Submitted:
23 March 2023
Posted:
24 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Description of the Source Characteristics of the Isolates Collected
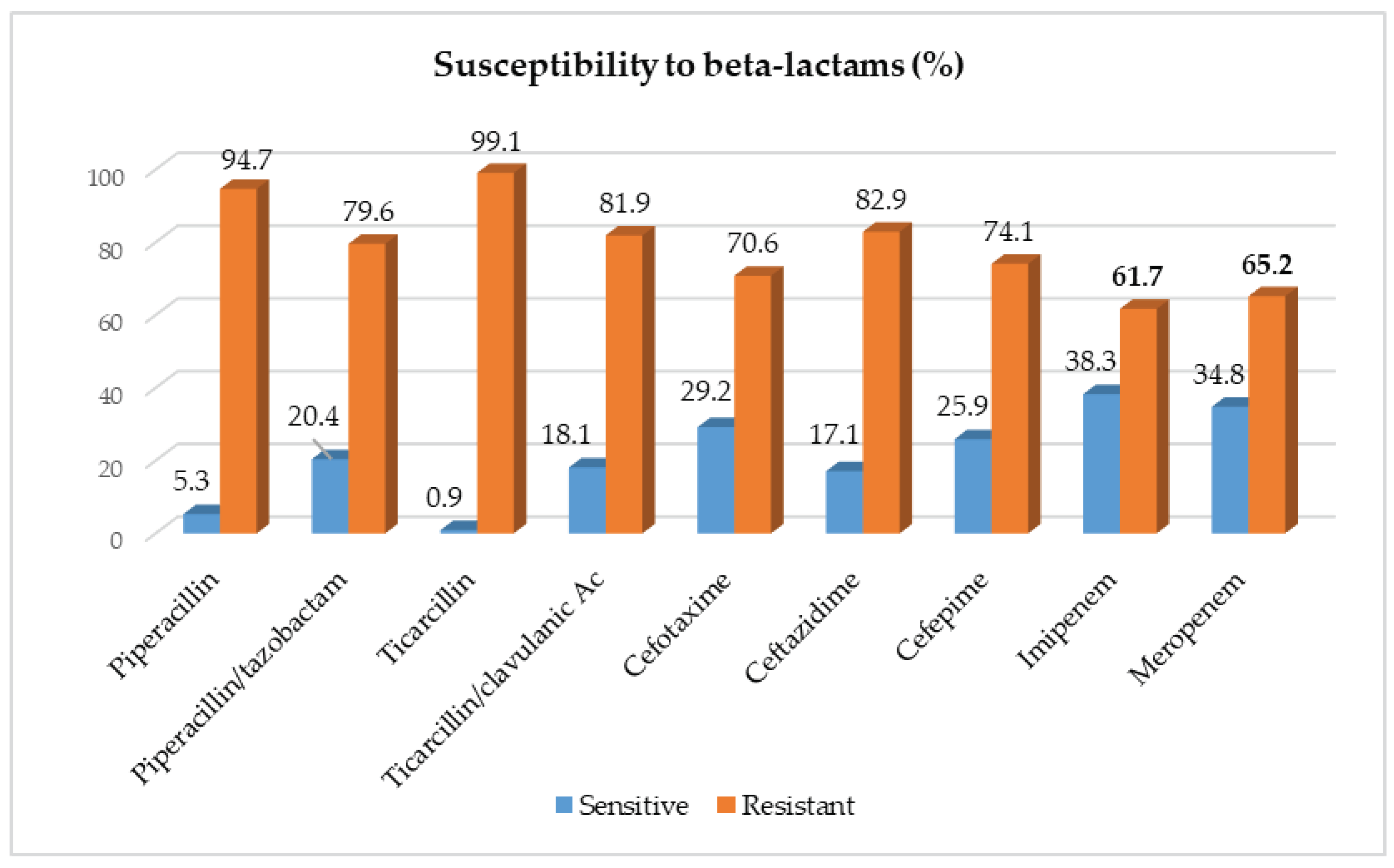
2.2. Susceptibility of Acinetobacter baumanii Isolates to Beta-Lactams
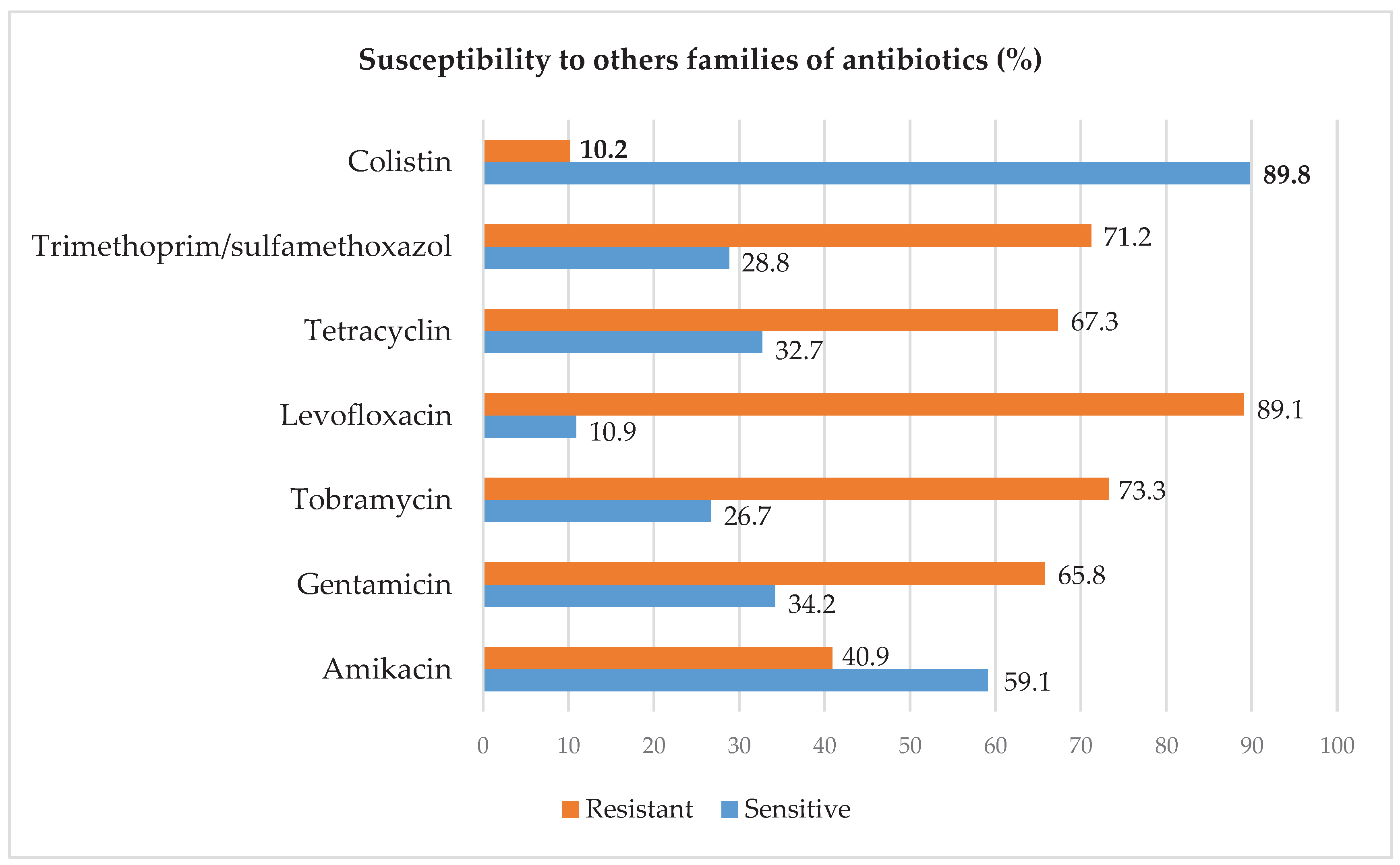
2.3. Resistance Profile of Acinetobacter baumanii to Other Families of Antibiotics
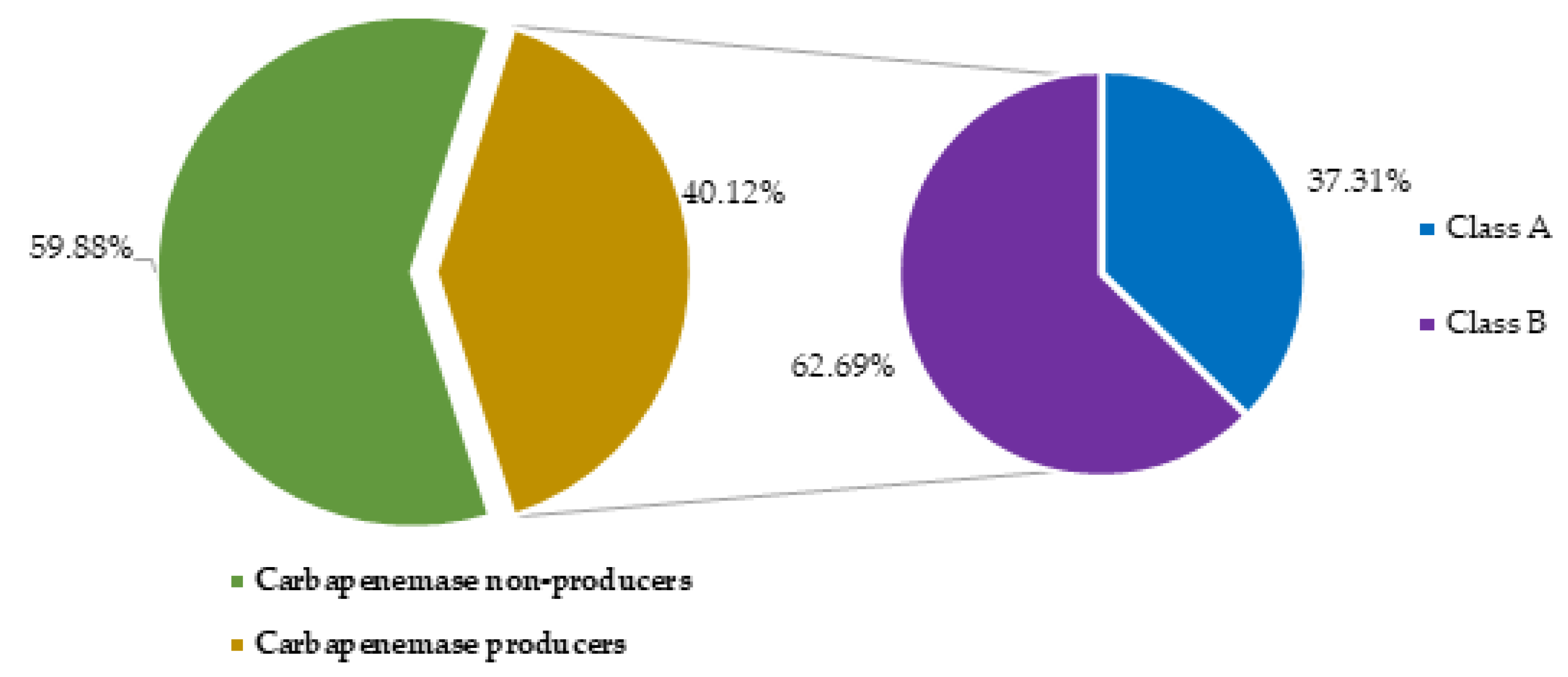
2.4. Prevalence of carbapenemase producing Acinetobacter baumanii
2.5. Analysis of risk factors related to Acinetobacter baumanii’s carbapenemase production
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Type, Site, and Duration of Study
4.2. Sampling Method and Selection Criteria
4.3. Re-Identification and Samples Processing
4.4. Data Evaluation and Analysis
4.5. Ethical Considerations
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Consent for Publication
References
- Bouvet PJM, Grimont PAD. Taxonomy of the genus Acinetobacter with the recognition of Acinetobacter baumannii sp. Nov., Acinetobacter haemolyticus sp. Nov., Acinetobacter johnsonii sp. Nov., and Acinetobacter junii sp. Nov. and emended descriptions of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and Acinetobacter lwoffii. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1986;36:228-240.
- Lo, Gora & Dieng, Assane & Diallo, Awa & Samb, Marieme & Tine, Alioune & Mbaye, Serigne & Ndiaye, Lo & Farba, Karam & Diagne-Samb, Habsa & Ngom-Cisse, Safietou & Ndoye, Aissatou & Diop-Ndiaye, Halimatou & Kane, Coumba & Gaye-Diallo, Aissatou & Mboup, Souleymane & Saad, Cheikh & Boye, Bouh & Camara, Makhtar. (2022). Molecular Epidemiology of Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates in a Senegalese University Teaching Hospital. Journal of Advances in Microbiology. 22. 73-82. [CrossRef]
- Mizan K, Lemma D, Baye G, Feleke M. Bacilles Gram négatifs non fermantaires du glucose produisant des carbapénémases en Afirque, Pseudomonas aeruginosa et Acinetobacter baumanii. Revue internationale de Microbiologie 2020.P42.
- Yoon-Kyoung Hong & Hyunkeun Kim and Kwan Soo Ko: Two types of colistin hetero-resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates, 2020, Emerging Microbes & Infections.
- Raro OHF, Gallo SW, Ferreira CAS, Oliveira SD. Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii contamination in an intensive care unit. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2017;50(2):167-172. [CrossRef]
- Organization WHO. WHO Publishes List of Bacteria for Which New Antibiotics Are Urgently Needed. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2017. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2017/bacteria-antibiotics-needed/en/ [Google Scholar].
- Yoon-Kyoung Hong & Hyunkeun Kim and Kwan Soo Ko : Two types of colistin hetero-resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates, 2020, Emerging Microbes & Infections.
- Nordmann P.Carbapenemase-proucing Enterobacteriaceae : overview of a major public health challenge.Med Mal Infect 2004 ; 44 :51-56.
- Nordman P,Naas T,Poirel L Global spread of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae Emerg Infect Dis 2012 ; 17 : 1791-1798.
- Olaniyi Ayobami, Niklas Willrich, Thomas Harder, Iruka N. Okeke, Tim Eckmanns and Robby Markwart; The incidence and prevalence of hospital-acquired (carbapenem-resistant) Acinetobacter baumannii in Europe, Eastern Mediterranean and Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis, 2019, Emerging Microbes & Infections.
- Nabila Benamrouche, Ourida Lafer, Lahcen Benmahdi, Akila Benslimani, Wahiba Amhis, Houria Ammari, and al; Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolated in Algerian hospitals, 2020, Journal of Infection in Developing Countries.
- David O. Ogbolu, Oyebode A. Terry Alli, Adeolu S. Oluremi, Y. Temilola, Ogunjimi, D, Contribution of NDM and OXA-type carbapenemases to carbapenem resistance in clinical Acinetobacter baumannii from Nigeria, 2020, Infectious Diseases. [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel C. Eze1, Mohamed E. El Zowalaty and Manormoney Pillay. Medical Microbiology, Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences, College of Health Sciences. Antibiotic resistance and biofilm formation of Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from high risk effluent water in tertiary hospitals in South Africa, 2021, Journal of Global Antimicrobial Resistance. [CrossRef]
- Mizan Kindu, Lemma Derseh, Baye Gelaw, Feleke Moges. Carbapenemase-Producing Non-Glucose-Fermenting Gram-Negative Bacilli in Africa, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hindawi. International Journal of Microbiology. Volume 2020, Article ID 9461901, 18 pages. [CrossRef]
- Rao MR, Urs TA, Chitharagi VB, et al. Rapid identification of carbapenemases by CarbAcineto NP test and the rate of beta-lactamases among Acinetobacter baumannii from a teaching hospital. Iranian Journal of Microbiology. 2022 Apr;14(2):174-180. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okalla Ebongue, Cecile & Mengue, Emmanuel & Jean Pierre, Nda Mefoo & Tsiazok, Martial & Raymond, N'GUESSAN & Ngo Bum, Elisabeth. (2015). Antimicrobial Multi-Resistance of Acinetobacter baumanii Isolated from Clinical Specimens in Douala (Cameroon). Journal of Diseases and Medicinal Plants. Vol. 1. pp. 31-36. [CrossRef]
- Castilho SRA, Godoy CSM, Guilarde AO, Cardoso JL, André MCP, Junqueira-Kipnis AP, Kipnis A. Acinetobacter baumannii strains isolated from patients in intensive care units in Goiânia, Brazil: Molecular and drug susceptibility profiles. PLoS One. 2017 ;12(5):e0176790. 5 May. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkataraman R, Yadav U. Catheter-associated urinary tract infection: an overview. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 29;34(1):5-10. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonomou O., Sarrou S., Papagiannitsis C. C, et al. Rapid dissemination of colistin and carbapenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in central Greece: mechanisms of resistance, molecular identification and epidemiological data. BMC Infectious Diseases. 2015;15:p. 559. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1297-x. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar] [Ref list]. [CrossRef]
- Perovic O., Chetty V. Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance from sentinel public hospitals, South Africa. Commun Dis Surveill Bull. 2015;14:56–67. [Google Scholar] [Ref list].
- Anane YA, Apalata T, Vasaikar S, Okuthe GE, Songca S. Molecular Detection of Carbapenemase-Encoding Genes in Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates in South Africa. Int J Microbiol. 2020 Jun 13;2020:7380740. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, M. A. et al. Propranolol, chlorpromazine and diclofenac restore susceptibility of extensively drug-resistant (XDR)-Acinetobacter baumannii to fluoroquinolones. PLoS ONE 15, e0238195. [CrossRef]
- Verma, P. , Maurya, P., Tiwari, M. & Tiwari, V. In-silico interaction studies suggest RND efflux pump mediates polymyxin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 37, 95–103. [CrossRef]
- Asif, M. , Alvi, I. A. & Rehman, S. U. In sight into Acinetobacter baumannii: pathogenesis, global resistance, mechanisms of resistance, treatment options, and alternative modalities. Infect. Drug Resist. 11, 1249. [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Baky, R. M. et al. Antimicrobial resistance pattern and molecular epidemiology of ESBL and MBL producing Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from hospitals in Minia. Egypt. Alex Med. 56, 4–13. [CrossRef]
- Tunyapanit W., Pruekprasert P., Laoprasopwattana K., Chelae S. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from hospital patients. ScienceAsia. 2014;40(1):28–34. doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2014.40.028. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]. [CrossRef]
- D. van Duin and Y. Doi, “The global epidemiology of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae,” Virulence, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 460–469, 2017. View at: Publisher Site | Google Scholar.
- L. Dortet, L. Poirel, and P. Nordmann, “Worldwide dissemination of the NDM-type carbapenemases in Gram-negative bacteria,” BioMed Research International, vol. 2014, Article ID 249856, 12 pages, 2014. View at: Publisher Site | Google Scholar.
- H. Solgi, F. Badmasti, C. G. Giske, S. Aghamohammad, and F. Shahcheraghi, “Molecular epidemiology of NDM-1-and OXA-48-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in an Iranian hospital: clonal dissemination of ST11 and ST893,” Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, vol. 73, no. 6, pp. 1517–1524, 2018. View at: Publisher Site | Google Scholar.
- McConnell M.J., Actis L., Pachon J. Acinetobacter baumannii: Human infections, factors contributing to pathogenesis and animal models. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013;37:130–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2012.00344.x. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar] [Ref list]. [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Twentieth informational supplement, document M100s-S27. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Wayne, PA. USA (2017).
- Giani T, Tascini C, Arena F, Ciullo I, Conte V, Leonildi A, et al. Rapid detection of intestinal carriage of Klebsiella pneumoniae producing KPC carbapenemase during an outbreak. J Hosp Infect. 2012;81(2):119–22. [CrossRef]
- Franklin C, Liolios L, and Peleg AY. 2006. Phenotypic detection of carbapenem-susceptible metallo-β-lactamase-producing gram-negative bacilli in the clinical laboratory. J. Clin. Microbiol. 44:3139–3144. [CrossRef]
- Lowe M, Ehlers MM, Ismail F, Peirano G, Becker PJ, Pitout JDD, et al. Acinetobacter baumannii: epidemiological and beta-lactamase data from two tertiary academic hospitals in Tshwane, South Africa. Front Microbiol 2018;9:1280. [CrossRef]
| Characteristcs | Categories | Number (N=167) | Percentage (%) |
| <10 | 29 | 17.37 | |
| Partcipant’s age (years) | [10-39[ | 92 | 55.09 |
| 40≤ | 46 | 27.54 | |
| Participant’s gender | Female | 79 | 47.31 |
| Male | 88 | 52.69 | |
| DSMPH | 14 | 8.38 | |
| Health care facility | HGY | 20 | 11.98 |
| HMR1 | 15 | 8.98 | |
| Laquintinie | 118 | 70.66 | |
| Urine | 44 | 26.35 | |
| Sample type | Blood | 37 | 22.16 |
| Vaginal swab | 8 | 4.79 | |
| Pus | 78 | 46.71 | |
| Antibiotherapy | Non | 66 | 39.52 |
| Oui | 101 | 60.48 | |
| Frequent hospitalisation | Non | 85 | 50.90 |
| Oui | 82 | 49.10 |
| Characteristics | CPAB | P-value | ||||
| N | n | n/N(%) | ||||
| Total | 167 | 67 | 100 | - | ||
| Age | <10 | 29 | 15 | 51.72 | ||
| [10-39] | 92 | 32 | 34.78 | 0.23 | ||
| 40≤ | 46 | 20 | 43.48 | |||
| Gender | Female | 79 | 26 | 32.91 | 0.07 | |
| Male | 88 | 41 | 46.59 | |||
| Health care facility | DSMPH | 14 | 0 | 0.00 | ||
| HGY | 20 | 0 | 0.00 | |||
| HMR1 | 15 | 8 | 53.33 | 0.81 | ||
| Laquintinie | 118 | 59 | 50.00 | |||
| Urine | 44 | 23 | 52.27 | |||
| Sample type | Blood | 37 | 17 | 45.95 | 0.11 | |
| Vaginal swab | 8 | 2 | 25.00 | |||
| Pus | 78 | 25 | 32.05 | |||
| Variables | Categories | Carbapenemase producing Acinetobacter baumanii | OR (95%CI) | P-value |
| n (%) | ||||
| Antibiotherapy | No | 2 (3.03) | 1 | Ref |
| Yes | 65 (64.36) | 57.78 (13.35-250.07) | <0.0001 | |
| Hospial food consumption | No | 55 (40.15) | 1 | Ref |
| Yes | 12 (40.00) | 0.99 (0.44-2.23) | 0.99 | |
| Frequent hospitalisation | No | 5 (5.88) | 1 | Ref |
| Yes | 62 (75.61) | 49.60 (17.63-139.57) | <0.0001 | |
| Using common toilet | No | 2 (20.00) | 1 | Ref |
| Yes | 65 (41.40) | 2.83 (0.58-13.74) | 0.32 |
| Variables | Categories | Ajusted-OR (95%CI) | P-value |
| Antibiotherapy | No | 1 | Ref |
| Yes | 6.00 (0.92-38.98) | 0.06 | |
| Frequent hospitalisation | No | 1 | Ref |
| Yes | 16.53 (4.36-62.66) | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





