1. Introduction
With the advent of newer strategies and aids that claim to prevent sport injuries, it has become difficult to decide if these strategies or aids are significant at the scientific level. A novel product widely used among athletes and clinicians nowadays is the kinesiology tape, often referred to as a K-tape. Kinesiology tape, developed by Kenzo Kase in the 1970s is a water-resistant, air permeable and elastic tape which possesses properties of elasticity and recoil. It can stretch up to 120-140% of its original length and, because of these properties, it has become famous for its use amongst the clinical and athletic population. According to the creator of this tape, this tape works in four different ways. Firstly, it strengthens the weakened muscles, thereby enhancing muscle function, secondly, it helps in movement of muscles hence also improving circulation, thirdly it causes neurological suppression of pain, and fourthly, it relieves abnormal muscle tension by relaxing the fascia and the muscle so that smooth movements are produced [
1]. The fifth mechanism which is very important to this study is that kinesiology tape causes increase in proprioception, owing to its special features. Due to cutaneous application of the tape, shear and compressive forces activate the cutaneous mechanoreceptors which relay important information regarding proprioception [
2]. K-tape has been much researched for its effects on proprioception which is one of the somatic senses. Proprioception is derived from two Latin words ‘
receptus’ meaning to receive and
‘propius’ meaning one’s own. The term was coined by Sherrington and is defined as the ability of the body to sense body’s movement and position [
3]. It is a complex neuromuscular process which allows the body to maintain orientation and stability during activities.
Considering the fact that knee joint is one of the most stressed and shock-absorbing joint of the human body, it is no surprise that 60% off all sport injuries consist of knee injuries [
4]. It has been speculated that majority of these injuries occur due to a number of predisposing factors such as gender, age, declining muscle strength, muscle fatigue and poor proprioception to name a few. It has been researched previously that poor joint position sense can increase the risk of injury in knee joint [
5]. This can be explained by the fact that proprioception provides protection against excessive movements in the knee, secondly it stabilizes the posture and thirdly, it provides coordination of movements in the lower extremity so that this complex joint can assist in movements both in daily life and in sports.
In recent years. there has been increased use of kinesiology tape for rehabilitation and prevention of sport injuries. This special tape which possesses properties of elasticity and recoil has been scientifically proven to enhance proprioception. Moreover, since the tape allows free range of motion and can be worn by athletes for long periods, this has led to its increased use among athletes. It has been concluded in many studies that this special tape can prevent sports injuries and has beneficial effects on both joint position sense and muscle function as well [
6].
Kinesiology tape and its effects has been studied extensively in the past and it has been used in both sports and preventive medicine. It has proven its effectiveness in many degenerative musculoskeletal conditions and has been employed in a number of treatment protocols for musculoskeletal and sports injuries. However, there have been controversial results published previously on its effectiveness when used on healthy subjects. In one study it was revealed that kinesiology taping shortens time required for reaching the peak torque in healthy subjects during isometric knee extension [
7]. However, another study did not record any significant difference in the electromyographic readings taken at the quadriceps muscle after kinesiology tape application, which is contrary to the first study [
7]. Similarly previous studies conducted on investigating the effects of kinesiology tape on joint position sense have been quite ambiguous. One study concluded that quadriceps muscle kinesiology tape application improves the threshold for detection of passive movement in the knee and can be seen as a vessel for prevention strategy [
8]. On the contrary, another study stated that kinesiology taping application seems insignificant to improve knee joint position sense [
9].
Because of the wide array of results existing in previous literature the main aim of the study was to combine two parameters of proprioception together i.e., joint position sense and force sense which has not been investigated before in combination, to validate the previous researches and implicate the use of kinesiology taping in healthy subjects.
The main purpose of the study was to find out the short-term effects of kinesiology taping of quadriceps muscles in terms of both joint position sense and force sense in healthy subjects. We hypothesized that muscle length might be influenced by immediate kinesiology tape application which might alter proprioception and secondly, we hypothesized that kinesiology taping alters muscle strength by a direct impact on mechanoreceptors and similarly it might reduce absolute errors in force matching tasks in healthy individuals.
2. Materials and Methods
The study was an experimental cross-sectional study and in order to test our two hypotheses, we firstly tested subjects for unilateral joint position sense and secondly for force sense with and without tape. We randomized the participants for kinesiology tape application to avoid the adaptation factor which could mimic the learning effect of these tests for purpose of reliable outcomes and hence, 6 subjects had tests with kinesiology tape applied on the second laboratory visit while remaining 6 had kinesiology tape applied on the first day of visit. All of the subjects (M = 7, F = 5) were young and physically active and had no history of any significant trauma to the lower limb within the past five years and no active musculoskeletal complaint was reported at the time of experiment. Their baseline characteristics are provided in
Table 1.
A computerized and custom-built isokinetic dynamometer ((Multicont II, Mediagnost, Budapest, and Mechatronic Kft, Szeged, Hungary) was employed for this experiment.
2.1. Joint Position Testing
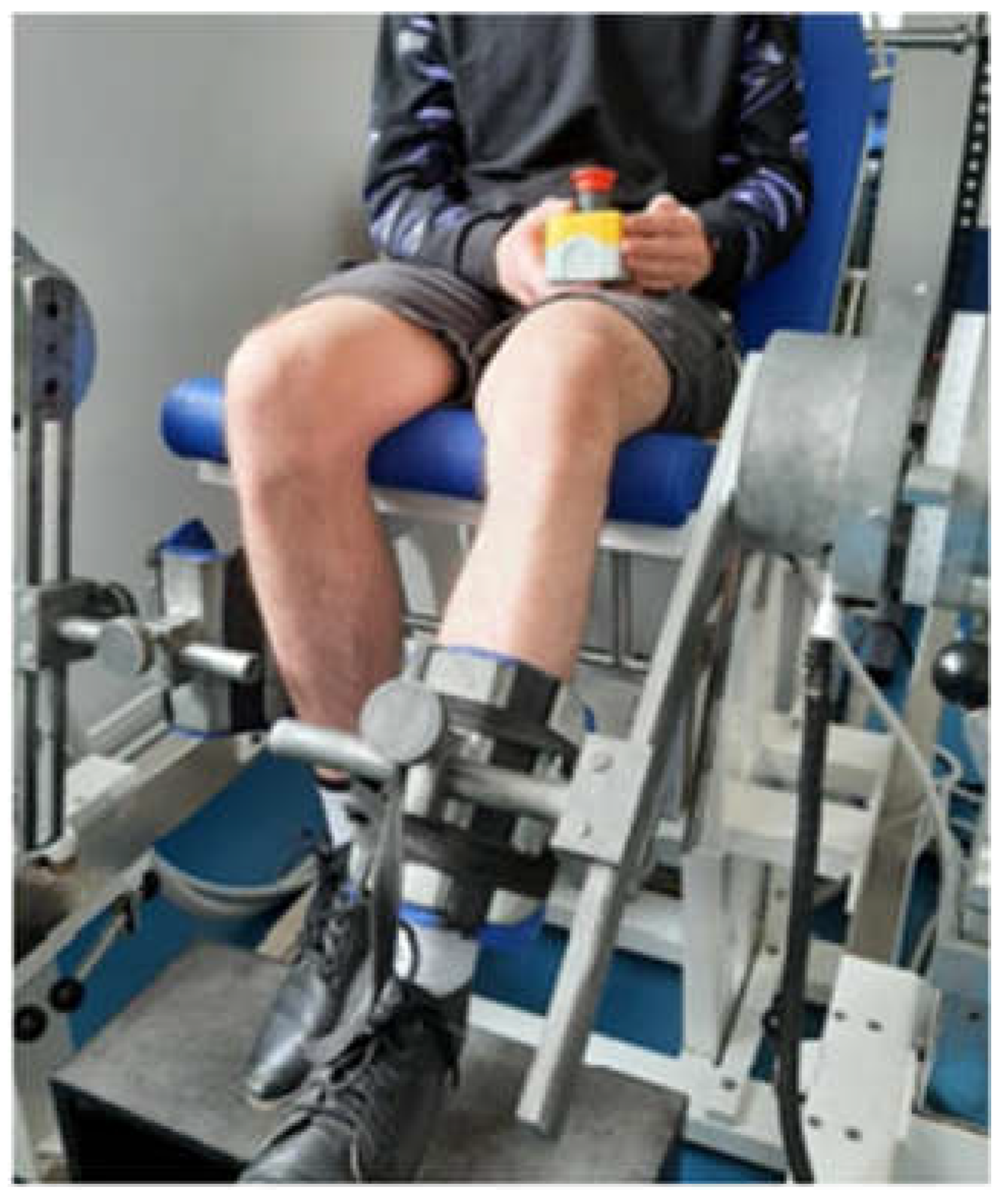
For joint position testing protocol as shown in
Figure 1, subjects were requested to sit on the seat of the dynamometer. The left lower leg was secured to the lever arm with the help of securing bands which were tied around the ankle cuffs at the same level above ankle for each subject, depending on their lower leg length for all trials of the experiment. The resting angle of the lever arm was set at 50° and from here it went through 15°, 20°, 25°, 75°,80° and 85° in randomized order twice with the experimenter controlling the order so as to complete twelve trials, (two trials for each angle) for every participant. The subjects were notified when they had to memorize the angle because the machine stopped for 5 seconds during that. After that the machine went back to the resting angle and then back to target angle, which the subject had to perceive and then press the pusher button so that the machine stops, and the angle can be recorded by the experimenter.
2.2. Force Sense Testing
For the second part of hypothesis testing, which focused on the force sense, we used the same apparatus and first asked the subjects to do a general warm-up on a stationary bike for three minutes. After that both the legs of the subjects were secured to the lever arms with securing bands around the ankle cuffs at the same level as before and the machine was set for isometric contraction for 13 seconds starting from 50° of knee flexion which is the most optimum angle for training [
11]. Before the actual MVIC, warmups at 50% and 90% of maximum effort were given. After recording the maximum of both right and left legs, we moved on to the target force matching protocol.
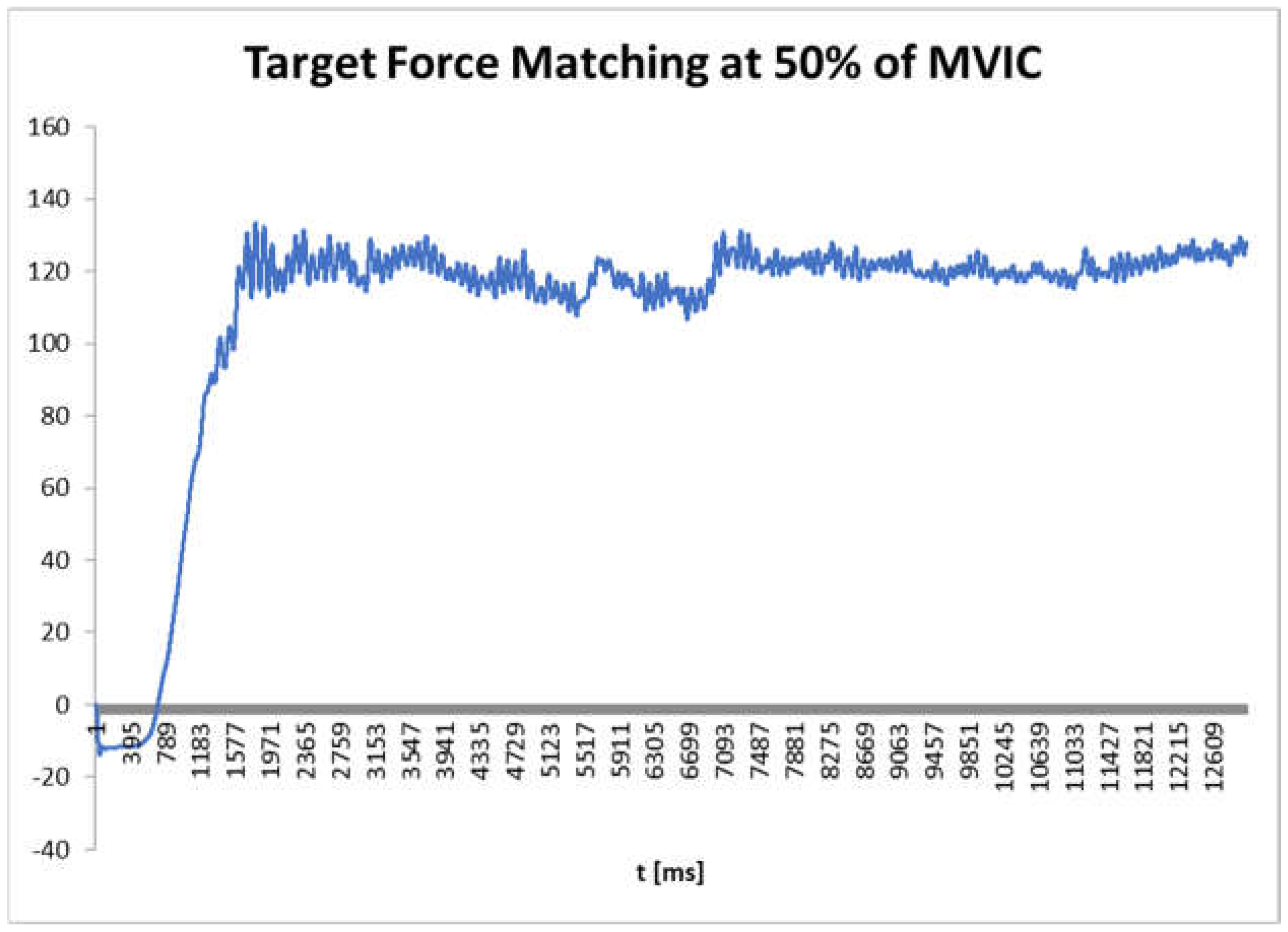
After the maximum voluntary isometric contraction (MVIC) reading were obtained, we set the target isometric voluntary contraction at 50% of the MVIC for each subject as shown in
Figure 2 and asked them to produce the same force on the left leg first without the screen feedback and in the end with feed-back again. Two trials were taken for each condition with and without tape on separate days.
2.2. Taping Method
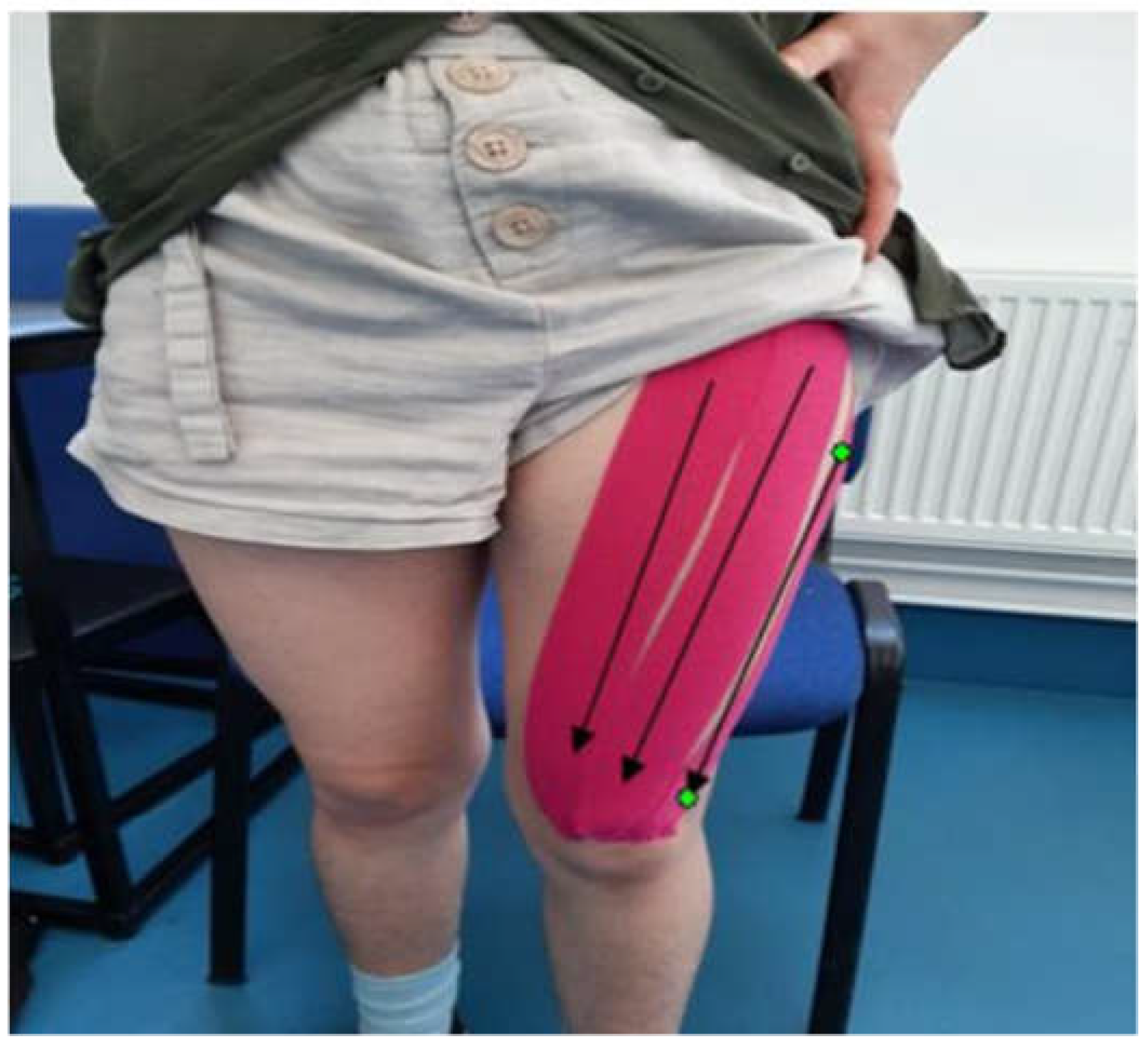
The taping method was the same for all applicants as shown in
Figure 3. With the knee bent at 90° of flexion we applied the tape (Movomed kinesiology Tape 5 × 5 cm, Manufactured by Movomed Manufacturer Limited, Hungary) in the origin to insertion direction for the three muscles including rectus femoris, vastus lateralis and medialis. This taping method in the origin to insertion direction has previously been employed in a kinesiology tape study [
12] and it was previously cited in literature that taping from origin to insertion provides more benefits in terms of muscle performance, as compared to the one applied in reverse direction which helps in reducing tone of the muscles [
13]. For all subjects, measurements were taken prior to the application of tape from:
1) anterior superior iliac spine to the superior border of patella
2) from greater trochanter to the lateral superior region of patella
3) between the intertrochanteric line to the medial superior aspect of patella.
The tape was stretched to about 35-40% of its original length during application longitudinally and diagonally.
2.4. Statistical Analyses
Data were stored and analyzed using IBM-SPSS version 28.0.1.1. Mean and standard deviation were reported for baseline quantitative variables like age, weight, height and body mass index (BMI) and absolute errors were taken for joint angle measurements and mean target force production. Data was collected in Multicont software which recorded perceived joint angle to the nearest two decimal places in the eccentric/concentric contraction program. For force sense protocol, an isometric test program was used which recorded time, the power output and the angle of lever arm. We collected outputs in the form of joint angles in degrees, maximum voluntary isometric contractions in Nm, and target force contractions at 50% of MVIC in Nm for the last 8000 milliseconds for all subjects for both conditions, i.e., with and without tape. We applied repeated measures Two –Way ANOVA to check for differences between groups in small and large muscle lengths and applied paired t-test to check for differences in MVIC and for differences in absolute errors reported from target force matching task (both with vision and without vision) between taped and un-taped conditions. p-values less than 0.05 were considered significant during the statistical analyses and bar-graphs were also used to give graphical presentation of the results.
3. Results
The Shapiro Wilk test of normality revealed that the data was normally distributed. (
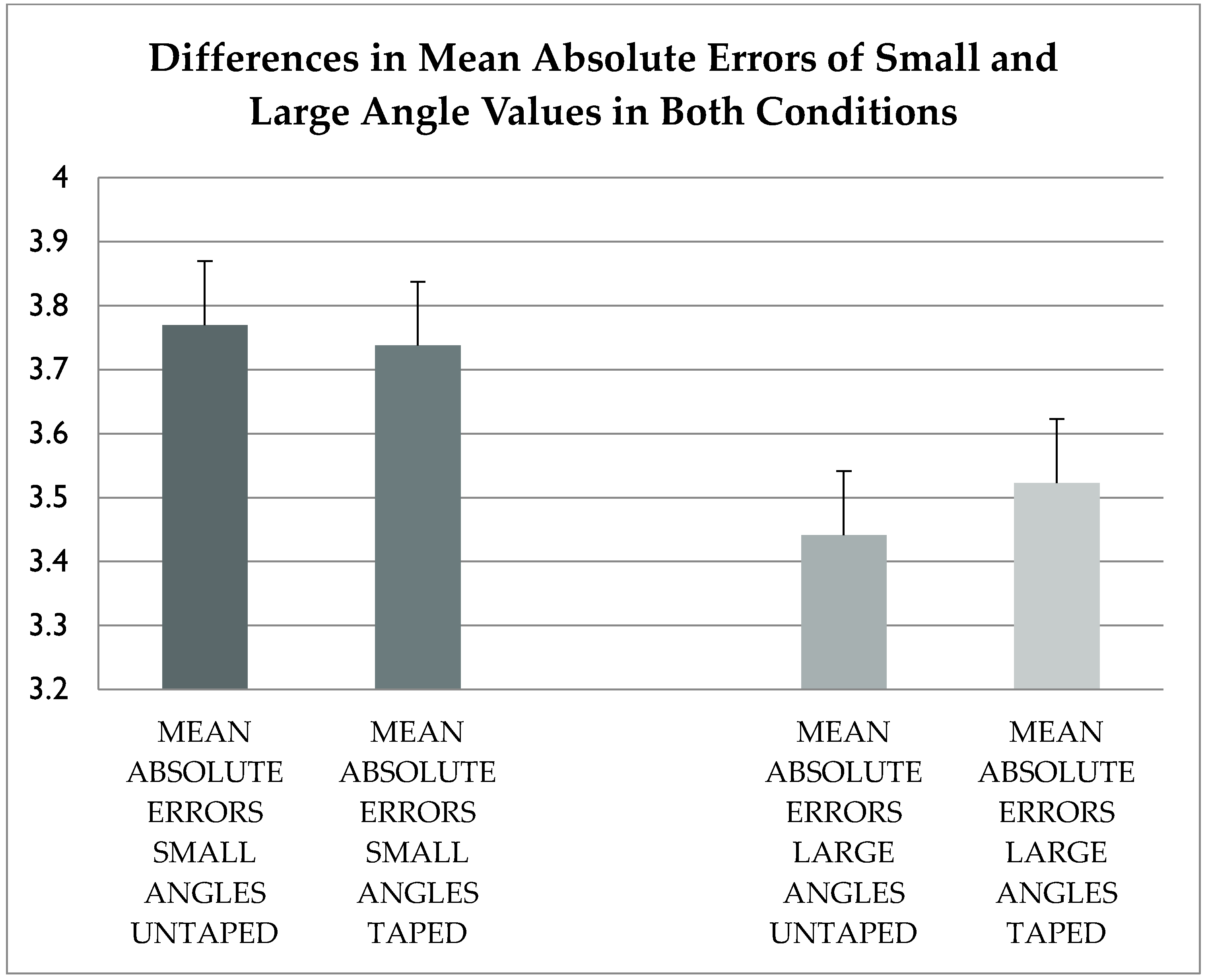
p > 0.05). The differences in mean absolute errors between two muscle length and the two conditions are shown in
Figure 4.
Table 2 depicts that errors increased in the taped conditions for 15 and 75° respectively.
A two-way repeated measures ANOVA result revealed that no significant interaction was found between the two muscle lengths (small and large) and two conditions (taped and un-taped). We also did not observe any main condition effect on the muscle lengths. F (1, 11) = 0.02,
p = 0.8. The paired t-test conducted also suggested no significant difference between the un-taped and taped conditions in terms of torque production [p = 0.67) although mean MVIC increased in the taped condition slightly as shown in
Figure 5, yet this was not statistically significant.
Figure 6 highlights that the mean absolute errors increased in target force matching tasks between the two conditions (taped and untaped) both with vision and without vision. Moreover, no significant difference was found between target force matching without vision untaped vs. without vision taped [
p = 0.38] and with vision taped vs. without vision untaped[
p = 0.52].
4. Discussion
Kinesiology tape has been researched and known for its potential effects among a wide array of musculoskeletal disorders. However, the present study gave an insight into its use among healthy individuals and implicated that there are no significant beneficial effects of kinesiology tape after immediate application on quadriceps muscle. Our results are in harmony with previous researches which suggested no evident benefits of kinesiology tape in terms of joint position sense when it was applied on quadriceps muscles [
9,
14]. Hence it is probable to state that the elasticity and shear forces provided by kinesiology tape are not really enough to impact mechanoreceptors which aid in proprioception in healthy individuals. Although we noted mean increases in torque after kinesiology tape application, yet these increments were statistically insignificant. These results are again in harmony with previous research which indicated that although a peak power increase in isometric quadriceps contraction was noticed after quadriceps muscle kinesiology taping but again the strength remained the same therefore, we can state that short-term kinesiology tape application to quadriceps muscle to increase muscle strength is not very promising. (Wei et al., 2020) Our results are also in accordance with other studies which indicated that no increases in healthy individuals were reported when kinesiology tape was applied over the quadriceps muscles [
6,
16]. Thus it is sufficient to say that the stretch provided by the tape application on quadriceps muscle does not impacts either the special excitatory inter-neurons nor alters force-tension relationship why is why no significant differences were reported between the two conditions. In contrast, a study reported increases in quadriceps strength and an improvement in lower extremity function among healthy non-athletes after applying kinesiology tape to the quadriceps femoris with patellar correction technique. In this, unlike the present study, a “Y” shaped strip was applied to the knee (from the lateral edge of the patella to its medial region, creating a circle around it). It is believed that this technique aimed to mechanically correct the position of the patella and consequently, the observed positive effects may have been directly influenced by the application of this extra strip. The stimuli promoted in the knee mechanoreceptors may have added to the stimuli promoted by the direct application of KT on the skin above the quadriceps, thereby improving the strength and function of these individuals [
17]. Moreover, target force matching tasks were employed to see if kinesiology tape offered any advantage because of its properties of stretch and recoil to aid in muscle memory, but it seemed that it did not really assisted in it as well. We also applied the tape in origin to insertion direction which was previously indicated to increase muscle force, but yet changes were consistent in untaped and taped conditions, hence immediate cutaneous application of the tape is not capable of relaying important information to the brain regarding proprioception in healthy individuals which was previously denoted in a study [
2]. It is possible that the normal neuromuscular system of the healthy individuals assessed in our study (without any pain or neuromuscular deficits), could have contributed to the lack of effect in tactile stimuli and the alteration in motor unit recruitment of quadriceps femoris, thus not offering support for any significant effects between the two conditions,
5. Conclusions
The present study urges practitioners working in the field of preventive medicine and therapy to document and investigate proper use of therapeutic aids which are marketed commercially for boosting training parameters like proprioception. This study gave an insight into different elements of proprioception including joint position sense and force sense together to see how this complex system works in healthy individuals. In future, it is suggested to conduct a comparative study between the groups to see the short-term and long-term application effects of kinesiology tape and compare it with proprioceptive training controls to see if any significant difference exists among them. Moreover, it might also be a novel idea to incorporate active range of motion for joint position sense testing to see if any difference exists between them and the current study group.
Author Contributions
“Conceptualization, M.M. and M.V.; methodology, M.M. and M.V.; software, M.M. and M.V.; validation, M.M. and M.V.; formal analysis, M.M. and M.V.; investigation, M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.; writing—review and editing, M.M and M.V.; supervision, M.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study due to the fact that the study posed no harm to the participants and study was done on human subjects after their informed consent was obtained and fell into the standards of the research studies requiring no institutional review for the University of Pécs.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the participants to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The data for the research can be downloaded at: Maqsood, Mariam; Váczi, Márk (2023), “Immediate Effects of Quadriceps Muscle Kinesiology Taping on Joint Position Sense and Force Sense in Healthy Individuals.”, Mendeley Data, V2, doi: 10.17632/vrvrdkjmtj.2
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kase K., Tatsuyuki H., Tomoki O. (1996) Development of Kinesio™ tape Kinesio™ Taping Perfect Manual. Kinesio Taping Association 6-10, 117-118.
- Murray H. (2001) Effects of Kinesio™ taping on muscle strength after ACL-repair. Available from URL:http://www.kinesiotaping.com April 15, 2002, 1-3.
- Sherrington, C. S. (1911). Lecture IV: Interaction between reflexes. In C. S. Sherrington, The integrative action of the nervous system. (pp. 114–149). Yale University Press. [CrossRef]
- Rishiraj, N., Taunton, J. E., Lloyd-Smith, R., Woollard, R., Regan, W., & Clement, D. B. (2009). The Potential Role of Prophylactic/Functional Knee Bracing in Preventing Knee Ligament Injury: Sports Medicine, 39(11), 937–960. [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, S., & Shields, R. K. (2005). Influence of age on dynamic position sense: Evidence using a sequential movement task. Experimental Brain Research, 164(1), 18–28. [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.-C., Wong, A. M. K., Pei, Y.-C., Wu, K. P., Chou, S.-W., & Lin, Y.-C. (2008). Effect of Kinesio taping on muscle strength in athletes—A pilot study. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport, 11(2), 198–201. [CrossRef]
- Yeung, S. S., Yeung, E. W., Sakunkaruna, Y., Mingsoongnern, S., Hung, W. Y., Fan, Y. L., & Iao, H. C. (2015). Acute Effects of Kinesio Taping on Knee Extensor Peak Torque and Electromyographic Activity After Exhaustive Isometric Knee Extension in Healthy Young Adults. Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine, 25(3), 284–290. [CrossRef]
- Janwantanakul, P., & Gaogasigam, C. (2005). Vastus lateralis vastus medialis obliquus muscle activity during the application of inhibition and facilitation taping techniques. Clinical Rehabilitation, 19(1), 12–19. [CrossRef]
- Torres, R., Trindade, R., & Gonçalves, R. S. (2016). The effect of kinesiology tape on knee proprioception in healthy subjects. Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies, 20(4), 857– 862. [CrossRef]
- Hadamus, Anna & Białoszewski, Dariusz & Korabiewska, Izabela. (2009). The Effect of Kinesiology Taping and Muscle Fatigue on Movement Control in the Shoulder Joint - Preliminary Report. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research. 32. S92. [CrossRef]
- Váczi, M., Tihanyi, J., Hortobágyi, T., Rácz, L., Csende, Z., Costa, A., & Pucsok, J. (2011). Mechanical, Biochemical, and Electromyographic Responses to Short-Term Eccentric–Concentric Knee Extensor Training in Humans. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 25(4), 922–932. [CrossRef]
- Choi, I. R., & Lee, J. H. (2018). Effect of kinesiology tape application direction on quadriceps strength. Medicine, 97(24). [CrossRef]
- Kase K., Tatsuyuki H., Tomoki O. (1996) Development of Kinesio™ tape Kinesio™ Taping Perfect Manual. Kinesio Taping Association 6-10, 117-118.
- Hosp, S., Bottoni, G., Heinrich, D., Kofler, P., Hasler, M., & Nachbauer, W. (2015). A pilot study of the effect of Kinesiology tape on knee proprioception after physical activity in healthy women. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport, 18(6), 709–713. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z., Wang, X.-X., & Wang, L. (2020). Effect of Short-Term Kinesiology Taping on Knee Proprioception and Quadriceps Performance in Healthy Individuals. Frontiers in Physiology, 11, 603193. [CrossRef]
- de Jesus, J. F., Franco, Y. R., Nannini, S. B., Nakaoka, G. B., Dos Reis, A. C., & Bryk, F. F. (2017). THE EFFECTS OF VARIED TENSIONS OF KINESIOLOGY TAPING ON QUADRICEPS STRENGTH AND LOWER LIMB FUNCTION. International journal of sports physical therapy, 12(1), 85–93.
- Aktas G, Baltaci G. Does kinesiotaping increase knee muscles strength and functional performance? Isokinet Exerc Sci. 2011;19:149–155. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).