Submitted:
20 April 2023
Posted:
21 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
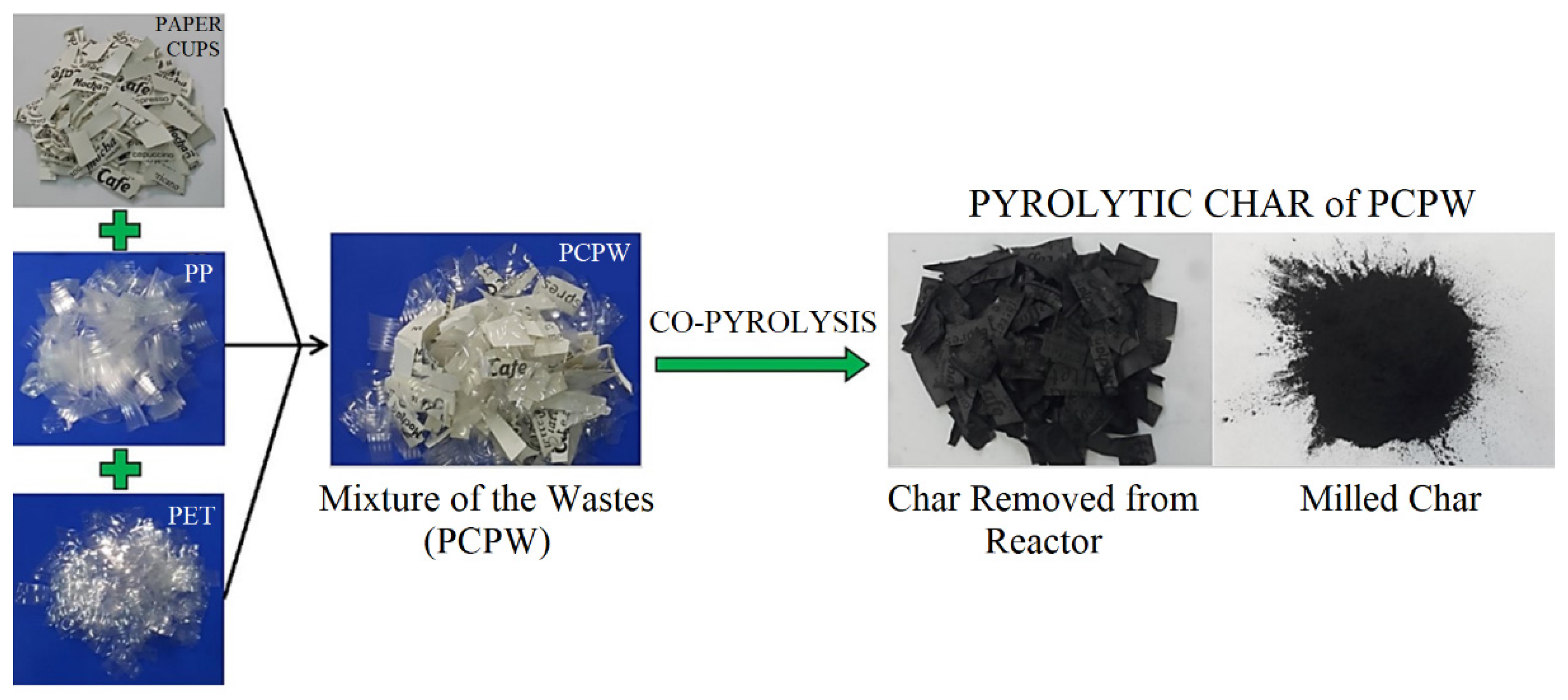
2.1. Materials
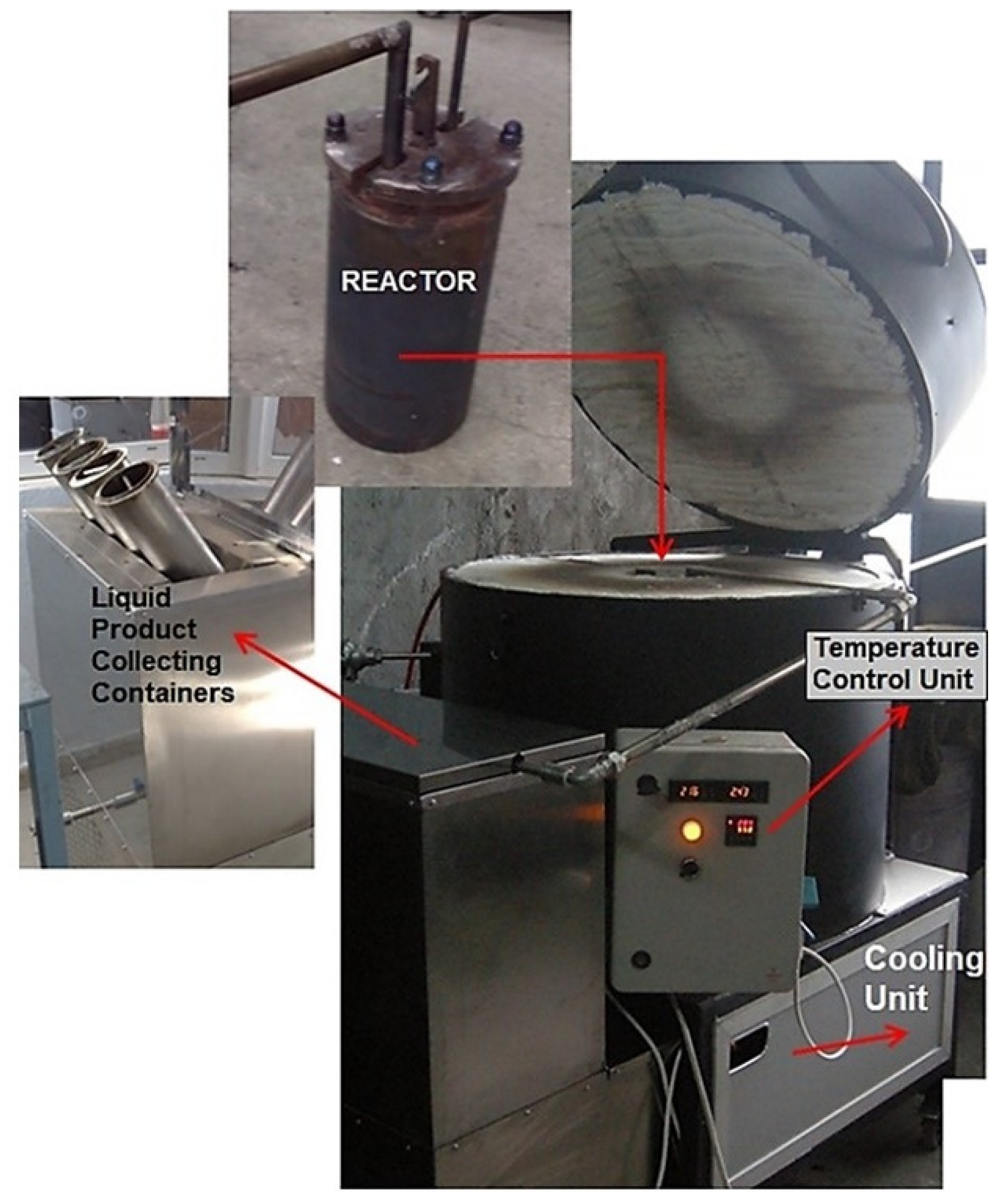
2.2. Co-Pyrolysis Method
- the synergistic interaction among cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin;
- the synergistic interaction between the biomasses and plastic melt;
- the synergistic interaction among the vapors of plastic and biomass.
2.3. Properties of the Char
2.4. Softening Point, Penetration and Specific Gravity Tests
2.5. Penetration Index (PI)
2.6. Rotational Viscosity (RV) Test
2.7. Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR) Test
2.8. Storage Stability Test
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Production of the Co-pyrolysis Char
3.2. Product Yields from Co-pyrolysis of PCPW
3.3. CHN Elemental Analysis Results
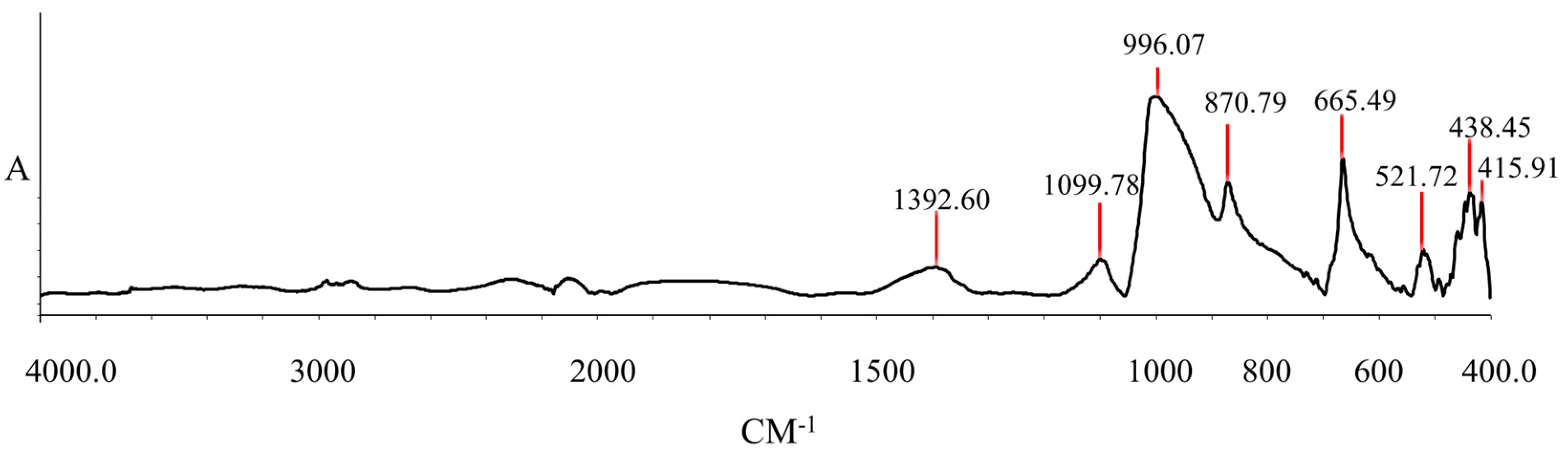
3.4. FTIR Test Results
3.5. Bitumen Modification
3.6. Softening Point, Penetration and Specific Gravity Test Results
3.7. Penetration Index (PI) Results
3.8. Rotational Viscosity (RV) Test Results
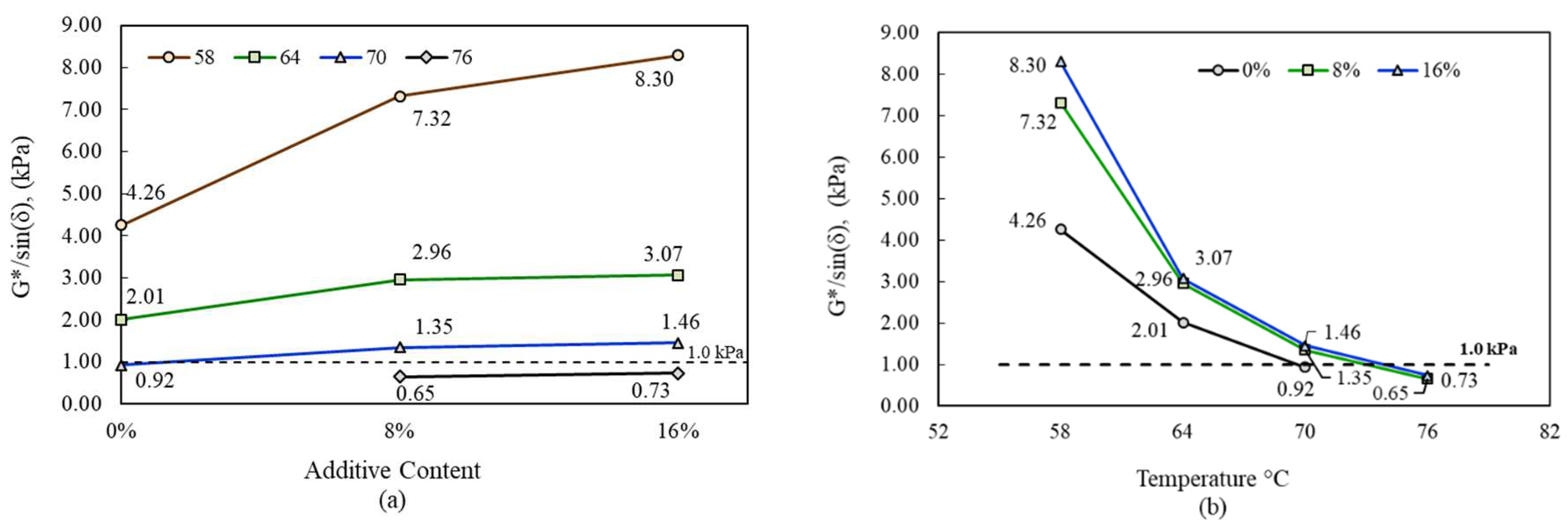
3.9. Dynamic Shear Rheometer Results
3.10. Performance Grades of Bituminous Binders
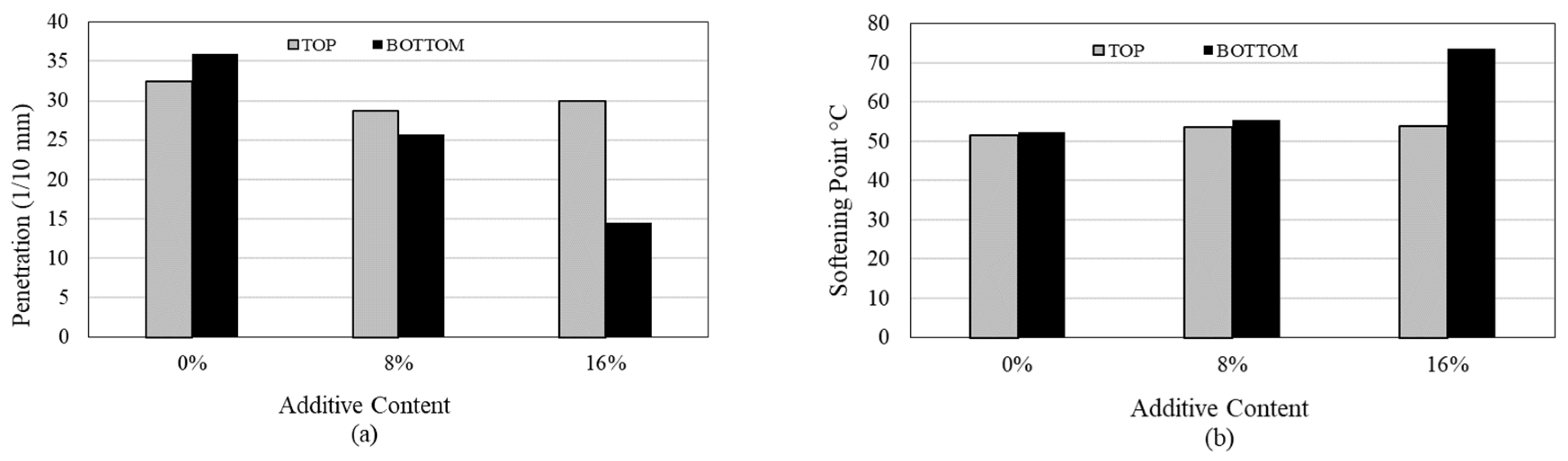
3.11. Storage Stability Test Results
4. Conclusions
- The char produced from co pyrolysis of different raw materials including paper cups, PP and PET plastic wastes improved the rutting resistance and the viscosity of neat bitumen.
- It was determined that the PCPW co pyrolysis char reduced the penetration value and increased the softening point of neat bitumen. In addition, this co pyrolysis char additive decreased the temperature sensitivity of neat bitumen and positively affected on the pure bitumen properties.
- The highest viscosity increment which is approximately 82.5% at 135°C was acquired by using this char additive for 16% ratio in bitumen. In addition, all binders did not exceed the 3000cp specification limit.
- The highest rutting resistance increment which is approximately 59% at 70°C was obtained by using 16% additive in pure bitumen.
- This char additive raised the high temperature PG of neat bitumen from PG64 to PG70.
- According to the test results, the PCPW char additive increased the rutting resistance of neat bitumen at high temperatures.
- From the storage stability test results, it can be said that the binder modified with this pyrolytic char had a good storage stability when this char was used at 8% ratio in pure bitumen.
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunter, R.N.; Self, A.; Read, J. The Shell Bitumen Handbook, 6th ed.; Gerlis, R., Taylor, R., Shell International Petroleum Company Ltd, ICE Publishing, Westminster, London, 2015.
- McGennis, R.B.; Shuler, S.; Bahia, H.U. Background of Superpave Asphalt Binder Test Methods. FHWA SA 94-069. Asphalt Institute, Washington, 1994.
- Porto, M.; Caputo, P.; Loise, V.; Eskandarsefat, S.; Teltayev, B.; Rossi, C.O. Bitumen and bitumen modification: A review on latest advances. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 742. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, X.; Polaczyk, P.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, M.; Huang, B. The utilization of waste plastics in asphalt pavements: A review. Cleaner Materials. 2021, 2, 100031. [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Zaidi, S.B.A.; Ahmed, I. Performance evaluation of asphalt binders modified with waste engine oil and various additives. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Dai, Q.; You, Z.; Wang, H.; Peng, C. Rheological performance of bio-char modified asphalt with different particle sizes. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1665. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Choudhary, R.; Narzari, R.; Kataki, R.; Shukla, S.K. 2018. Evaluation of bio-asphalt binders modified with biochar: a pyrolysis by-product of mesua ferrea seed cover waste. Cogent Eng. 2018, 5, 1548534. [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Dai, J.; Fu, Z.; Li, C.; Wen, Y.; Jia, M.; Wang, Y.; Shi, K. Biochar for asphalt modification: A case of high-temperature properties improvement. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150194. [CrossRef]
- Çeloğlu, M.E.; Yılmaz, M.; Kök, B.V.; Yalçın, E. Effects of various biochars on the high temperature performance of bituminous binder. 6th Eurasphalt & Eurobitume Congress, Prague, Czech Republic, 1-3 June 2016.
- Martinez-Toledo, C.; Valdes-Vidal, G.; Calabi-Floody, A.; Gonzalez, M.E.; Reyes-Ortiz, O. 2022. Effect of biochar from oat hulls on the physical properties of asphalt binder. Materials. 2022, 15, 7000. [CrossRef]
- Rondon-Quintana, H.A.; Reyes-Lizcano, F.A.; Chaves-Pabon, S.B.; Bastidas-Martinez, J.G.; Zafra-Mejia, C.A. Use of Biochar in Asphalts: Review. Sustainability. 2022, 14, 4745. [CrossRef]
- Czajczynska, D.; Anguilano, L.; Ghazal, H.; Krzyzynska, R.; Reynolds, A.J.; Spencer, N.; Jouhara, H. Potential of pyrolysis processes in the waste management sector. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2017, 3, 171-197. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Burra, K.G.; Lei, T.; Gupta, A.K. Co-pyrolysis of waste plastic and solid biomass for synergistic production of biofuels and chemicals-A review. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2021, 84, 100899. [CrossRef]
- Seah, C. C.; Tan, C. H.; Arifin, N.A.; Hafriz, R.S.R.M.; Salmiaton, A.; Nomanbhay,S.; Shamsuddin, A.H. Co-pyrolysis of biomass and plastic: Circularity of wastes and comprehensive review of synergistic mechanism. Results Eng. 2023, 17, 100989. [CrossRef]
- Demirbaş, A. Mechanism of liquefaction and pyrolysis reactions of biomass. Energy Convers. Manag. 2000, 41, 633-646. [CrossRef]
- Çepelioğullar, Ö.; Pütün, A.E. Products characterization study of a slow pyrolysis of biomass-plastic mixtures in a fixed-bed reactor. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis. 2014, 110, 363–374.
- Zhou, X.; Broadbelt, L.J.; Vinu, R. Mechanistic understanding of thermochemical conversion of polymers and lignocellulosic biomass. Chapter Two, Adv. Chem. Eng. 2016, 49, pg: 95-198. [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Ruj, B.; Sadhukhan, A.K.; Gupta, P. A TG-FTIR investigation on the co-pyrolysis of the waste HDPE, PP, PS and PET under high heating conditions. J. Energy Inst. 2020, 93, 1020-1035. [CrossRef]
- Uzoejinwa, B.B.; He, X.; Wang, S.; Abomohra, A.E., Yamin, H.; Wang, Q. Co-pyrolysis of biomass and waste plastics as a thermochemical conversion technology for high-grade biofuel production: Recent progress and future directions elsewhere worldwide. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 163, 468–492. [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.; Xiong, Q.; Yang, L.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, S.; Li, H.; Huang, H. An overview on engineering the surface area and porosity of biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 144204. [CrossRef]
- Esso, S.B.E.; Xiong, Z.; Chaiwat, W.; Kamara, M.F.; Longfei, X.; Xu, J.; Ebako, J.; Jiang, L.; Su, S.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, J. Review on synergistic effects during co-pyrolysis of biomass and plastic waste: Significance of operating conditions and interaction mechanism. Biomass Bioenergy. 2022, 159, 106415. [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, S.; Fujita, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Kameda, T.; Saito, Y.; Yoshioka, T. Impacts of pyrolytic interactions during the co-pyrolysis of biomass/plastic: Synergies in Lignocellulose-polyethylene system. Journal of the Japan Institute of Energy, 2019, 98, 202-219. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Sahoo, A.; Mohanty, K. Pyrolysis kinetics and synergistic effect in co-pyrolysis of Samanea saman seeds and polyethylene terephthalate using thermogravimetric analyser. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121608. [CrossRef]
- Sajdak, M. Impact of plastic blends on the product yield from co-pyrolysis of lignin-rich materials, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis. 2017, 124, 415–425. [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Li, G.; Zhou, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y. Thermal behavior and kinetic study of co-pyrolysis of microalgae with different plastics. Waste Manage. 2021, 126, 331–339.
- AASHTO T-315. Standard test method for determining the rheological properties of asphalt binder using a dynamic shear rheometer. Washington DC, 2012.
- ASTM D-4402. Standard test for viscosity determination of asphalt at elevated temperatures using a rotational viscometer. West Conshohocken, 2002.
- EN-13399. Bitumen and bituminous binders-Determination of storage stability of modified bitumen, 2017.
- ASTM D-36. Standard test for softening point of bitumen (ring-and-ball apparatus). West Conshohocken, 2006.
- ASTM D-5. Standard test for penetration of bituminous materials. West Conshohocken, 2006.
- ASTM D-70. Standard test method for specific gravity and density of semi-solid bituminous materials (pycnometer method), 2003.
- Biswal, B.; Kumar, S.; Singh, R.K. Production of hydrocarbon liquid by thermal pyrolysis of paper cup waste. Journal of Waste Management, 2013, 731858. [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wu, K.; Chen, Y.; Hu, H.; Yang, M. Study on pyrolytic kinetics and behavior: The co-pyrolysis of microalgae and polypropylene. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 522–528. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Wang, W.; Ji, G.; Zhao, M.; Li, A. Kinetics, product evolution, and mechanism for the pyrolysis of typical plastic waste. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2022, 10, 91−103.
- EN-14023. Bitumen and bituminous binders-Specification framework for polymer modified bitumens, 2010.
- Martin Lara, M.A.; Pinar, A.; Ligero, A.; Blazquez, G.; Calero, M. Characterization and use of char produced from pyrolysis of post-consumer mixed plastic waste. Water, 2021, 13, 1188. [CrossRef]

| Test | Result |
|---|---|
| Softening Point (°C) | 50 |
| Viscosity (135°C) (cp) | 468.80 |
| Penetration (1/10 mm) | 46.2 |
| Penetration Index (PI) | -1.38 |
| Specific Gravity | 1.039 |
| Solid Product | Liquid Product | Gas Product | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Yields (%) | 15.6 | 21.7 | 62.7 |
| Elements | Carbon (%) | Hydrogen (%) | Nitrogen (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elemental Composition of PCPW Char | 75.7420 | 1.9604 | 0.2792 |
| Additive Content | 0% | 8% | 16% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (1/10 mm) | 46.2 | 43.43 | 35.37 |
| Softening Point (°C) | 50 | 52.25 | 54.25 |
| Specific Gravity | 1.039 | 1.070 | 1.087 |
| Additive Content | 0% | 8% | 16% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration Index (PI) | -1.38 | -0.98 | -0.96 |
| Additive Content | 0% | 8% | 16% |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Failure Temperature (°C) | 69.6 | 72.5 | 73.3 |
| High Temperature PG | PG 64 | PG 70 | PG 70 |
| Additive Content |
Softening Point °C | Softening Point Difference (°C) |
Penetration (1/10 mm) | Penetration Difference (1/10 mm) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top Part | Bottom Part | Top Part | Bottom Part | |||
| 0% | 51.50 | 52.25 | 0.75 | 32.40 | 35.93 | 3.53 |
| 8% | 53.75 | 55.50 | 1.75 | 28.75 | 25.73 | 3.02 |
| 16% | 54.00 | 73.50 | 19.50 | 29.90 | 14.48 | 15.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





