1. Introduction
In Morocco, agriculture is a crucial sector that contributes significantly to the economy and plays an important role in combating rural exodus. It creates nearly 38% of total employment, with 73.7% of employment in rural areas, and provides more than 65% of the income for the rural population [
1]. Its contribution to the country's annual GDP ranges between 11% and 14%, with an average of 12.5% over the period 2000-2020 [
2]. The main cereal crops are soft wheat, hard wheat, and barley, which play a major role in national agriculture, covering around 59% of the national agricultural land area [
3], which reaches 8.8 million hectares [
4]. Cereal farming represents 93% of the cultivated land in arid and semi-arid regions, while moister regions and irrigated areas are reserved for high-value export crops, influenced by the international division of labor and macroeconomic policies [
5]. Given that each Moroccan consumes 255 kg of wheat per year, four times the global average [
6], imports of main cereals increased by 911% between 1971 and 2021 [
7]. In this context, early forecasting of cereal crop yields is crucial to assist policymakers and cereal marketing institutions in planning imports and better coping with global food price fluctuations. This forecast would also strengthen the capacities of agricultural importers to manage global food price fluctuations and ensure the sustainability of the national cereal market supply.
The available field data are difficult to use for predicting environmental changes at the regional level, as these data are acquired at small spatial and temporal scales and vary in terms of type and reliability [
8]. In contrast, remote sensing is capable of providing data in a synoptic manner, with a more extensive spatial coverage [
9]. As such, remote sensing is an effective tool for obtaining information on crop characteristics, estimating cultivated area, and monitoring changes they undergo, primarily focusing on crop growth status and final harvest, at a relatively low cost [
9,
10,
11]. This technology has been used in the agricultural field since the 1970s [
12,
13].
Vegetation indices such as leaf area index (LAI), vegetation condition index (VCI), percent of average seasonal greenness (PASG), vegetation supply water index (VSWI), normalized difference red edge (NDRE), enhanced vegetation index (EVI), and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) have been widely used to assess plant water stress, tree growth, crop phenology, monitor canopy chlorophyll content, and classify terrestrial vegetation cover. Therefore, these indices are useful for monitoring vegetation cover health, assessing the impacts of agroclimatic conditions on crops, and predicting grain yield based on vegetation greenness level [
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23]. Therefore, they are useful for strengthening and improving early warning systems.
The NDVI is a widely used remote sensing index for evaluating vegetation cover due to its robustness and sensitivity to vegetation, as well as the availability of long time series from remote sensing. There is a strong linear correlation between NDVI and vegetation biomass [
24]. However, it has limitations, particularly in terms of soil background brightness and saturation in cases of high vegetation cover [
11,
12,
13]. It is defined the difference between the reflectance of the red band (0.66 μm) and the near-infrared band (0.86 μm), divided by their sum [
25]. It was first used in a study conducted in the Great Plains of the United States in 1973 [
26]. NDVI is considered an important predictor of crop yield, especially in rainy areas, while precipitation and temperature have been more important in arid areas with low rainfall [
27].
Recently, several studies have been conducted based on NDVI to predict cereal yields, evaluate crop phenological characteristics, measure crop canopy coverage, and study ecological responses to environmental changes such as drought, flooding, and frost [
8], [
19,
28,
29,
30.
31,
32,
33,
34].
Currently, satellite data from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Terra spacecraft's Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) are freely accessible. Through atmospheric correction and cloud filtering by the MODIS scientific team, these data, which include NDVI, have created new opportunities for real-time crop monitoring [
13,
35]. Given the dramatic economic and social consequences of food deficits in Morocco, it is crucial to predict yields and monitor the state of agricultural production. In this regard, there are various methods for predicting cereal crop yields, including statistical models based on multiple linear regression, where NDVI data is used as predictors of yields [
9,
22,
29].
The objective of this study is to evaluate the relationship between MODIS NDVI data at different dates during the period of 2000-2020 and the yield of major cereal crops in the Fez-Meknes region, as well as to determine the most favorable date for more reliable prediction of cereal yields in the Fez-Meknes region. MODIS-derived NDVI data have not yet been utilized for the purpose of predicting crop yields in this region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Yield data for Main Cereals
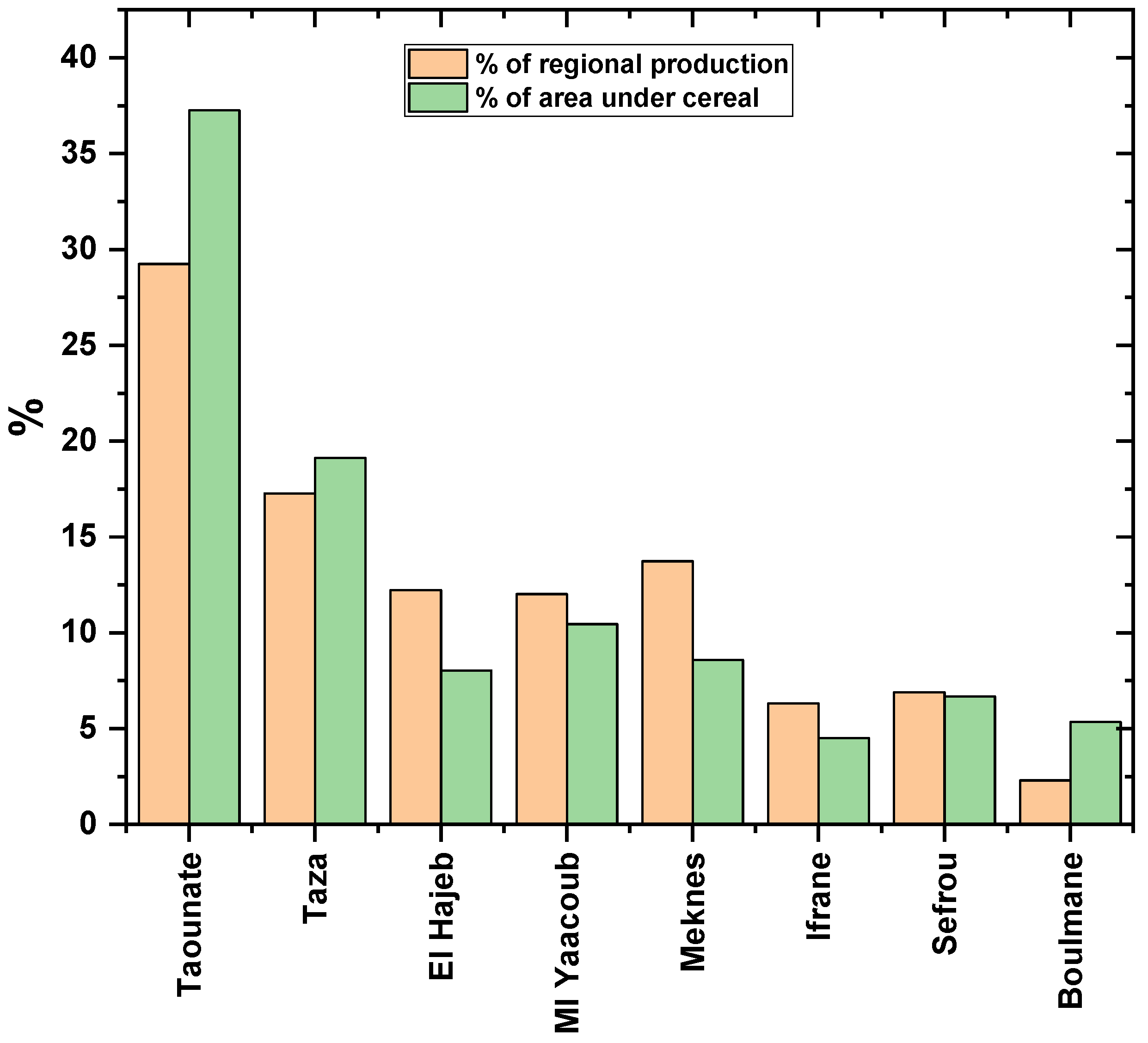
The region of Fez-Meknes was selected for this study due to its significant contribution to national production (20%) and the prevalence of cereal crops, which account for 53% of agricultural land in the region. The Ministry of Agriculture, Marine Fisheries, Rural Development, and Forestry (MAMFRDF) provided statistics on cereal yields in quintals (q; 1 q = 100 kg), cultivated land in hectares (ha), and production in tons covering the period from 2000 to 2020 (N=20). The land cultivated in cereal crops is concentrated in the province of Taounate and the province of Taza, which account for 37% and 19% respectively of the region total. Cereal cultivation is lower in the provinces of Ml Yaacoub (10.4%), Meknes (8.5%), El Hajeb (8.03%), Sefrou (6.7%), Boulmane (5.3%), and Ifrane (4.5%). Similarly, nearly half of the regional cereal production (48%) is provided by two provinces: Taounate, which contributes 30%, and Taza, which contributes 18%. The provinces with remarkable contributions have a large agricultural area reserved for cereal crops, except for Meknes, which only allocates 8.5% of its regional agricultural area to cereal crops but contributes 13.7% to regional cereal production. This is due to favorable soil conditions, the role of inputs such as nitrogen fertilization and pesticides, and the intensive use of agricultural technology during planting, weed treatment, and harvesting. The El Hajeb and Moulay Yaacoub regions have 8% and 10% of the agricultural area dedicated to cereal crops but produce 12% of the regional production each, as illustrated in
Figure 1.
2.1. Remote Sensing Data
The MODIS NDVI data for the mean time series for the Fez-Meknes region in this study were obtained from the Global Agricultural Monitoring System (GLAM) (
https://glam1.gsfc.nasa.gov/ (accessed on February 15, 2023)), which provides global NDVI data every eight days in near real-time. These datasets are derived from satellite images captured by sensors on NASA's Terra spacecraft at medium spatial resolution of 500 meter. They undergo atmospheric correction and cloud filtering on a per-pixel basis through the efforts of the MODIS science team. This system was established in 2000 by NASA in collaboration with the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as part of the Global Agricultural Monitoring Project, which aims to provide objective and regular assessments of global agricultural production forecasts and conditions affecting food security worldwide [
22,
36]. Using MODIS NDVI data, analysts can track the progress of the growing season, perform interannual comparisons of seasonal dynamics, and inform policymakers about the agricultural situation.
2.3 Statistical Analysis
The relationship between the 8-day NDVI of cultivated land and grain yield was calculated for each year of the study and for each province in the region individually using the Pearson correlation coefficient and linear regression method. The performance of the model was evaluated using the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) [
37]. The results of the correlation coefficients for all regional provinces and during different NDVI dates will be illustrated in a table. The color of each cell will depend on the value of the correlation coefficient. The results of the linear regression will be presented in graphs that include the regression equations and determination coefficients. The analyses were conducted using R studio, Excel 2016, and Origin 2023. For spatial analyses, maps were created using ArcMap 10.3.
3. Results
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Variability of Grain Yield and NDVI
During the period of 2000-2020, the province of Meknes had the highest grain yield among the main cereals, with 22 q/ha. Specifically, wheat grain yield was very high at 23.7 q/ha, compared to barley which was 18.6 q/ha. The provinces of El Hajeb, Taza, Ml Yaacoub, Ifrane, and Sefrou also recorded average grain yields (respectively 18.5, 17.4, 17.3, 17.09, and 17.07 q/ha). On the other hand, the provinces of Taounate (15.5 q/ha) and Boulmane (12.2 q/ha) had low yields. However, the regional yield of main cereals remains higher than the national yield.
The interannual coefficient of variation in the yield of major cereals was highest in the provinces of Taza (50%) and Ml Yaacoub (43%). For the provinces of El Hajeb, Meknes, Sefrou, and Taounate, it ranged from 37% to 41%. The mountainous provinces of the region recorded relatively lower temporal variation, reaching 29% and 31% respectively for the provinces of Boulmane and Ifrane. In comparison, the national coefficient of variation was 35% for the period 2000-2020. This indicates that most provinces in the region (75%) exhibit higher variability than that revealed at the national level. The Fez-Meknes region is quite exposed to the risk of agricultural drought, with the provinces located in the plains more vulnerable compared to those in the Middle Atlas Mountains (Ifrane and Boulmane). This can be explained by the effect of higher relative humidity at higher altitudes, due to the effect of temperature decreasing with altitude. Additionally, local showers tend to affect mountainous provinces more than plains provinces.
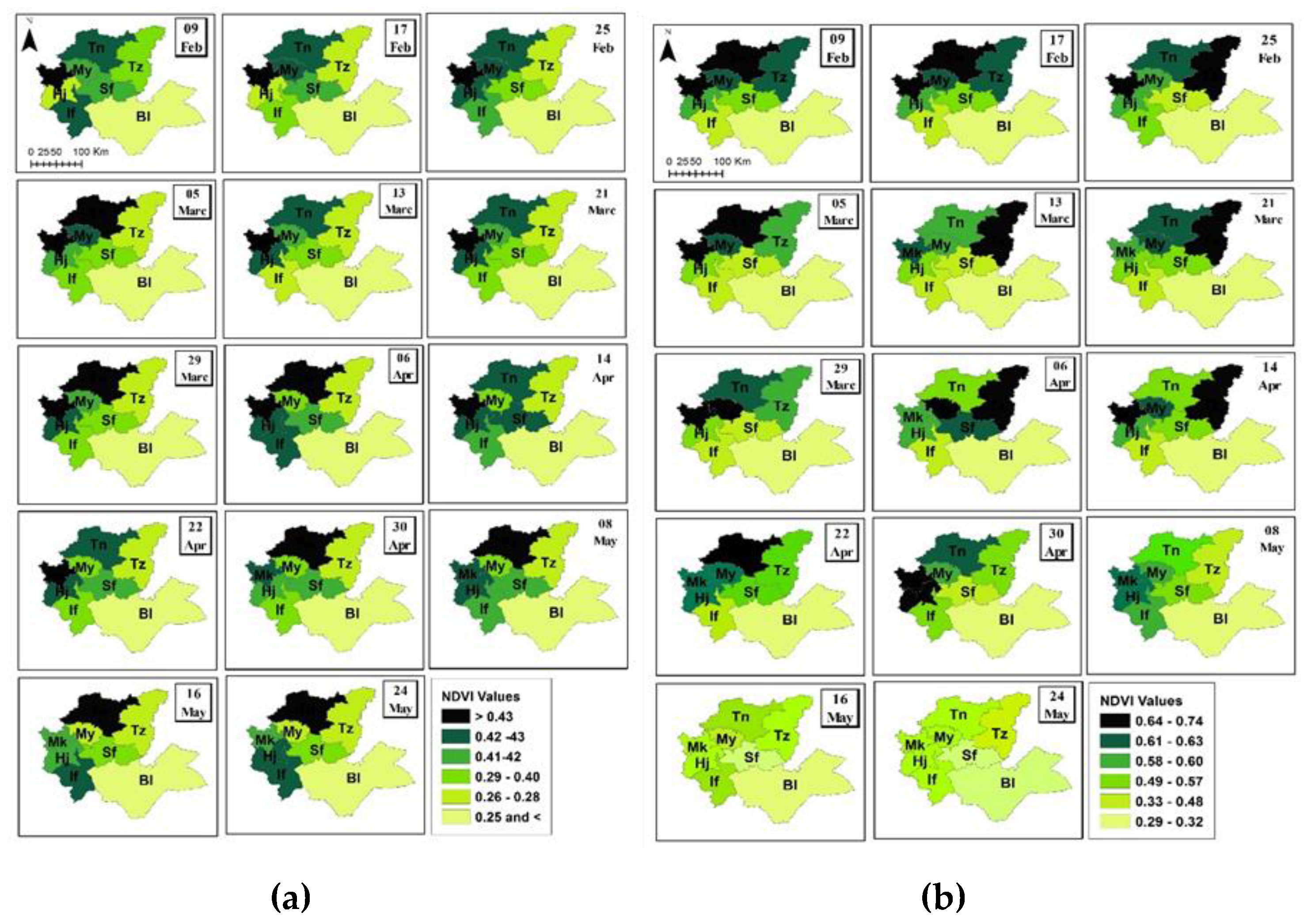
The highest average NDVI for the study period (2000-2020) averaged over the growing season taken into account in the study (mid-December to early June) was observed in the provinces of Meknes and Taounate, with values of 0.54 and 0.52, respectively. The lowest NDVI was recorded in the provinces of Sefrou and Ifrane, with a value of 0.42. The temporal variability of NDVI reached its maximum in the provinces of Taza and Ml Yaacoub (16% and 18%, respectively), while it was relatively moderate in the provinces of Taounate (13%) and El Hajeb (11%). On the other hand, it was low in the provinces of Boulmane (CV 8%), Ifrane (CV 9%), as well as in the provinces of Meknes and Sefrou (10%).
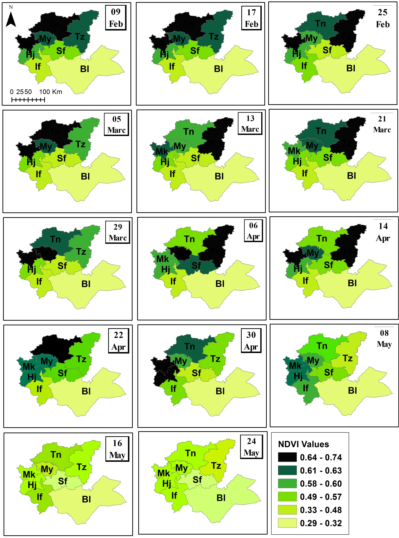
The NDVI is largely affected by changes in water availability for crops, which has an impact on their final yield. For example, during the 2006-2007 agricultural year, which was classified as dry on a climatic level, with a regional average yield of 5.20 q/ha, the NDVI varied between 0.31 and 0.53 in the province of Meknes, between 0.26 and 0.44 in the province of Ml Yaacoub, between 0.23 and 0.36 in the province of Taza, between 0.30 and 0.42 in the province of Ifrane, between 0.26 and 0.48 in the province of El Hajeb, between 0.23 and 0.26 in the province of Boulmane, between 0.41 and 0.51 in the province of Taounate, and between 0.32 and 0.45 in the province of Sefrou. In contrast, during the 2012-2013 agricultural campaign, which was classified as wet with a regional average yield of 21.5 q/ha, the NDVI values rapidly increased during the months of February, March, and April, which are decisive months for cereal harvesting. In general, the values varied between 0.58 and 0.74 in the north of the region and between 0.28 and 0.57 in the south of the region during these months. It is possible to observe differences in the NDVI index between the two agricultural campaigns, from February to April, due to contrasting climatic conditions. However, these differences decreased in May as cereals entered the senescence phase, a period characterized by a decrease in precipitation and an increase in temperatures. This occurred whether it was a dry or wet year, as illustrated in
Figure 2.
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Variability of Grain Yield and NDVI
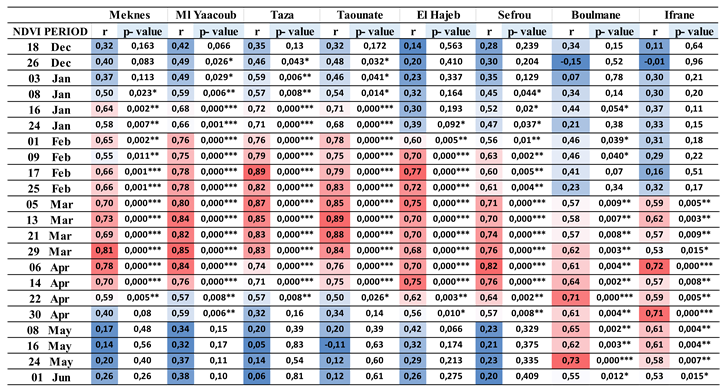
The results of the correlation analysis between wheat and barley yields are presented in
Table 1. Strong relationships were observed at different periods in all regional provinces. The strongest relationships (greater than 0.70) were found from mid-January to early April for the province of Taza, as well as in the province of Taounate, and from early February to mid-April in the provinces of Ml Yaacoub and El Hajeb. Therefore, the cereal harvest can be estimated in these two provinces from early winter. In addition, strong and positive correlations were observed in the provinces of Meknes and El Hajeb between early March and mid-April. In these provinces, the correlation coefficient increased in mid-February into the spring, where it exceeded 0.80. The correlation coefficients demonstrated a highly significant relationship between NDVI and yield (probability level of 0.1%) between January 16th and April 14th, particularly in the provinces of Taza, Taounate, and Ml Yaacoub, and between February 9th and April 14th for the provinces of El Hajeb and Meknes. Furthermore, in the mountainous provinces, the strongest link appears between the end of April and the end of May, especially for the province of Boulmane, and between the beginning and end of April for the province of Ifrane. The coefficients are significant at the probability level of 1% and 0.1% from March 5th to May 24th.
However, very weak correlations were recorded at the beginning and end of the growing season in the provinces that were marked by early sowing and are located in the plains and plateaus of the Fez-Meknes region, such as Meknes, Ml Yaacoub, Taza, Taounate, El Hajeb, and Sefrou. The mountainous provinces recorded positive correlations ranging from moderate to high in May and early June due to late sowing and low temperatures. Negative correlations are very rare and were recorded only three times (-0.15, -0.11, and -0.01) at the beginning and end of the growing season, notably in the provinces of Taounate, Ifrane, and Boulmane (
Table 1).
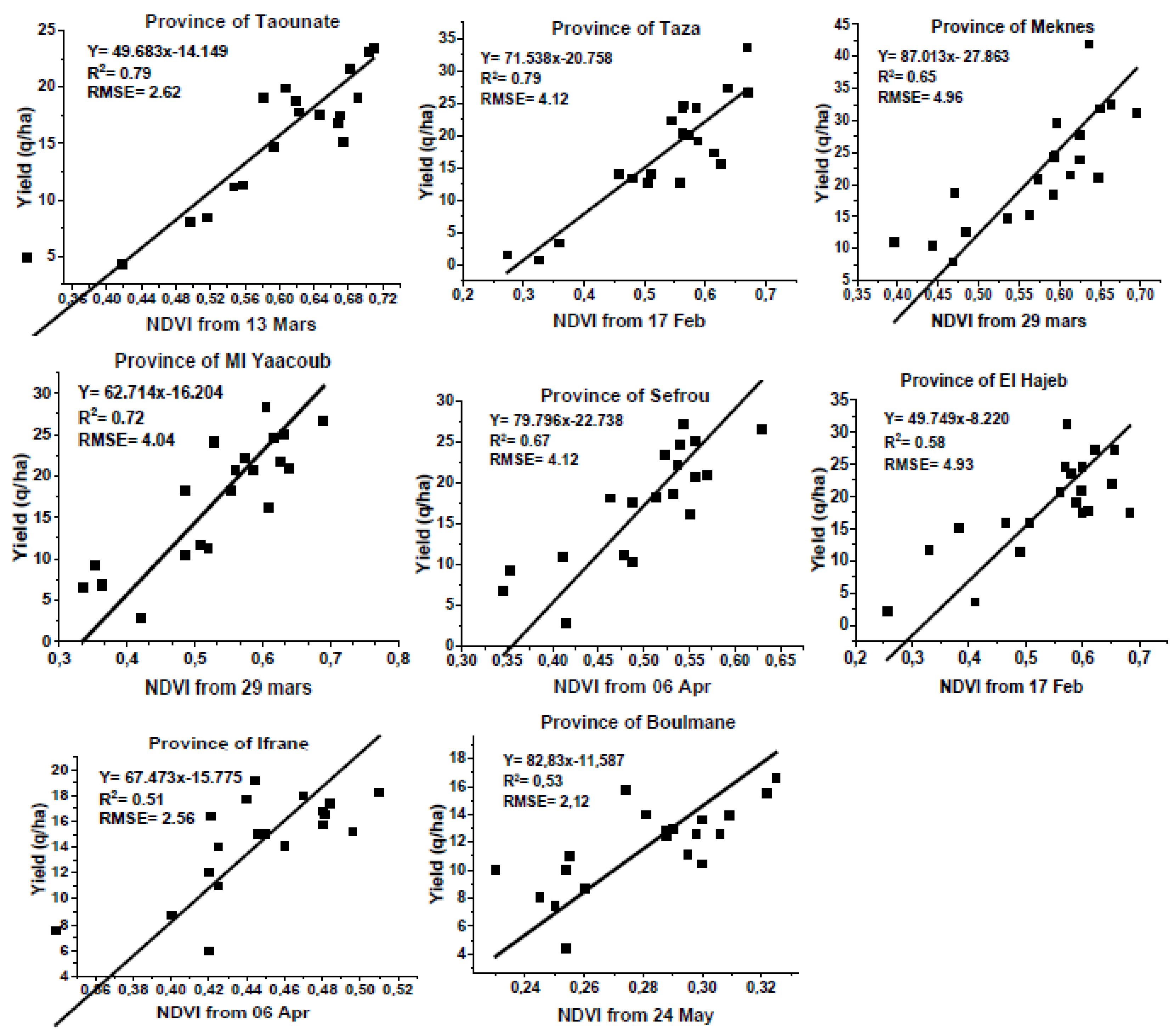
Linear regression was applied to the dates with the highest correlation between Modis-NDVI and grain yield to predict grain yield in the provinces of the region based on observed NDVI (
Figure 3). Indeed, regression functions varied from year to year, possibly due to sowing dates and weather conditions. Regression line slopes ranged from 49 to 87 q/ha per unit, indicating that a 0.1 increase in NDVI results in an expected increase in grain yield of 4.9 to 8.7 q/ha, with an average of 6.8 q/ha. The correlation between wheat and barley yield and NDVI was very strong, with a regression coefficient ranging from 0.77 to 0.89 in the provinces of Taza, Taounate, Ml Yaacoub, Sefrou, El Hajeb, and Meknes, indicating that developed models explain 58 to 79% of the variability in wheat and barley yields. In the two mountainous provinces of the region (Boulmane and Ifrane), the relationship between Modis-NDVI and grain yield was the weakest (R
2 0.51 to 0.53). The best prediction model was found in the provinces of Taza and Taounate. These results are promising as these two provinces produce almost 50% of the region's cereal production. The NDVI in the second and third decades of March and the first decade of April, during the grain heading and flowering phase, had the strongest impact on the expected yield of rainfed cereal crops in the region. The Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) relative to the prediction of cereal yield from regression models varied from 212 to 496 kg/ha (2.12 to 4.96 q/ha).
4. Discussion
The aim of this agroclimatic study is to examine the relationship between the NDVI variation and cereal yield in the Fez-Meknes region, located in the central-north of Morocco. This region is primarily focused on rainfed cereal cultivation, notably wheat and barley, and their by-products such as wheat bran and straw, which are essential feed for livestock. Additionally, a comparative analysis of cereal production and consumption, particularly for wheat, which is most widely consumed by the population at 255 kg/inhabitant/year, shows that the gap is widening in favor of imports, which have increased by 911% between 1971 and 2021. As a result, Morocco is dependent on the international market, where the import dependence rate has reached 39.8%, while food self-sufficiency represented 60.2% in the last decade (2012-2021). Therefore, predicting yields is crucial for the local population and national economy, as it ensures the country's food security and maintains the supply of the national market in main cereals, given the weight of this region in national production (20%).
It appears from the temporal analysis of the strongest relationship between wheat and barley yield and Modis-NDVI values through the correlation coefficient in the region of Fez-Meknes (r= 0.70 to 0.89) that it is lower than that obtained by [
22], where they exceeded 0.90 in some months. However, our results are superior to those noted by [
29] in their study of the relationship between Modis-NDVI and grain yield of crops in semi-arid and subhumid agroclimatic zones in Canada (r = 0.48 to 0.78). The coefficients of determination obtained in most provinces of the region (R
2 = 0.58 to 0.79) are higher than those observed by [
22] in Central Europe, where the authors found that the R
2 of the relationship between cereal yield and NDVI of the total agricultural surface (R
2 = 0.49 to 0.64). Furthermore, these coefficients are higher than those found by [
15] in Italy, where R
2 oscillated between 0.01 and 0.46 in the context of the correlation between AVHRR-NDVI and wheat yield. Similarly, [
29] found that the coefficient of determination between spring wheat and barley yield on the one hand and Modis-NDVI on the other hand varied between 0.47 and 0.90. In relation to our study, [
35] reported a coefficient of determination (R
2) of 0.65 to 0.87 between Modis-NDVI data and winter wheat production in the Shandong province of China. Additionally, and closer to our study area, [
38] observed in Tunisia a coefficient of determination ranging from 0.39 to 0.70 between durum and soft wheat yield and NDVI derived from SPOT-Vegetation.
Cereal yields can be predicted about 3 months before the start of the harvest for the provinces of Taza and El Hajeb, 58 days before the harvest for Taounate, 52 days before for Meknes and Ml Yaacoub, 40 days for Sefrou and 66 days for Boulmane. It should be noted that the harvest period is established according to the date of the prediction obtained by linear regression, taking into account the beginning of the harvest in the plain and plateau provinces, which often begins on June 1, and July 1 for the mountain provinces. Indeed, the two most productive provinces of the main cereals in the region (Taza and Taounate), have predictable yields as early as January with the correlation coefficient reaching 0.72, significant at the level α=0.05. This result is similar to that obtained by [
39] who were able to predict crop yield before 10 weeks. [
22] were able to predict the yield of cereals (wheat, barley, rye and triticale) 3-4 months before harvest in many Central European countries, while [
40] were able to predict the yield of wheat and maize 6-8 weeks before harvest in the Tisza River Basin in Central Europe. Furthermore, [
27] found that wheat yield in Morocco can be estimated two months before harvest based on the three factors considered (NDVI/AVHRR, precipitation, temperature), to which our results compare favorably despite the use of only one predictor (NDVI/ MODIS). This may be in part because MODIS observations have a higher spatial resolution than AVHRR and thus may be more sensitive to interannual variation in crop growth. Further research is needed to improve our results further by applying the crop mask to the NDVI map.
Generally, these results are valuable for policymakers who must make decisions regarding the planning of cereal imports. This is particularly important in light of the agricultural sector’s vulnerability to climate changes.
5. Conclusions
This paper presents an effective system to evaluate the relationship between MODIS NDVI and grain yield, and to determine the most favorable date to predict harvest. Crop yield is largely dependent on the characteristics of the crop at each stage of development. Strong correlations of up to 0.89 were found between NDVI, which is primarily related to observed fluctuations in photosynthetic activity, and grain yield of cereals three months before harvest in some provinces. The linear regression model explained between 58% and 79% of the variability in yield in regional provinces with high cereal cultivation, while it explained between 51% and 53% of the variability in mountainous provinces, due to a low useful agricultural area devoted to main cereals. The RMSE varies between 2.12 to 4.96 q/ha. The spring season represents the best period for estimating grain yield, as it coincides with the heading and flowering phase of the main cereals. The results presented demonstrated a highly significant relationship between MODIS NDVI and grain yield. These results are promising in terms of early yield prediction, especially since wheat flour consumption in Morocco is three times higher than the world average. Thus, remote sensing plays an important role in estimating grain yields. Thus, MODIS-NDVI data can be a powerful tool for predicting yield in provinces with large agricultural areas dedicated to cereals. They are therefore essential for administrations in charge of food security decisions within the Fez-Meknes region or in the country in general.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.M. and H.M.; methodology, B.M., K.R.; formal analysis, B.H.; writing—original draft preparation, K.R and M.A.; writing—review and editing, All; visualization, N.K. and B.M.; supervision, N.K., K.R., Z.D. and B.M.; project administration, B.M. and H.M.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The remote sensing datasets of NDVI was downloaded from the Global Agricultural Monitoring System (GLAM) (
https://glam1.gsfc.nasa.gov/ (accessed on February 15, 2023)). The grain yield data was obtained from the Ministry of Agriculture, Marine Fisheries, Rural Development, and Forestry.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Mr. S. Mestari, Head of the Surveys and Censuses Department at the Ministry of Agriculture, Maritime Fishing, Rural Development and Water and Forests, who gave us the statistical data on the main cereals in Fez-Meknes region.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- M. Elboukhary El Intidami and F. Benamar, “Adoption de la technologie d’irrigation localisée (TIL) par les agriculteurs de la province de Zagora : Rôles des perceptions aux attributs de la technologie,” International Journal of Accounting, Finance, Auditing, Management and Economics, vol. 1, no. 2, Art. no. 2, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- World Bank, “Agriculture and food,” World Bank, 2021. https://www.banquemondiale.org/fr/topic/agriculture/overview (accessed Feb. 26, 2022).
- R. Harbouze, J.-P. Pellissier, J.-P. Rolland, and W. Khechimi, “Rapport de synthèse sur l’agriculture au Maroc,” CIHEAM-IAMM, Research Report, 2019. Accessed: Jun. 12, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02137637.
- MAPMEFDR, “Agriculture en chiffres.” 2019. Accessed: Jun. 23, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.agriculture.gov.ma/fr/publications/agriculture-en-chiffres-2018-edition-2019.
- R. Balaghi, “Wheat grain yield forecasting models for food security in Morocco,” Université de liège, Belgique, 2006. [CrossRef]
- Z. Bishaw, Y. A. Yigezu, A. Niane, R. J. Telleria, and D. Najjar, “Political economy of the wheat sector in Morocco: seed systems, varietal adoption, and impacts,” International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas.Beirut, Lebanon, 2019, p. 300.
- ONICL, “importations_cereales,” https://www.onicl.org.ma/portail/, 2022. https://www.onicl.org.ma/portail/sites/default/files/FichierPage/importations_cereales.pdf (accessed Jun. 23, 2021).
- N. Pettorelli, J. O. Vik, A. Mysterud, J.-M. Gaillard, C. J. Tucker, and N. C. Stenseth, “Using the satellite-derived NDVI to assess ecological responses to environmental change,” Trends in ecology & evolution, vol. 20, no. 9, pp. 503–510, 2005.
- Idrissi, S. Nadem, A. Boudhar, and T. Benabdlouahab, “Review of wheat yield estimating methods in Morocco,” African Journal on Land Policy and Geospatial Sciences, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 818–831, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. bent salama Erhili, “ Using remote sensing technology to monitor and detect changes in vegetation cover in the area between the cities of Makkah and Taif (en arabe),” 2013. [CrossRef]
- N. T. Son, C. F. Chen, C. R. Chen, V. Q. Minh, and N. H. Trung, “A comparative analysis of multitemporal MODIS EVI and NDVI data for large-scale rice yield estimation,” Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, vol. 197, pp. 52–64, Oct. 2014. [CrossRef]
- D. K. Bolton and M. A. Friedl, “Forecasting crop yield using remotely sensed vegetation indices and crop phenology metrics,” Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, vol. 173, pp. 74–84, May 2013. [CrossRef]
- Wu et al., “Challenges and opportunities in remote sensing-based crop monitoring: A review,” National Science Review, 2022.
- N. Al-Ansari, S. A. Abed, and S. H. Ewaid, “Agriculture in Iraq,” Journal of Earth Sciences and Geotechnical Engineering, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 223–241, 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. Benedetti and P. Rossini, “On the use of NDVI profiles as a tool for agricultural statistics: The case study of wheat yield estimate and forecast in Emilia Romagna,” Remote Sensing of Environment, vol. 45, no. 3, pp. 311–326, Sep. 1993. [CrossRef]
- Boiarskii and H. Hasegawa, “Comparison of NDVI and NDRE Indices to Detect Differences in Vegetation and Chlorophyll Content,” Journal of mechanics of continua and mathematical sciences, vol. spl1, Nov. 2019. [CrossRef]
- R. S. Defries and J. R. G. Townshend, “NDVI-derived land cover classifications at a global scale,” International Journal of Remote Sensing, vol. 15, no. 17, pp. 3567–3586, Nov. 1994. [CrossRef]
- Hakam, A. Baali, K. Azennoud, A. Lyazidi, and M. Bourchachen, “Assessments of Drought Effects on Plant Production Using Satellite Remote Sensing Technology, GIS and Observed Climate Data in Northwest Morocco, Case of the Lower Sebou Basin,” International Journal of Plant Production, pp. 1–16, 2023. [CrossRef]
- W. G. N. N. Jayawardhana and V. M. I. Chathurange, “Extraction of Agricultural Phenological Parameters of Sri Lanka Using MODIS, NDVI Time Series Data,” Procedia Food Science, vol. 6, pp. 235–241, Jan. 2016. [CrossRef]
- B. Jaziri, H. Samaali, and M. Mjejra, “L'apport des indices SPI et NDVI pour l'évaluation des conditions du risque de sécheresse aux alentours du Barrage Sejnane (Tunisie Septentrionale).,” Analale Universitatii Bucuresti. Seria Geografie, 2018.
- LLOYD, “A phenological classification of terrestrial vegetation cover using shortwave vegetation index imagery,” International Journal of Remote Sensing, vol. 11, no. 12, pp. 2269–2279, Dec. 1990. [CrossRef]
- Panek and D. Gozdowski, “Analysis of relationship between cereal yield and NDVI for selected regions of Central Europe based on MODIS satellite data,” Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment, vol. 17, p. 100286, Jan. 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Ali et al., “Improving drought mitigation strategies and disaster risk reduction through MODIS and TRMM-based data in relation to climate change over Pakistan,” Environ Sci Pollut Res, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Ren, Z. Chen, Q. Zhou, and H. Tang, “Regional yield estimation for winter wheat with MODIS-NDVI data in Shandong, China,” International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 403–413, Dec. 2008. [CrossRef]
- C. M. Viana, S. Oliveira, S. C. Oliveira, and J. Rocha, “Land Use/Land Cover Change Detection and Urban Sprawl Analysis,” in Spatial Modeling in GIS and R for Earth and Environmental Sciences, H. R. Pourghasemi and C. Gokceoglu, Eds., Elsevier, 2019, pp. 621–651. [CrossRef]
- J. W. Rouse, R. H. Haas, D. W. Deering, J. A. Schell, and J. C. Harlan, “Monitoring the Vernal Advancement and Retrogradation (Green Wave Effect) of Natural Vegetation,” E75-10354, Nov. 1974. Accessed: Aug. 12, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/19750020419.
- R. Balaghi, B. Tychon, H. Eerens, and M. Jlibene, “Empirical regression models using NDVI, rainfall and temperature data for the early prediction of wheat grain yields in Morocco,” International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 438–452, Dec. 2008. [CrossRef]
- houssaine Bouras et al., “Linkages between Rainfed Cereal Production and Agricultural Drought through Remote Sensing Indices and a Land Data Assimilation System: A Case Study in Morocco,” Remote Sensing, vol. 12, no. 24, Art. no. 24, Jan. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. S. Mkhabela, P. Bullock, S. Raj, S. Wang, and Y. Yang, “Crop yield forecasting on the Canadian Prairies using MODIS NDVI data,” Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, vol. 151, no. 3, pp. 385–393, Mar. 2011. [CrossRef]
- M. Gandhi, S. Parthiban, N. Thummalu, and A. Christy, “Ndvi: Vegetation Change Detection Using Remote Sensing and Gis – A Case Study of Vellore District,” Procedia Computer Science, vol. 57, pp. 1199–1210, Jan. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanian, A. Mohammadzadeh, and S. Jamali, “Linear and Non-Linear Vegetation Trend Analysis throughout Iran Using Two Decades of MODIS NDVI Imagery,” Remote Sensing, vol. 14, no. 15, Art. no. 15, Jan. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, L. Roytman, N. Y. Krakauer, M. Nizamuddin, and M. Goldberg, “Use of vegetation health data for estimation of Aus rice yield in Bangladesh,” Sensors, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 2968–2975, 2009. [CrossRef]
- S. Sruthi and M. A. M. Aslam, “Agricultural Drought Analysis Using the NDVI and Land Surface Temperature Data; a Case Study of Raichur District,” Aquatic Procedia, vol. 4, pp. 1258–1264, Jan. 2015. [CrossRef]
- T. R. Tenreiro, M. García-Vila, J. A. Gómez, J. A. Jiménez-Berni, and E. Fereres, “Using NDVI for the assessment of canopy cover in agricultural crops within modelling research,” Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, vol. 182, p. 106038, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhou, M. L. Sommer, and F. Hochholdinger, “Cold response and tolerance in cereal roots,” Journal of Experimental Botany, vol. 72, no. 21, pp. 7474–7481, Nov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Tucker and E. Pack, “Global Agricultural Monitoring System,” GIMMS Global Agricultural Monitoring, 2000. https://glam1.gsfc.nasa.gov/api/doc/about (accessed Dec. 16, 2022).
- F. C. Kahimba, P. R. Bullock, R. Sri Ranjan, and H. W. Cutforth, “Evaluation of the SolarCalc model for simulating hourly and daily incoming solar radiation in the Northern Great Plains of Canada,” Can. Biosyst. Eng., no. 51, pp. 1–11, 2009.
- M. Meroni, E. Marinho, N. Sghaier, M. M. Verstrate, and O. Leo, “Remote Sensing Based Yield Estimation in a Stochastic Framework — Case Study of Durum Wheat in Tunisia,” Remote Sensing, vol. 5, no. 2, Art. no. 2, Feb. 2013. [CrossRef]
- P. Bognár et al., “Yield forecasting for wheat and corn in Hungary by satellite remote sensing,” International journal of remote sensing, vol. 32, no. 17, pp. 4759–4767, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Nagy, J. Fehér, and J. Tamás, “Wheat and maize yield forecasting for the Tisza river catchment using MODIS NDVI time series and reported crop statistics,” Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, vol. 151, pp. 41–49, Aug. 2018. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).