Submitted:
21 April 2023
Posted:
23 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
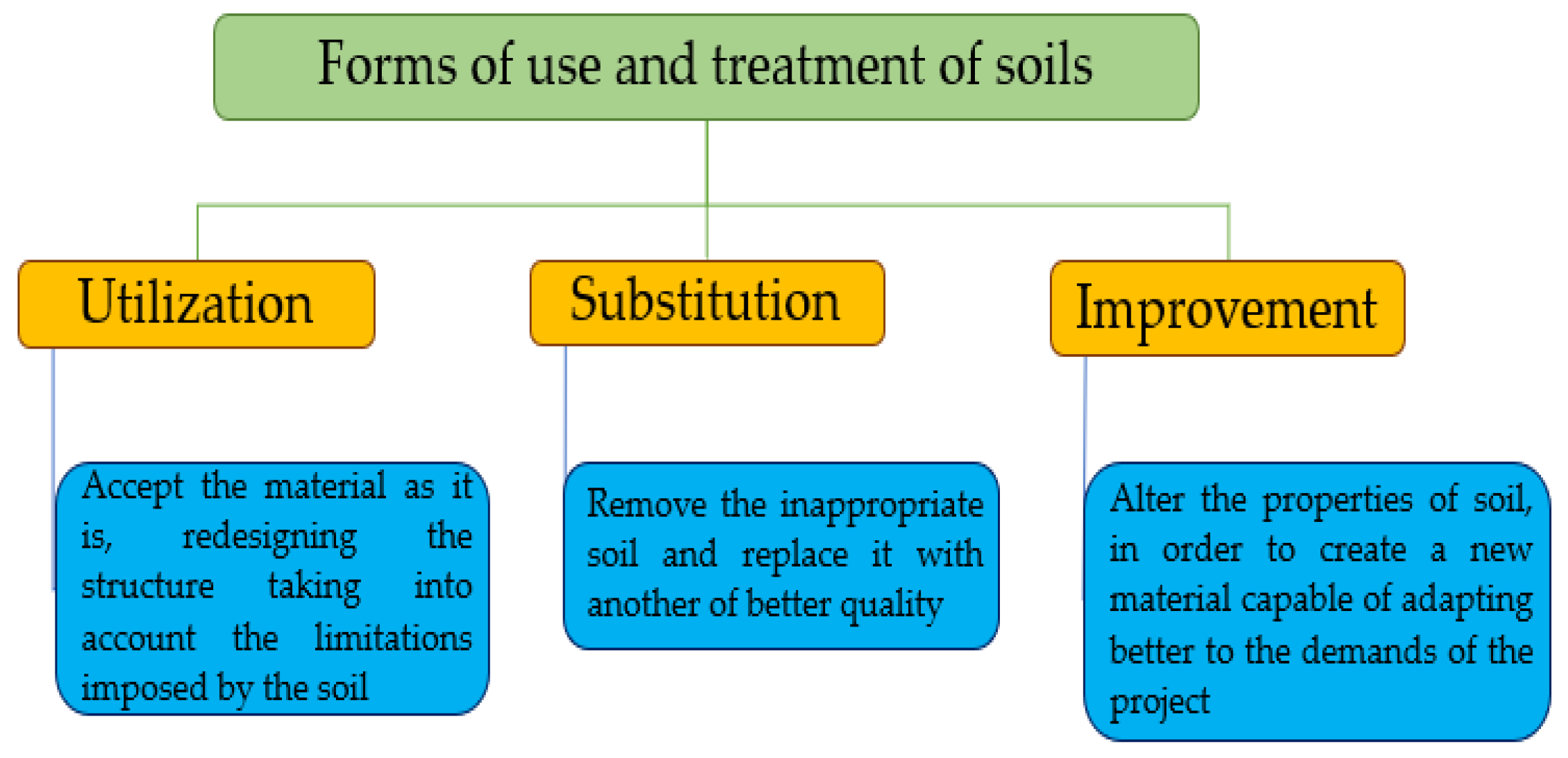
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Article Selection Criteria
2.2. Search Result
2.3. Information Analysis
3. Soil stabilization with fibers
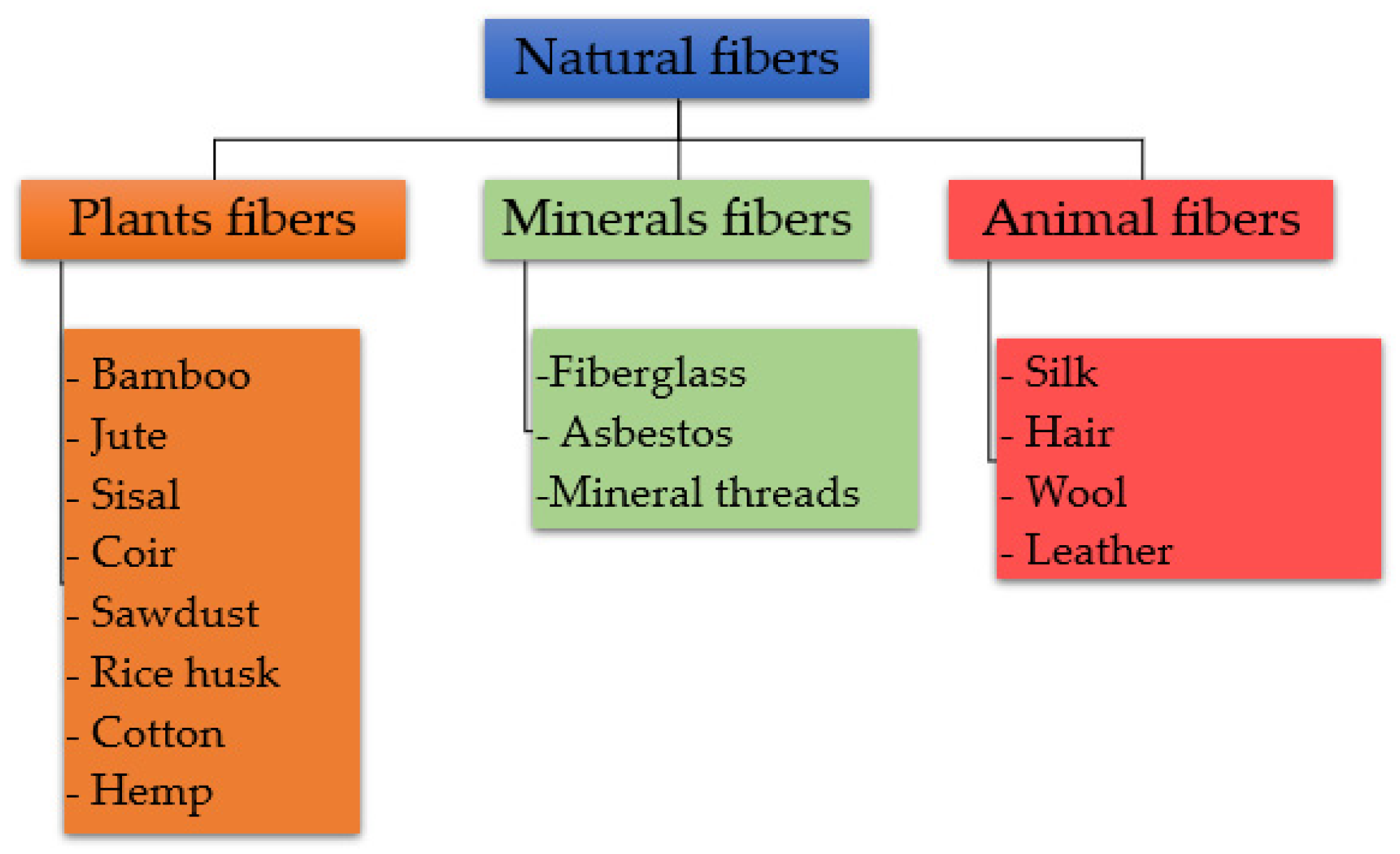
3.1. Mercerization of natural fibers
3.2. Sawdust
3.2.1. Soil stabilization with sawdust
3.2.2. Sawdust-based biocomposites
4. Results
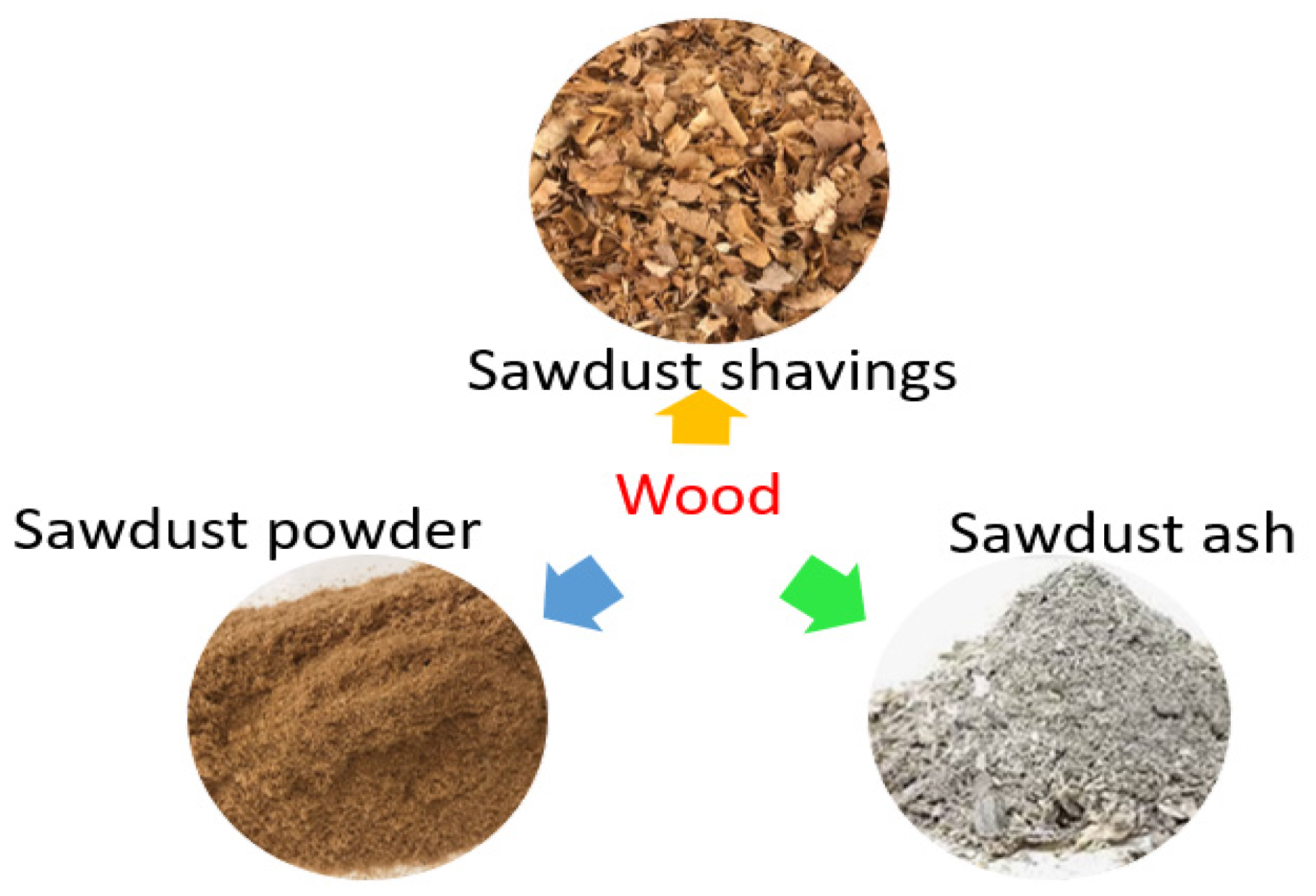
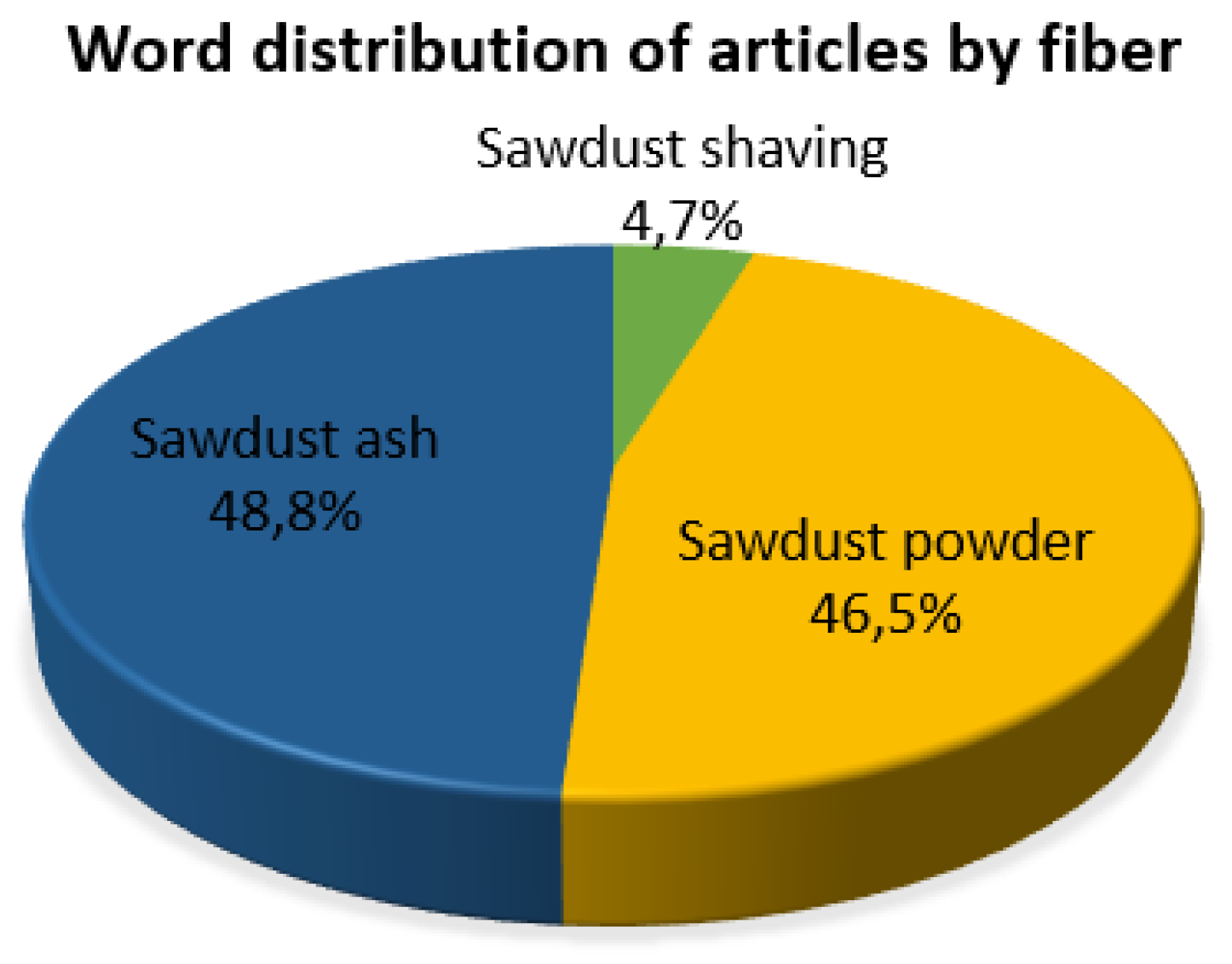
4.1. Sawdust shavings
4.2. Sawdust powder
4.3. Sawdust ash
5. Discussion
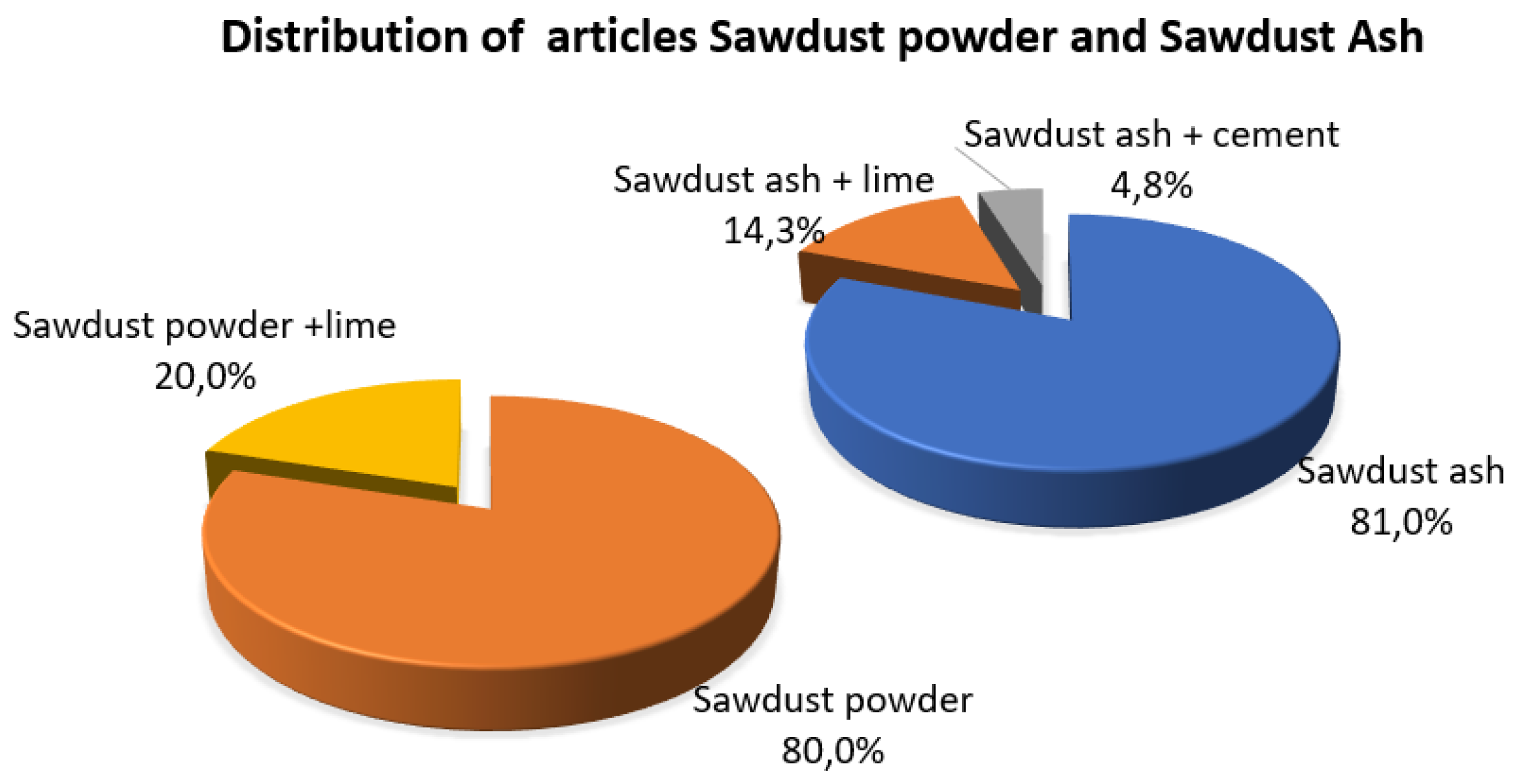
5.1. Types of waste from sawdust fibers
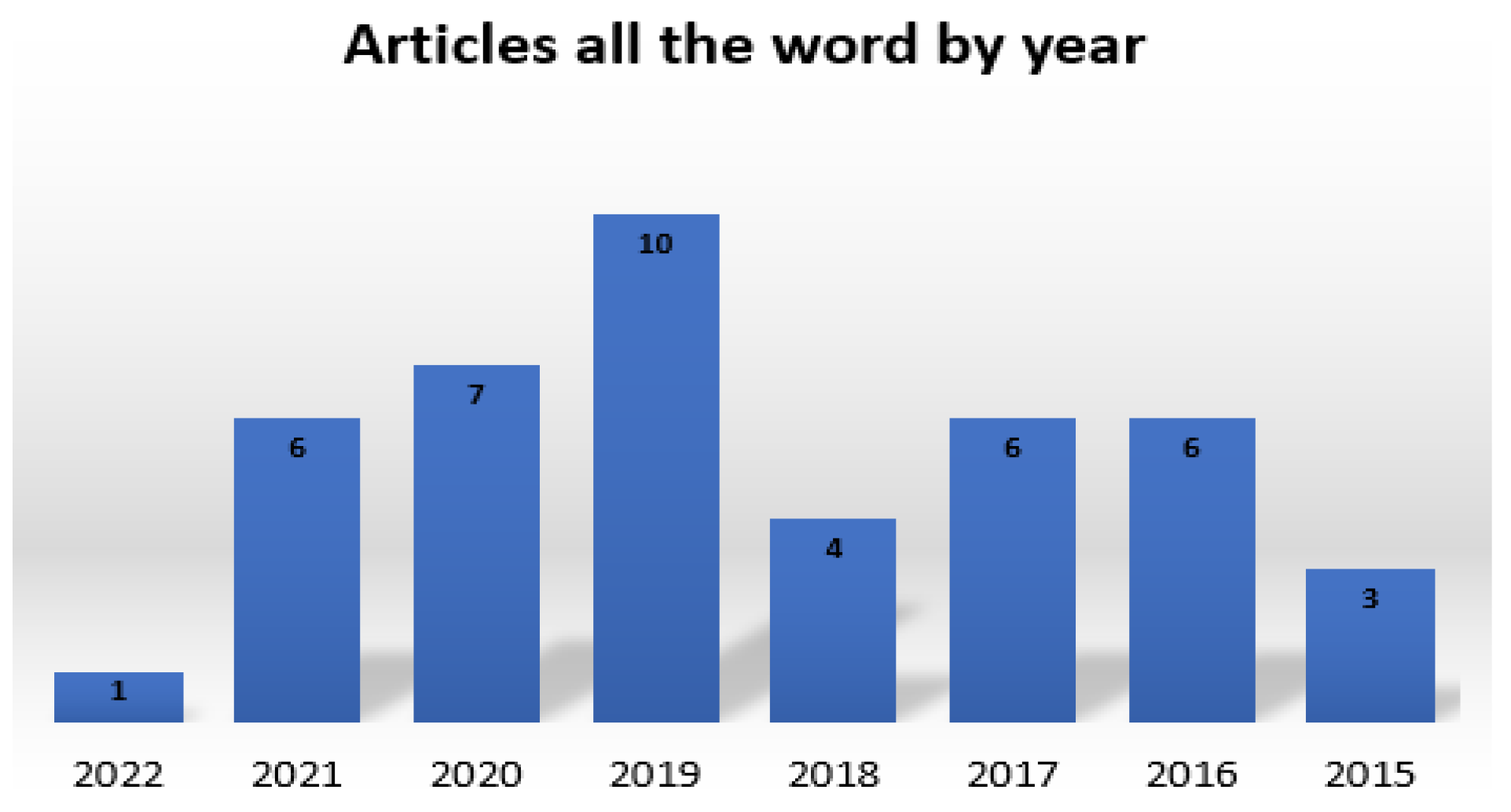
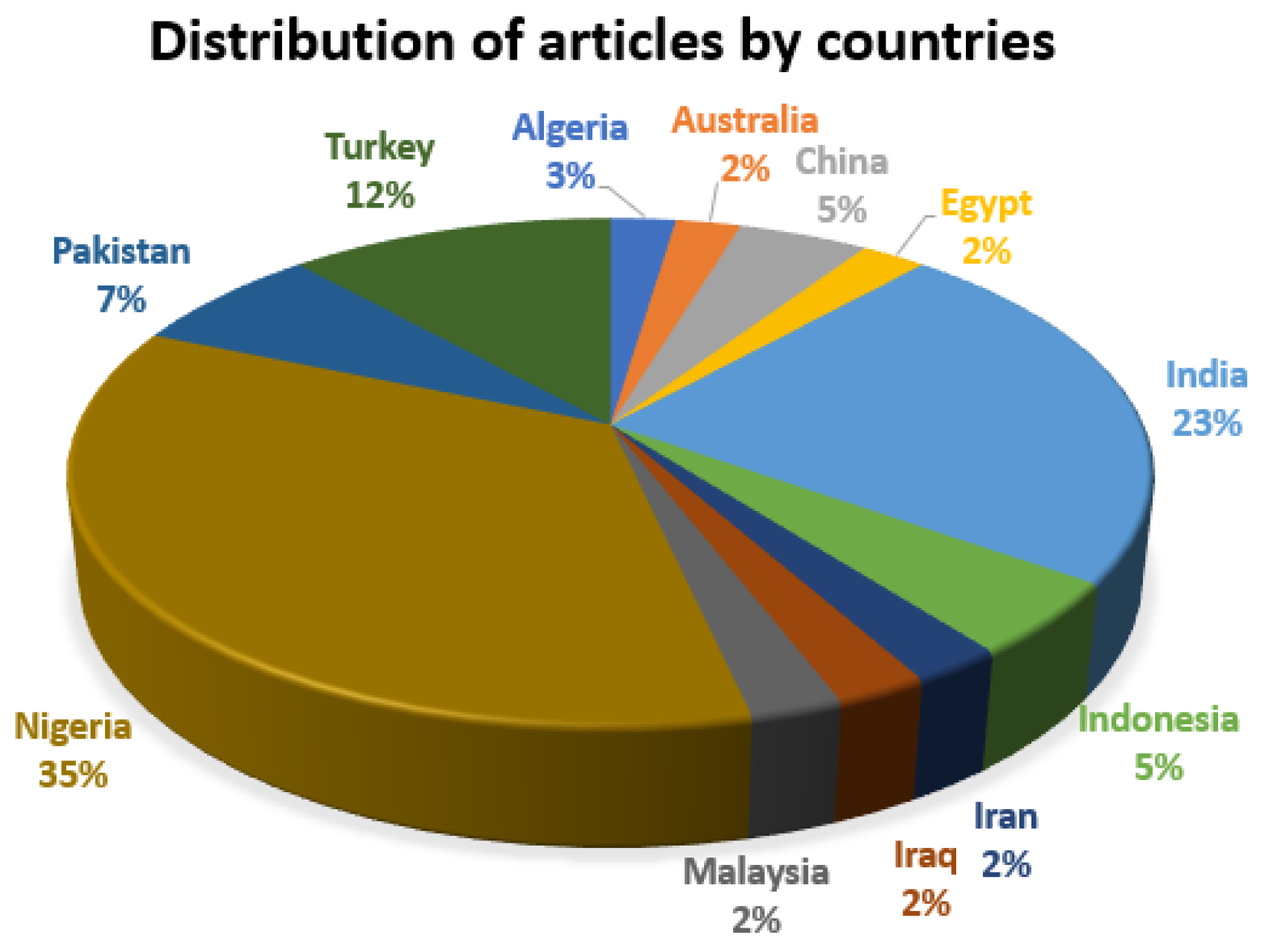
5.2. Year and country of publication
5.3. Types of soils treated
5.4. Fiber orientation
5.5. Fiber length and size
5.6. Added percentage of fibers
5.7. Component mixing method
5.8. Fiber surface treatment
5.9. Additives to the soil/fiber mixture
5.10. Results of improvement of soil properties
6. Conclusions
6.1. Other Research Priorities
- −
- Encourage the use of materials of natural origin more respectful of the environment, which contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions produced, in many cases, by the techniques currently used in soil reinforcement.
- −
- Analysis of the different sources of supply and procurement of sawdust fibers as one of the residues of the wood industry. Based on the underestimation of the actual volume of sawdust produced by an appreciable number of sawmills not officially registered.
- −
- Study of the biodegradability of sawdust as a drawback for its use and analysis of the efficiency of the different chemical treatment alternatives before its addition to soils.
- −
- The validation and standardization of the experimental results obtained for the mechanical properties of sawdust fibers after alkaline treatment are necessary to optimize the pretreatment processes and the methodology of application of the fiber in the soil reinforcement.
- −
- More detailed analysis of the effects of curing time on the parameters of mechanical strength of soils reinforced with sawdust fibers previously subjected to alkaline treatments.
- −
- More thorough analysis of factors that may affect the strength of sawdust-reinforced soils, for example, fiber length, the ratio of fiber percentage to soil mass, coefficient of friction between fiber and soil,
- −
- More detailed study of variables such as age, type of wood species, soil moisture, the climate in the chemical composition (cellulose, lignin, and hemicellulose content), and mechanical properties of sawdust fibers, and their impact on the engineering improvement of soils.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yarbaşı, N., & Kalkan, E. Stabilization of Clayey Soils by Using the Organic Waste-Material. International Journal of Science and Engineering Applications. 2020, 9(11), 129-132. [CrossRef]
- Brahmachary, T. K., & Rokonuzzaman, M. Investigation of random inclusion of bamboo fiber on ordinary soil and its effect CBR value. International Journal of Geo-Engineering 2018, 9(1). [CrossRef]
- Duque Escobar, G.; Escobar Potes, C.E. Geomecánica. In Ingeniería Civil; Universidad Nacional de Colombia: Bogotá, Colombia, 2016.
- Khan, A. N., Ansari, Y., Mahvi, S., Junaid, M., Iqbal, K. Different Soil Stabilization Techniques. International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology. 2020, 29(9). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/350630921.
- Ale, T. O. Effect of drying temperature on the engineering properties of stabilised and natural soils for road construction. Engineering Heritage Journal. 2020, 6(1). [CrossRef]
- Das, B. M., & Sivakugan, N. Fundamentals of geotechnical engineering. Cengage Learning, 2016.
- Garg, R., Biswas, T., Alam, M. D., Kumar, A., Siddharth, A., & Singh, D. R. Stabilization of expansive soil by using industrial waste. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 2021, (Vol. 2070, No. 1, p. 012238). IOP Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Amakye, S. Y., & Abbey, S. J. Understanding the performance of expansive subgrade materials treated with non-traditional stabilisers: a review. Cleaner Engineering and Technology 2021, 4, 100159. [CrossRef]
- Dayioglu, M., Cetin, B., & Nam, S. Stabilization of expansive Belle Fourche shale clay with different chemical additives. Applied Clay Science 2017, 146, 56-69. [CrossRef]
- Al-Kalili, A., Ali, A. S., & Al-Taie, A. J. A Review on Expansive Soils Stabilized with Different Pozzolanic Materials. Journal of Engineering 2022, 28(1), 1-18. [CrossRef]
- Wani, I. Y., Khurshid, M. T., & Sharma, E. N. Analysis of geotechnical properties of an expansive soil mixed with polypropylene, saw dust ash and egg shell powder. International Journal of Engineering Applied Sciences and Technology. 2019, 4(7), 376-381. [CrossRef]
- Niyomukiza, J. B., Wardani, S. P. R., & Setiadji, B. H. The influence of Keruing sawdust on the geotechnical properties of expansive Soils. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 2020, (Vol. 448, No. 1, p. 012040). IOP Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Asuri, S., Keshavamurthy, P. Expansive Soil Characterisation: an Appraisal. INAEL1, Indian National Academy of Engineering 2016, 29–33. [CrossRef]
- Mahima, D., & Sini, T. Effect of Sawdust Ash and Coir Fibre on the Strength Characteristics of Kaolinite Clay. International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT). 2019, Vol. 8 (06). [CrossRef]
- Afrin, H. A review on different types soil stabilization techniques. International Journal of Transportation Engineering and Technology. 2017, 3(2), 19-24. [CrossRef]
- Dang, L., Hasan, H., Fatahi, Z., Jones, R., Khabbaz, H. Enhancing the Engineering Properties of Expansive Soil Using Bagasse Ash and Hydrated Lime. International Journal of GEOMATE 2016, 11(3):2447–2454. [CrossRef]
- Charis, G., Danha, G., & Muzenda, E. A review of timber waste utilization: Challenges and opportunities in Zimbabwe. Procedia Manufacturing 2019, 35, 419-429. [CrossRef]
- Sun, S., Liu, B., & Wang, T. Improvement of expansive soil properties using sawdust. The Journal of Solid Waste Technology and Management. 2018, 44(1), 78-85. [CrossRef]
- Akinwumi, I. I., Ojuri, O. O., Ogbiye, S. A., & Booth, C. A. Engineering properties of tropical clay and bentonite modified with sawdust. Acta Geotechnica Slovenica 2017, 14(2), 47-56.
- Puppala, A. J., & Pedarla, A. Innovative ground improvement techniques for expansive soils. Innovative Infrastructure Solutions. 2017, 2(1), 1-15. [CrossRef]
- James, J. Sugarcane press mud modification of expansive soil stabilized at optimum lime content: Strength, mineralogy and microstructural investigation. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering. 2020, 12, 395-402. [CrossRef]
- Gomes Correia, A.;Winter, M.G.; Puppala, A.J. A review of sustainable approaches in transport infrastructure geotechnics. Transp. Geotech. 2016, 7, 21–28. [CrossRef]
- Ikeagwuani, C. C., Agunwamba, J. C., Nwankwo, C. M., & Eneh, M. Additives optimization for expansive soil subgrade modification based on Taguchi grey relational analysis. International Journal of Pavement Research and Technology 2021, 14(2), 138-152. [CrossRef]
- Hamzah, N., Yusof, N. A. M., & Rahimi, M. I. H. M. Assessment of compressive strength of peat soil with sawdust and Rice Husk Ash (RHA) with hydrated lime as additive. In MATEC Web of Conferences 2019, Vol. 258, p. 01014. EDP Sciences. [CrossRef]
- Khademi, F., & Budiman, J. Expansive soil: causes and treatments. i-Manager's Journal on Civil Engineering 2016, 6(3), pp., 1−13. [CrossRef]
- Ikeagwuani, C. C., & Nwonu, D. C. Emerging trends in expansive soil stabilisation: A review. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering. 2019, 11(2), 423-440. [CrossRef]
- Oluremi, J. R., Elsaigh, W. A., Ikotun, B. D., Osuolale, O. M., Adedokun, S. I., Oyelakin, S. E., & Ayodele, O. P. Strength enhancement in high silica wood ash stabilized lateritic soil using sodium tetraoxosulphate VI (Na2SO4) as activator. International Journal of Pavement Research and Technology 2021, 14(4), 410-420. [CrossRef]
- Patel, S. K., & Singh, B. Strength and deformation behavior of fiber-reinforced cohesive soil under varying moisture and compaction states. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 2017, 35(4), 1767-1781. [CrossRef]
- Firoozi, A. A., Guney Olgun, C., Firoozi, A. A., & Baghini, M. S. Fundamentals of soil stabilization. International Journal of Geo-Engineering 2017, 8(1), 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, S., & Soundara, B. Swelling behaviour of expansive soils with recycled geofoam granules column inclusion. Geotextiles and Geomembranes 2019, 47(1), 1-hma11. [CrossRef]
- Bordoloi, S., Yamsani, S. K., Garg, A., Sreedeep, S., & Borah, S. Study on the efficacy of harmful weed species Eicchornia crassipes for soil reinforcement. Ecological Engineering 2015, 85, 218-222. [CrossRef]
- Owamah, H. I., Atikpo, E., Oluwatuyi, O., & Oluwatomisin, A. M. Geotechnical properties of clayey soil stabilized with cement-sawdust ash for highway construction. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management 2017, 21(7), 1378-1381. [CrossRef]
- Chittoori, B., & Neupane, S. Evaluating the application of microbial induced calcite precipitation technique to stabilize expansive soils. In Civil Infrastructures Confronting Severe Weathers and Climate Changes Conference 2018 (pp. 10-19). Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
- Kang, X., Kang, G. C., Chang, K. T., & Ge, L. Chemically stabilized soft clays for road-base construction. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 2015, 27(7). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/267211309. [CrossRef]
- Mahedi, M., Cetin, B., & White, D. J. Performance evaluation of cement and slag stabilized expansive soils. Transportation Research Record 2018, 2672(52), 164-173. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320172459. [CrossRef]
- Miao, S., Shen, Z., Wang, X., Luo, F., Huang, X., & Wei, C. Stabilization of highly expansive black cotton soils by means of geopolymerization. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 2017, 29(10). [CrossRef]
- Adedokun, S. I., & Oluremi, J. R. A review of the stabilization of lateritic soils with some agricultural waste products. International Journal of Engineering 2019, 17(2).
- Niyomukiza, J. B., Wardani, S. P. R., & Setiadji, B. H. The Effect of Curing Time on the Engineering Properties of Sawdust and Lime Stabilized Expansive Soils. In 2nd International Symposium on Transportation Studies in Developing Countries (ISTSDC 2019) (2020, February). (pp. 157-161). Atlantis Press. [CrossRef]
- Agaiby, S., Hassan, A. W., Dakhli, A. H., & Elhakim, A. Sawdust Effect on Compressibility and Shear Strength Characteristics of Highly Organic Clay. ERJ. Engineering Research Journal 2022, 45(3), 379-387. [CrossRef]
- Afolayan, O. D., Olofinade, O. M., & Akinwumi, I. I. Use of some agricultural wastes to modify the engineering properties of subgrade soils: A review. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 2019, Vol. 1378, No. 2, p. 022050. IOP Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Garg, A., Bordoloi, S., Mondal, S., Ni, J. J., & Sreedeep, S. Investigation of mechanical factor of soil reinforced with four types of fibers: An integrated experimental and extreme learning machine approach. Journal of natural fibers. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Dauda D. & Dominic M. Effectiveness of agricultural wastes in soil stabilization. Sustainability, Agri, Food and Enviromental Research 2022, 10(X). [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.N.; Ahmad,W.; Khan, K.; Ahmad, A. A Comprehensive Review of Types, Properties, Treatment Methods and Application of Plant Fibers in Construction and Building Materials. Materials 2022, 15, 4362. [CrossRef]
- Darvisi, A., Vosoughifar, H., Saeidijam, S., Torabi, M., & Rahmani, A. An experimental and prediction study on the compaction and swell–expansion behavior of bentonite clay containing various percentages of two different synthetic fibers. Innovative Infrastructure Solutions. 2020, 5(1), 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Irani, N., & Ghasemi, M. Effect of scrap tyre on strength properties of untreated and lime-treated clayey sand. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering. 2019, 25(9), 1609-1626. [CrossRef]
- Saberian, M., Mehrinejad Khotbehsara, M., Jahandari, S., Vali, R., & Li, J. Experimental and phenomenological study of the effects of adding shredded tire chips on geotechnical properties of peat. International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering. 2018, 12(4), 347-356. [CrossRef]
- Danso, H., Martinson, D. B., Ali, M., & Williams, J. B. Physical, mechanical and durability properties of soil building blocks reinforced with natural fibres. Construction and Building Materials. 2015, 101, 797-809. [CrossRef]
- Jayasree, P. K., Balan, K., Peter, L., & Nisha, K. K. Volume change behavior of expansive soil stabilized with coir waste. Journal of materials in Civil Engineering. 2015, 27(6), 04014195. [CrossRef]
- Vardhan, H., Bordoloi, S., Garg, A., Garg, A., & Sreedeep, S. Compressive strength analysis of soil reinforced with fiber extracted from water hyacinth. Engineering Computations. 2017, Vol. 34 No. 2, pp. 330-342. [CrossRef]
- Irani, N., & Ghasemi, M. Effects of the inclusion of industrial and agricultural wastes on the compaction and compression properties of untreated and lime-treated clayey sand. SN Applied Sciences 2020, 2(10), 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Wei, L., Chai, S. X., Zhang, H. Y., & Shi, Q. Mechanical properties of soil reinforced with both lime and four kinds of fiber. Construction and Building Materials 2018, 172, 300-308. [CrossRef]
- Bastasaa, J. D., Roxasa, A. J. B., Sagayapa, K. D., Salurioa, R. R. L., Sampayana, J. O., Taniñasa, H. L., & Amatosa Jr, T. A. Swell Classification Analysis for Re-engineering Expansive Soil using Agricultural Waste Materials. International Journal of Applied Engineering Research 2019, 14(10), 2399-2404. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333770206.
- Kumar, J. K., & Kumar, V. P. Experimental analysis of soil stabilization using e-waste. Materials Today: Proceedings 2020, 22, 456-459. [CrossRef]
- Chaugule, M., Deore, S., Gawade, K., Tijare, A., & Banne, S. Improvement of black cotton soil properties using e-waste. IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering 2017, 14(03), 76-81. [CrossRef]
- Veylon, G., Ghestem, M., Stokes, A., & Bernard, A. Quantification of mechanical and hydric components of soil reinforcement by plant roots. Canadian Geotechnical Journal 2015, 52(11), 1839-1849. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F., Han, J., Khatri, D. K., Parsons, R. L., Brennan, J. J., & Guo, J. Field installation effect on steel-reinforced high-density polyethylene pipes. Journal of Pipeline Systems Engineering and Practice 2016, 7(1), 04015013. [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Environment, Green Growth, Raw Materials. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/ green-growth/raw-materials/index_en.htm (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- Murray, A., Skene, K. & Haynes, K. The Circular Economy: An Interdisciplinary Exploration of the Concept and Application in a Global Context. J Bus Ethics 2017,140, 369–380. [CrossRef]
- Pehme, K. M., & Kriipsalu, M. Full-scale project: From landfill to recreational area. Detritus 2018, 1(1), 174-179. [CrossRef]
- Urbinati, A., Chiaroni, D., & Chiesa, V. Towards a new taxonomy of circular economy business models. Journal of Cleaner Production 2017, 168, 487-498. [CrossRef]
- Khan, S., & Khan, H. Improvement of mechanical properties by waste sawdust ash addition into soil. Jordan Journal of Civil Engineering 2016, 10(1).
- Upadhyay, P., & Singh, Y. Soil Stabilization Using Natural Fiber Coir. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology 2017. 4(12), 1808-1812.
- Qu, J. & Zhao, D. Stabilising the cohesive soil with palm fibre sheath strip. Road Materials and Pavement Design 2016, 17:1, 87-103. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., Guo, P., Dai, F., Li, X., Zhao, Y., & Liu, Y. Behavior and modeling of fiber-reinforced clay under triaxial compression by combining the superposition method with the energy-based homogenization technique. International Journal of Geomechanics 2018, 18(12). [CrossRef]
- Owoyemi, O. O. Effect of Sawdust on the Geotechnical Properties of a Lateritic Soil. Journal of Mining and Geology 2021, 57(1), 127-139. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/351094727.
- Sani, J. E., Afolayan, J. O., Chukwujama, I. A., & Yohanna, P. Effects of wood saw dust ash admixed with treated sisal fibre on the geotechnical properties of lateritic soil. Leonardo Electronic Journal of Practices and Technologies 2017, 31(2017), 59-76.
- Mwango, A., & Kambole, C. Engineering Characteristics and Potential Increased Utilisation of Sawdust Composites in Construction—A Review. Journal of Building Construction and Planning Research 2019, 7(3), 59-88. [CrossRef]
- Assiamah, S., Agyeman, S., Adinkrah-Appiah, K., & Danso, H. Utilization of sawdust ash as cement replacement for landcrete interlocking blocks production and mortarless construction. Case Studies in Construction Materials 2022, 16, e00945. [CrossRef]
- Niyomukiza, J. B., Wardani, S. P. R., & Setiadji, B. H. Recent advances in the stabilization of expansive soils using waste materials: A review. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2021, (Vol. 623, No. 1, p. 012099). IOP Publishing. [CrossRef]
- De Castrillo, M. C., Ioannou, I., & Philokyprou, M. Reproduction of traditional adobes using varying percentage contents of straw and sawdust. Construction and Building Materials 2021, 294, 123516. [CrossRef]
- Khtou, O., Aalil, I., Aboussaleh, M., & Wardi, F. Z. E. Mechanical Analysis of Fiber Reinforced Adobe. Civil Engineering and Architecture 2021, 9(7), 2160-2168. [CrossRef]
- Jannat, N., Latif Al-Mufti, R., Hussien, A., Abdullah, B., & Cotgrave, A. Influence of Sawdust Particle Sizes on the Physico-Mechanical Properties of Unfired Clay Blocks. Designs 2021, 5(3), 57. [CrossRef]
- Hejazi, S. M., Sheikhzadeh, M., Abtahi, S. M., & Zadhoush, A. A simple review of soil reinforcement by using natural and synthetic fibers. Construction and Building Materials 2012, 30, 100–116. [CrossRef]
- Vidal, H. The principle of reinforced earth. Highway Research Record 1969, 282, 1–16. http://onlinepubs.trb.org/Onlinepubs/hrr/1969/282/282-001.pdf.
- Gowthaman, S., Nakashima, K., & Kawasaki, S. A state-of-the-art review on soil reinforcement technology using natural plant fiber materials: Past findings, present trends and future directions. Materials 2018, 11(4). [CrossRef]
- Kielė, A., Vaičiukynienė, D., Tamošaitis, G., Pupeikis, D., & Bistrickaitė, R. Wood shavings and alkali-activated slag bio-composite. European journal of wood and wood products 2020, 78(3), 513-522. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V., Vinayak, H. K., & Marwaha, B. M. Enhancing compressive strength of soil using natural fibers. Construction and Building Materials 2015, 93, 943-949. [CrossRef]
- Hashim, M. Y., Amin, A. M., Marwah, O. M. F., Othman, M. H., Yunus, M. R. M., & Huat, N. C. The effect of alkali treatment under various conditions on physical properties of kenaf fiber. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2017(Vol. 914, No. 1, p. 012030). IOP Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Vettorelo, P. V., & Clariá, J. J. Suelos Reforzados con Fibras: Estado del Arte y Aplicaciones. Revista Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales 2014, 1(1):27–34.
- Hassan, M. M., & Wagner, M. H. Surface modification of natural fibers for reinforced polymer composites: a critical review. Reviews of Adhesion and Adhesives 2016, 4(1), 1-46. [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, G., & Singh, I. A Review on Effect of Pretreatment of Fibers on Physical and Mechanical Properties of Natural Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites. International Journal of Engineering Research in Current Trends (IJERCT) 2020, 2 (3).
- Matykiewicz, D., Barczewski, M., Mysiukiewicz, O., & Skórczewska, K. Comparison of various chemical treatments efficiency in relation to the properties of flax, hemp fibers and cotton trichomes. Journal of Natural Fibers 2021, 18(5), 735-751. [CrossRef]
- Adams, R. H., Cerecedo-López, R. A., Alejandro-Álvarez, L. A., Domínguez-Rodríguez, V. I., & Nieber, J. L. Treatment of water-repellent petroleum-contaminated soil from Bemidji, Minnesota, by alkaline desorption. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology 2016, 13(9), 2249-2260. [CrossRef]
- Koohestani, B., Darban, A. K., Mokhtari, P., Yilmaz, E. & Darezereshki, E. Comparison of different natural fiber treatments: a literature review. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology 2019, 16(1), 629-642. [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo-Quiceno, N., Ch, E. M. C., Restrepo-Osorio, A., & Santa, J. F. Improvement of mechanical properties of pineapple leaf fibers by mercerization process. Fibers and Polymers 2018, 19(12), 2604-2611. [CrossRef]
- Thyavihalli Girijappa, Y. G., Mavinkere Rangappa, S., Parameswaranpillai, J., & Siengchin, S. Natural fibers as a sustainable and renewable resource for development of eco-friendly composites: a comprehensive review. Frontiers in Materials 2019, 6, 226. [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J., & Fangueiro, R. Surface modification of natural fibers: a review. Procedia Engineering 2016, 155, 285-288. [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, A., & Ozbakkaloglu, T. A review of natural fiber composites: Properties, modification and processing techniques, characterization, applications. Journal of Materials Science 2019, 55(3), 829-892. [CrossRef]
- Rippon, J. A., & Evans, D. J. Improving the properties of natural fibres by chemical treatments. In Handbook of natural fibres 2020, (pp. 245-321). Woodhead Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, M. R., Siengchin, S., Parameswaranpillai, J., Jawaid, M., Pruncu, C. I., & Khan, A. A comprehensive review of techniques for natural fibers as reinforcement in composites: Preparation, processing, and characterization. Carbohydrate polymers 2019, 207, 108-121. [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S., Sirous, F., & Hussain, C. M. Sawdust, a versatile, inexpensive, readily available bio-waste: From mother earth to valuable materials for sustainable remediation technologies. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 2021, 295, 102492. [CrossRef]
- Fregoso-Madueño, J. N., Goche-Télles, J. R., Rutiaga-Quiñones, J. G., González-Laredo, R. F., Bocanegra-Salazar, M., & Chávez-Simental, J. A. Alternative uses of sawmill industry waste. Revista Chapingo. Serie Ciencias Forestales y del Ambiente 2017, XXIII(2),243-260. ISSN: 2007-3828. Available in: https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=62950747001. [CrossRef]
- Butt, WA, Gupta, K. y Jha, JN. Strength Behavior of Clayey Soil Stabilized with Saw Dust Ash. International Journal of Geo-Engineering 2016, 7 (1), 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Okedere, O. B., Fakinle, B. S., Sonibare, J. A., Elehinafe, F. B., & Adesina, O. A. Particulate matter pollution from open burning of sawdust in Southwestern Nigeria. Cogent Environmental Science 2017, 3(1), 1367112. [CrossRef]
- Medina-Martinez, C.J.; Sandoval-Herazo, L.C.; Zamora-Castro, S.A.; Vivar-Ocampo, R.; Reyes-Gonzalez, D. Natural Fibers: An Alternative for the Reinforcement of Expansive Soils. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9275. [CrossRef]
- Jairaj, C., Raghunandan, M. Compaction Characteristics and Strength of BC Soil Reinforced with Untreated and Treated Coir Fibers. Innovative Infrastructure Solutions 2018. [CrossRef]
- Qu, J., & Zhu, H. Function of Palm Fiber in Stabilization of Alluvial Clayey Soil in Yangtze River Estuary. Journal of Renewable Materials 2021, 9(4), 767. [CrossRef]
- Oderah, V. and Kalumba, D. Laboratory Investigation of Sugarcane Bagasse as Soil Reinforcement Material. In Geo-chine 2016 (2016July):61–68. [CrossRef]
- Khan, A., Jasim, OH, and Umar, D. Effect of Sawdust-Lime and Sawdust Ash-Lime on the Geotechnical the Geotechnical Properties of an Expansive. 2020 (August):0–8. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343600730.
- Ikeagwuani, C. C., Obeta, I. N., & Agunwamba, J. C. Stabilization of black cotton soil subgrade using sawdust ash and lime. Soils and Foundations 2019, 59(1), 162-175. [CrossRef]
- Singh, P., & Singh, B. (2019). Assessment of mechanical properties of biocomposite material by using sawdust and rice husk. Incas Bulletin, 11(3), 147-156. [CrossRef]
- Mouissa, F., Benyahia, A., Djehiche, M., Belmokre, K., Deghfel, N., Redjem, A., & Rahmouni, Z. E. A. The effect of chemical treatment on the mechanical and thermal properties of composite materials based on clay reinforced with sawdust. Matériaux & Techniques 2021, 109(1), 101. [CrossRef]
- Jangid, A. K., Khatti, J., & Bindlish, A. Stabilization of black cotton soil by 15% Kota stone slurry with wooden saw dust. International Journal of Advance Research in Science and Engineering 2018, 7(2), 108-114.
- Keramatikerman, M., Chegenizadeh, A., & Nikraz, H. Effect of sawdust on Cohesion of Sand-Sawdust mixture. International Journal of Engineering Applied Sciences and Technology (IJEAST) 2020, 4(11):14–16. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S., Verma, K., & Sharma, J. K. Experimental Study of Stabilization of Expansive Soil Mixed with Sawdust and Marble Dust. In Proceedings of the Indian Geotechnical Conference 2019 (pp. 535-547) 2021. Springer, Singapore. [CrossRef]
- Karteek, G. S. An Investigation on the Influence of Lime on Marine Clay Treated with Sawdust for Flexible Pavement Subgrade. International Journal On Recent & Innovative Trend In Technology 2018, 4(2).
- Johnson, S., & Gopinath, B. A Study on the Swell Behaviour of Expansive Clays Reinforced with Saw Dust, Coir Pith & Marble Dust. International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology (IJERT) 2016,5(9), 565-570. [CrossRef]
- Yarbaşı, N., & Kalkan, E. Investigation of Wet-Dry Cycle Effect on Swelling Behavior of Stabilized Expansive Soils. International Journal of Science and Engineering Applications 2020, 9(12), 153-157. [CrossRef]
- Kalkan, E., & Yarbaşı, N. The Effects of Pine Tree Sawdust on the Volume Compressibility of Expansive Soils. International Journal of Science and Engineering Applications 2020, 10(04):029–033. [CrossRef]
- Jasim, O. H., & Çetin, D. Effect of the Time on the Undrained Shear Strength and Permeability of Clay-Wooden Sawdust Mixtures Used to Improve Landfills Liner. In Key Engineering Materials 2020, (Vol. 857, pp. 311-318). Trans Tech Publications Ltd. [CrossRef]
- Jasim, O. H., & Çetin, D. Effect of sawdust usage on the shear strength behavior of clayey silt soil. Sigma Journal Engineering and Natural Sciences 2016, 34(1), 31-41. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/299285436.
- Farooq, M. U., Mujtaba, H., Farooq, K., Sivakugan, N., & Das, B. M. Evaluation of stability and erosion characteristics of soil embankment slope reinforced with different natural additives. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions of Civil Engineering 2020, 1-10. 44(0123456789):515–24. [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y., Seibou, A. O., Li, M., Kaci, A., & Ye, J. Bamboo Sawdust as a Partial Replacement of Cement for the Production of Sustainable Cementitious Materials. Crystals 2021, 11(12), 1593. [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, R., Amooei, A. A., Amel Sakhi, M., & Karimi, A. Experimental Study on Influence of Using Urease Enzyme on Stabilized Sandy Soil’s Engineering Property by Zeolite and Sawdust. International Journal of Maritime Technology 2021, 15, 17-27.
- Oriaje, A. T., Adeyemo, K. A., & Ojo, O. Y. Stabilization of Lateritic Soil with Mahogany (Hardwood) Sawdust Ash. Journal of Engineering and Environmental Sciences 2021,. [CrossRef]
- Ayodele, A. L., Oketope, O. M., & Olatunde, O. S. Effect of sawdust ash and eggshell ash on selected engineering properties of lateralized bricks for low cost housing. Nigerian Journal of Technology 2019, 38(2), 278-282. [CrossRef]
- Obeta, I. N., Ikeagwuani, C. C., Attama, C. M., & Okafor, J. Stability and durability of sawdust ash-lime stabilised black cotton soil. Nigerian Journal of Technology 2019, 38(1), 75-80. [CrossRef]
- Kolo, S. S., Jimoh, Y. A., Yusuf, I., Adeleke, O. O., Balarebe, F., & Shehu, M. Sawdust ash stabilization of weak lateritic soil. 3rd International Engineering Conference (IEC 2019), 2019.
- Fapohunda, C. A., Amu, O. O., & Babarinde, O. F. Evaluation of Geotechnical and Structural Performance of Cement-Stabilized Soil with Saw Dust Ash (SDA). Arid zone journal of engineering, technology and environment 2019, 15(3), 628-637. https://www.azojete.com.ng/index.php/azojete/article/view/43.
- Ogundipe, O. M., Adekanmi, J. S., Akinkurolere, O. O., & Ale, P. O. Effect of compactive efforts on strength of laterites stabilized with sawdust ash. Civil Engineering Journal 2019, 5(11), 2502-2514. [CrossRef]
- Etim, E., Ikeagwuani, C. C., Ambrose, E. E., & Attah, I. C. Influence of sawdust disposal on the geotechnical properties of soil. EJGE 2017, 22(Bund12), 4769-4780. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/319468685.
- Nnochiri, E. S., Emeka, H. O., & Tanimola, M. Geotechnical characteristics of lateritic soil stabilized with sawdust ash-lime mixtures. Civil Engineering Journal 2017, (1). [CrossRef]
- Ikeagwuani, C. C. Compressibility characteristics of black cotton soil admixed with sawdust ash and lime. Nigerian Journal of Technology 2016, 35(4), 718-725. [CrossRef]
- Ilori, A. O., & Udo, E. A. Investigation of geotechnical properties of a lateritic soil with saw dust ash. IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering 2015, 12(1), 11-14. [CrossRef]
- Adetoro, A. E., & Oladapo, S. A. Effects of Sawdust and Palm Kernel Shell Ashes on Geotechnical Properties of Emure/Ise-orun Local Government Areas Soil, Nigeria. Scientific Research Journal (SCIRJ) 2015, 3(VII), 35-38.
- Rai, H. Effect on Maximum Dry Density and Optimum Moisture Content of Expansive Soil on Addition of Sawdust Ash. International Journal of Applied Engineering Research 2019, 14(9).
- Kale, R. Y., Chaudhari, K., Bhadange, K., Chune, V., Kadu, G., & Tidke, A. Effect of saw dust ash and lime on expansive soil (black cotton soil). International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) 2019. 6(4).
- Venkatesh, A., & Reddy, G. S. Effect Of Waste Saw Dust Ash On Compaction And Permeability Properties Of Black Cotton Soil. International Journal of Civil Engineering Research 2016, 7(1), 27-32.
- Naranagowda, M. J., Nithin, N. S., Maruthi, K. S., & Mosin Khan, D. S. Effect of saw dust ash and fly ash on stability of expansive soil. International Journal of Research in Engineering and technology 2015, 4(7), 83-86.
- Karim, H., Al-Recaby, M., & Nsaif, M. Stabilization of soft clayey soils with sawdust ashes. In MATEC Web of Conferences 2018. (Vol. 162, p. 01006). EDP Sciences. [CrossRef]

| Criterion | Eligibility | Exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Literature type Language Timeline Countries and region |
Research article journal English ≥ 2015 All the world |
Review article journal, book, book chapter Non-English <2015 None |
| Fiber Type | Fiber information | Optimal content (%) | Methods | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length (mm) | Range reinforcement (%) | ||||
| Bamboo fiber | 10 and 20 | 0.2 to 1.4 | 1.2 | Compaction, Unconfined compression, CBR1 | [2] |
| Jute fiber | 10 and 30 | 0.25 to 1.5 | 1.25 | CBR1 | [53] |
| Coir fiber | 10 and 20 | 0 to 3.0 | 0.5 | Compaction | [96] |
| Palm fiber | 5, 10, 15 and 20 | 0.1 to 0.6 | 0.4 | UCS2 | [97] |
| Bagasse fiber | 0.3 to 1.7 | 1.4 | Direct shear | [98] | |
| Country | Year | Materials information | Optimal content (%) | Parameters | Ref. | |
| Soil | Fiber | |||||
| Algeria | 2021 | Bou-Saâda region | Sawdust treated with NaOH solution; Percentage: 0.5 to 2.5 | Variable | Mechanical tests, SEM, XRD | [102] |
| India | 2018 | Black cotton soil, Borkheda, Kota | Wood sawdust; Percentage: 2.5 to 12.5 | 5 | Compaction, unconfined compression | [103] |
| Country | Year | Materials information | Optimal content (%) | Parameters | Ref. | |
| Soil | Fiber | |||||
| Australia | 2020 | Sand, the average particle size of 1.2 mm | Sawdust powder; Percentage: 3 to 10 | Variable | Compaction, direct shear | [104] |
| Nigeria | 2021 | Ogbomosho | Passing through N° 40 sieve opening; Percentage: 2.5 to 15 |
Variable | Plasticity, compaction, CBR, unconfined compression, permeability | [65] |
| Nigeria | 2017 | Covenant University, Ota | Passing through N° 40 sieve opening; Percentage: 2 to 8 | Proportional | Compaction, unconfined compression, permeability | [19] |
| Egypt | 2022 | Kafr Elsheikh | Sawdust passing through N° 40 sieve opening; Percentage: 10, 15 and 20 | 15 sawdust; 5% cement |
Vane shear test, direct shear test, compressibility | [39] |
| India | 2021 | Black cotton, Fatehpur Rajasthan | Sawdust and marble dust powder; Percentage: 2 to 10 sawdust; 5 to 15 Marble powder | Variable | Compaction, unconfined compression | [105] |
| India | 2018 | Kakinada | Sawdust and lime | 15 sawdust 4 lime |
Compaction, CBR | [106] |
| India | 2016 | Palakkad | Sawdust and coir pith; Percentage: 2 to 12 | Variable | Compaction, unconfined compression, swelling pressure | [107] |
| Turkey | 2020 | CH, Erzurum | Pine, passing through N° 4 sieve opening; Percentage: 0.5 to 1.5 | Proportional | Compaction, unconfined compression | [1] |
| Turkey | 2020 | CH, Erzurum | Pine, passing through N° 4 sieve opening; Percentage: 0.5 to 1.5 | Inversely proportional | Swelling Pressure | [108] |
| Turkey | 2020 | CH, Erzurum | Pine, passing through N° 4 sieve opening; Percentage: 0.5 to 1.5 | Inversely proportional | Coefficient of volume compressibility | [109] |
| Turkey | 2020 | Istanbul | Passing through N° 20 sieve opening; Percentage: 1 to 5 | 3 immediate tests; 2 long-term tests | Triaxial tests UU, permeability, triaxial tests UU | [110] |
| Turkey | 2016 | Istanbul | Passing through N° 20 sieve opening; Percentage: 1 to 5 | 3 | Compaction, unconfined compression | [111] |
| Pakistan | 2019 | Punjab | Ground sawdust, D50=0.25mm; Percentage: 1 to 7 | 5 | Unconfined compression, triaxial tests UU | [112] |
| China | 2021 | Zhejiang, | Particle between 0.037 and 0.16 mm; Percentage: 1 to 7 | Variable | Compressive and flexural strength | [113] |
| China | 2018 | CH, Nanjing | Particles smaller than 1 mm; Percentage: 2.5 to 12.5 | 7.5 | Direct shear, unconfined compression, swelling Pressure | [18] |
| Indonesia | 2020 | Semarang-Purwodadi road | Keruing sawdust passing through N° 20 sieve opening; Percentage: 3 to 7 | Variable | Compaction, unconfined compression, plasticity, CBR | [12] |
| Indonesia | 2019 | Central Java Province | Sawdust-lime; Sawdust Passing through N° 40 sieve opening; Percentage: 3 to 5 | Variable | Compaction, unconfined compression, swell index, plasticity | [38] |
| Malaysia | 2019 | Sungai Besar | Sawdust, Rice Husk Ash Percentage: 2 to 5 | 4 | Compaction, unconfined compression | [24] |
| Iran | 2021 | Sand, Qom | Sawdust between sieves N° 16 and 30; Percentage: 4 to 12 | Variable | Compaction, unconfined compression | [114] |
| Country | Year | Materials information | Optimal content (%) | Parameters | Ref. | |
| Soil | Fiber | |||||
| Nigeria | 2021 | Oke Baale, Osogbo, Osun | Mahogany sawdust ash passing through N° 200 sieve opening; Percentage: 2 to 6 | Variable | Plasticity, CBR | [115] |
| Nigeria | 2019 | Adamawa State Polytechnic, | Sawdust ash; Percentage: 4 to 20 | 16 | Compaction, CBR, SEM, XRD | [100] |
| Nigeria | 2019 | Ile-Ife, Osun state | Sawdust ash and egg shell ash; Percentage: 2 to 16 | 2 to 4 | Compaction | [116] |
| Nigeria | 2019 | Adamawa State Polytechnic, Yola | Sawdust ash and lime | 4 lime and 16 sawdust ash | Durability index, unconfined compressive | [117] |
| Nigeria | 2019 | Federal University Technology Minna | Sawdust ash passing through N° 200 sieve opening; Percentage: 2 to 10 | 4 | Plasticity, compaction, unconfined compression | [118] |
| Nigeria | 2019 | Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Osun state | Sawdust ash Passing through N° 70 sieve opening; Percentage: 2 to 10 | Variable | Compaction, unconfined compression, CBR | [119] |
| Nigeria | 2019 | Ado-Ekiti and Ado-Iworoko road | Sawdust ash passing through N° 30 sieve opening; Percentage: 2 to 10 | Variable | Compaction, unconfined compression, CBR | [120] |
| Nigeria | 2017 | Zaria | Sawdust ash and sisal; Percentage: 2 to 8 | 0.75 sisal and 6 sawdust ash | Compaction, unconfined compression | [66] |
| Nigeria | 2017 | Enugu | Sawdust ash passing through N° 200 sieve opening; Percentage: 1 to 15 | Variable | Plasticity, compaction, permeability | [121] |
| Nigeria | 2017 | Federal University of Technology, Akure | Sawdust ash passing through N° 70 sieve opening and lime; Percentage: 2 to 10 | 6 | Compaction, unconfined compression | [122] |
| Nigeria | 2016 | black cotton, Numan | Sawdust ash passing through N° 200 sieve opening and lime; Percentage: 2 to 10 | Variable | Plasticity, compaction, Compressibility | [123] |
| Nigeria | 2015 | Obafemi Awolowo University. Ile Ife | Sawdust ash passing through N° 40 sieve opening; Percentage: 2 to 20 | 12 | Compaction, unconfined compression | [124] |
| Nigeria | 2015 | Emure/Ise, Orun | Palm Kernel Shell and sawdust ash; Percentage: 2 to 8 | Variable | Compaction, plasticity | [125] |
| India | 2019 | Sitarganj | Sawdust Ash passing through N° 30 sieve opening; Percentage: 2 to 25 | Variable | Compaction, plasticity | [126] |
| India | 2019 | Black cotton soil | Sawdust ash and lime; Percentage: 1 to 5 | 2 | Compaction, unconfined compression, CBR | [127] |
| India | 2019 | Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala | Sawdust Ash; Percentage: 4 to 10 | 8 | Compaction, unconfined compression | [14] |
| India | 2016 | Rajouri | Sawdust Ash; Percentage: 4 to 12 | 4 | Compaction, unconfined compression, CBR | [93] |
| India | 2016 | Kopparthy village, Kadapa | Sawdust Ash; Percentage: 2 to 10 | Variable | Compaction, permeability | [128] |
| India | 2015 | Soraba Taluk, Karnataka | Sawdust Ash and fly ash; Percentage: 10, 20 and 30 | Variable | Compaction, unconfined compression, CBR, free swell index test | [129] |
| Pakistan | 2020 | CH, Istanbul | Sawdust-lime and sawdust ash-lime; Percentage: 1 to 5 | Variable | Compaction, unconfined compression, plasticity | [99] |
| Pakistan | 2016 | Tarnab | Sawdust Ash; Percentage: 2 to 12 | Variable | Permeability, direct shear, plasticity, compaction | [61] |
| Iraq | 2018 | Al-Maymunah, Maysan | Sawdust ash passing through N° 200 sieve opening; Percentage: 2 to 10 | 4 to 6 | Compaction, unconfined compression, CBR, | [130] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





