Submitted:
08 March 2023
Posted:
13 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
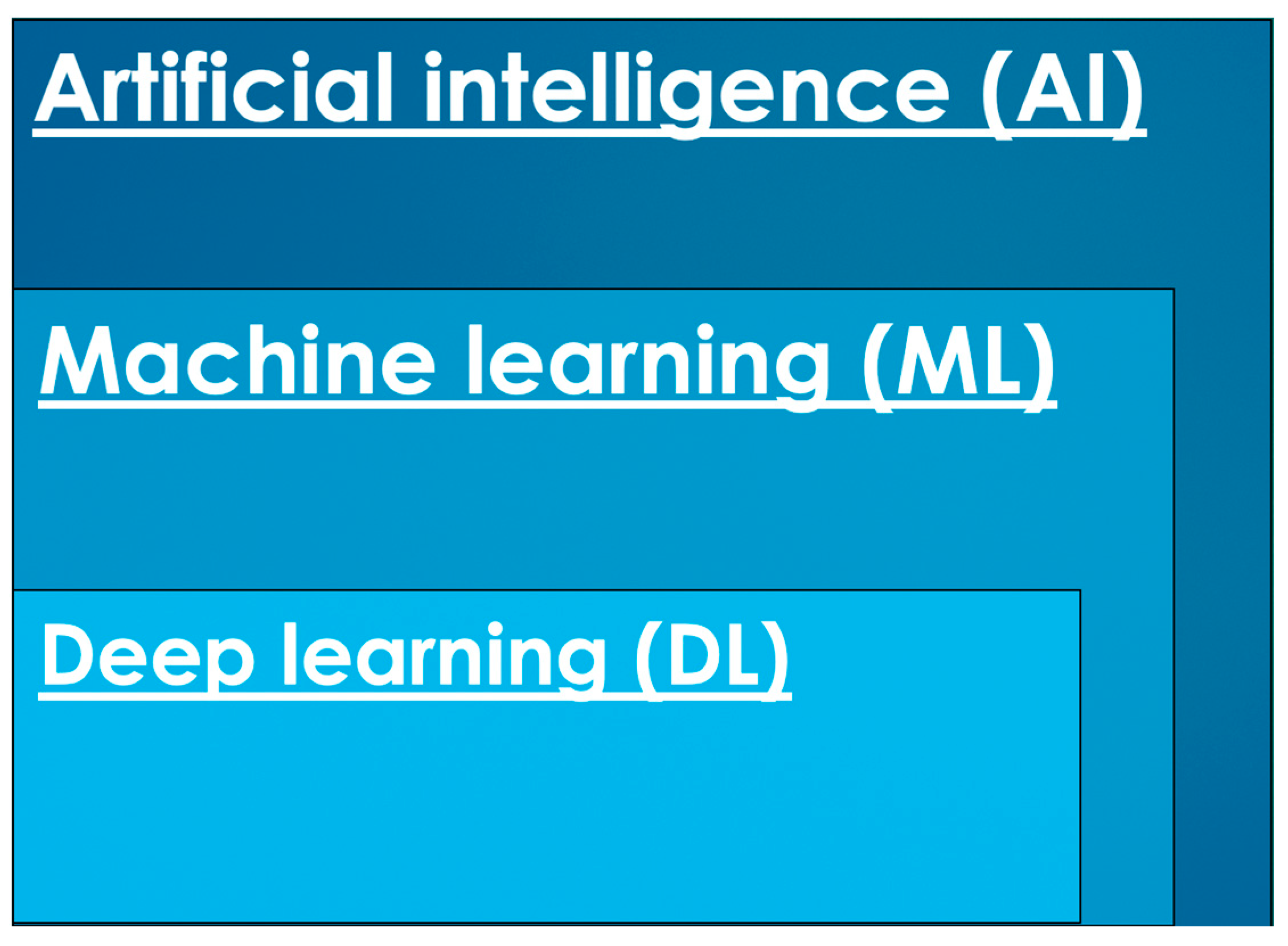
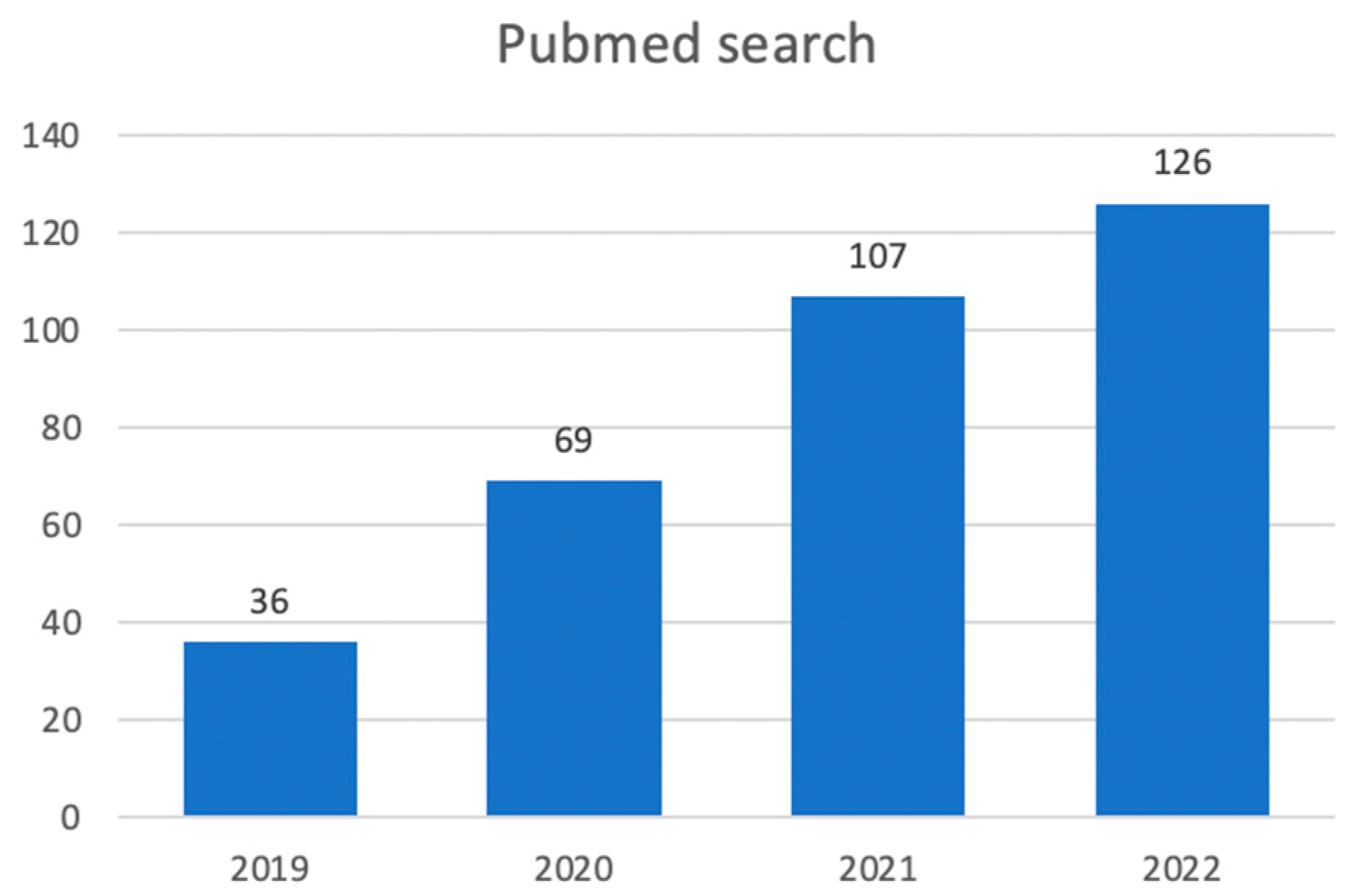
1. Introduction
2. Liver Transplant in HCC
3. Extending Milan
4. AI-Aided Evaluations in Candidates for LT with HCC
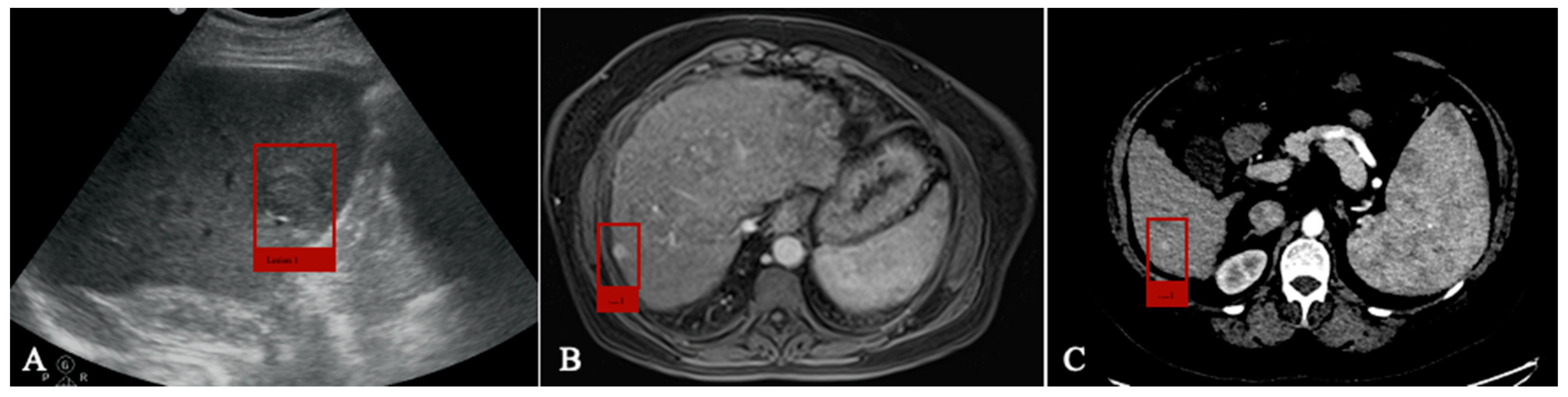
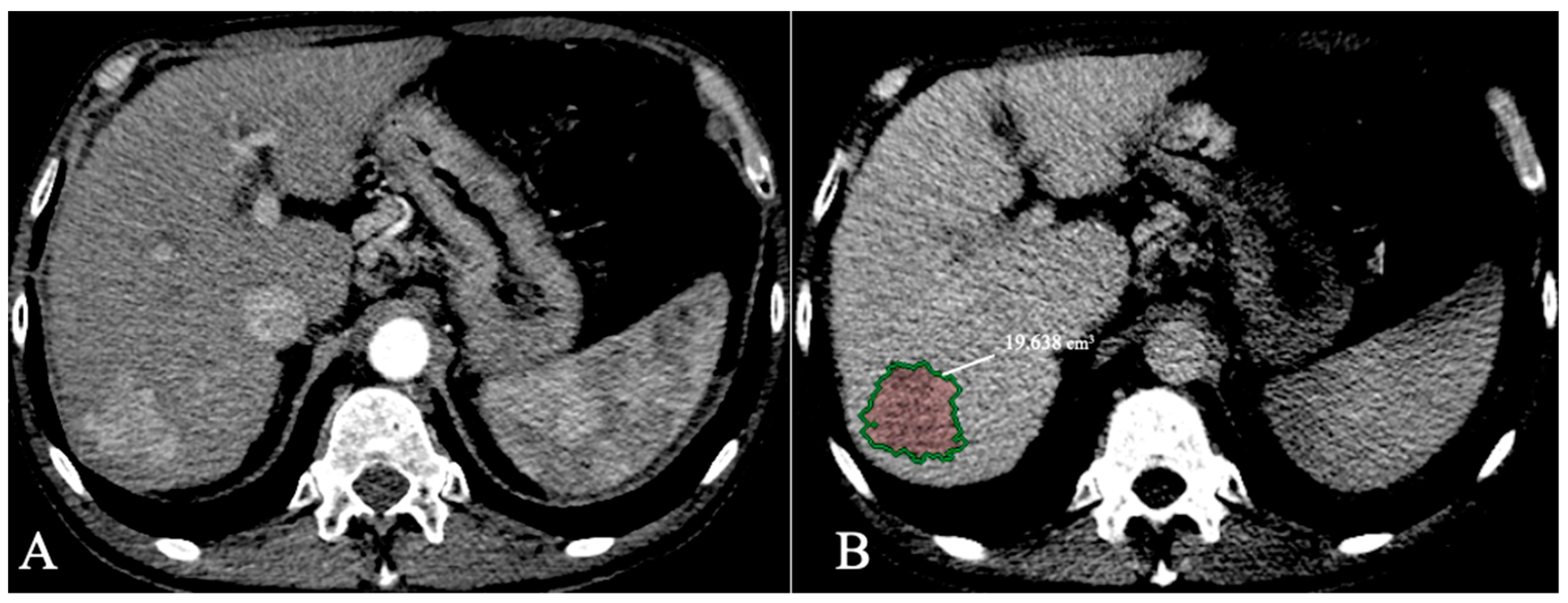
4.1. Detection
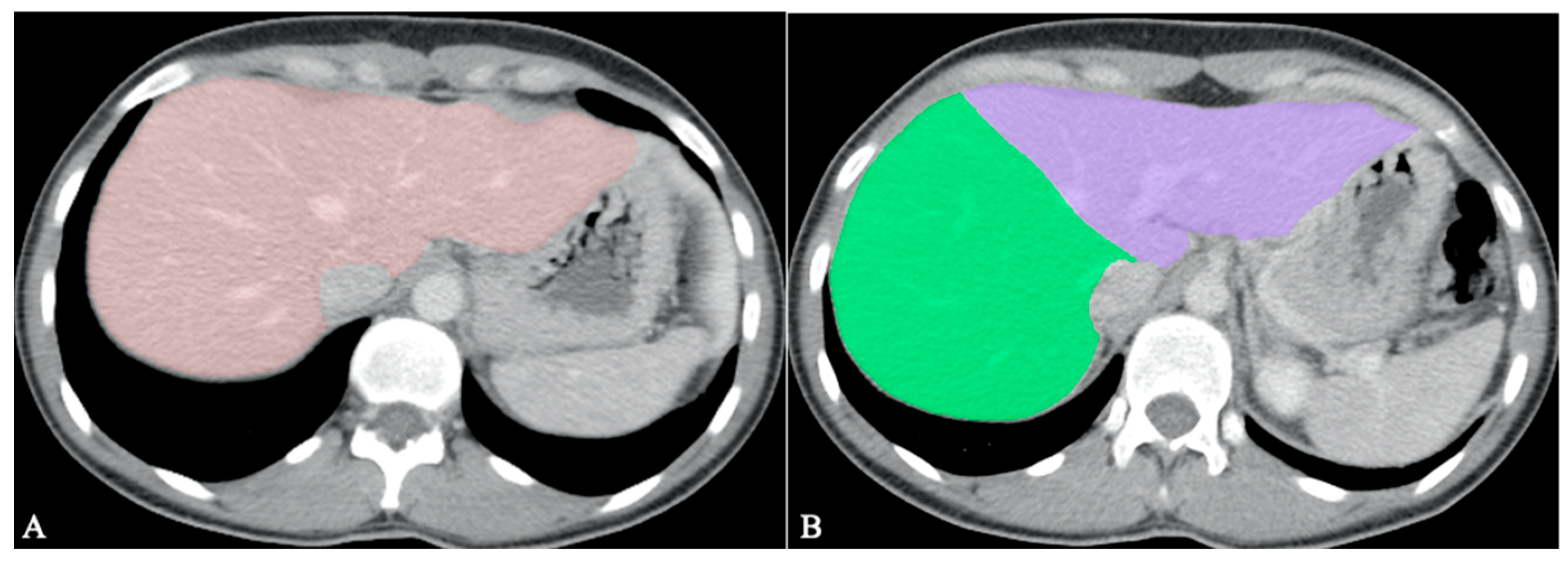
4.2. Segmentation
4.2. Classification
4.3.1. HCC Grading Prediction
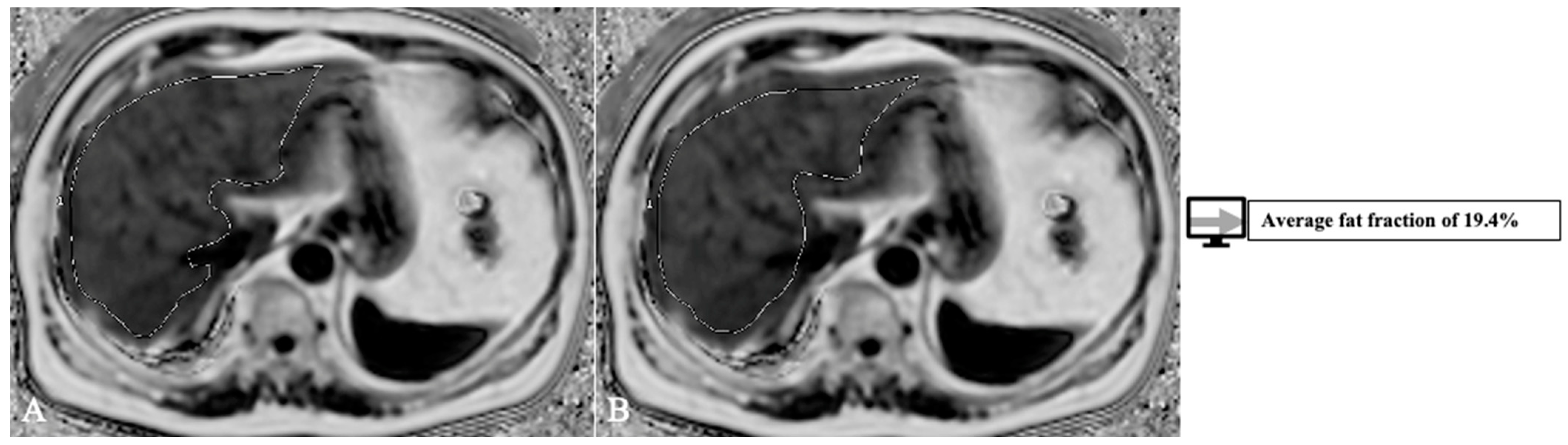
4.3.1. Molecular evaluation
4. Discussion and limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.G.; Lampertico, P.; Nahon, P. Epidemiology and surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: New trends. Journal of hepatology 2020, 72, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyemiju, T.; Abera, S.; Ahmed, M.; Alam, N.; Alemayohu, M.A.; Allen, C. ... & Global Burden of Disease Liver Cancer Collaboration. The burden of primary liver cancer and underlying etiologies from 1990 to 2015 at the global, regional, and national level: results from the global burden of disease study 2015. JAMA oncology 2017, 3, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Reeves, H.L.; Kotsiliti, E.; Govaere, O.; Heikenwalder, M. From NASH to HCC: current concepts and future challenges. Nature reviews Gastroenterology & hepatology 2019, 16, 411–428. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, A.R.; Rosso, N.; Bedogni, G.; Tiribelli, C.; Bellentani, S. Global epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: What we need in the future. Liver International 2018, 38, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, C.; Razavi, H.; Loomba, R.; Younossi, Z.; Sanyal, A.J. Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrates an exponential increase in burden of disease. Hepatology 2018, 67, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.R.; Lake, J.R.; Smith, J.M.; Schladt, D.P.; Skeans, M.A.; Harper, A.M.; Wainright, J.L.; Snyder, J.J.; Israni, A.K.; Kasiske, B.L. OPTN/SRTR 2016 Annual Data Report: Liver. Am J Transplant. 2018, 18 (Suppl 1), 172–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2018, 391, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, N.; Dodge, J.L.; Hirose, R.; Roberts, J.P.; Yao, F.Y. Predictors of low risk for dropout from the liver transplant waiting list for hepatocellular carcinoma in long wait time regions: Implications for organ allocation. Am J Transplant 2019, 19, 2210–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCulloch, W.S.; Pitts, W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. The bulletin of mathematical biophysics 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, S.; Song, K.D.; Chung, J.W. Basics of deep learning: a radiologist's guide to understanding published radiology articles on deep learning. Korean journal of radiology 2020, 21, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Timmeren, J.E.; Cester, D.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Alkadhi, H.; Baessler, B. Radiomics in medical imaging—“how-to” guide and critical reflection. Insights into imaging 2020, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; Lee, B.; Yoon, S. Deep learning in bioinformatics. Briefings in bioinformatics 2017, 18, 851–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, D.; Shimazaki, A.; Miki, Y. Technical and clinical overview of deep learning in radiology. Japanese journal of radiology 2019, 37, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minor, L.B. Harnessing the power of data in health. Stanford Med. Heal. Trends Rep. 2017.
- Briceño, J.; Cruz-Ramírez, M.; Prieto, M.; Navasa, M.; De Urbina, J.O.; Orti, R. ... & De La Mata, M. Use of artificial intelligence as an innovative donor-recipient matching model for liver transplantation: results from a multicenter Spanish study. Journal of hepatology 2014, 61, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briceño, J.; Ayllón, M.D.; Ciria, R. Machine-learning algorithms for predicting results in liver transplantation: the problem of donor–recipient matching. Current Opinion in Organ Transplantation 2020, 25, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsimas, D.; Kung, J.; Trichakis, N.; Wang, Y.; Hirose, R.; Vagefi, P.A. Development and validation of an optimized prediction of mortality for candidates awaiting liver transplantation. American Journal of Transplantation 2019, 19, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingfield, L.R.; Ceresa, C.; Thorogood, S.; Fleuriot, J.; Knight, S. Using artificial intelligence for predicting survival of individual grafts in liver transplantation: a systematic review. Liver Transplantation 2020, 26, 922–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Survarachakan, S.; Prasad, P. J. R.; Naseem, R.; de Frutos, J. P.; Kumar, R. P.; Langø, T. ... & Lindseth, F. Deep learning for image-based liver analysis—A comprehensive review focusing on malignant lesions. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine 2022, 102331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Yan, B.; Chang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, F. Trends in the application of deep learning networks in medical image analysis: Evolution between 2012 and 2020. European Journal of Radiology 2022, 146, 110069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, D.; Chapiro, J.; Paradis, V.; Seraphin, T.P.; Kather, J.N. Artificial intelligence in liver diseases: improving diagnostics, prognostics and response prediction. JHEP Reports 2022, 100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, K.G.; Schalekamp, S.; Rutten, M.J.; van Ginneken, B.; de Rooij, M. Artificial intelligence in radiology: 100 commercially available products and their scientific evidence. European radiology 2021, 31, 3797–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Regalia, E.; Doci, R.; Andreola, S.; Pulvirenti, A.; Bozzetti, F.; Gennari, L. Liver transplantation for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with cirrhosis. New England Journal of Medicine 1996, 334, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle, P.R.; Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Mazzaferro, V.; Piscaglia, F.; Raoul, J.L. ... & Vilgrain, V. EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of hepatology 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.; Cervantes, A.; Chau, I.; Daniele, B.; Llovet, J.M.; Meyer, T.; Martinelli, E. Hepatocellular carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Annals of Oncology 2018, 29, iv238–iv255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, A.B.; D’Angelica, M.I.; Abbott, D.E.; Anaya, D.A.; Anders, R.; Are, C.; Bachini, M.; Borad, M.; Brown, D.; Burgoyne, A.; Chahal, P.; Chang, D.T.; Cloyd, J.; Covey, A.M.; Glazer, E.S.; Goyal, L.; Hawkins, W.G.; Iyer, R.; Jacob, R.; Kelley, R.K.; Kim, R.; Levine, M.; Palta, M.; Park, J.O.; Raman, S.; Reddy, S.; Sahai, V.; Schefter, T.; Singh, G.; Stein, S.; Vauthey, J.; Venook, A.P.; Yopp, A.; McMillian, N.R.; Hochstetler, C.; Darlow, S.D. Hepatobiliary Cancers, Version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology, Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, 19(5), 541-565. Retrieved Dec 28 2021, 2022, from https://jnccn.org/view/journals/jnccn/19/5/article-p541.xml. [CrossRef]
- Heimbach, J.K.; Kulik, L.M.; Finn, R.S.; Sirlin, C.B.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R. ... & Marrero, J. A. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 358–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- https://www.eurotransplant.org.
- Murali, A.R.; Patil, S.; Phillips, K.T.; Voigt, M.D. Locoregional therapy with curative intent versus primary liver transplant for hepatocellular carcinoma: systematic review and meta-analysis. Transplantation 2017, 101, e249–e257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.Y.; Ferrell, L.; Bass, N.M.; Watson, J.J.; Bacchetti, P.; Venook, A.; Roberts, J.P. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: expansion of the tumor size limits does not adversely impact survival. Hepatology 2001, 33, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Llovet, J.M.; Miceli, R.; Bhoori, S.; Schiavo, M.; Mariani, L. ... & Metroticket Investigator Study Group. Predicting survival after liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the Milan criteria: a retrospective, exploratory analysis. The lancet oncology 2009, 10, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Sposito, C.; Zhou, J.; Pinna, A.D.; De Carlis, L.; Fan, J.; Cucchetti, A. Metroticket 2.0 model for analysis of competing risks of death after liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvoux, C.; Roudot–Thoraval, F.; Decaens, T.; Pessione, F.; Badran, H.; Piardi, T. ... & Liver Transplantation French Study Group. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a model including α-fetoprotein improves the performance of Milan criteria. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Department of Health and Human Services. OPTN/UNOS Liver and Intestinal Organ Transplantation Committee. https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/media/1922/liver_hcc_criteria_for_auto_approval_20160815.pdf. Accessed December 13, 2018.
- DuBay, D.; Sandroussi, C.; Sandhu, L.; Cleary, S.; Guba, M.; Cattral, M.S.; Grant, D.R. Liver transplantation for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma using poor tumor differentiation on biopsy as an exclusion criterion. Annals of surgery 2011, 253, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toso, C.; Trotter, J.; Wei, A.; Bigam, D.L.; Shah, S.; Lancaster, J.; Kneteman, N.M. Total tumor volume predicts risk of recurrence following liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Transplantation 2008, 14, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.S.; Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.L.; Zhang, M.; Wu, L.M. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Hangzhou experiences. Transplantation 2008, 85, 1726–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Q.; Nicolini, D.; Inostroza Nunez, M.; Iesari, S.; Goffette, P.; Agostini, A.; Lerut, J. A Novel Prognostic Index in Patients With Hepatocellular Cancer Waiting for Liver Transplantation. Annals of surgery 2016, 264, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, B.; Mehta, N.; Sapisochin, G.; Roberts, J.P.; Yao, F.Y. Alpha-fetoprotein level> 1000 ng/mL as an exclusion criterion for liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma meeting the Milan criteria. Liver Transplantation 2014, 20, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapisochin, G.; Goldaracena, N.; Laurence, J.M.; Dib, M.; Barbas, A.; Ghanekar, A.; Grant, D.R. The extended Toronto criteria for liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective validation study. Hepatology 2016, 64, 2077–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, T.; Goto, R.; Watanabe, M.; Kawamura, N.; Takada, Y. Liver transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: How Should We Improve the Thresholds? Cancers 2022, 14, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuluvath, P.J.; To, C.; Amjad, W. Role of locoregional therapies in patients with hepatocellular cancer awaiting liver transplantation. Official journal of the American College of Gastroenterology| ACG 2021, 116, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, N.; Bhangui, P.; Yao, F.Y.; Mazzaferro, V.; Toso, C.; Akamatsu, N.; Soin, A. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Working group report from the ILTS transplant oncology consensus conference. Transplantation 2020, 104, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzartzeva, K.; Obi, J.; Rich, N.E.; Parikh, N.D.; Marrero, J.A.; Yopp, A.; Singal, A.G. Surveillance imaging and alpha fetoprotein for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: a meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1706–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, L.R.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zaiem, F.; Almasri, J.; Prokop, L.J.; Heimbach, J.K.; Mohammed, K. Imaging for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2018, 67, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, D.S.; Olthoff, K.M. Standardizing MELD exceptions: current challenges and future directions. Current transplantation reports 2014, 1, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.D. Current status of deep learning applications in abdominal ultrasonography. Ultrasonography 2021, 40, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiyarattanachai, T.; Apiparakoon, T.; Marukatat, S.; Sukcharoen, S.; Yimsawad, S.; Chaichuen, O.; Chaiteerakij, R. The feasibility to use artificial intelligence to aid detecting focal liver lesions in real-time ultrasound: a preliminary study based on videos. Scientific reports 2022, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.G.; Ahn, G.; Park, S.H.; Kim, S.Y. ... & Kim, N. (2019, March). Automatic hepatocellular carcinoma lesion detection with dynamic enhancement characteristic from multi-phase CT images. In International Forum on Medical Imaging in Asia 2019 (Vol. 11050, pp. 203–208). SPIE.
- Kim, D.W.; Lee, G.; Kim, S.Y.; Ahn, G.; Lee, J.G.; Lee, S.S. ... & Kim, N. Deep learning–based algorithm to detect primary hepatic malignancy in multiphase CT of patients at high risk for HCC. European Radiology 2021, 31, 7047–7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Min, J.H.; Kim, S.K.; Shin, S.Y.; Lee, M.W. Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging using deep learning classifier: a multi-center retrospective study. Scientific reports 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabijańska, A.; Vacavant, A.; Lebre, M.A.; Pavan, A.L.; de Pina, D.R.; Abergel, A. ... & Magnin, B. (2018). U-CatcHCC: An accurate HCC detector in hepatic DCE-MRI sequences based on an U-Net framework. In Computer Vision and Graphics: International Conference, ICCVG 2018, Warsaw, Poland, September 17-19, 2018, Proceedings (pp. 319-328). Springer International Publishing.
- Gotra, A.; Sivakumaran, L.; Chartrand, G.; Vu, K.N.; Vandenbroucke-Menu, F.; Kauffmann, C.; Tang, A. Liver segmentation: indications, techniques and future directions. Insights into imaging 2017, 8, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ginneken, B., Heimann, T., & Styner, M. (2007, October). 3D segmentation in the clinic: A grand challenge. In MICCAI workshop on 3D segmentation in the clinic: a grand challenge(Vol. 1, pp. 7–15).
- Deng, X., & Du, G. (2008, September). 3D segmentation in the clinic: a grand challenge II-liver tumor segmentation. In MICCAI workshop.
- Bilic, P.; Christ, P.F.; Vorontsov, E.; Chlebus, G.; Chen, H.; Dou, Q.; Fu, C.; Han, X.; Heng, P.; Hesser, J.W.; Kadoury, S.; Konopczynski, T.K.; Le, M.; Li, C.; Li, X. , Lipková, J., Lowengrub, J.S.; Meine, H.; Moltz, J.H.; Pal, C.J.; Piraud, M.; Qi, X.; Qi, J.; Rempfler, M.; Roth, K.; Schenk, A.; Sekuboyina, A.K.; Zhou, P.; Hülsemeyer, C.; Beetz, M.; Ettlinger, F.; Grün, F.; Kaissis, G.; Lohöfer, F.; Braren, R.F.; Holch, J.W.; Hofmann, F.O.; Sommer, W.H.; Heinemann, V.; Jacobs, C.; Mamani, G.E.; Ginneken, B.V.; Chartrand, G.; Tang, A.; Drozdzal, M.; Ben-Cohen, A.; Klang, E.; Amitai, M.M.; Konen, E.; Greenspan, H.; Moreau, J.; Hostettler, A.; Soler, L.; Vivanti, R.; Szeskin, A.; Lev-Cohain, N.; Sosna, J.; Joskowicz, L.; Menze, B.H. The Liver Tumor Segmentation Benchmark (LiTS). Medical image analysis 2019, 84, 102680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.R.; Rabi, S. Study of morphological variations of liver in human. Translational Research in Anatomy 2019, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernuccio, F.; Whitney, S.A.; Ravindra, K.; Marin, D. CT and MR imaging evaluation of living liver donors. Abdominal Radiology 2021, 46, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, M.C.; Tan, C.H.; Cai, J.; Zheng, J.; Kow, A.W.C. CT volumetry of the liver: where does it stand in clinical practice? Clinical radiology 2014, 69, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couinaud, C. (1957). Le foie: études anatomiques et chirurgicales. Masson.
- Tian, J., Liu, L., Shi, Z., & Xu, F. (2019, October). Automatic couinaud segmentation from CT volumes on liver using GLC-UNet. In Machine Learning in Medical Imaging: 10th International Workshop, MLMI 2019, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2019, Shenzhen, China, October 13, 2019, Proceedings (pp. 274-282). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Wang, M.; Jin, R.; Lu, J.; Song, E.; Ma, G. Automatic CT liver Couinaud segmentation based on key bifurcation detection with attentive residual hourglass-based cascaded network. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2022, 144, 105363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Xu, H.; Zheng, D.; Yang, Z. Automated segmentation of liver segment on portal venous phase MR images using a 3D convolutional neural network. Insights into Imaging 2022, 13, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamar, M.; Selzner, M. Steatotic donor livers: Where is the risk-benefit maximized? Liver Transplantation 2017, 23, S34–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yersiz, H.; Lee, C.; Kaldas, F.M.; Hong, J.C.; Rana, A.; Schnickel, G.T.; Petrowsky, H. Assessment of hepatic steatosis by transplant surgeon and expert pathologist: a prospective, double-blind evaluation of 201 donor livers. Liver Transplantation 2013, 19, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Liu, S.; Du, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, J.; Dong, Q.; Xin, Y. Diagnostic value of MRI-PDFF for hepatic steatosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis. European radiology 2019, 29, 3564–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Pastor, A.; Alberich-Bayarri, A.; Lopez-Gonzalez, R.; Marti-Aguado, D.; França, M.; Bachmann RS, M.; Marti-Bonmati, L. Precise whole liver automatic segmentation and quantification of PDFF and R2* on MR images. European radiology 2021, 31, 7876–7887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousabarah, K.; Letzen, B.; Tefera, J.; Savic, L.; Schobert, I.; Schlachter, T.; Lin, M. Automated detection and delineation of hepatocellular carcinoma on multiphasic contrast-enhanced MRI using deep learning. Abdominal Radiology 2021, 46, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vugt, J.L.A.; Levolger, S.; De Bruin, R.W.F.; van Rosmalen, J.; Metselaar, H.J.; IJzermans, J.N.M. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the impact of computed tomography–assessed skeletal muscle mass on outcome in patients awaiting or undergoing liver transplantation. American Journal of Transplantation 2016, 16, 2277–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafaat, O.; Liu, Y.; Jackson, K.R.; Motter, J.D.; Boyarsky, B.J.; Latif, M.A.; Weiss, C.R. Association between abdominal CT measurements of body composition before deceased donor liver transplant with posttransplant outcomes. Radiology 2022, 212403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozynek, M.; Kucybała, I.; Urbanik, A.; Wojciechowski, W. Use of artificial intelligence in the imaging of sarcopenia: A narrative review of current status and perspectives. Nutrition 2021, 89, 111227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc-Durand, P.; Schiratti, J.B.; Schutte, K.; Jehanno, P.; Herent, P.; Pigneur, F.; Jégou, S. Abdominal musculature segmentation and surface prediction from CT using deep learning for sarcopenia assessment. Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging 2020, 101, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, S.; Bechstein, W.O.; Steinmüller, T.; Herrmann, M.; Radke, C.; Berg, T.; Neuhaus, P. Vascular invasion and histopathologic grading determine outcome after liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. Hepatology 2001, 33, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, S.; Kato, T.; Berho, M.; Misiakos, E.P.; O'Brien, C.; Reddy, K.R.; Tzakis, A.G. Impact of histological grade of hepatocellular carcinoma on the outcome of liver transplantation. Archives of surgery 2001, 136, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins-Filho, S.N.; Paiva, C.; Azevedo, R.S.; Alves VA, F. Histological grading of hepatocellular carcinoma—a systematic review of literature. Frontiers in medicine 2017, 4, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Court, C.M.; Harlander-Locke, M.P.; Markovic, D.; French, S.W.; Naini, B.V.; Lu, D.S.; Agopian, V.G. Determination of hepatocellular carcinoma grade by needle biopsy is unreliable for liver transplant candidate selection. Liver transplantation 2017, 23, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Zhang, L.; Ning, P.; Ding, F.; Wu, F.; Lu, G.; Ma, J. Preoperative prediction for pathological grade of hepatocellular carcinoma via machine learning–based radiomics. European Radiology 2020, 30, 6924–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Tan, H.; Gao, F.; Hai, J.; Ning, P.; Chen, J.; Shi, D. Predicting the grade of hepatocellular carcinoma based on non-contrast-enhanced MRI radiomics signature. European radiology 2019, 29, 2802–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, G.; Xie, G.; Zhang, L. Grading of hepatocellular carcinoma based on diffusion weighted images with multiple b-values using convolutional neural networks. Medical physics 2019, 46, 3951–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, C.; Fan, G.; Chen, G.; Heng, H.; Dai, Y. Grading of hepatocellular carcinoma using 3D SE-DenseNet in dynamic enhanced MR images. Computers in biology and medicine 2019, 107, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.K.; Qi, C.Y.; Chen, D.; Li, S.Q.; Fu, S.J.; Peng, B.G.; Liang, L.J. Prognostic significance of glypican-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Bmc Cancer 2014, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.L.; Zhu, Z.J.; Teng, D.H.; Yao, Z.; Gao, W.; Shen, Z.Y. Glypican-3 expression and its relationship with recurrence of HCC after liver transplantation. World Journal of Gastroenterology: WJG 2012, 18, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Li, Z.; Gao, P.J.; Gao, J.; Zhu, J.Y. Prognostic value of glypican-3 in patients with HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation. Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International 2015, 14, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, D.; Xie, Y.; Wei, J.; Li, W.; Ye, Z.; Zhu, Z. ... & Li, X. MRI-based radiomics signature: a potential biomarker for identifying glypican 3-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 2020, 52, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, H.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Sheng, R.; Zeng, M. Radiomics on Gadoxetate Disodium-enhanced MRI: Non-invasively Identifying Glypican 3-Positive Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Postoperative Recurrence. Academic Radiology 2023, 30, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miltiadous, O.; Sia, D.; Hoshida, Y.; Fiel, M.I.; Harrington, A.N.; Thung, S.N.; Llovet, J.M. Progenitor cell markers predict outcome of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma beyond Milan criteria undergoing liver transplantation. Journal of hepatology 2015, 63, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wan, Y.; Xu, L.; Wu, Y.; Shen, X.; Wang, J. ... & Xu, X. MRI-Radiomics prediction for cytokeratin 19-Positive hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter study. Frontiers in Oncology 2021, 11, 672126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.B.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Shim, J.H.; Lee, S.S.; Byun, J.H. ... & Lee, N. K. MRI features for predicting microvascular invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Liver Cancer 2021, 10, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Park, C.K.; Min, J.H.; Lee, J.E.; Choi, Y.H.; Lee, B.R. Imaging features of gadoxetic acid–enhanced and diffusion-weighted MR imaging for identifying cytokeratin 19-positive hepatocellular carcinoma: a Retrospective Observational Study. Radiology 2018, 286, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.S.; Choi, J.Y. MRI features of hepatocellular carcinoma related to biologic behavior. Korean journal of radiology 2015, 16, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler, L.; A Hostettler, V. Agnus, A. Charnoz, J. Fasquel, J. Moreau, A. Osswald, M. Bouhadjar, and J. Marescaux. “3D image reconstruction for comparison of algorithm database: A patient specific anatomical and medical image database.” IRCAD, Strasbourg, France, Tech. Rep (2010).
- Kavur, A.E.; Selver, M.A.; Dicle, O.; Barıs, M.; Gezer, N.S. CHAOS-combined (CT-MR) healthy abdominal organ segmentation challenge data. Med. Image Anal 2019, 69, 101950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardobi, N.; Dal Palù, A.; Pedrini, F.; Beleù, A.; Nocini, R.; De Robertis, R. ... & D’Onofrio, M. An Overview of Artificial Intelligence Applications in Liver and Pancreatic Imaging. Cancers 2021, 13, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongan, J.; Moy, L.; Kahn Jr, C.E. Checklist for artificial intelligence in medical imaging (CLAIM): a guide for authors and reviewers. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence 2020, 2, e200029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sengupta, S.; Lakshminarayanan, V. Explainable deep learning models in medical image analysis. Journal of Imaging 2020, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| CRITERIA | REPORT |
| MILAN [25] | One lesion ≤5 cm or maximum 3 lesions each ≤3 cm; |
| University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) [32] |
One lesion ≤6.5 cm or maximum 3 lesions with the largest tumor diameter ≤4.5 cm and a total tumor diameter ≤8; |
| Up-to-7 [33] | The sum of the number of lesions and the diameter of the largest lesion ≤7; |
| Updated Up-to-7 /Metroticket V2.0 [34] | A combination of the sum of the number of lesions, the largest lesion diameter and AFP; |
| AFP model [35] | A score based on largest tumour diameter, number of nodules and AFP; A result of ≤ 2 is an indication of transplant; |
| UNOS criteria [36] | One lesion ≥2 cm and ≤5 cm or maximum 3 lesions each ≥1 cm and ≤3; AFP ≤1000 ng/dl |
| Extended Toronto [37] | No tumour size and number limit; Biopsy needed beyond Milan to exclude poorly differentiated; |
| Total tumor volume (TTV) [38] | TTV of less than 115 cm3; |
| Hangzhou criteria [39] | Total tumor diameter ≤8 cm or >8 cm with histopathologic grade 1 or 2, and a preoperative AFP value of ≤400 |
| TRAIN score [40] | mRECIST response; AFP slope; Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR); Waitlist time; |
| Author | Year | Modality | AI-method | Sensitivity |
| Tiyarattanachai et al.[50] | 2022 | US | DL | 89.8% |
| Lee et al. [51] | 2019 | CECT | DL | 93.8% |
| Kim et al. [52] | 2021 | CECT | DL | 84.8% |
| Kim et al. [53] | 2020 | MRI | DL | 87% |
| Fabijańska et al. [54] | 2018 | MRI | DL | 90.8% |
| Author | Year | Scope | Modality | AI-method | DICE score |
| Tian et al. [63] | 2019 | Couinaud segmentation | CECT | DL | 92.46% |
| Wang et al. [64] | 2022 | Couinaud segmentation | CECT | DL | 84% |
| Han et al. [65] | 2022 | Couinaud segmentation | MRI | DL | 90.2% |
| Jimenez-Pastor et al. [69] | 2021 | Liver segmentation, fat and iron quantification | MRI | DL | 93% |
| Bousabarah et al. [70] | 2021 | Liver and HCC segmentation | MRI | DL | 91% for liver 68% for HCC |
| Durand et al. [74] | 2020 | Sarcopenia evaluation | CT | DL | 97% |
| Author | Year | Scope | Data | AI-method | AUC |
| Mao et al. [79] | 2020 | Grading prediction | CECT+Clinical | Radiomics | 0.801 |
| Wu et al. [80] | 2019 | Grading prediction | MRI+Clinical | Radiomics | 0.8 |
| Zhou et al. [81] | 2019 | Grading prediction | DWI MRI | DL | 0.83 |
| Zhou et al. [82] | 2019 | Grading prediction | DCE MRI | DL | 0.83 |
| Author | Year | Scope | Data | AI-method | AUC |
| Gu et al. [86] | 2020 | GPC3 prediction | DCE-MRI (Gd- DTPA)+Clinical | Radiomics | 0.914 |
| Chong et al. [87] | 2023 | GPC3 prediction | DCE-MRI (Gd-EOB-DTPA)+Clinical | Radiomics | 0.943 |
| Yang et al. [89] | 2021 | CK19 prediction | MRI | Radiomics | 0.79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





