1. Introduction
The severity of Covid-19 (in terms of infection and mortality) varies drastically across countries. It is rather difficult to pinpoint all of the factors that explain cross-country differences in the infection rate (measured as the number of cases per million of the population) and the case mortality rate (the ratio of deaths to cases). It has also become clear that high infection rates and high mortality rates do not go together. The figures available at the end of August 2021 show almost zero rank correlation between the two rates. A country may have a high level of infections but few people die than in other countries with comparable infection rates. The opposite is also true, as some countries have low infection rates but high mortality rates. An aberration that has been observed is that the US and UK, which are ranked as the top two countries in terms of preparedness (measured by the global health security index), have very high infection and mortality rates. It is intuitive to suggest that infections and mortality are determined by a variety of factors acting simultaneously, which makes it hazardous to derive inference by explaining cross-country differences in terms of one or few factors.
The severity of Covid-19 is influenced, inter alia, by the political system and economic development. The Lowy Institute (2021) suggests that the political system is relevant because it reflects how governments convince or compel their citizens to adhere to preventive measures such as stay-at-home orders, lockdowns, and border closures. The results presented by the Institute show that, on average, countries with authoritarian governments had no prolonged advantage in suppressing the virus. Economic development (or whether the underlying country is rich or poor) is a determining factor, in the sense that countries with higher per capita incomes have more resources available to fight the pandemic. The Lowy Institute shows that developed countries have performed better on average than developing countries for most of the crisis to date. This may or may not be true, depending on how the data are interpreted and at what point in time, as the situation changes over time.
The objective of this paper is to use extreme bounds analysis to identify the factors that determine the infection and case mortality rates in developed and developing countries to find out if the same or different factors are more important in one group of countries than the other. We start by an examination of the factors accounting for differences in severity and the identification of potential explanatory variables. This is followed by a description of the methodology and the presentation of some stylised facts derived from the data. The empirical results are then discussed, and some concluding remarks are presented in the last section.
2. Accounting for Differences between Developed and Developing Countries
With respect to the severity of Covid-19, one important factor that explains differences between developed and developing countries is associated with the transmission of disease through international travel. Some of the worst-hit countries are homes to some of the world’s busiest airports, handling hundreds of millions of passengers every year. People living in rich developed countries have the luxury of frequent international travel and enjoy strong global trade links, particularly with China, where the outbreak originated. The affluence that allows international travel is conducive to a swift spreading of the virus, which reduces the reaction time. On the other hand, lower levels of travel to low to middle-income countries could help explain why they were able to escape the virus, at least in the early days of the pandemic, which gave them time to prepare and introduce some form of physical distancing. Naturally, there are exceptions—for example, Thailand, a developing country, has a major airport and receives significant numbers of visitors. The effect of international travel and international tourist arrivals, and the related issue of the effectiveness of quarantine, have been examined by Yu and Keralis (2020), Wells et al. (2020), Brumfiel and Wilburn (2020), Pillinger (2020), Jerving (2020), and by Stanhope and Weinstein (2020). Moosa and Khatatbeh (2020), who describe the imposition of international travel restrictions to prevent the spread of the Coronavirus as a “controversial issue”, find that international tourist arrivals have a greater effect on the severity of Covid-19 than any of the other factors they examined. A summary of these studies can be found in Moosa (2021).
Readiness and response to Covid-19 have played a role, but there is no conspicuous developing/developed divide here. Middle-income Asian countries have done well because of experience and preparation. For these countries, such as Vietnam and Thailand, this is not the first pandemic threat, which has given them the experience required to direct resources for the purpose of managing the spread. As a result, the lockdowns happened quickly, as did mass testing and high-tech contact tracing procedures. Furthermore, measures of lockdown and social distancing are likely to be more effective in developing countries because people tend to have more accommodative attitude to government instructions. In developed countries, on the other hand, top government officials have been caught in violation of the lockdown and social distancing rules (for example, the cases of Dominic Cummings and Matt Hancock in the UK).
The lack of recent experience in some developed countries may have played a role in aggravating the situation. On the other hand, tackling the spread of the coronavirus in some developed countries was adversely affected by the lack of proper leadership and governance, as well as complacency and overconfidence. The WHO announced a “public health emergency of international concern” on 30 January 2020, but nothing much was done in the developed world until 11 March, when the WHO called Covid-19 a “pandemic”. Again, much of this can be said about Brazil, a developing country that is currently one of the top three countries (with the US and India) in terms of the number of confirmed cases. Moosa (2021) presents an exposition of three cases of mishandling the pandemic: the US, UK and Brazil. In the UK, for example, Calvert et al. (2020) argue that the government failed to prepare adequately for the pandemic, both in the long term and in the weeks running up to the lockdown. Wall (2020) suggests that Britain lacks the capacity to track infected people and warns that “any lifting of the lockdown will result in a massacre”. O’Grady (2020) argues that “while countries around the world began to lock down workplaces, schools, and public gatherings in response to the rapidly spreading coronavirus, the United Kingdom’s initial strategy sent many into an uproar”. In the case of Brazil, Lipson (2020) puts the blame squarely on Bolsonaro for “his populist zeal and anti-science approach to government”. Likewise, Phillips (2020) blames Bolsonaro, “whose jumbled and dysfunctional handling of a pandemic he has called a ‘fantasy’ has made Boris Johnson’s widely panned response look sober and efficient”. As for the US, Moosa (2021) lists some of the most outrageous announcements made by Donald Trump on the pandemic.
The most vulnerable to Covid-19 are the old and those with pre-conditions. This factor is both positive and negative for developing countries. According to current epidemiological evidence, there is a marked difference in the age profile of vulnerable populations: the case mortality rate for people over 60 years of age appears to be up to 100 times higher than those below the age of 60, leading to substantially higher mortality rates in older age groups (Verity et al., 2020). Developing countries, being at an earlier phase of the demographic transition, have younger populations. The ratio of people over 60 years to total population is 1:20 and 1:10 in a typical low-income and middle-income country, respectively. In comparison, this ratio is 1:5 in developed countries. Therefore, the mortality risk of Covid-19 is significantly lower in low- and middle-income countries than in high-income, developed countries (Walker et al., 2020).
However, it is not only age. Developed countries are plagued by a higher incidence of affluence diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension and obesity. Low- and lower-middle income countries, on the other hand, have a lower prevalence of diseases known to exacerbate symptoms of Covid-19, such as cardiovascular disease, chronic respiratory disease, and diabetes, even controlling for age differences (World Health Organization, 2019, 2020). But then lower-income countries have a higher prevalence of infectious diseases and (in some cases) higher HIV infections, which weaken immunity if unattended. These differences are bound to lead to different risk profiles across the developing/developed divide (Walker et al. 2020).
Developing countries have sub-standard healthcare systems (making them unable to provide even basic services), weak and mismanaged national economies, limited access to financial and skilled human resources, and under-educated populations. They face limited (and shrinking) financial resources, and they are also burdened by overcrowded cities, informal labour markets, poor governance, and (in some cases) fragility and conflict (Loayza and Pennings, 2020). Developing countries have limited ability to cope with the pandemic and related trade-offs. In developed countries, the lives-versus-livelihoods trade-off can be eased with available financial resources. Developing countries face different trade-offs from those faced by developed countries. Given the lack of the financial muscle needed to cope with the pandemic, developing countries suffer more from the contraction in economic activity caused by adherence to strict suppression measures. This may lead to further aggravation of the effect of the pandemic. In general, it is difficult to pinpoint all of the factors that determine the severity of Covid-19 and how these factors operate in developed and developing countries.
3. Identifying Potential Explanatory Variables
It is a monumental task to identify, and collect data on, all of the potential explanatory variables that explain cross-country differences in infection and case mortality rates. This is problematic for empirical work, because the results tend to be sensitive to the selected set of explanatory variables. Our objective here is less humble and more realistic: out of a reasonably wide set of potential explanatory variables, we try to find out how important they are for explaining the severity of Covid-19 in developing and developed countries. We will also attempt to find out whether the factors determining the severity of Covid-19 in developed countries are different from those determining the outcome in developing ones.
No single theoretical model can be used to identify the explanatory variables. Barr and Tassier (2020a) start with a theoretical model of the determinants of the reproduction rate,
R, because this parameter determines the growth of cases over time. This is given by the equation
where
is the number of cases at time
t and
is the initial number of cases at time 0. The reproduction rate is calculated as follows:
where
C is the contact rate (the number of interactions that people have per day),
T is the transmission rate (the probability that any one infected individual will pass it to another if and when contact is made),
D is the duration (the time from infection to recovery, or death), and
S is the susceptibility rate (the fraction of the people who can still be infected at any given point in time). On the assumptions that
T,
S and
D are constant and that
, it follows that
where
. The determining factors, therefore, are those that impact
C. Barr and Tassier (2020a) assume that
C depends on population density, which is the variable of interest, and “control” variables. In their empirical model, however, they do not include population density as one explanatory variable. Rather, they use as explanatory variables population, land area, GDP (as a proxy for “economic density”), the proximity of a major airport and various measures of time, including days since the first case.
Following Barr and Tassier (2020a), we will use time since the first case and population density as explanatory variables. Barr and Tassier (2020b) argue that the reproduction rate “misses a portion of the story” because an infectious disease does not enter all countries at the same time. It is intuitive to suggest that, ceteris paribus, the longer the time it has been since the discovery of the first case, the larger will be the number of cases. Population density, on the other hand, is a major determinant of the contact rate and hence the number of cases and consequently deaths (for example, Hu et al., 2013). Ignoring the ceteris paribus condition has led Barr and Tassier (2020b) to come up with the concept of the “density paradox”, as they wonder about the role of population density in spreading the virus. For example, they wonder why Asian countries (such as South Korea, Japan, Taiwan and Singapore) have successfully controlled the virus spread. They also wonder why, for example, the epicentre in Italy is Milan (not Rome) whereas the Chinese epicentre is Wuhan (China’s 10th largest city) rather than Shanghai, which is China’s largest city.
The role played by population density in spreading pandemics and epidemics has been examined, inter alia, by Tarwater and Martin (2001), Maybery (1999), Li et al. (2018), and by Sumdani et al. (2014). Tarwater and Martin (2001) reach the conclusion that because density affects the contact rate, it has a “dramatic effect on the distribution of contacts over time, the magnitude of the outbreak, and, ultimately, the spread of disease”. Likewise, Maybery (1999) concludes that the number of new infections is strongly related to the distribution of susceptible contacts. Li et al. (2018), on the other hand, argue that the evidence is inconclusive on possible links between population density and the propagation and magnitude of epidemics. Sumdani et al. (2014) suggest that population density affects the transmission characteristics predicted by the epidemiology model.
More recently, the role of population density was examined by Sy et al. (2021) who reveal that the contact rate is higher in dense areas. Likewise, Martins-Filho (2021) emphasises the role played by population density by investigating the effect on the spread of Covid-19 in the counties of Sergipe state, Northeast Brazil, a region that has the largest concentration of highly vulnerable people in the country. Moosa and Khatatbeh (2021b) show that population density has a significantly positive effect on the number of cases but not the number of deaths, as the latter is better explained by measures of preparedness. Plausible explanations are presented for the results to conclude that the “density paradox” is not really a paradox. On the other hand, Jo et al. (2021) find that the connectivity measure, particularly a measure of network centrality, was a better indicator of Covid-19 proliferation than the density measures.
Another population-related factor that pertains to population density is urban population, the concentration of population in crowded cities or urban centres (hence, the term “urban density”). It is taken to be a separate variable that is distinct from population density because while the population density of a particular country is low, concentration in urban centres leads to a higher contact rate and hence infection rate. Florida (2020) refers to “the very same clustering of people that makes our great cities more innovative and productive also makes them, and us, vulnerable to infectious disease”. However, some observers disagree, arguing that while New York has done badly, other crowded cities like Singapore, Seoul, and Shanghai have done rather well. Fang and Wahba (2020) even argue that, in some cases, urban population density can be a blessing because economies of scale make it necessary for cities to meet a certain threshold of population density to offer higher-grade facilities and services to their residents. Desai (2020) emphasise the role of urban density, arguing that while high-density urban agglomerations may be sustainable in terms of the economies of scale their populations provide, these same urban spaces are nearly defenceless in times of unprecedented disease outbreaks. Acuto (2020) highlights the importance of urban density by arguing that the Covid-19 crisis has “changed the face of many of our cities and questioned how we should manage urban life in the wake of a pandemic”.
Some recent studies dispute the role of urban density. McFarlane (2021) examines the effect of urban density on the spread of Covid-19, arguing that density was conducive to the spread of the virus initially, but as the pandemic progressed, a “density-as-pathology” belief gave way to a more nuanced geographical understanding of the urban dimensions of the crisis, focusing on connections, spatial conditions, domestic overcrowding and poverty. Khan et al. (2021) argue that urban density is erroneously regarded as the main factor in the spread of Covid-19 in cities, suggesting instead that the culprits include income inequality, provision of healthcare, living conditions and government responsiveness play a key role in the spread of contagion. On the other hand, Moosa and Khatatbeh (2021a) find that the infection rate depends on urban density rather than the overall population density, and that the mortality rate depends on the age structure of the population and population density rather than urban density.
Important factors that are ignored by Barr and Tassier (2020a) are measures of preparedness and related factors, such as the quality of the healthcare system. For this reason, we consider six such variables, including prevention (the emergence or release of pathogens), detection and reporting, speed of response (mitigation of the spread of an epidemic), quality of the healthcare system, compliance with international norms, and the risk environment (a country’s vulnerability to biological threats). These variables are the constituent components of the global health security (GHS) index, which is prepared jointly by the Nuclear Threat Initiative (NTI) and the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security (JHU) (in co-operation with the Economist Intelligence Unit, EIU).
1 These factors have been used rarely in the empirical studies of the determinants of the severity of Covid-19. For example, Chaudhry et al. (2020) reveal the role played by full lockdowns and reduced country vulnerability to biological threats. Moosa and Khatatbeh (2020) find that the risk environment is a robust determinant of the population mortality rate and that prevention is a robust determinant of the case mortality rate.
Bell (2020) tries to dispel misconceptions regarding the overall score of 83.5 (out of a possible 100) received by the US. She argues that the score and rank assigned to the US do not indicate that the country is adequately prepared to respond to potentially catastrophic outbreaks of infectious disease. She also argues that significant preparedness gaps remain in the US and that some of those gaps are playing out in the current crisis. The response of the US to the Covid-19 outbreak to date shows that capacity alone is insufficient if it is not fully leveraged. The problem in the US, however, is lack of access to healthcare, on which the US is ranked as 175 out of 195 countries. A lack of guaranteed access to healthcare for all citizens leaves them vulnerable in times of emergency, including health workers, as there is no federal commitment to prioritising healthcare services for workers who become sick.
The age structure of the population (measured, for example, by the percentage of population over 65) is more relevant to the mortality rate than the infection rate. Dowda et al. (2020) highlight the important role of demography and demonstrate how the age structure of a population may help explain differences in mortality rates across countries and how transmission unfolds. They examine the role of age structure in deaths in Italy and South Korea and illustrate how the pandemic could unfold in populations with similar sizes but different age structures, showing a dramatically higher burden of mortality in countries with older versus younger populations. Bilgili et al. (2021) find that the shares of median age, age 65, and age 70 and older population have significant positive impacts on the spread of Covid-19 and that the share of age 70 and older people in the population has a relatively greater influence on the spread of the pandemic. Blyuss and Kyrychko (2021) use an age-structured version of a SEIR-type model, which allows the inclusion of more accurate data on age-specific rates of hospitalisation and Covid-related mortality. Monod et al. (2021) find that adults aged 20 to 34 and 35 to 49 have sustained Covid-19 transmission in the US, with reproduction numbers consistently above one.
The last variable to be used here is the number of tests, which may have contrasting effect on the infection rate and mortality rates. Massive testing, followed by the isolation of infected people, should reduce the infection and consequently the mortality rate. On the other hand, more testing reveals more (hidden) cases. By using panel data, Razzak (2020) finds “reasonable evidence” indicating that testing for the virus reduces death. More specifically, he finds that, on average, a one percent increase in daily testing reduces the number of deaths by about 4 a day. Pilecco et al. (2021) find low correlation between the number of tests and the mortality rate. Mercer and Salit (2021) argue that countries with high testing rates were able to control transmission effectively during the initial stages of the pandemic. Cohen and Leshem (2021) show that for small new outbreaks, controlled testing can prevent the large spread of new waves.
4. Methodology
In a typical cross-sectional study, when a large number of explanatory variables are available, the starting point is a regression of the form
Following the examination of the results obtained from the full regression, it is highly tantalising to try various combinations of the explanatory variables and report the one or ones that tell a good story. The objective is typically to find as many significant coefficients as possible, except that significance is sought from a single regression chosen out of possibly hundreds that are estimated in an exercise of data mining. Young and Holsteen (2017) argue that theory rarely says which variables should appear in the model, suggesting that “theory can be tested in many different ways and modest differences in methods may have large influence on the results”. Gilbert (1986) argues on similar grounds, suggesting that published results are accepted because the reported regression equation has coefficients that are correctly signed and statistically significant. However, he notes that these significant coefficients cannot be taken as evidence for or against the hypotheses under investigation, wondering about the other 999 regressions assigned to the bin.
To circumvent this problem, Leamer (1983, 1985) proposed extreme bounds analysis (EBA), which is a sensitivity analysis that enables the selection of the explanatory variables to be included in empirical models. A simple form of EBA involves the estimation of a series of regressions where each of the potential explanatory variables is treated in turn as the variable of interest. For each variable of interest, a large number of regressions are run, with different combinations of
h variables out of the remaining
, such that
. Instead of estimating one equation, or estimating many and deriving inference from one only, this procedure requires the estimation of
m equations per variable of interest, such that
If
is the variable of interest, then for given values of
n and
h, the first and last equations are
and
In EBA, inference is based on the estimated coefficient, , not from one equation, but rather from the whole set of values derived from the m estimated equations.
According to Leamer’s EBA, the variable of interest (
in equations 6 and 7) is a robust determinant of
Y if the coefficient
does not change sign and significance. This is a rather difficult test to pass, particularly for high values of
n, because if the coefficient changes sign and/or significance in one out of thousands of regressions, the variable is deemed fragile (the one rotten apple critique).
2 The emphasis, however, shifts from significance (in one estimated equation) to robustness (in a large set of estimated equations).
To deal with the excessive stringency of Leamer’s EBA, which also overlooks the distribution of , Sala-i-Martin (1997) has come up with an alternative EBA test. This test involves the same procedure and number of regressions, but the criterion used to determine robustness is different. For this purpose, the entire distribution of is analysed to determine the fraction of the cumulative distribution function (CDF) lying on each side of zero, CDF(0). If at least 95% of the CDF lies on either side of zero, the variable is considered robust—otherwise, it is fragile.
This methodology is adequate for the issue under consideration. For one thing we are not attempting to identify and measure all of the potential explanatory variables. For example, an important variable pertains to lockdown, social distancing, quarantine, border closure, etc. It is not an easy task to find a unified representation of these factors because they vary drastically in terms of form, severity and timing. The second consideration is that finding an exhaustive list of the potential explanatory variables is not possible. For example, Klees (2016) believes that “all relevant variables that may affect the dependent variable can never be included”. Meng (2019) refers to “an unknown number of relevant factors”, some of which may be unknown to the economist, making it impossible to claim that all important variables are included in the model. Instead, this methodology allows us to execute two humble but realistic and feasible tasks. The first is to rank (in terms of importance) the variables that affect the infection and mortality rates in developing and developed countries. The second is to find out if common factors are important for the determination of the severity of Covid-19 in both developing and developed countries.
5. Data and Stylised Facts
The empirical results are based cross-sectional data covering 148 countries. The IMF classification is used to divide the sample into a sub-sample for developed countries (33) and another for developing countries (115). The definitions of the variables and data sources can be found in
Table 1. Data on the numbers of cases and deaths were recorded up to the end of August 2021. We have two dependent variables: the infection rate (
Y1), measured as the number of cases per million, and the case mortality rate (
Y2), measured as the ratio of deaths to cases. The eleven explanatory variables are
X1,…..,
X11 as defined in the
Table 1.
To start with, the data show that the infection rate and case mortality rate do not go together.
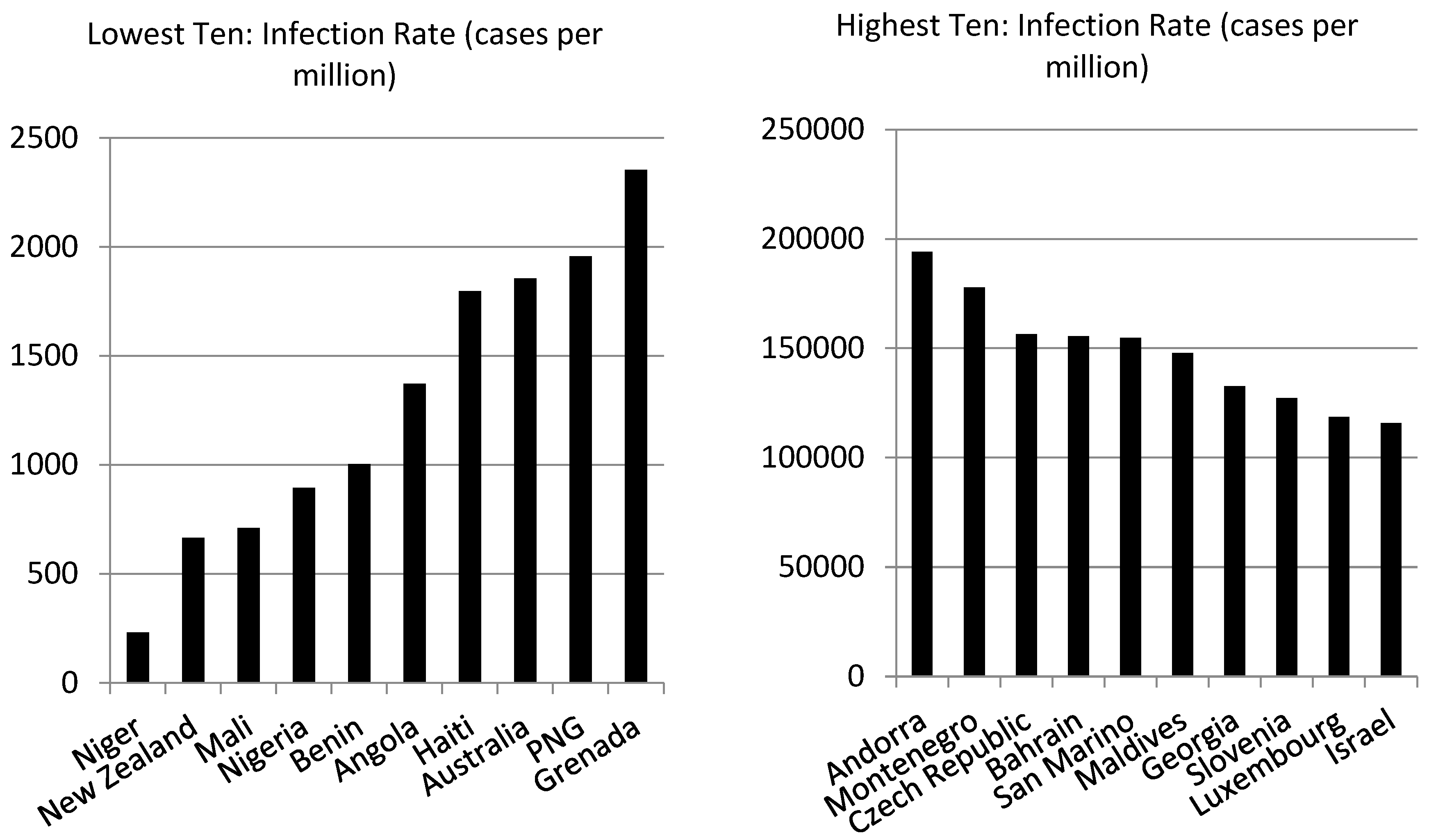
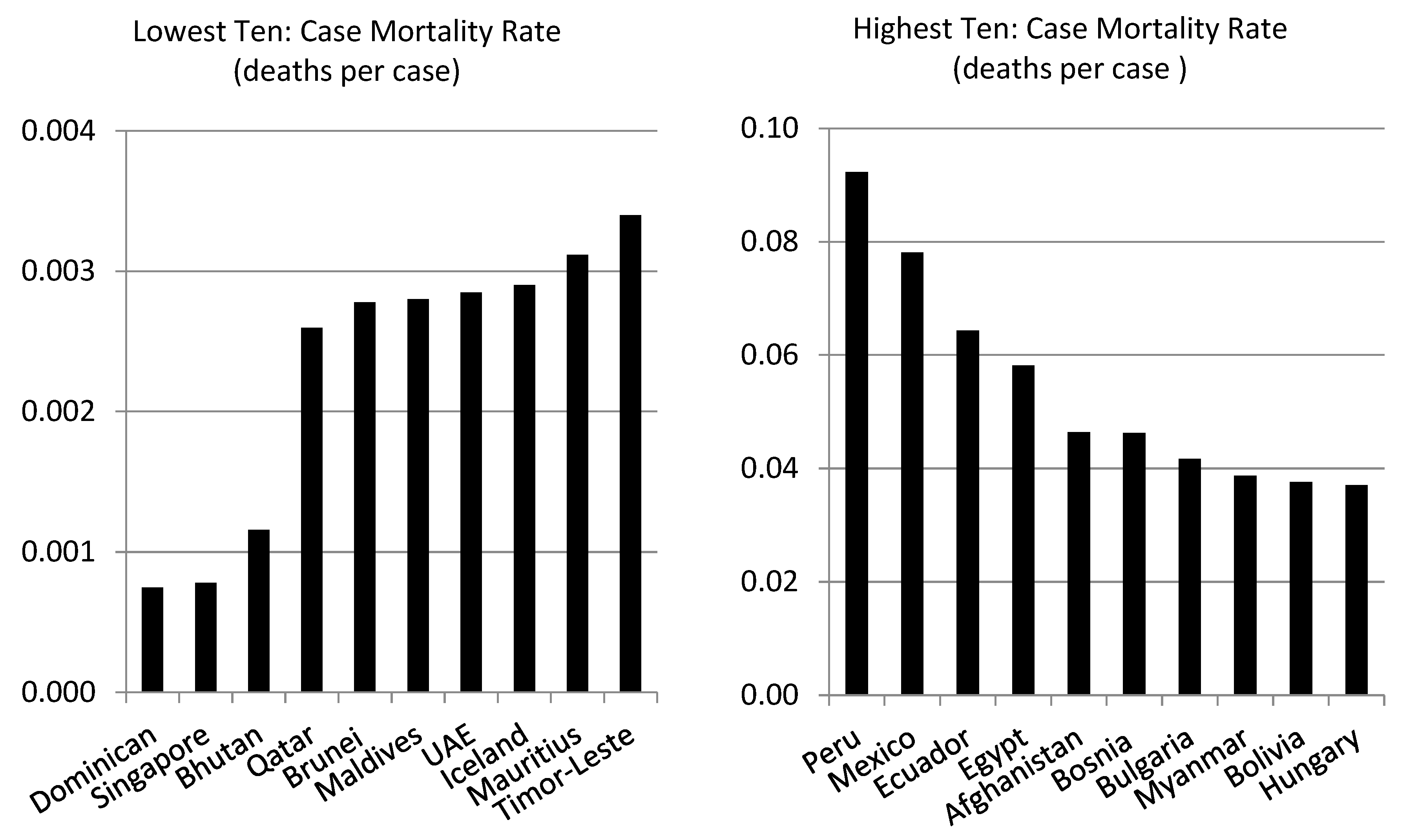
Table 2 contains examples of countries with high infection rates, and vice versa. Out of 148 countries, Angola has the highest infection rate, but ranks 25 in terms of the mortality rate. On the other extreme, Niger has the lowest infection rate but ranks 133 in terms of the mortality rate.
Consider now the US and UK, which have high infection and mortality rates, even though they rank highly in terms of preparedness for pandemics. At the end of August 2021, the UK was ranked 126 in terms of the infection rate, with 97,083 cases per million, while the US was at 138, with 114,813 cases per million. In terms of the mortality rate, the UK was ranked 90, with 0.020 deaths per case while the US was ranked 73, with 0.017 deaths per case. A question that arises here is why the performance of the US and UK has been worse than that of some developing (even impoverished) countries such as Haiti (in terms of infections) and the Maldives (in terms of mortality). We have already seen why the US and UK provide two prominent cases of mishandling the crisis. The other implication is that factors other than the level of development and availability of resources play a role in spreading the virus.
Table 3 displays comparative statistics of infection and mortality rates in developed and developing countries. We can see that, on average, developed countries have higher infection rates than developing countries (just over 72,000 infections per million compared to just over 42,000). The mortality rate, on the other hand, is lower in developed countries (1.5% compared to 2.1%). Cross-country variation in the two rates (measured by the coefficient of variation) is, as expected, higher in developing countries.
Table 4 shows how developed and developing countries compare with respect to the infection rate, mortality rate and the eleven factors envisaged to determine the two rates. The comparison is based on the numbers of developed and developing countries included in the lowest and highest ten, with respect to each variable. We can see that most countries in the lowest ten infection and mortality rates are developing countries, but 6 out of 10 countries that have the highest infection rate are developing countries and so are 9 out of ten countries with respect to the mortality rate.
Figure 1 shows the individual countries in the lowest and highest ten. Developing countries fall predominantly in the lowest 10 with respect to all explanatory variables, except population density.
6. Empirical Results
The EBA results are presented in
Table 5, which reports the percentage of the cumulative distribution function lying on one side of zero, CDF(0). For each variable of interest, we run 120 regressions, each of which contains a unique combination of the remaining explanatory variable. No free variable is employed because this is a new strand of research, as Covid-19 is still a new phenomenon. For an explanatory variable to be a robust determinant of the dependent variable at the 5% significance level, the condition
must be satisfied.
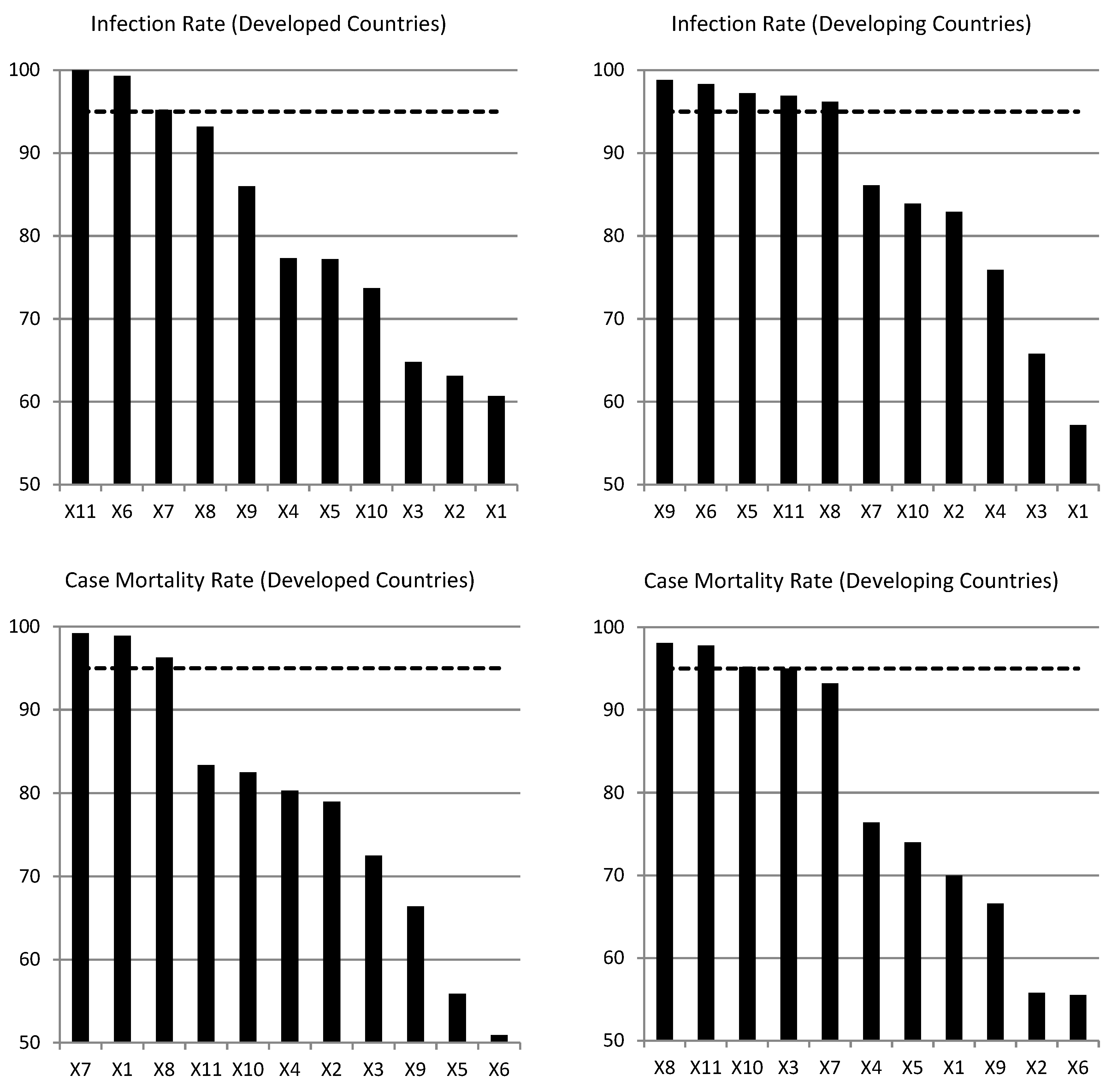
Consider first the infection rate, measured as cases per million of the population. For developed countries, the robust variables are the risk environment, population density and tests per million. For developing countries, the robust variables are compliance with international norms, the risk environment, population over 65, urban population and the number of tests. While, as expected, different robust variables determine the infection rates in developed and developing countries, the two common factors are the risk environment and the number of tests per million. As for the mortality rate, the robust determinants for developed countries are prevention, population density and population over 65. For developing economies, the robust determinants of the mortality rate are rapid response, population over 65, time since the first case and the number of tests. In this case, the only common factor is population over 65, which makes a lot of sense.
Robust variables can be ranked in terms of importance with respect to their impact on the infection and mortality rates. In
Figure 2 we can see the 11 explanatory variables ranked according to CDF(0), with a dotted line at 95% to identify the robust variables. The most important determinant of the infection rate for developed countries is the number of tests and the least important is prevention. For developing countries, on the other hand, the most and least important determinants of the infection rate are urban population and prevention, respectively. As for the mortality rate, the most and least important determinants for developed countries are population density and the risk environment, respectively. For developing countries, they are population over 65 and detection and reporting, respectively.
Overall, the infection and mortality rates do not depend on the same factors in developed as in developing countries, but two common factors turn out to be the risk environment and the number of tests for the infection rate. Population over 65 is the common factor for the mortality rate, which makes a lot of sense. Determinants of the infection rate that are important for developing countries, but not for developing ones, are compliance with international norms and urban population. This is probably because developed countries tend to be more compliant with international norms and because urban centres in developed countries are more equipped to deal with a pandemic than their counterparts in developing countries. As far as the mortality rate is concerned, factors that appear robust in developing countries only are rapid response, time since first reported case and tests per million.
7. Concluding Remarks
The message conveyed by the results obtained from the empirical analysis presented in this paper are that different characteristics of developed and developing countries lead to differences in the factors that determine the severity of Covid-19, where severity is measured by the infection rate (cases per million) and the case mortality rate (deaths per case). Yet, some common factors emerge, including the risk environment and the number of tests for the infection rate, and the percentage of population over 65 for the mortality rate. A caveat that must be borne in mind is that the term “developing countries” covers countries that are much more diversified than those covered by the term “developed countries”. Still, the analysis is based on the IMF’s classification of countries into developing and developed. Perhaps a more disaggregated classification will produce more revealing results.
We must also bear in mind some data-related problems, particularly with respect to the numbers of confirmed cases and deaths. For example, the British government did not count deaths in aged care facilities and in people’s homes for weeks. Big divergence of case mortality rates, even among developed countries, raises suspicion about the accuracy of the data. This is perhaps because a large number of deaths are not attributed to Covid-19 when they should be. We cannot overlook the possibility of cover-ups in some countries. However, even if the official data represent a partial reflection of the truth, the results presented in this study provide useful information that may aid decision-making in the fight against the pandemic.
Notes
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
See, for example, the critique of Leamer’s EBA presented by McAleer et al. (1985) and the reply of Cooley and LeRoy (1986). |
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from public domain sources. These data were derived from the resources listed in
Table 1.
Funding Statement
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Appendix A. List of Developed Countries
| Australia |
Hungary |
Netherlands |
| Austria |
Iceland |
New Zealand |
| Belgium |
Ireland |
Norway |
| Canada |
Israel |
Portugal |
| Czech Republic |
Italy |
Singapore |
| Denmark |
Japan |
Slovak Republic |
| Estonia |
Korea |
Slovenia |
| Finland |
Latvia |
Sweden |
| France |
Lithuania |
Switzerland |
| Germany |
Luxembourg |
United Kingdom |
| Greece |
Malta |
United States |
Appendix B. List of Developing Countries
| Afghanistan |
Gabon |
Pakistan |
| Albania |
Gambia |
Panama |
| Algeria |
Georgia |
Papua New Guinea |
| Andorra |
Grenada |
Paraguay |
| Angola |
Guatemala |
Peru |
| Antigua |
Guinea-Bissau |
Philippines |
| Argentina |
Guyana |
Poland |
| Armenia |
Haiti |
Qatar |
| Azerbaijan |
Honduras |
Romania |
| Bahamas |
India |
Russian Federation |
| Bahrain |
Indonesia |
Rwanda |
| Bangladesh |
Iran |
San Marino |
| Barbados |
Iraq |
Sao Tome and Principe |
| Belarus |
Jamaica |
Saudi Arabia |
| Belize |
Jordan |
Senegal |
| Benin |
Kazakhstan |
Serbia |
| Bhutan |
Kenya |
South Africa |
| Bolivia |
Kyrgyz Republic |
Sri Lanka |
| Bosnia |
Lebanon |
St. Vincent |
| Botswana |
Libya |
Suriname |
| Brazil |
Liechtenstein |
Thailand |
| Brunei |
Malawi |
Timor-Leste |
| Bulgaria |
Malaysia |
Togo |
| Cabo Verde |
Maldives |
Trinidad and Tobago |
| Cambodia |
Mali |
Tunisia |
| Chile |
Mauritania |
Turkey |
| Colombia |
Mauritius |
Uganda |
| Costa Rica |
Mexico |
Ukraine |
| Croatia |
Moldova |
United Arab Emirates |
| Cuba |
Mongolia |
Uruguay |
| Djibouti |
Montenegro |
Uzbekistan |
| Dominica |
Morocco |
Venezuela |
| Dominican Republic |
Mozambique |
Vietnam |
| Ecuador |
Myanmar |
Zambia |
| Egypt |
Namibia |
Zimbabwe |
| El Salvador |
Nepal |
|
| Equatorial Guinea |
Niger |
|
| Eswatini |
Nigeria |
|
| Ethiopia |
North Macedonia |
|
| Fiji |
Oman |
|
References
- Acuto, M. (2020) COVID-19: Lessons for an Urban(izing) World, One Earth. doi: 10.1016/j.oneear.2020.04.004. [CrossRef]
- Barr, J.M. and Tassier, T. (2020a) Modeling the Impact of Density on the Spread of the Corona Virus, Working Paper, 3 April. https://buildingtheskyline.org/wp-content/ uploads/2019/10/Theory-and-Empirical-Model-6April20.pdf.
- Barr, J.M. and Tassier, T. (2020b) Escape from New York? Density and the Coronavirus Trajectory, 20 April. https://buildingtheskyline.org/covid19-and-density/.
- Bell, J. (2020) The U.S. and COVID-19: Leading the World by GHS Index Score, Not by Response, 21 April. https://www.nti.org/analysis/atomic-pulse/us-and-covid-19-leading-world-ghs-index-score-not-response/.
- Bilgili, F., Dundar, M., Kuşkaya, S., Lorente, D.B., Ünlü, F., Gençoğlu, P., and Muğaloğlu, E. (2021) The Age Structure, Stringency Policy, Income, and Spread of Coronavirus Disease 2019: Evidence From 209 Countries, Frontiers in Psychology, 12 February. [CrossRef]
- Blyuss, K.B. and Kyrychko, Y.N. (2021) Effects of Latency and Age Structure on the Dynamics and Containment of COVID-19, Journal of Theoretical Biology (published online, 21 March). [CrossRef]
- Brumfiel, G. and Wilburn, T. (2020) Countries Slammed their Borders Shut to Stop Coronavirus. But Is It Doing Any Good?, NPR, 15 May.
- Calvert, J., Arbuthnott, G. and Leake, J. (2020) Coronavirus: 38 Days when Britain Sleepwalked into Disaster, Sunday Times, 19 April.
- Chaudhry, R., Dranitsaris, G., Mubashir, T., Bartoszko, J. and Riazi, S. (2020) A Country Level Analysis Measuring the Impact of Government Actions, Country Preparedness and Socioeconomic Factors on COVID-19 Mortality and Related Health Outcomes, Lancet Regional Health, 1 August.
- Cohen, K. and Leshem, A. (2021) Suppressing the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic Using Controlled Testing and Isolation, Scientific Reports, 11, 6279. [CrossRef]
- Cooley, T.F. and LeRoy, S.F. (1986) What will Take the Con Out of Econometrics? A Reply to McAleer, Pagan, and Volker, American Economic Review, 76, 504-507.
- Desai, D.D. (2020) Urban Densities and the Covid-19 Pandemic: Upending the Sustainability Myth of Global Megacities, ORF Occasional Papers, No. 244.
- Dowda, J.B., Andrianoa, L., Brazela, D.M., Rotondia, V., Blocka, P., Dinga, X. and Millsa, M.C. (2020) Demographic Science Aids in Understanding the Spread and Fatality Rates of COVID-19, PNAS, 5 May. https://www.pnas.org/content/117/18/ 9696.
- Fang, W. and Wahba, S. (2020) Urban Density is not an Enemy in the Coronavirus Fight: Evidence from China. World Bank Blogs, 20 April. https://blogs.worldbank.org/ sustainablecities/urban-density-not-enemy-coronavirus-fight-evidence-china.
- Florida, R. (2020) The Geography of Coronavirus, 3 April. https://www.citylab.com/equity/ 2020/04/coronavirus-spread-map-city-urban-density-suburbs-rural-data/609394/.
- Gilbert, C.L. (1986) Professor Hendry’s Econometric Methodology, Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics, 48, 283-307.
- Hu, H., Nigmatulina, K. and Eckhoff, P. (2013) The Scaling Of Contact Rates With Population Density For The Infectious Disease Models, Mathematical Biosciences, 244, 125-134. [CrossRef]
- Jerving, S. (2020) How Effective are Travel Restrictions? A Look at Approaches to Contain Coronavirus, Devex, 28 February.
- Jo, Y., Hong, A. and Sung, H. (2021) Density or Connectivity: What are the Main Causes of the Spatial Proliferation of COVID-19 in Korea? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18, 5084.
- Khan, I., Iftikhar, M.N. and Ali, S.H. (2021) Cities and COVID-19: Navigating the New Normal, Global Sustainability (published online, 9 March). [CrossRef]
- Klees, S.J. (2016) Inferences from Regression Analysis: Are they Valid? Real-World Economics Review, 74, 85-97.
- Leamer, E. (1983) Let’s Take the Con Out of Econometrics, American Economic Review, 73, 31-43.
- Leamer, E. (1985) Sensitivity Analyses Would Help, American Economic Review, 75, 308-13.
- Li, R., Richmond, P. and Roehner, B. (2018) Effect of Population Density on Epidemics, Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 510, 713-724.
- Lipson, D. (2020) This is Where They Went Wrong, ABC News, 20 May.
- Loayza, N.V. and Pennings, S. (2020) Macroeconomic Policy in the Time of COVID-19: A Primer for Developing Countries, Research & Policy Brief No. 28, World Bank.
- Lowy Institute (2021) Covid Performance Index: Deconstructing Pandemic Responses, January. https://interactives.lowyinstitute.org/features/covid-performance/.
- Martins-Filho, P.R. (2021) Relationship between Population Density and COVID-19 Incidence and Mortality Estimates: A County-Level Analysis, Journal of Infection and Public Health, 14, 1087–1088. [CrossRef]
- Maybery, P. (1999) The Effects of Population Density on the Spread of Disease, Texas Medical Center Dissertations. https://digitalcommons.library.tmc.edu/dissertations/ AAI9929469.
- McAleer, M., Pagan, A.R. and Volker, P.A. (1985) What will Take the Con out of Econometrics? American Economic Review, 75, 293-307.
- McFarlane, C. (2021) Repopulating Density: COVID-19 and the Politics of Urban Value, Urban Studies (published online, 9 June).
- Meng, S. (2019) Patentism Replacing Capitalism: A Prediction from Logical Economics, New York: Palgrave-Macmillan.
- Mercer, T.R. and Salit, M. (2021) Testing at Scale During the COVID-19 Pandemic, Nature Reviews Genetics, 22, 415–426. [CrossRef]
- Monod, M. et al. (2021) Age Groups that Sustain Resurging COVID-19 Epidemics in the United States, Science, 26 March. [CrossRef]
- Moosa, I.A. (2021) The Economics of Covid-19: Implications of the Pandemic for Economic Thought and Public Policy, Cheltenham: Edward Elgar.
- Moosa, I.A. and Khatatbeh, I.N. (2020) International Tourist Arrivals as a Determinant of the Severity of Covid-19: International Cross-Sectional Evidence, Journal of Policy Research in Tourism, Leisure and Events (published online, 17 December). [CrossRef]
- Moosa, I.A. and Khatatbeh, I.N. (2021a) Robust and Fragile Determinants of the Infection and Case Fatality Rates of Covid-19: International Cross-Sectional Evidence, Applied Economics, 53, 1225-1234. [CrossRef]
- Moosa, I.A. and Khatatbeh, I.N. (2021b) The density paradox: Are densely-populated regions more vulnerable to Covid-19?, International Journal of Health Planning and Management (published online, 18 May).
- O’Grady, C. (2020) The U.K. Backed off on Herd Immunity, National Geographic, 20 March.
- Phillips, T. (2020) The Country is Adrift: Echoes of Spanish Flu as Brazil’s Covid-19 Catastrophe Deepens, The Guradian, 14 June.
- Pilecco, F.B. et al. (2021) The Effect of Laboratory Testing on COVID-19 Monitoring Indicators: An Analysis of the 50 Countries With the Highest Number of Cases, Epidemiol Serv Saude, 30(2):e2020722.
- Pillinger, M. (2020) Virus Travel Bans are Inevitable but Ineffective, Foreign Policy, 23 February.
- Razzak, W.A. (2020) Does Testing for Coronavirus reduce Deaths?, Massey University, Discussion Papers, No 20.05. https://www.massey.ac.nz/massey/learning/colleges/ college-business/school-of-economics-and-finance/research/discussion-paper-series.cfm.
- Sala-i-Martin, X. (1997) I Just Ran Two Million Regressions, American Economic Review, 87, 178-183.
- Stanhope, J. and Weinstein, P. (2020) Travel Restrictions and Evidence-Based Decision Making for Novel Epidemics, Medical Journal of Australia, 213, 431-431.
- Sumdani, H., Frickle, S., Le, M., Tran, M. and Zaleta, C.K. (2014) Effects of Population Density on the Spread of Disease, Technical Report 2014-05, University of Texas at Arlington.
- Sy, K.T.L., White, L.F. and Nichols, B.E. (2021) Population Density and Basic Reproductive Number of COVID-19 across United States Counties, PLOS ONE, 16(4): e0249271 (published online, 21 April). [CrossRef]
- Tarwater, P.M. and Martin, C.F. (2001) Effects of Population Density on the Spread of Disease, Complexity, 6, 29-36. [CrossRef]
- Verity, R. et al. (2020) Estimates of the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Model-Based Analysis, The Lancet Infectious Diseases. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/ laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(20)30243-7/fulltext.
- Walker, P.G.T. et al. (2020) The Global Impact of COVID-19 and Strategies for Mitigation and Suppression, Report 12, Imperial College, London.
- Wall, D. (2020) Britain: As COVID-19 Deaths Mount, Why is Boris Johnson Still Popular?, 21 April. https://www.greenleft.org.au/content/britain-covid-19-deaths-mount-why-boris-johnson-still-popular.
- Wells, C.R., Sah, P., Moghadas, S.M., Pandey, A. Shoukat, A., Wang, Y., Zheng, W., Meyers, L.A., Singer, B.H. and Galvani, A.P. (2020) Impact of International Travel And Border Control Measures on the Global Spread of the Novel 2019 Coronavirus Outbreak, PNAS, 117, 7504-7509.
- World Health Organization (2019) World Health Statistics 2019: Monitoring Health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals, Geneva. https://www.who.int/gho/ publications/world_health_statistics/2019/en/.
- World Health Organization (2020) Coronavirus: Overview. https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus.
- Young, C. and Holsteen, K. (2017) Model Uncertainty and Robustness: A Computational Framework for Multimodel Analysis, Sociological Methods and Research, 46, 3-40.
- Yu, W. and Keralis, J. (2020) Controlling COVID-19: The Folly of International Travel Restrictions, Health and Human Rights Journal, 6 April.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).