1. Introduction
Machine learning-based person re-identification systems have become increasingly important for a variety of security and safety tasks. These systems typically employ a mapping function that learns to embed images into a compact Euclidean space, often a unit sphere [
3,
4]. The goal of this embedding is to ensure that images of the same person are mapped to adjacent feature points, while images of different individuals are mapped to distant feature points. In an ideal setting, the embedding approach should be resistant to real-world situational changes, such as differences in pedestrian position, orientation, and occlusion within a single scene. Additionally, the embedding approach should not rely on clothing appearance, given that individuals may wear different clothing over time, spanning days or weeks.
The performance of many machine learning-based tracking and re-identification applications is significantly influenced by the image acquisition systems utilized, such as static cameras, as well as the associated costs of data collection. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have recently emerged as a viable alternative for monitoring public spaces, offering a low-cost means of data collection while covering broad and challenging-to-access regions [
5,
6,
7,
8]. The advancements in UAV technology have greatly benefited multi-object tracking (MOT), particularly pedestrian tracking and re-identification, by providing a practical solution to various challenges such as occlusion, moving cameras, and difficult-to-reach locations. Compared to static cameras, UAVs are considerably more flexible, allowing for adaptability in emplacement location and direction in the three-dimensional (3D) space.
In a previous study, we presented a solution to the problem of pedestrian tracking and re-identification from aerial devices. Our approach involved modeling each identity as a von-Mises Fisher (vMF) distribution, which was inspired by a methodology proposed by [
9] for image classification and retrieval. Specifically, we learned a compact embedding for each identity in a unit sphere using a base convolutional neural network (CNN) encoder.
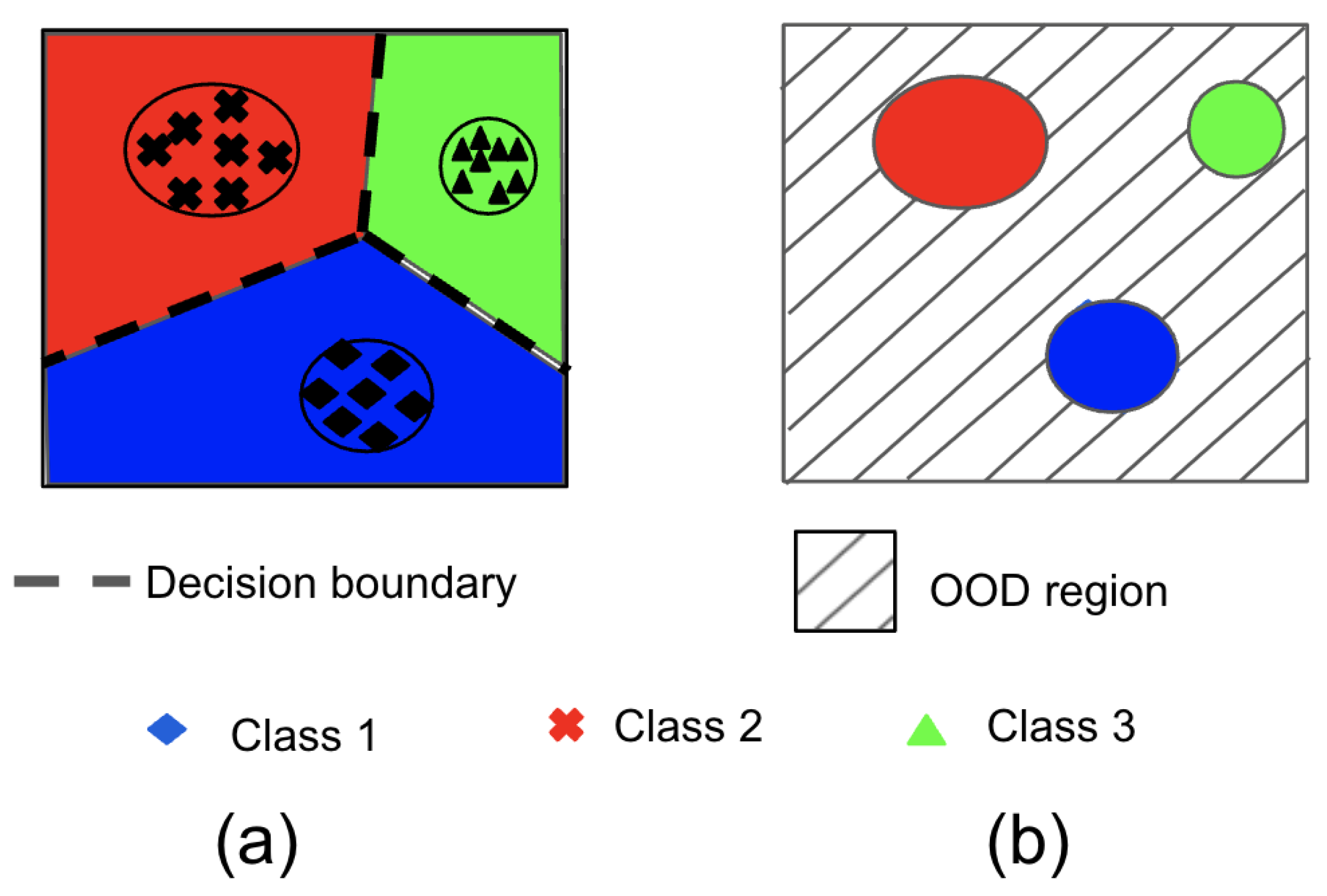
Figure 1 is an illustration of one of the deep learning classification models biggest limitation. This limitation happens when it comes to detecting out-of-distribution data. Since the embeddings are learned from only in-distribution data, they may not be able to accurately represent or detect data that is significantly different from what they were trained on. This means that deep learning models can struggle to identify and handle novel or anomalous data, which is a significant challenge in many real-world applications.
In an open-world environment, it is highly likely that a deployed model will encounter new pedestrians that it has not learned to recognize, which falls under the category of OOD. Additionally, the model is expected to encounter objects that differ from humans, which also are referred to as OOD data points. The OOD data points can be classified into two types of shifts: non-semantic shifts such as new pedestrians, and semantic shifts such as objects that differ from humans. The definition of semantic shifts is drawn from [
10]. Therefore, the detection of OOD is crucial in ensuring the robustness of trained models in real-world scenarios.
In order to tackle the challenge of OOD detection, one possible approach is to train a deep learning classifier to distinguish between ID and OOD using real-world OOD data points. However, obtaining or generating sufficient real-world OOD data points in high-dimensional pixel space is a challenging and intractable task. To address this issue, a recent study by [
2] proposed a framework called Virtual Outlier Synthetic (VOS), which synthesizes virtual outliers in the embedding space in an online manner. This framework utilizes the compact embedding of samples from the same object to generate virtual outliers, using a class-conditional multivariate Gaussian distribution, which is consistent with the objective of the vMF method.
The recognition of pedestrians and detection of Out-Of-Distribution (OOD) objects is of great importance for developing robust and efficient surveillance systems. In light of this, the combination of the von Mises-Fisher (vMF) method and Virtual Outlier Synthetic (VOS) framework presents a promising solution for improving the accuracy of pedestrian re-identification and OOD detection. Building upon our previous research, we propose an integrated end-to-end learning framework that leverages the vMF method for modeling each ID, enabling simultaneous recognition of individuals and detection of OOD objects. Our proposed approach builds on the strengths of both the vMF and VOS methods, with the vMF method providing a compact embedding for pedestrian recognition and the VOS framework synthesizing virtual outliers for effective OOD detection.
The present paper makes the following key contributions:
A novel end-to-end framework for re-identifying pedestrians and detecting OOD instances from aerial devices.
The first method, to the best of our knowledge, that leverages online virtual outlier synthetic to address OOD in pedestrian re-identification.
The structure of this paper is as follows.
Section 2 provides a background and related work overview.
Section 3 presents a review of the preliminaries related to vMF method and VOS, providing a basic understanding of directional statistics, along with a review of the VOS framework.
Section 4 describes the dataset case study. In
Section 5, we propose our online pedestrian re-identification and OOD detection framework. In
Section 6, we present the experimental results. Finally, we conclude with a summary of our contributions and potential future work in
Section 7.
2. Related Work
2.1. Pedestrian Re-identification
Research on pedestrian re-identification encompasses various aspects, ranging from feature-based [
11] to metric-based [
12] approaches, as well as from hand-crafted features to deeply learned features [
13,
14]. In this paper, we focus on three recent and relevant sub-areas within the pedestrian re-identification topic.
Open-world person re-identification is a specific instance of set matching, where the goal is to match one-to-one between two pedestrian sets, namely the probe and gallery sets. This task assumes that each person appears in both sets and aims to identify matching pairs. The open-world setting means that the identity of the pedestrians in the probe set may not be known in advance, which adds an additional layer of complexity to the problem. This is in contrast to the closed-world setting, where all pedestrian identities are known beforehand. In this work, we focus on the open-world person re-identification problem, where the gallery set is assumed to be known.
The generalized-view re-identification problem involves learning discriminative features from two different views obtained by two distinct, stationary cameras [
15,
16]. However, collecting, annotating, and matching data from two separate cameras can be expensive in practical scenarios.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in pedestrian re-identification from drones, leading to the development of new benchmark datasets [
7,
17]. Drones offer a novel tool for data acquisition, particularly in the field of video surveillance and analysis. This presents new opportunities and challenges for pedestrian detection, tracking, and re-identification, as it helps to overcome some of the limitations associated with static cameras.
2.2. Out Of Distribution Detection
The OOD (Out-of-Distribution) problem may be treated as a classification task, wherein denotes the ID, where , and for C classes. A distribution is utilized to produce . To predict class probabilities, many classification models, including deep neural networks, are trained on datasets. When the model is used in production in the open world, it encounters data derived from a different distribution during inference, where . These two distributions are not identical. A direct approach involves sampling from the distribution. However, sampling from the high-dimensional pixel space is complex and impractical.
The disparity between distributions and can be classified into two primary categories, namely semantic and non-semantic shifts. A semantic shift arises when a novel class appears in , while a non-semantic shift arises when instances of objects from the same class that are present in appear differently in comparison to those observed during the training phase. The latter type is akin to an anomaly detection configuration. To enable the model to function effectively in the production setting, it must detect these types of shifts in the data.
In recent years, many studies have addressed the issue of detecting out-of-distribution (OOD) samples in a classification task setup. A binary scoring function is commonly used in these studies, where a high score is assigned to data points from the in-distribution (ID) and a low score is assigned to OOD samples. This scoring function can be learned using energy models, linear transformations with deep neural networks, or a combination of both techniques.
2.3. Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection refers to the identification of unusual events, items, or observations that deviate significantly from expected behaviors or patterns. In the context of computer vision, outliers, noise, and novel objects are detected as anomalies when compared to the distribution of known objects. This problem is often encountered in various industrial applications where acquiring images of normal samples is easy, but specifying expected variations in defects is difficult and costly. Such scenarios are often referred to as out-of-distribution (OOD) detection problems, where a model is required to distinguish between samples drawn from the training data distribution and those lying outside its support. Existing work on anomaly detection is predominantly based on learning compact visual representations in a latent space using auto-encoders and GANs. Unsupervised methods using pre-trained CNNs, such as PatchCore and SPADE, as well as PaDIM, are widely used in industrial applications.
Pedestrian re-identification can be framed as an anomaly detection problem, where the task is to identify pedestrians from the known training data distribution and to detect pedestrians that do not belong to this distribution as outliers or anomalies. These anomalous pedestrians could arise due to a variety of reasons such as novel viewpoints, changes in illumination, or occlusions.
2.4. Deep Metric Learning
In numerous machine learning applications, such as multi-object tracking (MOT), it is crucial to establish a measure of similarity among data objects. Metric learning aims to learn a mapping function that quantifies this similarity. Specifically, the objective of metric learning is to minimize the distance between data points belonging to the same category while maximizing the distance between data points from different categories.
In recent years, deep learning has demonstrated remarkable performance in various machine learning tasks, including image classification, image embedding, and multiple object tracking (MOT). The superior representational power of deep learning in extracting highly abstract non-linear features has resulted in the emergence of a new research area known as Deep Metric Learning (DML) [
9,
18,
19,
20]. This field aims to learn a mapping function that quantifies the similarity between data points, with the objective of minimizing the similarity between data points from the same category and maximizing the distance between data points from different categories.
Multiple Object Tracking (MOT) has been enhanced by the success of Deep Metric Learning (DML), which involves training a neural network to extract features and learn a similarity measure between object instance patches.
3. Preliminaries
3.1. Directional Statistics in Machine Learning
Directional data refers to points in a Euclidean space whose norm is constrained to be one, denoted by , where represents the Euclidean norm of order two. In other words, these points lie on the surface of a unit sphere. The statistical analysis of such data is referred to as directional statistics.
The topic of directional statistics has gained a lot of attention due to high demands from fields such as machine learning or the availability of big data sets that necessitate adaptive statistical methodologies, as well as technical improvements. Recently, directional statistics method has led to tremendous success in many computer vision tasks, such as image classification and retrieval [
9], pose estimation [
21], and face verification [
22]. It has also been introduced to other machine learning fields such as text mining [
23].
3.1.1. Von Mises-Fisher Distribution
Von Mises-Fisher Distribution (vMF) is a probability distribution function for directional data. It can be seen as a Gaussian distribution since they have very similar properties. In a directional data space
, the probability distribution density function defined as:
where,
is the mean direction of the distribution,
is a concentration parameter which can be seen as the standard deviation for Gaussian distribution,
p is the space dimension,
is a normalization term and
is the modified Bessel function of the first kind with order
v.
Given
N samples from a vMF distribution, we can estimate its parameters as follows:
and
In (16), .
3.1.2. Learning von-Mises Fisher Distribution
The learning problem is defined as follows. Given C identities, the goal is to learn a vMF distribution for every ID parameterized by , where .
Given a point
x in the mapping space, the normalized probability of x belonging to a chosen class
c is defined as
Equation (
4) can be used to increase the likelihood that the sample belongs to the correct class while decreasing the likelihood that it belongs to other classes. Given a mini-batch with
N samples and for a
C identity, we can maximize the following objective function:
Where
X and
Y represent the data points in the mini-batch and their ID labels,
contains the deep model parameters, and
,
. For a simplification purpose, we assumed
to be a constant for all IDs, and by applying the negative likelihood, Equation (
6) can be simplified to:
In [
9], a learning algorithm (Algorithm 1) based on alternative learning is proposed to overcome the difficulty of optimizing both the neural network parameters
and the von Mises-Fisher (vMF) mean direction distributions
. In this algorithm, the mean directions are first fixed, and then the neural network parameters are trained for several iterations before updating them using the training data set. The mean direction update is based on the estimation using all training data points. The algorithm converges when the mean directions and loss are stagnant. Given a class
i with
N training data points, let
denote the mapping of the
sample using the current mapping function, where
. The mean direction of class
i can be updated using the following formula:
|
Algorithm 1 VMF learning algorithm. |
|
In the inference phase, the identification (ID) label of a given object can be predicted by computing the cosine similarity between the object’s feature vector and the learned mean directions. The object will be labeled with the ID of the mean vector that is closest in terms of cosine similarity.
3.2. Visual Outlier Synthetic
The synthesis of outliers is a potent method for generating synthetic data points, and various approaches have been developed to synthesise images in computer vision. Among these approaches, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) [
24] are the most widely used and straightforward technique. However, synthesising images in the high-dimensional pixel space is challenging to optimize and track. To overcome this challenge, [
2] proposed the "Visual Outlier Synthetic" (VOS) framework that synthesizes virtual outliers in the embedding space in an online manner. Their method depends on the model learning the embedding of the ID objects to generate hard virtual outliers.
The Visual Outlier Synthetic (VOS) framework is predicated on the assumption that the feature representation of object instances in the embedding space conforms to a class-conditional multi-variate Gaussian distribution. Specifically, objects belonging to the same class form a multi-variate Gaussian distribution within the latent representational space.
3.2.1. Learning of Class-Conditional Multi-Variate Gaussian Distribution
Given a coreset that represents the embeddings of the objects, it is possible to learn a class-conditional Gaussian distribution by estimating its parameters. Specifically, from the coreset, the empirical class mean
and covariance
of the training samples
can be computed as follows:
Where is the number of objects in class k, and N is the total number of objects.
3.2.2. Sampling from the Features Representational Space
The authors propose to generate virtual outliers by sampling from the feature representation space using the class-conditional multivariate distributions described above. The virtual outliers are generated in an online manner, with the learning progress resulting in increasingly compact embeddings for each class. Sampling virtual outliers from the learned class-conditional distribution aligns with this objective and helps to achieve a more compact embedding.
The sampling of virtual outliers for a given class is achieved by drawing samples from the class-conditional Gaussian distribution using the expression , where is the estimated covariance matrix of the coreset for that class. The sampled virtual outliers are restricted to the sublevel set based on the likelihood, ensuring that they align with the underlying distribution of the class. Additionally, the magnitude of is set to be sufficiently small so that the generated outliers are situated in the vicinity of the class boundary.
3.2.3. Out of Distribution Detection
The VOS framework utilized a linear transformation to differentiate between virtual outliers. Specifically, they employed a Fully Connected Pooling (FCP) layer that learned to delimit the precise boundaries surrounding the ID. Additional information regarding the classification process between In-Domain (ID) and Out-of-Domain (OOD) instances, as well as the learning algorithm employed, can be found in the original publication.
4. Dataset Description
In recent times, pedestrian tracking and re-identification have become a topic of significant interest owing to their wide-ranging applications, including but not limited to surveillance systems and traffic control. Nevertheless, tracking and re-identification of individuals present a substantial challenge due to the limitations of the acquisition system, particularly when using stationary cameras. In recent years, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) have emerged as a promising alternative for monitoring public areas, as they offer an inexpensive mean of data collection while effectively covering large and remote areas that may otherwise be inaccessible.
The
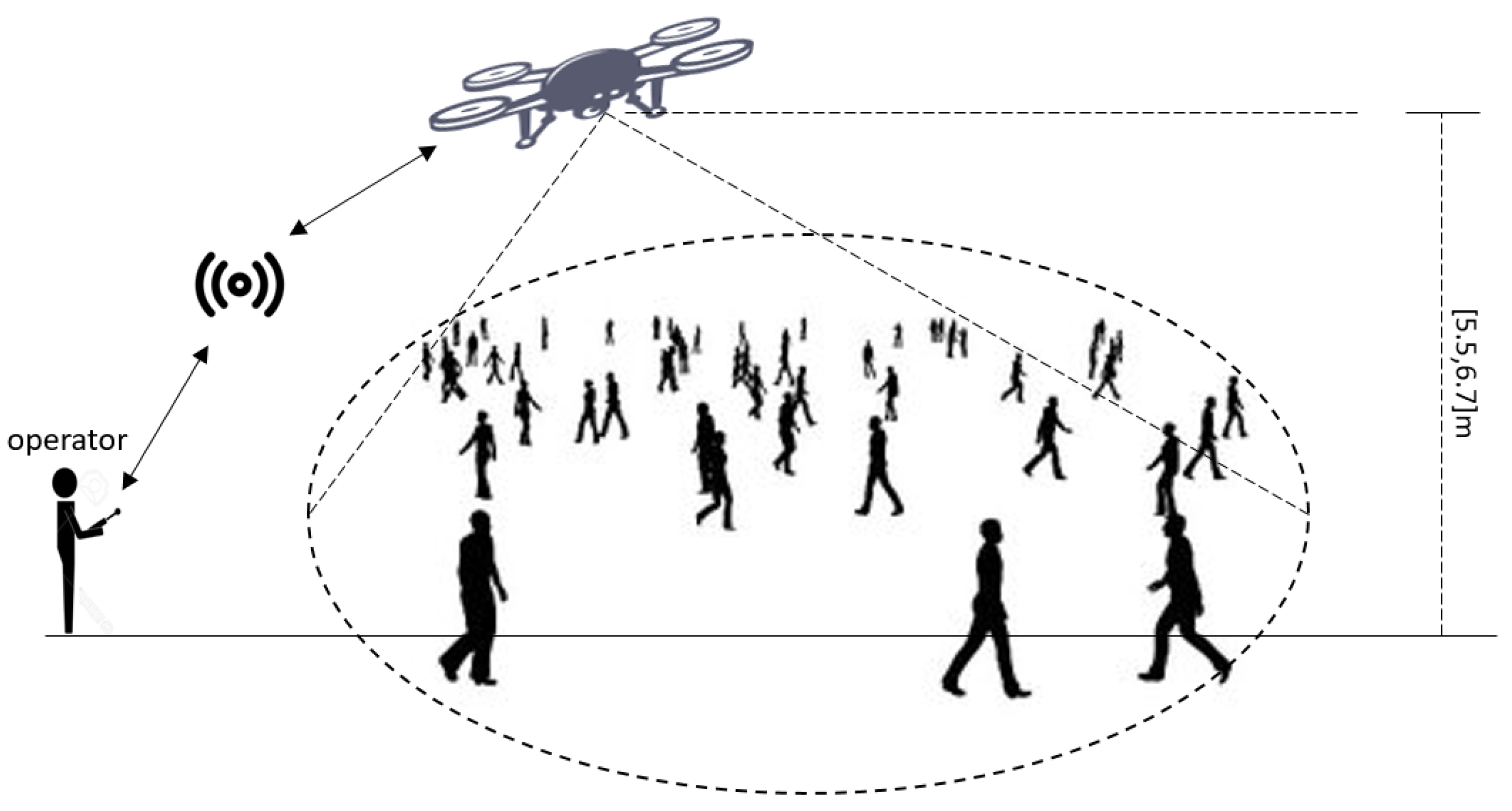
P-DESTRE dataset, developed by researchers from the University of Beira Interior (Portugal) and the JSS Science and Technology University (India), is a fully annotated dataset for detecting, tracking, re-identificating, and searching pedestrians from aerial devices [
17]. The dataset was collected using "DJI Phantom 4" drones piloted by humans to fly and collect data from a volunteer audience walking at altitudes ranging from 5.5 to 6.7 meters. An illustration of how the data was acquired is showed in
Figure 2 along with a statistic summary detailed in
Table 1. The dataset comprises 75 videos recorded at a rate of 30 Frame Per Second (fps), containing a total of 318,745 annotated instances of 269 different IDs.
The primary distinguishing feature of the P-DESTRE dataset is the pedestrian search challenge, where data is collected over long periods with constant ID labels across observations. This characteristic distinguishes it from comparable datasets, making it an excellent case study for training and evaluating frameworks for pedestrian tracking and re-identification from aerial devices. In this context, re-identification techniques cannot rely on clothing appearance-based features, which is a key property that distinguishes search from the less challenging re-identification problem.
The P-DESTRE dataset was used for all experiments, and it provides a unique and valuable resource for research on pedestrian tracking and re-identification from aerial devices. In the future, the researchers plan to explore more aerial datasets for further investigation.
5. Methodology
In our prior publication [
1], we introduced a method founded on directional statistics that enables the learning of a condensed representation for each identification (ID) within a unit spherical space. The ID data obtained was a collection of von-Mises-Fisher (vMF) distributions that were parameterized by
, where
. The learning procedure for this method was detailed in Section II. The aim of this method was to track and re-identify a set of pre-defined pedestrians. Nonetheless, in an open-world scenario such as security environments, the prospect of encountering new pedestrians not present in the dataset is highly probable. Consequently, the model must be capable of detecting such pedestrians as out-of-distribution (OOD).
The proposed scoring functions presented for discriminating between ID and OOD are chiefly derived from the compressed representation of the objects within the ID. These functions enforce the embedding of each class within a compact cluster by the convolutional neural networks (CNNs).
Motivated by this observation, the potential synergy between the vMF-based model and OOD scoring functions warrants exploration. Inspired by the two works presented in the previous section, we propose a framework that merges both approaches.
5.1. Out of Distribution Pedestrian Based on Von-Mises Fisher Distribution
5.1.1. Learning
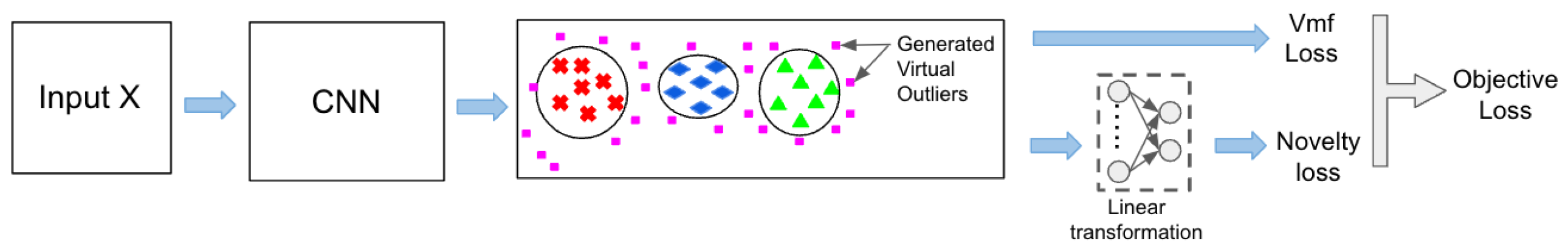
We propose an end-to-end learning framework for pedestrian re-identification and novelty detection that is as simple to train as the traditional training method with soft-max loss. The framework consists of three main components: a representational visual feature based on a convolutional neural network (CNN), the adoption of the VOS method to detect out-of-distribution (OOD) pedestrians, and the generation of hard virtual outliers by sampling from the embedding space. We posit that sampling from the embedding space can not only aid in detecting novelty but also help build a robust model. By assuming that the score function will help to learn a more compact embedding for each identification while simultaneously detecting OOD pedestrians as non-semantic shifts, we generate hard virtual outliers.
Figure 3 illustrates the proposed framework during the training phase.
Once the hard virtual outliers are generated, two parallel heads are computed. The first head computes the von-Mises-Fisher (vMF) loss using the embeddings of the identification. The second head computes the novelty loss over the binary output of the linear transformation. This loss aims to distinguish between virtual outliers and identification embeddings. The objective loss is then computed by taking a weighted sum of the two losses.
In the VOS framework, the uncertainty loss (novelty loss) is defined using the binary sigmoid loss.
Where, represents the weights of the classification head for novelty detection. is the energy score function. is the weights of the CNNs base encoder.
To train this framework in an end-to-end manner, we combine the two losses to form one objective training loss.
This is a weighted loss, where
is the weighted of the uncertainty loss.
|
Algorithm 2 The learning algorithm. |
|
Input: ID data , queue size for Gaussian density estimation, weight for uncertainty regularization, and . |
|
Output: pedestrian re-identification parameterized by , and novelty detector parameterized by
|
|
While train do:
|
- 1.
Initialize CNN parameters . - 2.
-
Repeat:
- (a)
Estimate mean directions using (8) and all the training data. - (b)
-
For several iteration:
- i
update the ID queue with the embeds of training inputs. - ii
Estimate the multi-variate distribution using the . - iii
sample virtual outlier - iv
compute the objective loss using Equation 16.
- (c)
Train CNN for several iterations and update .
- 3.
Until convergence.
|
5.1.2. Inference
In the inference process for a given pedestrian input, two main parts are involved. The first part involves utilizing the OOD scoring function
to determine whether the pedestrian is OOD or not. This decision can be made based on a chosen threshold, which is determined by the experimental settings.
Once a pedestrian input is determined to be an ID, the proposed framework uses the vMF framework as the second step to re-identify the pedestrian. The re-identification process involves measuring the similarity between the input embedding in the unit sphere and the learned mean direction . This comparison is achieved by calculating the cosine similarity between the input pedestrian and the mean direction associated with each pedestrian ID. The input pedestrian is then assigned to the ID of the pedestrian with the highest cosine similarity to its mean direction.
6. Experiments
In this section, we present a comprehensive summary of the experiments conducted to assess the performance of our proposed framework. We followed a standard procedure in all experiments, which involved training the proposed framework on the training set of the in-distribution (ID) dataset, denoted as . The evaluation was performed on the union of two sets: the validation set of the ID, denoted as , and the out-of-distribution (OOD) dataset, denoted as . It is crucial to note that the ID and OOD datasets should not have any overlapping person identities.
The setting of the ID and OOD datasets can be performed in two distinct ways. Firstly, two separate datasets with no common person identities can be selected and set as the ID and OOD datasets, respectively. Secondly, the same dataset can be divided into ID and OOD by splitting each set into ID and OOD with a predetermined ratio, for the training, validation, and testing sets.
It is important to emphasize that during both the training and validation phases, the framework does not have access to the OOD dataset. The performance of the model was monitored based on the validation set of the ID and the online generated virtual outliers. This involved selecting the appropriate model checkpoint and optimizing the hyper-parameters of the framework. During the testing phase, we used both the test set of and to evaluate the model’s long-term re-identification and OOD detection capabilities.
6.1. Two Different Datasets Setting
6.1.1. ID Dataset
The P-DESTRE dataset (accessed on 5 March 2023) was utilized as the (ID) data in the pedestrian re-identification experiments. A thorough description of the P-DESTRE dataset can be found in Section III. To perform the experiments, the data was randomly divided into 5 folds, with each fold consisting of a 50% learning set, a 10% gallery set, and a 40% query set. This division of data into folds helps to ensure a fair evaluation of the models and provides a comprehensive understanding of the performance of the models across different data splits. Additionally, this also helps to mitigate the risk of overfitting and provides a more robust evaluation of the models, given that the models are tested on unseen data. By using a randomly divided dataset, the results of the experiments are more representative of the models’ general performance and can be better compared to other models and their results. The detailed information about this split is provided in
http://p-destre.di.ubi.pt/pedestrian_detection_splits.zip (accessed on 5 March 2023).
6.1.2. OOD Dataset
As OOD, we used
CUHK03-NP, which is a widely used dataset in the field of pedestrian re-identification. It contains 14,097 images of 1,467 identities [
13] (accessed on 5 March 2023). All the splits were used in the evaluation as an
. The CUHK03-NP dataset is a commonly used benchmark dataset in the field of computer vision and machine learning, particularly for evaluating person re-identification algorithms. The dataset was collected from two camera views at the Chinese University of Hong Kong and consists of 1467 identities captured in a multi-shot manner. Each identity is captured with both color and depth images, providing a rich source of information for developing and testing algorithms. The dataset has become a popular choice for researchers due to its large scale and the presence of challenging conditions, such as occlusions and viewpoint changes, which pose difficulties for re-identification algorithms. The CUHK03-NP dataset has been used in many recent studies, demonstrating its utility as a benchmark for evaluating the performance of re-identification algorithms under various conditions.
Table 2 summarises the dataset properties.
6.1.3. Training Details
From each image, the bounding boxes are cropped and scaled to patches of dimension
. For the prepossessing, the input patches are normalized using the mean and standard deviation learned from imagenet dataset. The feature extractor architecture is made up of two parts: a base model and a header. As a base model, we used Wide ReseNet-50 (WRN) [
25], with a header consisting of two Fully connected Pooling Layers (FPL) of sizes
. The feature extractor was trained using 50 epochs with a batch size of 64. 128 is the embedding space dimension. The used optimizer is Adam with a learning rate starting with
and decreasing by a factor of
every 25 of the training epochs. We set the concentration parameter
to 15 for the learning algorithm hyper-parameter. This number produced the best outcomes experimentally. We update the mean directions after every epoch.
For hyper-parameters related to VOS, we used 500 samples per identity to estimate the class-conditional Gaussians. We set . We sampled 1000 virtual outliers from the embedding space. We also set . The linear transformation consists of two layers . The first layer has a number of nodes equal to the number of identities so that the energy based can be computed per identity as designed in VOS.
6.1.4. Two Datasets Settings
In evaluating the framework’s capability in detecting Out-of-Distribution (OOD) samples, we employed the Area Under the Curve (AUC) based on Precision/Recall curve metric. This metric was chosen for a number of compelling reasons. Firstly, it is a more accurate metric when dealing with imbalanced data, which is the case in the ratio of ID vs OOD samples in the open world scenario. Secondly, it is preferred when the positive class, in this case ID, is of utmost importance. The results in
Table 3 summarize the performance of a pedestrian tracking and re-identification framework based on the Area Under the Curve based on Precision/Recall curve (AUC-PR) metric. The framework was tested using two datasets, the ID dataset P-DESTRE and the OOD dataset CUHK03-NP. The results show that the framework had a performance of 63.10% ± 1.64% AUC-PR using the Wide Residual Network (WRN) as its backbone. This suggests that the framework performed well in detecting ODD samples, however, the results should be interpreted with caution as the standard deviation of the results is not provided, which can give an indication of the variance in the performance of the model. Additionally, it would be beneficial to compare the performance with other existing methods to put the results into perspective.
6.2. One Dataset Setting
Another way to evaluate the framework is on the same pedestrian dataset but divided into ID and OOD by identities. Detecting OOD data points in a different dataset setting is expected to be easier comparing to the one dataset setting regarding the image acquisition setups. The differences between the two image acquisitions such as the type of cameras, the angle, and the lighting can play a role in obtaining a separable embedding between ID and OOD. Although, it is important to detect OOD from a different setup, it also important to test the model on ID and OOD from the same image acquisition setup. We believe that the one dataset setup is more likely to happen in the open world environment. In addition, to detect the non-semantic shifts (new pedestrians) in the same setup is more challenging and the model has to rely on features such as face and body characteristics rather than clothing appearances.
Since the P-DESTRE dataset is randomly divided into folds, we divided each fold to two datasets, ID and OOD based on the identities. The division ration is for ID and OOD respectively. It is worth mentioning that this division is preformed for each fold.
For the training details, everything is almost the same as in the two different dataset settings, except we lowered the value to . This can be explained by the fact that distinguishing the ID from the OOD in this setting is more challenging and requires harder virtual outlier to learn a better score function .
We evaluate the model the same way we evaluated the two different dataset settings. The results presented in
Table 4 show the performance of a framework using the WRN backbone on the ID dataset. The performance is evaluated using the Area Under the Curve based on Precision-Recall (AUC-PR) metric and the results are reported as the mean ± standard deviation over multiple runs. The results show that the framework has an AUC-PR of 55.19% ± 3.02%. This indicates that the framework has moderate performance in identifying instances of the positive class (ID) in the P-DESTRE dataset, with some variance in performance between runs.
6.3. Long-Term Pedestrian Re-Identification
The effectiveness of our re-identification method can be evaluated using two methods. Firstly, we calculate the nearest mean direction of the IDs using equation
. Secondly, we assess the top-N recall performance using commonly used metrics in the field. The results, summarized in
Table 5, demonstrate a significant improvement over other state-of-the-art methods in different metrics. This confirms that the vMF-based feature extractor is able to learn robust features that help in recognizing a person, rather than their clothing appearance. Furthermore, our results show that the integration of the vMF method with the VOS framework leads to even better re-identification performance, as it creates a synergy that pushes the embedding of each identity to be more compact and distinct from other identities and out-of-distribution samples. The comparison between the method ArcFace with COSAM and the proposed vMF identifier with and without the VOS framework was performed in terms of Mean Average Precision (mAP), Rank-1 accuracy, Rank-20 accuracy and Mean Direction. The results indicate that the vMF identifier, both with and without VOS, significantly outperforms the ArcFace with COSAM method. With a mAP of 40.85% ± 3.42%, the vMF identifier achieved a higher performance compared to the ArcFace with COSAM which had a mAP of 34.90% ± 6.43%. Similarly, the Rank-1 accuracy and Rank-20 accuracy were higher for the vMF identifier with values of 63.81% ± 4.50% and 88.61% ± 8.50%, respectively, compared to the 49.88% ± 8.01% and 70.10% ± 11.25% achieved by the ArcFace with COSAM. Furthermore, the vMF identifier also outperformed the ArcFace with COSAM in terms of the Mean Direction with a value of 64.45% ± 3.90%. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed vMF identifier in pedestrian re-identification.
6.4. Analysis
Figure 4 presents a binary confusion matrix that delineates instances of ID and OOD, whereby the model prediction is compared to the ground truth. In delving deeper into examples of wrong predictions, we observed that these instances were frequently mapped in close proximity to the decision boundary where low energy function is learned.
In the case of the example where OOD was predicted as ID, we noted that when an individual’s image was captured from the back, it was often predicted as ID. Conversely, when the same individual’s image was captured from the front, the model predicted it as ID with greater accuracy.
In the instance where ID was predicted as OOD, our analysis suggested that this was a limitation of the trained model. Further improvements in the model are needed to better distinguish between similar-looking identities.
7. Conclusions
In this study, we present an extension of our previous work on pedestrian re-identification using the vMF distribution. We have revisited this method and combined it with the Visual Object Segmentation (VOS) framework to propose a new approach that we believe is worth exploring for the pedestrian re-identification problem. Our proposed framework is evaluated on a pedestrian dataset acquired from aerial devices. The results demonstrate that our approach improves long-term re-identification performance not only over previously applied methods but also over the same method without the VOS. Our goal is to detect non-semantic shifts as out-of-distribution (OOD) data. However, the experiments also reveal that it is more challenging to detect non-semantic shifts when the OOD data comes from the same acquisition setup.
As a future direction, we plan to extend our study to a more diverse range of datasets.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
The objective of this study is to augment the dependability, security, and safety of machine learning pedestrian tracking and re-identification models. The research conducted herein has the potential to generate direct societal benefits and impact safety and surveillance applications, including public area monitoring. Regulatory compliance has been upheld throughout the course of our study. By undertaking this research, we seek to advance the understanding of the problem of pedestrian monitoring and re-identification in practical settings, thus heightening public awareness of safety concerns. We anticipate no deleterious effects from the pursuit of this investigation.
References
- Bouzid, A.; Sierra-Sosa, D.; Elmaghraby, A. Directional Statistics-Based Deep Metric Learning for Pedestrian Tracking and Re-Identification. Drones 2022, 6, 328. [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wang, Z.; Cai, M.; Li, Y. VOS: Learning What You Don’t Know by Virtual Outlier Synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.01197 2022. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.H.; Wang, Y.; Weinberger, K.Q.; Campbell, M. Deep Person Re-identification for Probabilistic Data Association in Multiple Pedestrian Tracking. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.08565 2018. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.F.; Shin, H.; Ju, J.; Ko, H. Online pedestrian tracking with multi-stage re-identification. 2017 14th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS). IEEE, 2017, pp. 1–6.
- Bonetto, M.; Korshunov, P.; Ramponi, G.; Ebrahimi, T. Privacy in mini-drone based video surveillance. 2015 11th IEEE international conference and workshops on automatic face and gesture recognition (FG). IEEE, 2015, Vol. 4, pp. 1–6.
- Hirzer, M.; Beleznai, C.; Roth, P.M.; Bischof, H. Person re-identification by descriptive and discriminative classification. Scandinavian conference on Image analysis. Springer, 2011, pp. 91–102.
- Layne, R.; Hospedales, T.M.; Gong, S. Investigating open-world person re-identification using a drone. European conference on computer vision. Springer, 2014, pp. 225–240.
- Singh, A.; Patil, D.; Omkar, S. Eye in the sky: Real-time Drone Surveillance System (DSS) for violent individuals identification using ScatterNet Hybrid Deep Learning network. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2018, pp. 1629–1637.
- Zhe, X.; Chen, S.; Yan, H. Directional statistics-based deep metric learning for image classification and retrieval. Pattern Recognition 2019, 93, 113–123. [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Shen, Y.; Jin, H.; Kira, Z. Generalized odin: Detecting out-of-distribution image without learning from out-of-distribution data. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020, pp. 10951–10960.
- Zheng, W.S.; Gong, S.; Xiang, T. Person re-identification by probabilistic relative distance comparison. CVPR 2011. IEEE, 2011, pp. 649–656.
- Dikmen, M.; Akbas, E.; Huang, T.S.; Ahuja, N. Pedestrian recognition with a learned metric. Asian conference on Computer vision. Springer, 2010, pp. 501–512.
- Li, W.; Zhao, R.; Xiao, T.; Wang, X. Deepreid: Deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2014, pp. 152–159.
- Yi, D.; Lei, Z.; Liao, S.; Li, S.Z. Deep metric learning for person re-identification. 2014 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 2014, pp. 34–39.
- Avraham, T.; Gurvich, I.; Lindenbaum, M.; Markovitch, S. Learning implicit transfer for person re-identification. European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2012, pp. 381–390.
- Koestinger, M.; Hirzer, M.; Wohlhart, P.; Roth, P.M.; Bischof, H. Large scale metric learning from equivalence constraints. 2012 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, 2012, pp. 2288–2295.
- Kumar, S.A.; Yaghoubi, E.; Das, A.; Harish, B.; Proença, H. The p-destre: A fully annotated dataset for pedestrian detection, tracking, and short/long-term re-identification from aerial devices. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 2020, 16, 1696–1708. [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, A. Automatic target recognition with deep metric learning. 2020.
- Schroff, F.; Kalenichenko, D.; Philbin, J. Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2015, pp. 815–823.
- Rippel, O.; Paluri, M.; Dollar, P.; Bourdev, L. Metric learning with adaptive density discrimination. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.05939 2015. [CrossRef]
- Prokudin, S.; Gehler, P.; Nowozin, S. Deep directional statistics: Pose estimation with uncertainty quantification. Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), 2018, pp. 534–551.
- Hasnat, M.; Bohné, J.; Milgram, J.; Gentric, S.; Chen, L.; others. von mises-fisher mixture model-based deep learning: Application to face verification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.04264 2017.
- Straub, J.; Chang, J.; Freifeld, O.; Fisher III, J. A Dirichlet process mixture model for spherical data. Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. PMLR, 2015, pp. 930–938.
- Salimans, T.; Goodfellow, I.; Zaremba, W.; Cheung, V.; Radford, A.; Chen, X. Improved techniques for training gans. Advances in neural information processing systems 2016, 29.
- Zagoruyko, S.; Komodakis, N. Wide residual networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1605.07146 2016. [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Guo, J.; Xue, N.; Zafeiriou, S. Arcface: Additive angular margin loss for deep face recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019, pp. 4690–4699. [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, A.; Nambiar, A.; Mittal, A. Co-segmentation inspired attention networks for video-based person re-identification. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019, pp. 562–572. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).