Submitted:
27 March 2023
Posted:
28 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Secondly, with the help of α-relation on conditional attributes and equivalence relation on decision attributes, the intuitionistic fuzzy nano lower approximation space, and intuitionistic fuzzy nano upper approximation space along with boundary regions are found.
- Thirdly, the certain and possible fuzzy rules are generated from two approximations.
2. Related Works
3. Problem Definitions
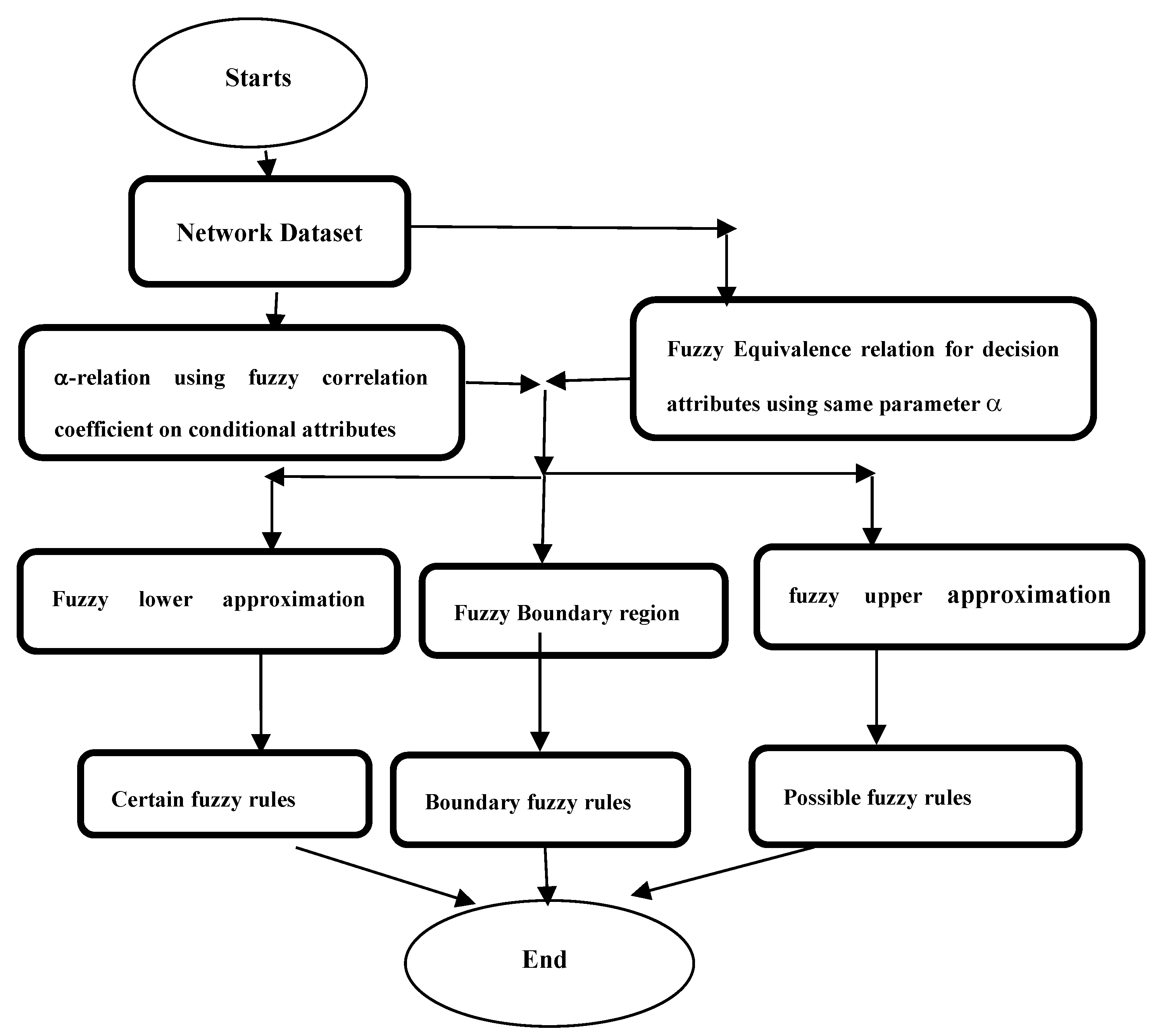
4. Proposed Algorithm
| Algorithm. |
| Input (U, C∪D), α // C, the conditional fuzzy attributes, D, the decision fuzzy attributes Step1. Create α-relation on C using correlation coefficient. Step2. Create the fuzzy equivalence relation for D. Step3. Apply ‘infimum’ operator on the fuzzy granules of records of U brought up by C. Step4. Construct separately nano lower approximation space () Nano upper approximation space for D and the result of fuzzy granules after applying ‘infimum’ to C. Step5. Find boundary regions. Step6. Generate certain fuzzy rules from Nano lower approximation space, possible fuzzy rules from Nano upper approximation, and boundary rules from boundary regions. |
5. Complexity Analysis
6. Experimental Analysis and Results.
- A.
- Datasets
- B.
- Experimental Results and Analysis
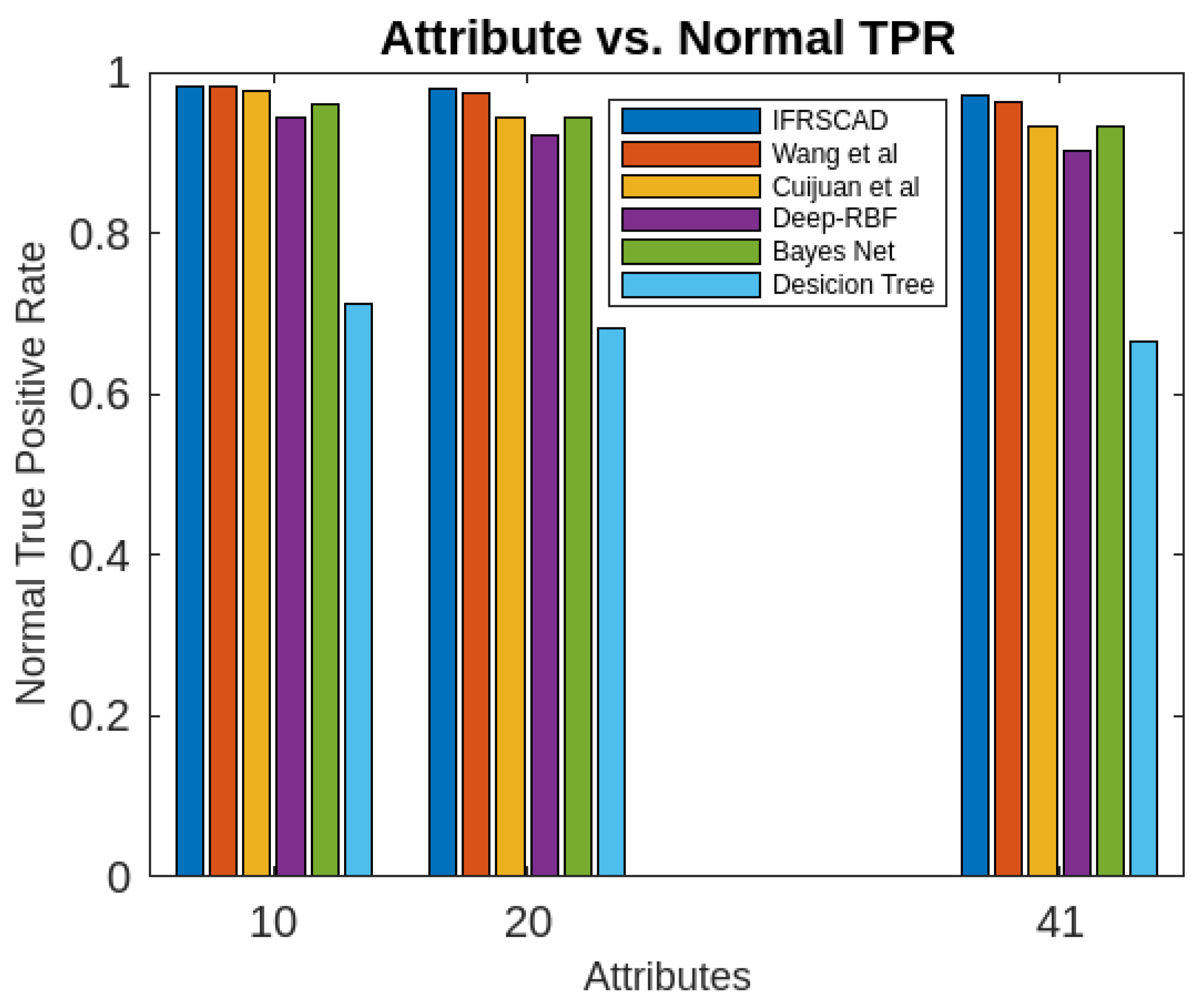
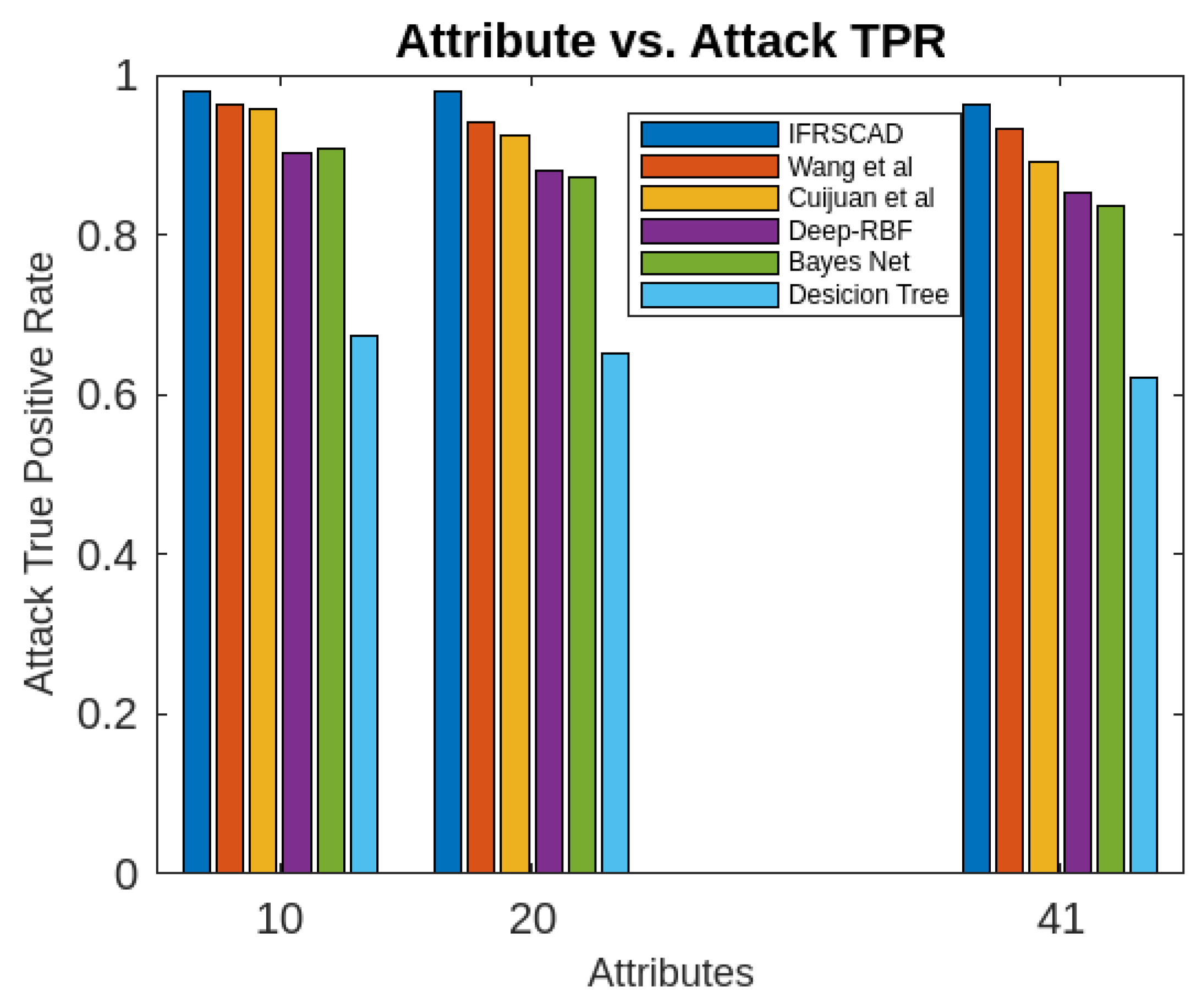
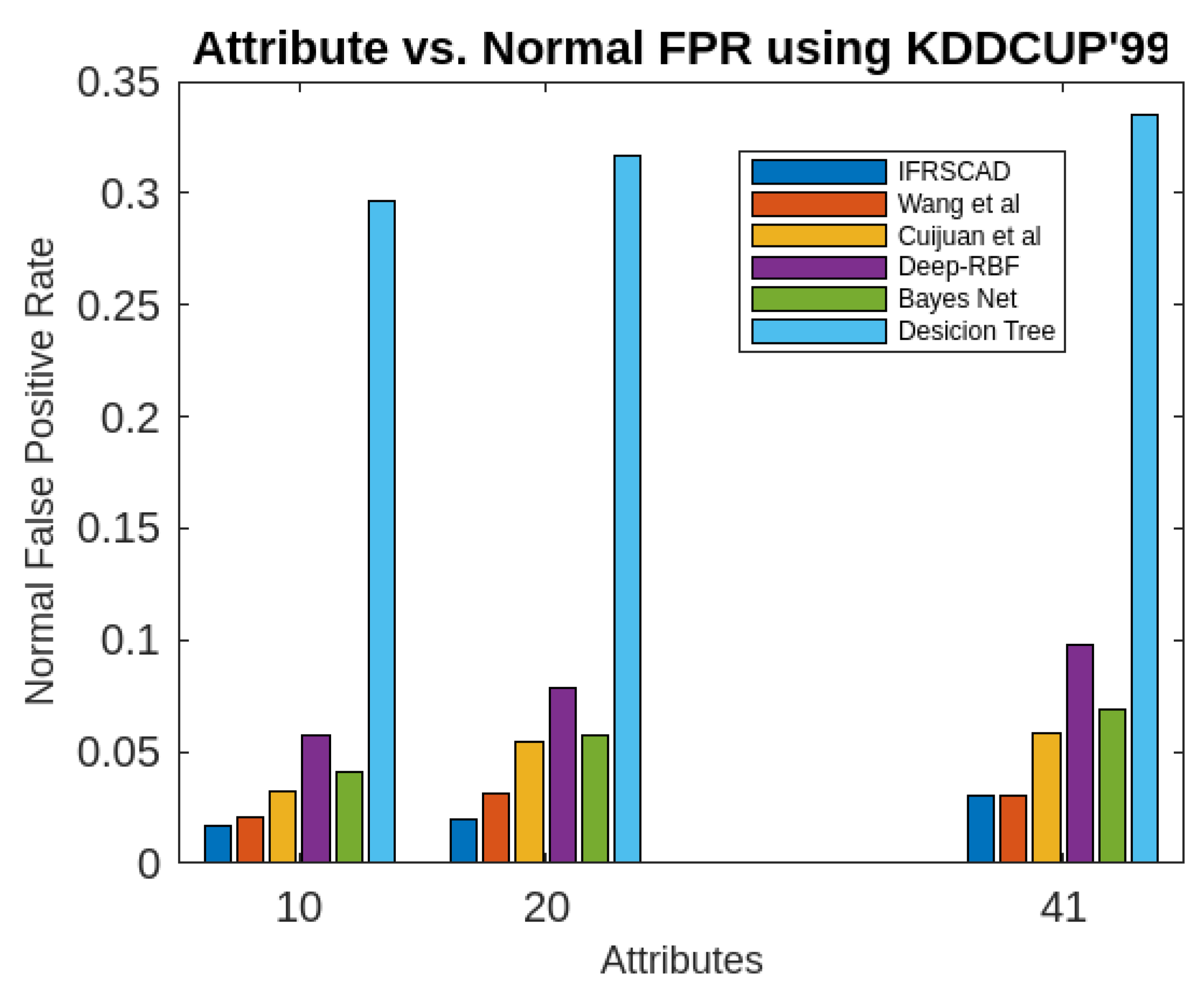
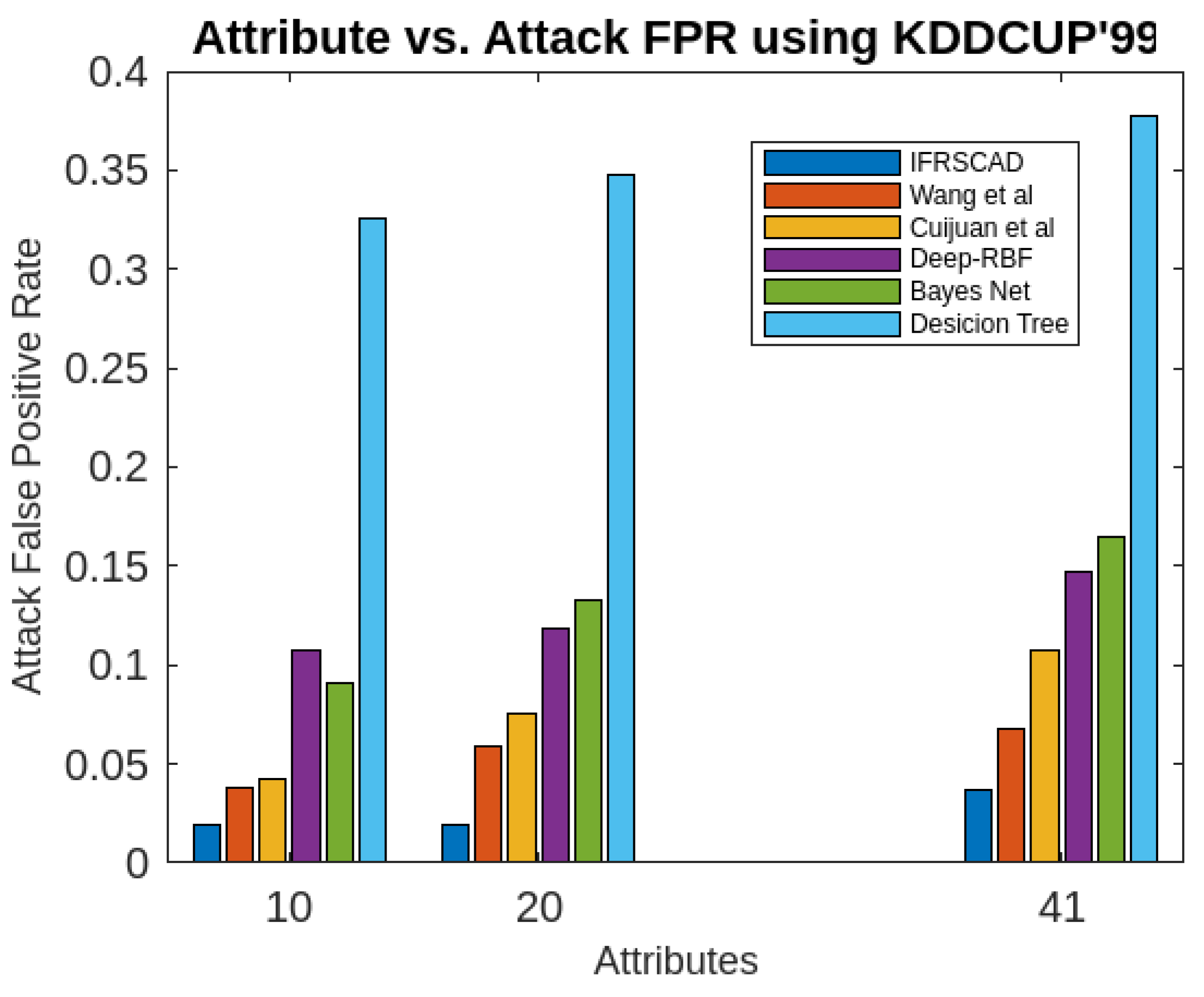
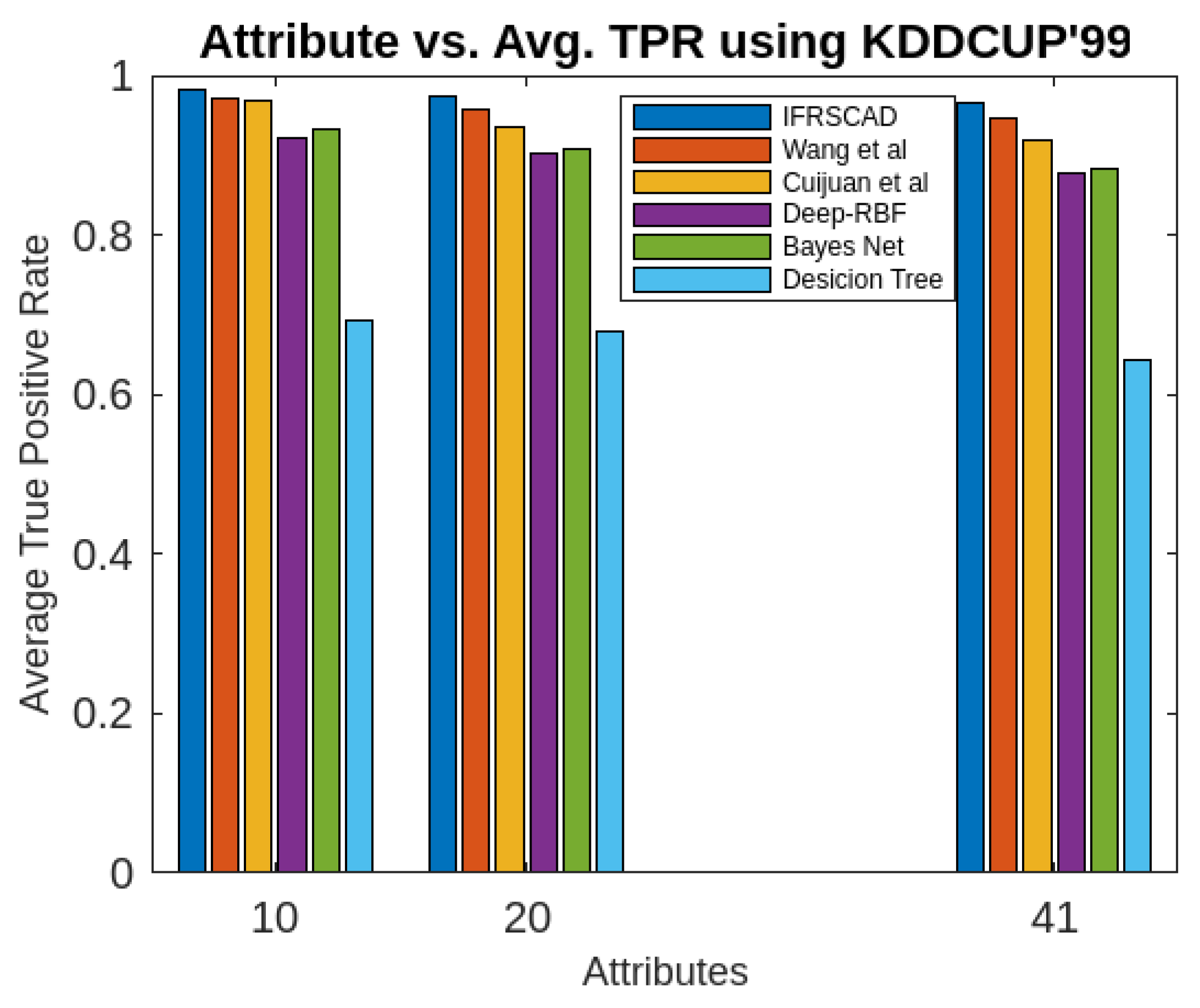
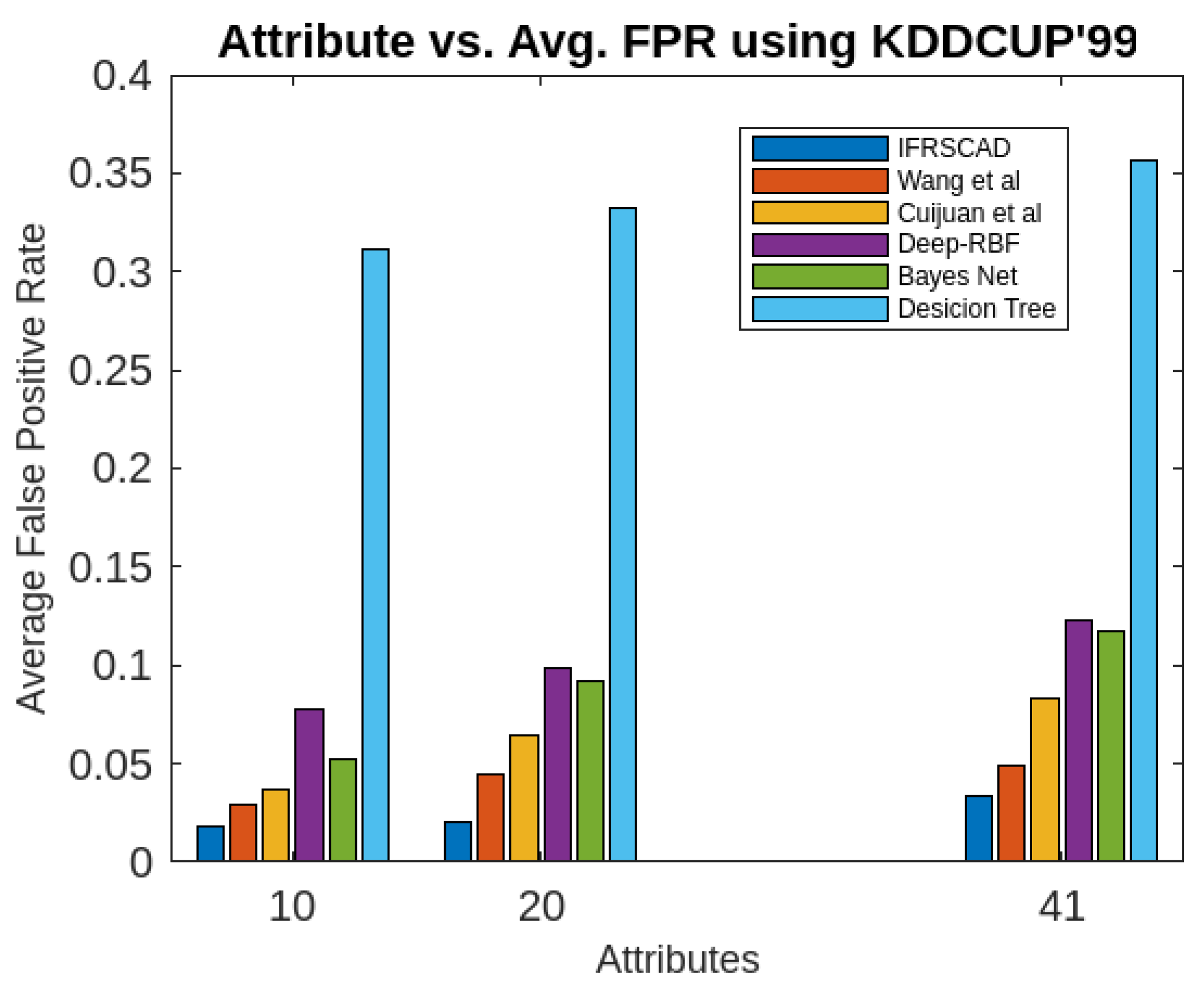
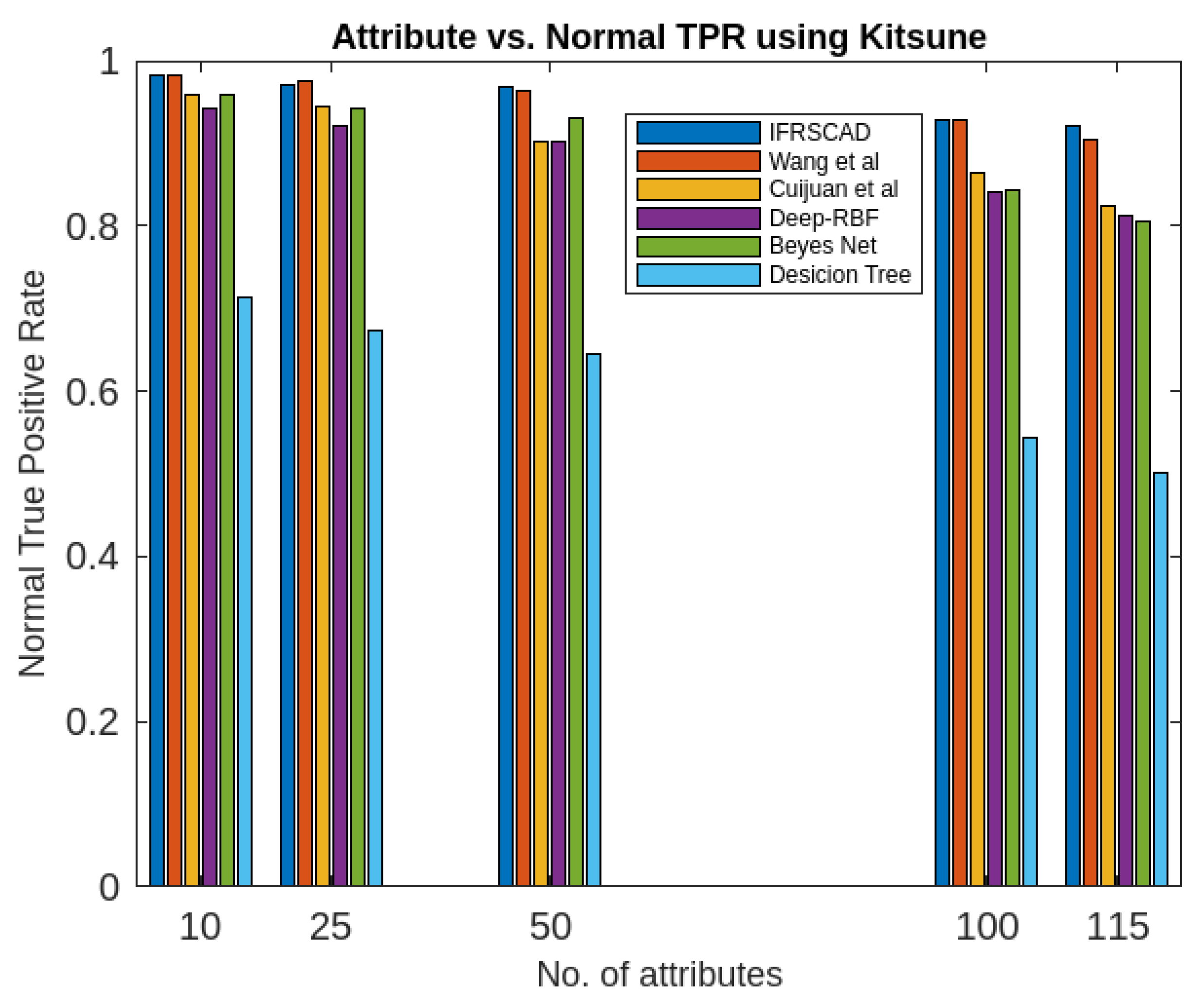
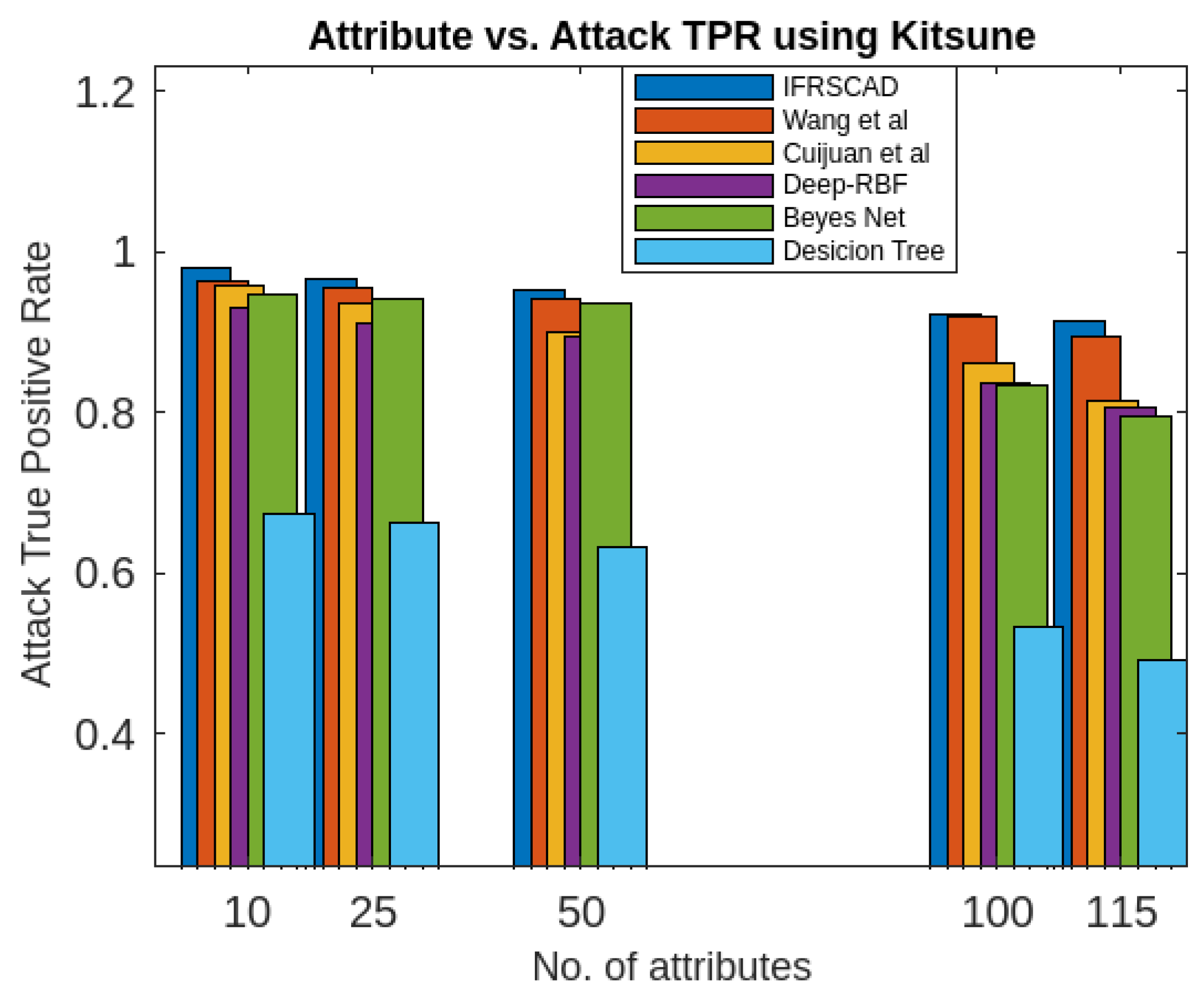
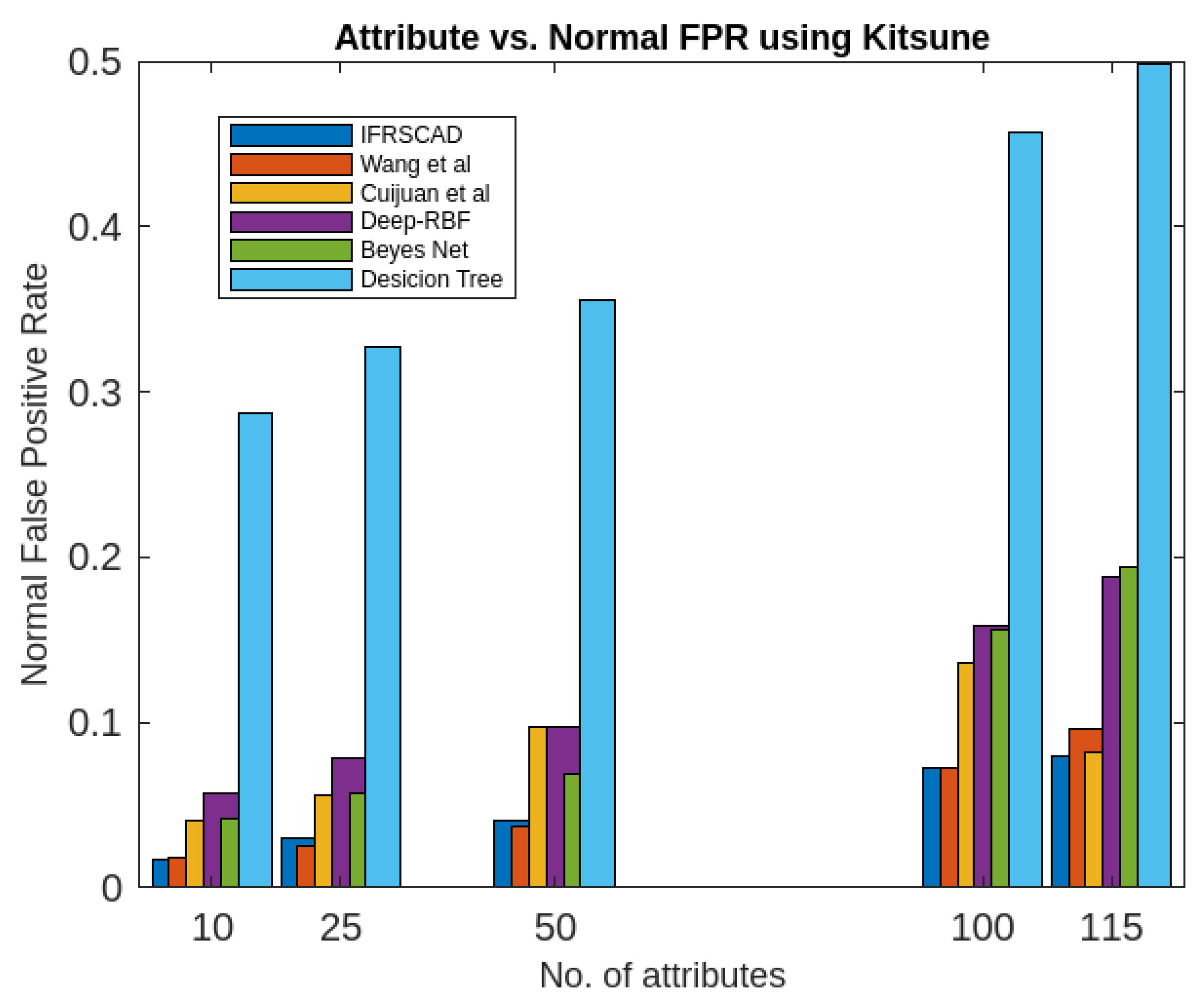
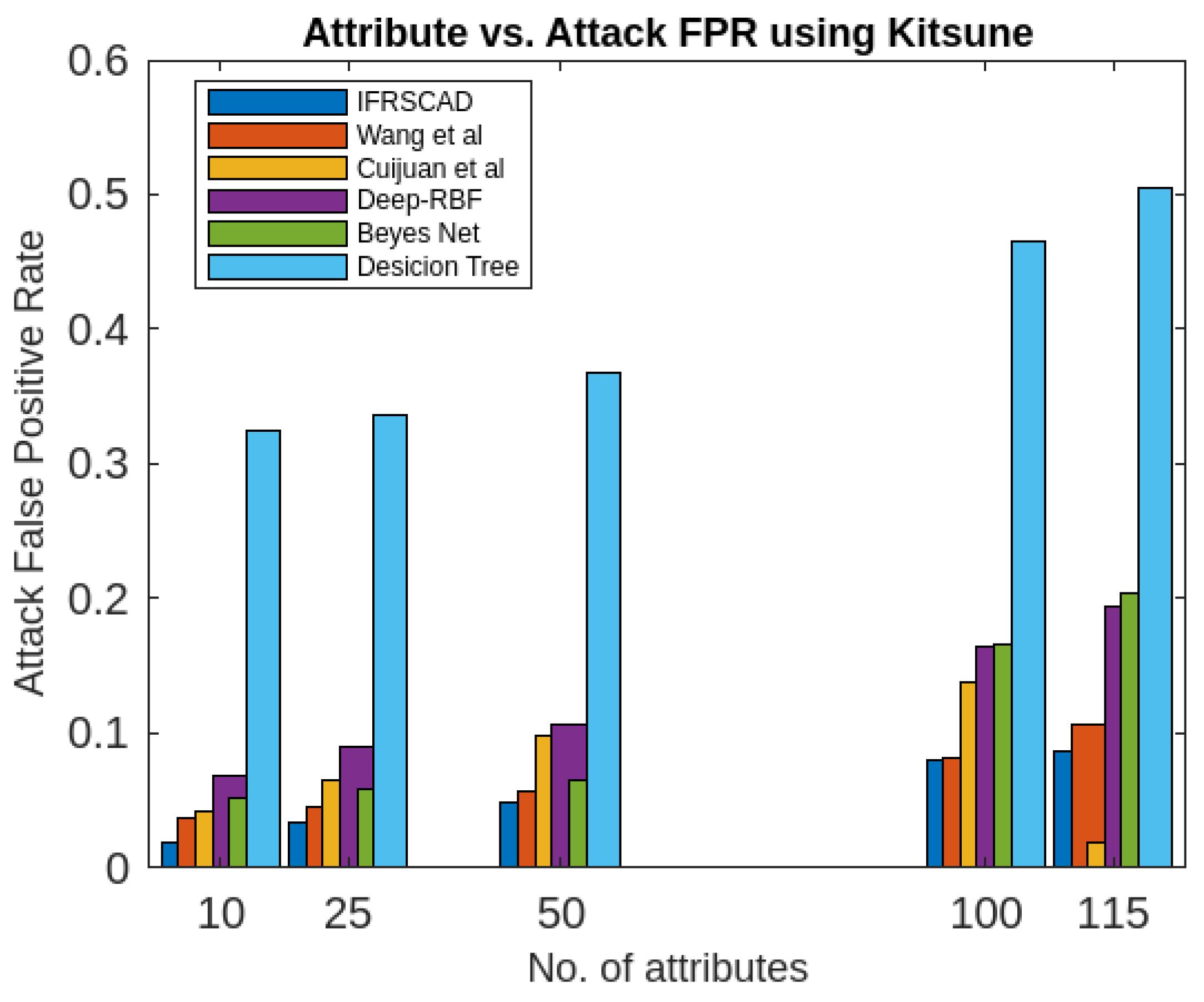
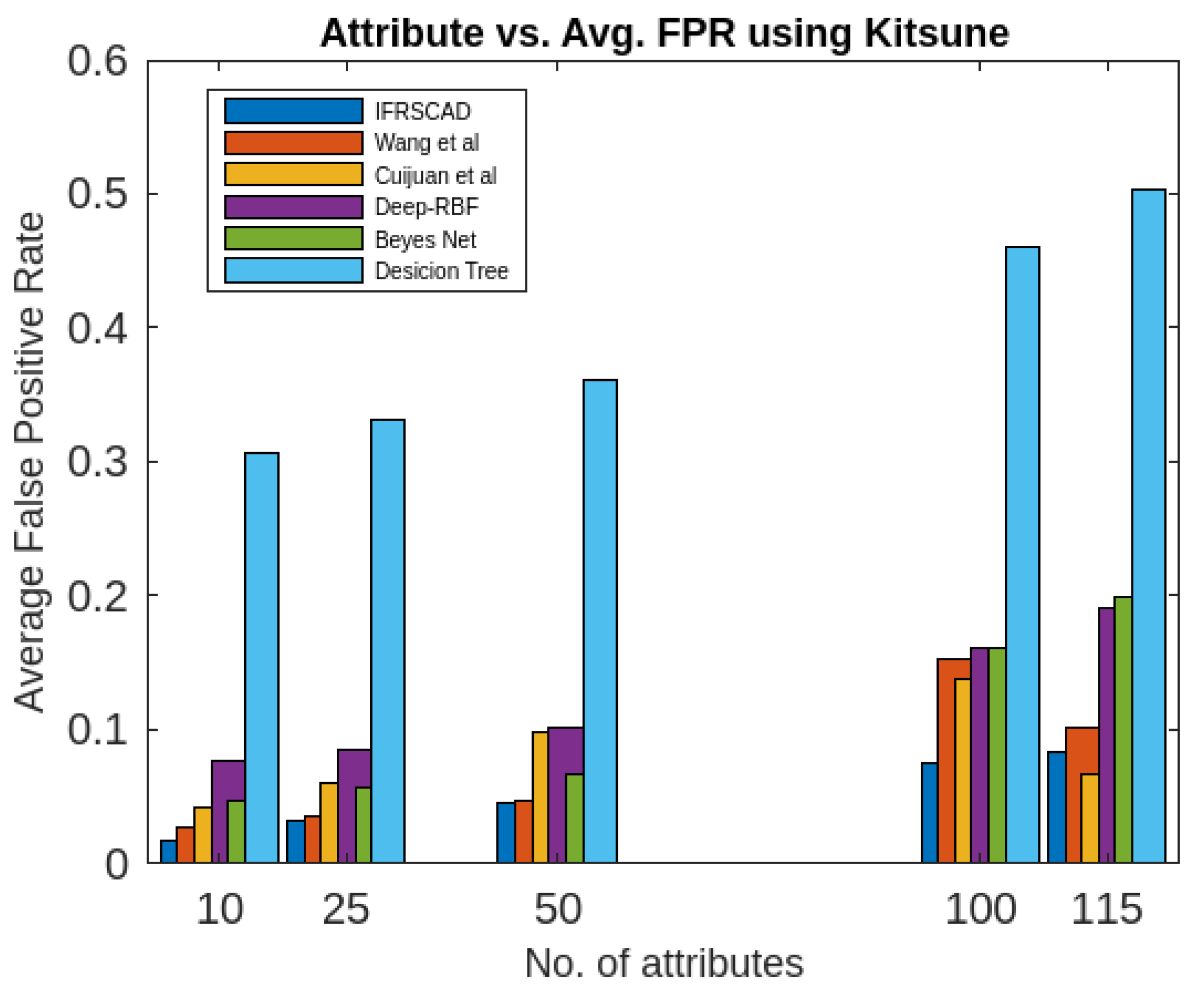
- The decision tree-based algorithm [13] has poorest detection rate. It has 71.31-66.45% of Normal TPR, 67.44-62.23% of Attack TPR, 29.69-33.51% of Normal FPR, and 32.56-37.71% of Attack FPR for ascending order of attribute sizes (from 10-41) of dataset KDDCUP’99 [44]. Similarly, it has 71.31-50.12% of Normal TPR, 67.45-49.34% of Attack TPR, 28.69-49.88% of Normal FPR, and 32.56-50.56% of Attack FPR for ascending order of attribute sizes (from 10-115) of dataset Kitsune [45]. It shows the algorithm has poorest performances and which decreases with the increase in dimension size of the dataset.
- Deep-RBF Network-based algorithm [15] is better than the decision tree-based algorithm [13] and It has 94.25-90.24% of Normal TPR, 90.23-85.25% of Attack TPR, 5.75-9.75% of Normal FPR, and 9.75-14.75% of Attack FPR for ascending order of attribute sizes (from 10-41) of dataset KDDCUP’99 [44]. Similarly, it has 94.25-81.21% of Normal TPR, 93.11-80.56% of Attack TPR, 9.75-18.79% of Normal FPR, and 9.73-19.44% of Attack FPR for ascending order of attribute sizes (from 10-115) of dataset Kitsune [45].
- Bayes Network-based algorithm [14] is better than Decision tree based algorithm [13] and Deep-RBF Network-based algorithm [15] in terms of detection rates. It has 85.87-93.13% of Normal TPR, 90.87-83.49% of Attack TPR, 4.13-6.87% of Normal FPR, and 9.136-16.51% of Attack FPR for ascending order of attribute sizes (from 10-41) of dataset KDDCUP’99 [44]. Similarly, it has 95.87-80.55% of Normal TPR, 94.8-79.53% of Attack TPR, 4.13-19.45% of Normal FPR, and 5.20-20.47% of Attack FPR for ascending order of attribute sizes (from 10-115) of dataset Kitsune [45]. Although the algorithm is quite efficient but its performance decreases with the increase in the dimension of datasets.
- Cuijuan et al’s algorithm [16] is better than all the previous three algorithms as per as detection rates is concern. It has 97.75-93.25% of Normal TPR, 95.25-89.25% of Attack TPR, 3.20-5.807% of Normal FPR, and 4.25-10.75% of Attack FPR for ascending order of attribute sizes (from 10-41) of dataset KDDCUP’99 [44]. Similarly, it has 95.95-82.32% of Normal TPR, 95.75-89.25% of Attack TPR, 4.05-8.132% of Normal FPR, and 4.25-18.58% of Attack FPR for ascending order of attribute sizes (from 10-115) of dataset Kitsune [45]. Its performance also decreases proportionately with the increase in the dimension of datasets.
- Wang et al’s algorithm [17] is the most efficient in comparison to all the aforesaid algorithms. It has 98.21-96.25% of Normal TPR, 96.21-93.25% of Attack TPR, 2.12-3.02% of Normal FPR, and 3.79-6.75% of Attack FPR for ascending order of attribute sizes (from 10-42) of dataset KDDCUP’99 [44]. Similarly, it has 98.20-90.44% of Normal TPR, 96.21-89.33% of Attack TPR, 1.79-9.56% of Normal FPR, and 3.79-10.67% of Attack FPR for ascending order of attribute sizes (from 10-115) of dataset Kitsune [45]. Its performance also decreases proportionately with the increase in the dimension of datasets.
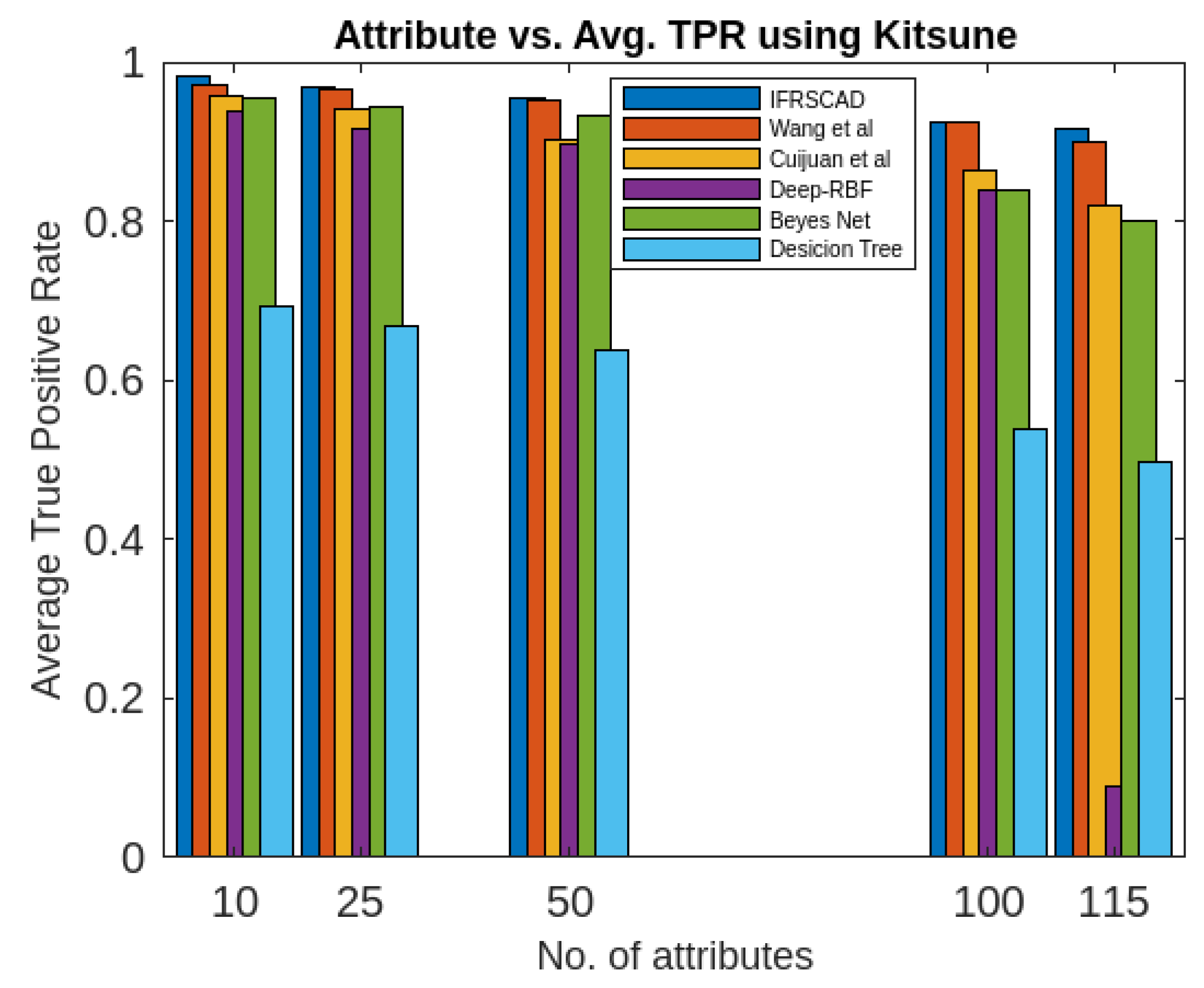
- The proposed algorithm (IFRSCAD) has 98.342-96.99% of Normal TPR, 98.04-96.29% of Attack TPR, 1.658-3.01% of Normal FPR, and 1.96-3.71% of Attack FPR for ascending order of attribute sizes (from 10-42) of dataset KDDCUP’99 [44]. Similarly, it has 98.351-91.989% of Normal TPR, 98.02-91.289% of Attack TPR, 1.658-8.011% of Normal FPR, and 1.96-8.711% of Attack FPR for ascending order of attribute sizes (from 10-115) of dataset Kitsune [45]. Its performance also decreases proportionately with the increase in the dimension of datasets. It is clear from the data that the proposed algorithm has more TPR and less FPR. The differences between Normal TPR and Attack TPR, Normal FPR and Attack FPR are also less in comparison other methods. The performance decrement is less with the increase in dimensions. Obviously, the proposed algorithm has mores average TPR and less average FPR than others.
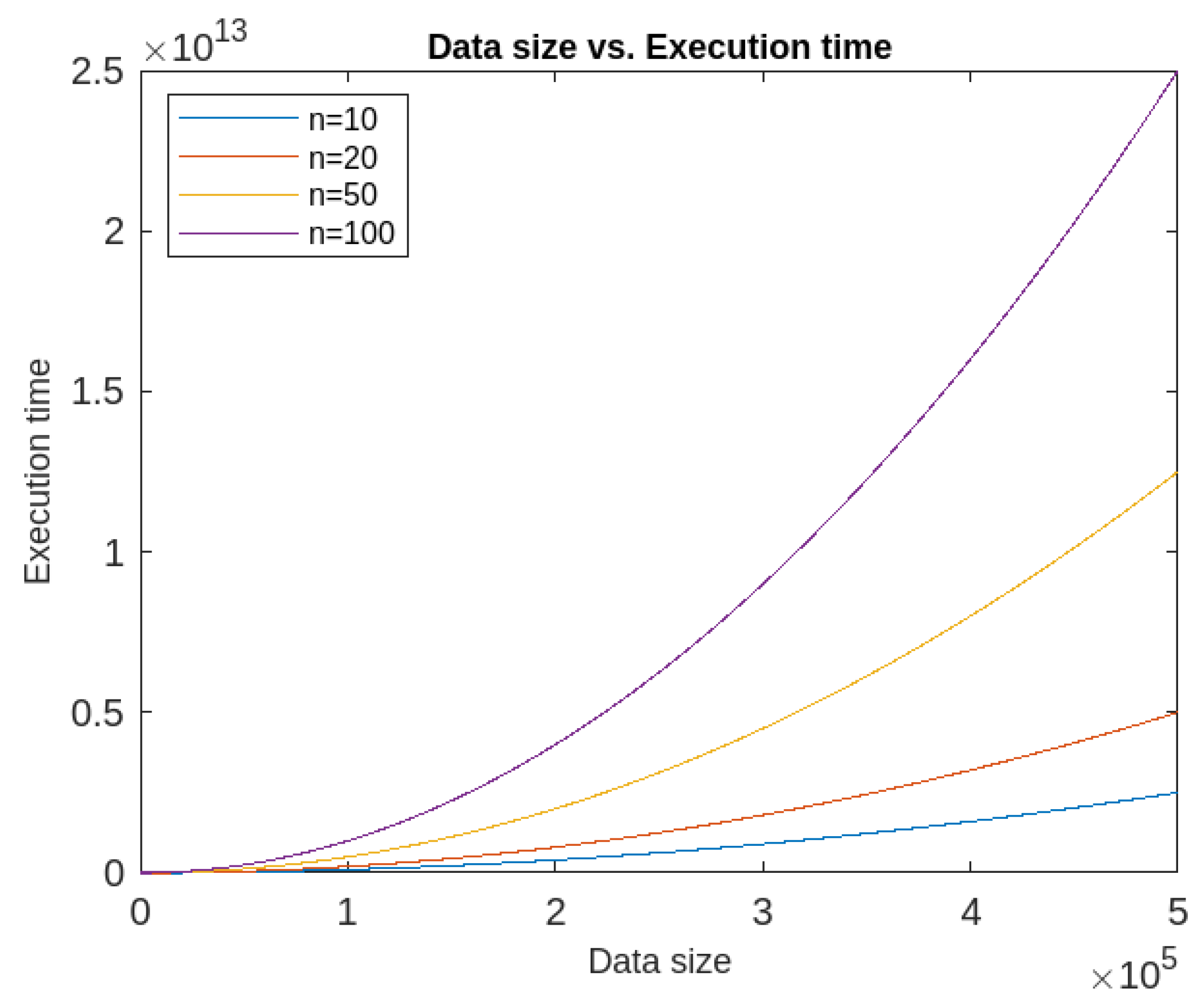
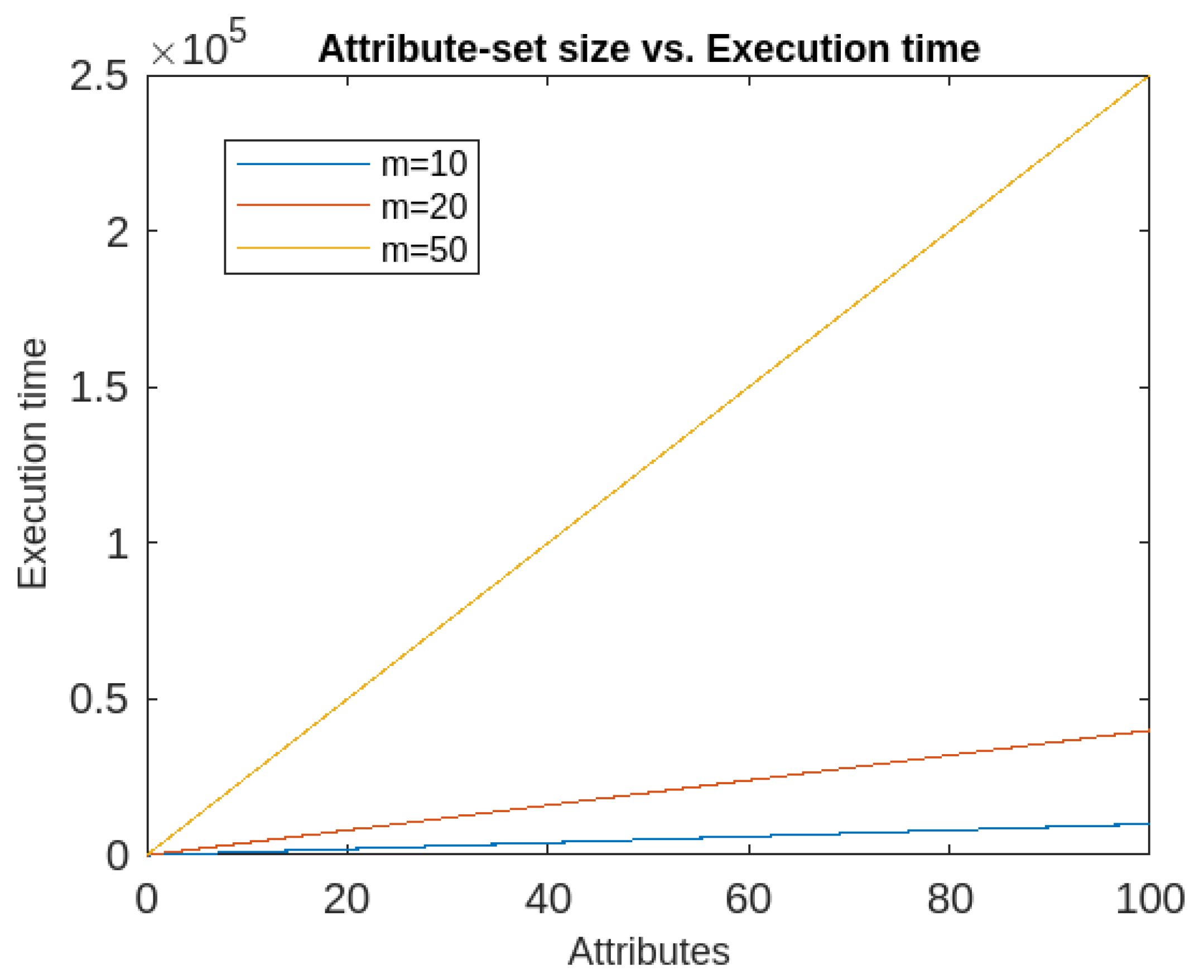
- Also, the execution time of the proposed algorithm depends upon two factors namely dimension and size of the datasets. It has been found that if the dimension is kept constant, the algorithm has quadratic execution time, whereas if the data size is kept constant, it runs in linear time. So the proposed algorithm’s time complexity is more dependent on the data size than the number of attributes. The time-complexity graphs are given in Figure 14 and Figure 15.
7. Conclusions, Limitations and Lines for Future works
7.1. Conclusions
- In this article, we have proposed an algorithm based on hybrid approach consisting both rough set theory and fuzzy set theory for the detection of anomaly.
- The algorithm is a classification based algorithm which takes the advantages of softness property both rough and fuzzy set theory to deal with uncertainty in the dataset. The obtained rules can be expressed using intuitionistic fuzzy sets.
- The proposed algorithm's performance is demonstrated by experimental analysis and with datasets KDD CUP'99 [44] network anomaly detection dataset and Kitsune [45] Network Attack dataset which shows that. The comparative analysis shows that the proposed algorithm outperforms a couple of well-known classification based algorithms.
- Finally, the proposed algorithm’s time complexity is found to be less dependent on dimension of the dataset rather more dependent on the size of the datasets. However, detection rate depends more on dimensions as evident from the obtained results.
7.2. Limitations and Lines for Future work
- Firstly, although the run-time of the proposed algorithm is less dependent of dimension of dataset, it detection rate decreases proportionately with the increase in dimension.
- Secondly, the algorithm lacks efficacy in dealing with continuous data as rough set can’t handle continuous data and finding correlation coefficient in continuous would be difficult.
- Finally, the algorithm in current form is inefficient to deal with real time data
- Efficient algorithm can be design to find anomalies from high dimensional data with continuous attributes.
- Efficient algorithm can be design to find real time anomalies in high-dimensional, heterogeneous data with continuous attributes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, V.; Banejee, A.; and Chandola, V.; Anomaly detection: A survey, ACM Computing Surveys, vol. 41, July 2009. [CrossRef]
- Hodge, V.; and Austin, J.; A survey of outlier detection methodologies, Artificial Intelligence Review, vol. 22, pp. 85-126, October 2004. [CrossRef]
- Jyothsna, V.; and Prasad, K. M,; Anomaly-Based Intrusion Detection System, Computer and Network Security, 2019.
- Jabez, J.; and Muthikumar, B.;, Intrusion Detection System (IDS): Anomaly Detection using Outlier Detection Approach, Procedia Computer Science 2015, 48, 338-346. [CrossRef]
- Abdulla Al Mamuna, S M ; and Valimaki, Juha,; Anomaly Detection and Classification in Cellular Networks Using Automatic Labeling Technique for Applying Supervised Learning, Procedia Computer Science 140, pp. 186–195, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, D.; and Majumdar, N. S.; Anomaly detection in multidimensional data using negative selection algorithm, Proceedings of the 2002 Congress - Volume 02, CEC ’02, pp. 1039–1044, USA, 2002. [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.; and Hadi, A. S.; Anomaly Detection Methods for Categorical Data: A Review. 1, 1, pp. 1-35, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Mazarbhuiya, F. A.; Alzaharani, M. Y.; and Lilia, G,; Anomaly Detection using Agglomerative Hierarchical Clustering Algorithm, Information Science and Application 2018, LNEE, Vol. 514, pp. 475-484, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Mazarbhuiya, F. A.; Alzaharani, M. Y.; and A. K. Mahanta, Detecting Anomaly Using Partitioning Clustering with Merging; ICIC Express Letters Vol. 14(10), Japan, pp. 951-960, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Mazarbhuiya, F. A.; Detecting Anomaly using Neighborhood Rough Set based Classification Approach, ICIC Express Letters, Vol. 17(1), January, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Pujari, A. K.; Data Mining Techniques, University Press, 2001.
- Mazarbhuiya, F.A. Detecting Anomaly using Neighborhood Rough Set based Classification Approach. ICIC Express Lett. 2023, 17, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasov, V L; and Nechitaylo, N M,; Decision Trees-based Anomaly Detection in Computer Assessment Results, Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2001 (2021) 012033, IOP Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Dufraisse, E.; Leray, P.; Nedellec, R.; and Benkhelif, T.; Interactive Anomaly Detection in Mixed Tabular Data using Bayesian Networks, 10th International Conference on Probabilistic Graphical Models (PGM 2020), Sep 2020, Aalborg, Denmark. ffhal-03014622f.
- Matthew Burruss, Shreyas Ramakrishna, and Abhishek Dubey, “Deep-RBF Networks for Anomaly Detection in Automotive Cyber-Physical Systems”, Autonomous Driving and Assured Autonomy, August 2021. [CrossRef]
- Liu Cuijuan, Li Yuanyuan, and Qin Yankai, Research on Anomaly Intrusion Detection Based on Rough Set Attribute Reduction, Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Computer Application and System Modeling (2012), Published by Atlantis Press, Paris, France, pp. 607-610, 2012. [CrossRef]
- J. Wang, H. Zhao, J. Xu, H. Li, H. Zhu, S. Chao, C. Zheng, Using Intuitionistic Fuzzy Set for Anomaly Detection of Network Traffic from Flow Interaction, IEEE Access, Vol. 4, 2016, pp. 596–601. [CrossRef]
- Mazarbhuiya, F.A.; AlZahrani, M.Y.; Georgieva, L. Anomaly Detection Using Agglomerative Hierarchical Clustering Algorithm; ICISA 2018; Lecture Notes on Electrical Engineering (LNEE); Springer: Hong Kong, 2019; Volume 514, pp. 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linquan, X.; Wang, W.; Liping, C.; Guangxue, Y. An Anomaly Detection Method Based on Fuzzy C-means Clustering Algorithm. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on Networking and Network Security, Jinggangshan, China, 2–4 April 2010; pp. 089–092. [Google Scholar]
- Mazarbhuiya, F.A.; AlZahrani, M.Y.; Mahanta, A.K. Detecting Anomaly Using Partitioning Clustering with Merging. ICIC Express Lett. 2020, 14, 951–960. [Google Scholar]
- Retting, L.; Khayati, M.; Cudre-Mauroux, P.; Piorkowski, M. Online anomaly detection over Big Data streams. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 29 October–1 November 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alguliyev, R.; Aliguliyev, R.; Sukhostat, L. Anomaly Detection in Big Data based on Clustering. Stat. Optim. Inf. Comput. 2017, 5, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghawli, A.S. Complex methods detect anomalies in real time based on time series analysis. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Alawami, M.A.; Kim, E.; Oh, S.; Park, J.; Kim, H. A Comparative Study of Time Series Anomaly Detection, Models for Industrial Control Systems. Sensors 2023, 23, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Hua, Q.; Zhang, H.; Tan, X.; Nan, Y.; Chen, R.; Shu, X. Research on anomaly detection and real-time reliability evaluation with the log of cloud platform. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 7183–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halstead, B.; Koh, Y.S.; Riddle, P.; Pechenizkiy, M.; Bifet, A. Combining Diverse Meta-Features to Accurately Identify Recurring Concept Drit in Data Streams. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeeb, R.A.A.; Nasauddin, F.; Gani, A.; Hashem, I.A.T.; Amanullah, A.M.E.; Imran, M. Clustering-based real-time anomaly detection—A breakthrough in big data technologies. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2022, 33, e3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazarbhuiya, F. A.; Shenify, M.; A Mixed Clustering Approach for Real-Time Anomaly Detection, Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4151. [CrossRef]
- L. A. Zadeh,” Fuzzy Sets as Basis of Theory of Possibility”, Fuzzy Sets and Systems 1, (1965), pp. 3-28. [CrossRef]
- K. T. Atanassov, “Intuitionistic fuzzy sets”. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 20(1), (1986), pp. 87–96.
- T. Gerstenkorn, and J. Manko, “Correlation of Intuitionistic fuzzy sets”, Fuzzy Sets and Systems, vol. 44, 1991, pp. 29-43. [CrossRef]
- L. A. Zadeh, Similarity relations and fuzzy orderings, Information Science, Vol. 3, 1971, pp 177-200. [CrossRef]
- S. R. Kannan, and R. K. Mohapatra, New notions for fuzzy equivalence using α-cut relation, IOP Conf. Series: Journal of Physics: Conf. Series, 1344, 2019, pp. 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Z. Pawlak, Rough sets, International Journal of Computer and Information Sciences, vol. 11, pp. 341–356, 1982. [CrossRef]
- Robert, R. Nowicki, Rough Set Based Classification Systems, Springer, 2019. [CrossRef]
- El M. Maroune, and Z. Elhoussaine, A fuzzy neighborhood rough set method for anomaly detection in large scale data, International Journal of Artificial Intelligence, Vol. 9(1), pp. 1-10, March 2020. [CrossRef]
- Yuwen Li, Shoushui Wei, Xing Liu, and Zhimin Zhang, A Novel Robust Fuzzy Rough Set Model for Feature Selection, Conplexity, Hindawi, 2021, pp. 1-12. [CrossRef]
- M. L. Thivagar, C. Richard, On nano forms of weakly open sets. International Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Invention. 1(1), pp. 31–37, 2013.
- M. Lellis Thivagar, and S.P.R. Priyalatha, Medical diagnosis in an indiscernibility matrix based on nano topology, Cogent Mathematics (2017), 4: 1330180, pp. 1-9. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Al Shumrani, S. Topal, F. Smarandache, and C. Ozel, Covering-Based Rough Fuzzy, Intuitionistic Fuzzy and Neutrosophic Nano Topology and Applications, IEEE Access, Vo. 7, December, 2019, pp. 172839-172846. [CrossRef]
- D. Dubois and H. Prade, Rough fuzzy sets and fuzzy rough sets, Int. J. Gen. Syst., vol. 17, no. 2/3, pp. 191–209, Jun. 1990. [CrossRef]
- P. Maji, and S. Pal, Fuzzy–Rough Sets for Information Measures and Selection of Relevant Genes from Microarray Data, IEEE Transactions on Systems, man, and cybernetics—part b: cybernetics, vol. 40, no. 3, june 2010. [CrossRef]
- W. Chimphlee, H. Abdulla, M. H. M. Noor, and S. Srinoy, Anomaly-based intrusion detection using Fuzzy-Rough Clustering, Proc. of ICHIT 2006, IEEE Explore, South Korea. [CrossRef]
- KDD Cup’99 Data, http://kdd.ics.uci.edu/databases/kddcup99/kddcup99.html (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Kitsune Network Attack dataset, https://github.com/ymirsky/Kitsune-py (accessed 12 December 2021).
- E. G. Eman, An operation on intuitionistic Fuzzy Matrices, Filomat 34(1), 2020, pp. 79-88. [CrossRef]
| Dataset | Dataset Characteristics | Attribute Characteristics | No. of Instances | No. of Attributes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KDDCUP’99 Network Anomaly | Multivariate | Numeric, categorical, temporal | 4,898,431 | 41 |
| Kitsune Network Attack | Multivariate, sequential, time-series | Real, temporal | 27,170,754 | 115 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





