Submitted:
08 April 2023
Posted:
10 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Proposing Deep Plume Rise Network (DPRNet), a deep learning method for PR measurements, by incorporating PC recognition and image processing-based measurements. We have provided a reproducible algorithm to recognize PCs from RGB images accurately.
- To the best of our knowledge, this paper estimates the PCs’ neutral buoyancy coordinates for the first time, which is of the essence in environmental studies. This online information can help update related criteria, such as the live air-quality health index (AQHI).
- A pixel-level recognition dataset, Deep Plume Rise Dataset (DPRD), containing: 1) 2500 fine segments of PCs, 2) The upper and lower boundaries of PCs, 3) The image coordinates of smokestack exit, 4) The centerlines and NBP image coordinates of PCs, is presented. As is expected, the DPRD dataset includes one class, namely PC. Widely-used DCNN-based smoke recognition methods are employed to evaluate our dataset. Furthermore, this newly generated dataset was used for PR measurements.
2. Theoretical background
2.1. Briggs PR prediction
2.2. CNN and convolutional layer
2.3. Mask R-CNN
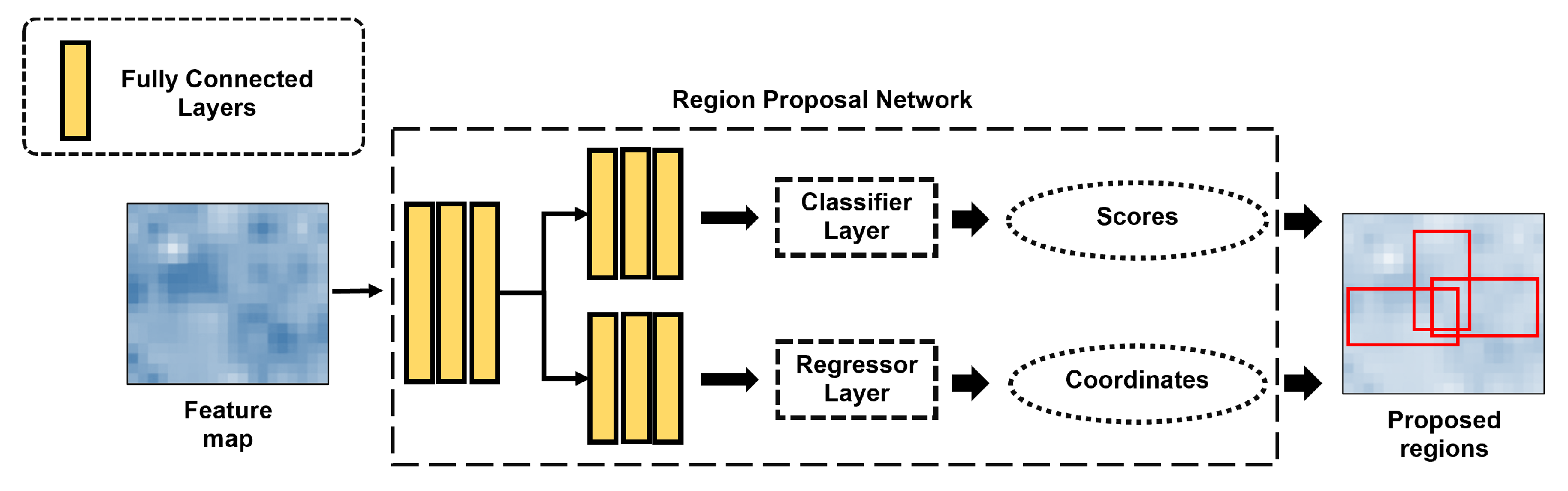
2.3.1. RPN
2.3.2. Loss function
3. Methodology
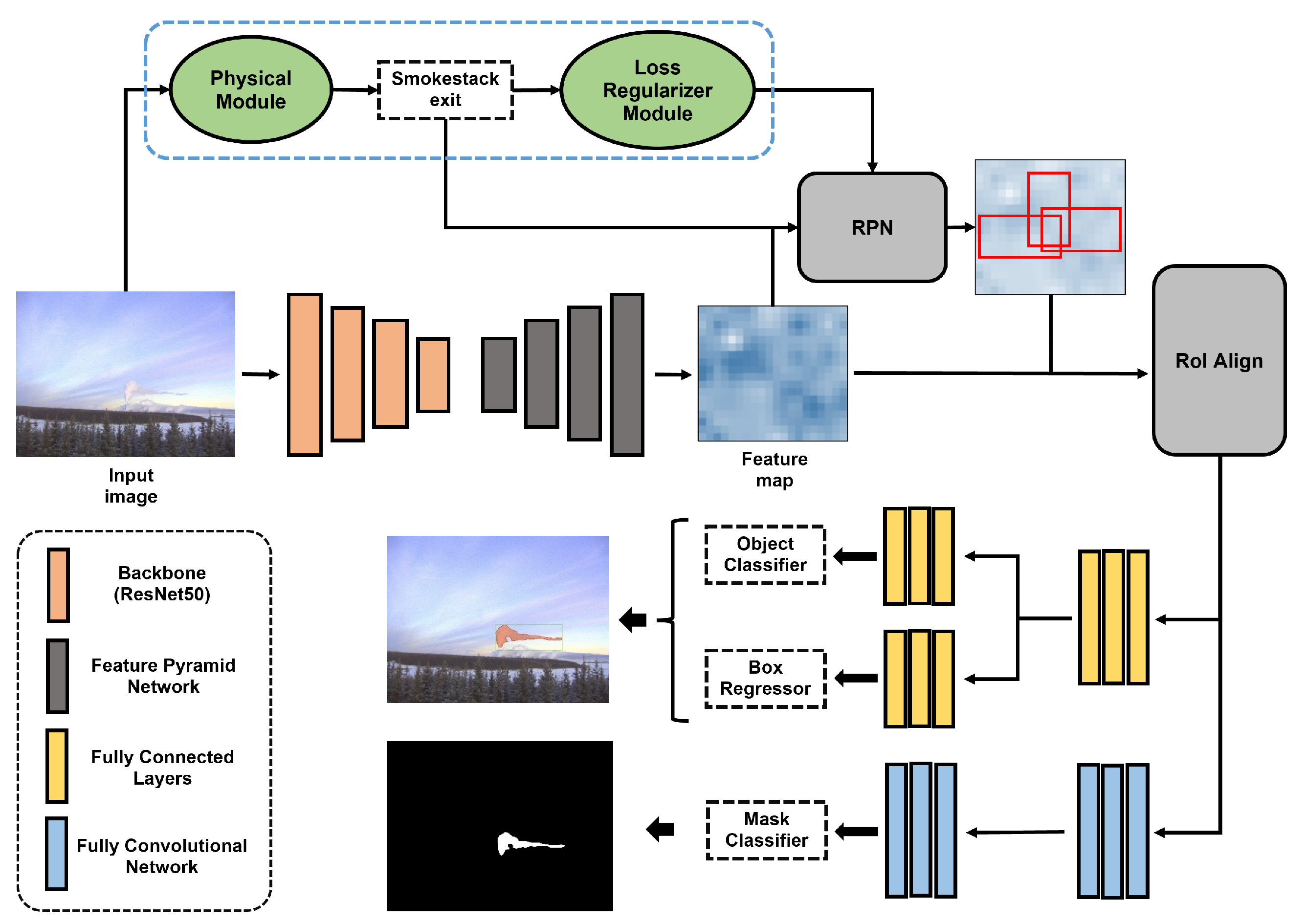
3.1. DPRNet
3.1.1. Physical module
3.1.2. Loss regularizer module
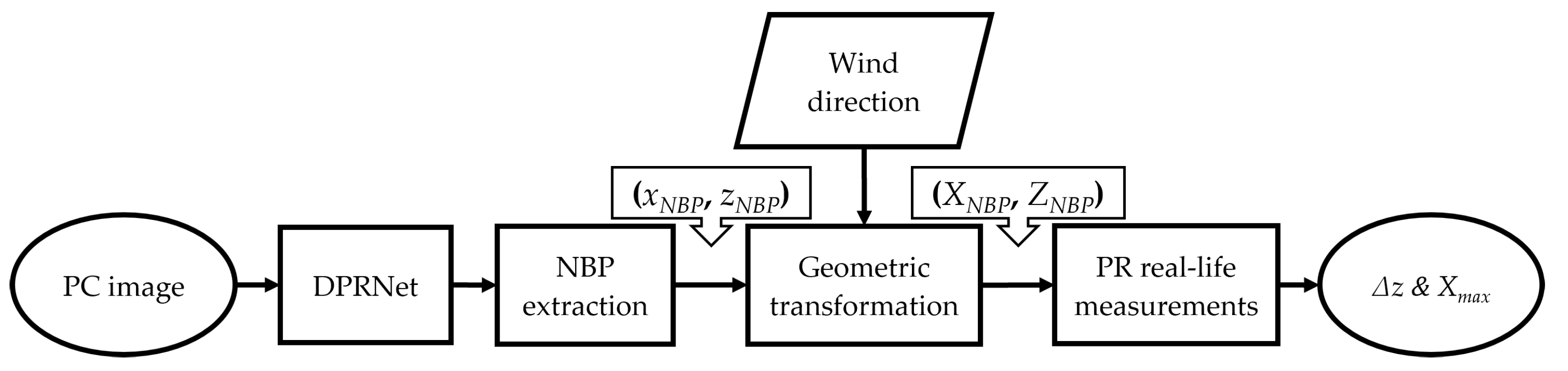
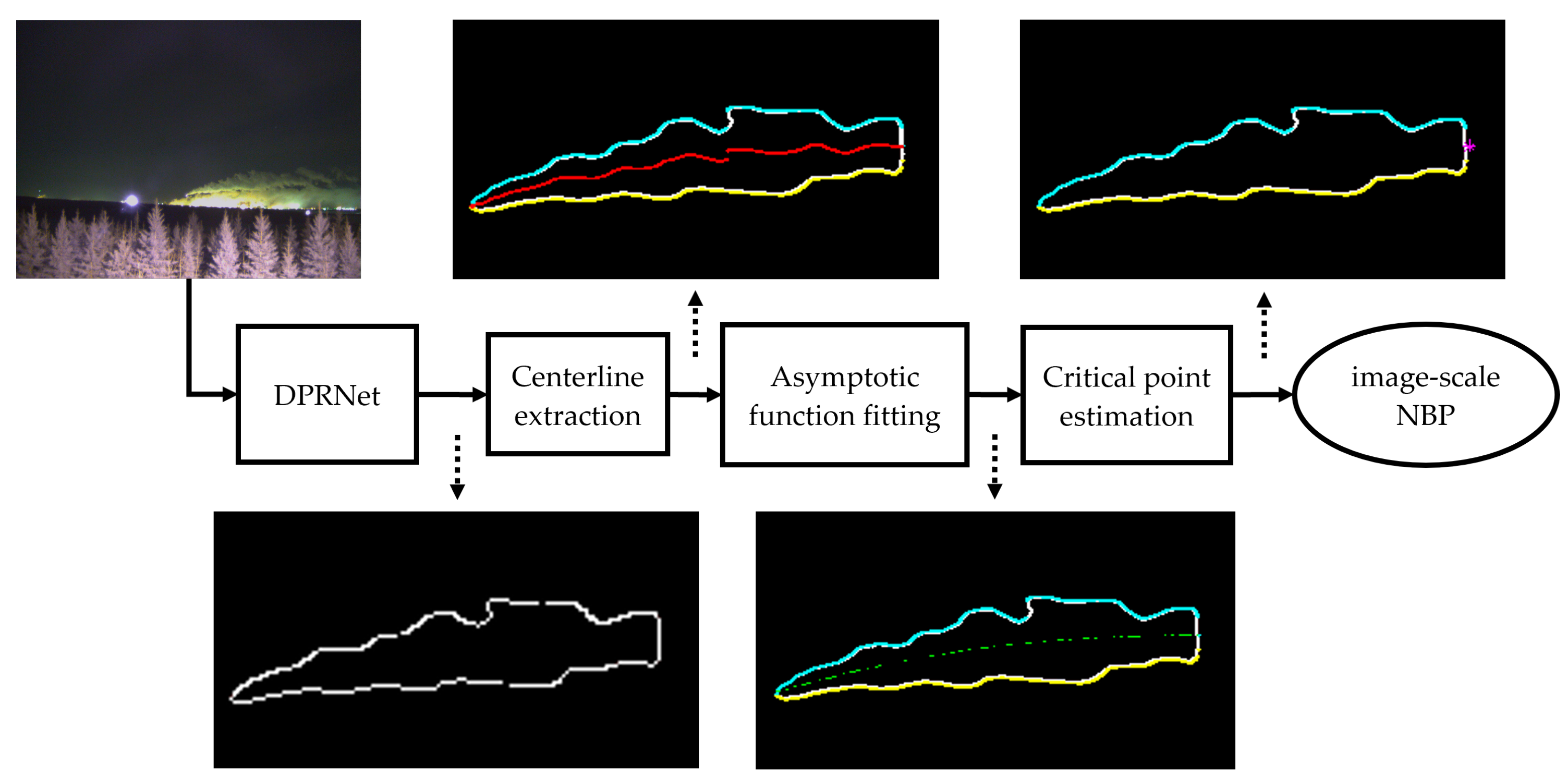
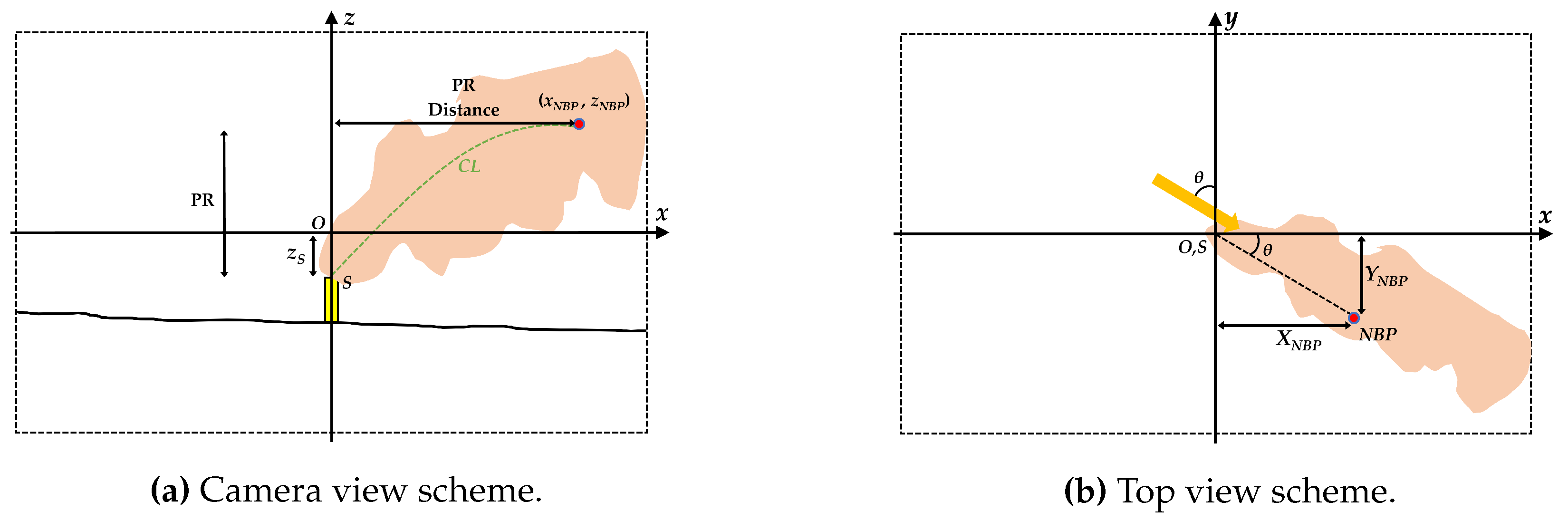
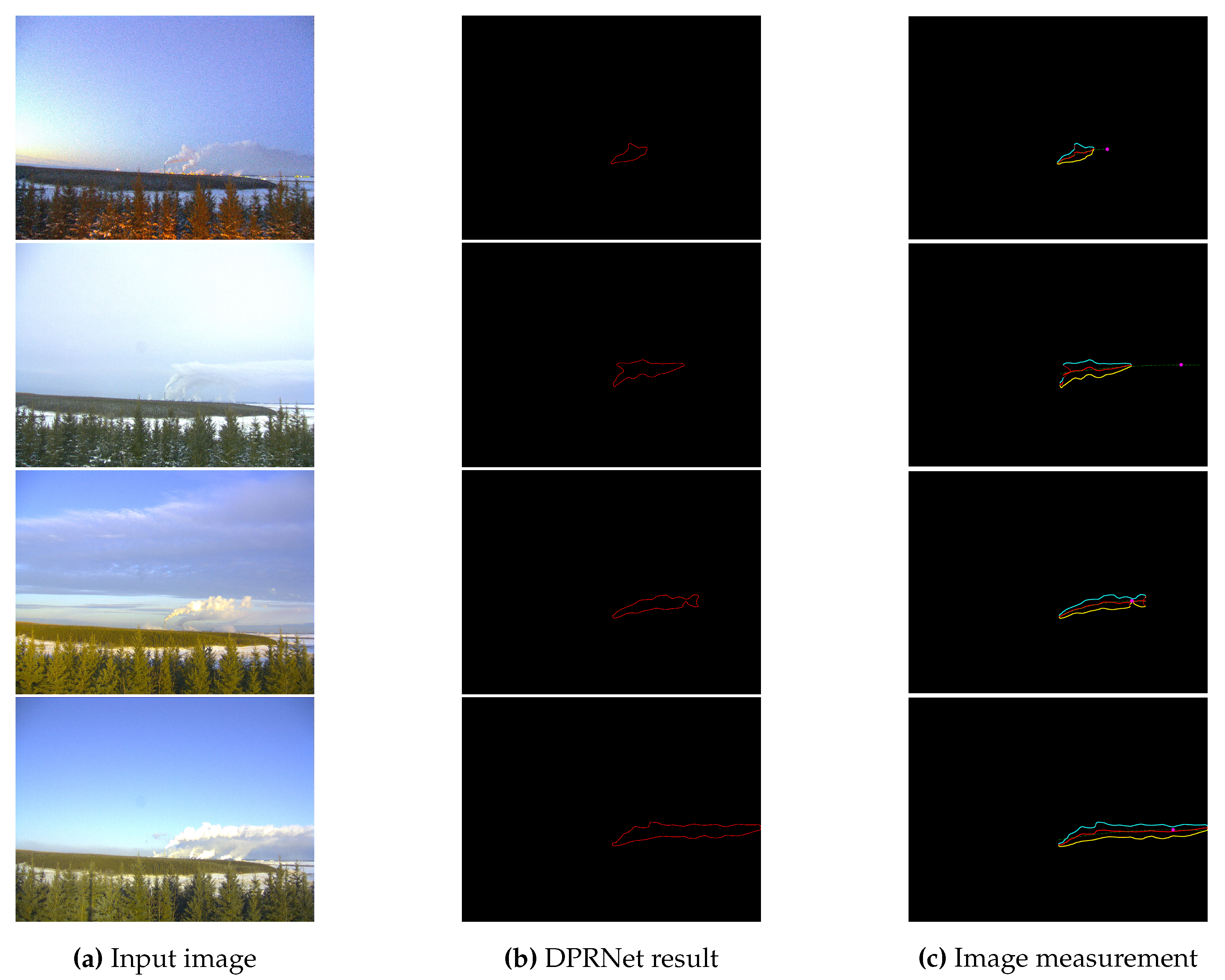
3.2. NBP extraction
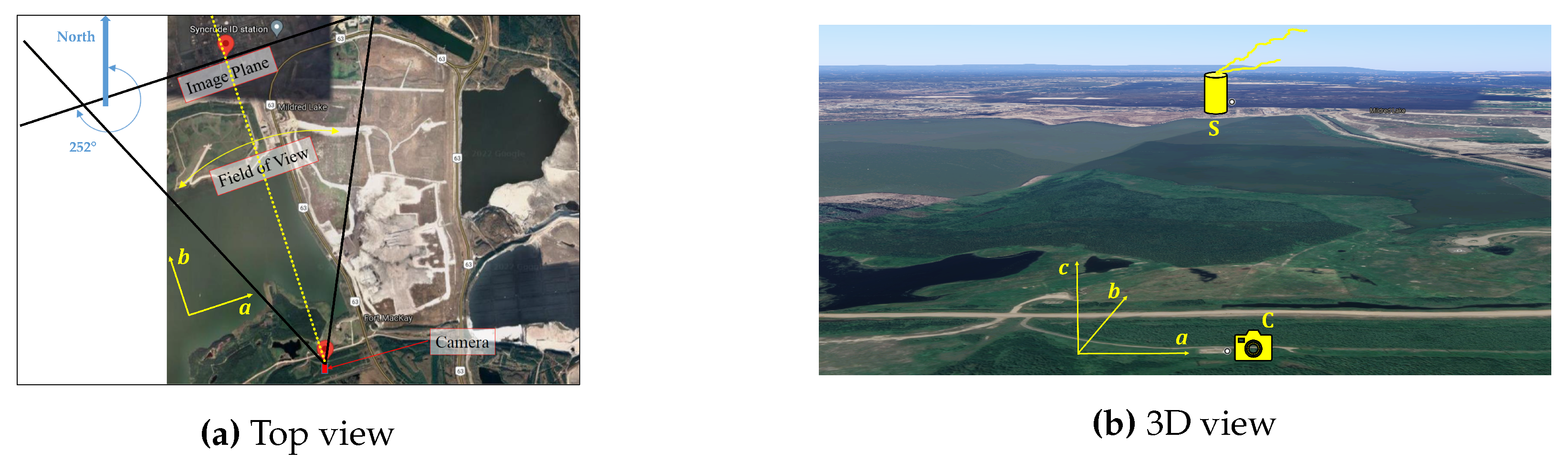
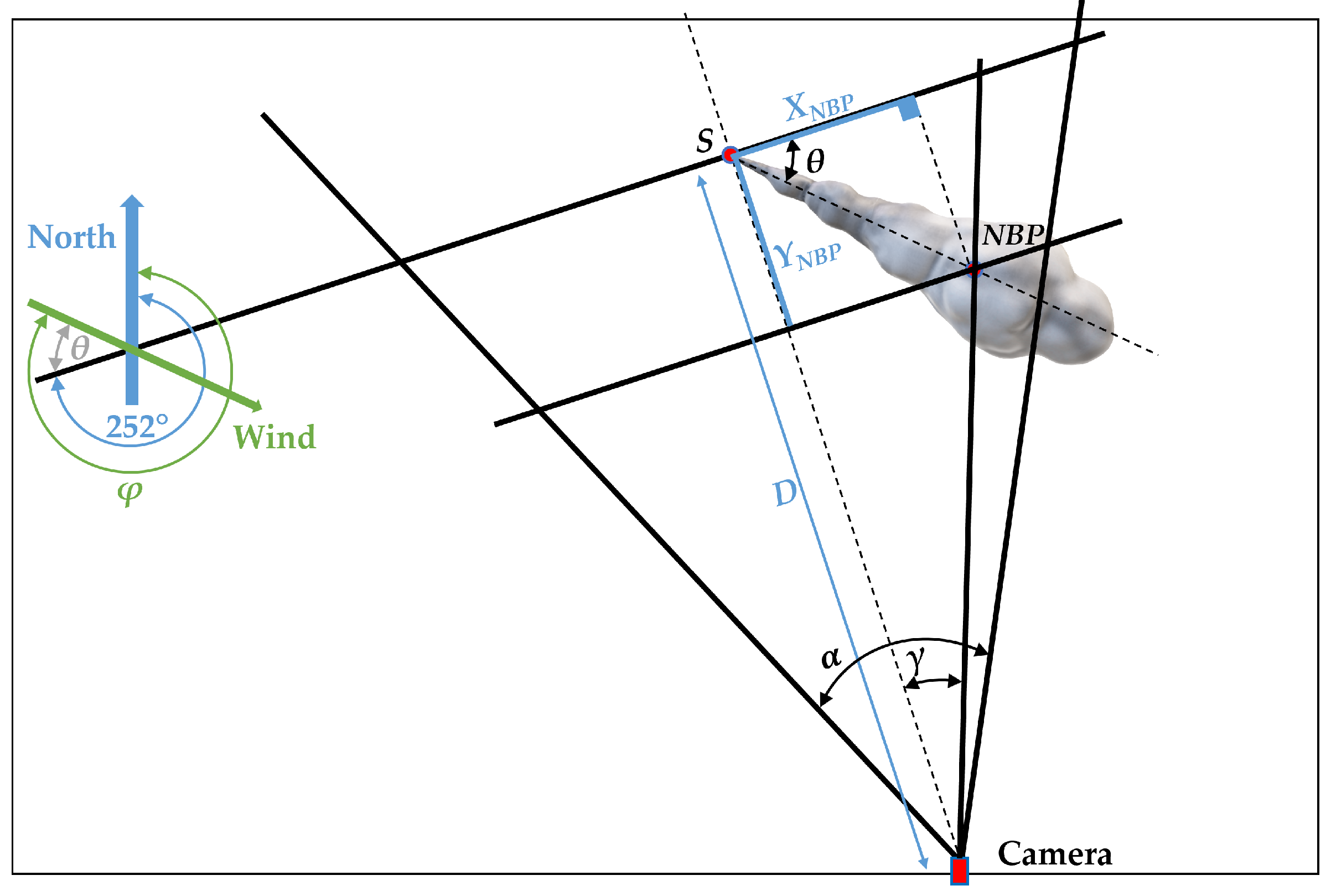
3.3. Geometric transformation
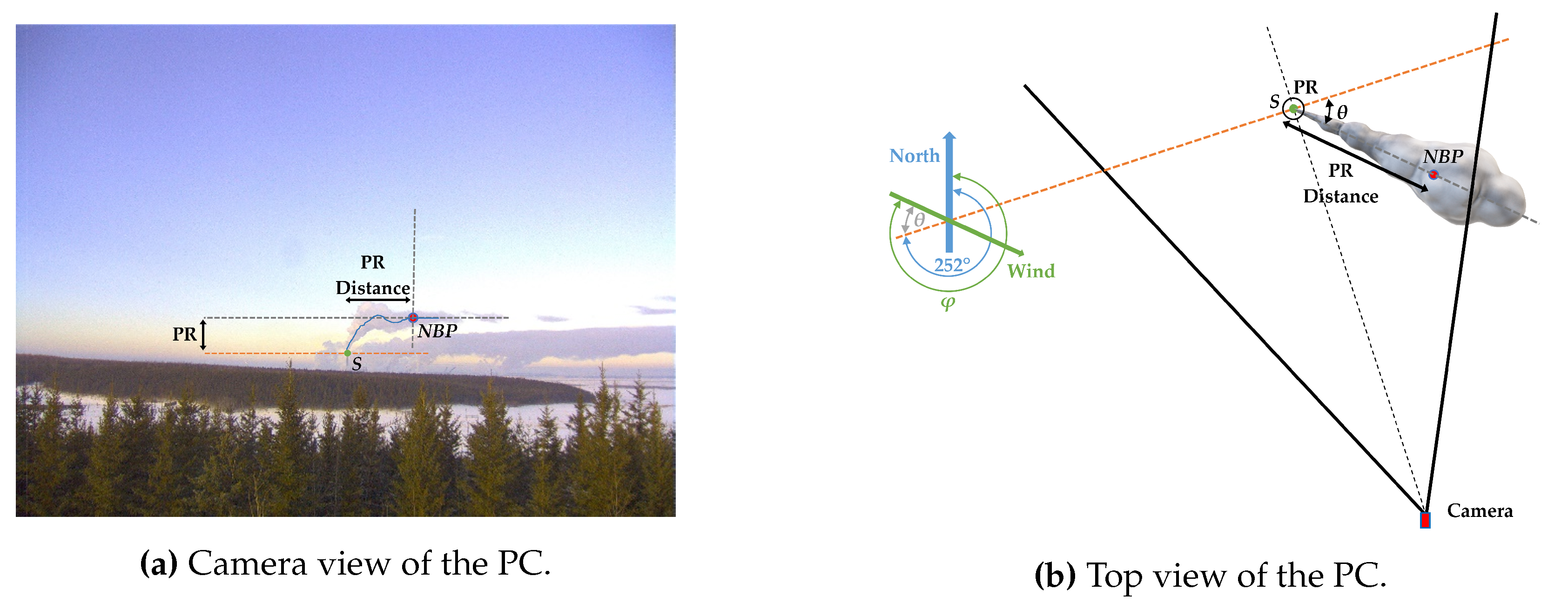
4. Experimental results and discussion
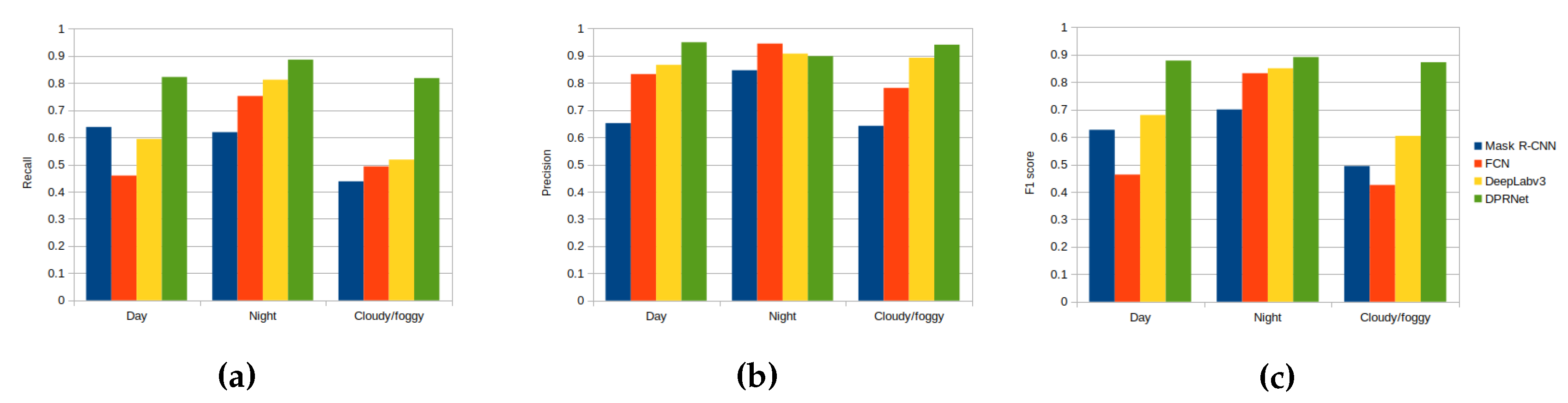
4.1. Site description
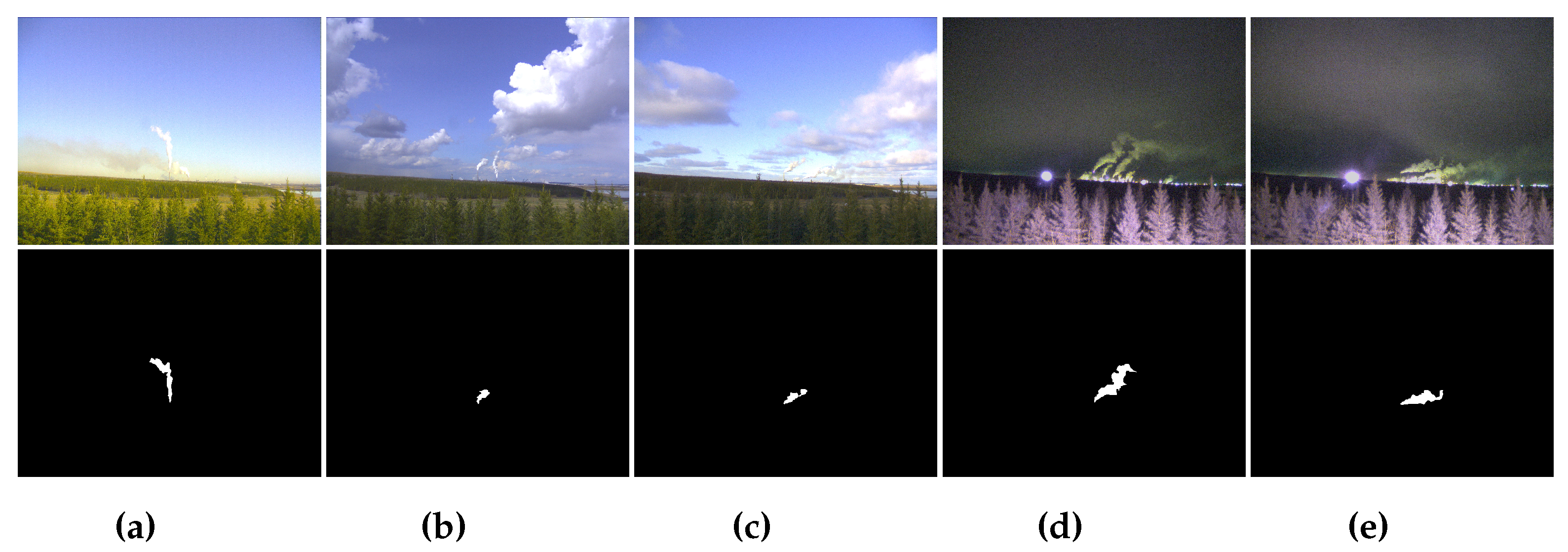
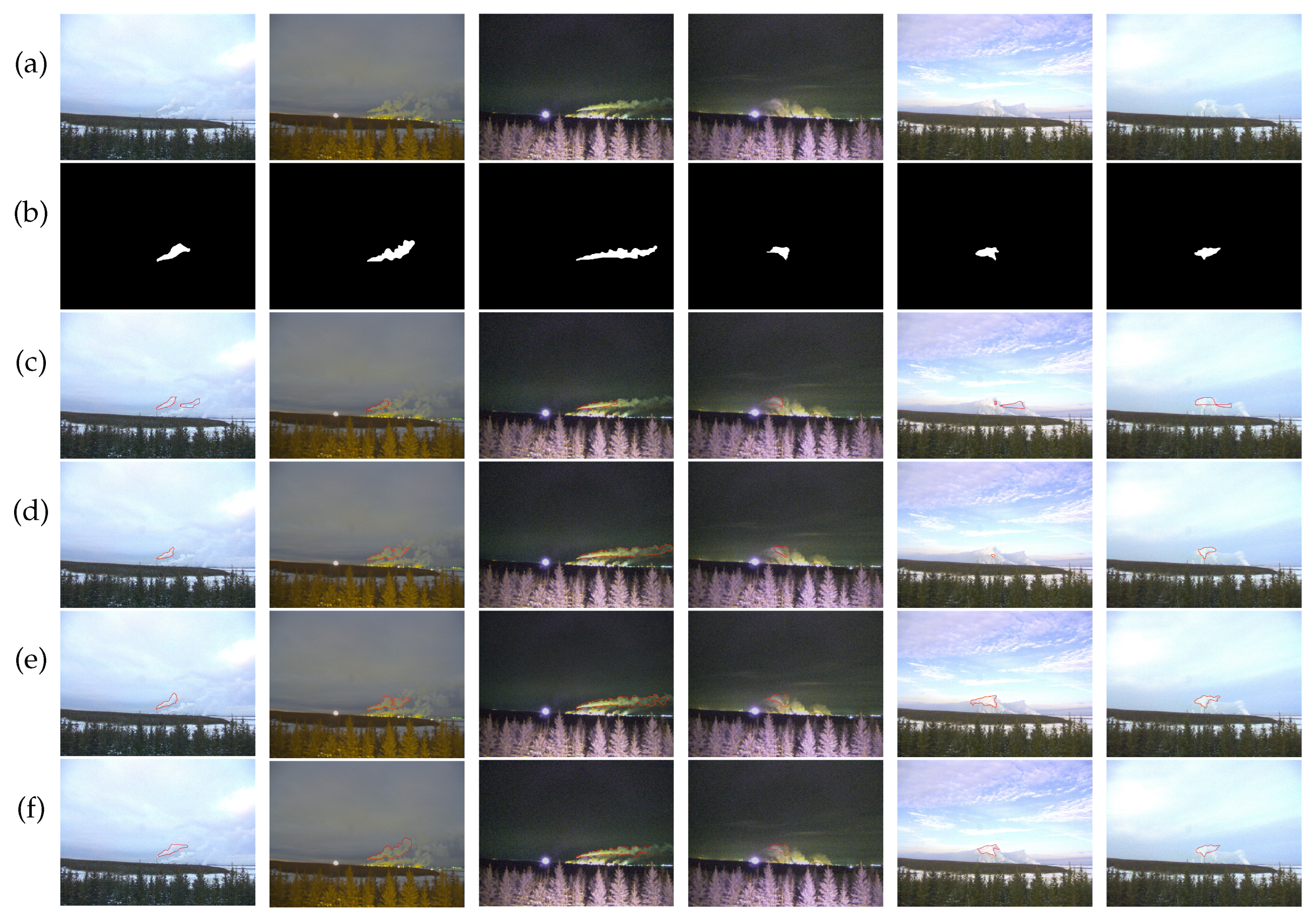
4.2. Deep Plume Rise Dataset (DPRD)
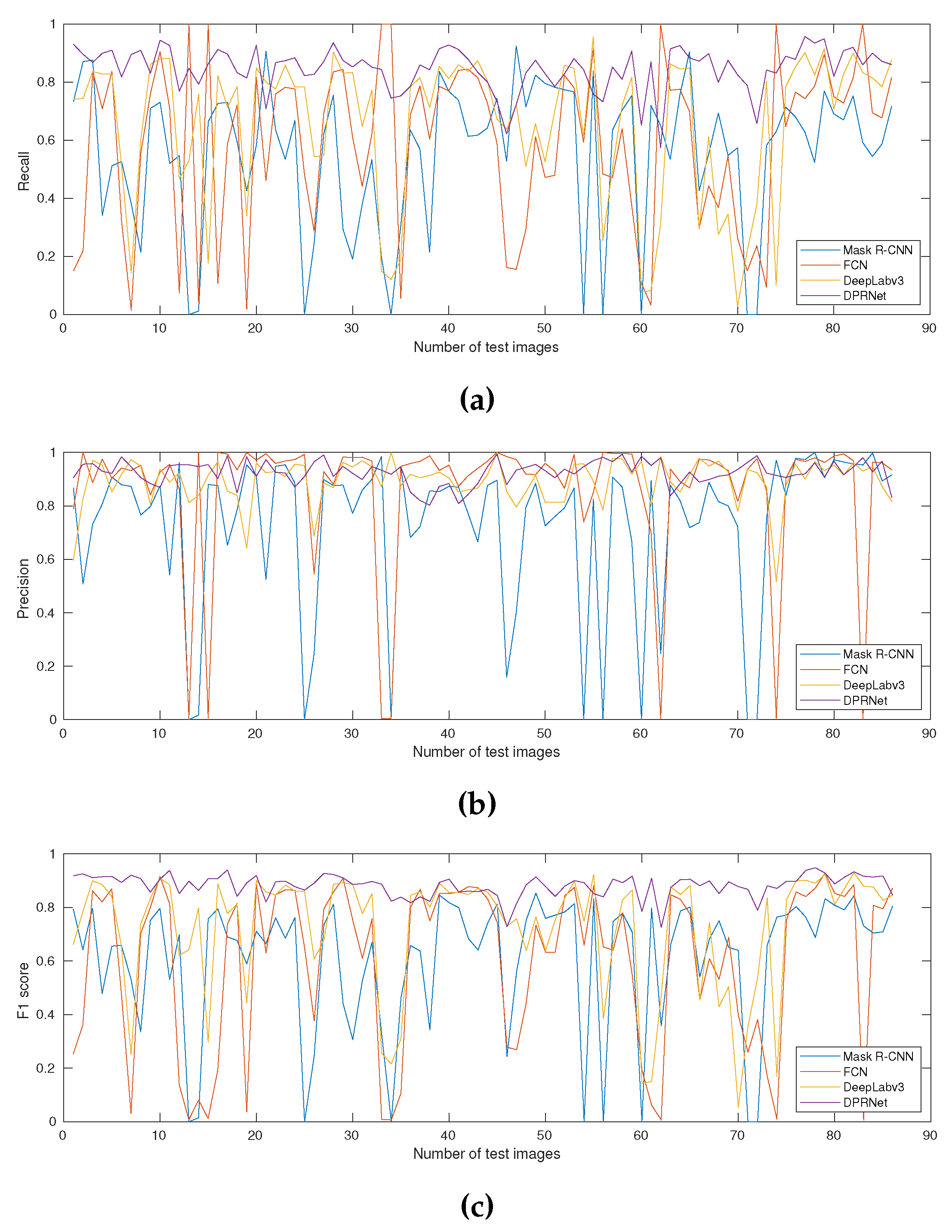
4.3. Model validation metrics
4.4. Comparison with existing smoke recognition methods
4.5. Plume rise measurement
5. Conclusion
- Generalizing DPRNet to predict the PC and PC centerline simultaneously.
- Reinforcing DPRNet to recognize multi-source PCs occurring in industrial environments.
- Conducting comparative studies using meteorological and smokestack measurements between the estimated PR and PR distance from the proposed framework and the Briggs parameterizations equations.
- Briggs parameterization modification via estimated PR and PR distance from the proposed framework.
Acknowledgments
References
- G. A. Briggs, “Plume rise predictions,” in Lectures on air pollution and environmental impact analyses, pp. 59–111, Springer, 1982.
- K. Ashrafi, A. A. Orkomi, and M. S. Motlagh, “Direct effect of atmospheric turbulence on plume rise in a neutral atmosphere,” Atmospheric Pollution Research, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 640–651, 2017.
- G. A. Briggs, “Plume rise: A critical survey.,” tech. rep., Air Resources Atmospheric Turbulence and Diffusion Lab., Oak Ridge, Tenn., 1969.
- G. Briggs, “Plume rise predictions, lectures on air pollution and environment impact analysis,” Am. Meteorol. Soc., Boston, USA, vol. 10, p. 510, 1975.
- J. Bieser, A. Aulinger, V. Matthias, M. Quante, and H. D. Van Der Gon, “Vertical emission profiles for europe based on plume rise calculations,” Environmental Pollution, vol. 159, no. 10, pp. 2935–2946, 2011.
- B. Bringfelt, “Plume rise measurements at industrial chimneys,” Atmospheric Environment (1967), vol. 2, no. 6, pp. 575–598, 1968.
- P. Makar, W. Gong, J. Milbrandt, C. Hogrefe, Y. Zhang, G. Curci, R. Žabkar, U. Im, A. Balzarini, R. Baró, et al., “Feedbacks between air pollution and weather, part 1: Effects on weather,” Atmospheric Environment, vol. 115, pp. 442–469, 2015.
- C. Emery, J. Jung, and G. Yarwood, “Implementation of an alternative plume rise methodology in camx,” Novato, CA, 2010.
- D. Byun, “Science algorithms of the epa models-3 community multiscale air quality (cmaq) modeling system,” EPA/600/R-99/030, 1999.
- B. E. Rittmann, “Application of two-thirds law to plume rise from industrial-sized sources,” Atmospheric Environment (1967), vol. 16, no. 11, pp. 2575–2579, 1982.
- W. G. England, L. H. Teuscher, and R. B. Snyder, “A measurement program to determine plume configurations at the beaver gas turbine facility, port westward, oregon,” Journal of the Air Pollution Control Association, vol. 26, no. 10, pp. 986–989, 1976.
- P. Hamilton, “Paper iii: plume height measurements at northfleet and tilbury power stations,” Atmospheric Environment (1967), vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 379–387, 1967.
- D. Moore, “A comparison of the trajectories of rising buoyant plumes with theoretical/empirical models,” Atmospheric Environment (1967), vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 441–457, 1974.
- G. Sharf, M. Peleg, M. Livnat, and M. Luria, “Plume rise measurements from large point sources in israel,” Atmospheric Environment. Part A. General Topics, vol. 27, no. 11, pp. 1657–1663, 1993.
- H. Webster and D. Thomson, “Validation of a lagrangian model plume rise scheme using the kincaid data set,” Atmospheric Environment, vol. 36, no. 32, pp. 5031–5042, 2002.
- M. Gordon, S.-M. Li, R. Staebler, A. Darlington, K. Hayden, J. O’Brien, and M. Wolde, “Determining air pollutant emission rates based on mass balance using airborne measurement data over the alberta oil sands operations,” Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, vol. 8, no. 9, pp. 3745–3765, 2015.
- M. Gordon, P. A. Makar, R. M. Staebler, J. Zhang, A. Akingunola, W. Gong, and S.-M. Li, “A comparison of plume rise algorithms to stack plume measurements in the athabasca oil sands,” Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, vol. 18, no. 19, pp. 14695–14714, 2018.
- A. Akingunola, P. A. Makar, J. Zhang, A. Darlington, S.-M. Li, M. Gordon, M. D. Moran, and Q. Zheng, “A chemical transport model study of plume-rise and particle size distribution for the athabasca oil sands,” Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, vol. 18, no. 12, pp. 8667–8688, 2018.
- F. Isikdogan, A. C. Bovik, and P. Passalacqua, “Surface water mapping by deep learning,” IEEE journal of selected topics in applied earth observations and remote sensing, vol. 10, no. 11, pp. 4909–4918, 2017.
- F. Isikdogan, A. Bovik, and P. Passalacqua, “Rivamap: An automated river analysis and mapping engine,” Remote Sensing of Environment, vol. 202, pp. 88–97, 2017.
- K. Gu, J. Qiao, and W. Lin, “Recurrent air quality predictor based on meteorology-and pollution-related factors,” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 14, no. 9, pp. 3946–3955, 2018.
- K. Gu, J. Qiao, and X. Li, “Highly efficient picture-based prediction of pm2. 5 concentration,” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 66, no. 4, pp. 3176–3184, 2018.
- J. Gubbi, S. Marusic, and M. Palaniswami, “Smoke detection in video using wavelets and support vector machines,” Fire Safety Journal, vol. 44, no. 8, pp. 1110–1115, 2009.
- F. Yuan, “Video-based smoke detection with histogram sequence of lbp and lbpv pyramids,” Fire safety journal, vol. 46, no. 3, pp. 132–139, 2011.
- F. Yuan, “A double mapping framework for extraction of shape-invariant features based on multi-scale partitions with adaboost for video smoke detection,” Pattern Recognition, vol. 45, no. 12, pp. 4326–4336, 2012.
- F. Yuan, J. Shi, X. Xia, Y. Fang, Z. Fang, and T. Mei, “High-order local ternary patterns with locality preserving projection for smoke detection and image classification,” Information Sciences, vol. 372, pp. 225–240, 2016.
- F. Yuan, Z. Fang, S. Wu, Y. Yang, and Y. Fang, “Real-time image smoke detection using staircase searching-based dual threshold adaboost and dynamic analysis,” IET Image Processing, vol. 9, no. 10, pp. 849–856, 2015.
- F. Yuan, L. Zhang, X. Xia, B. Wan, Q. Huang, and X. Li, “Deep smoke segmentation,” Neurocomputing, vol. 357, pp. 248–260, 2019.
- S. Khan, K. Muhammad, T. Hussain, J. Del Ser, F. Cuzzolin, S. Bhattacharyya, Z. Akhtar, and V. H. C. de Albuquerque, “Deepsmoke: Deep learning model for smoke detection and segmentation in outdoor environments,” Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 182, p. 115125, 2021.
- Y.-k. Shi, Z. Zhong, D.-X. Zhang, and J. Yang, “A study on smoke detection based on multi-feature,” Journal of Signal Processing, vol. 31, no. 10, pp. 1336–1341, 2015.
- C. Yuan, Z. Liu, and Y. Zhang, “Learning-based smoke detection for unmanned aerial vehicles applied to forest fire surveillance,” Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, vol. 93, no. 1, pp. 337–349, 2019.
- A. Filonenko, D. C. Hernández, and K.-H. Jo, “Fast smoke detection for video surveillance using cuda,” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 725–733, 2017.
- R. I. Zen, M. R. Widyanto, G. Kiswanto, G. Dharsono, and Y. S. Nugroho, “Dangerous smoke classification using mathematical model of meaning,” Procedia Engineering, vol. 62, pp. 963–971, 2013.
- H. Wang and Y. Chen, “A smoke image segmentation algorithm based on rough set and region growing,” Journal of Forest Science, vol. 65, no. 8, pp. 321–329, 2019.
- W. Zhao, W. Chen, Y. Liu, X. Wang, and Y. Zhou, “A smoke segmentation algorithm based on improved intelligent seeded region growing,” Fire and Materials, vol. 43, no. 6, pp. 725–733, 2019.
- M. Ajith and M. Martínez-Ramón, “Unsupervised segmentation of fire and smoke from infra-red videos,” IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 182381–182394, 2019.
- K. Dimitropoulos, P. Barmpoutis, and N. Grammalidis, “Higher order linear dynamical systems for smoke detection in video surveillance applications,” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 27, no. 5, pp. 1143–1154, 2016.
- H. N. Pham, K. B. Dang, T. V. Nguyen, N. C. Tran, X. Q. Ngo, D. A. Nguyen, T. T. H. Phan, T. T. Nguyen, W. Guo, and H. H. Ngo, “A new deep learning approach based on bilateral semantic segmentation models for sustainable estuarine wetland ecosystem management,” Science of The Total Environment, vol. 838, p. 155826, 2022.
- B. Shi, M. Patel, D. Yu, J. Yan, Z. Li, D. Petriw, T. Pruyn, K. Smyth, E. Passeport, R. D. Miller, et al., “Automatic quantification and classification of microplastics in scanning electron micrographs via deep learning,” Science of The Total Environment, vol. 825, p. 153903, 2022.
- K. Muhammad, S. Khan, V. Palade, I. Mehmood, and V. H. C. De Albuquerque, “Edge intelligence-assisted smoke detection in foggy surveillance environments,” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 1067–1075, 2019.
- M. Liu, X. Xie, G. Ke, and J. Qiao, “Simple and efficient smoke segmentation based on fully convolutional network,” DEStech Trans. Comput. Sci. Eng.(ica), 2019. [CrossRef]
- Y. Jia, H. Du, H. Wang, R. Yu, L. Fan, G. Xu, and Q. Zhang, “Automatic early smoke segmentation based on conditional generative adversarial networks,” Optik, vol. 193, p. 162879, 2019.
- F. Yuan, Z. Dong, L. Zhang, X. Xia, and J. Shi, “Cubic-cross convolutional attention and count prior embedding for smoke segmentation,” Pattern Recognition, vol. 131, p. 108902, 2022.
- K. He, G. Gkioxari, P. Dollár, and R. Girshick, “Mask r-cnn,” in Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 2961–2969, 2017.
- T. Luhmann, S. Robson, S. Kyle, and I. Harley, Close range photogrammetry: principles, techniques and applications, vol. 3. Whittles publishing Dunbeath, 2006.
- B. Hwang, J. Kim, S. Lee, E. Kim, J. Kim, Y. Jung, and H. Hwang, “Automatic detection and segmentation of thrombi in abdominal aortic aneurysms using a mask region-based convolutional neural network with optimized loss functions,” Sensors, vol. 22, no. 10, p. 3643, 2022.
- R. Girshick, “Fast r-cnn,” in Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 1440–1448, 2015.
- A. De Visscher, Air dispersion modeling: foundations and applications. John Wiley & Sons, 2013.
- A. J. Cimorelli, S. G. Perry, A. Venkatram, J. C. Weil, R. J. Paine, R. B. Wilson, R. F. Lee, W. D. Peters, and R. W. Brode, “Aermod: A dispersion model for industrial source applications. part i: General model formulation and boundary layer characterization,” Journal of applied meteorology, vol. 44, no. 5, pp. 682–693, 2005.
- D. B. Turner and R. Schulze, “Atmospheric dispersion modeling: Trinity consultants.”,” 2007.
- S. Ji, W. Xu, M. Yang, and K. Yu, “3d convolutional neural networks for human action recognition,” IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 221–231, 2012.
- S. Albawi, T. A. Mohammed, and S. Al-Zawi, “Understanding of a convolutional neural network,” in 2017 international conference on engineering and technology (ICET), pp. 1–6, Ieee, 2017.
- X. Chen and A. Gupta, “An implementation of faster rcnn with study for region sampling,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.02138, 2017.
- K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, and J. Sun, “Deep residual learning for image recognition,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 770–778, 2016.
- J. Long, E. Shelhamer, and T. Darrell, “Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 3431–3440, 2015.
- L.-C. Chen, Y. Zhu, G. Papandreou, F. Schroff, and H. Adam, “Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation,” in Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp. 801–818, 2018.
- Gonzales, Rafael C and Wintz, Paul, “Digital image processing,” in Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc., 1987.
- Dougherty, Geoff, “Pattern recognition and classification: an introduction,” in Springer Science & Business Media, 2012.
- Berg, Lothar, “Introduction to the operational calculus,” in Elsevier & Business Media, 2013.


| Reported ID | Latitude | Longitude | (m) | (m) | () | (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Syn. 12908 | 57.041 | -111.616 | 183.0 | 7.9 | 12.0 | 427.9 |
| Syn. 12909 | 57.048 | -111.613 | 76.2 | 6.6 | 10.1 | 350.7 |
| Syn. 13219 | 57.296 | -111.506 | 30.5 | 5.2 | 8.8 | 355.0 |
| Syn. 16914 | 57.046 | -111.602 | 45.7 | 1.9 | 12.0 | 643.4 |
| Syn. 16915 | 57.046 | -111.604 | 31.0 | 5.0 | 9.0 | 454.5 |
| Syn. 16916 | 57.297 | -111.505 | 31.0 | 5.2 | 9.2 | 355.0 |
| Model | Recall | Precision | F1 score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mask R-CNN | 0.556 | 0.727 | 0.607 |
| FCN | 0.591 | 0.859 | 0.599 |
| DeepLabv3 | 0.654 | 0.892 | 0.721 |
| DPRNet | 0.846 | 0.925 | 0.881 |
| Image | Date | Time | (deg.) | (deg.) | (m) | (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | 2019-11-08 | 18-00-13 | 12.16 | -239.8 | 177 | 1685 |
| I2 | 2019-11-09 | 15-00-13 | 3.46 | -248.5 | 450.3 | 3287 |
| I3 | 2019-11-14 | 10-00-16 | 10.41 | -241.6 | 266.8 | 2280 |
| I4 | 2019-11-16 | 11-00-12 | 10.83 | -241.1 | 300.5 | 2905 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





