Submitted:
29 March 2023
Posted:
03 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
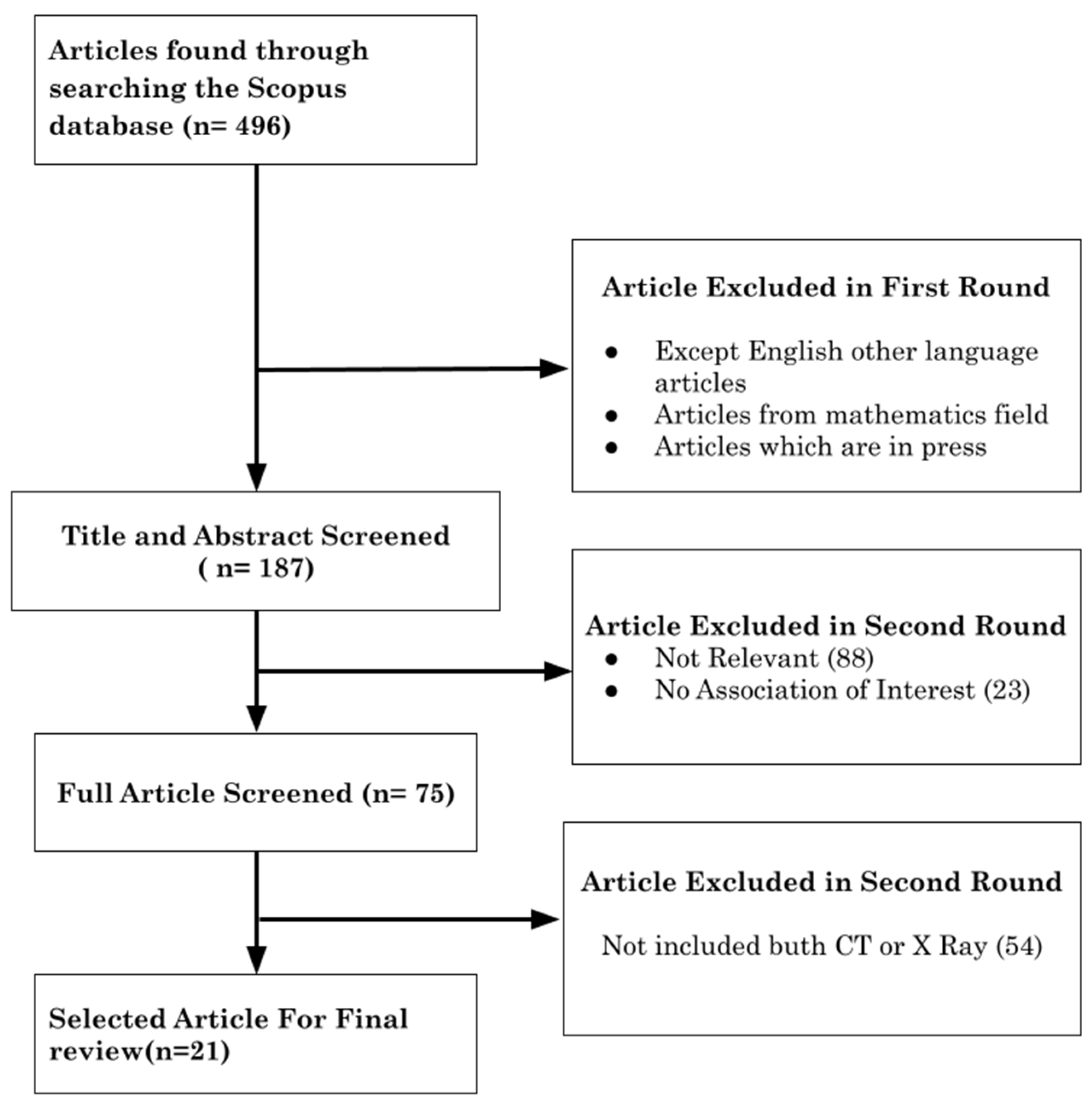
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction
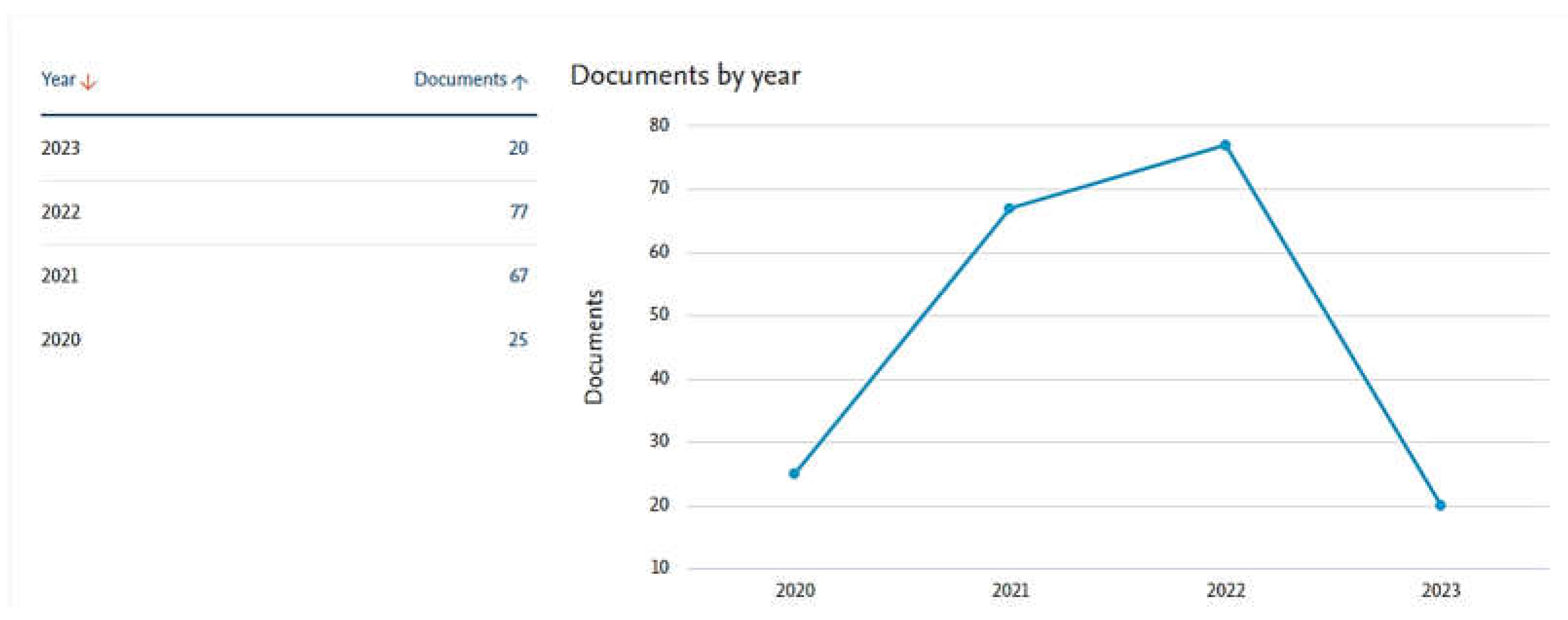
3. Data Analysis
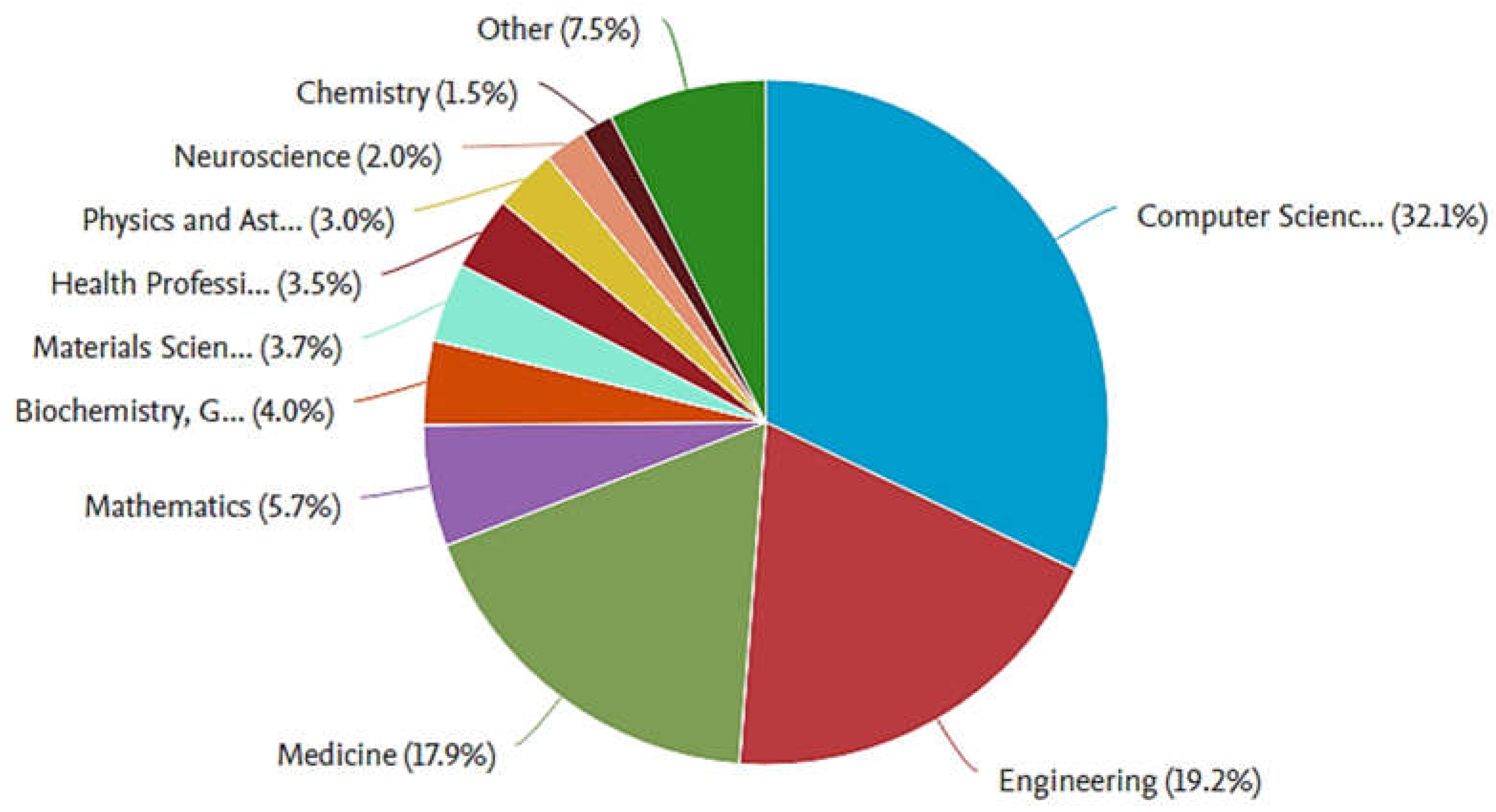
3.1. Publication Type
3.2. Research Purposes and Objectives
| Brief Description | Reference | Frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Detection | Early detection of this disease | [42] | 4 |
| Detect Covid-19 patient | [43] | ||
| Detection of Covid-19 | [44] | ||
| Covid-19 detection via features extraction | [45] | ||
| Detection by CT and X-ray image together (with developed architecture/model) |
Detect pneumonia and Covid-19. | [46] | 3 |
| Detection via Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) -tailored Deep Neural Network (DNN) | [47] | ||
| Detect through hybrid deep neural networks (HDNNs), | [36] | ||
| Detection by CT and X-ray image separately (with developed architecture/model) |
Predicts Covid-19 detection by multimodal covid network (MMCovid-NET) | [48] | 9 |
| Accurate diagnose of Covid-19 by light CNN model with watershed-based region-growing segmentation | [49] | ||
| Automatic detection by Multilayer Spatial Covid Convolutional Neural Network (MSCovCNN) | [50] | ||
| Early detection of Covid patient by proposed InceptionResNetV2 model | [34] | ||
| Differentiate Covid pneumonia normal sample by proposed SCoVNet architecture | [37] | ||
| Modified MobileNetV2 model to understand the what features of CT/X-ray images used to know the reason behind Covid-19 | [51] | ||
| Develop Modified ResNet50, accurate, fast, and cheap auxiliary diagnostic tool for detection |
[33] | ||
| DenseNet-121 model to image segregation |
[52] | ||
| Intelligent decision support system for Covid-19 empowered with deep learning (ID2S-Covid19-DL) To detect covid-19 | [53] | ||
| detection and analysis of Covid-19 through unsupervised learning (with developed architecture) |
Unsupervised deep learning-based Covid-19 detection by Autoencoder3-ResNet50 (GMM) model | [41] | 1 |
| Detection through differentiation between covid, pneumonia and normal patient (with developed architecture/model) |
Accurate and efficient method to detect Covid-19 by CovidCon | [54] | 4 |
| Distinguish between Covid-19 patients with others by NasNetMobile model | [38] | ||
| Differentiate Covid-19 pneumonia, non-Covid-19 pneumonia and nonpneumonia diseases | [39] | ||
| Differentiation between Covid-19, non-Covid-19 and pneumonia by CNN-based Covid-19 detection model | [35] |
3.3. Exploration of used data
3.4. Context of Study
3.5. Exploring the AI Techniques
4. Future Research Opportunities
- Use of a Large Set of Data in Research – There are opportunities to gather substantial amounts of data and make them accessible to researchers so they can run various tests. Such initiatives will be incredibly helpful in the battle against the pandemic. Global data were used in all disease detection study projects. However, we suggest that more work in this area could benefit from using a variety of worldwide data sources. Future studies could look into whether larger databases could produce more well-structured, verified, and generalised results. Additional research could be done to create an algorithm that is more efficient and effective. With enough information in the future, the claims made in the research can be investigated further.
- Development of New Algorithm – New algorithms can be developed in future for more efficient and accurate detection of Covid-19. CNN with multiple layer can be developed for more refined result. The structural architecture of machine learning algorithm can be modified in near future by observing the potential performance level through this literature review.
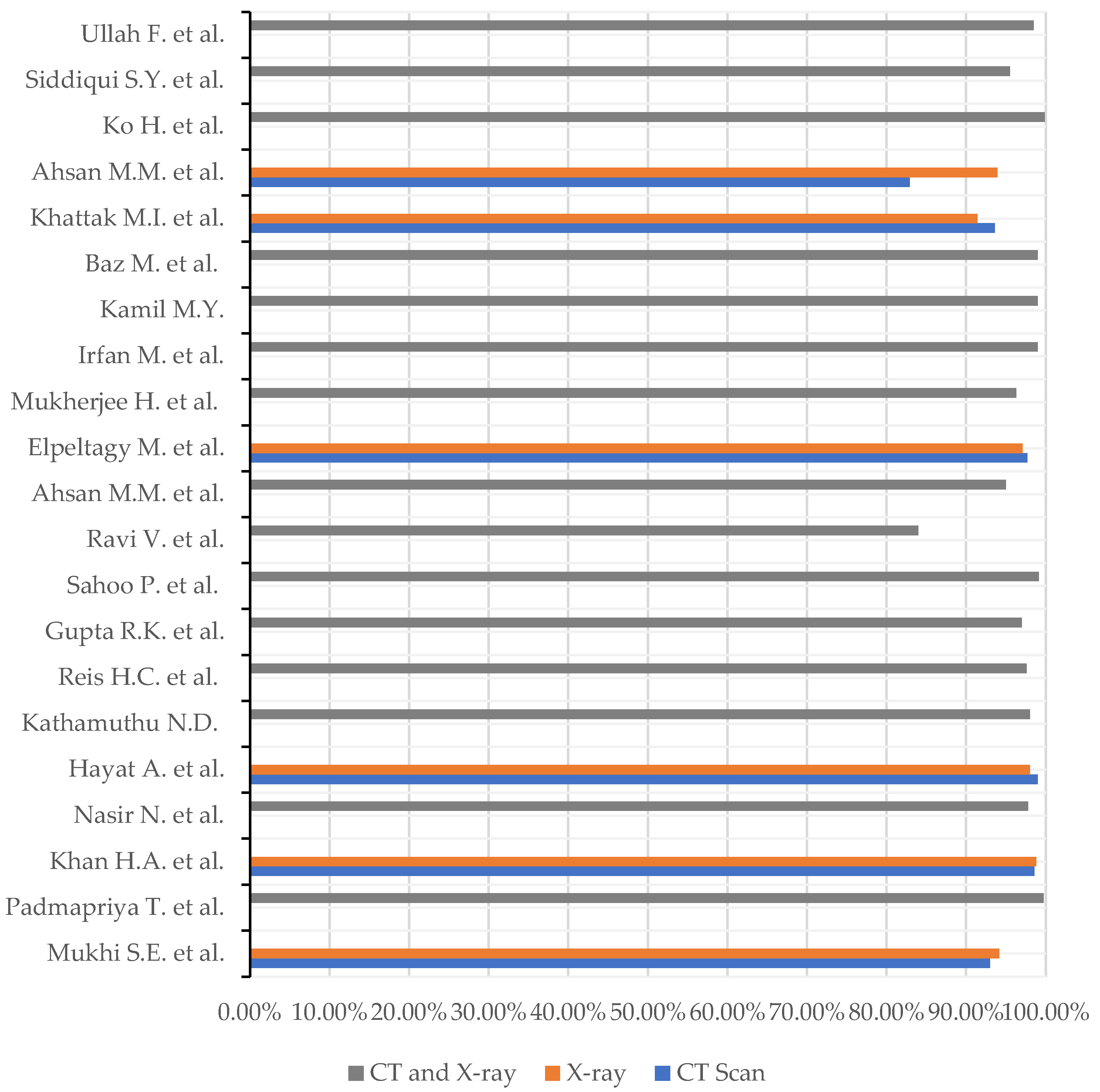
- Hybrid Data – Among 21 articles only three of them used Hybrid data to detect Covid-19. Use of hybrid data should be more. Because hybrid data gives more accurate and effective result in diagnosis of Covid-19. Because hybrid data consider CT scan image and X-ray image together as a single image, the retrieved data from that image is more accurate as input to any algorithm.
- Other Data Should Include – In these articles we noticed that when researcher use CT scan and X-ray data usually they do not consider any other kind of data like health history, pathological, clinical etc. with exception of one Article [43]. If researcher include other related data for the research, the study will be strong and detection process will be more accurate.
- Managing the ICU Surge during the Covid-19 Crisis - According to reports, some hospitals chose to only treat young patients, abandoning elderly patients who had a lower chance of surviving because the hospitals were running low on supplies. Further study can be done to determine which individuals, based on their X-ray and CT scan report, are more likely to be critical cases. This would assist hospitals in identifying patients who can be treated at home versus those who require intensive care unit assistance. Studies that concentrate on ICU admission could help some patients be discharged early, freeing up room for those who really need it. Studies can also help to delay the early discharge of ICU patients.
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, M.K. , et al., COVID-19 mortality and Progress toward vaccinating older adults—World Health Organization, worldwide, 2020–2022. MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 2023. 72(5): p. 113-118.
- Bhadra, A., A. Mukherjee, and K. Sarkar, Impact of population density on Covid-19 infected and mortality rate in India. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 2021. 7(1): p. 623-629. [CrossRef]
- Sadowski, A. , et al., Big data insight on global mobility during the Covid-19 pandemic lockdown. Journal of Big Data, 2021. 8(1): p. 78. [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, I. and P. Maity, COVID-19 outbreak: Migration, effects on society, global environment and prevention. Science of The Total Environment, 2020. 728: p. 138882. [CrossRef]
- Banakar, M. , et al., COVID-19 transmission risk and protective protocols in dentistry: a systematic review. BMC Oral Health, 2020. 20(1): p. 275.
- Ciotti, M. , et al., The COVID-19 pandemic. Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences, 2020. 57(6): p. 365-388.
- Islam, M.N. , et al., A Survey on the Use of AI and ML for Fighting the COVID-19 Pandemic. ArXiv, 2020. abs/2008.07449.
- Zakharov, V. About the Evolution of the Concept of “Artificial Intelligence”. in 2021 International Conference Engineering Technologies and Computer Science (EnT). 2021.
- Bashshur, R.L. , et al., Sustaining and Realizing the Promise of Telemedicine. Telemedicine and e-Health, 2013. 19(5): p. 339-345. [CrossRef]
- S.K, L., et al., Online clinical decision support system using optimal deep neural networks. Applied Soft Computing, 2019. 81: p. 105487. [CrossRef]
- Belciug, S. and F. Gorunescu, Era of Intelligent Systems in Healthcare, in Intelligent Decision Support Systems—A Journey to Smarter Healthcare, S. Belciug and F. Gorunescu, Editors. 2020, Springer International Publishing: Cham. p. 1-55.
- Rahmani, A.M. , et al. Machine Learning (ML) in Medicine: Review, Applications, and Challenges. Mathematics, 2021. 9. [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N. , et al., A Systematic Review on the Use of AI and ML for Fighting the COVID-19 Pandemic. IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence, 2020. 1(3): p. 258-270. [CrossRef]
- Kaul, V., S. Enslin, and S.A. Gross, History of artificial intelligence in medicine. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 2020. 92(4): p. 807-812. [CrossRef]
- Haenlein, M. and A. Kaplan, A Brief History of Artificial Intelligence: On the Past, Present, and Future of Artificial Intelligence. California Management Review, 2019. 61(4): p. 5-14. [CrossRef]
- Benko, A. and C. Sik Lányi, History of Artificial Intelligence, in Encyclopedia of Information Science and Technology, Second Edition, D.B.A.M. Khosrow-Pour, Editor. 2009, IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA. p. 1759-1762.
- Garbuio, M. and N. Lin, Artificial Intelligence as a Growth Engine for Health Care Startups: Emerging Business Models. California Management Review, 2019. 61(2): p. 59-83. [CrossRef]
- Dash, S. , et al., Big data in healthcare: management, analysis and future prospects. Journal of Big Data, 2019. 6(1): p. 54. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S. , et al., Medical Diagnostic Systems Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) Algorithms: Principles and Perspectives. IEEE Access, 2020. 8: p. 228049-228069. [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.-H., A. L. Beam, and I.S. Kohane, Artificial intelligence in healthcare. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2018. 2(10): p. 719-731.
- Chowdhury, M.E.H. , et al., Can AI Help in Screening Viral and COVID-19 Pneumonia? IEEE Access, 2020. 8: p. 132665-132676.
- Abdulkareem, M. and S.E. Petersen, The Promise of AI in Detection, Diagnosis, and Epidemiology for Combating COVID-19: Beyond the Hype. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence, 2021. 4. [CrossRef]
- Dong, D. , et al., The Role of Imaging in the Detection and Management of COVID-19: A Review. IEEE Reviews in Biomedical Engineering, 2021. 14: p. 16-29. [CrossRef]
- Howell, J.D. , EARLY CLINICAL USE OF THE X-RAY. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc, 2016. 127: p. 341-349.
- Behling, R. , Medical X-ray sources now and for the future. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2017. 873: p. 43-50.
- Schmidt Charles, W. , CT Scans: Balancing Health Risks and Medical Benefits. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2012. 120(3): p. a118-a121.
- Al-Sharify, Z.T., T. A. Al-Sharify, and N.T. Al-Sharify. A critical review on medical imaging techniques (CT and PET scans) in the medical field. in IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. 2020. IOP Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Albawi, S., T. A. Mohammed, and S. Al-Zawi. Understanding of a convolutional neural network. in 2017 International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICET). 2017.
- Noble, W.S. , What is a support vector machine? Nature Biotechnology, 2006. 24(12): p. 1565-1567.
- Jahromi, A.H. and M. Taheri. A non-parametric mixture of Gaussian naive Bayes classifiers based on local independent features. in 2017 Artificial Intelligence and Signal Processing Conference (AISP). 2017.
- LaValley, M.P. , Logistic Regression. Circulation, 2008. 117(18): p. 2395-2399.
- Mucherino, A., P. J. Papajorgji, and P.M. Pardalos, k-Nearest Neighbor Classification, in Data Mining in Agriculture, A. Mucherino, P.J. Papajorgji, and P.M. Pardalos, Editors. 2009, Springer New York: New York, NY. p. 83-106.
- Elpeltagy, M. and H. Sallam, Automatic prediction of COVID- 19 from chest images using modified ResNet50. Multimed Tools Appl, 2021. 80(17): p. 26451-26463. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K. , et al., An AI-enabled pre-trained model-based Covid detection model using chest X-ray images. Multimed Tools Appl, 2022. 81(26): p. 37351-37377. [CrossRef]
- Baz, M. , et al., Utilization of Artificial Intelligence in Medical Image Analysis for COVID-19 Patients Detection. Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing, 2021. 30(1). [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M. , et al. Role of Hybrid Deep Neural Networks (HDNNs), Computed Tomography, and Chest X-rays for the Detection of COVID-19. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2021. 18. [CrossRef]
- Hayat, A. , et al., Novel Comparative Study for the Detection of COVID-19 Using CT Scan and Chest X-ray Images. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2023. 20(2). [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.M. , et al. COVID-19 Symptoms Detection Based on NasNetMobile with Explainable AI Using Various Imaging Modalities. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction, 2020. 2, 490-504. [CrossRef]
- Ko, H. , et al., COVID-19 Pneumonia Diagnosis Using a Simple 2D Deep Learning Framework With a Single Chest CT Image: Model Development and Validation. J Med Internet Res, 2020. 22(6): p. e19569. [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F. , et al., Explainable artificial intelligence approach in combating real-time surveillance of COVID19 pandemic from CT scan and X-ray images using ensemble model. J Supercomput, 2022. 78(17): p. 19246-19271. [CrossRef]
- Ravi, V. and T.D. Pham, Unsupervised Deep learning-based Feature Fusion Approach for Detection and Analysis of COVID-19 using X-ray and CT Images. The Open Bioinformatics Journal, 2022. 15(1). [CrossRef]
- Mukhi, S.E., R. T. Varshini, and S.E.F. Sherley, Diagnosis of COVID-19 from Multimodal Imaging Data Using Optimized Deep Learning Techniques. SN Computer Science, 2023. 4(3): p. 212.
- Nasir, N. , et al., Multi-modal image classification of COVID-19 cases using computed tomography and X-rays scans. Intelligent Systems with Applications, 2023. 17: p. 200160. [CrossRef]
- Kathamuthu, N.D. , et al., A deep transfer learning-based convolution neural network model for COVID-19 detection using computed tomography scan images for medical applications. Advances in Engineering Software, 2023. 175: p. 103317. [CrossRef]
- Kamil, M.Y. , A deep learning framework to detect Covid-19 disease via chest X-ray and CT scan images. International Journal of Electrical & Computer Engineering (2088-8708), 2021. 11(1). [CrossRef]
- Reis, H.C. and V. Turk, COVID-DSNet: A novel deep convolutional neural network for detection of coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) cases from CT and Chest X-Ray images. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 2022. 134: p. 102427.
- Mukherjee, H. , et al., Deep neural network to detect COVID-19: one architecture for both CT Scans and Chest X-rays. Applied Intelligence, 2021. 51(5): p. 2777-2789. [CrossRef]
- Padmapriya, T., T. Kalaiselvi, and V. Priyadharshini, Multimodal covid network: Multimodal bespoke convolutional neural network architectures for COVID-19 detection from chest X-ray's and computerized tomography scans. International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, 2022. 32(3): p. 704-716.
- Khan, H.A. , et al. Novel Light Convolutional Neural Network for COVID Detection with Watershed Based Region Growing Segmentation. Journal of Imaging, 2023. 9. [CrossRef]
- Khattak, M.I. , et al., Automated detection of COVID-19 using chest x-ray images and CT scans through multilayer-spatial convolutional neural networks. International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence, 2021. 6: p. 15-24. [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.M. , et al. Detection of COVID-19 Patients from CT Scan and Chest X-ray Data Using Modified MobileNetV2 and LIME. Healthcare, 2021. 9. [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F. , et al., Explainable artificial intelligence approach in combating real-time surveillance of COVID19 pandemic from CT scan and X-ray images using ensemble model. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2022. 78(17): p. 19246-19271. [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.Y. , et al., Intelligent decision support system for COVID-19 empowered with deep learning. Comput. Mater. Contin, 2021. 66: p. 1719-1732. [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P. , et al., Potential diagnosis of COVID-19 from chest X-ray and CT findings using semi-supervised learning. Physical and Engineering Sciences in Medicine, 2022. 45(1): p. 31-42. [CrossRef]
- Myles, A.J. , et al., An introduction to decision tree modeling. Journal of Chemometrics, 2004. 18(6): p. 275-285. [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.Y. and Y. Lu, Decision tree methods: applications for classification and prediction. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry, 2015. 27(2): p. 130-5. [CrossRef]
- More, A.S. and D. P. Rana. Review of random forest classification techniques to resolve data imbalance. in 2017 1st International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Information Management (ICISIM). 2017.
- Rasamoelina, A.D., F. Adjailia, and P. Sinčák. A Review of Activation Function for Artificial Neural Network. in 2020 IEEE 18th World Symposium on Applied Machine Intelligence and Informatics (SAMI). 2020.
- Vinogradova, K., A. Dibrov, and G. Myers, Towards Interpretable Semantic Segmentation via Gradient-Weighted Class Activation Mapping (Student Abstract). Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020. 34(10): p. 13943-13944. [CrossRef]
- Das, P. and A. Ortega. Gradient-Weighted Class Activation Mapping for Spatio Temporal Graph Convolutional Network. in ICASSP 2022 - 2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). 2022.
- Belkina, A.C. , et al., Automated optimized parameters for T-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding improve visualization and analysis of large datasets. Nature Communications, 2019. 10(1): p. 5415. [CrossRef]
- Rajinikanth, V. , et al. A Customized VGG19 Network with Concatenation of Deep and Handcrafted Features for Brain Tumor Detection. Applied Sciences, 2020. 10. [CrossRef]
- Qassim, H., A. Verma, and D. Feinzimer. Compressed residual-VGG16 CNN model for big data places image recognition. in 2018 IEEE 8th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC). 2018.
- Baldassarre, F., D. G. Morín, and L. Rodés-Guirao, Deep koalarization: Image colorization using cnns and inception-resnet-v2. arxiv preprint . arXiv:1712.03400, 2017.
- Liu, J. and X. Wang, Early recognition of tomato gray leaf spot disease based on MobileNetv2-YOLOv3 model. Plant Methods, 2020. 16(1): p. 83. [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, D. and H.A. Ella, GSA-DenseNet121-COVID-19: a hybrid deep learning architecture for the diagnosis of COVID-19 disease based on gravitational search optimization algorithm. arXiv preprint. arXiv:2004.05084, 2020.
- Shadin, N.S., S. Sanjana, and N.J. Lisa. COVID-19 Diagnosis from Chest X-ray Images Using Convolutional Neural Network(CNN) and InceptionV3. in 2021 International Conference on Information Technology (ICIT). 2021.
- Rahimzadeh, M. and A. Attar, A modified deep convolutional neural network for detecting COVID-19 and pneumonia from chest X-ray images based on the concatenation of Xception and ResNet50V2. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, 2020. 19: p. 100360. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q. , Image retrieval method based on deep learning semantic feature extraction and regularization softmax. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2020. 79(13): p. 9419-9433. [CrossRef]
- Krogh, A. , What are artificial neural networks? Nature Biotechnology, 2008. 26(2): p. 195-197.
| Literature | Data Source | Data Volume |
|---|---|---|
| [42] | Kaggle | 2482 CT scans image and 31 Covid positive along with 10,192 normal X-ray image |
| [48] | GitHub | 108,948 images |
| [49] | Kaggle | 3829 X-rays and 3829 X-rays |
| [43] | GitHub | 535 CT and X-ray images and 485 clinical notes related with them |
| [37] | Mendeley Data | 17,599 images |
| [44] | Kaggle | 2481 images |
| [46] | Kaggle | 2357 CT scan data, 2515 chest X-ray data and 2400 CT and chest X-ray hybrid data |
| [34] | Kaggle, GitHub | 5856 chest X-ray & CT dataset |
| [54] | Kaggle, GitHub | 2905 unique images for X-ray 617,775 images from 4154 patients |
| [41] | Mendeley Data | 8,055 CT scan and 9,544 X-ray images |
| [51] | Kaggle | 2591 mixed data |
| [33] | GitHub | 17100 X−ray and CT images |
| [47] | Kaggle, GitHub | 168 Covid and 168 normal cases for the both X-ray and CT scan images |
| [36] | GitHub, Covid-19 radiography database, Kaggle, Covid-19 image data collection, and Actual Med Covid-19 Chest X-ray Dataset | 3500 infected and 1500 healthy controls |
| [45] | D. S. Kermany, et al., "Identifying medical diagnoses and treatable diseases by image-based deep learning," J. P. Cohen, P. Morrison, and L. Dao, "Covid-19 image data collection," |
images of normal 805 and Covid-19 195 |
| [35] | Kaggle | Covid-19 400 Pneumonia 402 non-Covid 406 |
| [50] | Kaggle and Git Hub | 723 X-ray and 3228 CT scans images |
| [38] | Kaggle | 400 chest X-ray images, and 400 CT scan images |
| [39] | Wonkwang University Hospital(WKUH) and Chonnam National University Hospital (CNUH), Italian Society of Medical and Interventional Radiology(SIRM) public database. | 3993 images. |
| [53] | - | 527 images |
| [52] | From Git hub, Italian Society of Medical and Interventional Radiology, Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), Radiopaedia, and SIRM) and Kaggle repository. | 1229 SARS-CoV-2,1161 negative |
| Article | Algorithm and Model | Result |
|---|---|---|
| [42] | CNN with Deep Neural
|
|
| [48] | Bespoke CNN
|
99.75% accuracy |
| [49] |
Light CNN (Watershed based region growing segmentation) |
|
| [43] | Multi-modal system
|
Accuracy with 97.8% |
| [37] | CNN
|
|
| [44] | CNN
|
|
| [46] |
Deep CNN (Covid-DSNet developed) |
∙ 97.60 % accuracy |
| [34] | CNN
|
|
| [54] | CovidCon |
|
| [41] | Convolutional auto encoders with pre-trained CNN
|
|
| [51] | Deep CNN
|
|
| [33] |
CNN ResNet50 |
|
| [47] | Tailored Deep CNN | 96.28% Accuracy |
| [36] | Hybrid Deep Neural Networks (HDNNs) |
|
| [45] | VGG-19 |
|
| [35] | CNN |
|
| [50] | MSCovCNN |
|
| [38] | CNN
|
|
| [39] | FCONet |
|
| [53] | ID2S-Covid19-DL |
|
| [52] | CLAHE
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





