Submitted:
15 March 2023
Posted:
20 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
Source of Data and Study Population
Weighting
- HV005 is the final household survey weight variable, from the household recode (HR) dataset.
- is the number of finalized EAs in stratum or region for the strata. The number of interviewed EAs, was calculated from the household (HR) dataset.
- is the number of households in stratum for all strata.
- is the number of households in the whole of Uganda according to the Uganda Population and Housing Census of 2014.
- is the number of households in EA per EA. These numbers were estimated using the average number of households in each EA in strata according to the most recent Uganda Population and Housing Census data of 2014.
- is the number of complete households in the survey.
- is the approximated household number at the time of the survey in the whole country. This was approximated by the number of households in Uganda according to the Uganda Population and Housing Census of 2014.
Multilevel mixed effects models
- is the natural logarithm.
- is the probability of testing positive for malaria for the child in the household and EA.
- is the average log-odds of malaria infection.
- is a covariate at level-1 for the child in the household and EA.
- denotes the slope related with representing the association between the individual child covariates and the log-odds of malaria infection.
- is the EA random effect.
- is the household random effect.
Model comparison
- is the design effect.
- is the intra-class correlation for the variable in question.
- is the size of the cluster.
3. Results
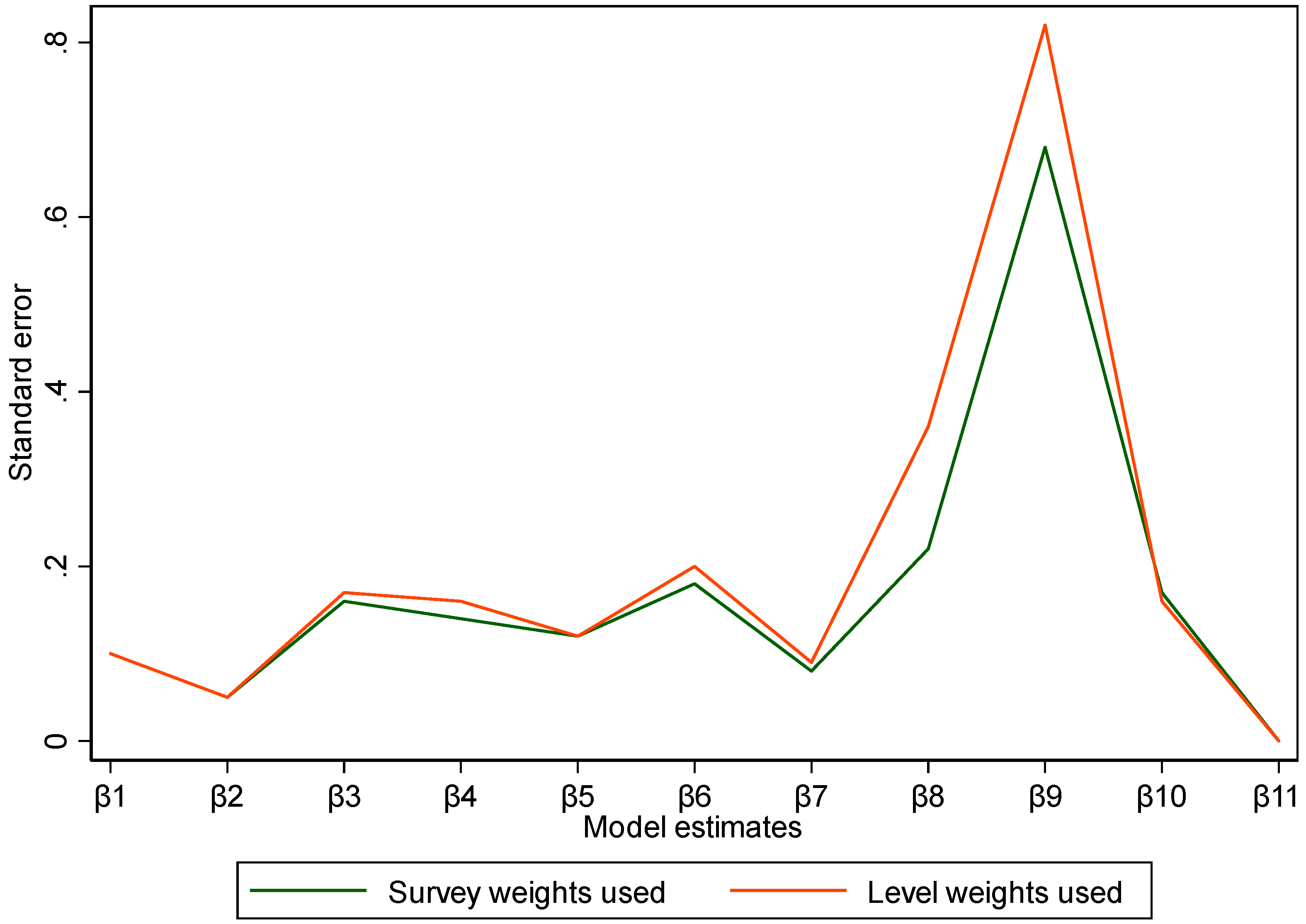
Comparison of Models Using Standard Errors of Model Estimates
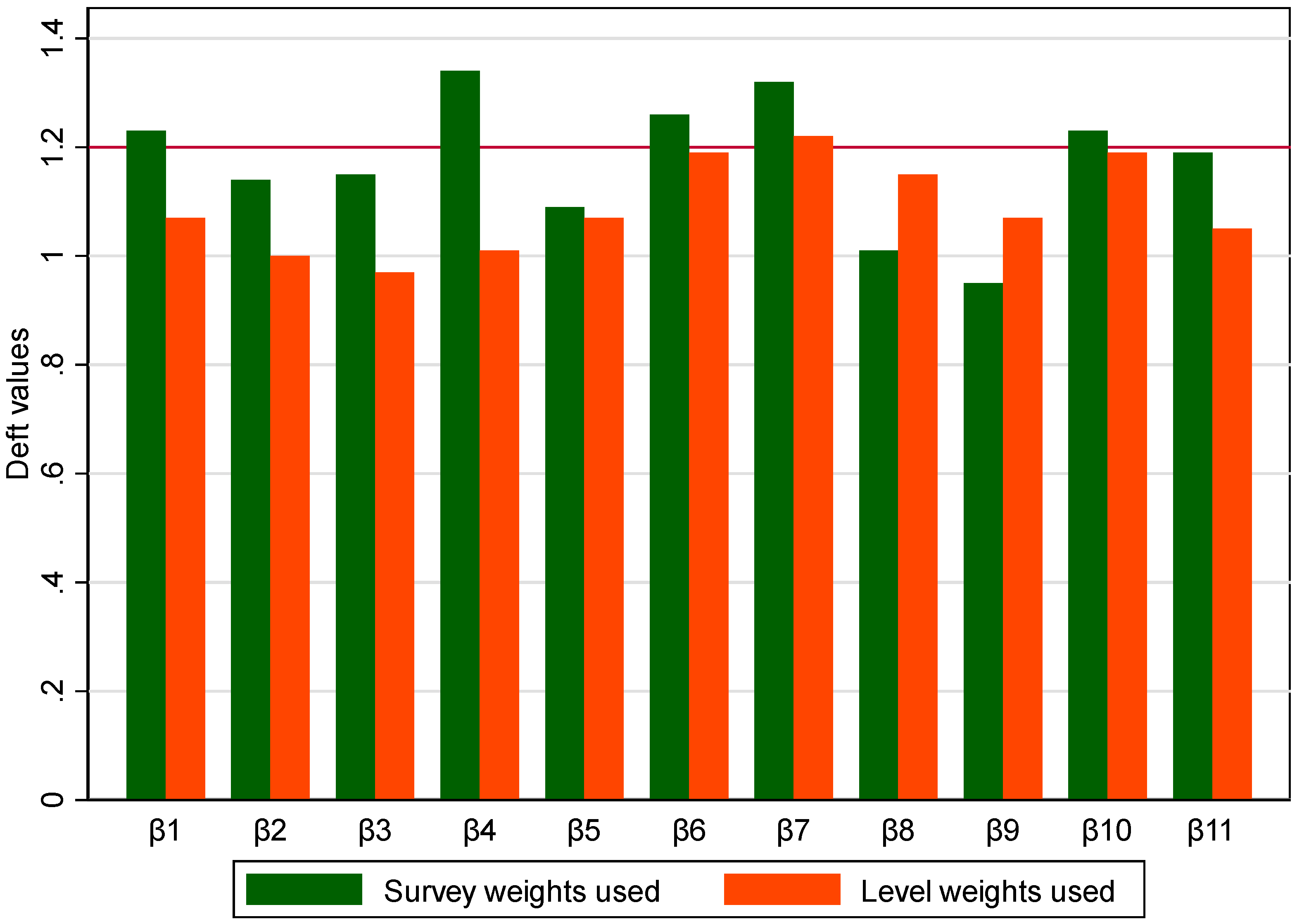
Comparison of Models Using Design Factor Values of Model Estimates
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Funding
References
- Bethlehem, J. G., & Keller, W. J. (1987). Linear weighting of sample survey data. Journal of official statistics, 3(4), 141-153. https://www.scb.se/contentassets/ca21efb41fee47d293bbee5bf7be7fb3/linear-weighting-of-sample-survey-data.pdf.
- Brick, J. Michael. 2013. "Unit Nonresponse and Weighting Adjustments: A Critical Review." Journal of Official Statistics 29 (3): 329–353. [CrossRef]
- Cai, Tianji. 2013. "Investigation of Ways to Handle Sampling Weights for Multilevel Model Analyses." Sociological Methodology 43 (1): 178-219. [CrossRef]
- Carle, Adam C. 2009. "Fitting multilevel models in complex survey data with design weights: Recommendations." BMC Med Res Methodol 9 (49). [CrossRef]
- Chen, Qixuan, Andrew Gelman, Melissa Tracy, Fran H Norris, and Sandro Galea. 2015. "Incorporating the sampling design in weighting adjustments for panel attrition." Stat Med 34 (28): 3637-47. [CrossRef]
- Daniels, Michael J., Francesca Dominici, and Scott Zeger. 2004. "Underestimation of Standard Errors in Multi-Site Time Series Studies." Epidemiology 15 (1): 57-62. https://www.jstor.org/stable/20485840.
- Dargatz, D A, and G W Hill. 1996. "Analysis of survey data." Preventive Veterinary Medicine 28 (4): 225-237. [CrossRef]
- Davern, Michael, Arthur Jones, James Lepkowski, Gestur Davidson, and Lynn A. Blewett. 2007. "Estimating Regression Standard Errors with Data from the Current Population Survey’s Public Use File." Inquiry 44: 211–224. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.5034/inquiryjrnl_44.2.211.
- Elkasabi, Mahmoud, Ruilin Ren, and Thomas W. Pullum. 2020. Multilevel Modeling Using DHS Surveys: A Framework to Approximate Level-Weights. I: Reports No. 27, Rockville, Maryland, USA; 27.
- Gelman, Andrew. 2007. "Struggles with Survey Weighting and Regression Modeling." Statist. Sci 22 (2): 153-164. [CrossRef]
- Graubard, Barry, and Edward L Korn. 1996. "Modelling the sampling design in the analysis of health surveys." Stat Methods Med Res 5 (3): 263-81. [CrossRef]
- Hakim, Ferdous, Rijwan Bhuiyan, Khaleda Akter, and Mostafa Zaman. 2020. "Weighting National Survey Data for Bangladeshi Population." Research Methods Cases. [CrossRef]
- Kalton, Graham, and Ismael Flores-Cervantes. 2003. "Weighting Methods." Journal of Official Statistics 19 (2): 81-97. http://www.sverigeisiffror.scb.se/contentassets/ca21efb41fee47d293bbee5bf7be7fb3/weighting-methods.pdf.
- Kim, Jae Kwang, and C. J. Skinner. 2013. "Weighting in survey analysis under informative sampling." Biometrika 100 (2): 385–398. [CrossRef]
- Lavrakas, Paul J. 2008. Encyclopedia of survey research methods. S: Oaks, Carifonia. [CrossRef]
- Lepkowski, James M., William D. Mosher, Robert M Groves, Brady T. West, and James Wagner. 2013. Responsive design, weighting, and variance estimation in the 2006-2010 National Survey of Family Growth. /: National Center for Health Statistics. https, 2206.
- Liao, Dan, and Richard Valliant. 2012. "Variance inflation factors in the analysis of complex survey data." Survey Methodology 38 (1): 53-62. https://www.rti.org/publication/variance-inflation-factors-analysis-complex-survey-data/fulltext.pdf.
- Little, Roderick J, and Sonya Vartivarian. 2003. "On weighting the rates in non-response weights." Stat Med 22 (9): 1589-99. [CrossRef]
- Nahorniak, Matthew, David P Larsen, Carol Volk, and Chris E Jordan. 2015. "Using Inverse Probability Bootstrap Sampling to Eliminate Sample Induced Bias in Model Based Analysis of Unequal Probability Samples." PLoS One 10 (6): e0131765. [CrossRef]
- NMCD, UBOS, and ICF. 2020. Uganda Malaria Indicator Survey 2018-19. /: and Rockville, Maryland, USA: Uganda National Malaria Control Division (NMCD), Uganda Bureau of Statistics (UBOS), and ICF. https.
- Pfeffermann-a, Danny. 1993. "The Role of Sampling Weights When Modeling Survey Data." International Statistical Review 61 (2): 317-337. [CrossRef]
- Pfeffermann-b, Danny. 1996. "The use of sampling weights for survey data analysis." Stat Methods Med Res 239-261. [CrossRef]
- Rabe-Hesketh, Sophia, and Anders Skrondal. 2006. "Multilevel Modelling of Complex Survey Data." Journal of the Royal Statistical Society 169 (4): 805–827. http://www.jstor.org/stable/3877401.
- Seaman, Shaun R, and Ian R White. 2013. "Review of inverse probability weighting for dealing with missing data." Statistical Methods in Medical Research 22 (3): 278–295. [CrossRef]
- Skinner, Chris, and Ben Mason. n.d. "Weighting in the regression analysis of survey data with a cross-national application." The Canadian Journal of Statistics 40 (4): 697-711. [CrossRef]
- Sturgis, Patrick. 2004. "Analysing Complex Survey Data: Clustering, Stratification and Weights." social research UPDATE (43). https://sru.soc.surrey.ac.uk/SRU43.PDF.
- UBOS, and ICF. 2018. Uganda Demographic and Health Survey 2016. /: and Rockville, Maryland, USA: Uganda Bureau of Statistics (UBOS) and ICF. https.
- Wagemaker, Hans, ed. 2020. Reliability and Validity of International Large-Scale Assessment. S: Switzerland. [CrossRef]
- West, Brady T., Linda Beer, Garrett W. Gremel, John Weiser, Christopher H. Johnson, Shikha Garg, and Jacek Skarbinski. 2015. "Weighted Multilevel Models: A Case Study." Am J Public Health 105 (11): 2214–2215. [CrossRef]
- Wun, Lap-Ming, Trena M Ezzati-Rice, Nuria Diaz-Tena, and Janet Greenblatt. 2007. "On modelling response propensity for dwelling unit (DU) level non-response adjustment in the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS)." Stat Med 26 (8): 1875-84. [CrossRef]
| Steps | HH and EA weights | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Apply the estimated normalization factor to de-normalize the final survey weight | |
| 2 | , | |
| 3 | ||
| Model estimates | Survey weighted model | Level weighted model | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | SE | P | (95% CI) | OR | SE | P | (95% CI) | ||||
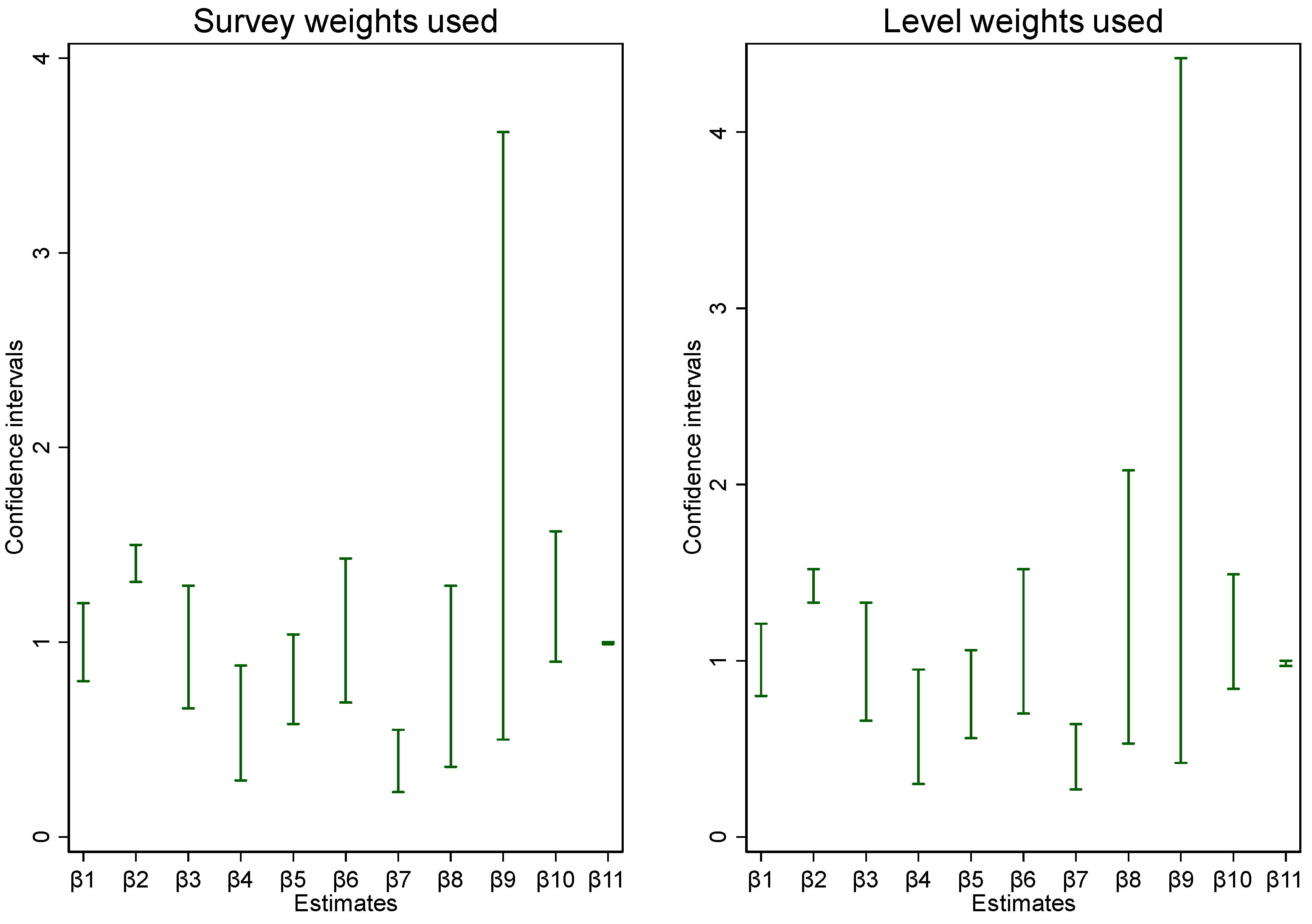
| β1 | 0.98 | 0.10 | 0.85 | 0.80 | 1.20 | 0.98 | 0.10 | 0.88 | 0.80 | 1.21 | |
| β2 | 1.40 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 1.31 | 1.50 | 1.42 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 1.33 | 1.52 | |
| β3 | 0.92 | 0.16 | 0.63 | 0.66 | 1.29 | 0.94 | 0.17 | 0.72 | 0.66 | 1.33 | |
| β4 | 0.50 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.29 | 0.88 | 0.53 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.30 | 0.95 | |
| β5 | 0.78 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.58 | 1.04 | 0.77 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.56 | 1.06 | |
| β6 | 0.99 | 0.18 | 0.96 | 0.69 | 1.43 | 1.03 | 0.20 | 0.87 | 0.70 | 1.52 | |
| β7 | 0.36 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 0.55 | 0.42 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.27 | 0.64 | |
| β8 | 0.68 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.36 | 1.29 | 1.05 | 0.36 | 0.90 | 0.53 | 2.08 | |
| β9 | 1.35 | 0.68 | 0.55 | 0.50 | 3.62 | 1.37 | 0.82 | 0.60 | 0.42 | 4.42 | |
| β10 | 1.19 | 0.17 | 0.23 | 0.90 | 1.57 | 1.12 | 0.16 | 0.44 | 0.84 | 1.49 | |
| β11 | 0.98 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.97 | 1.00 | |
| CI: Confidence interval, OR: Odds ratio, SE: Standard error, P: p-value. | |||||||||||
| Model estimates | Survey weighted model | Level weighted model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deff | Deft | Deff | Deft | ||
| β1 | 1.52 | 1.23 | 1.13 | 1.07 | |
| β2 | 1.31 | 1.14 | 1.01 | 1.00 | |
| β3 | 1.32 | 1.15 | 0.95 | 0.97 | |
| β4 | 1.79 | 1.34 | 1.02 | 1.01 | |
| β5 | 1.18 | 1.09 | 1.15 | 1.07 | |
| β6 | 1.58 | 1.26 | 1.42 | 1.19 | |
| β7 | 1.75 | 1.32 | 1.48 | 1.22 | |
| β8 | 1.01 | 1.01 | 1.32 | 1.15 | |
| β9 | 0.91 | 0.95 | 1.14 | 1.07 | |
| β10 | 1.51 | 1.23 | 1.41 | 1.19 | |
| β11 | 1.43 | 1.19 | 1.10 | 1.05 | |
| Deff: Design effect, Deft: Design factor. | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





