1. Introduction
Germ cell cancer (GCC) represents one of the most common solid neoplasms affecting young adult men aged 18-44 years [
1]. The retroperitoneal lymph nodes are the most frequent site of metastasis in advanced testicular tumors. The European Association of Urology (EAU) Guidelines on testicular cancer suggest retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND) as the primary treatment in a) high risk stage IB patients, b) highly selected non-seminoma patients, c) patients with contraindication to adjuvant chemotherapy and unwilling to accept surveillance, d) in postpubertal teratoma with somatic malignant component, and e) in metastatic disease after chemotherapy for stage II or III seminomatous or non-seminomatous germ-cell tumours (NSGCT), depending on the tumor size or after lack of response to chemotherapy [
2].
The rationale for post chemotherapy retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (PC-RPLND) is to remove persistent retroperitoneal lymph nodes. Approximately 30%–40% of metastatic NSGCTs exhibit residual tumors after first-line chemotherapy that may contain necrosis/fibrosis (40%–50%), mature teratomas (20%–40%) or viable carcinoma cells (10–20%) [
3].
Regrettably, modern imaging techniques poorly differentiated residual necrosis/fibrosis, teratoma, or viable cancer after chemo-therapy [
4] and neither predict whether the residual masses can be successfully resected or not.
Currently, a shift in the imaging field is taking place: with new interest from qualitative interpretation of medical imaging to an emphasis on extraction of quantitative information from medical imaging (namely, radiomics). Radiomics refers to the extraction and analysis of large numbers of advanced quantitative imaging features (radiomic features, RF) from medical images using high throughput methods. Radiomics has two main arms based on how imaging information is transformed into mineable data: handcrafted radiomics and deep learning [
5]. Radiomics is an attractive research topic in uro-oncology [
6]. Volume rendering is a set of computer methods to get an image projection; rendered computerized tomography is not sufficient to get a precise visual classification. For this reason, this last task must be complemented with manually or semi-automatic segmentation [
7]. The subsequent analysis of radiomics features finally aims at supporting clinical decision-making and overcomes the limitations of a purely visual image interpretation [
8].
Complete resection of residual retroperitoneal masses in GCC is challenging, even for experienced surgeons, due to their deep anatomic location, desmoplastic reaction, dense peritumoral adhesions and proximity to major blood vessels or organs. An accurate understanding of the anatomy of the retroperitoneum before the surgical approach is essential to ensure the achievement of the procedure especially for young surgeons during the learning curve.
We hypothesized that computerized tomography segments rendering with radiomics extraction could identify whether PC-RP residual masses are resectable during pre-operative stage by young surgeons.
2. Material and methods
2.1. Study Design and Clinical Data
The proposed single-institution and ambispective study, included patients diagnosed with NSGCT between January 1, 2016, and October 31, 2021, who had residual retroperitoneal masses after chemotherapy and had undergone PC-RPLND by two-surgeons (one training surgeon and one senior surgeon). The study complies with the Declaration of Helsinki and local ethics committee approval (Instituto Nacional de Cancerologia)was obtained (n. 2020/0123).
For analyses, we selected 30 patients from database of 570 patients who underwent to PC-RPLND (retrospective group) and 30 news patients (prospective group) with tumor size from 1 to 13 cm. We considered retrospective group, as historical cohort, to compare and to explore the difference of the resectability in those cases studied pre-operative only 2D convencional computerized tomography (CT) versus prospective group studied by 3D reconstruction.
The decision to perform pcRPLND was individualized and was taken after discussion in the multi-specialty approach. According to our institution policy, PC-RPLND is performed in patients with NSGCT and a post-chemotherapy retroperitoneal nodal mass more than 1 cm with normal tumor markers. It is also indicated for patients with seminoma and retroperitoneal nodal mass bigger than 3 cm that is positive on a positron emission tomography (PET) combined with the computerized tomography (CT).
Patients underwent clinical examination and testing of serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) one week before the PC-RPLND. CT of chest, abdomen, and pelvis were performed four weeks prior to the procedure or after four or six weeks after the beginning of the last cycle of chemotherapy.
CS I seminoma, with high risk for recurrence, received two adjuvant courses of carboplatin and CS I non-seminoma adjuvant chemotherapy with bleomycin, etoposide, platinum (BEP)X 1. CS IIA/ IIB NSGCT have been treated with BEP X 3 or X4 according to risk categories.
For this study the inclusion criteria were a) residual nodal size > 1 cm, after frontline cisplatin-based chemotherapy, on CT imaging measured through transverse axial dimension for NSGCT; b) residual nodal size < 1 cm in patients with intermediate or poor prognosis or pure teratoma in primary orchiectomy specimen and c) residual nodal size >3 cm for seminoma.
Exclusion criteria were absence of contrast-enhanced CT imaging data after chemotherapy, insufficient image quality due to e.g., motion artifacts, CT performed outside our institution, and images with tumor size >13 cm; in the retrospective group,we excluded patients without complete clinical data and pre-operative and intraoperative records.
Clinical data included: age, prognostic group according International Germ Cell Cancer Collaborative Group (IGCCCG) classification, serum markers at diagnosis, primary histopathology, serum markers before PC-RPLND, type of PC-RPLND (standard, salvage, desperation and redo-surgery), histopathology of PC-RPLND, evaluation pre-surgery by an expert surgeon; outcomes of PC-RPLND (unresectable: yes vs no).
2.2. Data analysis
We divided patients into a retrospective (n=30) and prospective (n=30) group. Patients in the retrospective group were evaluated before surgery using a conventional CT approach (without 3D reconstruction), while the patients in the prospective were evaluated and segmented using 3D Slicer software. Specifically, 3D Slicer has been used to extract radiomics variables that can predict tumours resectability.
Briefly, all pre-operative CT imaging was evaluated by one expert surgeon, with more than ten years of experience in retroperitoneal surgery, and by junior surgeon in training. From the imaging study, they assessed whether masses were resectable. Statistical analyses of clinical data were performed with SPSS (version 25). Continuous variables are presented as median and interquartile range (IQR) and compared using a two-sample t-test or Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Categorical variables are presented as frequency and percentages and compared between groups using chi-squared or Fischer’s exact test.
We used the Pyradiomics python package (Version 3.6) integrated in 3D Slicer for radiomics feature extraction, SciPy and scikit-learn libraries for data analysis. CT imaging of the 60 patients corresponding to lymph nodes (LN) was segmented and radiomics features for each LN were extracted after standardized image processing. After stepwise feature reduction based on reproducibility, variable importance, and correlation analyses, radiomics features were selected.
A Fisher’s exact test was used to determine if there are non-random associations between preoperatively evaluation and surgery results in both groups (using python Scipy library). A two-proportion difference test was performed to determine whether the difference between two proportions of correct association was significant.
3. Results
Table 1 summarizes the clinical information of the patients included in this study (n=60). The median age of all patients was 25.50 (IQR= 17-56). The median size of residual tumour was 89 cm
3. There were no significant differences between the two subgroups. Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3 are examples of prospective cases in which the tumour analysed pre-operatively with 3D images is totally resected by a young surgeon.
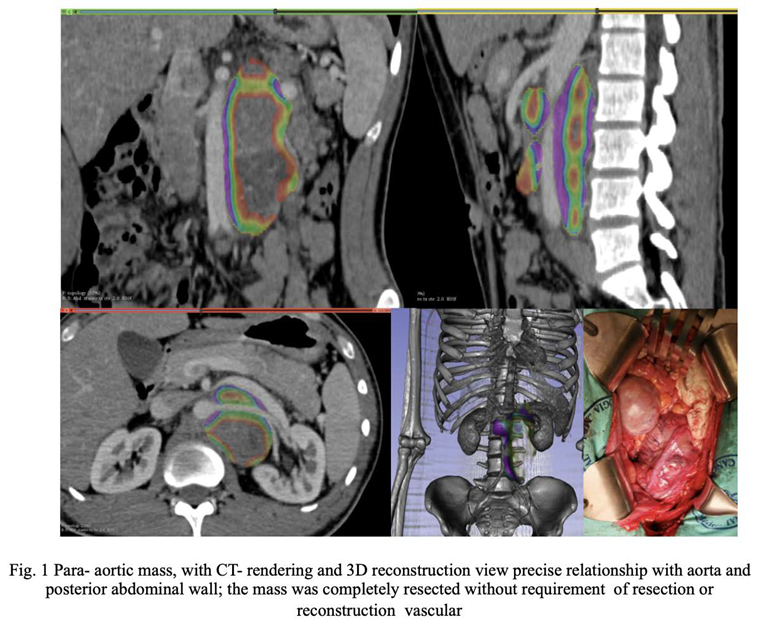
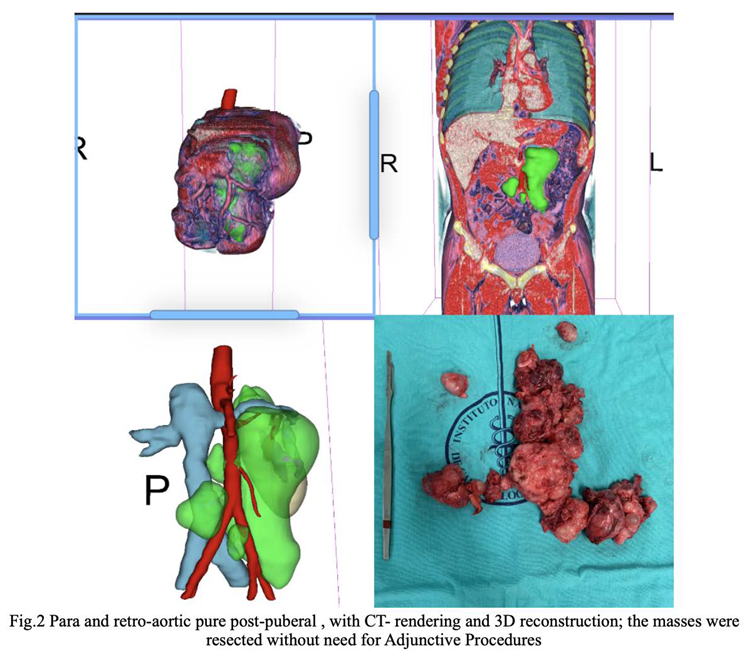
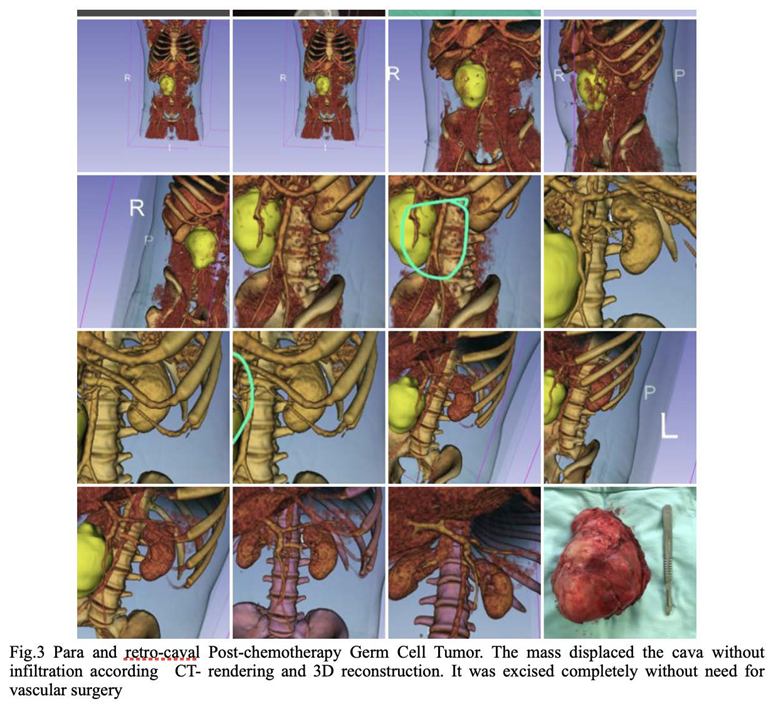
CatFisher’s exact test was used to determine if there were non-random associations between preoperative evaluation and surgical outcomes in both prospective group (denoted as Group A) and retrospective group (denoted as Group B). The test showed p-values of 0.13 and 1 for Group A and Group B, respectively. The null hypothesis in both groups is not rejected since there was no statistical significance. The Group B offers much more evidence against the null hypothesis than the Group A. A two-proportion difference test was then performed to determine whether the difference between two proportions of correct association was significant. It showed a p-value of 0.009149 (IC 0.1-0.63); proportion of correct classification, p-value of 0.645 (IC 0.55- 0.87) and 0.275 (IC 0.11-0.43) for the prospective and the retrospective group, respectively.
After stepwise feature reduction based thirteen shape features were selected: Elongation, Flatness, LeastAxisLength, MajorAxisLength, Maximum 2D-Diameter Column, Maximum 2D-Diameter Row, Maximum 2D-Diameter Slice, Maximum 3D-Diameter, Mesh Volume, Minor Axis Length, Sphericity, Surface Area, Surface Volume Ratio.
Using the Pyradiomics package, a logistic regression was performed (with the scikit-learn python library) using the entire dataset (n=60). The algorithm identified 29 true negative cases (VPN), 13 true positive cases (PPV), 11 false negative cases, and 7 false positives (
Figure 4); with Accuracy: 0.7, Precision: 0.65. Using a random sample of n=30, the best result had an Accuracy of 0.73 and Precision of 0.83, with a p-value of 0.025 for the Fisher’s exact test.
4. Discussion
The aim of the study is the prediction of tumor resectability by radiomics segmentation. This topic is critical for the surgeon since retroperitoneal surgery is a very complex procedure, therefore it is desirable to pre-operatively predict any surgical difficulties. For this reason, we considered two groups of patients: the retrospective group in which patients were evaluated using a conventional CT approach (without 3D reconstruction) and the prospective group in which patients were evaluated and segmented using the 3D Slicer software. The 3D Slicer was also used to identify thirteen radiomics features that may predict tumor resectability. At this point, logistic regression was performed using the whole data set (retrospective and prospective group together): 29 true negative cases, 13 true positive cases, 11 false negative cases, and 7 false positives were identified with an accuracy of 0.7. Accuracy increased to 0.73 using a random sample of 30 cases. Finally, our statistical analyses showed that there were no non-random associations between preoperative evaluation and surgical outcomes in both the prospective and retrospective studies. However, the retrospective group offered much more evidence against the null hypothesis than the prospective group. The difference between proportions test showed that the expert surgeon’s prediction was better by looking at the 3D image than conventional tomography.
The retroperitoneum represents the first metastatic site in 75-90% of NSGCTs of the testis. PC-RPLND represents an integral part of the multimodality treatment in patients with advanced testicular germ cell tumours and it is recommended for residual tumours in the retroperitoneum as soon as possible after chemotherapy. A meaningful benefit regarding progression-free survival and cancer-specific survival achieved with immediate surgical approach [
9]. The recommendation for resection of residual masses is based on the observation that in 35–40% of cases mature teratoma and in 10–15% persistent viable cancer can be found in the PC-RPLND specimen [
2,
3]. A complete resection of all residual masses during PC-RPLND can be therapeutic, especially in the presence of teratoma, teratoma with somatic transformation or masses resistant to chemotherapy.
Patients with teratoma in the PC-RPLND specimen have excellent disease-free survival of 75–80%, while those with viable GCT have a decreased chance of survival. Surgical approaches are available in the context of open and minimally invasive access [
2].
PC-RPLND is a highly complex procedure, compared with standard retroperitoneal surgery, and may require adjunctive procedures, because residual masses can involve adjacent visceral or vascular structures.
Notions of the retroperitoneal anatomy, experience with surgical techniques of the vascular and intestinal structures, and knowledge of the natural history of testicular cancer are imperative for a successful surgery [
9].
Conventional cross-sectional imaging and magnetic resonance imaging identifies the shape and size of the post-chemotherapy residual retroperitoneal masses, the anatomy of major vessels, presence of anatomical variations of relevant structures such as accessory renal arteries, retroaortic veins or variants of the vena cava or duplicated ureters. When the residual masses are large,can be expected involvement of the inferior vena cava (IVC) and the abdominal aorta in about 6–10% and 2%, respectively [
9,
10]. However, these approaches are not able to recognize whether the residual mass is resectable or if it holds viable tumour cells or fibrosis [
11].
The 3D Slicer program has been used in the context of retroperitoneal tumours to determine radiomics variables that can predict their histology. Baessler et al. identified 5 physical characteristics of tomography, which in an initial model predicted malignancy vs. fibrosis or necrosis with a sensitivity greater than 95% in the pre-test phase, which in its prospective application was adjusted to approximately 85% [
12]. The presence of fibrosis or desmoplastic reaction in the post-chemotherapy residual masses could complicate the surgical resection. The reaction induced by chemotherapy in residual masses often results in a more difficult resection, with firm adherence to the great vessels and adjacent organs. During the surgery, careful handling is required to avoid injury of the ureter, bowel, and vessels. We propose that CT segments rendering with radiomics feature extraction is essential to support experienced surgeons and junior doctors in training during the preoperative stage of the PC-RPLND.
Nowadays, medical image analysis, particularly computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging, has grown exponentially and offers to plan surgical procedures more precisely, leading to less invasive and more informative diagnoses. Although these tools provide high-resolution two-dimensional images, their ability to describe complex three-dimensional structures is limited [
13].
Three-dimensional reconstruction methods offer a better understanding of anatomical complexity, allowing rotations and segmentations in the virtual model [
14]. This ability has proven useful for the visualization of complex structures such as congenital heart defects and aneurysms. However, the differences between the real anatomical structures and the interpretation of virtual images in three dimensions are still being studied [
13,
14,
15,
16].
It’s important to draw up adequate imaging before the surgery, and we argue that CT rendering and radiomics features are superior to conventional imaging during pre-operative work-out. In this study, we suggest that CT and segments rendering help to predict the resectability of the residual mass and help young surgeons to recognize the anatomy of the tumour. This tool is useful for surgeons in training. Until now, it has not been described as a technique to improve the surgical skill in retroperitoneal surgery. The difference between proportions test allowed us to confirm that there is a significant difference in the prediction made by the expert surgeon when observing the conventional tomography vs observing the 3D image, the latter being a better tool compared to the former. Our findings show that the radiomics algorithm is more accurate and precise in cases where the post-chemotherapy residual masses are not resectable.
To our knowledge, no previous study has evaluated the prediction of the resectability of retroperitoneal residual masses. However, there is data concerning the need for adjunctive procedures in PC-RPLND, such as nephrectomy, vascular resection or reconstruction, inferior vena cava resection or repair, aortic replacement, duodenectomy, ureteral repair,ect [
14]. Johnson and colleagues described that dominant mass size and degree of circumferential vessel involvement (>135 for the vena cava and >330 for the aorta) predicted resection or reconstruction [
17]. Clinical predictors of the need for additional procedures are risk group, tumour size, final retroperitoneal pathology, elevated markers [
15,
18].
Have to keep in mind that PC-RPLND remains a challenging operation with morbidity of 12% to 32 and 0.8% mortality in experienced specialist centres [
19,
20]. Three-dimensional visualization of the anatomical regions that need to be evaluated for a retroperitoneal lymph node dissection allows us to understand and optimize the procedure, better appreciating the anatomy and planning the surgical route to follow and so improve perioperative outcome and decrease complications.
CT rendering with radiomics extraction could help predict the result of the surgery more objectively and not dictated by the operator’s experience or skills alone. That said, we believe that radiomics algorithms have the potential to be a useful tool for predicting surgical outcomes in retroperitoneal surgery. Our findings highlight that an artificial intelligence (AI) model is required in the pre-operative planning of advanced testicular tumors compared to the traditional pre-planning by conventional imaging. Currently AI models and machine learning models are gaining popularity in the field of urology [
21,
22,
23], our results represent the application of AI model and the utility of handcrafted radiomics in uro-oncology.
There are limitations to our study. Prediction of resectability depended on surgeon experience, although CT rendering with radiomics extraction allowed safe resection of retroperitoneal tumour. Further, our findings are based on findings from only one institution, and we were not able to externally validate the model. Therefore, this study provides clues but not sufficient evidence to prove that the proposed AI model can help new surgeons predict if a tumor will be resectable or not. A crucial aspect in the case of testicular cancer is the young age of the patients and, consequently, every attempt should be made to provide curative intent in such cases. For this reason, if an AI model can improve the prediction of tumor resectability needs to be demonstrated unequivocally. We also encourage other research groups to address this issue.
5. Conclusion
While computed tomography allows surgeons to have an overall location of the tumour and could help during surgery planning, CT and segment renderings give us a complete view of the proximity of adjacent vessels and organs. The use of 3D reconstruction adds a more sensitive way of predicting resectability than conventional CT images. The inclusion of radiomics features to build an artificial intelligence model may improve the prediction of resectability in post-chemotherapy RPLND. This tool would be of great support in a teaching hospital, allowing surgery to be planned and complications anticipated, and most importantly, avoid reaching the point of no return.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Anna Scavuzzo and Miguel Angel Jimenez Rios. Data curation: Jimenez Guedulain N., Muruato Araiza S., Cendejas Gomez J.D.J., Quiroz Compeán A., Victorio Vargas O.D. Formal analysis: Pavel Figueroa. Funding acquisition: none. Investigation: Anna Scavuzzo. Methodology: Anna Scavuzzo, Pavel Figueroa and, Jimenez Guedulain N. Project administration: Anna Scavuzzo, Figueora Rodriguez, Jimenez Guedulain N., Muruato Araiza S., Cendejas Gomez J.D.J., Quiroz Compeán A., Victorio Vargas O.D., Jimenez Rios M.A. Supervision: Miguel Angel Jimenez Rios. Validation: Anna Scavuzzo. Visualization: Jimenez Guedulain N., Muruato Araiza S., Cendejas Gomez J.D.J., Quiroz Compeán A., Victorio Vargas O.D. Writing—original draft, Anna Scavuzzo, Pavel Figueroa. Writing—review & editing: Alessandro Stefano, Anna Scavuzzo, Pavel Figueroa and Miguel Angel Jimenez Rios.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The image dataset and the code used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Park, J.S.; Kim, J.; Elghiaty, A.; Ham, W.S. Recent global trends in testicular cancer incidence and survival. Medicine 2018, 97, e12390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laguna, M.P.; Albers, P.; Algaba, F.; et al. EAU Guidelines on Testicular Cancer; EAU Guidelines Office: Arnhem, The Netherlands, 2022; ISBN 978-94-92671-16-5. [Google Scholar]
- Daneshmand, S.; Albers, P.; Fosså, S.D.; Heidenreich, A.; Kollmannsberger, C.; Krege, S.; Nichols, C.; Oldenburg, J.; Wood, L. Contemporary management of postchemotherapy testis cancer. Eur. Urol. 2012, 62, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakileh, G.A.; Ruf, C.; Heidenreich, A.; Dieckmann, K.-P.; Lisson, C.; Prasad, V.; Bolenz, C.; Zengerling, F. Contemporary options and future perspectives: Three examples highlighting the challenges in testicular cancer imaging. World J. Urol. 2022, 40, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, W.; Seetha, S.T.; Refaee, T.A.G.; Lieverse, R.I.Y.; Granzier, R.W.Y.; Ibrahim, A.; Keek, S.A.; Sanduleanu, S.; Primakov, S.P.; Beuque, M.P.L.; et al. Radiomics: From qualitative to quantitative imaging. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Remulla, D.; Nguyen, J.H.; Dua, A.; Liu, Y.; Dasgupta, P.; Hung, A.J. Current status of artificial intelligence applications in urology and their potential to influence clinical practice. BJU Int. 2019, 124, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefano, A.; Comelli, A. Customized Efficient Neural Network for COVID-19 Infected Region Identification in CT Images. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasini, G.; Bini, F.; Russo, G.; Comelli, A.; Marinozzi, F.; Stefano, A. matRadiomics: A Novel and Complete Radiomics Framework, from Image Visualization to Predictive Model. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenreich, A.; Paffenholz, P.; Nestler, T.; Pfister, D. Management of residual masses in testicular germ cell tumors. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2019, 19, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsyouf, M.; Daneshmand, S. Intricacies of retroperitoneal lymph node dissection for testis cancer. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2022, 32, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joice, G.A.; Rowe, S.P.; Gorin, M.A.; Pierorazio, P.M. Molecular Imaging for Evaluation of Viable Testicular Cancer Nodal Metastases. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2018, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baessler, B.; Nestler, T.; dos Santos, D.P.; Paffenholz, P.; Zeuch, V.; Pfister, D.; Maintz, D.; Heidenreich, A. Radiomics allows for detection of benign and malignant histopathology in patients with metastatic testicular germ cell tumors prior to post-chemotherapy retroperitoneal lymph node dissection. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 2334–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Luo, C. Evaluation of clinical application of multi-slice computerized tomography in primary retroperitoneal tumors. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Ding, B.; Yu, G.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Chen, X. Three-dimensional printing—Assisted planning for complete and safe resection of retroperitoneal tumor. J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 2020, 28, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodoussipour, S.; Daneshmand, S. Postchemotherapy Resection of Residual Mass in Nonseminomatous Germ Cell Tumor. Urol. Clin. North Am. 2019, 46, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Lin, S.; Tan, T.; Yang, J.; Pan, J.; Hu, C.; Li, J.; Zou, Y. Impact of 3D Printing Technology on Comprehension of Surgical Anatomy of Retroperitoneal Tumor. World J. Surg. 2018, 42, 2339–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.C.; Smith, Z.L.; Nottingham, C.; Schwen, Z.R.; Thomas, S.; Fishman, E.K.; Lee, N.J.; Pierorazio, P.M.; Eggener, S.E. Clinical and Radiographic Predictors of Great Vessel Resection or Reconstruction During Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection for Testicular Cancer. Urology 2019, 123, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, C.; Pfister, D.; Busch, J.; Bingöl, C.; Ranft, U.; Schrader, M.; Dieckmann, K.-P.; Heidenreich, A.; Albers, P. Residual tumor size and IGCCCG risk classification predict additional vascular procedures in patients with germ cell tumors and residual tumor resection: a multicenter analysis of the German Testicular Cancer Study Group. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, C.; Foster, R.S.; Masterson, T.A. Complications of Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection. Urol. Clin. North Am. 2019, 46, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, R.; Di Natale, R.; Sheinfeld, J. Current controversies on the role of retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy for testicular cancer. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2019, 37, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Ibarrola, R.; Hein, S.; Reis, G.; Gratzke, C.; Miernik, A. Current and future applications of machine and deep learning in urology: A review of the literature on urolithiasis, renal cell carcinoma, and bladder and prostate cancer. World J. Urol. 2020, 38, 2329–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, N.; Weight, C. “The Algorithm Will See You Now”: The Role of Artificial (and Real) Intelligence in the Future of Urology. Eur. Urol. Focus 2021, 7, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.B.; Haque, T.; Roberts, S.; Rambhatla, S.; Cacciamani, G.; Dasgupta, P.; Hung, A.J. Artificial Intelligence Applications in Urology. Urol. Clin. North Am. 2022, 49, 65–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).









