Submitted:
06 April 2023
Posted:
10 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Initiation of DNA Replication at Origins
3. Replication Forks
- a. CDC45/MCM2-6/GINS complex
- b. The replicative DNA polymerases
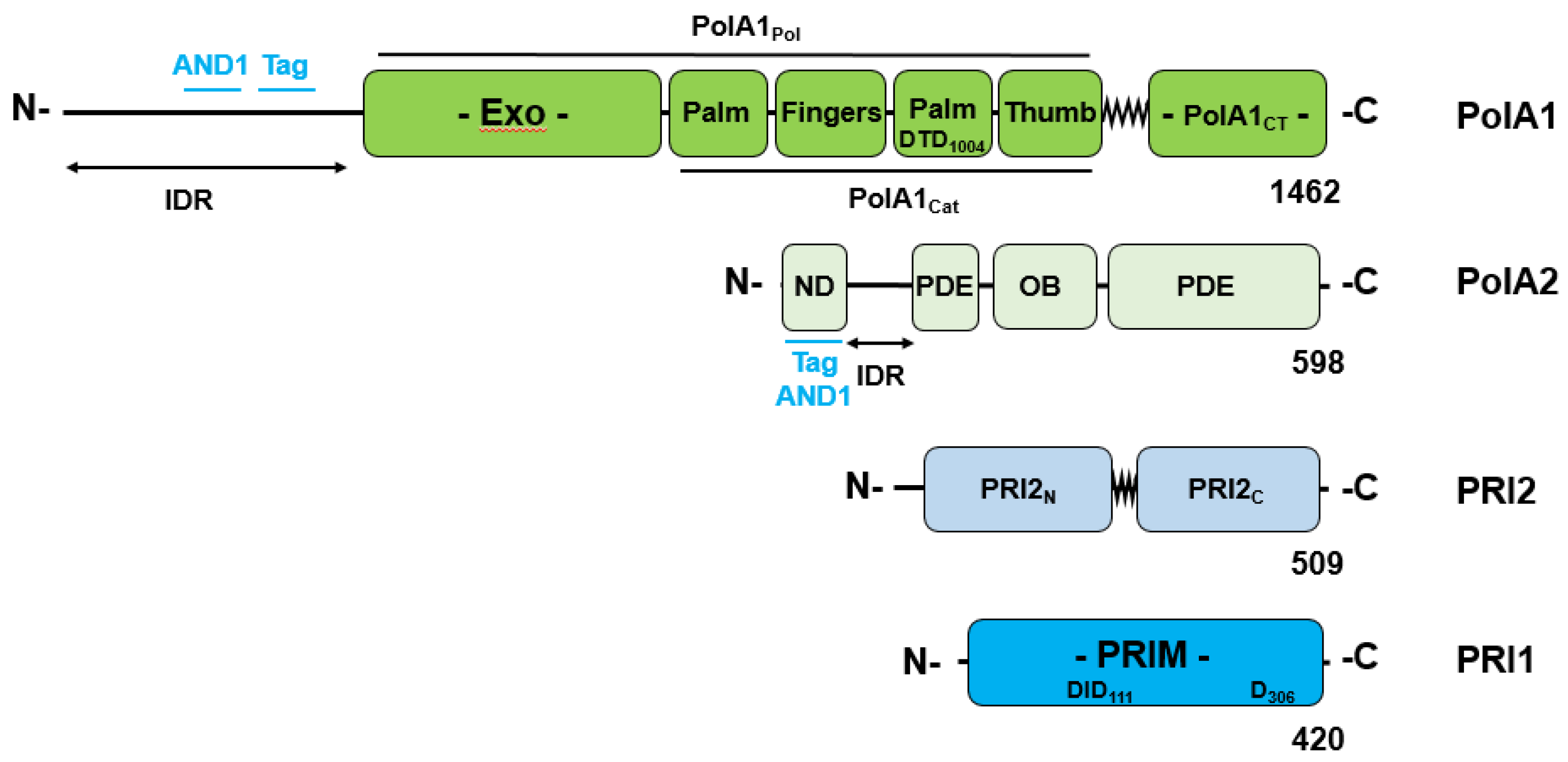
- b1. DNA polymerase α-DNA primase
- b2. DNA polymerase δ
- b3. DNA polymerase ε
- c. CMG-associated replication factors – members of the replication protection complex
- d. Additional factors supporting eukaryotic DNA replication
- d1. Replication Protein A
- d2. Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen and Replication factor C
3.1. Leading Strand Synthesis
3.2. Lagging Strand Synthesis and the Initiation of Okazaki Fragment Synthesis
- a. Biochemical model systems for the initiation of Okazaki fragment synthesis
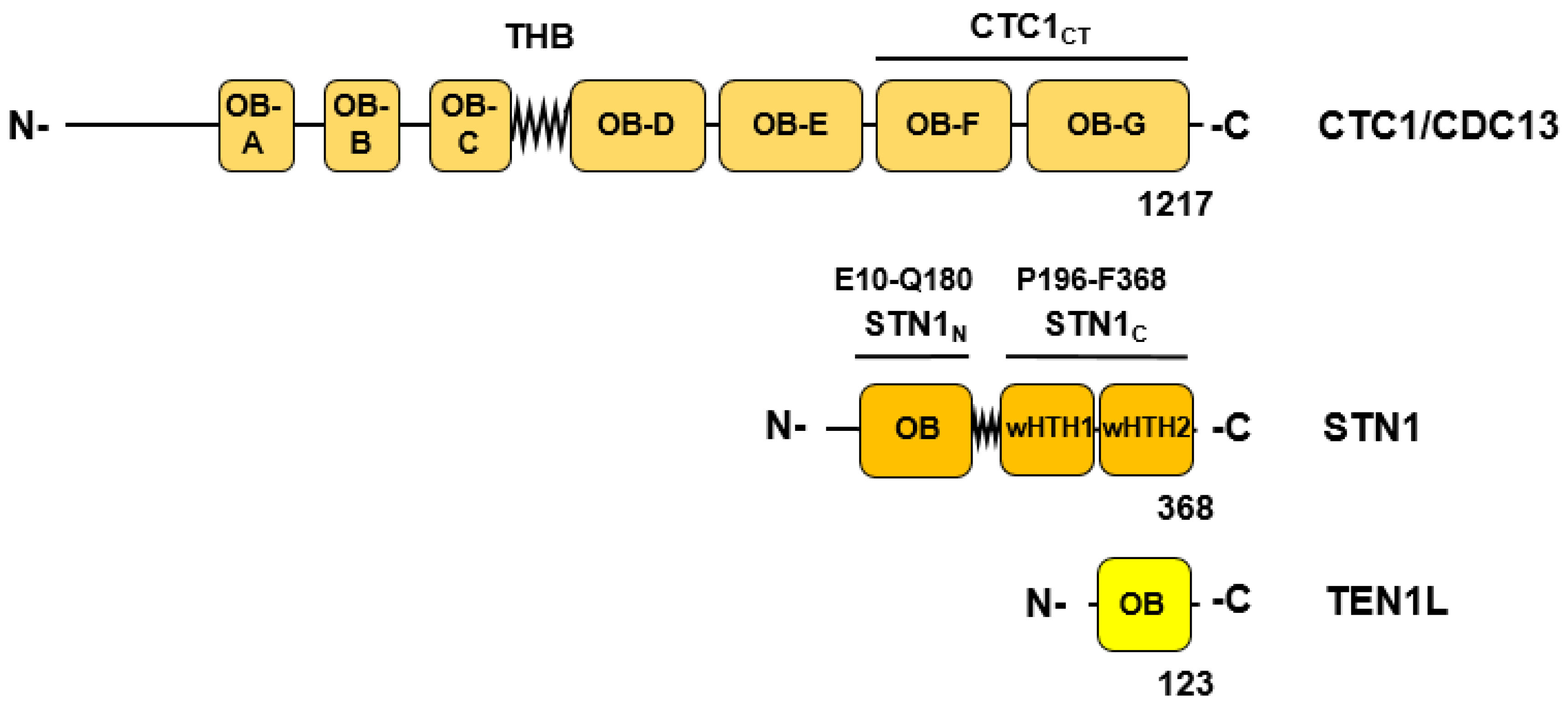
- a1. Lagging strand synthesis initiation at telomeres
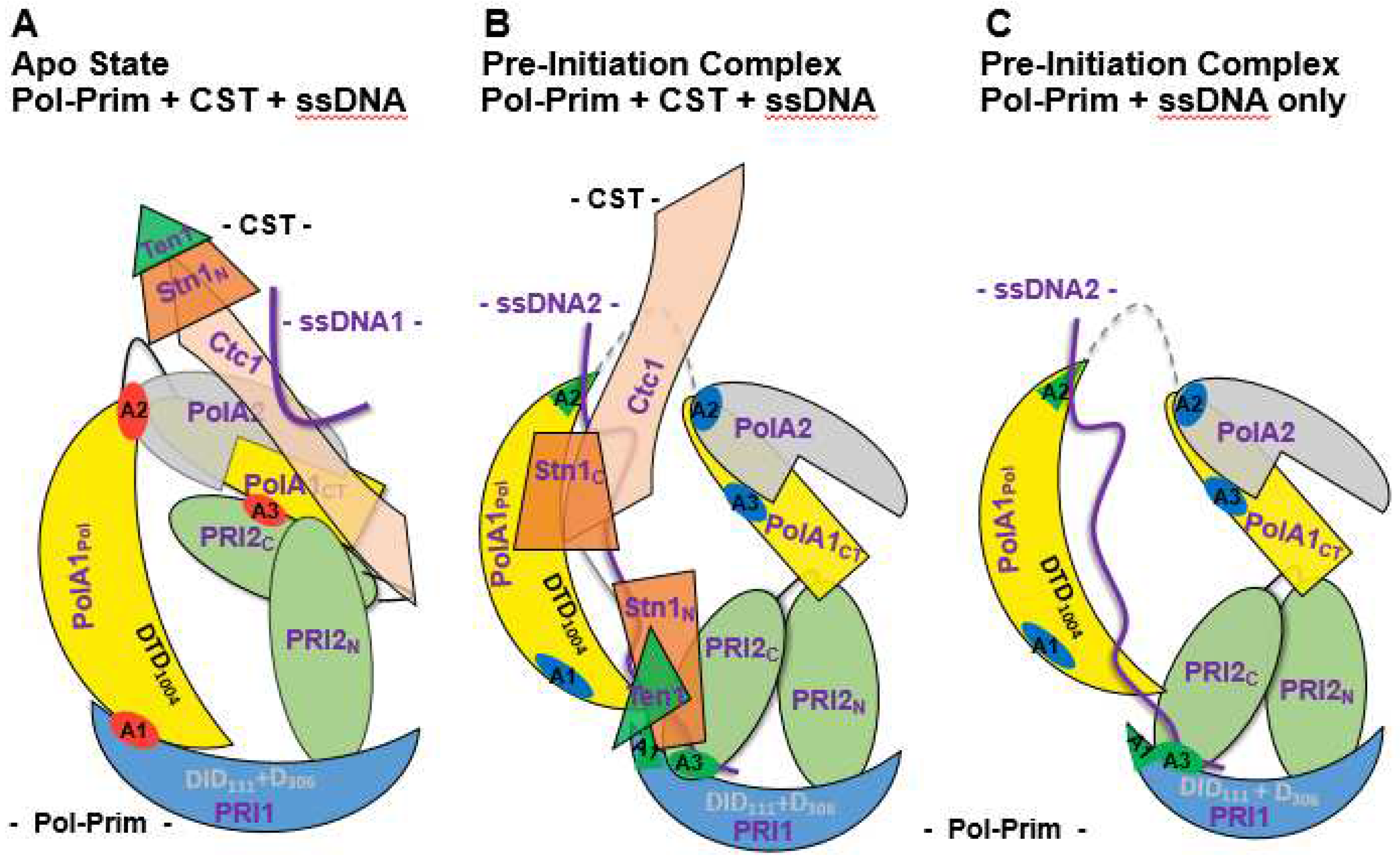
- a2. CST remodels DNA polymerase α and DNA primase to initiate Okazaki fragment synthesis
- a3. SV40 T antigen, RPA, and DNA polymerase α-primase collaborate during the initiation of Okazaki fragments
- a4. Elaborated activities of Okazaki fragment synthesis in yeast and human
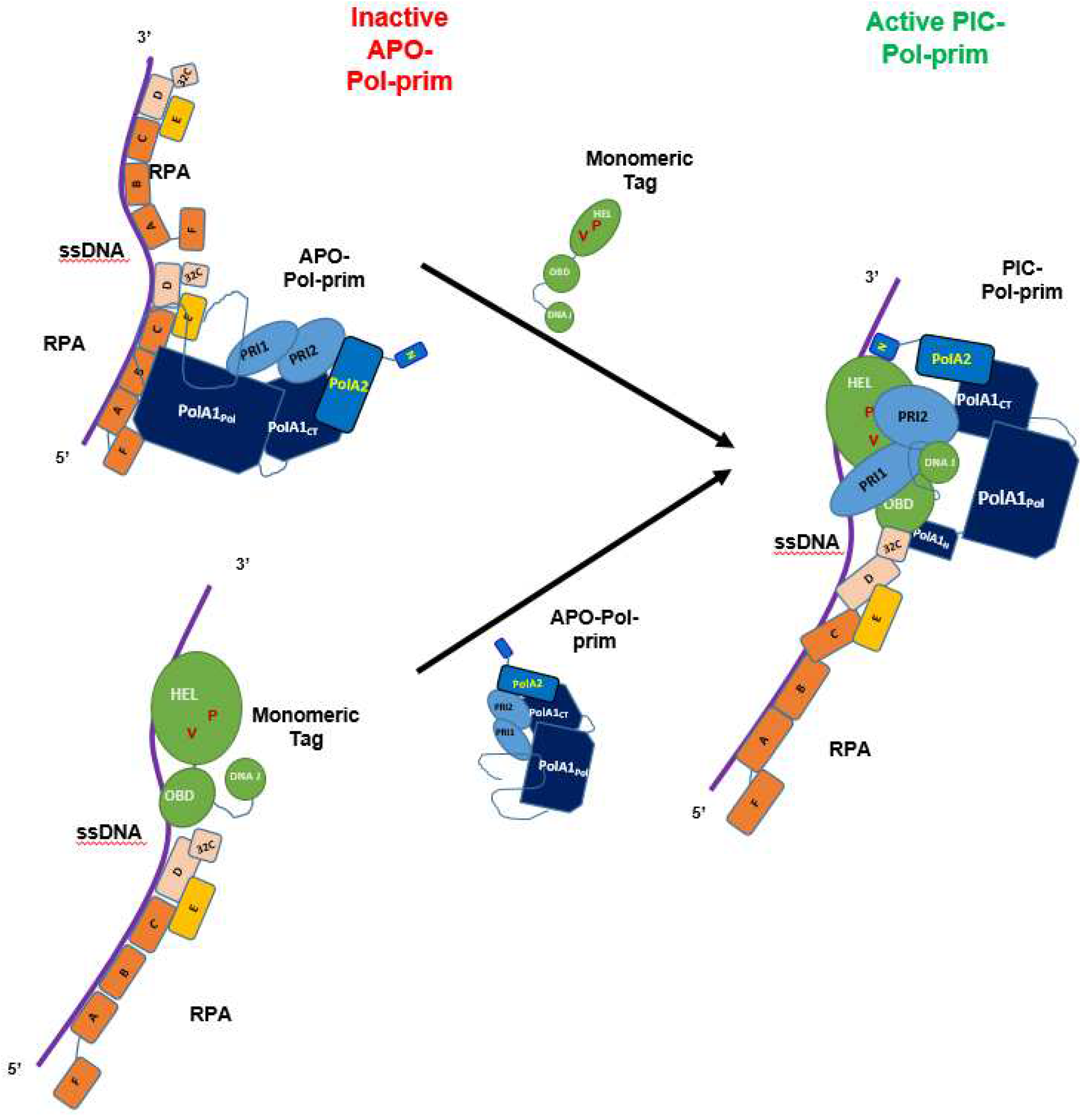
- a5. Initiation of lagging strand synthesis at replication forks by Pol-prim
4. Outlook
Acknowledgements
References
- Hanahan, D. and R.A. Weinberg. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleichert, F.; Botchan, M.R.; Berger, J.M. Mechanisms for initiating cellular DNA replication. Science 2017, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgers, P.M.; Kunkel, T.A. Eukaryotic DNA Replication Fork. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 417–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D. and M. O'Donnell. The Eukaryotic Replication Machine. Enzymes 2016, 39, 191–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blow, J.J.; Laskey, R.A. A role for the nuclear envelope in controlling DNA replication within the cell cycle. Nature 1988, 332, 546–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.J.; Cech, T.R. Shaping human telomeres: from shelterin and CST complexes to telomeric chromatin organization. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Diffley, J.F. The Initiation of Eukaryotic DNA Replication. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2022, 91, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Stillman, B. Origins of DNA replication in eukaryotes. Mol. Cell 2023, 83, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.; DePamphilis, M. Metabolism of Okazaki fragments during simian virus 40 DNA replication. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 11495–11504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.J.; Whitehouse, I. Intrinsic coupling of lagging-strand synthesis to chromatin assembly. Nature 2012, 483, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasheuer, H.P., R. Smith, C. Bauerschmidt, F. Grosse, and K. Weisshart. Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication: regulation and mechanisms. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 2002, 72, 41–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guilliam, T.A. Mechanisms for Maintaining Eukaryotic Replisome Progression in the Presence of DNA Damage. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasheuer, H.P., H. Pospiech, and J. Syväoja, Progress towards the anatomy of the eukaryotic DNA replication fork, in Genome Integrity: Facets and Perspectives,, D.H. Lankenau, Editor. [: 2007, Springer, 2007; Genome Dynamics & Stability, Vol. 1, Berlin-Heidelberg-NewYork. p. 27 - 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
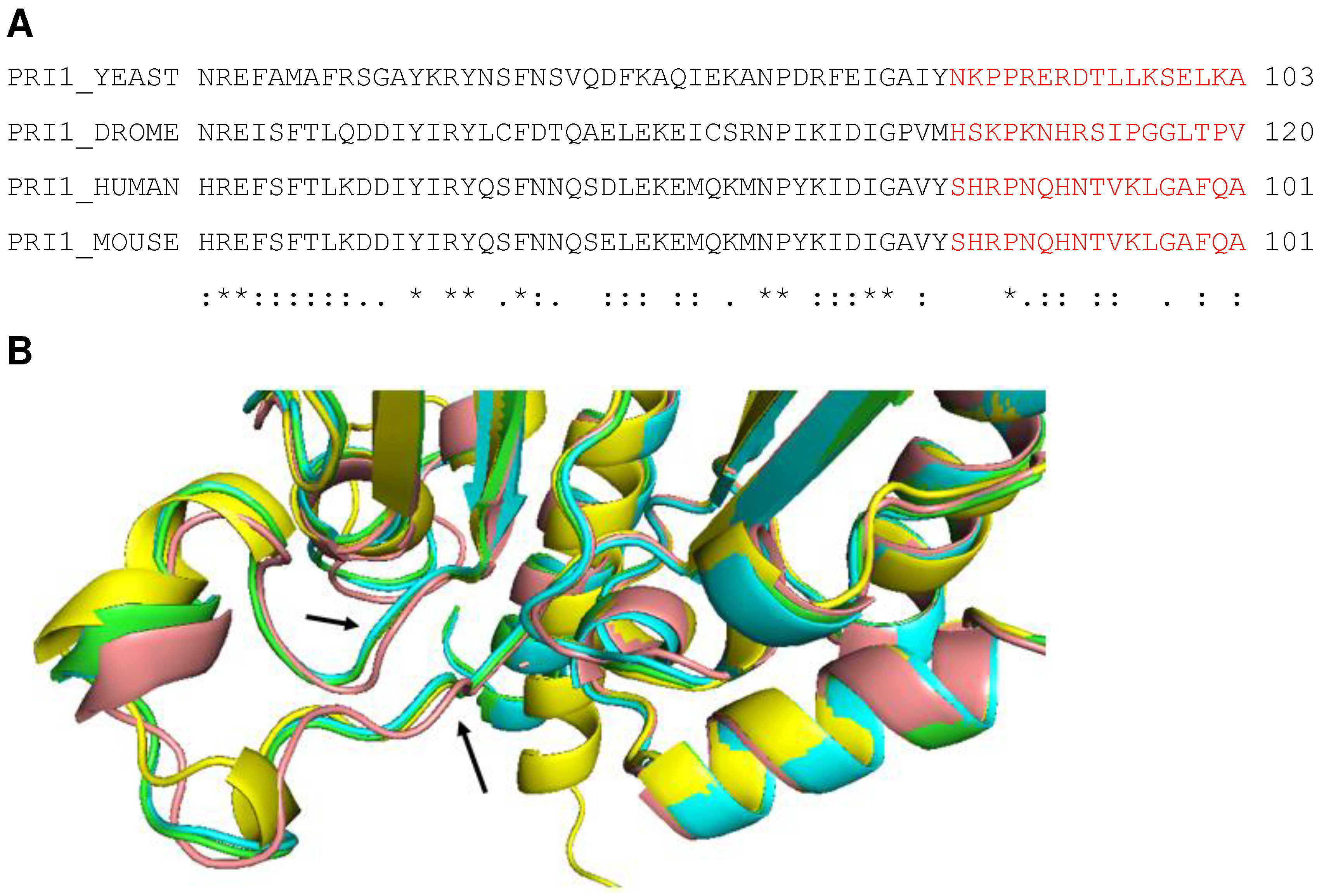
- Baranovskiy, A.G.; Tahirov, T.H. Elaborated Action of the Human Primosome. Genes 2017, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranovskiy, A.G.; Zhang, Y.; Suwa, Y.; Babayeva, N.D.; Gu, J.; Pavlov, Y.I.; Tahirov, T.H. Crystal Structure of the Human Primase. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 5635–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.W.; Zinder, J.C.; Svetlov, V.; Bush, M.W.; Nudler, E.; Walz, T.; de Lange, T. Cryo-EM structure of the human CST–Polα/primase complex in a recruitment state. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2022, 29, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Lin, X.; Chavez, B.L.; Agrawal, S.; Lusk, B.L.; Lim, C.J. Structures of the human CST-Polα–primase complex bound to telomere templates. Nature 2022, 608, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadlbauer, F., A. Brueckner, C. Rehfuess, C. Eckerskorn, F. Lottspeich, V. Förster, B.Y. Tseng, and H.P. Nasheuer. DNA replication in vitro by recombinant DNA-polymerase-α-primase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 222, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Ramírez, R.; Klinge, S.; Sauguet, L.; Melero, R.; Recuero-Checa, M.A.; Kilkenny, M.; Perera, R.L.; García-Alvarez, B.; Hall, R.J.; Nogales, E.; et al. Flexible tethering of primase and DNA Pol α in the eukaryotic primosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 8187–8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schub, O.; Rohaly, G.; Smith, R.W.; Schneider, A.; Dehde, S.; Dornreiter, I.; Nasheuer, H.-P. Multiple Phosphorylation Sites of DNA Polymerase α-Primase Cooperate to Regulate the Initiation of DNA Replication in Vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 38076–38083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilkenny, M.L.; Simon, A.C.; Mainwaring, J.; Wirthensohn, D.; Holzer, S.; Pellegrini, L. The human CTF4-orthologue AND-1 interacts with DNA polymerase α/primase via its unique C-terminal HMG box. Open Biol. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voitenleitner, C.; Rehfuess, C.; Hilmes, M.; O’rear, L.; Liao, P.-C.; Gage, D.A.; Ott, R.; Nasheuer, H.-P.; Fanning, E. Cell Cycle-Dependent Regulation of Human DNA Polymerase α-Primase Activity by Phosphorylation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voitenleitner, C.; Fanning, E.; Nasheuer, H.-P. Phosphorylation of DNA polymerase α-primase by Cyclin A-dependent kinases regulates initiation of DNA replication in vitro. Oncogene 1997, 14, 1611–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Arnett, D.R.; Yu, X.; Brewster, A.; Sowd, G.A.; Xie, C.L.; Vila, S.; Gai, D.; Fanning, E.; Chen, X.S. Structural Basis for the Interaction of a Hexameric Replicative Helicase with the Regulatory Subunit of Human DNA Polymerase α-Primase. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 26854–26866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasheuer, H.P.; Moore, A.; Wahl, A.F.; Wang, T.S. Cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of human DNA polymerase alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 7893–7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A., R. W.P. Smith, A.R. Kautz, K. Weisshart, F. Grosse, and H.P. Nasheuer. Primase activity of human DNA polymerase α-primase. Divalent cations stabilize the enzyme activity of the p48 subunit. J Biol Chem. 1998, 273, 21608–21615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnianni, R.A.; Zhou, Z.-X.; Lujan, S.A.; Al-Zain, A.; Garcia, V.; Glancy, E.; Burkholder, A.B.; Kunkel, T.A.; Symington, L.S. DNA Polymerase Delta Synthesizes Both Strands during Break-Induced Replication. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baretić, D.; Jenkyn-Bedford, M.; Aria, V.; Cannone, G.; Skehel, M.; Yeeles, J.T. Cryo-EM Structure of the Fork Protection Complex Bound to CMG at a Replication Fork. Mol. Cell 2020, 78, 926–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauerschmidt, C., S. Pollok, E. Kremmer, H.P. Nasheuer, and F. Grosse. Interactions of human Cdc45 with the Mcm2-7 complex, the GINS complex, and DNA polymerases delta and epsilon during S phase. Genes Cells 2007, 12, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambus, A.; Jones, R.C.; Sanchez-Diaz, A.; Kanemaki, M.; van Deursen, F.; Edmondson, R.D.; Labib, K. GINS maintains association of Cdc45 with MCM in replisome progression complexes at eukaryotic DNA replication forks. Nature 2006, 8, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Georgescu, R.; Langston, L.; Yao, N.Y.; Yurieva, O.; Zhang, D.; Finkelstein, J.; Agarwal, T.; E O'Donnell, M. Mechanism of asymmetric polymerase assembly at the eukaryotic replication fork. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambus, A.; van Deursen, F.; Polychronopoulos, D.; Foltman, M.; Jones, R.C.; Edmondson, R.D.; Calzada, A.; Labib, K. A key role for Ctf4 in coupling the MCM2-7 helicase to DNA polymerase α within the eukaryotic replisome. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 2992–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, R.; Nasheuer, H.-P. Regulation of Cdc45 in the cell cycle and after DNA damage. Biochem Soc Trans 2009, 37, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornreiter, I.; Copeland, W.C.; Wang, T.S.-F. Initiation of Simian Virus 40 DNA Replication Requires the Interaction of a Specific Domain of Human DNA Polymerase α with large T Antigen. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, F.; Simon, A.C.; Bazan, M.A.O.; Kilkenny, M.L.; Wirthensohn, D.; Wightman, M.; Matak-Vinkovíc, D.; Pellegrini, L.; Labib, K. Ctf4 Is a Hub in the Eukaryotic Replisome that Links Multiple CIP-Box Proteins to the CMG Helicase. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, B.; Feldkamp, M.D.; Cortez, D.; Chazin, W.J.; Friedman, K.L.; Fanning, E. Simian Virus Large T Antigen Interacts with the N-Terminal Domain of the 70 kD Subunit of Replication Protein A in the Same Mode as Multiple DNA Damage Response Factors. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0116093–e0116093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, P.D.; Warren, E.M.; Zhang, H.; Friedman, D.B.; Lary, J.W.; Cole, J.L.; Tutter, A.V.; Walter, J.C.; Fanning, E.; Eichman, B.F. Domain Architecture and Biochemical Characterization of Vertebrate Mcm10. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 3338–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricke, R.M.; Bielinsky, A.-K. Mcm10 Regulates the Stability and Chromatin Association of DNA Polymerase-α. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fien, K.; Cho, Y.-S.; Lee, J.-K.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Tappin, I.; Hurwitz, J. Primer Utilization by DNA Polymerase α-Primase Is Influenced by Its Interaction with Mcm10p. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 16144–16153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, R., M. D. Rainey, C. Santocanale, and H.P. Nasheuer. Cell cycle-dependent formation of Cdc45-Claspin complexes in human cells are compromized by UV-mediated DNA damage. FEBS J 2013, 280, 4888–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, S., K. Rehmet, C. Concannon, and H.P. Nasheuer. Eukaryotic single-stranded DNA binding proteins: central factors in genome stability. Subcell Biochem 2010, 50, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Wold, M.S. Replication protein A: Single-stranded DNA's first responder. BioEssays 2014, 36, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wold, M.S. REPLICATION PROTEIN A: A Heterotrimeric, Single-Stranded DNA-Binding Protein Required for Eukaryotic DNA Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997, 66, 61–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maréchal, A.; Zou, L. RPA-coated single-stranded DNA as a platform for post-translational modifications in the DNA damage response. Cell Res. 2014, 25, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baris, Y.; Taylor, M.R.G.; Aria, V.; Yeeles, J.T.P. Fast and efficient DNA replication with purified human proteins. Nature 2022, 606, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.S.; Tumbale, P.P.; Arana, M.E.; Rana, J.A.; Williams, R.S.; Kunkel, T.A. High-fidelity DNA ligation enforces accurate Okazaki fragment maturation during DNA replication. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casteel, D.E., S. Zhuang, Y. Zeng, F.W. Perrino, G.R. Boss, M. Goulian, and R.B. Pilz. A DNA Polymerase-{alpha}{middle dot}Primase Cofactor with Homology to Replication Protein A-32 Regulates DNA Replication in Mammalian Cells. J Biol Chem 2009, 284, 5807–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Song, H.; Chan, H.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Sušac, L.; Zhou, Z.H.; Feigon, J. Structure of Tetrahymena telomerase-bound CST with polymerase α-primase. Nature 2022, 608, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Weiner, B.E.; Zhang, H.; Fuller, B.E.; Gao, Y.; Wile, B.M.; Zhao, K.; Arnett, D.R.; Chazin, W.J.; Fanning, E. Structure of a DNA Polymerase α-Primase Domain That Docks on the SV40 Helicase and Activates the Viral Primosome. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17112–17122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, C.L.; Barbour, A.T.; Wuttke, D.S. Filling in the blanks: how the C-strand catches up to the G-strand at replicating telomeres using CST. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2022, 29, 730–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwubiko, N.; Borst, A.; A Diaz, S.; Passkowski, K.; Scheffel, F.; Tessmer, I.; Nasheuer, H.P. SV40 T antigen interactions with ssDNA and replication protein A: a regulatory role of T antigen monomers in lagging strand DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 3657–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.S.; Spenkelink, L.M.; Schauer, G.D.; Yurieva, O.; Mueller, S.H.; Natarajan, V.; Kaur, G.; Maher, C.; Kay, C.; O’donnell, M.E.; et al. Tunability of DNA Polymerase Stability during Eukaryotic DNA Replication. Mol. Cell 2019, 77, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwubiko, N.O.; Scheffel, F.; Tessmer, I.; Nasheuer, H.P. SV40 T antigen helicase domain regions responsible for oligomerisation regulate Okazaki fragment synthesis initiation. FEBS Open Bio 2022, 12, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Yuan, Z.; Georgescu, R.; Li, H.; O'Donnell, M. The eukaryotic CMG helicase pumpjack and integration into the replisome. Nucleus 2016, 7, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaithiyalingam, S.; Arnett, D.R.; Aggarwal, A.; Eichman, B.F.; Fanning, E.; Chazin, W.J. Insights into Eukaryotic Primer Synthesis from Structures of the p48 Subunit of Human DNA Primase. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 426, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeeles, J.T.; Janska, A.; Early, A.; Diffley, J.F. How the Eukaryotic Replisome Achieves Rapid and Efficient DNA Replication. Mol. Cell 2016, 65, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaug, A.J.; Goodrich, K.J.; Song, J.J.; Sullivan, A.E.; Cech, T.R. Reconstitution of a telomeric replicon organized by CST. Nature 2022, 608, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.J.; Barbour, A.T.; Zaug, A.J.; Goodrich, K.J.; McKay, A.E.; Wuttke, D.S.; Cech, T.R. The structure of human CST reveals a decameric assembly bound to telomeric DNA. Science 2020, 368, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lange, T. Shelterin-Mediated Telomere Protection. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2018, 52, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diede, S.J.; E Gottschling, D. Telomerase-Mediated Telomere Addition In Vivo Requires DNA Primase and DNA Polymerases α and δ. Cell 1999, 99, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lue, N.F.; Chan, J.; Wright, W.E.; Hurwitz, J. The CDC13-STN1-TEN1 complex stimulates Pol α activity by promoting RNA priming and primase-to-polymerase switch. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5762–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaoka, H.; Nishiyama, A.; Saito, M.; Ishikawa, F. Xenopus laevis Ctc1-Stn1-Ten1 (xCST) Protein Complex Is Involved in Priming DNA Synthesis on Single-stranded DNA Template in Xenopus Egg Extract. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranovskiy, A.G.; Babayeva, N.D.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, J.; Suwa, Y.; Pavlov, Y.I.; Tahirov, T.H. Mechanism of Concerted RNA-DNA Primer Synthesis by the Human Primosome. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 10006–10020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganduri, S.; Lue, N.F. STN1–POLA2 interaction provides a basis for primase-pol α stimulation by human STN1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 9455–9466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, J.A.; Wang, F.; Chaiken, M.F.; Kasbek, C.; Chastain, P.D., II; Wright, W.E.; Price, C.M. Human CST promotes telomere duplex replication and general replication restart after fork stalling. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 3537–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasbek, C.; Wang, F.; Price, C.M. Human TEN1 Maintains Telomere Integrity and Functions in Genome-wide Replication Restart. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 30139–30150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieminuszczy, J.; Broderick, R.; Niedzwiedz, W. EXD2 - a new player joins the DSB resection team. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 1519–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirman, Z.; Cai, S.; de Lange, T. CST/Polα/primase-mediated fill-in synthesis at DSBs. Cell Cycle 2022, 22, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirman, Z.; Lottersberger, F.; Takai, H.; Kibe, T.; Gong, Y.; Takai, K.; Bianchi, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Durocher, D.; de Lange, T. 53BP1–RIF1–shieldin counteracts DSB resection through CST- and Polα-dependent fill-in. Nature 2018, 560, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirman, Z.; Sasi, N.K.; King, A.; Chapman, J.R.; de Lange, T. 53BP1–shieldin-dependent DSB processing in BRCA1-deficient cells requires CST–Polα–primase fill-in synthesis. Nature 2022, 24, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordermeer, S.M.; Adam, S.; Setiaputra, D.; Barazas, M.; Pettitt, S.J.; Ling, A.K.; Olivieri, M.; Álvarez-Quilón, A.; Moatti, N.; Zimmermann, M.; et al. The shieldin complex mediates 53BP1-dependent DNA repair. Nature 2018, 560, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Nabetani, A.; Shimamura, S.; Tamura, M.; Yonehara, S.; Saito, M.; Ishikawa, F. RPA-like Mammalian Ctc1-Stn1-Ten1 Complex Binds to Single-Stranded DNA and Protects Telomeres Independently of the Pot1 Pathway. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- I Arunkumar, A.; Klimovich, V.; Jiang, X.; Ott, R.D.; Mizoue, L.; Fanning, E.; Chazin, W.J. Insights into hRPA32 C-terminal domain–mediated assembly of the simian virus 40 replisome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisshart, K.; Förster, H.; Kremmer, E.; Schlott, B.; Grosse, F.; Nasheuer, H.-P. Protein-Protein Interactions of the Primase Subunits p58 and p48 with Simian Virus 40 T Antigen Are Required for Efficient Primer Synthesis in a Cell-free System. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17328–17337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melendy, T.; Stillman, B. An interaction between replication protein A and SV40 T antigen appears essential for primosome assembly during SV40 DNA replication. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 3389–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K.L. and T.J. Kelly. The effects of T antigen and replication protein A on the initiation of DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase a-primase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 2108–2115. [Google Scholar]
- Challberg, M.D.; Kelly, T.J. Animal Virus DNA Replication. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1989, 58, 671–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Kelly, T.J. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1984, 81, 6973–6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowd, G.A.; Fanning, E. A Wolf in Sheep's Clothing: SV40 Co-opts Host Genome Maintenance Proteins to Replicate Viral DNA. PLOS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waga, S.; Bauer, G.; Stillman, B. Reconstitution of complete SV40 DNA replication with purified replication factors. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 10923–10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waga, S.; Stillman, B. THE DNA REPLICATION FORK IN EUKARYOTIC CELLS. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 721–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Klimovich, V.; I Arunkumar, A.; Hysinger, E.B.; Wang, Y.; Ott, R.D.; Guler, G.D.; Weiner, B.; Chazin, W.J.; Fanning, E. Structural mechanism of RPA loading on DNA during activation of a simple pre-replication complex. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 5516–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanning, E.; Klimovich, V.; Nager, A.R. A dynamic model for replication protein A (RPA) function in DNA processing pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 4126–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanning, E.; Knippers, R. STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF SIMIAN VIRUS 40 LARGE TUMOR ANTIGEN. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1992, 61, 55–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, K.A.; Lao, Y.; He, Z.; Ingles, C.J.; Wold, M.S. Role of Protein−Protein Interactions in the Function of Replication Protein A (RPA): RPA Modulates the Activity of DNA Polymerase α by Multiple Mechanisms. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 8443–8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maga, G., I. Frouin, S. Spadari, and U. Hubscher. Replication protein A as a "fidelity clamp" for DNA polymerase alpha. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, 18235–18242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, P.; Robles, M.T.S.; Pipas, J.M. Large T Antigens of Polyomaviruses: Amazing Molecular Machines. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 213–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.W.; Steffen, C.; Grosse, F.; Nasheuer, H.-P. Species Specificity of Simian Virus 40 DNA Replication in Vitro Requires Multiple Functions of Human DNA Polymerase α. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 20541–20548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadlbauer, F.; Voitenleitner, C.; Brückner, A.; Fanning, E.; Nasheuer, H.-P. Species-Specific Replication of Simian Virus 40 DNA In Vitro Requires the p180 Subunit of Human DNA Polymerase α-Primase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, T.; Hirabayashi, K.; Miyazawa, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Shoji, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Hanaoka, F.; Imamoto, N.; Torigoe, H. The intrinsically disordered N-terminal region of mouse DNA polymerase alpha mediates its interaction with POT1a/b at telomeres. Genes Cells 2021, 26, 360–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Georgescu, R.; Schauer, G.D.; Yao, N.Y.; Langston, L.D.; Yurieva, O.; Zhang, D.; Finkelstein, J.; E O'Donnell, M. Reconstitution of a eukaryotic replisome reveals suppression mechanisms that define leading/lagging strand operation. eLife 2015, 4, e04988–e04988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devbhandari, S.; Jiang, J.; Kumar, C.; Whitehouse, I.; Remus, D. Chromatin Constrains the Initiation and Elongation of DNA Replication. Mol. Cell 2016, 65, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurat, C.F.; Yeeles, J.T.; Patel, H.; Early, A.; Diffley, J.F. Chromatin Controls DNA Replication Origin Selection, Lagging-Strand Synthesis, and Replication Fork Rates. Mol. Cell 2016, 65, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeeles, J.T.P.; Deegan, T.D.; Janska, A.; Early, A.; Diffley, J.F.X. Regulated eukaryotic DNA replication origin firing with purified proteins. Nature 2015, 519, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.L.; Baris, Y.; Taylor, M.R.G.; Yeeles, J.T.P. Structure of a human replisome shows the organisation and interactions of a DNA replication machine. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e108819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilliam, T.A.; Yeeles, J.T.P. An updated perspective on the polymerase division of labor during eukaryotic DNA replication. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 55, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.R.; Yeeles, J.T. Dynamics of Replication Fork Progression Following Helicase–Polymerase Uncoupling in Eukaryotes. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 2040–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szambowska, A.; Tessmer, I.; Prus, P.; Schlott, B.; Pospiech, H.; Grosse, F. Cdc45-induced loading of human RPA onto single-stranded DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 3217–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, B.; Baryshnikova, A.; Brown, G.W. Unification of Protein Abundance Datasets Yields a Quantitative Saccharomyces cerevisiae Proteome. Cell Syst. 2018, 6, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Ukomadu, C.; Jha, S.; Senga, T.; Dhar, S.K.; Wohlschlegel, J.A.; Nutt, L.K.; Kornbluth, S.; Dutta, A. Mcm10 and And-1/CTF4 recruit DNA polymerase α to chromatin for initiation of DNA replication. Minerva Anestesiol. 2007, 21, 2288–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulian, M. and C.J. Heard. Intact DNA Polymerase a/Primase from Mouse Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 19407–19415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Nabetani, A.; Shimamura, S.; Tamura, M.; Yonehara, S.; Saito, M.; Ishikawa, F. RPA-like Mammalian Ctc1-Stn1-Ten1 Complex Binds to Single-Stranded DNA and Protects Telomeres Independently of the Pot1 Pathway. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surovtseva, Y.V.; Churikov, D.; Boltz, K.A.; Song, X.; Lamb, J.C.; Warrington, R.; Leehy, K.; Heacock, M.; Price, C.M.; Shippen, D.E. Conserved Telomere Maintenance Component 1 Interacts with STN1 and Maintains Chromosome Ends in Higher Eukaryotes. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, M.; Qin, J.; Songyang, Z.; Liu, D. OB Fold-containing Protein 1 (OBFC1), a Human Homolog of Yeast Stn1, Associates with TPP1 and Is Implicated in Telomere Length Regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 26725–26731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, A.; Hughes, T.R.; Nugent, C.I.; Lundblad, V. Cdc13 both positively and negatively regulates telomere replication. Minerva Anestesiol. 2001, 15, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesti, T., K. Flick, S. Keränen, J.E. Syväoja, and C. Wittenberg. DNA polymerase e catalytic domains are dispensable for DNA replication, DNA repair, and cell viability. Mol Cell 1999, 3, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A DiFrancesco, R.; Lehman, I.R. Interaction of ribonuclease H from Drosophila melanogaster embryos with DNA polymerase-primase. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 14764–14770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, P.; Braunshofer-Reiter, C.; Karwan, A.; Grimm, R.; Wintersberger, U. Purification of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNase H(70) and identification of the corresponding gene. FEBS Lett. 1999, 450, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwan, R., H. Blutsch, and U. Wintersberger. A ribonuclease H from yeast stimulates DNA polymerase in vitro. Adv Exp Med Biol 1984, 179, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemeier, A. and F. Grosse. A distinct form of ribonuclease H from calf thymus stimulates its homologous DNA-polymerase-alpha-primase complex. Eur J Biochem 1989, 185, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, M.; Ferrari, E.; De Felice, M.; Rossi, M.; Hübscher, U.; Pisani, F.M. The human GINS complex binds to and specifically stimulates human DNA polymerase α-primase. EMBO Rep 2006, 8, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Z.; De Falco, M.; Kamada, K.; Pisani, F.M.; Masai, H. The Mini-Chromosome Maintenance (Mcm) Complexes Interact with DNA Polymerase α-Primase and Stimulate Its Ability to Synthesize RNA Primers. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e72408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



