P-value |
| Requested admission to the INI |
4 (12.1%) |
45 (71.4%) |
<0.001 |
| Referral to ICU |
3 (8.8%) |
16 (24.6%) |
0.104 |
| Use of vasoactive drugs |
3 (8.8%) |
14 (21.5%) |
0.189 |
| Haemodialysis |
2 (5.9%) |
5 (7.6%) |
1 |
| Mechanical ventilation |
3 (8.8%) |
15 (23%) |
0.081 |
| Number of deaths |
3 (8.8%) |
30 (46.2%) |
<0.001 |
| Number of deaths during hospitalization |
3 (8.8%) |
18 (27.7%) |
|
| Hospitalization time resulting in death, in days (SD) |
12 (10-14) |
6 (5-18.5) |
<0.001 |
The time to finalize culture results was very close to the time between hospitalization and death among HIV- patients, and twice as long for HIV+ patients, as shown in Supplementary Table 2.
Univariate and multivariate analysis for factors associated with death in histoplasmosis is shown in Table 5. On univariate analysis, anemia, leukopenia, intensive care, use of vasopressor and mechanical ventilation were associated with death in HIV+; on multivariate analysis, only thrombocytopenia showed a near association with death.
Table 5.
– Univariate and multivariate analysis performed to assess factors associated with death in histoplasmosis, INI 2000-2018.
Table 5.
– Univariate and multivariate analysis performed to assess factors associated with death in histoplasmosis, INI 2000-2018.
| Variables |
|
Univariate |
Multivariate |
| |
|
OR [95%IC] |
P-value |
aOR [95%IC] |
P-value |
| Age |
|
1.02 (0.98-1.07) |
0.35 |
1.03 (0.97-1.1) |
0.32 |
| Gender |
Female |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
| |
Male |
0.15 (0.04-0.53) |
<0.01 |
0.08 (0.01-0.4) |
<0.01 |
| Disease Progression Time |
|
1 (0.97-1.02) |
0.74 |
1 (0.96-1.04) |
0.92 |
| HIV diagnosis |
Negative |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
| |
Positive |
7.47 (0.93-60.16) |
0.06 |
8.09 (0.87-75.55) |
0.07 |
| Weight loss |
No |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
| |
Yes |
1.33 (0.38-4.68) |
0.65 |
1.47 (0.25-8.59) |
0.67 |
| Splenomegaly |
No |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
| |
Yes |
1.24 (0.24-6.35) |
0.8 |
1.67 (0.19-14.87) |
0.65 |
| Anaemia |
No |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
| |
Yes |
5.64 (1.65-19.26) |
0.01 |
4.03 (0.81-20.08) |
0.09 |
| Leukopenia |
No |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
| |
Yes |
6.51 (1.82-23.3) |
<0.01 |
3.65 (0.7-19.11) |
0.12 |
| Thrombocytopenia |
No |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
| |
Yes |
2.57 (0.59-11.09) |
0.21
|
6.92 (0.97-49.56) |
0.05 |
| ICU admission |
No |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
| |
Yes |
19.25 (3.52-105.29) |
<0.01 |
- |
- |
| Use of vasoactive catecholamines |
No |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
| |
Yes |
73.33 (13.13-409.52) |
<0.01 |
- |
- |
| Haemodialysis |
No |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
| |
Yes |
2.95 (0.51-17.06) |
0.23
|
5.44 (0.43-68.86) |
0.19 |
| Mechanical ventilation |
No |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
| |
Yes |
62.07 (11.42-337.52) |
<0.01 |
- |
- |
4. Discussion
This study describes the 19-year experience with histoplasmosis cases at INI Evandro Chagas, Fiocruz, Rio de Janeiro, a referral institute for HIV/AIDS and for systemic mycosis since the late 1980’s, with an onsite referral Mycology Reference Laboratory. Of 204 cases of histoplasmosis diagnosed in the period from 2000 to 2018, 99 were included in this study, as they presented consistent clinical and laboratory data to support analysis. Of these, approximately 2/3 were HIV+ individuals. We highlight that INI is a referral center for HIV, and this is the largest public seen to, which justifies, albeit partially, the fact that the HIV+ group is almost twice as large as the HIV- group.
Sociodemographic features were similar in the HIV+ and HIV- groups, with few years of schooling and low income, which is often the case of patients attending the public health system in Brazil. The profile most encountered in both groups was of adult men, non-white and living in the city of Rio de Janeiro. These findings are probably justified by the majority of the INI HIV+ public being men who have sex with men (MSM), as the HIV epidemic in Brazil affects MSM disproportionately. Brazilian statistics reported in 2021 in Unaids, show that HIV seroprevalence in MSM is 18.3%[
8].
An important observation in our results is the lack of reported exposure risks to histoplasmosis in HIV+ patients; this is different from the multicenter study in Brazil, where there was exposure to bats, poultry farms and rural activities in a high proportion of patients with probable/proven histoplasmosis[
9]. However, the frequency of these exposures was not different between the groups with and without histoplasmosis[
9]. This leads us to recommend that a “typical” epidemiological history is not to be expected or relied on to make a diagnostic hypothesis of histoplasmosis in HIV+ patients, since most of them did not report a positive epidemiological history, unlike the HIV-, who presented exposure to bats and dust/soil in an expressive and statistically different frequency. The absence of a relevant epidemiological history in the HIV+ group can be considered in itself as a “risk factor” for the hypothesis of histoplasmosis not being raised, resulting in a delay in diagnosis or a non-diagnosis, as we saw in the autopsy study in Manaus[
10]. We noticed in our series that the diagnostic delay was longer in HIV+ patients, with a time from onset of clinical signs and symptoms to diagnosis of 22 weeks vs 8 weeks in HIV-, which very likely impacts mortality.
The disseminated clinical form in the HIV+ group was significantly more frequent than in the HIV- group (76.9% vs 35.2%). Hepatosplenomegaly, splenomegaly, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia were significantly more frequently found in HIV+ patients and should alert clinicians about histoplasmosis. Thrombocytopenia was not a feature of histoplasmosis in our series, differently from others[
11], although it had a near association to death in our multivariate analysis.
In Brazil, in 2021, 28% and 17% of people diagnosed with HIV had a first CD4 count of less than 200 cells/mm³ and 100 cells/mm³, respectively[
12]. The vast majority of HIV-infected individuals with histoplasmosis in INI were not taking ART: a proportion had stopped HIV treatment (18.5%) and many were naïve to antiretroviral therapy (41.5%), and the median CD4+ was 70 cells/mm3, indicating severe immunological impairment. This finding is like other series[
11,
13,
14]. It is well established that histoplasmosis is an opportunistic and overwhelming disease in patients with very low CD4 counts, and therefore, we believe that screening is necessary and desirable in immunosuppressed patients, particularly those with CD4+<100, for both cryptococcosis and histoplasmosis, the most important systemic mycoses in HIV/AIDS. No systematic screening was done in this retrospective series, but in patients who were ill, Western blot was requested, and, compared to the gold standard of culture results, it had a sensitivity around 90%, while double immunodiffusion, had a lower sensitivity, 65%, in HIV+ patients[
15]. Although culture results, especially from blood or bone marrow in the disseminated forms, are the gold diagnostic standard, a serious problem is the prolonged time required for the completion of cultures with identification of
H. capsulatum, which results in a risk of higher mortality for both groups. The time for the finalization of the culture results was approximately 13 days, directly impacting the outcome due to the consequent delay in the treatment with a specific antifungal. Thus, it is necessary to urgently make available other techniques that provide faster, more sensitive and specific results; in our service, we had WB as tool with internal validation[
15]. In the year 2020, with the COVID-19 pandemic, our institution acquired the urinary antigen test, but this was not available to the patients studied in this report.
WB is an excellent tool that results in a highly probable diagnosis of histoplasmosis. In our study, a sensitivity of 90% in HIV+ and 93.5% in HIV- was observed with the WB test. Details of the cases where the WB showed a false negative result, that is, positive culture for Hc and negative WB, were sought. There were 7 cases in total, 6 being HIV positive and 1 HIV negative. This group of patients warns us about the severity of immunosuppression in HIV-negative patients, especially in patients with leprosy reaction using high doses of corticosteroid therapy as well as HIV+ that may not express specific anti-Histoplasma antibodies. WB for HC was later re-tested in the two surviving HIV+ patients, who by then had CD4 counts >200, and was still negative (unpublished results). It is worth noting that in clinical practice, when faced with a case with nonspecific but suggestive clinical and laboratory features of histoplasmosis, empirical antifungal treatment should be considered in the severely ill patient even if the WB result or urinary antigen test is non- reagent, while waiting for culture results. Urinary antigen testing for Hc has been shown to be more than 90% sensitive and specific in HIV positive patients [9, 14, 16].
We highlight that co-infection with tuberculosis was documented in 1/5 of our HIV+ patients, which means that one should systematically investigate tuberculosis in patients with histoplasmosis, and vice versa, especially in those with severe immunodeficiency[
17]. In 2 recent Brazilian series, concomitant TB and histoplasmosis was documented in a similar proportion of cases. In Boigues et al., 6/23 (26%) HIV positive patients included in a hospital-based cohort in Center-West Brazil had concomitant TB-Hc[
18], while in a multicenter prospective study in the 5 regions of Brazil, tuberculosis was diagnosed in 19/123 (15.4%) of probable/proven cases of histoplasmosis[
9]. Blood cultures and bone marrow cultures are useful to diagnose disseminated tuberculosis and histoplasmosis. High sensitivity is observed when samples are processed using tests based on lysis systems (>80% sensitivity) [
19]. Although histoplasmosis and TB co-infection should always be investigated, this may not always occur due to the lack of trained clinical and laboratory personnel to make definite diagnoses.
In the specific diagnosis of histoplasmosis, there was statistical significance of a higher frequency of positive blood culture (HIV+ 32.3% vs HIV- 11.8%, p= 0.025) and positive bone marrow culture (HIV+ 36.9% vs HIV- 8.8%) for H. capsulatum, which should encourage early bone marrow biopsy in HIV+ patients with fever, wasting syndrome and hematological changes.
We found alarming data on hospitalization rate, severity of cases with need of referral to the ICU, length of stay, and death. Hospitalization rate was more than 70% in cases of HIV and histoplasmosis, approximately a quarter of which required intensive care/vasoactive drugs/mechanical ventilation and close to half (46%) had a fatal outcome in our series. The mortality rate of HIV-histoplasmosis coinfection was 17.7% and 13.6% in patients without HIV according to Caceres et al[
11]. In the prospective analysis of Falci et al, overall mortality at 30 days was 22.1%, and it was lower in those who had the urinary antigen test performed (14.3%)[
9]. Our retrospective study shows a disastrous scenario within a specialized service in infectious diseases previously to the availability of the urinary antigen test. Mortality in the HIV-negative group was lower, although of the few patients who were hospitalized, 3/4 (75%) died, and in one of them histoplasmosis was not even suspected, and specific antifungal treatment was not given. On univariate analysis for risks associated to death, we found leukopenia and anemia as risk factors, which probably reflect the disseminated form of the disease in advanced immunosuppression: all deaths in our study occurred in patients with the disseminated form. Multivariate analysis did not allow for further conclusions, given the small sample size, although it did suggest thrombocytopenia was a risk factor for death.
The main limitations of our study were i) its retrospective nature , resulting in some loss of information, ii) failure to follow up some patients at INI after diagnosis and iii)failure to perform necropsy in our service, which possibly resulted in not performing post-mortem diagnoses. A multivariate analysis for risk factors associated to death was not contributory due to the small sample size.
Finally, we acknowledge that a mortality rate of 46.1% in those coinfected with HIV and histoplasmosis in a service specialized in infectious disease such as INI, in a metropolis in Southeast Brazil, reveals a public health problem that is probably even greater in non-specialized services, since Brazil is an endemic country for this mycosis. The availability of the urinary antigen test will hopefully result in a better performance in the near future.
5. Conclusions
Histoplasmosis is a neglected endemic disease, and it should be remembered especially among the group of patients who present a compatible clinical presentation and have underlying immunosuppression caused by HIV or by immunosuppressive drugs. In this subset of patients, it is an aggressive systemic mycosis, which often presents in a disseminated form and results in severe damage and death before laboratory confirmation. Therefore, there is the urgent need to build local capacity for mycology diagnosis so that patients are managed appropriately. Not less importantly, we need to educate health professionals on histoplasmosis, to improve their capabilities to suspect and diagnose this severe condition. The lack of an epidemiological history compatible with histoplasmosis and the delay in diagnosing this disease, which has features similar to tuberculosis, are risk factors for higher mortality. The availability of composite highly sensitive diagnostic laboratory tests, rapidity in the results and adequate treatment will favor the survival of those infected by this mycosis.
Strategies need to be implemented by the public health systems in low- and middle-income endemic countries. In Brazil, a first step in this direction has been the compulsory notification of histoplasmosis since 2021 by two of its member states, and a further step shall be extending this to all states, as well as providing public health units with the urinary antigen test for histoplasma.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Table S1: Clinical specimens collected for culture in patients diagnosed with histoplasmosis, INI 2000-2018.; Table S2: Temporal comparison between obtaining the result of the culture and the date of hospitalization until death, INI 2000-2018.
Funding
RMZ-O is partially supported by grants by CNPq 308315/2021-9 and by FAPERJ E-26/200.381/2023.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the INI Research Ethics Committee; under CAAE number 98094718.4.0000.5262, on December 10, 2018.
Acknowledgments
We thank Julio Castro Alves de Lima e Silva for statistical analysis, and we thank all colleagues involved in patient care.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bahr NC, Antinori S, Wheat LJ, et al. Histoplasmosis infections worldwide: thinking outside of the Ohio River Valley. Curr Trop Med Rep 2015; 2: 70–80.
- Wheat, L.J. et al. Histoplasmosis. Infect Dis Clin N Am, v. 30 p. 207-227, 2016.
- Queiroz-Telles F, Fahal AH, Falci DR, Caceres DH, Chiller T, Pasqualotto AC. Neglected endemic mycoses. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017; 17:e367-77.
- Goodwin, R.A.; Lloyd, J.E.; Des Prez, R.M. Histoplasmosis in normal hosts. Medicine, v. 60, n. 4, p 231-266, 1981.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for managing advanced HIV disease and rapid initiation of antiretroviral therapy. 2017. https://www.who.int/hiv/pub/toolkits/advanced-HIV-disease-policy/en/.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Current Trends Update on Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) - United States. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, v. 35, 757-760,765-756. 1986.
- https://brasilsus.com.br/index.php/pdf/resolucao-ses-no-2485/ RESOLUÇÃO SES Nº 2485 DE 18 DE OUTUBRO DE 2021. DISPÕE SOBRE A RELAÇÃO DE DOENÇAS E AGRAVOS DE NOTIFICAÇÃO COMPULSÓRIA E VIGILÂNCIA SENTINELA E REVOGA A RESOLUÇÃO SES Nº 1.864 DE 25 DE JUNHO DE 2019.
- UNAIDS. Global HIV Statistics 2021. Available in: https://unaids.org.br/estatisticas.Acess in: January 30, 2022.
- Falci DR, Monteiro AA, Braz Caurio CF, Magalhães TCO, Xavier MO, Basso RP, et al. Histoplasmosis, An Underdiagnosed Disease Affecting People Living With HIV/AIDS in Brazil: Results of a Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study Using Both Classical Mycology Tests and Histoplasma Urine Antigen Detection. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019 Apr 13;6(4):ofz073. [CrossRef]
- Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas da Amazônia (INPA). Avaliable in: http://portal.inpa.gov.br/index.php/ultimas-noticias/3431-manaussedia-neste-fim-de-semana-o-ii-encontro-regional-de-histoplasmose-nas-americas.
- Hoyos Pulgarin JA, Alzate Piedrahita JA, Moreno Gómez GA, Sierra Palacio JF, Ordoñez KM, Arias Ramos D. Closing gaps in histoplasmosis: clinical characteristics and factors associated with probable/histoplasmosis in HIV/AIDS hospitalized patients, a retrospective cross-sectional study in two tertiary centers in Pereira, Colombia. AIDS Res Ther. 2021 Aug 12;18(1):51. [CrossRef]
- Relatório de Monitoramento Clínico do HIV 2021. Ministério da Saúde. Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde Departamento de Doenças de Condições Crônicas e Infecções Sexualmente Transmissíveis. Available in: file:///C:/Users/mauricio.neto/Downloads/internet_relatorio_de_monitoramento_clinico_do_hiv_2021_final_06.07.22_002.pdf. (accessed on 01 february 2023).
- Ramos IC, Soares YC, Damasceno LS, Libório MP, Farias LABG, Heukelbach J, et al. Predictive factors for disseminated histoplasmosis in AIDS patients with fever admitted to a reference hospital in Brazil. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2018 Jul-Aug;51(4):479-484. [CrossRef]
- Medina N, Rodriguez-Tudela JL, Aguirre L, Salazar LR, Gamboa O, Bonilla O, et al. Incidence of Histoplasmosis in a Cohort of People with HIV: From Estimations to Reality. Microorganisms. 2021 Dec 16;9(12):2596. [CrossRef]
- Almeida M de A, Pizzini CV, Damasceno LS, Muniz M de M, Almeida-Paes R, Peralta RH, et al. Validation of Western blot for Histoplasma capsulatum antibody detection assay. BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Feb 24; 16:87. [CrossRef]
- Vidal JE, Werlang PC, Muniz BM, Rego CM, Barbalho RE, Baptista AM, et al. Combining urine antigen and blood polymerase chain reaction for the diagnosis of disseminated histoplasmosis in hospitalized patients with advanced HIV disease. Med Mycol. 2021; 59:916–22. [CrossRef]
- Kuate NPM, Ekeng BE, Kwizera R, Mandengue C, Bongomin F. Histoplasmosis overlapping with HIV and tuberculosis in sub-Saharan Africa: challenges and research priorities. Ther Adv Infectious Dis 2021, Vol. 8: 1–7.
- Boigues, B.C.S.; Paniago, A.M.M.; Lima, G.M.E.; Nunes, M.O.; Uehara, S.N.O. Clinical outcomes and risk factors for death from disseminated histoplasmosis in patients with AIDS who visited a high-complexity hospital in Campo Grande, MS, Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2018, 51, 155–161.
- Caceres DH and Valdes A. Histoplasmosis and Tuberculosis Co-Occurrence in People with Advanced HIV. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 73;. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).