1. Introduction
Solar energy boasts rich reserves, wide distribution, and a high degree of environmental friendliness. In China, over two-thirds of the country's regions receive annual radiation exceeding 5020MJ/㎡, while numerous winter heating areas possess considerable solar energy resources, providing an optimal basis for promoting the utilization of solar energy[
1,
2]. However, despite the potential for replacing conventional energy sources with solar energy to reduce building heating energy consumption and carbon emissions, solar energy utilization still encounters stability issues. Furthermore, the supply of solar energy utilization systems conflicts with the building environment's construction load. This conflict is mainly due to the mismatch between the peak periods of solar energy supply and the trough periods of building heat load, and vice versa. Therefore, the development of high-performance and reliable heat storage equipment that can efficiently store and allocate solar energy resources is a crucial solution to address this problem.
Traditional heat storage tanks use water as the storage medium, which takes up large space, has low heat storage density, and suffers from severe heat loss. Compared with sensible heat storage, PCMs have higher heat storage capacity per unit volume, a stable temperature during melting or solidification phases, and can absorb or release large amounts of latent heat. Using PCMs as the storage medium can downsize the equipment and facilitate the stable operation of the system. However, most PCMs have poor thermal conductivity, which reduces heat transfer efficiency and affects device performance. Therefore, optimizing the design of phase change thermal storage devices and exploring the performance variation rules have certain research significance.
Based on whether the fluid is in contact with the phase-change material, phase-change heat storage devices can be divided into direct contact and indirect contact types. The use of direct contact devices is complex and rare in practical applications. Indirect contact phase change thermal storage devices encapsulate the PCM through heat exchangers, making the operation more convenient and avoiding the loss of PCMs. PCMs are often encapsulated in rectangular containers, slender coils, and cylindrical containers. According to their packaging forms, indirect contact phase change thermal storage devices are mainly divided into three structures: plate, stacked, and tube-shell.
The structure of a flat-plate phase change TES system is relatively simple, and the plate size is a crucial factor affecting its performance. Many researchers have explored this issue. Prieto[
3] et al. investigated the relationship between the thickness of the phase change plate and heat transfer efficiency, finding that reducing the thickness can enhance the heat transfer effect, increasing the heat transfer rate up to five times. Stacked TES systems are filled with encapsulated small-volume PCMs, and the heat transfer fluid flows through the gaps in the PCM stack, providing a larger heat transfer area than other methods. Reda[
4] studied the effects of different diameters on the heat storage process of a stacked TES system with spherical encapsulation, finding that smaller diameter phase change spheres have relatively high heat transfer efficiency. Shamsi[
5] et al. simulated the heat storage process of a stacked bed TES system and found that increasing the temperature or flow rate of the heat transfer fluid can improve the heat storage rate and amount. Compared with other methods, the shell-and-tube type TES system has a higher heat storage density per unit volume, simpler encapsulation of the PCM, and is easier to combine with various forms of heat exchangers, making it a preferred choice for over 70% of latent heat TES (LHTES) systems[
6]. Vyshak[
7] et al. studied the total time required for PCM to melt in containers with three different geometric configurations (rectangular, cylindrical, and cylindrical shell) with the same volume and heat transfer surface area, finding that cylindrical shells require the shortest time for equal energy storage under the same PCM mass and heat transfer surface area, and this geometric effect becomes more pronounced as the PCM mass increases. The common shell-and-tube heat transfer components are coil and jacket types. Coil types can achieve longer heat transfer paths in small sizes, effectively increasing the heat transfer time between the fluid and PCM, thereby improving heat transfer efficiency[
8]. Liang[
9] et al. simulated the effect of different pipe length-to-diameter ratios and PCM volume ratios on the performance of a shell-and-tube type phase change TES system, finding that effective energy storage ratio increases with an increase in the pipe length-to-diameter ratio and that there is an optimal PCM volume ratio. Only when the PCM volume ratio is greater than a certain value can an increase in the effective thermal conductivity of the PCM effectively improve the effective energy storage ratio.
Increasing the heat transfer area between the heat transfer fluid and PCM is an effective means of enhancing heat transfer efficiency, and attaching fins is a common way to increase the heat transfer area. Numerous studies have shown that the thermal performance of phase change thermal storage devices can be significantly improved by adding fins. Tay[
10] et al. attached fins and pin fins to the heat transfer tube to enhance heat transfer efficiency in the intensification device and compared the improvement effects of the two through numerical simulation and experimental research. The results showed that the heat storage effect of fins was better, and the heat storage time was shortened by 25% compared with pin fins. Rathod[
11] et al. conducted a comparative study on the heat storage performance of the phase change thermal storage device before and after the addition of fins. The results showed that the heat storage efficiency was significantly improved after adding three longitudinal fins. When the inlet temperatures of the heat transfer fluid were 80°C and 85°C, the heat storage time was shortened by 12.5% and 24.52%, respectively. Mat[
12] et al. studied the inner fins, outer fins, and inner and outer fins enhancement technologies in the triplex-tube heat exchanger (TTHX), as well as the influence of fin length on the enhancement technology. The results showed that the three enhancement technologies did not have a significant difference in the PCM melting rate. Compared with the three-tube heat exchanger without fins, the time for complete melting of the inner and outer fins with a length of 42 mm was reduced by 43.3%.
The number, thickness, shape, and arrangement of fins have an impact on the performance of phase change TES systems. Al-Abidi[
13] et al. numerically simulated the melting heat transfer process of PCM with fins inside and outside of a triple-tube heat exchanger (TTHX) and found that the melting time was influenced by the number of fins, the length of fins, and the thickness of fins. The complete melting times for 4, 6, and 8 fins were 69.5%, 56.5%, and 43.4%, respectively, compared to no fins. The melting times for fins with lengths of 10 mm, 20 mm, 30 mm, and 42 mm were 73.9%, 60.8%, 47.8%, and 43.4%, respectively, compared to no fins. The melting times for fins with thicknesses of 1 mm, 2 mm, 3 mm, and 4 mm were 43.4%, 39%, 39%, and 35%, respectively, compared to no fins. Yuan[
14] et al. simulated a cylindrical phase change TES unit using paraffin RT82 as the PCM and established different numerical models by changing the number and width of fins and the radius of the cylindrical TES tube to compare their TES performance and obtain optimal model parameters. Castell[
15] et al. conducted experimental research on a phase change TES system with fins and pointed out that the melting rate increased with the decrease of fin spacing and the increase of the temperature difference between the heat transfer fluid and the PCM. Shatikian[
16] et al. studied the effect of different fin thicknesses on the TES process of a phase change TES system, and found that increasing the fin thickness accelerated the melting of the PCM, but shortened the fin spacing and reduced the amount of PCM. A reasonable configuration of fin thickness and spacing can improve the heat transfer performance of the TES system.
Alvaro[
17] et al. conducted a comparative study between a pure water TES system and a plate heat storage system using paraffin as a PCM. The results showed that the volume of the phase change heat storage system was half that of the pure water system when storing the same amount of heat, and it had better heat storage and release capacity. Prieto[
18] et al. investigated the effect of different PCMs on the heat storage and release performance of the same structure, and the results showed that paraffin with higher enthalpy had stronger heat storage capacity and longer heat release duration, while stearic acid with higher heat transfer coefficient had better heat transfer effect and could better meet the load demand during peak hours. Bansal[
19] et al. used organic acid as the phase change heat storage material and verified the applicability of the heat transfer model combining solar collectors and phase change heat storage under various operating conditions using numerical simulation. The results showed that the system combining PCMs and collectors was superior to the system separating PCMs and collectors. Rathod[
20] et al. used the AHP method combined with TOPSIS and fuzzy TOPSIS methods to select the optimal PCM for a solar hot water system. Xu[
21] et al. used the AHP and TOPSIS methods to select the optimal PCM for a solar air conditioning system and validated the selected results through Ashby's method.
Al-Abidi[
22] et al. investigated the application of a three-tube heat exchanger in a liquid desiccant air conditioning system, studying three different processes: inner tube heating, outer tube heating, and double-side tube heating, and analyzing the temperature gradients of PCM in radial, angular, and axial directions. The results showed that double-side tube heating could achieve complete PCM melting in a shorter time and at a lower inlet temperature. Hosseini[
23] et al. conducted experimental research and simulation analysis on a horizontally positioned shell-and-tube latent heat storage unit, showing that raising the temperature of the heat transfer fluid can shorten the melting time of the PCM, and the melting time of the PCM was reduced by 37% when the inlet water temperature was 80°C. Rathod[
24] et al. conducted experimental research on the vertical shell-and-tube unit during the heat storage process, changing the inlet flow rate and the temperature of the heat transfer fluid to observe the melting differences in the unit. The results showed that reducing the mass flow rate or inlet temperature of the heat transfer fluid would increase the total melting time of the PCM, and the effect of the fluid inlet temperature on the melting of the unit during the PCM melting process was more significant than the mass flow rate. Wang[
25] et al. simulated the heat storage performance of a shell-and-tube phase change heat storage unit, showing that increasing the inlet flow rate of the heat transfer fluid would decrease the total energy efficiency ratio of the unit while increasing the heat storage rate and raising the inlet temperature of the heat transfer fluid could simultaneously improve the heat storage rate and energy efficiency ratio of the unit.
The design and enhancement of heat exchange in phase change thermal storage devices can be summarized as follows: (1) Compared to direct and indirect contact-type phase change thermal storage devices, the tube-and-shell structure has advantages such as versatility in combination with various heat exchangers, convenient packaging, and high heat storage density, making it more favored by researchers. (2) The performance of phase change thermal storage devices is affected by factors such as the number, thickness, spacing, shape, and arrangement of fins. (3) The heat storage effect of phase change thermal storage devices is influenced by factors such as the inlet temperature and flow rate of the heat exchange fluid, and flow direction.
There are still several issues in the current research on phase change thermal storage devices: (1) Regarding device design, the function of phase change thermal storage devices is relatively single, mostly used for indoor heating or providing hot water for residential use during winter. Most studies use expensive copper as the heat exchange component in the device, which poses difficulties for household use or large-scale production. (2) In terms of numerical simulation, the heat exchange tube is often simplified as a partial tube section, and the heat storage and release process is simulated and analyzed. However, the numerical model is significantly different from the actual structure. For example, for longer coiled pipes, the temperature of the heat exchange fluid changes during flow, resulting in discrepancies between the results obtained from analyzing partial pipe sections and the actual performance. (3) In terms of operating conditions, most studies focus on the effects of heat exchange fluid temperature and flow rate on the heat storage performance of the device and the effects of heat exchange fluid flow rate and initial device temperature on the heat release performance of the device. Research on the effects of heat exchange fluid flow direction on the heat storage performance of the device and the effects of heat exchange fluid temperature on the heat release performance of the device is limited. (4) In terms of performance analysis, some studies only evaluate the performance of the device based on the melting or solidification effect of the PCM, without considering the heat storage capacity, instantaneous power, and effective heat release efficiency of the device under different operating conditions.
This paper has mainly accomplished the following tasks: (1) Development of a phase change thermal energy storage device with a small footprint, high energy storage density, and excellent thermal storage and release performance. The device can effectively balance the energy supply and demand in buildings, and in combination with the design of electric heating plates, it is conducive to the comprehensive utilization of renewable energy, making it an efficient and stable solar thermal storage technology. (2) The experimental and numerical simulation methods were combined to verify the reliability of the numerical simulation through experiments. The effects of various factors on the thermal storage and release performance of the phase change thermal energy storage device were studied. The influence of the fin structure of the device on its performance was also investigated through simulation.
The structure of this paper is as follows:
Section 2 introduces the physical model, control equations, and numerical simulation methods.
Section 3 describes the phase change experiments.
Section 4 summarizes and analyzes the experimental results.
Section 5 uses numerical simulation methods to study the performance of the phase change thermal storage device.
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Physical model
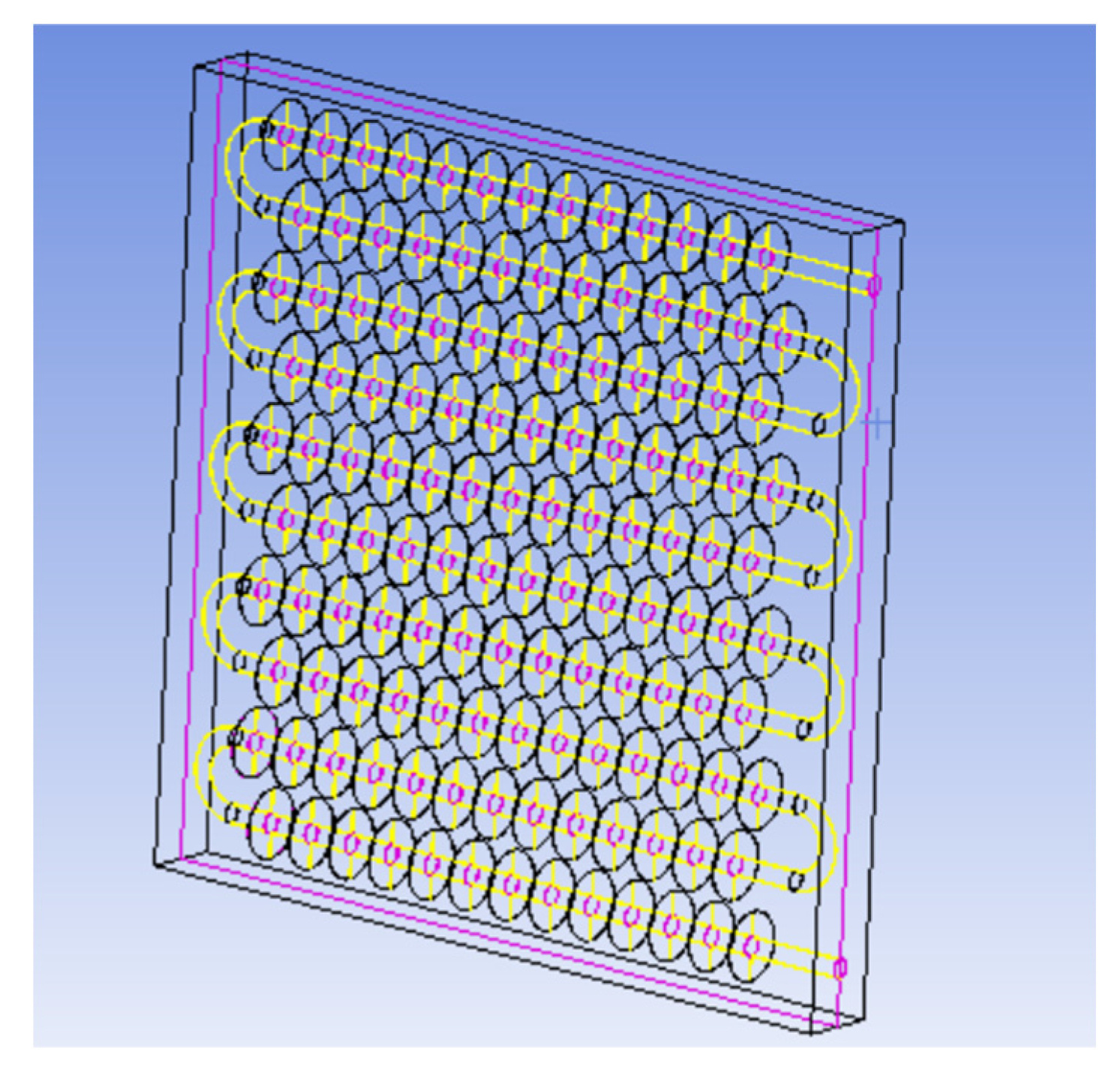
The physical model diagram of the phase change TES device studied in this paper is shown in
Figure 1. The physical model of the device mainly consists of a metal coil with fins and a square box outside the device. The internal space of the box is 820 mm long, 290 mm wide, and 800 mm high. There is one group of serpentines with fins inside the box, and each group of coils is composed of 10 straight pipes with a length of 700 mm, 9 semicircular pipes with a radius of 38 mm, and inlet and outlet pipes. The fin thickness is 1 mm, and the fin spacing is 50 mm. The heat transfer fluid enters from the top of the coil and exits from the bottom.
Due to the extremely complex phase change process, the heat storage calculation process of the device is simplified by the following assumptions to reduce the computation time:
(1) The outer wall of the device box has good insulation properties, and the heat loss of the phase change device is ignored.
(2) The PCM is isotropic, and the physical parameters of the solid and liquid phases are constant and do not change with temperature.
(3) Natural convection heat transfer between liquid PCMs is considered by introducing the Boussinesq assumption.
(4) The heat transfer fluid is an incompressible Newtonian fluid.
(5) Axial heat conduction and viscous dissipation in the heat transfer fluid are neglected.
(6) Since the flow and heat transfer of water in the finned tube are axisymmetric, the phase change device can be simplified to a two-dimensional model.
2.2. Control equation
Based on the above assumptions, a transient two-dimensional control equation is established to describe the phase-change region. The continuity equation is used to describe the law of density change of the fluid, which states that the net mass inflow into a certain control volume per unit of time is equal to the increase in mass of the control volume during that time. In a Cartesian coordinate system, its differential form is as follows:
Here,
represents fluid density,
denotes time in seconds (s),
represents the x-component of the velocity vector in meters per second (m/s), and
represents the y-component of the velocity vector in meters per second (m/s).
The momentum conservation equation is used to describe the momentum equation of viscous incompressible fluids, which states that the rate of change of the total momentum of a control volume microelement in a unit of time is equal to the sum of all external forces acting on the microelement control volume during that time. In the Cartesian coordinate system, its differential form is expressed as:
Here, and represent the components of the volume force in the x and y directions, respectively, in units of Pa; represents the dynamic viscosity coefficient in units of N·s/m2; represents the pressure, in units of Pa.
The energy equation is the differential form of the first law of thermodynamics, which is a fundamental equation for analyzing flow systems with heat exchange. It describes the rate of change of the total energy of a control volume element over a unit of time, equal to the sum of the net rates of energy transfer in and out of the element, and the work done on the element by surface and body forces. In rectangular coordinates, its differential form is expressed as follows:
Here, denotes the temperature in Kelvin (K), represents the thermal conductivity of the fluid in units of W/(m·K), is the specific heat capacity at constant pressure in units of J/(kg·K), and stands for the source term.
The governing equations for the enthalpy-based model in this study are given as follows:
Here, represents the enthalpy of PCM in kJ/kg, represents the density of PCM in kg/m3, and represents the thermal conductivity of PCM in W/(m·K).
When the specific heat of the solid-liquid phase of the PCM is constant, the relationship between temperature and enthalpy is as follows:
Here, represents the latent heat of the phase-change material, measured in kJ/kg, represents the reference temperature, measured in K, and represents the enthalpy of the phase-change material at the reference temperature, measured in kJ/kg.
2.3. Numerical simulation
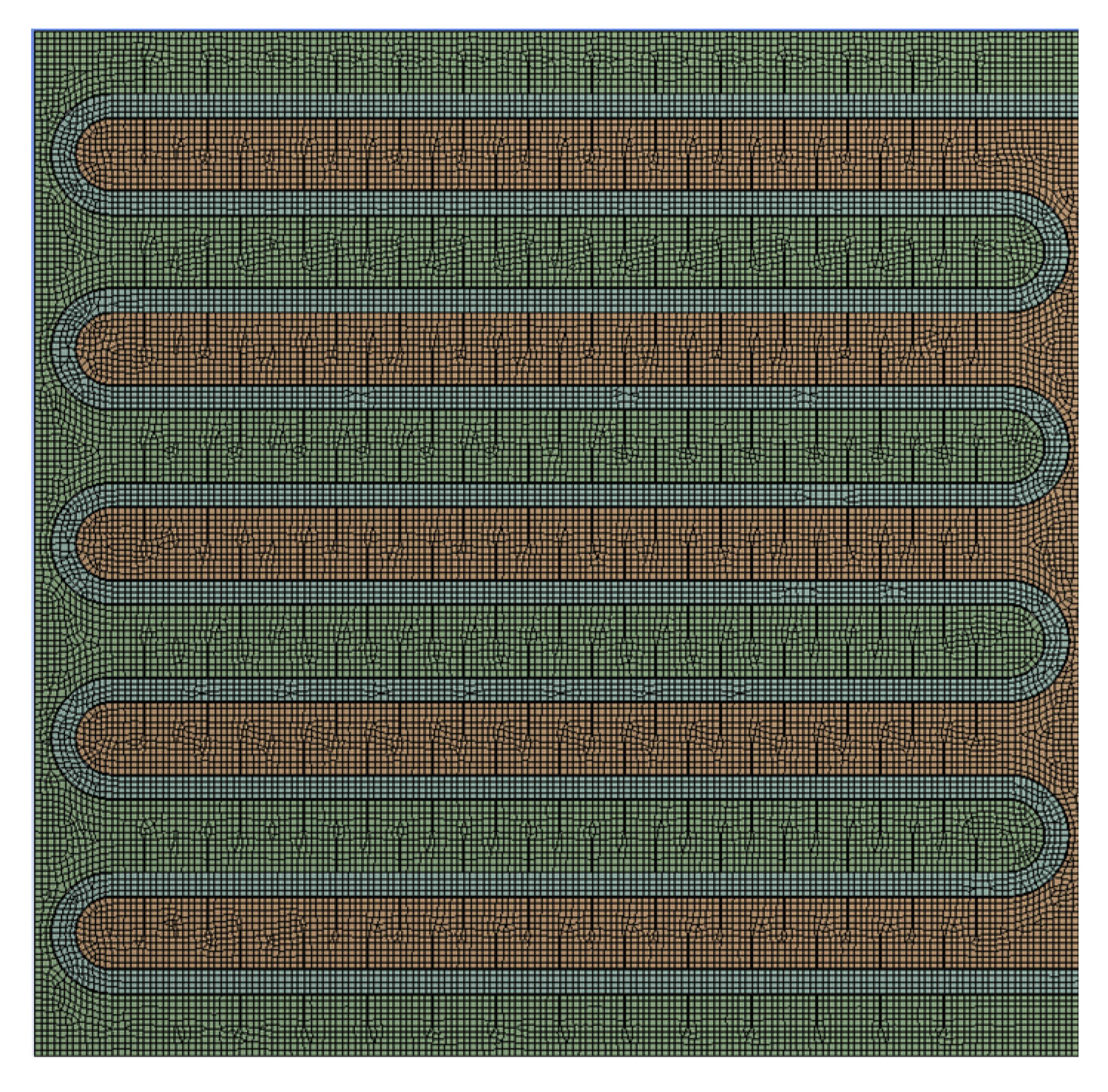
A 2D model of a phase change TES device was established using DesignModeler in ANSYS Workbench software for simulation. The model was then imported into the Meshing module for grid generation. The grid quality evaluation needed to consider the calculation time and accuracy of the numerical simulation. Therefore, a mesh independence test was performed to compare the simulation results of different mesh quantities. Considering both the calculation accuracy and speed, a mesh model with a quantity of 32118 was selected as shown in
Figure 3. The model was then imported into the FLUENT software for simulation, which is based on enthalpy-porosity and finite volume methods.
represents the solid phase line temperature of the PCM, expressed in Kelvin (K). represents the liquid phase line temperature of the PCM, expressed in Kelvin (K).
The energy storage performance of the phase change TES system determines the amount of usable energy during the night. The evaluation indicators for the energy storage process mainly include the inlet and outlet water temperature difference, the total amount of stored heat, and the average stored heat power.
Here, represents the stored heat capacity of the device in kJ, represents the average stored heat power in kW, is the start time of the energy storage process in seconds, is the end time of the energy storage process in seconds, ρ is the density of water in kg/m³ (assumed as 1000 kg/m³), is the specific heat capacity of water at constant pressure in kJ/(kg·K) (taken as 4.2 kJ/(kg·K)), V is the flow rate of the inlet water in m³/h, is the inlet temperature of the device in ℃, and is the outlet temperature of the device in ℃.
The heat release performance of the phase change TES system determines the energy utilization efficiency on the demand side. The evaluation indicators for the heat release process mainly include the inlet and outlet water temperature difference, effective heat release time, effective heat release efficiency, and heat release power. Among them, the effective heat release efficiency is defined as the ratio of the energy content in the water discharged from the TES during the effective heat release time to the stored heat energy in the TES at the beginning of the heat release process.
Here, represents the heat released by the device, measured in kJ; denotes the effective energy release efficiency; and represent the start and end times of the heat release process, measured in seconds.
The formula for calculating the instantaneous heat release power is as follows:
The Heat release conditions considered in this paper are classified into two types: effective heat release occurs when the device releases heat for heating and its heat release power is higher than the building heat load (
P≥0.338kW). According to the Building Water Supply and Drainage Design Code GB50015-2019, the recommended water temperature for shower use is 3740℃, while for washbasin spout uses it is 30℃. Additionally, the maximum daily water consumption quota per person per day is 4080L. Therefore, when the device releases heat for a domestic hot water supply, an outlet water temperature higher than 37°C (
≥37°C) is considered effective for showering and domestic hot water an outlet water temperature higher than 30°C (
≥30°C) is considered effective. This paper particularly emphasizes the heat release of the device when the outlet water temperature exceeds 37°C.
Figure 1.
Physical model of the phase change heat storage system.
Figure 1.
Physical model of the phase change heat storage system.
Figure 2.
A mesh model of phase change TES system.
Figure 2.
A mesh model of phase change TES system.
Figure 3.
Experimental setup for testing the performance of the phase change TES device.
Figure 3.
Experimental setup for testing the performance of the phase change TES device.
5. Optimizing Phase Change TES System Performance in Energies Journal Style
In this section, the impact of various factors on the TES process in the system was investigated using numerical simulation, providing a theoretical basis for the structural design and practical application of phase change TES systems.
5.1. Fin arrangements
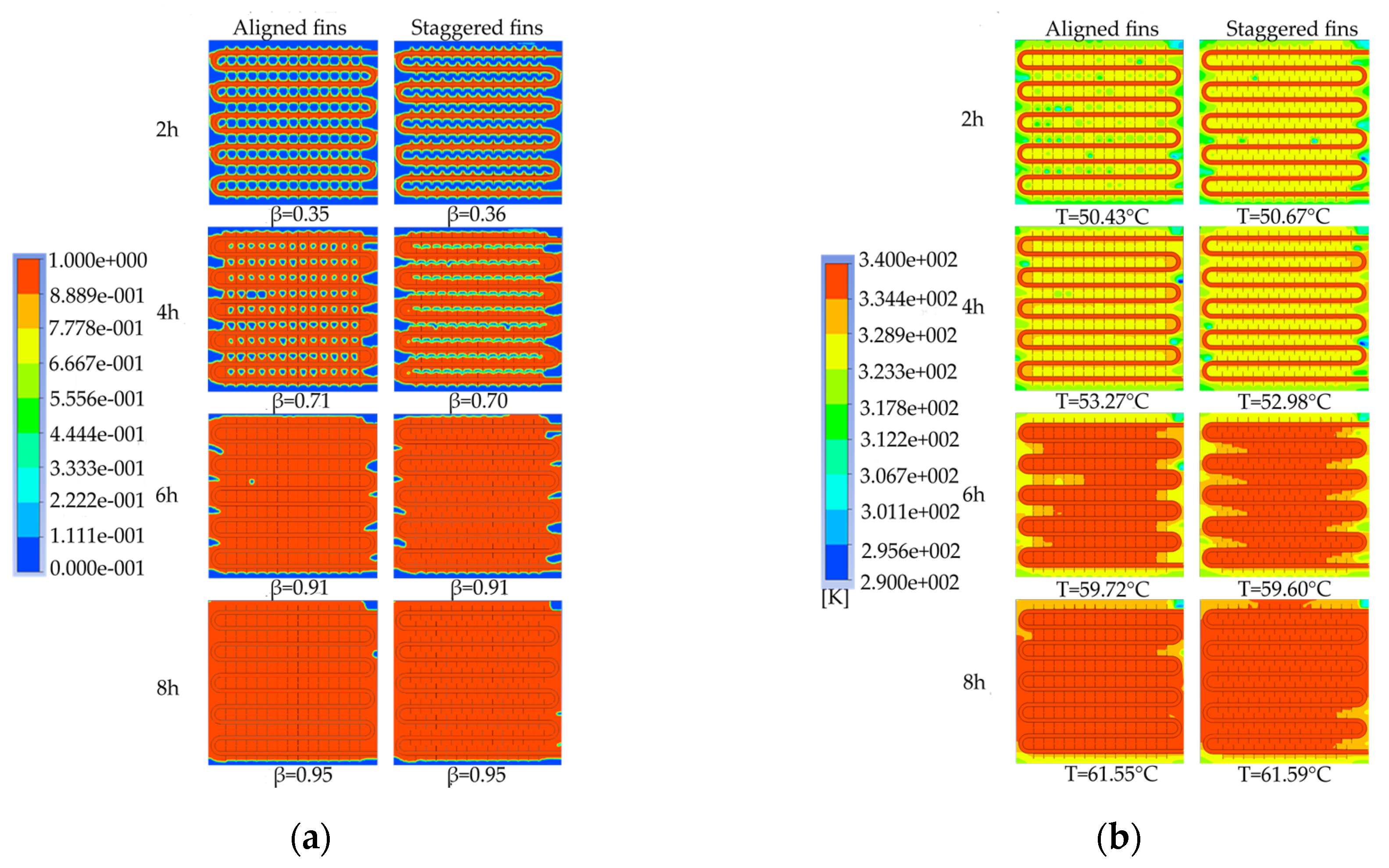
To investigate the influence of fin arrangement on the phase change heat storage process, device models with aligned and staggered fin arrangements were simulated to analyze the characteristics of liquid-phase fraction and temperature distribution at different times, and to compare the differences in the required time for completing the phase change heat storage.
Figure 26 shows the simulation results of the two different fin arrangements. As shown in
Figure 26a, the distribution of the melting region in the device with aligned fins is different from that in the device with staggered fins. The unfused area between the coils in the device with aligned fins is circular, while in the device with staggered fins, it is semicircular. However, the liquid-phase fraction of the two devices is almost the same at the same time, and both devices have a liquid-phase fraction of 0.95 at the end of the heat storage process. As shown in
Figure 26b, there are several small areas with relatively low temperatures between the coils in the device with aligned fins, while the temperature distribution inside the device with staggered fins is more uniform at the same time. After 4 hours of heat storage, the device with aligned fins has the highest average temperature, and the enclosed area formed by the fins and coil bends has better heat transfer efficiency and therefore heats up faster. When the heat storage time reaches 6 hours, the high-temperature area between the coils in the device with aligned fins is rectangular, while the high-temperature area between the coils in the device with staggered fins is trapezoidal with a wider upper part and a narrower lower part. The average temperature of both finned devices is around 59.7°C. When the heat storage time reaches 8 hours, the average temperatures of the two devices are 61.55°C and 61.59°C, respectively, and the device with staggered fins exhibits the best melting effect. Based on the entire phase change heat storage process, it can be concluded that the melting of the PCM in the heat storage device is mainly influenced by the distance to the pipe wall and fins, and there is no significant difference in melting efficiency between devices with aligned or staggered fins. The device with staggered fins has a slightly better heat storage effect than the device with aligned fins, but the difference is not significant.
Figure 27 shows the variation of the liquid fraction and average temperature of a phase change TES unit with different fin arrangements over time. The gray line represents the liquid fraction curve for the straight fins, while the red line corresponds to the temperature curve of the TES unit. The time required for 50% and 90% of the PCM to melt inside the TES unit with the two fin arrangements is 10170 s and 20920 s, and 10050 s and 21190 s, respectively. During the entire charging process, the liquid fraction curves of the TES unit with the two fin arrangements almost overlap, indicating that the difference in melting performance of the aligned or staggered fin arrangement is negligible. From the graph, it can be seen that the time required for the average temperature of the TES unit to reach 50℃ with the two fin arrangements is 6020 s and 5280 s, respectively. During the entire charging process, the average temperature curves of the TES unit with the two fin arrangements are almost the same, and the average temperature of the TES unit with the staggered fins is slightly higher than that with the aligned fins most of the time.
Therefore, it can be concluded that the TES unit with the staggered fin arrangement has better heat storage performance than the TES unit with the aligned fin arrangement, but the difference is not significant. Considering that the length of the fins is limited to less than half the tube spacing for aligned fin arrangements, while the length of the fins and tube spacing can be adjusted over a wider range for staggered fin arrangements, the fins in the TES unit should be preferably arranged in a staggered manner. However, if the conditions are restricted, the aligned fin arrangement can also be used, and the heat storage performance of the TES unit with the two fin arrangements will not differ significantly.
5.2. Fin arrangements
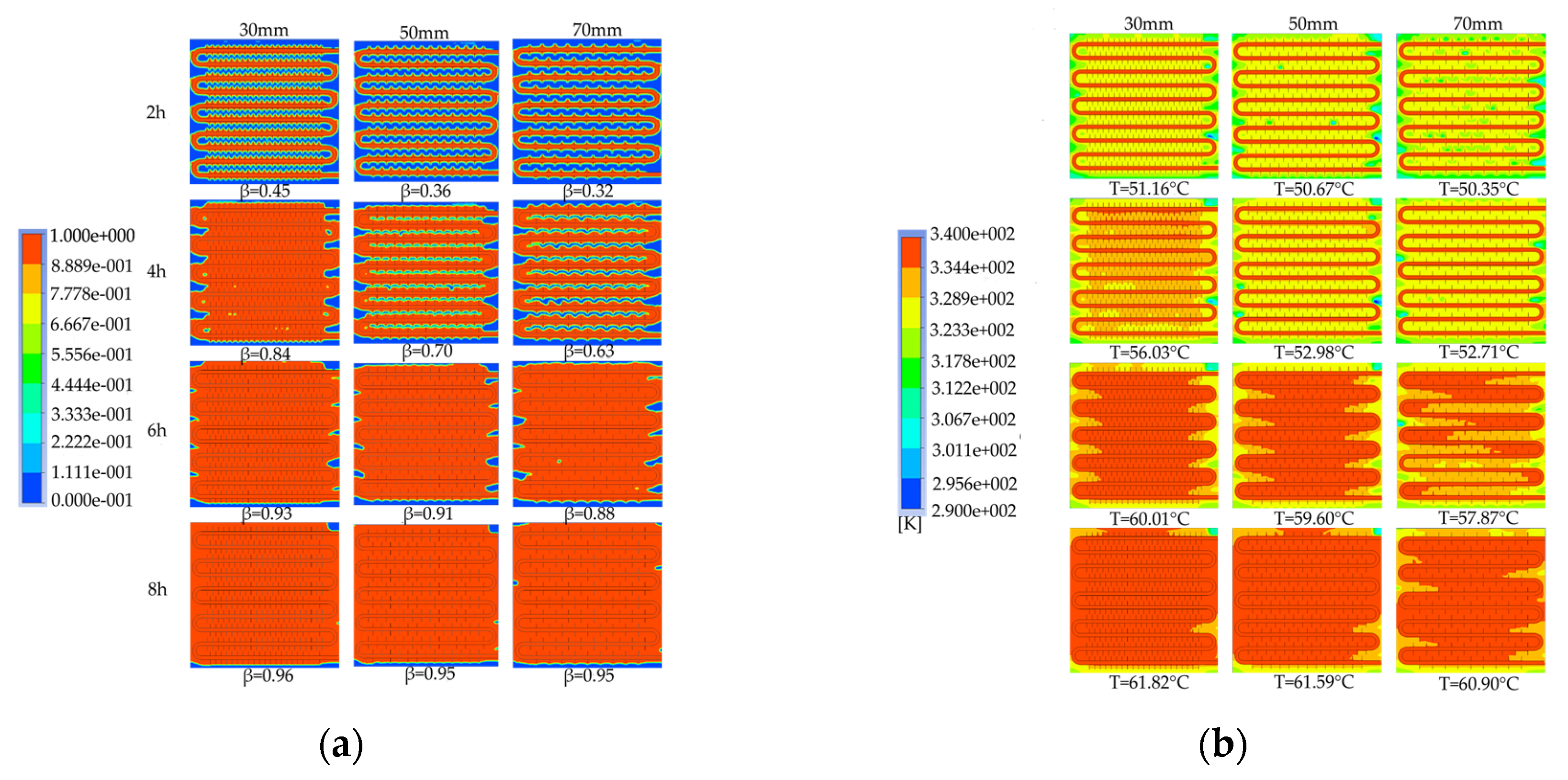
To investigate the effect of fin spacing on the heat storage process, simulation models with fin spacings of 30mm, 50mm, and 70mm were selected to analyze the liquid fraction and temperature distribution characteristics at different times and compare the differences in the required time for completing the phase change heat storage.
Figure 28 shows the simulated cloud maps of the devices with different fin spacings. As shown in
Figure 28a, the smaller the fin spacing, the fewer unmelted areas in the device, and the faster the melting rate of the PCM. When the heat storage duration reached 6 hours, the liquid fractions of the three working conditions were similar, and around 90% of the PCMs in the devices had melted. However, the device with denser fins had a higher liquid fraction. When the heat storage duration reached 8 hours, the liquid fractions of the devices with fin spacings of 50mm and 70mm were both 0.95, while the device with a fin spacing of 30mm had a slightly higher liquid fraction of 0.96. The figure also shows that the smaller the fin spacing, the smaller the unmelted area at the bottom, side walls, and corners of the device when the melting process was completed. As shown in
Figure 28b, the PCM near the fins and coils heated up first, while the temperature near the bent tubes and the corners of the device far from the heat exchange tubes and without fins was relatively low. When the heat storage duration reached 6 hours, the average temperature of the devices with fin spacings of 30mm and 50mm was around 60℃, while the device with a fin spacing of 70mm had a lower average temperature of 57.9℃. When the heat storage duration reached 8 hours, the temperature distribution inside the device with a smaller fin spacing was more uniform, and the average temperature of the device was higher, resulting in a larger heat storage capacity. The figure also shows that during the initial stage of heat storage, the temperature distribution inside the device was high in the middle and low around the periphery, while in the later stage of heat storage, the temperature at the top of the device was significantly higher than at the bottom. This was because during the initial stage of heat storage, the PCM in the device was in a solid state, and the heat was transferred through conduction. As the PCM gradually melted, the liquid PCM gathered at the top of the device due to the density difference, while the solid PCM sank due to gravity, resulting in a temperature stratification phenomenon in the vertical direction during the later stage of heat storage.
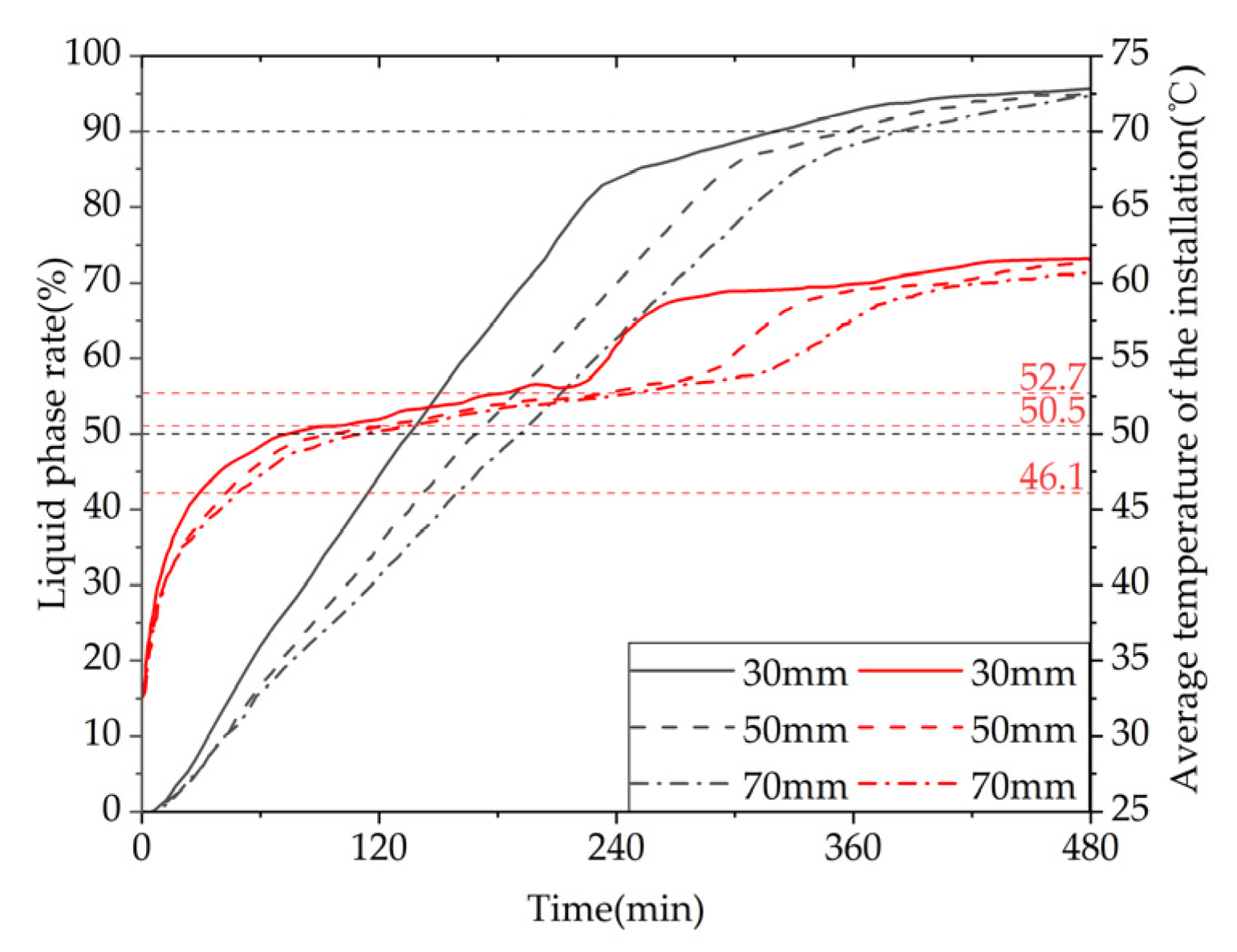
Figure 29 shows the variation curves of liquid fraction and average temperature with time for the phase change TES device under different fin spacings. The gray line represents the liquid fraction curve, and the red line represents the device temperature curve. It can be observed that there are differences in the rate of change of liquid fraction under different fin spacings, but the overall trend is consistent: the melting rate of the device is fast in the early stage of TES, and a clear inflection point appears in the later stage, with the liquid fraction curve relatively flat and the melting rate decreasing. This is because the solid-PCM dominates the device in the early stage, and the presence of fins increases the heat exchange area, resulting in a faster melting rate. In the later stage, most of the PCM around the fins and pipelines has melted, and the heat transfer coefficient of the PCM is small, resulting in a significant slowdown in the melting rate. The time required for 50% of the PCM in the device to melt under three different fin spacings is 7980s, 9940s, and 11170s, respectively. When the fin spacing is reduced from 70mm to 50mm or 30mm, the time required for 90% of the PCM to melt in the device is reduced by 11.01% and 28.56%, respectively. The time required for 90% of the PCM to melt in the device is 19140s, 21190s, and 22900s, respectively. When the fin spacing is reduced from 70mm to 50mm or 30mm, the time required for 90% of the PCM to melt in the device is reduced by 7.47% and 16.42%, respectively. It can be seen from the figure that there are differences in the average rate of change of the device under different fin spacings, but the overall trend is consistent. There are two clear inflection points during the TES stage: the first one appears when the solid-liquid phase change is completed, at which point the device changes from latent heat storage to sensible heat storage, and the temperature rise rate increases. The second one appears when the average temperature of the device is around 60℃ in the later stage of TES. This is because most of the PCM inside the device has melted, and the temperature distribution is more uniform than in the early stage, resulting in weaker natural convection. Heat transfer mainly occurs in the form of conduction, and the heat transfer coefficient of the PCM is small, resulting in a significant slowdown in the melting rate. The time required for the average temperature of the device under three different fin spacings to reach 60℃ is 21510s, 23710s, and 25110s, respectively. When the fin spacing is reduced from 70mm to 50mm or 30mm, the time required for the average temperature of the device to reach 60℃ is reduced by 5.58% and 14.34%, respectively.
Given the aforementioned, it can be inferred that for a given Heat storage condition, a smaller fin spacing leads to a faster melting rate of the PCM (PCM), resulting in a shorter completion time of the storage process, a more uniform melting degree of PCM within the device, a higher average temperature of the device, and a greater TES capacity. However, a reduction in the fin spacing will increase the number of fins, thereby reducing the PCM capacity within the device and increasing the manufacturing cost of the fins. Therefore, in practical applications, the choice of fin spacing should be based on a comprehensive consideration of the demand for use and the economic feasibility of the device. For solar energy-rich regions with support for longer storage times, there is no need for an excessively small fin spacing, whereas, for shorter storage times, a reduction in the fin spacing can be appropriate to enhance the TES performance of the device.
5.3. Fin thickness
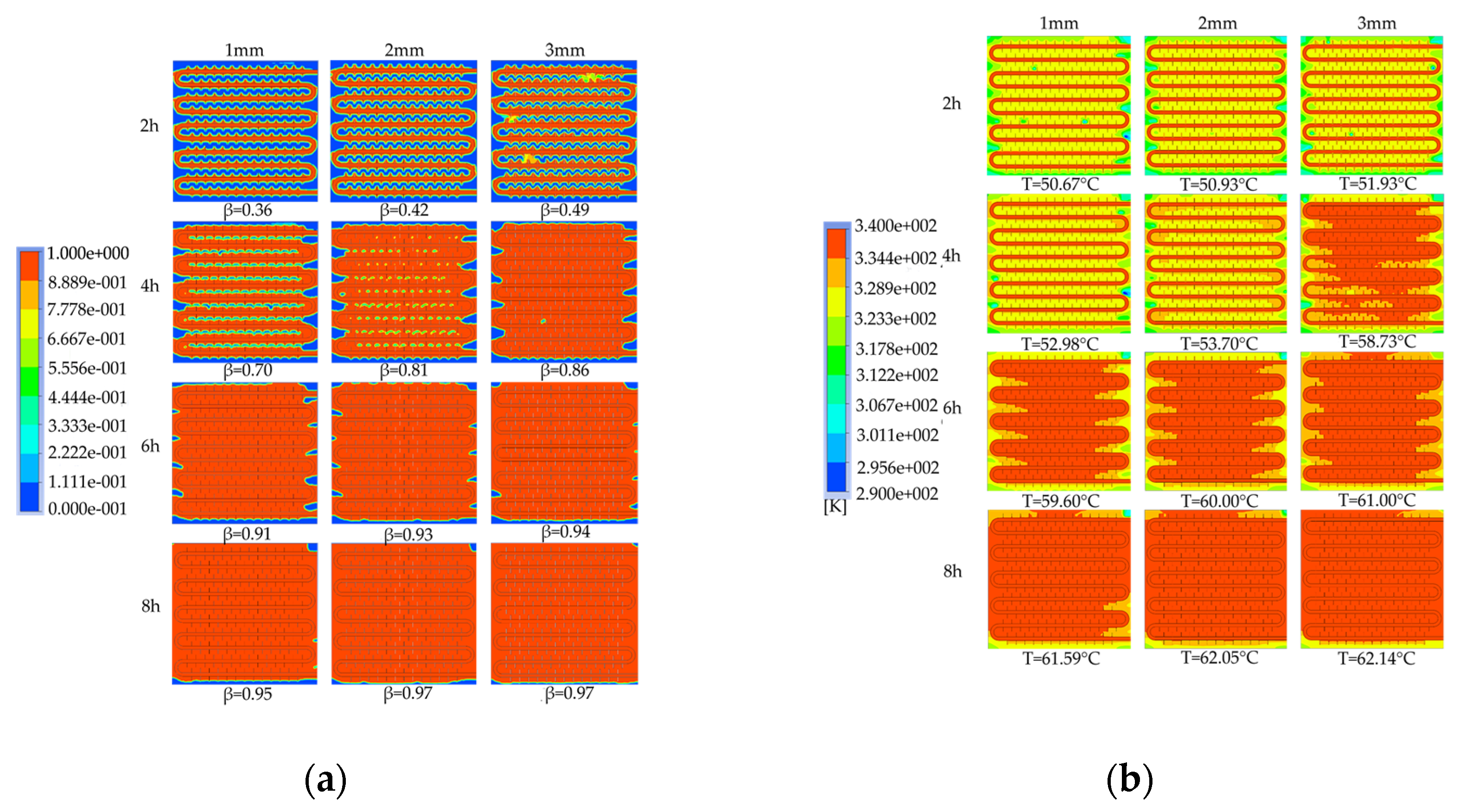
To investigate the effect of fin thickness on the heat storage process, device models with fin thicknesses of 1mm, 2mm, and 3mm were simulated to analyze the characteristics of liquid phase fraction and temperature distribution at different periods. The differences in the required time to complete the phase change heat storage were compared.
Figure 30 shows the simulation cloud maps of the devices under different fin thicknesses. As shown in
Figure 30a, under the same heat storage duration, the thicker the fin thickness, the faster the PCM melts. At 4h of heat storage duration, there are still many unmelted areas between coils in the device with 1mm thick fins, while almost all coils are melted in the device with 3mm thick fins and the liquid phase fraction reaches 0.86. When the heat storage duration is extended to 6h, the melting situation of the devices with 2mm and 3mm thick fins is similar, but both are significantly better than that of the device with 1mm thick fins, and the device with 3mm thick fins still has the highest liquid phase fraction. At 8h of heat storage duration, the liquid phase fraction of the devices with 2mm and 3mm fin thicknesses is both 0.97, slightly higher than that of the device with 1mm fin thickness. In addition, by comparing the liquid phase fraction distribution cloud maps of the three devices at the end of heat storage, it can be observed that the thicker the fin thickness, the smaller the unmelted area at the bottom, side walls, and corners of the device, and the improvement degree is better at the corners than at the bottom. This indicates that increasing the fin thickness can enhance the heat transfer effect of the fins in the fin thickness direction. Overall, it is found that increasing the fin thickness can improve the melting rate of the device, and the improvement effect is more significant in the early stages of heat storage. As shown in
Figure 30b, by comparing the temperature cloud maps after 2h of heat storage, it is found that the temperature distribution inside the device with 1mm thick fins is the most uneven, with multiple small areas of relatively low temperature between coils. After 4h of heat storage, the melting effect of the device with 3mm thick fins is significantly better than that of the other two devices, and the average temperature of the device reaches 58.73℃. The device with 1mm thick fins still has blue low-temperature areas, indicating the worst melting effect and the average temperature of the device is 52.98℃. When the heat storage duration is extended to 6h, the average temperatures of the three devices are all around 60℃, and the temperature of the device with 3mm thick fins reaches as high as 61℃. When the heat storage duration is extended to 8h, the device with the thickest fins has the best melting effect, and for each increase in fin thickness of 1mm, the average temperature of the device increases by 0.46℃ and 0.09℃, respectively. Overall, it is found that increasing the fin thickness can improve the average temperature and melting effect of the device, and the improvement effect is more significant in the early and middle stages of heat storage.
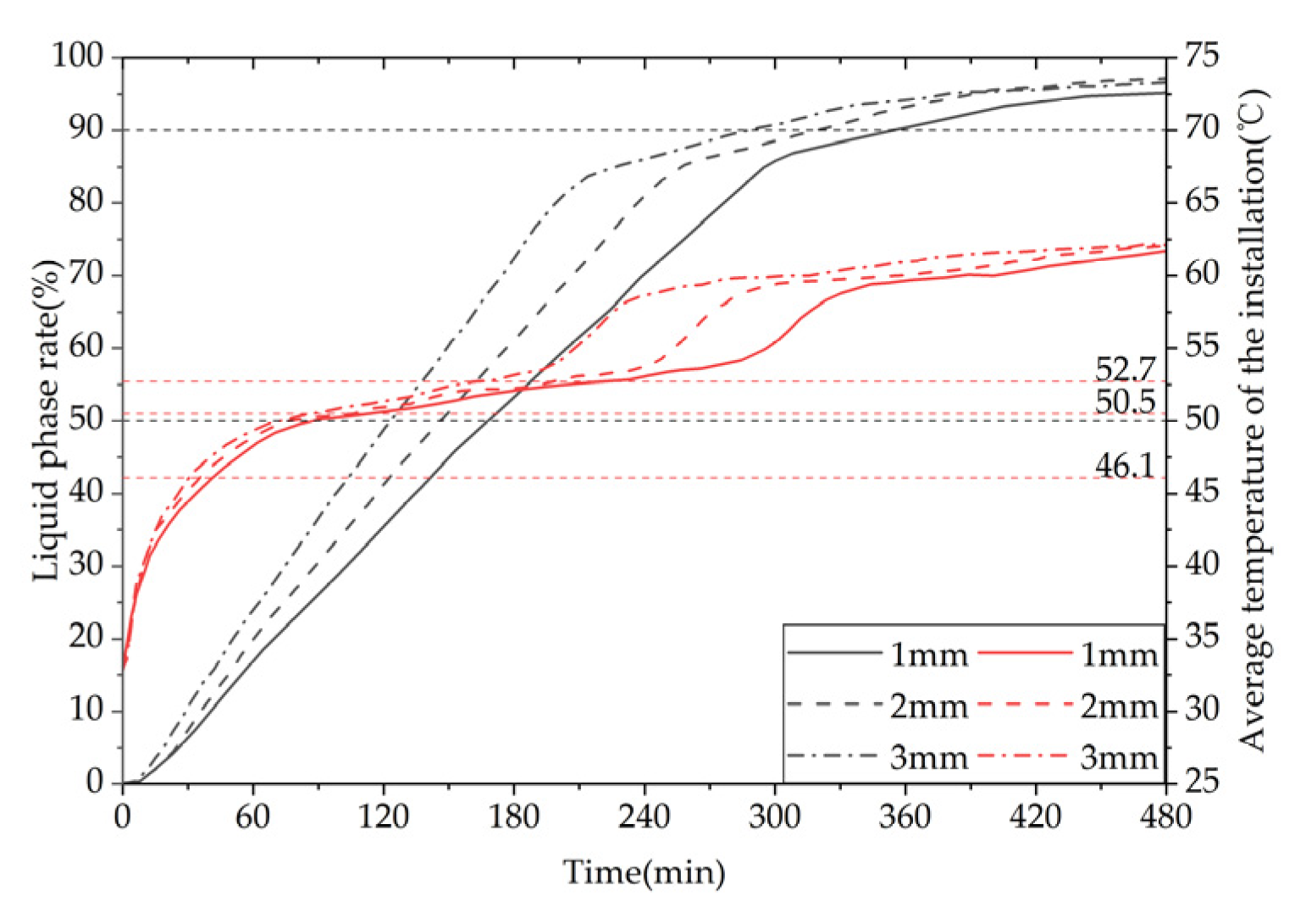
Figure 31 shows the comparison of the liquid phase and average temperature variation trend for a phase change TES device with different fin thicknesses. The gray line represents the liquid phase comparison curve, while the red line represents the device temperature curve. The melting times of 50% PCMs (PCM) inside the device correspond to three different fin thicknesses of 1 mm, 2 mm, and 3 mm, which are 9940 s, 8580 s, and 7290 s, respectively. When the fin thickness increases from 1 mm to 2 mm or 3 mm, the melting times of 50% PCM inside the device are reduced by 13.68% and 26.66%, respectively. The melting times of 90% PCM inside the device correspond to the three fin thicknesses of 1 mm, 2 mm, and 3 mm, which are 20710 s, 18620 s, and 16760 s, respectively. When the fin thickness increases from 1 mm to 2 mm or 3 mm, the melting times of 90% PCM inside the device are reduced by 10.09% and 19.07%, respectively. In conclusion, increasing the fin thickness can significantly enhance the melting efficiency of the device.
It can be inferred from the above that, under the same Heat storage conditions, an increase in fin thickness leads to a faster melting rate of PCM (PCM), a shorter time required for completing the heat storage process, a more uniform degree of PCM melting at the end of the process, a higher average temperature of the heat storage device, and a greater heat storage capacity. However, increasing the fin thickness reduces the PCM capacity of the device and raises the manufacturing cost of the finned tubes. Therefore, in practical applications, the selection of fin thickness should be based on a comprehensive consideration of the requirements for use and the economic feasibility of the device. For solar-rich regions with relatively long heat storage times, a fin thickness of no more than 2 mm is recommended, whereas, for shorter heat storage times, an increase in fin thickness can be considered to enhance the heat storage performance of the device.
5.4. Inlet flow direction and installation method
To investigate the effects of the flow direction and installation orientation on the phase change heat storage process, we simulated three different device models with different installation methods: vertical installation with the longer side parallel to the gravity direction, horizontal installation with fluid entering from the bottom and exiting from the top, and horizontal installation with fluid entering from the top and exiting from the bottom. We analyzed the characteristics of liquid phase rate and temperature distribution at different time points and compared the differences in the required time for completing the phase change heat storage.
Figure 32 presents the simulation contour maps of the device under different water inlet directions and installation methods. As shown in
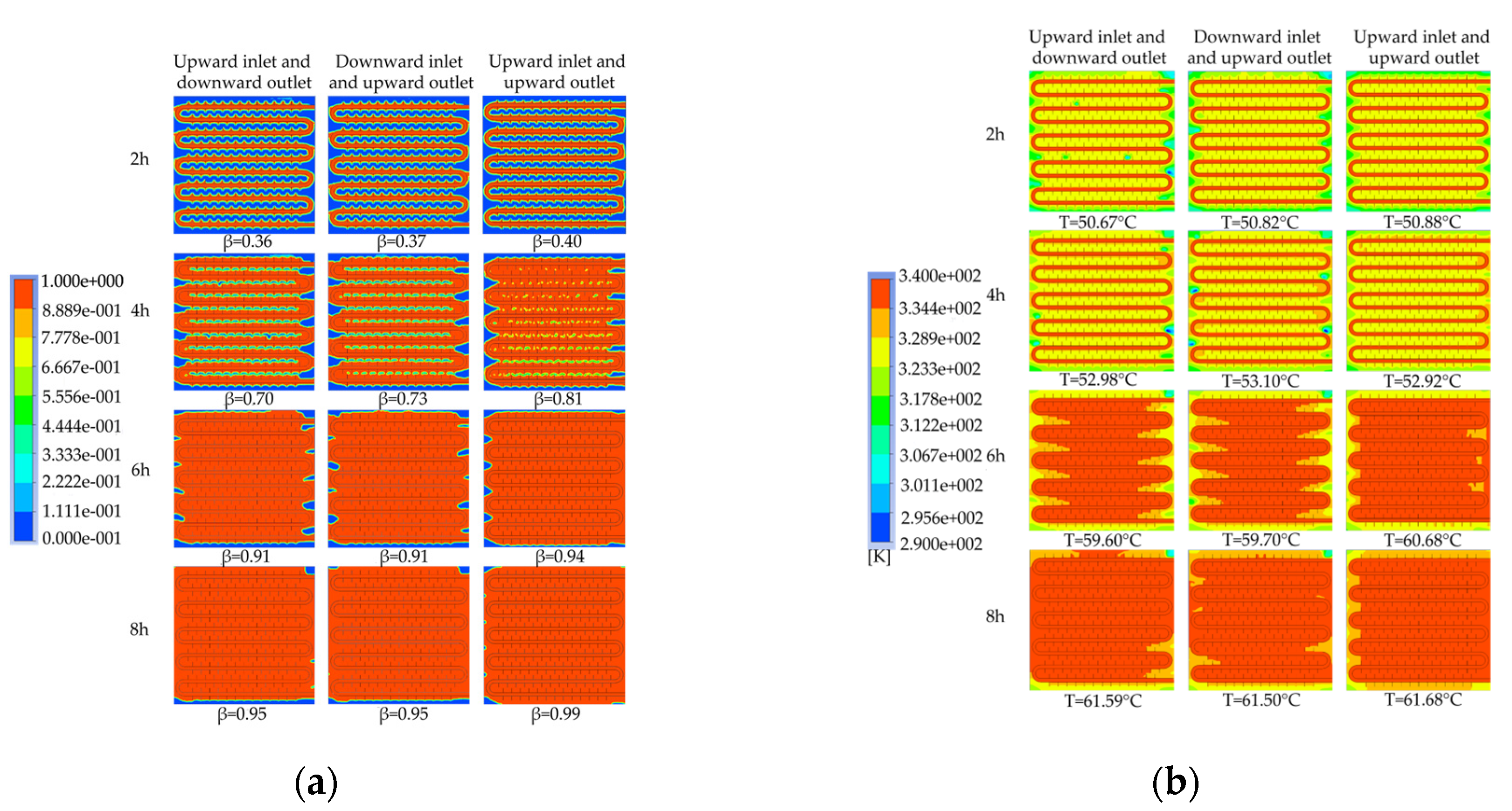
Figure 32a, when the heat storage time reached 4 hours, the liquid fraction of the device under the three working conditions was 0.70, 0.73, and 0.81, respectively. When the heat storage time reached 6 hours, the melting situation of the horizontally installed devices was similar, but both were behind the vertically installed device. When the heat storage time reached 8 hours, the liquid fraction of the horizontally installed devices was 0.95, while the vertically installed device reached a high liquid fraction of 0.99, and the remaining unmelted area was mainly distributed in the lower two corners of the device. Overall, the melting effect of the vertically installed device was significantly better than that of the horizontally installed device. Moreover, the heat transfer mode with down-in and up-out in the horizontally installed device was better than the up-in and down-out mode, and the improvement effect was more significant in the early stage of heat storage. As shown in
Figure 32b, when the heat storage time was 2 hours, the temperature distribution of the horizontally installed device with up-in and down-out was the most uneven, with multiple relatively low-temperature small areas between the coils. After 4 hours of heat storage, the average temperature of the device under the three working conditions was around 53 ℃. The average temperature of the horizontally installed device with down-in and up-out was the highest, reaching 53.10 ℃, while that of the vertically installed device was the lowest, at 52.92 ℃. When the heat storage time reached 6 hours, the average temperature of the device under the three working conditions was around 60 ℃. The temperature of the vertically installed device reached the highest at 60.68 ℃, and it had the most uniform temperature distribution among the three devices, followed by the horizontally installed device with down-in and up-out. When the heat storage time reached 8 hours, the melting effect of the vertically installed device was the best, and the average temperatures of the devices under the three working conditions were 61.59 ℃, 61.50 ℃, and 61.68 ℃, respectively.
Based on the overall heat storage process, it can be concluded that the melting effect of the vertically installed device is significantly better than that of the horizontally installed device. This is because the vertically installed device provides a larger spatial scale in the direction of gravity, which is conducive to the formation of natural convection inside the device. For devices installed horizontally, the downflow-upflow heat transfer method performs better than the upflow-downflow method in the early stage of heat storage. However, after a heat storage time exceeding 6 hours, the heat storage effect of the two inflow methods is not significantly different. This is because the hot fluid flows through the longer path of the coil, exchanging heat with the device as it flows, and the fluid temperature inside the pipe gradually decreases. Additionally, due to the density difference between the solid and liquid PCMs, the device experiences temperature stratification, where the upper part of the device has a higher temperature than the lower part during heat storage under the influence of gravity. When the device is horizontally installed, the downflow-upflow heat transfer method can increase the heat transfer temperature difference, thereby improving the heat transfer effect.
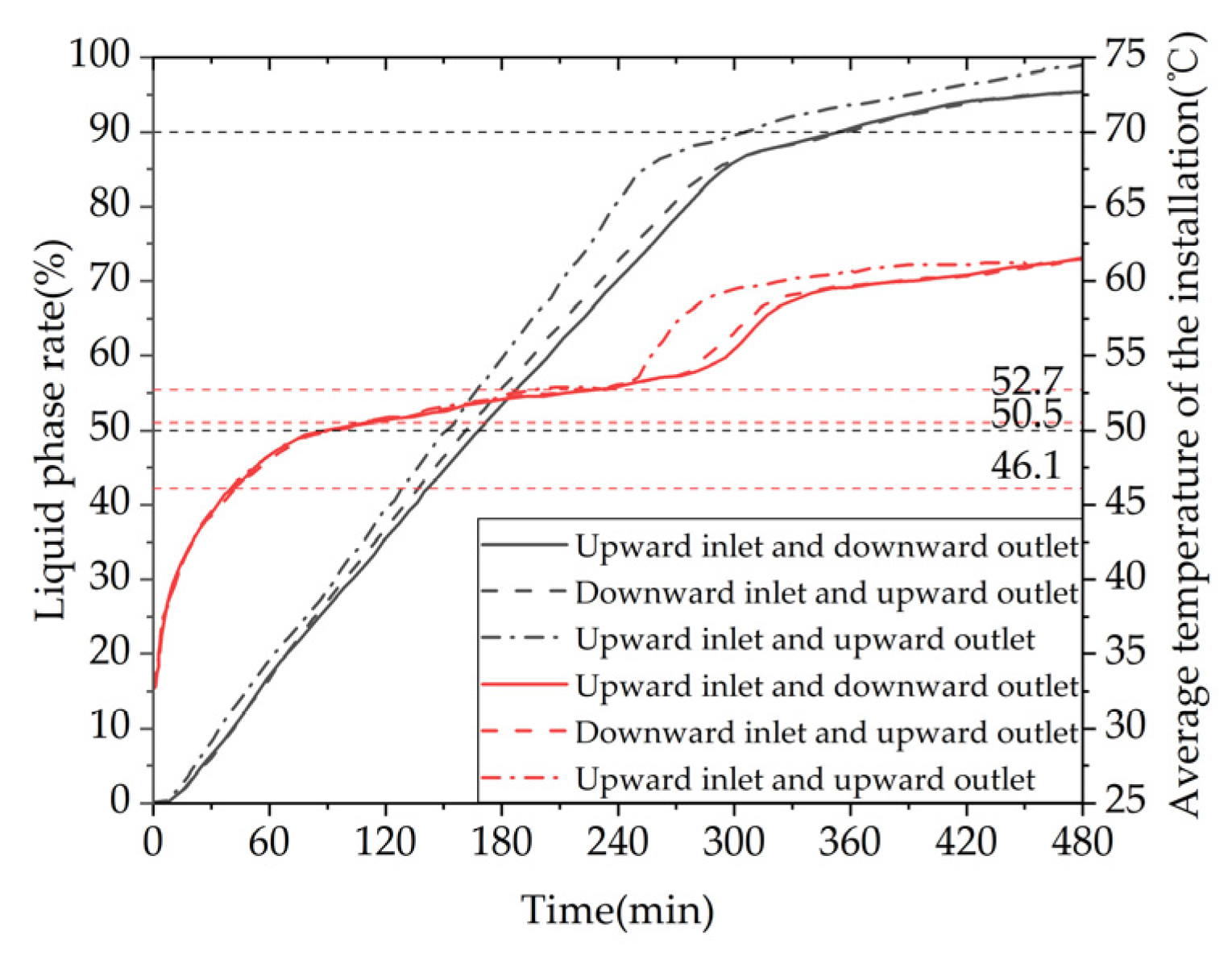
Figure 33 shows the variation curves of liquid fraction and the average temperature of the phase change TES device with different water inlet directions and installation methods over time. The gray line represents the liquid fraction curve, while the red line represents the device temperature curve. The time required for the liquid fraction to reach 50% under three operating conditions is 9940s, 9530s, and 8940s, respectively. When the operating condition is changed from horizontal up-in and down-out to horizontal down-in and up-out, or vertical up-in and up-out, the time required for 50% of the PCM in the device to melt is shortened by 4.12% and 10.06%, respectively. The time required for 90% of the PCM in the device to melt is 20710s, 20680s, and 17770s, respectively. When the operating condition is changed from horizontal up-in and down-out to horizontal down-in and up-out, or vertical up-in and up-out, the time required for 90% of the PCM in the device to melt is shortened by 0.14% and 14.20%, respectively. In conclusion, the heat storage performance of the device is significantly better in the vertical installation mode than in the horizontal installation mode, while the effect of changing the water inlet direction on the heat storage performance of the device is small in the horizontal installation mode. Additionally, the time required for the device's average temperature to reach 60℃ under the three operating conditions is 23720s, 23250s, and 19420s, respectively. When the operating condition is changed from horizontal up-in and down-out to horizontal down-in and up-out, or vertical up-in and up-out, the time required for the device average temperature to reach 60℃ is shortened by 1.98% and 18.13%, respectively. From the graph, it can be seen that within the first 4 hours of heat storage, the average temperatures of the device under the three operating conditions are similar, while after 4 hours, the vertical installation device has a significantly improved temperature rise rate.
6. Conclusions
This article presents an experimental study on the factors affecting the performance of a phase change TES system. The following conclusions are drawn:
(1) Inlet temperature has a significant impact on TES performance. For the charging process, a higher inlet temperature leads to an earlier start time of TES, faster attainment of the charging termination temperature, and an increase in both the total and the average charging power. For the discharging process, a higher inlet temperature delays the start time of discharging slows down the attainment of the discharging termination temperature, and prolongs the effective discharging time. However, this also reduces the effective discharging energy of in the system.
(2) Inlet flow rate has a certain impact on TES performance, but the improvement is limited. For the charging process, a higher inlet flow rate leads to faster attainment of the charging termination temperature, but the difference is not significant. Increasing the inlet flow rate can reduce the temperature difference between the inlet and outlet, thus improving the charging performance, but it also reduces the charging power. For the discharging process, a higher inlet flow rate leads to faster attainment of the discharging termination temperature and can improve the effective discharging energy and efficiency, as well as prolong the effective discharging time. However, the improvement is relatively limited.
(3) Changing the type of heat storage has a certain impact on the TES performance. Adding an electric heating plate to assist in the heating of the water can significantly accelerate the melting process of the phase change material and improve the charging power.
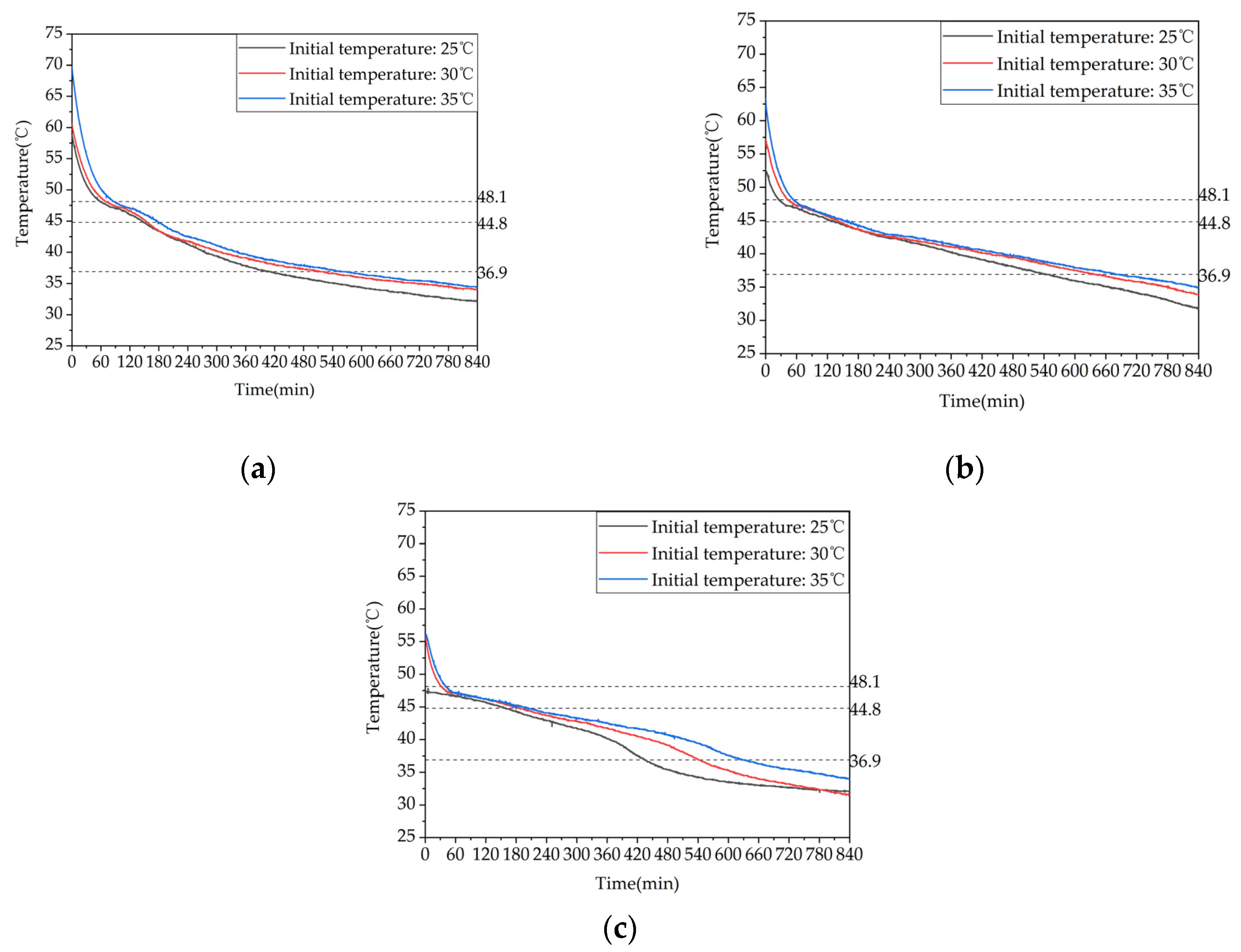
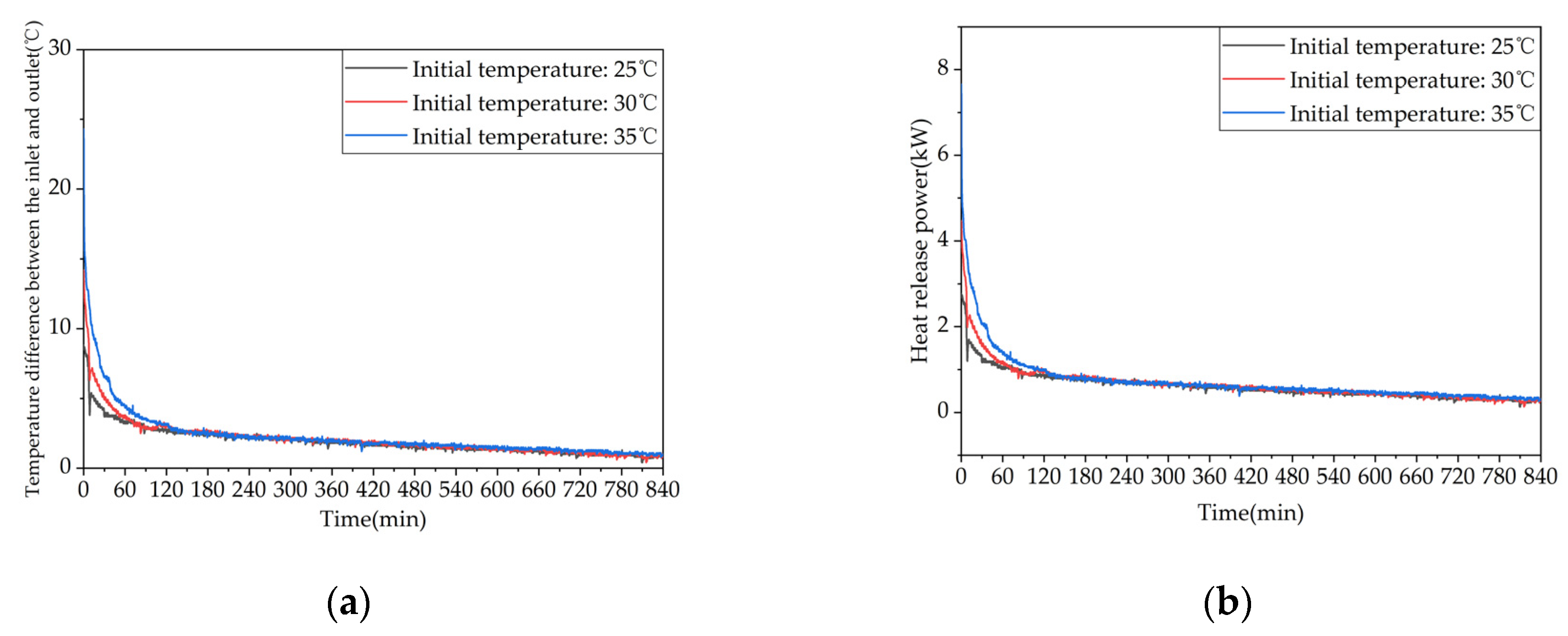
(4) Increasing the initial temperature of the TES can prolong the effective discharging time, improve the discharging performance, and significantly increase the sensible heat discharge power. However, when the temperature is increased beyond a certain point, the improvement effect gradually diminishes.
In addition, numerical simulation is conducted to optimize the structure and operating conditions of the TES system, and the following conclusions are drawn:
(1) The staggered placement of fins is slightly better than the aligned placement, but the difference is not significant.
(2) Reducing the fin spacing and increasing the fin thickness can improve the melting efficiency of the phase change material and shorten the TES time.
(3) The TES performance of the vertically installed system is significantly better than that of the horizontally installed system, and the difference is mainly reflected in the later stage of the TES. When the system is horizontally installed, the down-inlet and up-outlet heat exchange mode has slightly better charging performance than the up-inlet and down-outlet mode, and the difference is mainly reflected in the early stage of the TES.
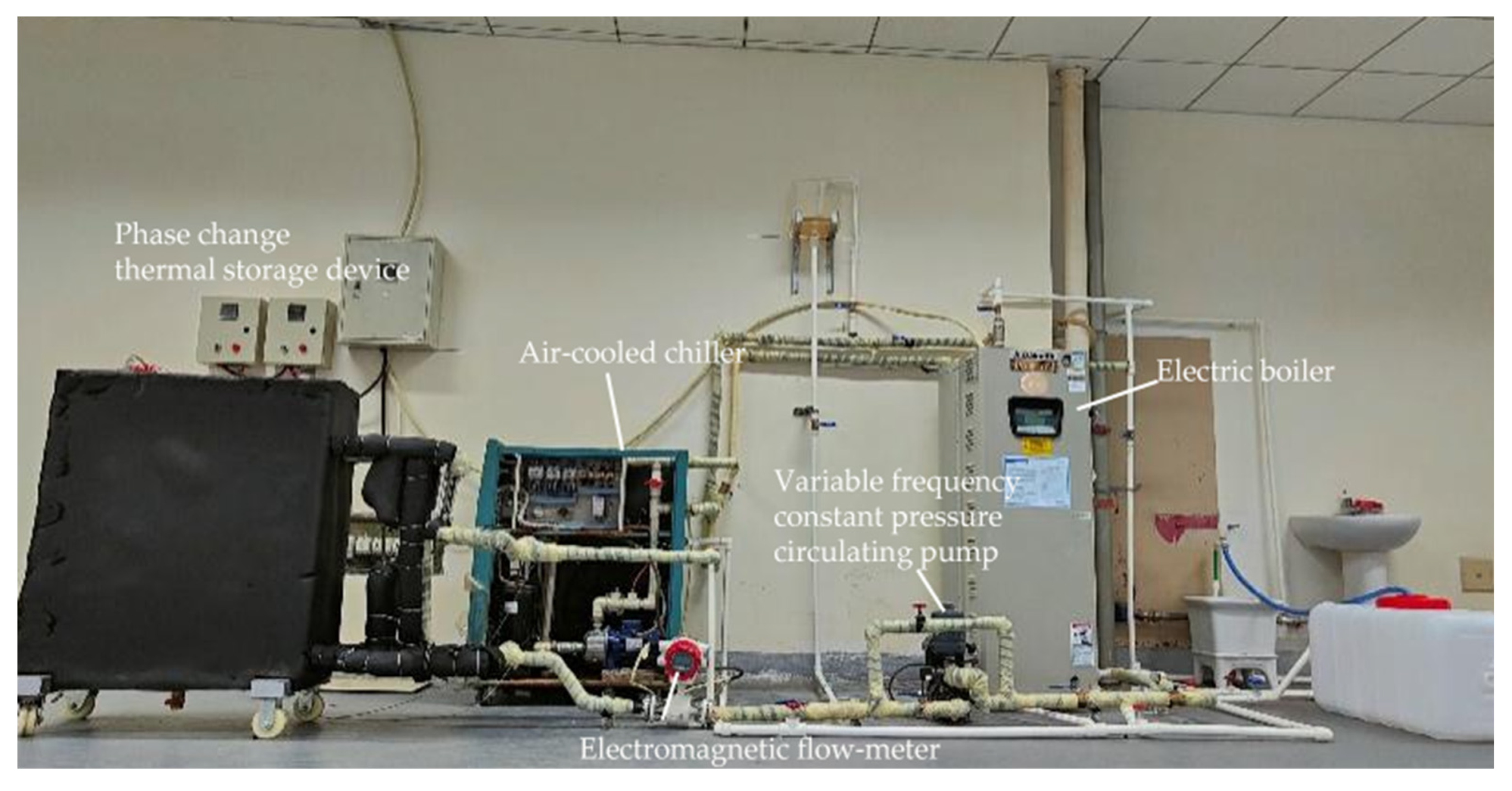
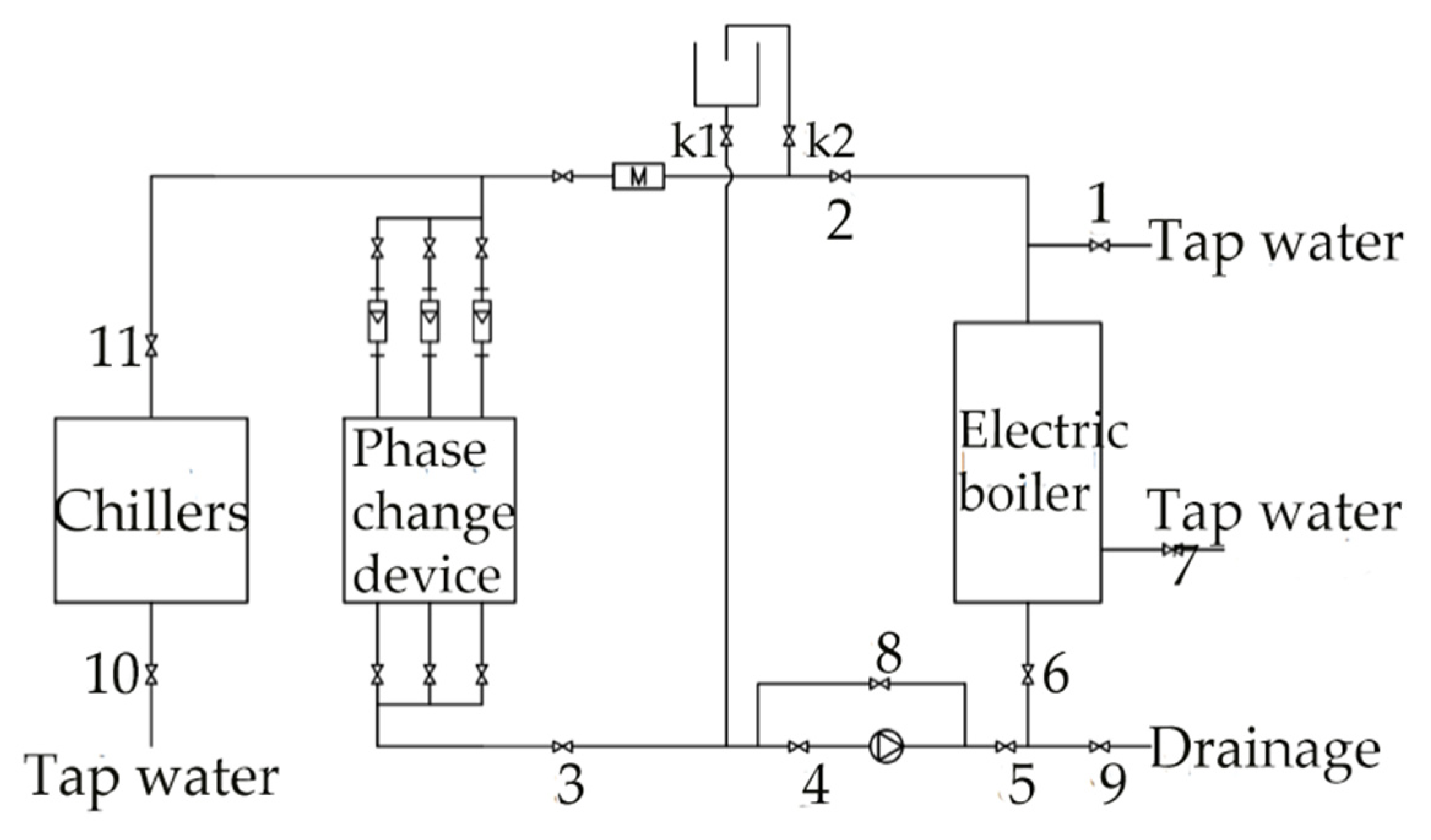
Figure 4.
Schematic of the experimental system.
Figure 4.
Schematic of the experimental system.
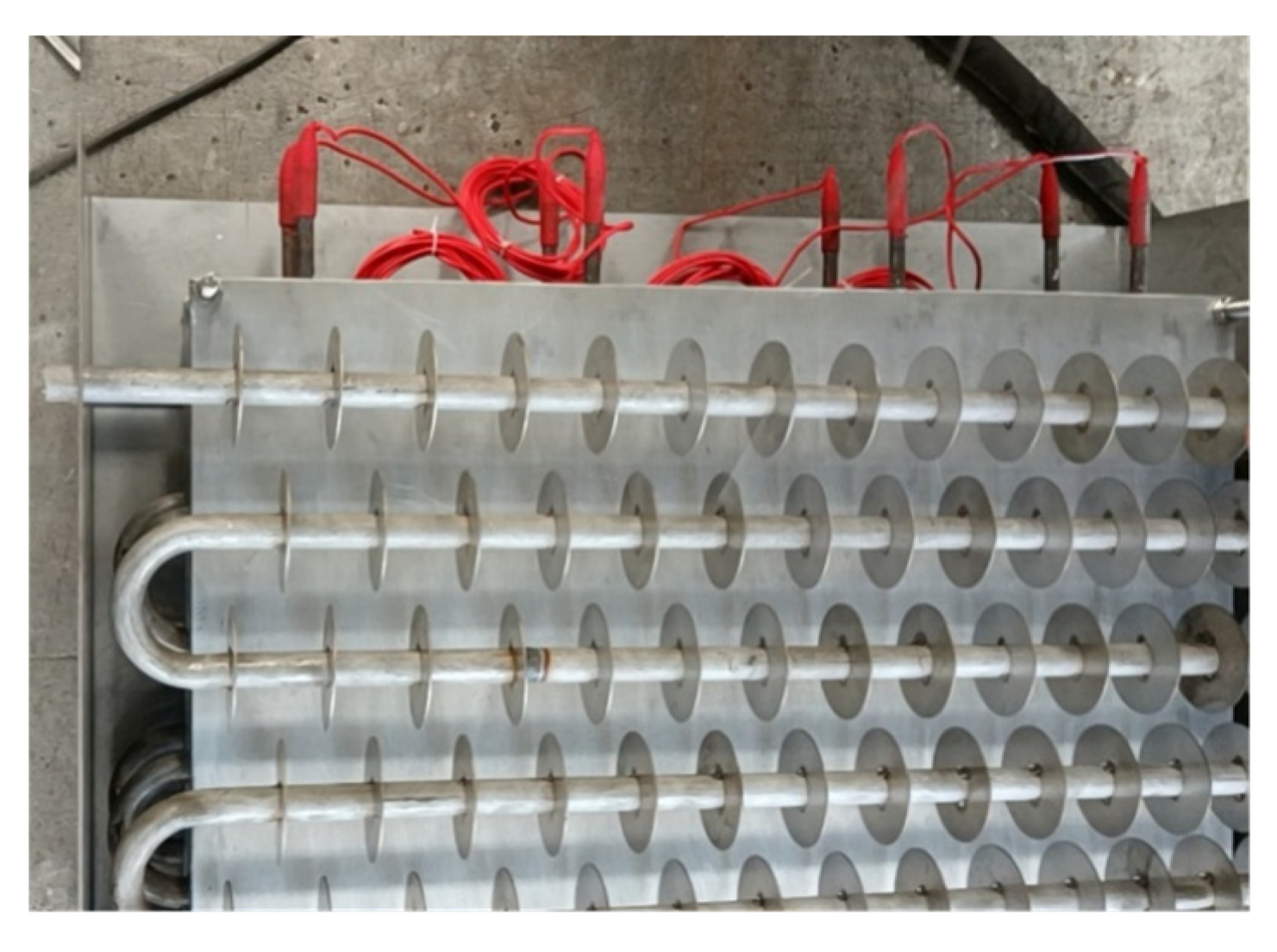
Figure 5.
The real structure of phase change TES device.
Figure 5.
The real structure of phase change TES device.
Figure 6.
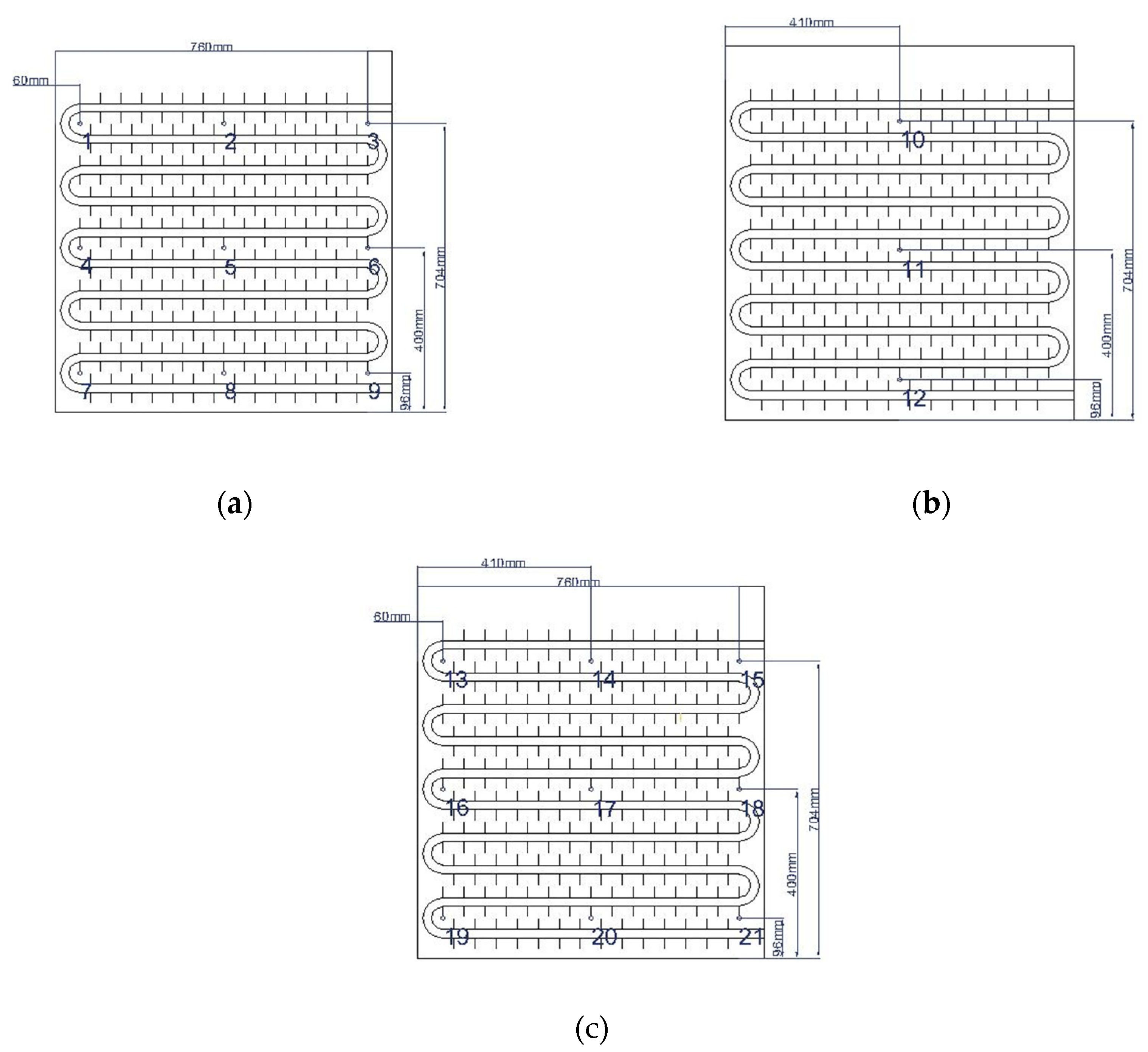
Diagram of temperature measurement points layout inside the phase change thermal storage device: (a) Tube coil 1; (b) Tube coil 2; (c) Tube coil 3.
Figure 6.
Diagram of temperature measurement points layout inside the phase change thermal storage device: (a) Tube coil 1; (b) Tube coil 2; (c) Tube coil 3.
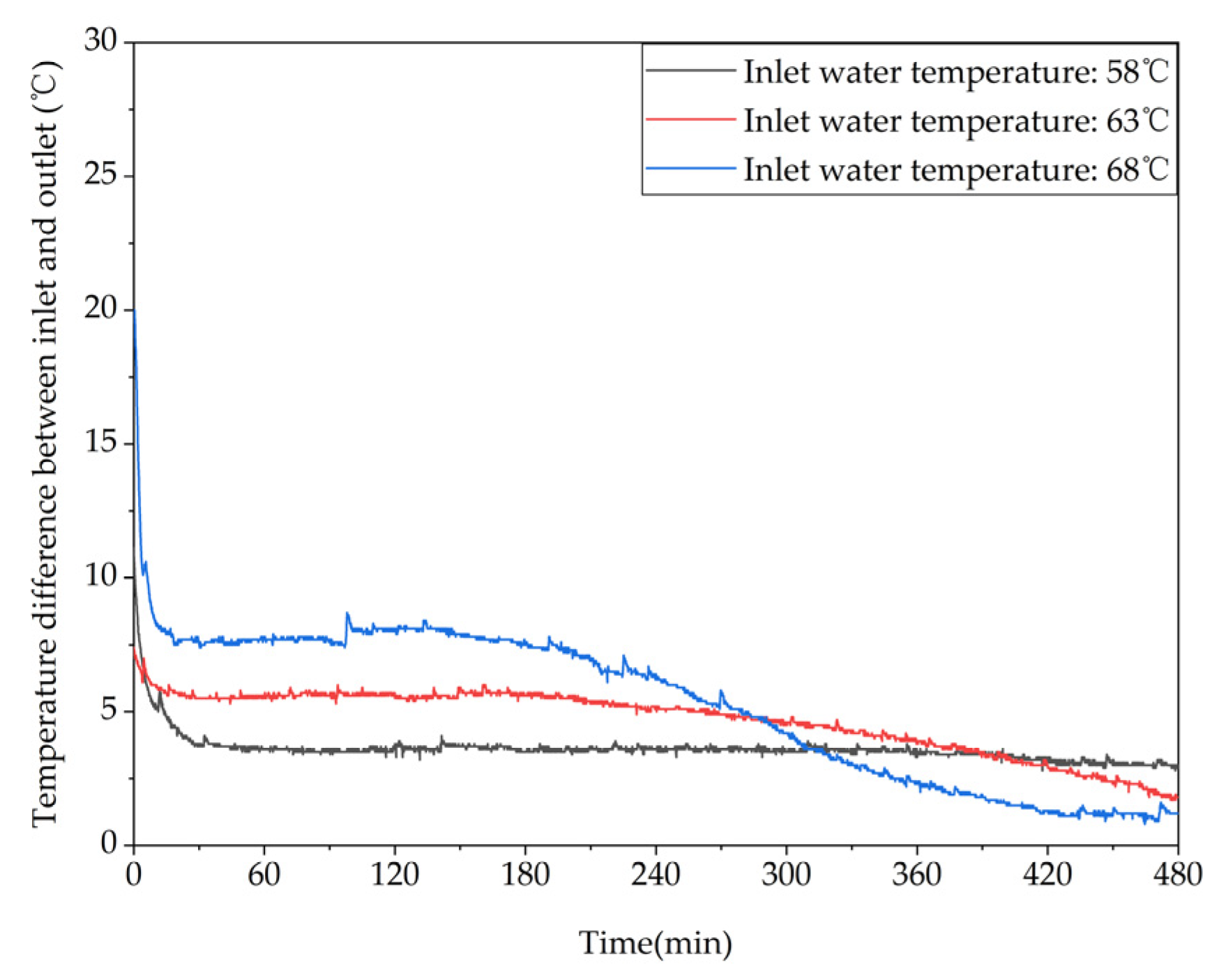
Figure 11.
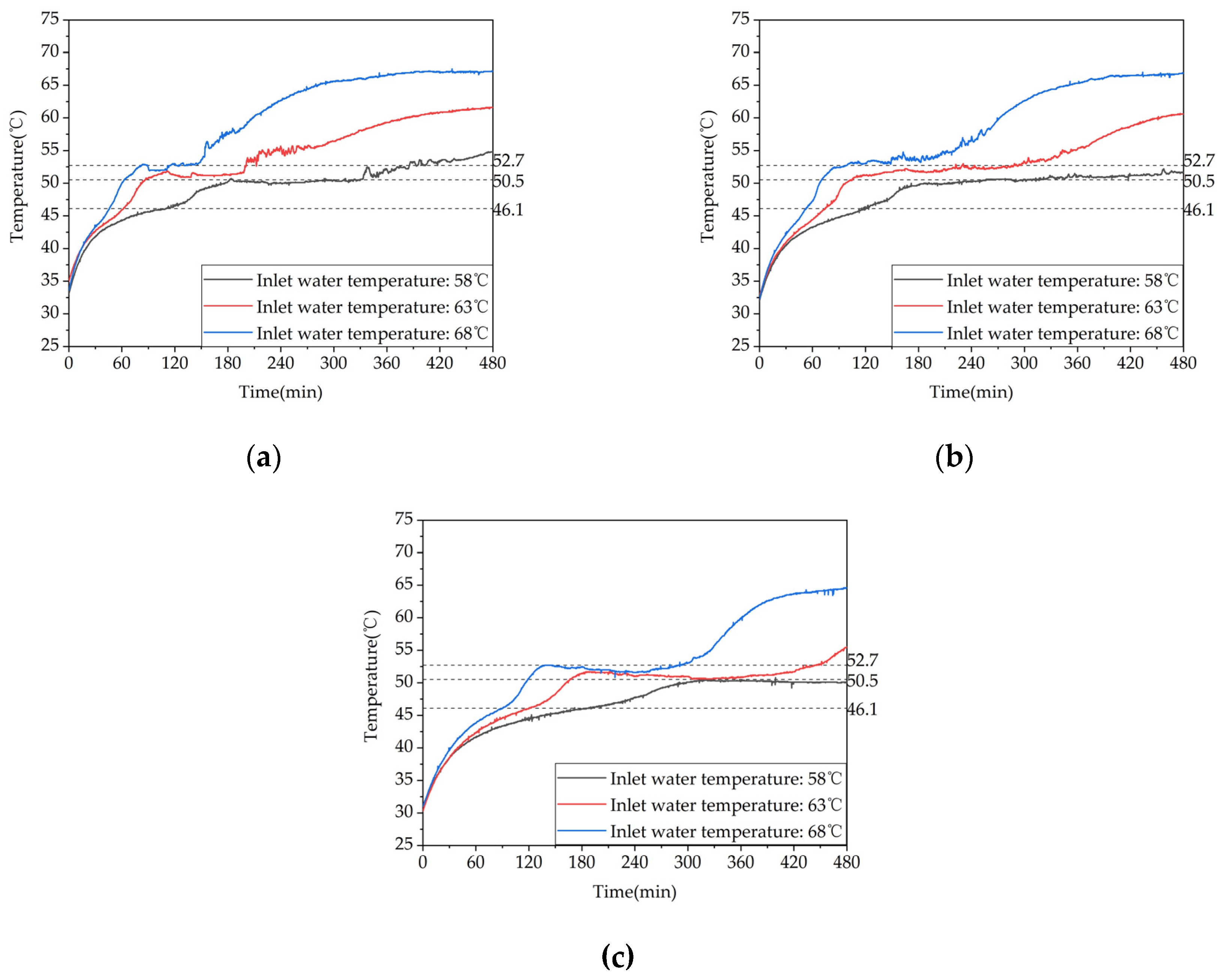
Different trends of the temperature difference between the inlet and outlet of the device over time under different inlet water temperatures.
Figure 11.
Different trends of the temperature difference between the inlet and outlet of the device over time under different inlet water temperatures.
Figure 12.
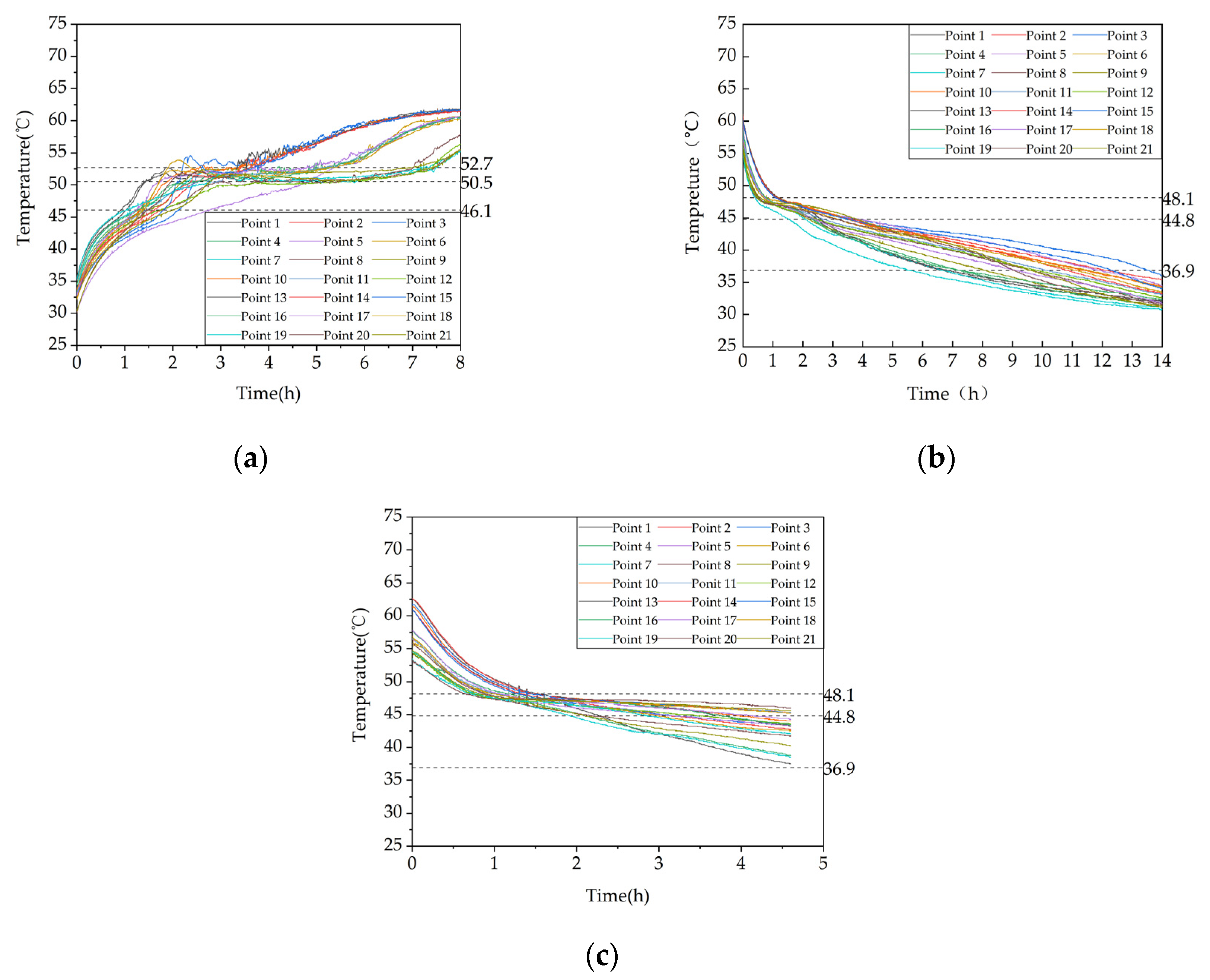
Temperature variation inside the phase change heat storage unit at typical locations under different Heat storage conditions: (a) Measuring point 13; (b) Measuring point 17; (c) Measuring point 21.
Figure 12.
Temperature variation inside the phase change heat storage unit at typical locations under different Heat storage conditions: (a) Measuring point 13; (b) Measuring point 17; (c) Measuring point 21.
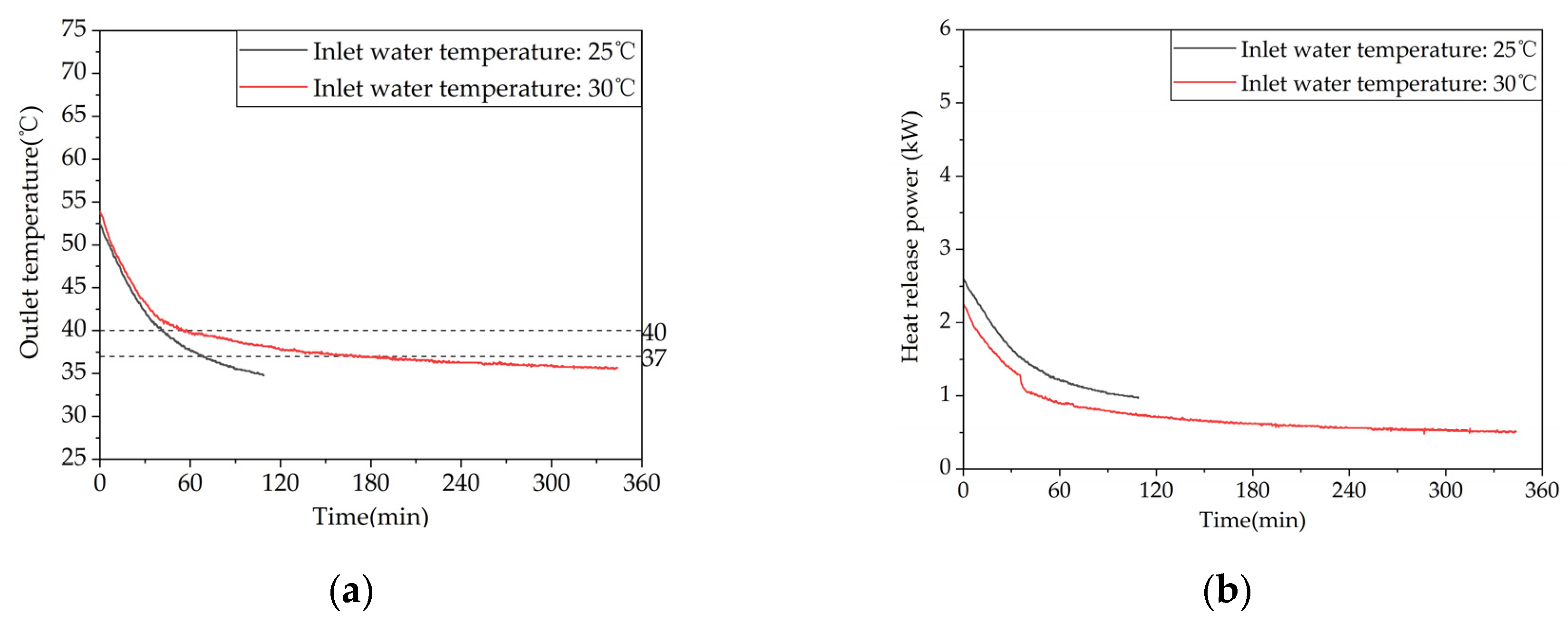
Figure 13.
Heat release performance of the device at different inlet water temperatures: (a) Temperature difference between inlet and outlet; (b) Instantaneous heat release power.
Figure 13.
Heat release performance of the device at different inlet water temperatures: (a) Temperature difference between inlet and outlet; (b) Instantaneous heat release power.
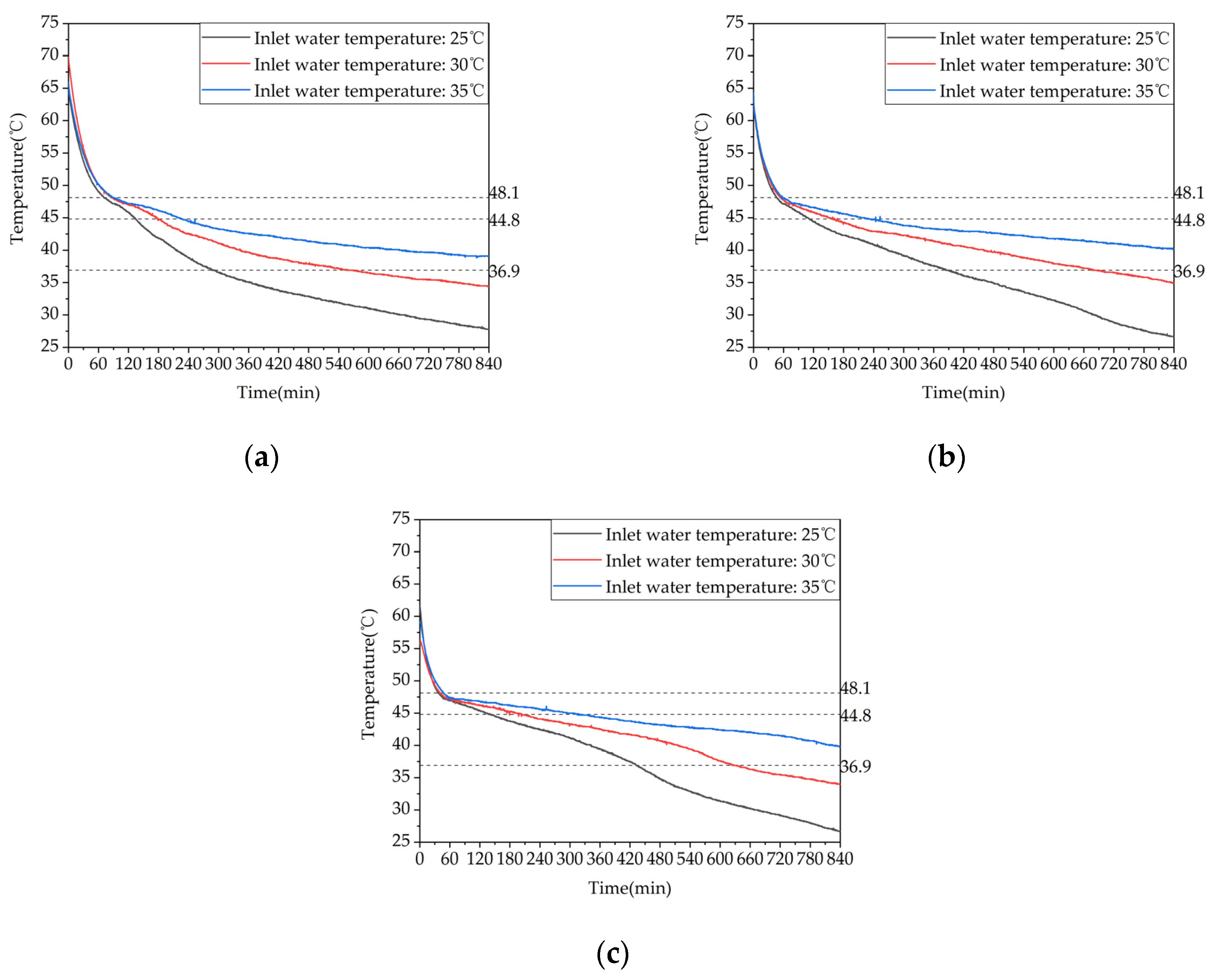
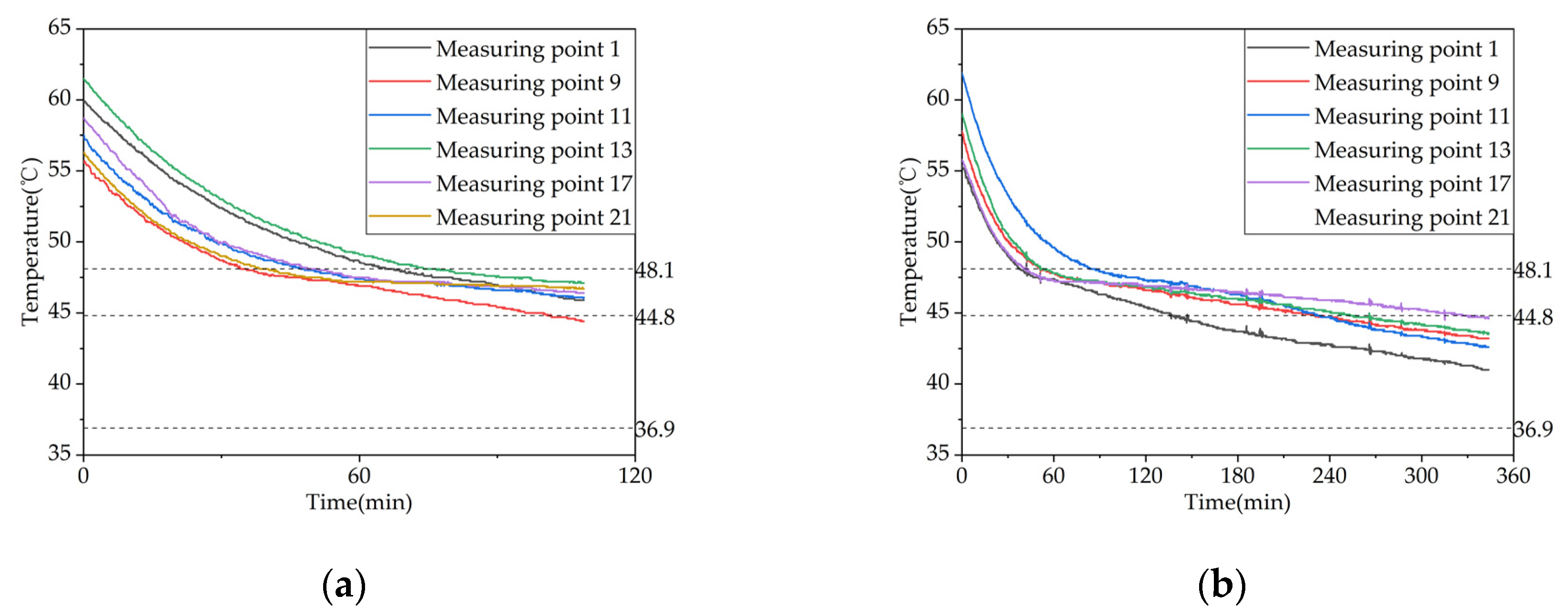
Figure 14.
Temperature variation inside the phase-change storage device for domestic hot water under different inlet water temperatures: (a) Inlet water temperature: 25℃; (b) Inlet water temperature: 25℃.
Figure 14.
Temperature variation inside the phase-change storage device for domestic hot water under different inlet water temperatures: (a) Inlet water temperature: 25℃; (b) Inlet water temperature: 25℃.
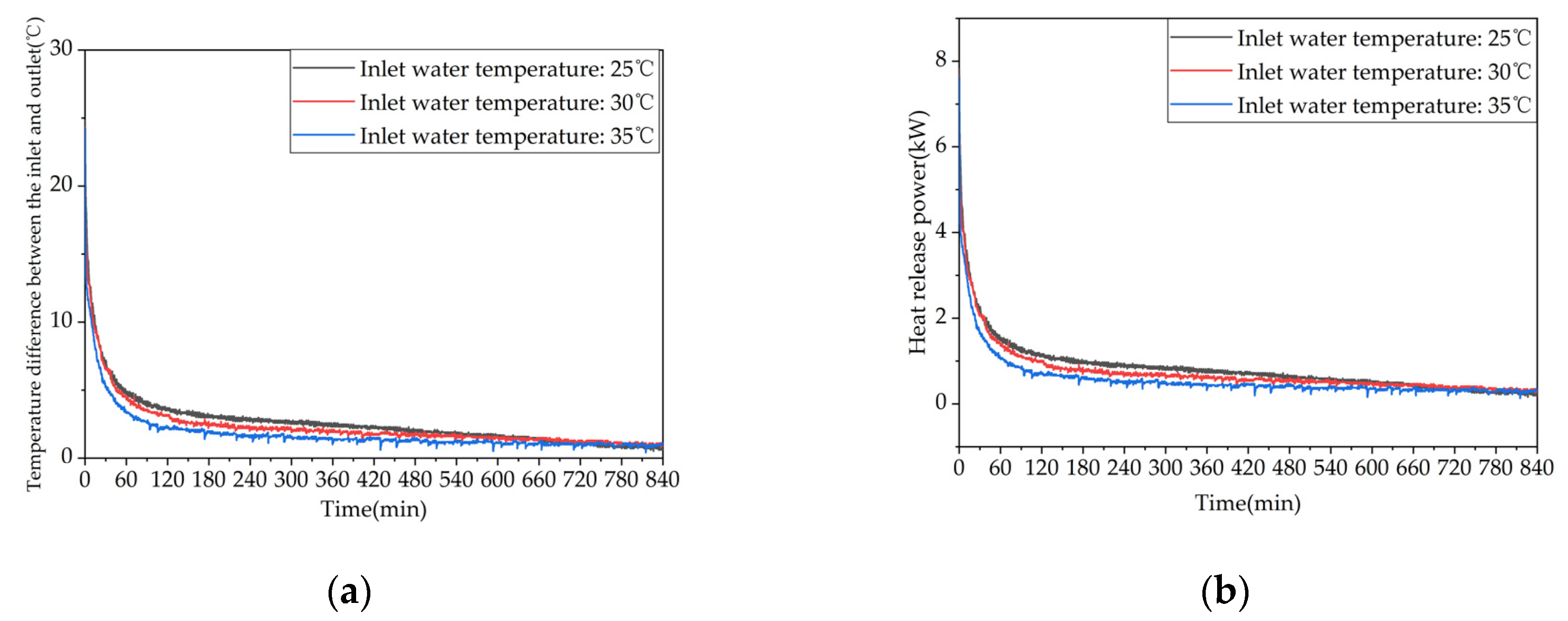
Figure 15.
Heat release performance of the device at different inlet water temperatures: (a) Temperature difference between inlet and outlet; (b) Instantaneous heat release power.
Figure 15.
Heat release performance of the device at different inlet water temperatures: (a) Temperature difference between inlet and outlet; (b) Instantaneous heat release power.
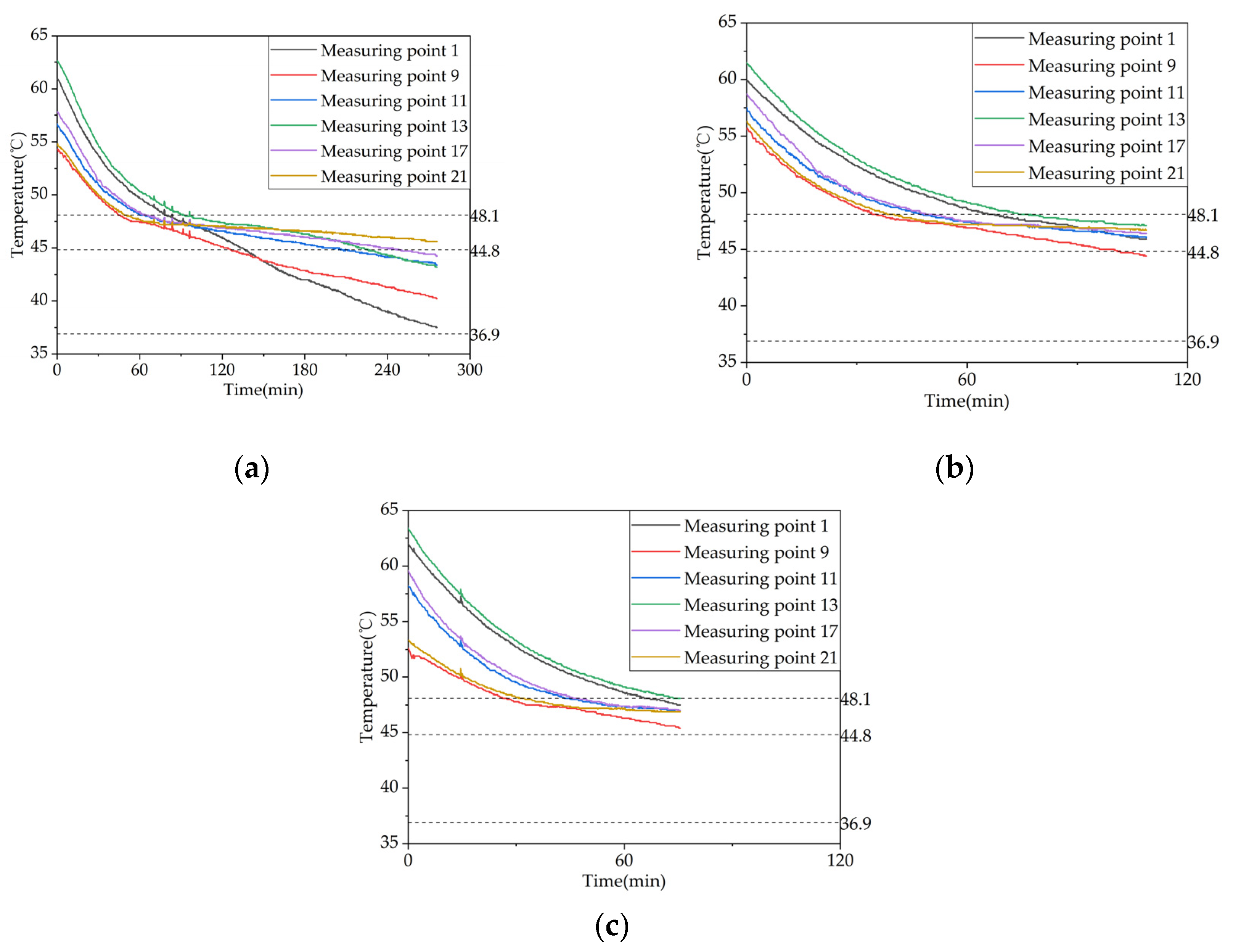
Figure 16.
Temperature variation inside the phase change heat storage unit at typical locations under different Heat storage conditions: (a) Measuring point 13; (b) Measuring point 17; (c) Measuring point 21.
Figure 16.
Temperature variation inside the phase change heat storage unit at typical locations under different Heat storage conditions: (a) Measuring point 13; (b) Measuring point 17; (c) Measuring point 21.
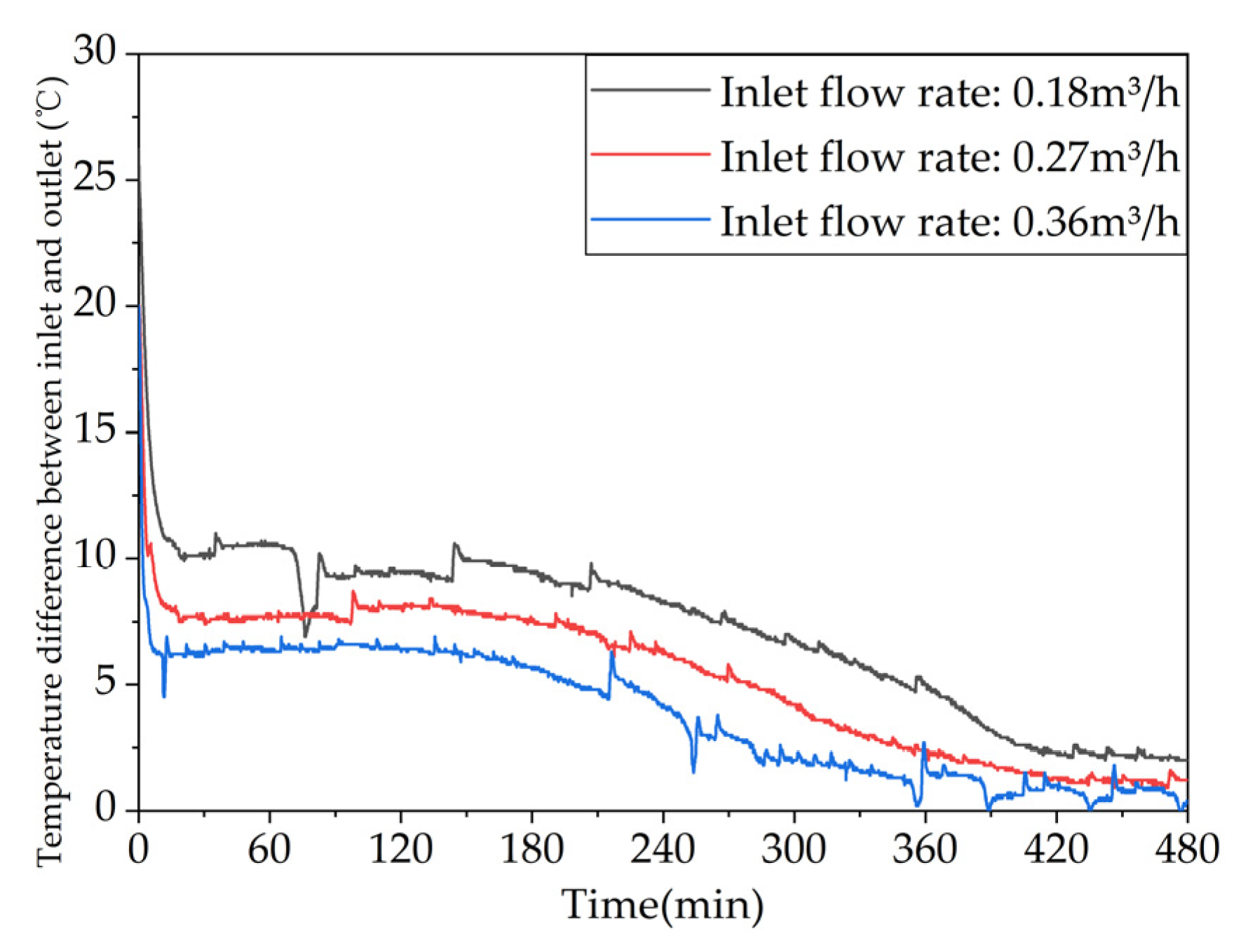
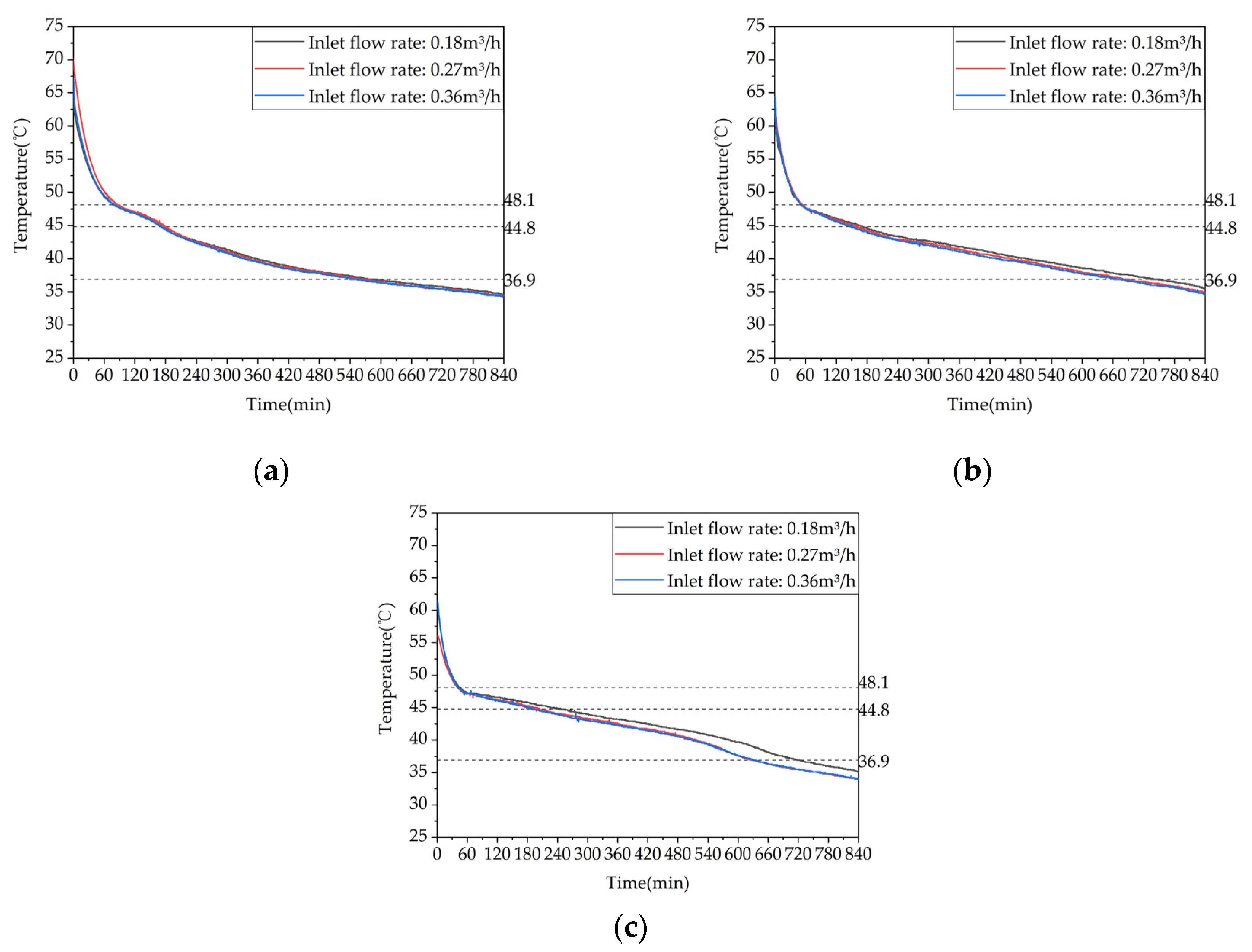
Figure 17.
Different trends of the temperature difference between the inlet and outlet of the device over time under different inlet flow rates.
Figure 17.
Different trends of the temperature difference between the inlet and outlet of the device over time under different inlet flow rates.
Figure 18.
Temperature variation inside the phase change heat storage unit at typical locations under different Heat storage conditions: (a) Measuring point 13; (b) Measuring point 17; (c) Measuring point 21.
Figure 18.
Temperature variation inside the phase change heat storage unit at typical locations under different Heat storage conditions: (a) Measuring point 13; (b) Measuring point 17; (c) Measuring point 21.
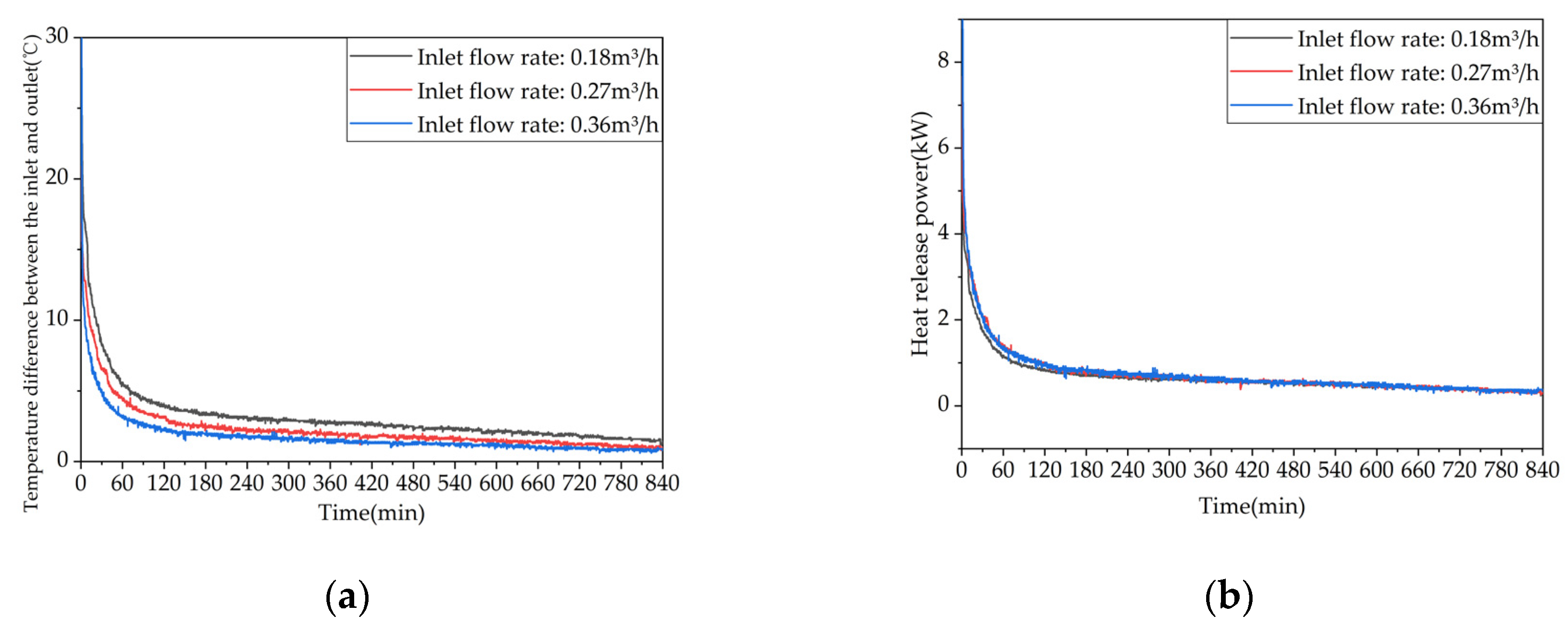
Figure 19.
Heat release capacity of the device at different inlet flow rates.: (a) Temperature difference between inlet and outlet; (b) Instantaneous heat release power.
Figure 19.
Heat release capacity of the device at different inlet flow rates.: (a) Temperature difference between inlet and outlet; (b) Instantaneous heat release power.
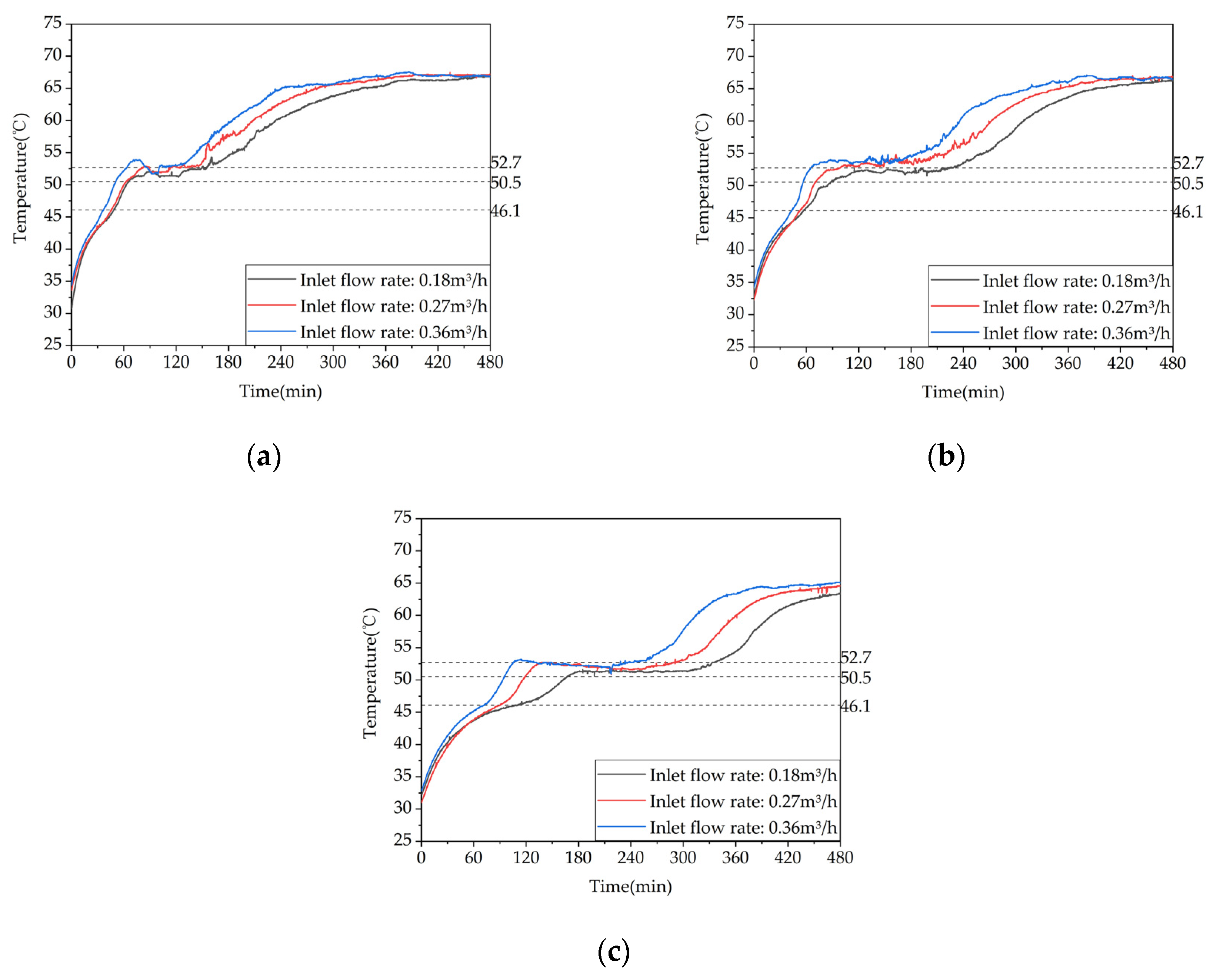
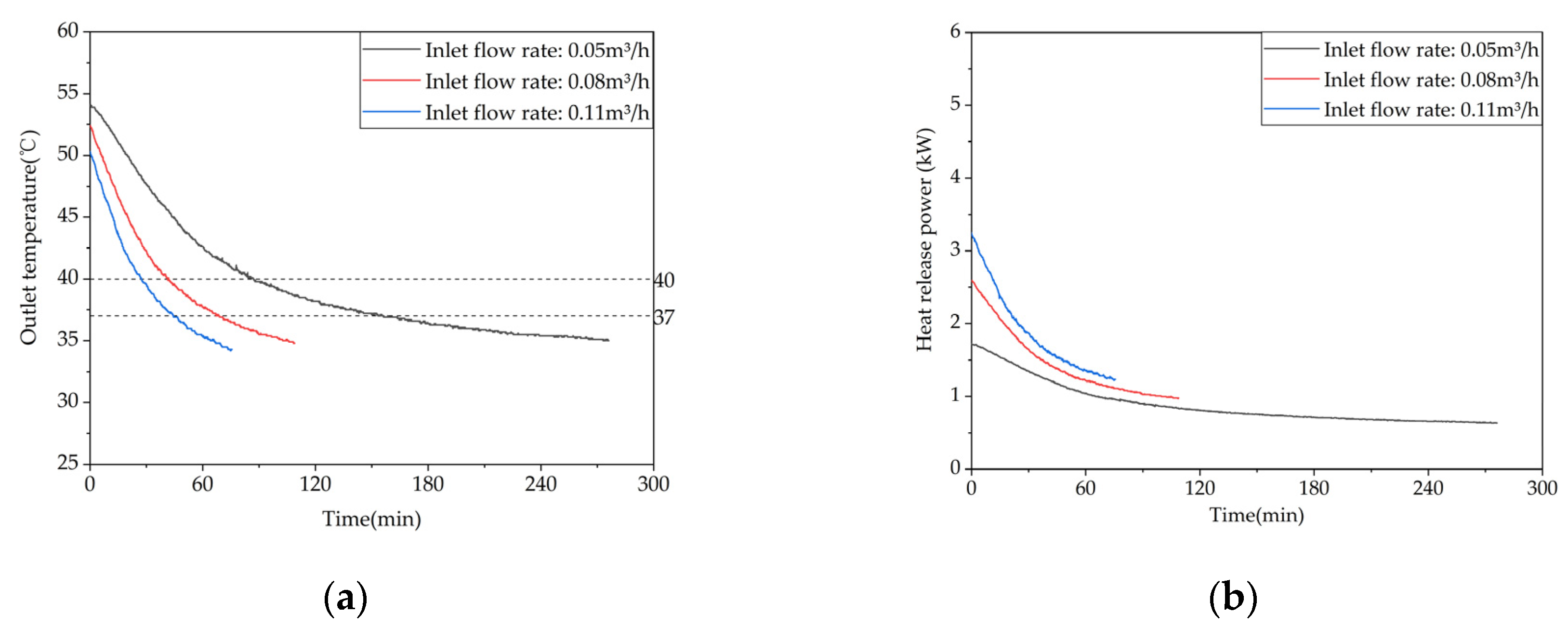
Figure 20.
Temperature variation inside the phase-change storage device for domestic hot water under different inlet water temperatures: (a) Inlet flow rate: 0.05 m³/h; (b) Inlet flow rate: 0.08 m³/h; (c) Inlet flow rate: 0.11 m³/h.
Figure 20.
Temperature variation inside the phase-change storage device for domestic hot water under different inlet water temperatures: (a) Inlet flow rate: 0.05 m³/h; (b) Inlet flow rate: 0.08 m³/h; (c) Inlet flow rate: 0.11 m³/h.
Figure 21.
Heat release capacity of the device at different inlet flow rates.: (a) Temperature difference between inlet and outlet; (b) Instantaneous heat release power.
Figure 21.
Heat release capacity of the device at different inlet flow rates.: (a) Temperature difference between inlet and outlet; (b) Instantaneous heat release power.
Figure 22.
Temperature variation inside the phase change heat storage unit at typical locations under different Heat storage conditions: (a) Measuring point 13; (b) Measuring point 17; (c) Measuring point 21.
Figure 22.
Temperature variation inside the phase change heat storage unit at typical locations under different Heat storage conditions: (a) Measuring point 13; (b) Measuring point 17; (c) Measuring point 21.
Figure 23.
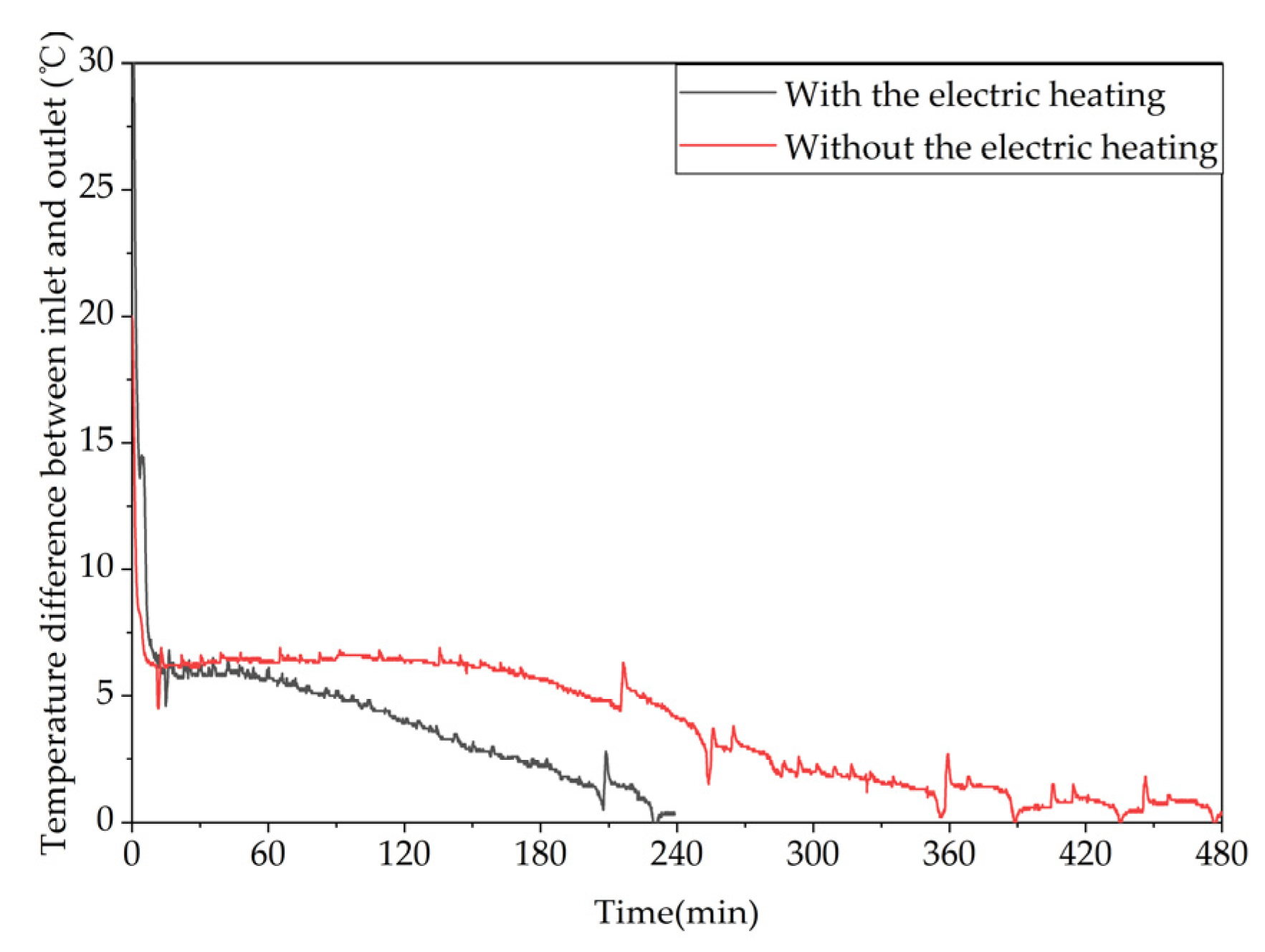
Different trends of the temperature difference between the inlet and outlet of the device over time under different heating methods.
Figure 23.
Different trends of the temperature difference between the inlet and outlet of the device over time under different heating methods.
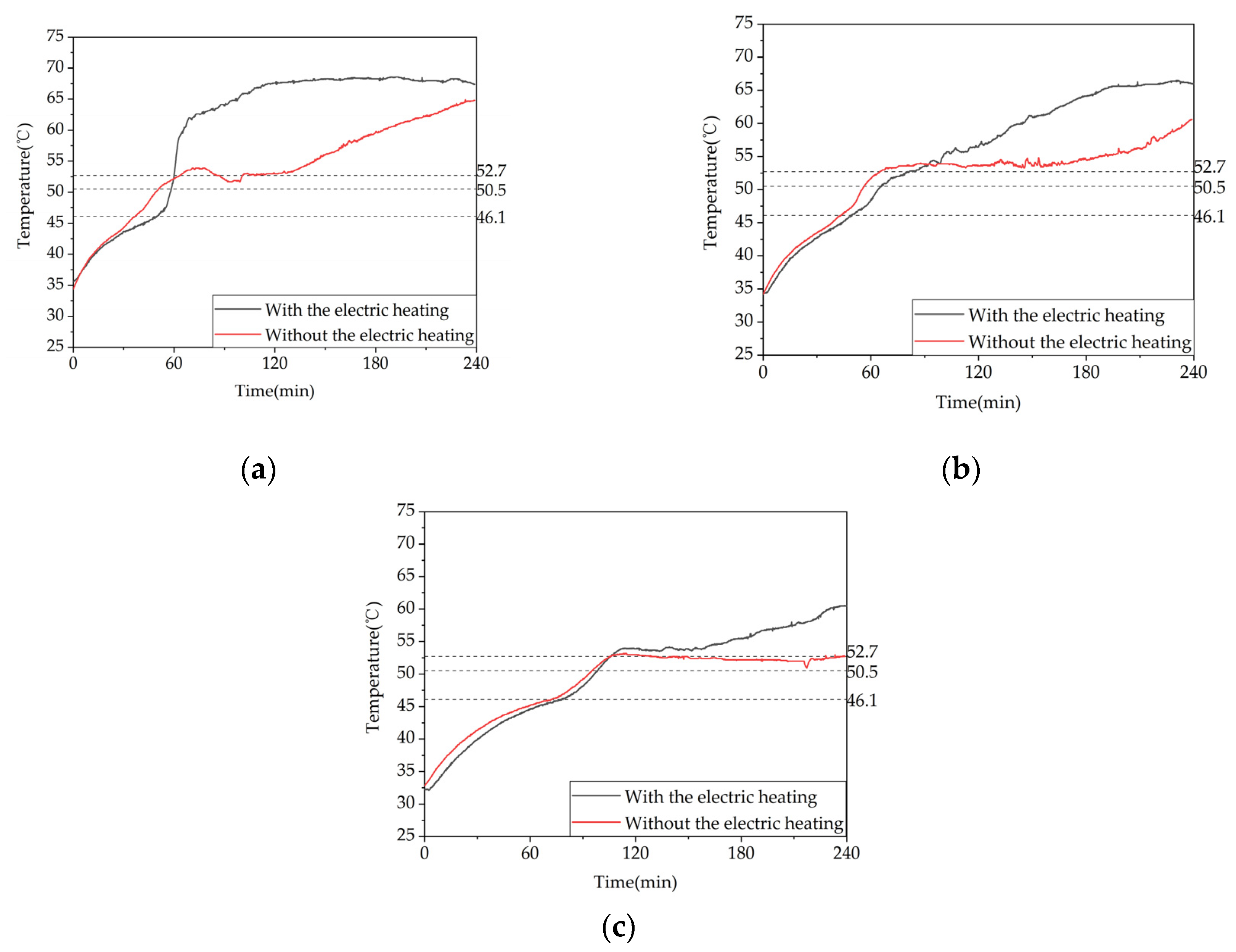
Figure 24.
Temperature variation inside the phase change heat storage unit at typical locations under different Heat storage conditions: (a) Measuring point 13; (b) Measuring point 17; (c) Measuring point 21.
Figure 24.
Temperature variation inside the phase change heat storage unit at typical locations under different Heat storage conditions: (a) Measuring point 13; (b) Measuring point 17; (c) Measuring point 21.
Figure 25.
Heat release capacity of the device at Initial temperature of the device: (a) Temperature difference between inlet and outlet; (b) Instantaneous heat release power.
Figure 25.
Heat release capacity of the device at Initial temperature of the device: (a) Temperature difference between inlet and outlet; (b) Instantaneous heat release power.
Figure 26.
The simulated contour maps for different fin arrangement configurations: (a) Liquid phase fraction; (b) Device temperature.
Figure 26.
The simulated contour maps for different fin arrangement configurations: (a) Liquid phase fraction; (b) Device temperature.
Figure 27.
The liquid fraction and average temperature of the phase change heat storage unit vary with different fin arrangements.
Figure 27.
The liquid fraction and average temperature of the phase change heat storage unit vary with different fin arrangements.
Figure 28.
The simulated contour maps for different fin spacing arrangements: (a) Liquid phase fraction; (b) Device temperature.
Figure 28.
The simulated contour maps for different fin spacing arrangements: (a) Liquid phase fraction; (b) Device temperature.
Figure 29.
The liquid fraction and average temperature of the phase change heat storage unit vary with different fin spacing.
Figure 29.
The liquid fraction and average temperature of the phase change heat storage unit vary with different fin spacing.
Figure 30.
The simulated contour maps for different fin thicknesses: (a) Liquid phase fraction; (b) Device temperature.
Figure 30.
The simulated contour maps for different fin thicknesses: (a) Liquid phase fraction; (b) Device temperature.
Figure 31.
The liquid fraction and average temperature of the phase change heat storage unit vary with different fin thicknesses.
Figure 31.
The liquid fraction and average temperature of the phase change heat storage unit vary with different fin thicknesses.
Figure 32.
Simulated flow visualization under different inlet directions and installation orientations: (a) Liquid phase fraction; (b) Device temperature.
Figure 32.
Simulated flow visualization under different inlet directions and installation orientations: (a) Liquid phase fraction; (b) Device temperature.
Figure 33.
The liquid fraction and average temperature of the phase change heat storage unit vary with different inlet flow directions and installation orientations.
Figure 33.
The liquid fraction and average temperature of the phase change heat storage unit vary with different inlet flow directions and installation orientations.
Table 1.
Detailed parameters of the main components inside the phase change TES device.
Table 1.
Detailed parameters of the main components inside the phase change TES device.
| Name |
Material |
Relevant parameters |
| heat storage tank |
304 stainless steel |
Internal Dimensions: 820×320×800mm |
| Wall Thickness: 2mm |
| Diameter: 18mm |
| External Diameter: 20mm |
| Finned tube coil |
304 stainless steel |
Vertical center distance between adjacent coils: 304mm |
| Horizontal center distance between adjacent coils: 80mm |
| Distance to the bottom wall of the box: 25mm |
| Distance to the top wall: 128mm |
| Electric heating plate |
Aluminium |
Dimensions: 700×25×800mm |
| Distance to the top wall surface: 80mm |
Table 2.
The main equipment and instrument parameters of the experiment.
Table 2.
The main equipment and instrument parameters of the experiment.
| Name |
Manufacturer source |
Model |
Relevant parameters |
| Electric boiler |
A.O. Smith |
DSE-50-90 |
Heating power: 18 kW |
| Temperature control range for water: 30~88℃ |
| Rated capacity: 190 L |
| Minimum differential temperature: 1℃ |
| Air-cooled chiller |
Zhongke Kechuangyi |
KYKY-LS 65A |
Cooling capacity: 6.5kW |
| Water temperature control range: 10~25℃ |
| Water tank capacity: 40L |
| Water control accuracy: ±0.2℃ |
| Variable frequency constant pressure circulating pump |
Grundfos |
CM5-3 |
Rated power: 650W |
| Max. variable flow rate: 4.7m3/h |
| Electromagnetic flowmeter |
Meikon |
LDG-SUP-DN10 |
Measurement range: 0~1.4m³/h |
| Accuracy class: ±0.5%R |
| Rotor flowmeter |
Juyi Instrument |
LZB-WS-10G |
Measurement range: 16~160L/h |
| Thermocouple |
Xiamen Mingkong |
K-type |
Length: 2.5m |
| Data logger |
Yokogawa |
MX-100 |
Inputs for DVC/TC/DI/RTD |
Table 4.
Heat storage test conditions.
Table 4.
Heat storage test conditions.
| Number |
The initial temperature of the device (℃) |
Inlet water temperature (℃) |
Inlet water flow rate (m³/h) |
Heat storage mode |
| 1 |
33 |
58 |
0.27 |
Hot water |
| 2 |
33 |
63 |
0.27 |
Hot water |
| 3 |
33 |
68 |
0.27 |
Hot water |
| 4 |
33 |
68 |
0.18 |
Hot water |
| 5 |
33 |
68 |
0.36 |
Electric heating plate + Hot water |
| 6 |
33 |
68 |
0.36 |
Hot water |
Table 5.
heat release test conditions.
Table 5.
heat release test conditions.
| Number |
Number |
The initial temperature of the device (℃) |
Inlet water temperature (℃) |
Inlet water flow rate (m³/h) |
| Heating release condition |
7 |
63 |
25 |
0.27 |
| 8 |
63 |
30 |
0.27 |
| 9 |
63 |
35 |
0.27 |
| 10 |
63 |
30 |
0.18 |
| 11 |
63 |
30 |
0.36 |
| 12 |
53 |
30 |
0.27 |
| 13 |
58 |
30 |
0.27 |
| Domestic hot water release condition |
14 |
58 |
25 |
0.05 |
| 15 |
58 |
25 |
0.08 |
| 16 |
58 |
25 |
0.11 |
| 17 |
58 |
30 |
0.08 |