Submitted:
24 April 2023
Posted:
25 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Background
2. NFAT Molecular Pathway
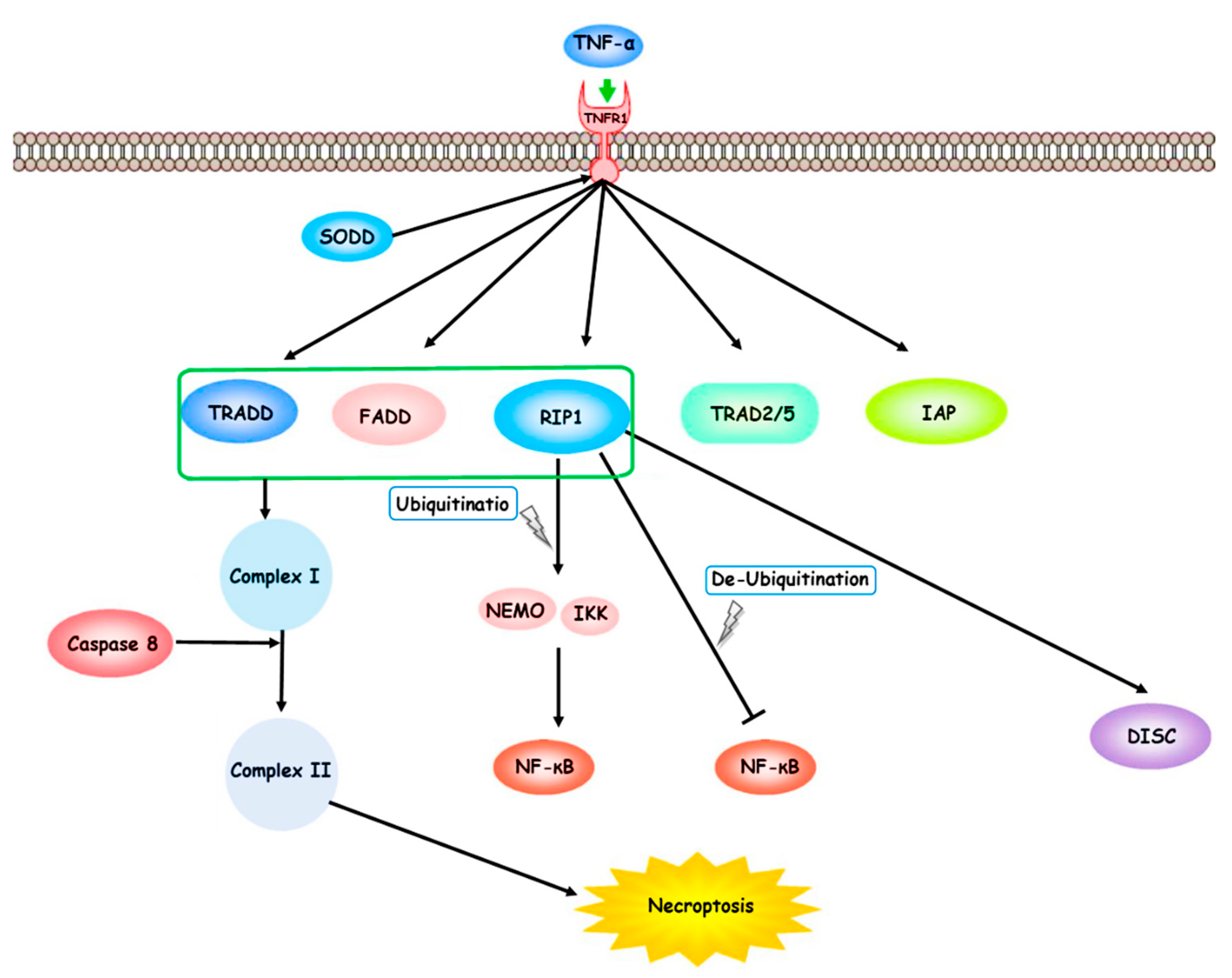
3. Necroptosis
4. Myocardial Injuries and the Role of Necroptosis
5. COVID-19 and Necroptosis
6. Conclusive Statement
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, Ensheng, Hongru Du, and Lauren Gardner. “An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time” The Lancet infectious diseases 20, no. 5 (2020): 533-534.
- Babapoor-Farrokhran, Savalan, Deanna Gill, Jackson Walker, Roozbeh Tarighati Rasekhi, Behnam Bozorgnia, and Aman Amanullah. “Myocardial injury and COVID-19: Possible mechanisms” Life Sciences (2020): 117723.
- Bonow, Robert O., Gregg C. Fonarow, Patrick T. O’Gara, and Clyde W. Yancy. “Association of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) with myocardial injury and mortality”JAMA cardiology (2020).
- Shi S, Qin M, Shen B, et al. association of cardiac injury with mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 inWuhan, China. JAMA Cardiol. Published online March 25, 2020.
- Guo T, Fan Y, Chen M, et al. Cardiovascular implications of fatal outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Cardiol. Published online March 27, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Yang C, Jin Z. An acute respiratory infection runs into the most common noncommunicable epidemic—COVID-19 and cardiovascular diseases. JAMA Cardiol. Published online March 25, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M.A. Crackower, R. Sarao, G.Y. Oudit, C. Yagil, I. Kozieradzki, S.E. Scanga, A.J. Oliveira-dos-Santos, J. da Costa, L. Zhang, Y. Pei, J. Scholey, C.M. Ferrario, A.S. Manoukian, M.C. Chappell, P.H. Backx, Y. Yagil, J.M. Penninger, Angiotensinconverting enzyme 2 is an essential regulator of heart function, Nature 417 (2002) 822–828. [CrossRef]
- K. Yamamoto, M. Ohishi, T. Katsuya, N. Ito, M. Ikushima, M. Kaibe, Y. Tatara, A. Shiota, S. Sugano, S. Takeda, H. Rakugi, T. Ogihara, Deletion of angiotensinconverting enzyme 2 accelerates pressure overload-induced cardiac dysfunction by increasing local angiotensin II, Hypertension 47 (2006) 718–726. [CrossRef]
- G.Y. Oudit, Z. Kassiri, C. Jiang, P.P. Liu, S.M. Poutanen, J.M. Penninger, J. Butany, SARS-coronavirus modulation of myocardial ACE2 expression and inflammation in patients with SARS, Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 39 (2009) 618–625. [CrossRef]
- G.Y. Oudit, Z. Kassiri, M.P. Patel, M. Chappell, J. Butany, P.H. Backx, R.G. Tsushima, J.W. Scholey, R. Khokha, J.M. Penninger, Angiotensin II-mediated oxidative stress and inflammation mediate the age-dependent cardiomyopathy in ACE2 null mice, Cardiovasc. Res. 75 (2007) 29–39. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Ying-Ying, Yi-Tong Ma, Jin-Ying Zhang, and Xiang Xie. “COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system” Nature Reviews Cardiology 17, no. 5 (2020): 259-260.
- Ahmad, Sheikh Fayaz, Mushtaq Ahmad Ansari, Khairy MA Zoheir, Saleh A. Bakheet, Hesham M. Korashy, Ahmed Nadeem, Abdelkader E. Ashour, and Sabry M. Attia. “Regulation of TNF-α and NF-κB activation through the JAK/STAT signaling pathway downstream of histamine 4 receptor in a rat model of LPS-induced joint inflammation” Immunobiology 220, no. 7 (2015): 889-898.
- AbdelMassiha, Antoine Fakhry, David Ramzyc, Lauren Nathanc, Silvia Azizc, Mirette Ashrafc, Nourhan Hatem Youssefc, Nouran Hafezc, Rana Saeedc, and Hala Aghaa. “Possible molecular and paracrine involvement underlying the pathogenesis of COVID-19 cardiovascular complications” pathogenesis 2, no. 8 (2020): 10-15. [CrossRef]
- Booz GW, Day JN, Baker KM. Interplay between the cardiac renin angiotensin system and JAK-STAT signaling: role in cardiac hypertrophy, ischemia/ reperfusion dysfunction, and heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2002; 34:1443–1453. [CrossRef]
- del Arco, Pablo Gómez, Sara Martı́nez-Martı́nez, Janet Lynn Maldonado, Inmaculada Ortega-Pérez, and Juan Miguel Redondo. “A role for the p38 MAP kinase pathway in the nuclear shuttling of NFATp.” Journal of Biological Chemistry 275, no. 18 (2000): 13872-13878.
- Haylett, Romney S., Norbert Koch, and Lothar Rink. “MHC class II molecules activate NFAT and the ERK group of MAPK through distinct signaling pathways in B cells” European journal of immunology 39, no. 7 (2009): 1947-1955.
- 10 Ho, A. M., Jain, J., Rao, A. and Hogan, P. G., Expression of the transcription factor NFATp in a neuronal cell line and in the murine nervous system. J. Biol. Chem. 1994. 269: 28181–28186. [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, N. R., Maizel, A. L., Wang, F. and Sharma, S., Comparative analysis of NFAT (Nuclear factor of activated T cells) complex in human T and B lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1993. 268: 14285–14293. [CrossRef]
- Aramburu, J., Azzoni, L., Rao, A. and Perussia, B., Activation and expression of the nuclear factors of activated T cells, NFATp and NFATc, in human natural killer cells: regulation upon CD16 ligand binding. J. Exp. Med. 1995. 182: 801–810. [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, L. E. and McCloskey, M. A., Fc epsilon RI-mediated induction of nuclear factor of activated T-cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1995. 270: 16333–16338.
- Shaw, J. P. , Utz, P. J., Durand, D. B., Toole, J. J., Emmel, E. A. and Crabtree, G. R., Identification of a putative regulator of early T cell activation genes. Science 1988. 241: 202–205. [CrossRef]
- Winslow, M. M. , Gallo, E. M., Neilson, J. R. and Crabtree, G. R., The calcineurin phosphatase complex modulates immunogenic B cell responses. Immunity 2006. 24: 141–152. [CrossRef]
- Barrington, R. A. , Borde, M. Rao, A., Caroll, M. C., Involvement of NFAT1 in B cell self-tolerance. J. Immunol. 2006. 177: 1510–1515.
- Peng, S. L. , Gerth, A. J., Ranger, A. M. and Glimcher, L. H., NFATc1 and NFATc2 together control both T and B cell activation and differentiation. Immunity 2001. 14: 13–20. [CrossRef]
- Tsatsanis, Christos, Christos Patriotis, and Philip N. Tsichlis. “Tpl-2 induces IL-2 expression in T-cell lines by triggering multiple signaling pathways that activate NFAT and NF-κB” Oncogene 17, no. 20 (1998): 2609-2618.
- Srivastava, Rakesh K., Carl Y. Sasaki, J. Marie Hardwick, and Dan L. Longo. “Bcl-2–mediated drug resistance: inhibition of apoptosis by blocking nuclear factor of activated T lymphocytes (NFAT)-induced Fas ligand transcription” The Journal of experimental medicine 190, no. 2 (1999): 253-266.
- Biswas, Rajat S., Hyuk J. Cha, J. Marie Hardwick, and Rakesh K. Srivastava. “Inhibition of drug-induced Fas ligand transcription and apoptosis by Bcl-XL” Molecular and cellular biochemistry 225, no. 1-2 (2001): 7-20.
- Hao, Shengli, Tomohiro Kurosaki, and Avery August. “Differential regulation of NFAT and SRF by the B cell receptor via a PLCγ–Ca2+-dependent pathway” The EMBO Journal22, no. 16 (2003): 4166-4177.
- Fiers W, Beyaert R, Boone E, et al. TNF-induced intracellular signaling leading to gene induction or to cytotoxicity by necrosis or by apoptosis. J Inflamm 1995;47:67–75.
- Kalai M, Van Loo G, Vanden Berghe T, et al. Tipping the balance between necrosis and apoptosis in human and murine cells treated with interferon and dsDNA. Cell Death Differ 2002;9:981–94.
- Hitomi J, Christofferson DE, Ng A, et al. Identification of a molecular signaling network that regulates a cellular necrotic cell death pathway. Cell 2008;135:1311–23. [CrossRef]
- Chen G, GoeddelDV. TNF-R1 signaling: a beautiful pathway. Science2002;296:1634–5. [CrossRef]
- Carswell EA, Old LJ, Kassel RL, Green S, Fiore N, Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1975;72:3666–70. [CrossRef]
- Laster SM, Wood JG, Gooding LR. Tumor necrosis factor can induce both apoptotic and necrotic forms of cell lysis. J Immunol 1988;141:2629–34.
- Andera, L. Signaling activated by the death receptors of the TNFR family. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub 2009;153:173–80.
- Chan FK, Chun HJ, Zheng L, Siegel RM, Bui KL, Lenardo MJ. A domain in TNF receptors that mediates ligand-independent receptor assembly and signaling. Science 2000;288:2351–4. [CrossRef]
- Wertz IE, Dixit VM. Ubiquitin-mediated regulation of TNFR1 signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2008;19:313–24. [CrossRef]
- Mahoney DJ, Cheung HH, Mrad RL, et al. Both cIAP1 and cIAP2 regulate TNFalpha-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008;105:11778–83.
- Varfolomeev E, Goncharov T, Fedorova AV, et al. c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 are critical mediators of tumor necrosis factor alpha(TNFalpha)- induced NF-kappaB activation. J Biol Chem 2008;283:24295–9.
- Kovalenko A, Chable-Bessia C, Cantarella G, Israel A, Wallach D,Courtois G. The tumor suppressor CYLD negatively regulates NF-κB signaling pathway by deubiquitination. Nature 2003;424:801–5.
- Alameda JP, Moreno-Maldonado R, Navarro M, et al. An inactivating CYLD mutation promotes skin tumor progression by conferring enhanced proliferative, survival and angiogenic properties to epidermal cancer cells. Oncogene 2010;29:6522–32. [CrossRef]
- Urbanik T, Kohler BC, Boger RJ, et al. Down-regulation of CYLD as a trigger for NF-k activation and a mechanism of apoptotic resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol 2011;38:121–31.
- Wertz IE, O’Rourke KM, Zhou H, et al. deubiquitination and ubiquitin ligase domains of A20 downregulate NF-κB signalling. Nature 2004;430:694–9.
- Shembade N, Ma A, Harhaj EW. Inhibition of NF-κB signaling by A20 through disruption of ubiquitin enzyme complexes. Science 2010;327:1135–9.
- Ea CK, Deng L, Xia ZP, Pineda G, Chen ZJ. Activation of IKK by TNF requires site-specific ubiquitination of RIP1 and polyubiquitin by NEMO. Mol Cell 2006;22:245–57.
- Wong WW, Gentle IE, Nachbur U, Anderton H, Vaux DL, Silke J. RIPK1 is not essential for TNFR1-induced activation of NF-κB. Cell Death Differ 2010;17:482–7.
- Lee TH, Shank J, Cusson N, Kelliher MA. The kinase activity of Rip1 is not required for tumor necrosis factor--induced IkB kinase or p38 MAP kinase activation or for the ubiquitination of Rip1 by Traf2. J Biol Chem 2004;279:33185–91.
- Schneider-BrachertW, Tchikov V, Merkel O, et al. Inhibition of TNF receptor 1 internalization by adenovirus 14.7K as a novel immune escape mechanism. J Clin Invest 2006;116:2901–13.
- Bertrand MJ, Milutinovic S, Dickson KM, et al. cIAP1 and cIAP2 facilitate cancer cell survival by functioning as E3 ligases that promotes RIP1 ubiquitination. Mol Cell 2008;30:689–700. [CrossRef]
- Lin Y, Choksi S, Shen HM, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-induced nonapoptotic cell death requires receptor-interacting protein-mediated cellular reactive oxygen species accumulation. J Biol Chem 2004;279:10822–8. [CrossRef]
- Chan FK, Shisler J, Bixby JG, et al. A role for tumor necrosis factor receptor-2 and receptor-interacting protein in programmed necrosis and antiviral responses. J Biol Chem 2003;278:51613–21. [CrossRef]
- Osborn SL, Diehl G, Han SJ, et al. Fas-associated death domain (FADD) is a negative regulator of T-cell receptor-mediated necroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010;107:13034–9. [CrossRef]
- Ermolaeva MA, Michallet MC, Papadopoulou N, et al. Function of TRADD in tumor necrosis factor 1 signaling and in TRIF-dependent inflammatory responses. Nat Immunol 2008;9:1037–46. [CrossRef]
- Wang L, Du F, Wang X. TNF-alpha induced two distinct caspase-8 activation pathways. Cell 2008;133:693–703. [CrossRef]
- Kim JW, Choi EJ, Joe CO. Activation of death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) by pro-apoptotic C-terminal fragment of RIP. Oncogene 2000;19:4491–9. [CrossRef]
- Feng S, Yang Y, Mei Y, et al. Cleavage of RIP3 inactivates its caspaseindependent apoptosis pathway by removal of kinase domain. Cell Signal 2007;19:2056–67. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Wei, Peng Liu, and Jianyong Li. “Necroptosis: an emerging form of programmed cell death” Critical reviews in oncology/hematology 82, no. 3 (2012): 249-258.
- World Health Organization. The top 10 causes of death. Fact sheet N8 310, 2014.
- Sugano M, Koyanagi M, Tsuchida K, Hata T, Makino N. In vivo gene transfer of soluble TNF-alpha receptor 1 alleviates myocardial infarction. FASEB J 2002;16:1421–1422. [CrossRef]
- Wollert KC, Heineke J, Westermann J, Ludde M, Fiedler B, Zierhut W, Laurent D, Bauer MK, Schulze-Osthoff K, Drexler H. The cardiac Fas (APO-1/CD95) Receptor/ Fas ligand system: relation to diastolic wall stress in volume-overload hypertrophy in vivo and activation of the transcription factor AP-1 in cardiac myocytes. Circulation 2000;101:1172–1178.
- Bialik S, Geenen DL, Sasson IE, Cheng R, Horner JW, Evans SM, Lord EM, Koch CJ, Kitsis RN. Myocyte apoptosis during acute myocardial infarction in the mouse localizes to hypoxic regions but occurs independently of p53. J Clin Invest 1997;100:1363–1372. [CrossRef]
- Sun M, DawoodF,WenWH,Chen M, Dixon I, KirshenbaumLA, Liu PP. Excessive tumor necrosis factor activation after infarction contributes to susceptibility of myocardial rupture and left ventricular dysfunction. Circulation 2004;110:3221–3228. [CrossRef]
- Kung G, Konstantinidis K, Kitsis RN. Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, in the heart. Circ Res 2011;108:1017–1036.
- Dorn GW, II. Apoptotic and non-apoptotic programmed cardiomyocyte death in ventricular remodelling. Cardiovasc Res 2009;81:465–473.
- Declercq W, Vanden Berghe T, Vandenabeele P. RIP kinases at the crossroads of cell death and survival. Cell 2009;138:229–232. [CrossRef]
- He S, Wang L, Miao L, Wang T, Du F, Zhao L, Wang X. Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha. Cell 2009;137: 1100–1111. [CrossRef]
- Zhang DW, Shao J, Lin J, Zhang N, Lu BJ, Lin SC, Dong MQ, Han J. RIP3, an energy metabolism regulator that switches TNF-induced cell death from apoptosis to necrosis. Science 2009;325:332–336. [CrossRef]
- Christofferson DE, Yuan J. Necroptosis as an alternative form of programmed cell death. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2010;22:263–268. [CrossRef]
- Cho YS, Challa S, Moquin D, Genga R, Ray TD, Guildford M, Chan FK. Phosphorylationdriven assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced inflammation. Cell 2009;137:1112–1123. [CrossRef]
- Welz PS, Wullaert A, Vlantis K, Kondylis V, Fernandez-Majada V, Ermolaeva M, Kirsch P, Sterner-Kock A, van Loo G, Pasparakis M. FADD prevents RIP3-mediated epithelial cell necrosis and chronic intestinal inflammation. Nature 2011;477:330–334. [CrossRef]
- Lim SY, Davidson SM, Mocanu MM, YellonDM, Smith CC. The cardioprotective effect of necrostatin requires the cyclophilin-D component of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 2007;21:467–469. [CrossRef]
- Oerlemans MI, Liu J, Arslan F, den Ouden K, van Middelaar BJ, Doevendans PA, Sluijter JP. Inhibition of RIP1-dependent necrosis prevents adverse cardiac remodeling after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion in vivo. Basic Res Cardiol 2012;107:270. [CrossRef]
- Smith CC, Davidson SM, Lim SY, Simpkin JC, Hothersall JS, Yellon DM. Necrostatin: a potentially novel cardioprotective agent. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 2007;21:227–233. [CrossRef]
- Luedde M, Lutz M, Carter N, Sosna J, Jacoby C, Vucur M, et al. RIP3, a kinase promoting necroptotic cell death, mediates adverse remodelling after myocardial infarction. Cardiovascular research. 2014;103(2):206-16. [CrossRef]
- Kaiser WJ, Upton JW, Long AB, Livingston-Rosanoff D, Daley-Bauer LP, Hakem R, Caspary T, Mocarski ES. RIP3 mediates the embryonic lethality of caspase-8-deficient mice. Nature 2011;471:368–372. [CrossRef]
- Oberst A, Dillon CP, Weinlich R, McCormick LL, Fitzgerald P, Pop C, Hakem R, Salvesen GS, Green DR. Catalytic activity of the caspase-8-FLIP(L) complex inhibits RIPK3-dependent necrosis. Nature 2011;471:363–367.
- Zhang, Ting, Yan Zhang, Mingyao Cui, Li Jin, Yimei Wang, Fengxiang Lv, Yuli Liu et al.””” ““CaMKII is a RIP3 substrate mediating ischemia-and oxidative stress–induced myocardial necroptosis” Nature medicine 22, no. 2 (2016): 175-182.
- Liu, Xiaojuan, Chao Zhang, Chi Zhang, Jingjing Li, Wanwan Guo, Daliang Yan, Chen Yang et al.””” ““Heat shock protein 70 inhibits cardiomyocyte necroptosis through repressing autophagy in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury” In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology-Animal 52, no. 6 (2016): 690-698.
- Yang, Tianshu, Changyu Cao, Jie Yang, Tianqi Liu, Xin Gen Lei, Ziwei Zhang, and Shiwen Xu. “miR-200a-5p regulates myocardial necroptosis induced by Se deficiency via targeting RNF11” Redox biology 15 (2018): 159-169.
- Zhou, Z. , Zhang, Y., Lin, L., Zhou, J., 2018a. Apigenin suppresses the apoptosis of H9C2 rat cardiomyocytes subjected to myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via upregulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 18 (2), 1560–1570. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P. , Hu, S., Jin, Q., Li, D., Tian, F., Toan, S., Li, Y., Zhou, H., Chen, Y., 2018. Ripk3 promotes ER stress-induced necroptosis in cardiac IR injury: a mechanism involving calcium overload/XO/ROS/mPTP pathway. Redox. Biol. 16, 157–168. [CrossRef]
- Dovey, C.M. , Diep, J., Clarke, B.P., Hale, A.T., McNamara, D.E., Guo, H., Brown Jr., N.W., Cao, J.Y., Grace, C.R., Gough, P.J., Bertin, J., Dixon, S.J., Fiedler, D., Mocarski, E.S.,Kaiser, W.J., Moldoveanu, T., York, J.D., Carette, J.E., 2018. MLKL requires the inositol phosphate code to execute necroptosis. Mol. Cell. 70 (5), 936–948.
- Dmitriev, Y. ,.V., Minasian, S.M., Demchenko, E.A., Galagudza, M.M., 2013. Study of cardioprotective effects of necroptosis inhibitors on isolated rat heart subjected to global ischemia-reperfusion. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 155 (2), 245–248.
- Koshinuma, S. , Miyamae, M., Kaneda, K., Kotani, J., Figueredo, V.M., 2014. Combination of necroptosis and apoptosis inhibition enhances cardioprotection against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Anesth. 28 (2), 235–241. [CrossRef]
- Bai, Jiannan, Qingchao Wang, Jiaxin Qi, Hongqiang Yu, Cong Wang, Xiaowei Wang, Yanru Ren, and Fude Yang. “Promoting effect of baicalin on nitric oxide production in CMECs via activating the PI3K-AKT-eNOS pathway attenuates myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury” Phytomedicine 63 (2019): 153035.
- Smith CA, Williams GT, Kingston R, Jenkinson EJ, Owen JJ. Apoptosis. Nature. 1989;338:10.
- Kitanaka C, Kuchino Y. Caspase-independent programmed cell death with necrotic morphology. Cell Death Differ. 1999;6:508-15. [CrossRef]
- Declercq W, Vanden Berghe T, Vandenabeele P. RIP kinases at the crossroads of cell death and survival. Cell. 2009;138:229-32. [CrossRef]
- Christofferson DE, Li Y, Hitomi J, Zhou W, Upperman C, Zhu H, Gerber SA, Gygi S, Yuan J. A novel role for RIP1 kinase in mediating TNFα production. Cell Death Dis. 2012;3:e320. [CrossRef]
- Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap P, Mizushima N, Cuny GD, Mitchison TJ, Moskowitz MA, Yuan J. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol. 2005;1:112-9.
- Degterev A, Hitomi J, Germscheid M, ”” Ch’en IL, Korkina O, Teng X, Abbott D, Cuny GD, Yuan C, Wagner G, Hedrick SM, Gerber SA, Lugovskoy A, Yuan J. Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of necrostatins. Nat Chem Biol. 2008;4:313-21.
- Koshinuma, Shizuka, Masami Miyamae, Kazuhiro Kaneda, Junichiro Kotani, and Vincent M. Figueredo. “Combination of necroptosis and apoptosis inhibition enhances cardioprotection against myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury” Journal of anesthesia 28, no. 2 (2014): 235-241.
- Cuadrado, Antonio, Marta Pajares, Cristina Benito, José Jiménez-Villegas, Maribel Escoll, Raquel Fernández-Ginés, Angel J. Garcia Yagüe et al. “Can activation of NRF2 be a strategy against COVID-19?.” Trends in Pharmacological Sciences (2020). [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, R. and Jaiswal, AK (1998) Nrf2 and Nrf1 in association with Jun proteins regulate antioxidant response element-mediated expression and coordinated induction of genes encoding detoxifying enzymes. Oncogene 17 (24), 3145-56.
- Cuadrado, A. et al. (2019)Therapeutic targeting of the NRF2 and KEAP1 partnership in chronic diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 18 (4), 295-317. [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado, A. et al. (2018) Transcription Factor NRF2 as a Therapeutic Target for Chronic Diseases: A Systems Medicine Approach. Pharmacol Rev 70 (2), 348-383. [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.D. and Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. (2014) The Nrf2 regulatory network provides an interface between redox and intermediary metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci 39 (4), 199-218. [CrossRef]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. et al. (2002) Direct evidence that sulfhydryl groups of Keap1 are the sensors regulating induction of phase 2 enzymes that protect against carcinogens and oxidants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99 (18), 11908-13. [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, P.S. et al. (2019) Dysregulation of Nrf2/Keap1 Redox Pathway in Diabetes Affects Multipotency of Stromal Cells. Diabetes 68 (1), 141-155.
- Schmidlin, C.J. et al. (2019) Redox regulation by NRF2 in aging and disease. Free Radic Biol Med 134, 702-707. [CrossRef]
- Wu, C. et al. (2020) Risk Factors Associated With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern Med. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q. et al. (2019) Role of Nrf2 and Its Activators in Respiratory Diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, 7090534. [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Herrera, M. et al. (2015) Common variants of NFE2L2 gene predisposes to acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with severe sepsis. Crit Care 19, 256. [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.C. et al. (2010) Functional haplotypes in the promoter region of transcription factor Nrf2 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Dis Markers 28 (3), 185-93.
- Kobayashi, E.H. et al. (2016) Nrf2 suppresses macrophage inflammatory response by blocking pro-inflammatory cytokine transcription. Nat Commun 7, 11624.
- Mills, E.L. et al. (2018) Itaconate is an anti-inflammatory metabolite that activates Nrf2 via alkylation of KEAP1. Nature 556 (7699), 113-117.
- Ishii, T. and Mann, G.E. (2014) Redox status in mammalian cells and stem cells during culture in vitro: critical roles of Nrf2 and cystine transporter activity in the maintenance of redox balance. Redox Biol 2, 786-94. [CrossRef]
- Harvey, C.J. et al. (2011) Targeting Nrf2 signaling improves bacterial clearance by alveolar macrophages in patients with COPD and in a mouse model. Sci Transl Med 3 (78), 78ra32. [CrossRef]
- Seelige, R. et al. (2017) The ancient cytokine IL-17D is regulated by Nrf2 and mediates tumor and virus surveillance. Cytokine 91, 10-12. [CrossRef]
- Saddawi-Konefka, R. et al. (2016) Nrf2 Induces IL-17D to Mediate Tumor and Virus Surveillance. Cell Rep 16 (9), 2348-58. [CrossRef]
- Brune, B. et al. (2013) Redox control of inflammation in macrophages. Antioxid Redox Signal 19 (6), 595-637. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N. et al. (2020) A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med 382 (8), 727-733.
- Chen, Y. et al. (2020) Structure analysis of the receptor binding of 2019-nCoV. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. [CrossRef]
- Lopes, R.D. et al. (2020) Continuing versus suspending angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers: Impact on adverse outcomes in hospitalized patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARSCoV- 2)--The BRACE CORONA Trial. Am Heart J 226, 49-59. [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.K. and Griendling, K.K. (2007) Angiotensin II cell signaling: physiological and pathological effects in the cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292 (1), C82-97. [CrossRef]
- Magrone, T. et al. (2020) Focus on Receptors for Coronaviruses with Special Reference to Angiotensin-converting Enzyme 2 as a Potential Drug Target – A Perspective. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets.
- Zhao, S. et al. (2018) Nrf2 Deficiency Up-regulates Intrarenal Angiotensin- Converting Enzyme-2 and Angiotensin 1-7 Receptor Expression and Attenuates Hypertension and Nephropathy in Diabetic Mice. Endocrinology 159 (2), 836-852.
- Nakagawa, K. et al. (2016) Viral and Cellular mRNA Translation in Coronavirus- Infected Cells. Adv Virus Res 96, 165-192.
- Krahling, V. et al. (2009) Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus triggers apoptosis via protein kinase R but is resistant to its antiviral activity. J Virol 83 (5), 2298-309. [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, M. et al. (2010) The selective autophagy substrate p62 activates the stress responsive transcription factor Nrf2 through inactivation of Keap1. Nat Cell Biol 12 (3), 213-23. [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, K. et al. (2012) Keap1 degradation by autophagy for the maintenance of redox homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109 (34), 13561-6. [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.P. et al. (2006) Modulation of the unfolded protein response by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein. J Virol 80 (18), 9279-87. [CrossRef]
- Cullinan, S.B. et al. (2003) Nrf2 is a direct PERK substrate and effector of PERKdependent cell survival. Mol Cell Biol 23 (20), 7198-209. [CrossRef]
- Loo, Y.M. et al. (2008) Distinct RIG-I and MDA5 signaling by RNA viruses in innate immunity. J Virol 82 (1), 335-45. [CrossRef]
- Burdette, D.L. et al. (2011) STING is a direct innate immune sensor of cyclic di- GMP. Nature 478 (7370), 515-8. [CrossRef]
- Sun, L. et al. (2012) Coronavirus papain-like proteases negatively regulate antiviral innate immune response through disruption of STING-mediated signaling. PLoS One 7 (2), e30802. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. et al. (2014) SARS coronavirus papain-like protease inhibits the type I interferon signaling pathway through interaction with the STING-TRAF3-TBK1 complex. Protein Cell 5 (5), 369-81. [CrossRef]
- Acharya, D. et al. (2020) Dysregulation of type I interferon responses in COVID-19. Nat Rev Immunol. [CrossRef]
- Olagnier, D. et al. (2017) Activation of Nrf2 Signaling Augments Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Oncolysis via Autophagy-Driven Suppression of Antiviral Immunity. Mol Ther 25 (8), 1900-1916. [CrossRef]
- Olagnier, D. et al. (2018) Nrf2 negatively regulates STING indicating a link between antiviral sensing and metabolic reprogramming. Nat Commun 9 (1), 3506. [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, J.A. et al. (2017) Modulation of Antiviral Immunity by Heme Oxygenase- 1. Am J Pathol 187 (3), 487-493. [CrossRef]
- Koliaraki, V. and Kollias, G. (2011) A new role for myeloid HO-1 in the innate to adaptive crosstalk and immune homeostasis. Adv Exp Med Biol 780, 101-11.
- Bafna, K. et al. (2020) Structural Similarity of SARS-CoV2 M(pro) and HCV NS3/4A Proteases Suggests New Approaches for Identifying Existing Drugs Useful as COVID-19 Therapeutics. ChemRxiv.
- Baez-Santos, Y.M. et al. (2015) The SARS-coronavirus papain-like protease: structure, function and inhibition by designed antiviral compounds. Antiviral Res 115, 21-38.
- Zhu, Z. et al. (2010) Biliverdin inhibits hepatitis C virus nonstructural 3/4A protease activity: mechanism for the antiviral effects of heme oxygenase? Hepatology 52 (6), 1897-905.
- Fillebeen, C. et al. (2005) Iron inactivates the RNA polymerase NS5B and suppresses subgenomic replication of hepatitis C Virus. J Biol Chem 280 (10), 9049-57. [CrossRef]
- Fillebeen, C. and Pantopoulos, K. (2010) Iron inhibits replication of infectious hepatitis C virus in permissive Huh7.5.1 cells. J Hepatol 53 (6), 995-9.
- Gao, Y. et al. (2020) Structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from COVID-19 virus. Science. [CrossRef]
- Tung, W.H. et al. (2011) Enterovirus 71 induces integrin beta1/EGFR-Rac1- dependent oxidative stress in SK-N-SH cells: role of HO-1/CO in viral replication. J Cell Physiol 226 (12), 3316-29.
- Ma, Z. et al. (2017) Carbon monoxide and biliverdin suppress bovine viral diarrhea virus replication. J Gen Virol 98 (12), 2982-2992.
- Kalyanaraman, H. et al. (2018) Protein Kinase G Activation Reverses Oxidative Stress and Restores Osteoblast Function and Bone Formation in Male Mice With Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 67 (4), 607-623. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Jun. “Tackle the free radicals damage in COVID-19” Nitric Oxide (2020).
- T. Akaike, M. Suga, H. Maeda, Free radicals in viral pathogenesis: molecular mechanisms involving superoxide and NO, Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 217 (1) (1998) 64–73.
- D. Sun, et al., Clinical Features of Severe Pediatric Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan: a Single ”” Center’s Observational Study, World J Pediatr, 2020. [CrossRef]
- E. Prompetchara, C. Ketloy, T. Palaga, Immune responses in COVID-19 and potential vaccines: lessons learned from SARS and MERS epidemic, Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 38 (1) (2020) 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Y. Li, et al., Retrospective analysis of laboratory testing in 54 patients with severeor critical-type 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia, Lab Invest. 100 (6) (2020) 794–800.
- K.J. Huang, et al., An interferon-gamma-related cytokine storm in SARS patients, J. Med. Virol. 75 (2) (2005) 185–194.
- A.R. Vaz, et al., Pro-inflammatory cytokines intensify the activation of NO/NOS, JNK1/2 and caspase cascades in immature neurons exposed to elevated levels of unconjugated bilirubin, Exp. Neurol. 229 (2) (2011) 381–390.
- J.B. Hibbs Jr.et al., Evidence for cytokine-inducible nitric oxide synthesis from Larginine in patients receiving interleukin-2 therapy, J. Clin. Invest. 89 (3) (1992) 867–877. [CrossRef]
- W.E. Samlowski, et al., Endothelial nitric oxide synthase is a key mediator of interleukin- 2-induced hypotension and vascular leak syndrome, J. Immunother. 34 (5) (2011) 419–427. [CrossRef]
- M. Tsujimoto, et al., Tumor necrosis factor provokes superoxide anion generation from neutrophils, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 137 (3) (1986) 1094–1100. [CrossRef]
- A. Kharazmi, et al., Interleukin 6 primes human neutrophil and monocyte oxidative burst response, Immunol. Lett. 21 (2) (1989) 177–184. [CrossRef]
- J.T. Colston, B. Chandrasekar, G.L. Freeman, A novel peroxide-induced calcium transient regulates interleukin-6 expression in cardiac-derived fibroblasts, J. Biol. Chem. 277 (26) (2002) 23477–23483. [CrossRef]
- R.A. Willis, et al., induction of nitric oxide synthase in subsets of murine pulmonary fibroblasts: effect on fibroblast interleukin-6 production, Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 71 (2) (1994) 231–239. [CrossRef]
- A. Rabinovitch, et al., Cytotoxic effects of cytokines on rat islets: evidence for involvement of free radicals and lipid peroxidation, Diabetologia 35 (5) (1992) 409–413. [CrossRef]
- N. Robledinos-Anton, et al., Activators and inhibitors of NRF2: a review of their potential for clinical development, 2019 Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019, p. 9372182. [CrossRef]
- L. Zhou, et al., Aging-related decline in the induction of Nrf2-regulated antioxidant genes in human bronchial epithelial cells, Redox. Biol. 14 (2018) 35–40. [CrossRef]
- Drenning, Jason A., Vitor A. Lira, Catherine G. Simmons, Quinlyn A. Soltow, Jeff E. Sellman, and David S. Criswell. “Nitric oxide facilitates NFAT-dependent transcription in mouse myotubes” American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology294, no. 4 (2008): C1088-C1095.
- Yang, Long, Hongshan Guan, Jionghong He, Liqun Zeng, Zhengqiang Yuan, Min Xu, Wenhui Zhang, Xiaole Wu, and Jing Guan. “VEGF increases the proliferative capacity and eNOS/NO levels of endothelial progenitor cells through the calcineurin/NFAT signalling pathway” Cell biology international 36, no. 1 (2012): 21-27.
- Tien, M. , Berlett, B. S., Levine, R. L., Chock, P. B. & Stadtman, E. R. Peroxynitrite-mediated modification of proteins at physiological carbon dioxide concentration: pH dependence of carbonyl formation, tyrosine nitration, and methionine oxidation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 7809–7814 (1999). [CrossRef]
- Davis, C. W. et al. Nitration of the mitochondrial complex I subunit NDUFB8 elicits RIP1- and RIP3-mediated necrosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 48, 306–317 (2010). [CrossRef]
- Cauwels, A. et al. Nitrite protects against morbidity and mortality associated with TNF- or LPS-induced shock in a soluble guanylate cyclase-dependent manner. J. Exp. Med. 206, 2915–2924 (2009). [CrossRef]
- Vandenabeele, Peter, Lorenzo Galluzzi, Tom Vanden Berghe, and Guido Kroemer. “Molecular mechanisms of necroptosis: an ordered cellular explosion” Nature reviews Molecular cell biology 11, no. 10 (2010): 700-714.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



