Submitted:
18 April 2023
Posted:
18 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subsection
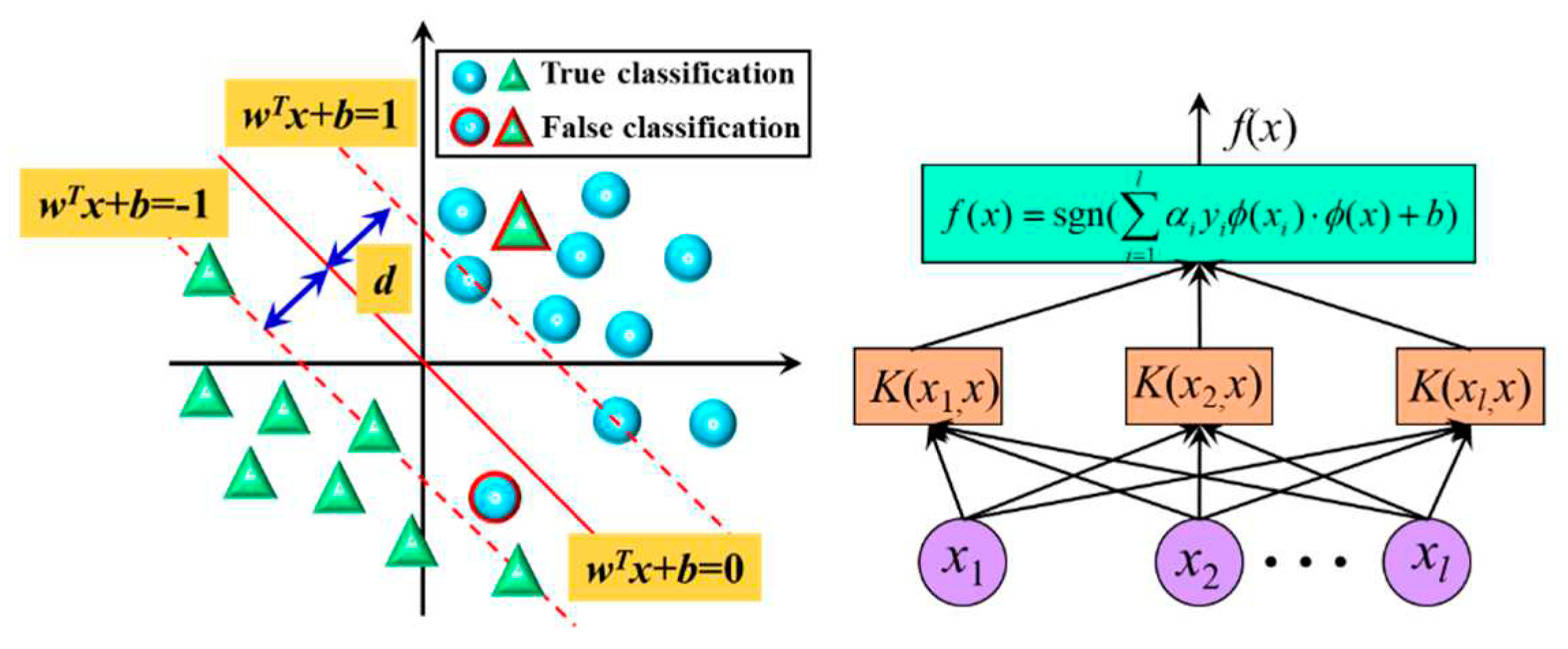
2.2. Support vector machine
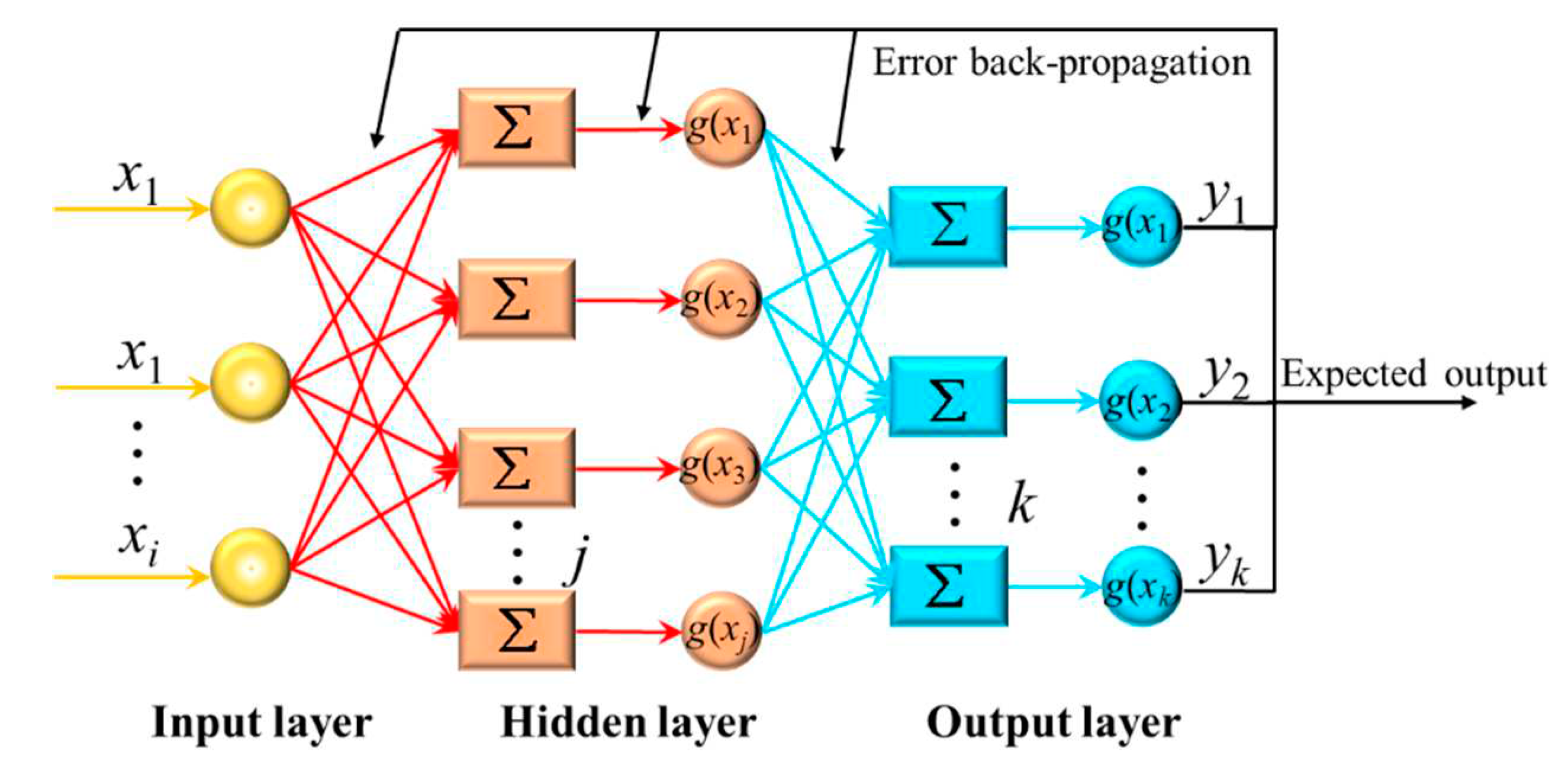
2.3. BP neural network
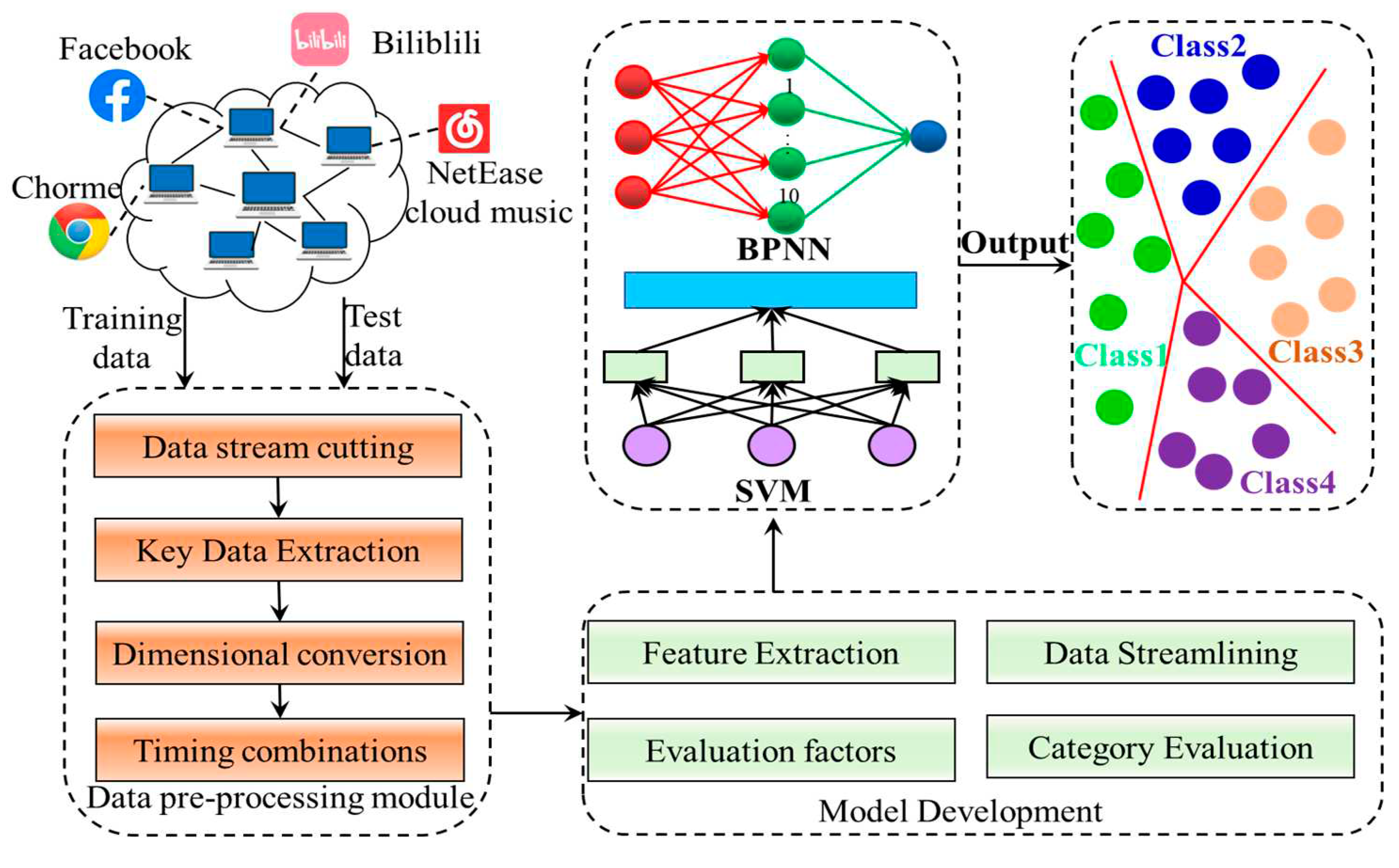
3. Model development
3.1. Dataset acquisition
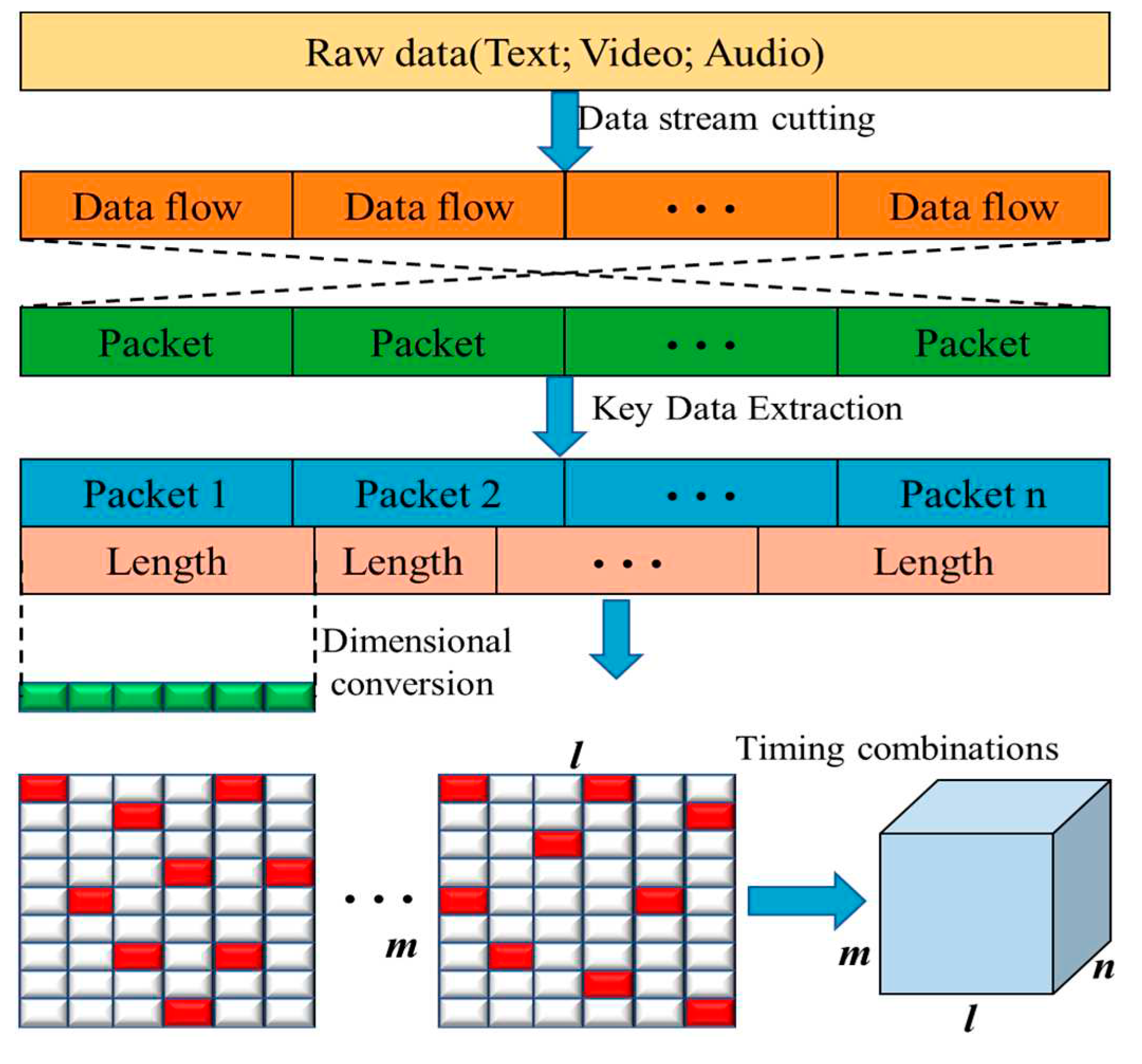
3.2. Data pre-processing module
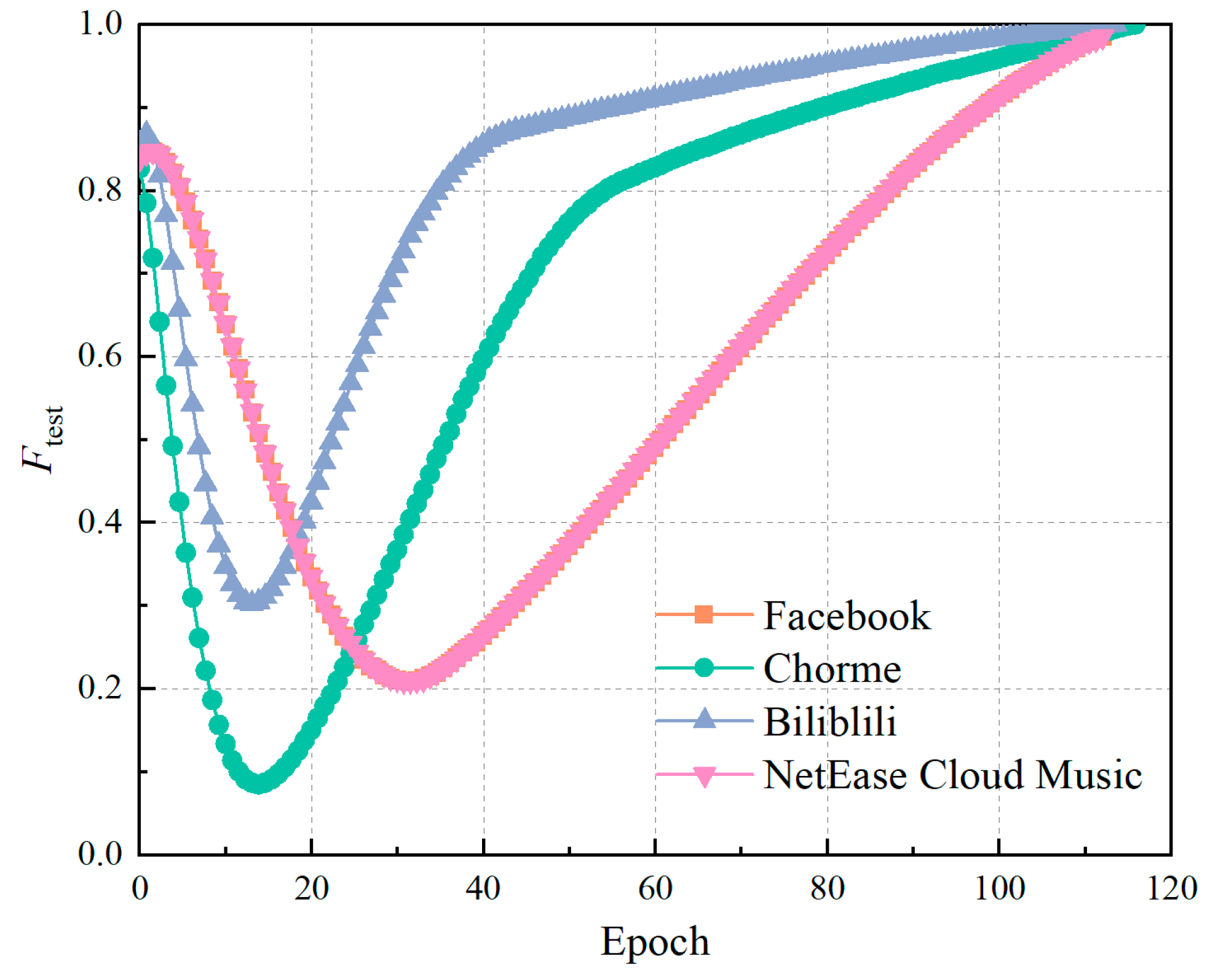
3.3. Model evaluation indicators
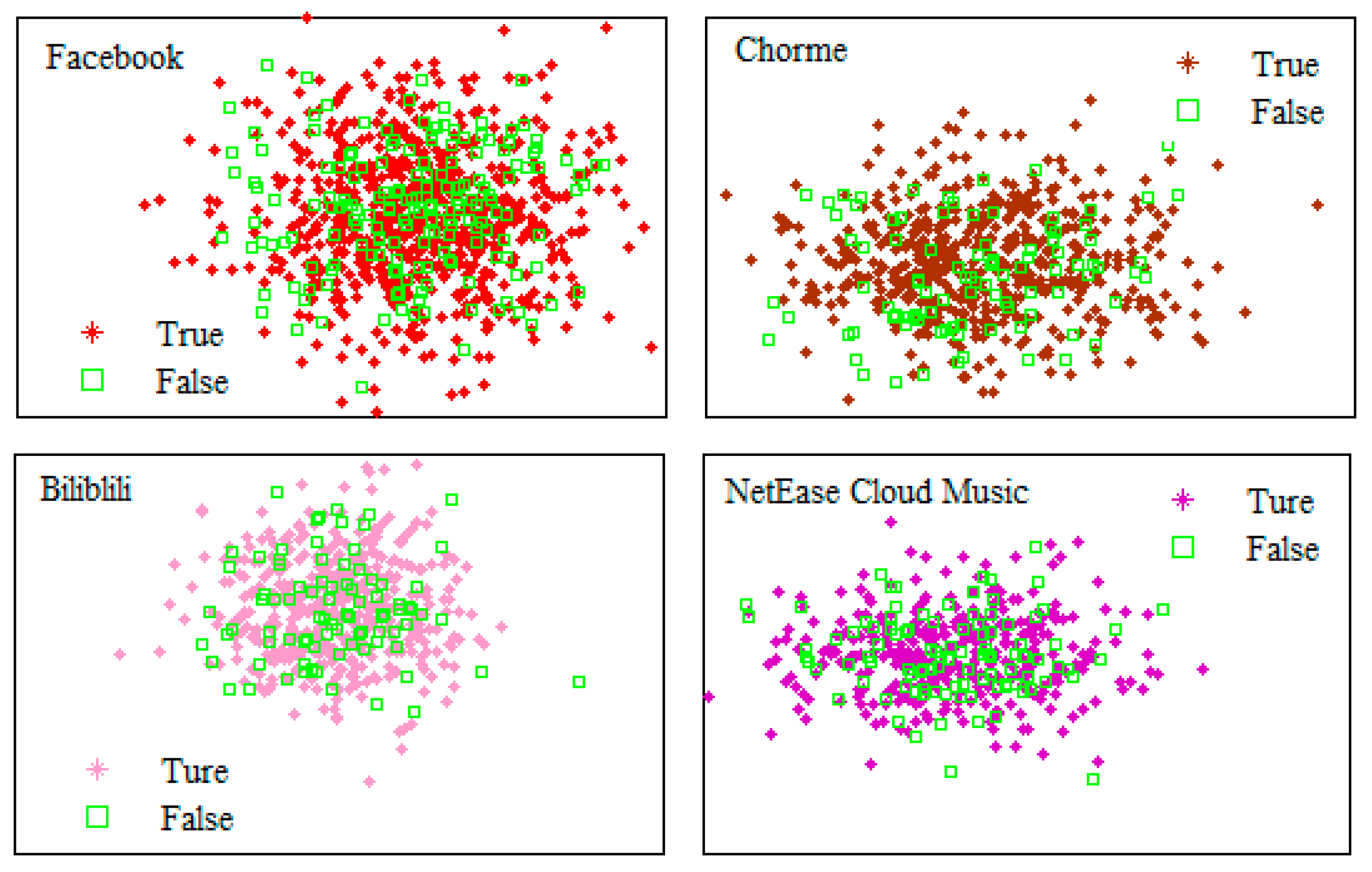
4. Experiments and results
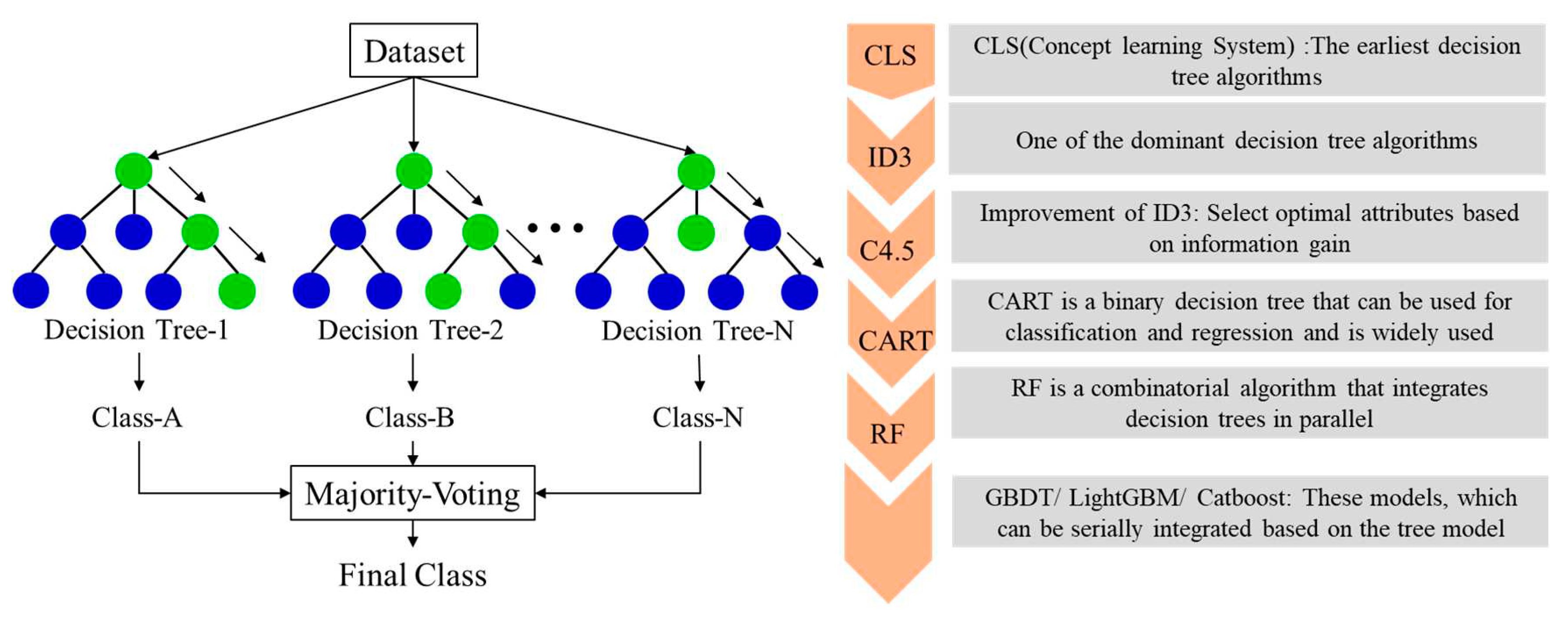
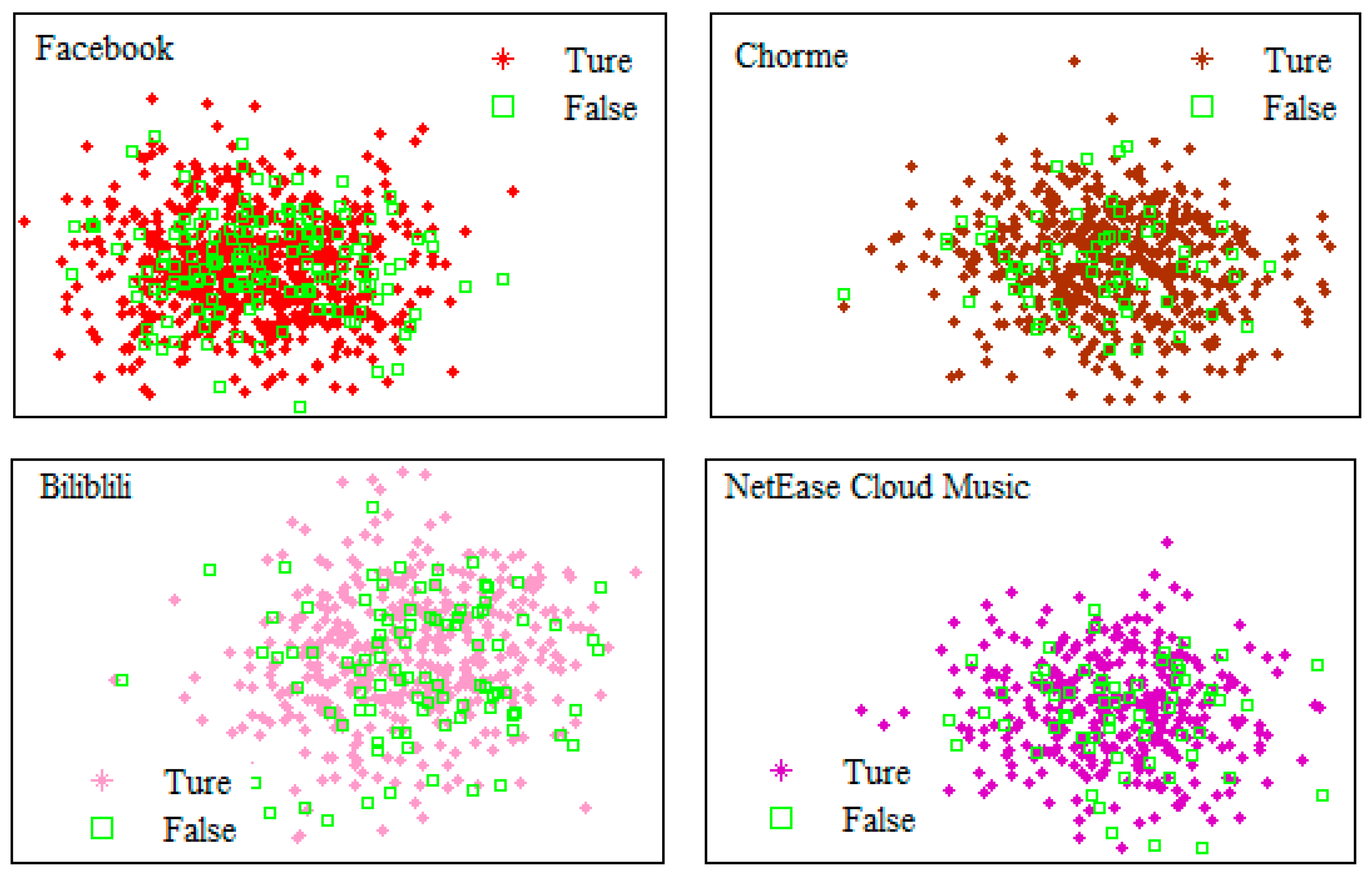
4.1. Results of the decision tree algorithm
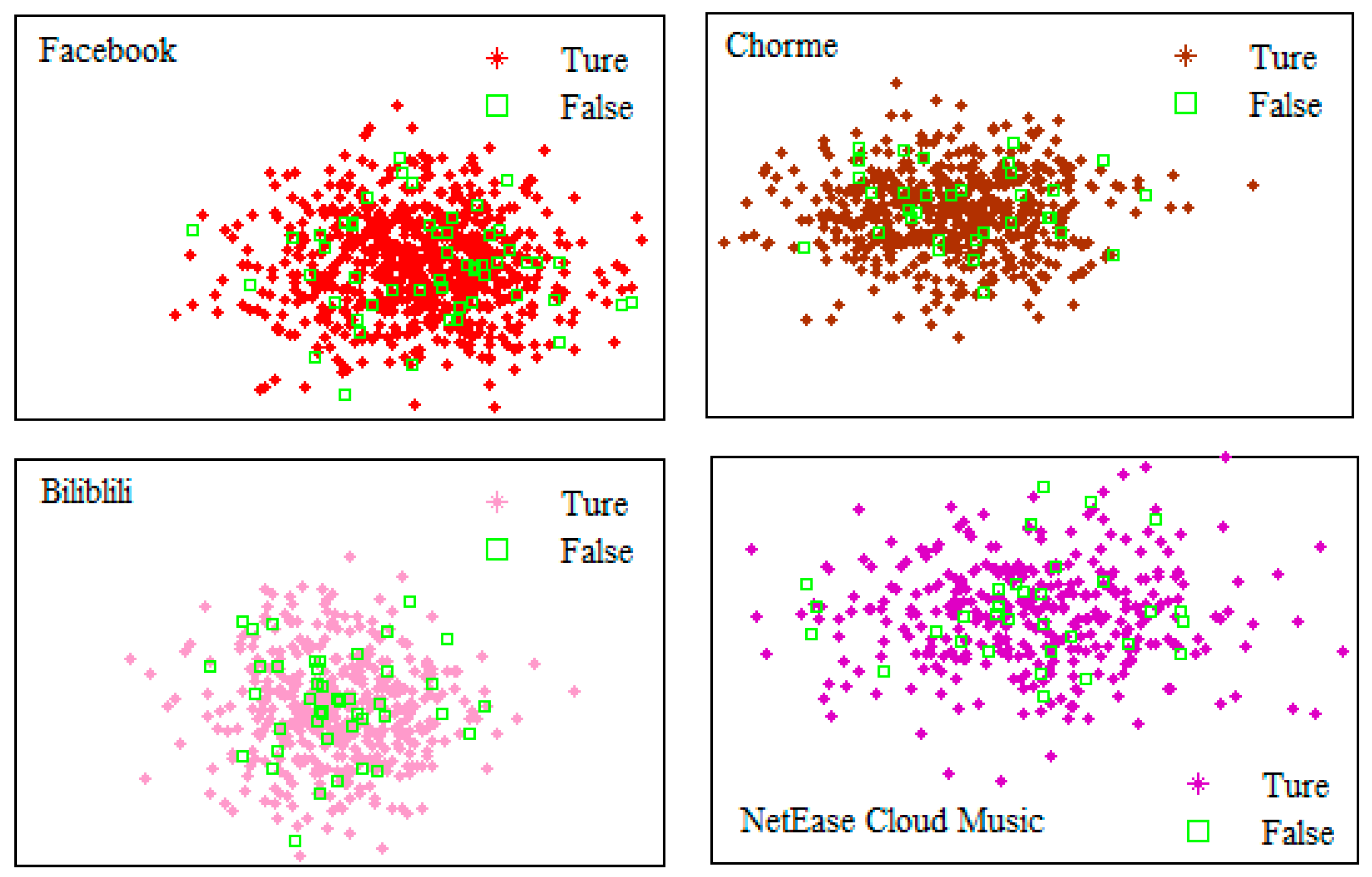
4.2. Results of support vector machine algorithm
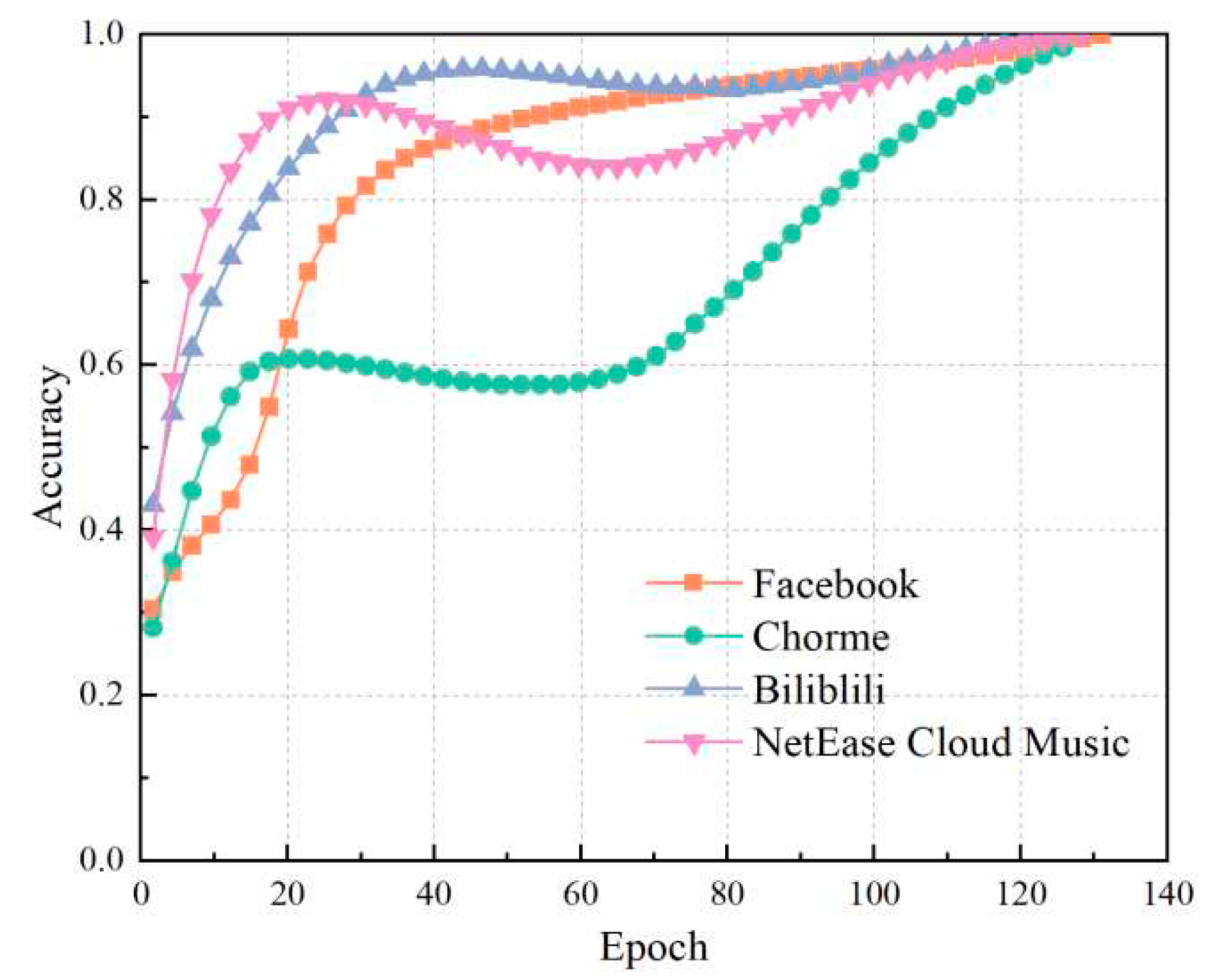
4.3. Results of neural network
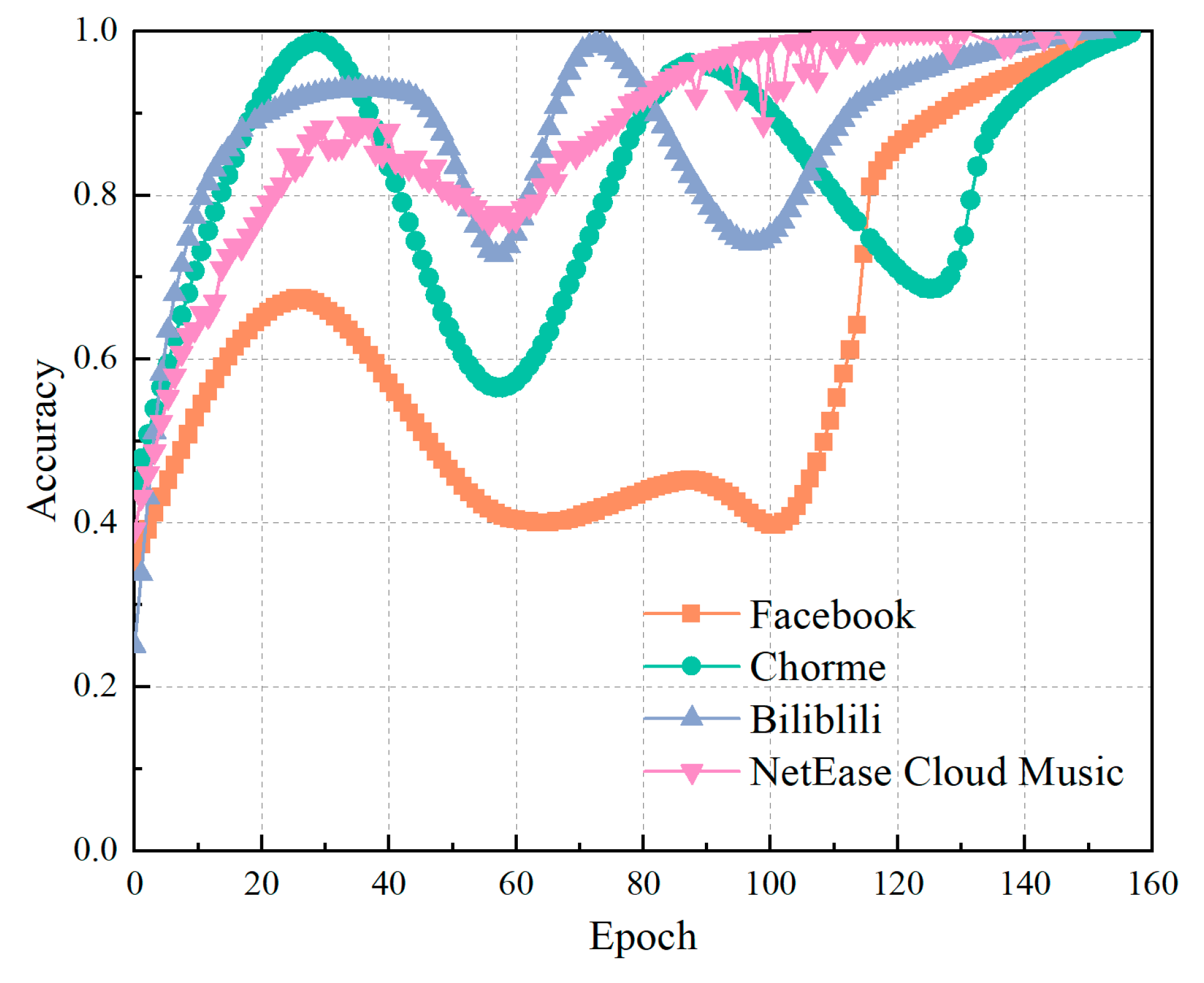
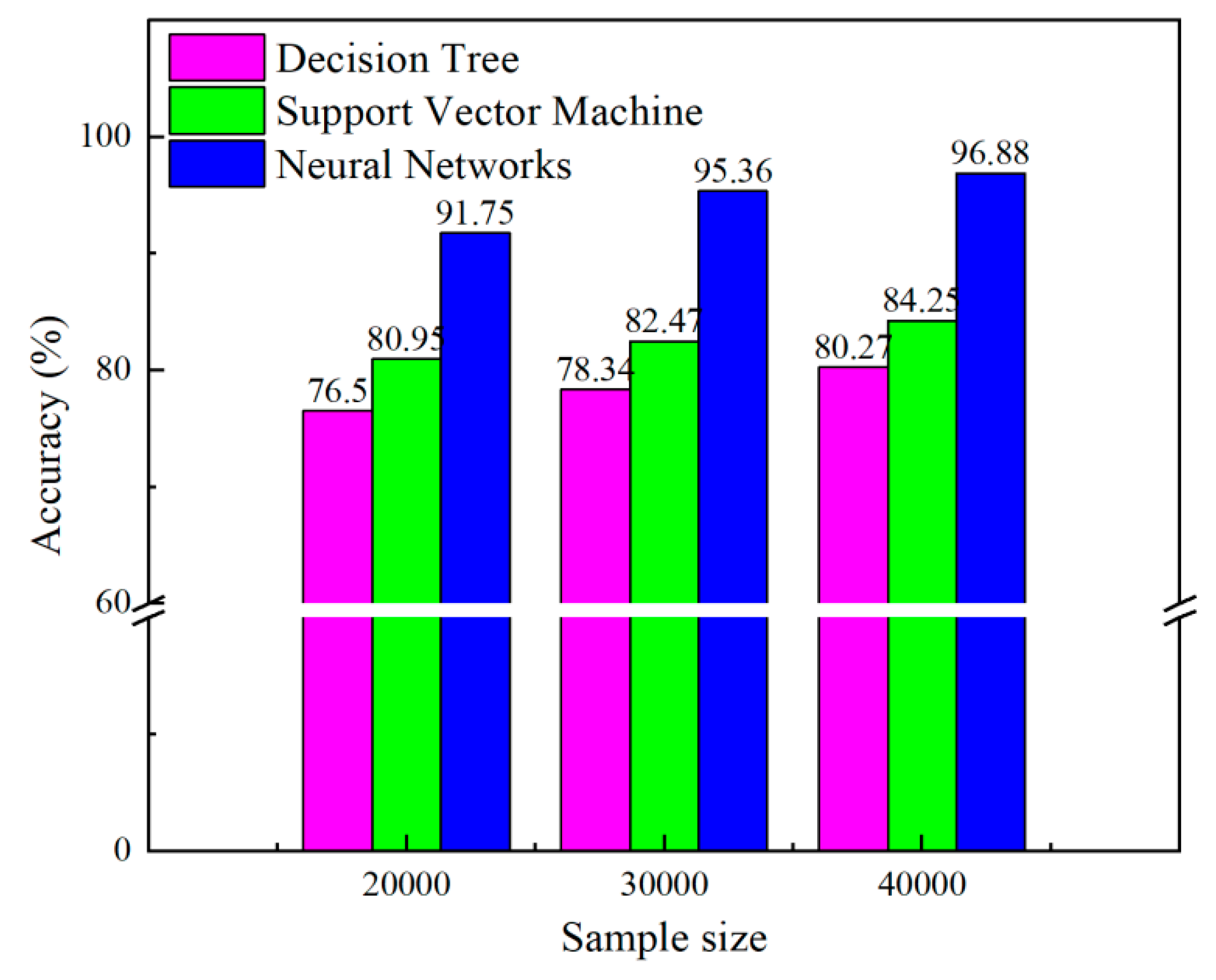
4.4. Effect of training samples on test accuracy
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Funding
References
- Dainotti, A.; Pescapé, A.; Claffy, K.C. Issues and Future Directions in Traffic Classification. IEEE Netw. 2012, 26, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Won, Y.J.; Chung, J.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Hong, J.W.K. Fine-Grained Traffic Classification Based on Functional Separation. Int. J. Netw. Manag. 2013, 23, 350–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, O.; Elhajj, I.H.; Kayssi, A.; Chehab, A. A Review on Machine Learning-Based Approaches for Internet Traffic Classification. [CrossRef]
- Lotfollahi, M.; Jafari Siavoshani, M.; Shirali Hossein Zade, R.; Saberian, M. Deep Packet: A Novel Approach for Encrypted Traffic Classification Using Deep Learning. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 1999–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Jin, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, W. DeepFlow: Deep Learning-Based Malware Detection by Mining Android Application for Abnormal Usage of Sensitive Data. Proc. - IEEE Symp. Comput. Commun. 2017, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erman, J.; Mahanti, A.; Arlitt, M.; Williamson, C. Identifying and Discriminating between Web and Peer-to-Peer Traffic in the Network Core. 16th Int. World Wide Web Conf. WWW2007 2007, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.; Zander, S.; Armitage, G. A Preliminary Performance Comparison of Five Machine Learning Algorithms for Practical IP Traffic Flow Classification. ACM SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 2006, 36, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Li, F.; He, Q.; Huang, M. Deep Learning–Based Network Application Classification for SDN. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2018, 29, e3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, B.; Hayes, M.; Seah, W.K.G. Developing a Traffic Classification Platform for Enterprise Networks with SDN: Experiences and Lessons Learned.
- Wang, W.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zeng, X.; Ye, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, M. HAST-IDS: Learning Hierarchical Spatial-Temporal Features Using Deep Neural Networks to Improve Intrusion Detection. [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Chen, Z.; Li, W. A Novel Intrusion Detection Model for a Massive Network Using Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 50850–50859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, S.; Liu, X. Deep Learning for Encrypted Traffic Classification: An Overview. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2019, 57, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S.K. Automatic Construction of Decision Trees from Data: A Multi-Disciplinary Survey. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 1998 24 1998, 2, 345–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavian, S.R.; Landgrebe, D. A Survey of Decision Tree Classifier Methodology. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1991, 21, 660–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Ma, X. Hybrid Decision Tree-Based Machine Learning Models for Short-Term Water Quality Prediction. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, S.; Rienties, B.; Khoja, S.A. The Role of Demographics in Online Learning; A Decision Tree Based Approach. Comput. Educ. 2019, 137, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheykhmousa, M.; Mahdianpari, M.; Ghanbari, H.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Ghamisi, P.; Homayouni, S. Support Vector Machine Versus Random Forest for Remote Sensing Image Classification: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 6308–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, J.; Garcia-Lamont, F.; Rodríguez-Mazahua, L.; Lopez, A. A Comprehensive Survey on Support Vector Machine Classification: Applications, Challenges and Trends. Neurocomputing 2020, 408, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, J.S.; Ananthi, J.V. RECURRENT NEURAL NETWORKS AND NONLINEAR PREDICTION IN SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES. J. Soft Comput. Paradig. (JSCP 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhou, P.; Yan, Y.; Agrawal, A.; Wang, Y.; Guo, D.; Goel, S. New Insights into the Methods for Predicting Ground Surface Roughness in the Age of Digitalisation. Precis. Eng. 2021, 67, 393–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Yan, Y.; Guo, D. Activation Functions Selection for BP Neural Network Model of Ground Surface Roughness. J. Intell. Manuf. 2020, 31, 1825–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Prevedouros, P.D. Performance and Challenges in Utilizing Non-Intrusive Sensors for Traffic Data Collection. Adv. Remote Sens. 2013, 2013, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Zhu, X.; Sun, J.; Li, S. Traffic Data Classification to Detect Man-in-the-Middle Attacks in Industrial Control System. Proc. - 2019 6th Int. Conf. Dependable Syst. Their Appl. DSA 2019 2020, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Application type | Training samples 1 | Training samples 2 | Training samples 3 | Training samples 4 | Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7000 | 10500 | 14000 | 700 | 35% | |
| Chorme | 5200 | 7800 | 10400 | 520 | 26% |
| Biliblili | 4400 | 6600 | 8800 | 440 | 22% |
| NetEase Cloud Music | 3400 | 5100 | 6800 | 340 | 17% |
| Total | 20000 | 30000 | 40000 | 2000 | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




