1. Introduction
Toxoplasmosis is known to be one of the most prevalent protozoan zoonoses caused by an intracellular Apicomplexan parasite
Toxoplasma gondii [
1,
2,
3].
T. gondii is distributed globally with a cosmopolitan host range [
4]. Felid species, including domestic cats and their relatives, are the definitive hosts and the only hosts that can shed oocysts into the environment [
5]. Environmental contamination is an important health issue, therefore detecting the occurrence of this parasite is crucial for the One Health approach [
6,
7]. Rodents pose a particular threat to public health because they are considered to be reservoirs (sources of
T. gondii infection for other organisms) and are intermediate hosts for
T. gondii [
8]. Rodents play a significant role in the food chain and as a consequence, in the transmission of pathogens to their predators, resulting in widespread cases of toxoplasmosis, also in human communities [
9]. Furthermore, these small mammals are considered to be markers for estimating contamination of the environment and also for assessment of the infection risk for definitive hosts of
T. gondii [
10,
11]. Toxoplasmosis occurs mostly in regions with a subtropical climate (oocysts persist under such environmental conditions) [
12]. The spread of
T. gondii depends on many factors, including both extrinsic factors (e.g. geographic location, habitat) and intrinsic factors (e.g. host sex, host age). Wild rodents become synanthropic as humans encroach on their natural habitats [
13].
The parasite’s life cycle is complex, with several infective forms and different transmission pathways [
14,
15]. Rodents and other warm-blooded animals act as intermediate hosts after ingesting food or water contaminated with oocysts [
16,
17]. After ingestion oocysts change into the tachyzoite stage and later directly into tissue cysts (bradyzoites). These parasitic forms can pass from host to host via the food chain or the placenta (as congenital toxoplasmosis). Animals such as pigs and dogs can become infected after eating rodents (reservoirs of infection), but only felids can shed
T. gondii oocysts into the environment [
18]. Rodents, being a frequent prey of felids, but also of other carnivores and omnivores are considered to play a key role in the maintenance of the
T. gondii life cycle [
10].
Laboratory detection of
T. gondii is necessary to establish the number of infected hosts [
19].
T. gondii detection can be conducted using serological tests, bioassay, histologic demonstration of the parasite and also by amplification of parasite-specific nucleic acid sequences using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) [
20,
21].
Considering the impact of rodents in the transmission of T. gondii to felid species, we conducted biomonitoring of T. gondii in Northeastern Poland. Our main aims were to assess the role of small free-living rodents in maintaining T. gondii, and to monitor prevalence and seroprevalence of the parasite in the seven wild rodent species endemic in the region (Microtus arvalis, Microtus agrestis, Apodemus sylvaticus, Apodemus agrarius, Apodemus flavicollis, Myodes glareolus, Mus musculus). We applied different diagnostic approaches, both molecular (PCR assay, nested-PCR assay) and serological techniques (ELISA method, agglutination test) in order to identify the best method for application in large scale biomonitoring of small mammals.
2. Materials and Methods
Our grassland study site is located near the University of Warsaw’s research station in Urwitałt, in North-eastern Poland. The location and methods of rodent trapping, sampling and processing of trapped animals have been described previously [
22,
23,
24,
25]. Briefly, rodents were trapped in 2021 and 2022 using wooden live-traps with seeds, peanut butter and fruits as a lure [
26,
27].
Map 1.
Sampling site (red mark) in Northeastern Poland (Google Maps, 2023). Our stuty site is located in Mazury Lake District (53°48'21.0"N 21°39'36.7"E). Black bar – 100 km.
Map 1.
Sampling site (red mark) in Northeastern Poland (Google Maps, 2023). Our stuty site is located in Mazury Lake District (53°48'21.0"N 21°39'36.7"E). Black bar – 100 km.
Genomic DNA from brains, spleens and blood samples was extracted using a commercial kit (A&A Biotechnology, Gdynia, Poland), following the manufacturer’s instructions. We applied the PCR assay provided by Schwab and Mc Devitt (2003) [
28]. Primers TOXO1 (5′GGAACTGCATCCGTTCATGAG3′) and TOXO2 (5′TCT TTA AAG CGT TCG TGG TC 3′) were used for amplification of the 194 bp fragment of the 35-fold-repetitive B1 gene [
29]. The reaction mixture volume was 25 μl.
To confirm and compare our results, nested PCRs targeting the B1 gene were performed [
30]. Inner primers: B1 up (5’-CGTCCGTCGTAATATCAG-3’) and B1 down (5’-GACTTCATGGGACGATATG-3’) were used for amplification of the 178 bp fragment of the B1 gene. Outer primers: B1 nested forward (5’-GGGAATGAAAGAGACGCTAATGTG-3’) and B1 nested reverse (5’-CTTTTCGCCAGCAGAGGG-3’) were used for amplification of the 94 bp fragment of the B1 gene (BMR Genomics, Padua, Italy). The reaction mixture volume was 25 μl.
Amplifications were performed in a ProFlex PCR System thermocycler (Applied Biosystems, USA). All PCR reactions were performed including T. gondii positive control (genomic DNA from T. gondii RH strain) to ensure the correct functioning of the reaction and negative control (water template) to ensure lack of contamination of the PCR components. PCR products were analysed using the Essential V6 Imaging Systems (UVITEC, GB) after electrophoresis on a 2% agarose gel (Sigma, St.Louis, Missouri) stained with Midori Green Advance DNA Stain (Nippon Genetics Europe GmbH, Germany).
Samples, which had been previously tested by molecular methods, were screened by a serological approach. Of 68 individual, we tested 56 individuals because we were not able to collect serum samples from 12 individuals. All serum samples were analysed according to the manufacturer’s instructions for application of the diagnostic commercial kit: an agglutination test (Toxo-Screen DA, bioMérieux, Marcy-l’Étoile, France). In addition, a bespoke ELISA described by Krupinska et al. (2023) test was used to detect antibodies against
T. gondii using a commercially available
T. gondii antigen (CD90 Creative Diagnostics, New York, USA) prepared from
T. gondii RH strain [
31].
Prevalence / seroprevalence is given with 95% confidence limits in parenthesis (CL95). We calculated the values using a bespoke software based on the work of Rohlf and Sokal [
32].
3. Results
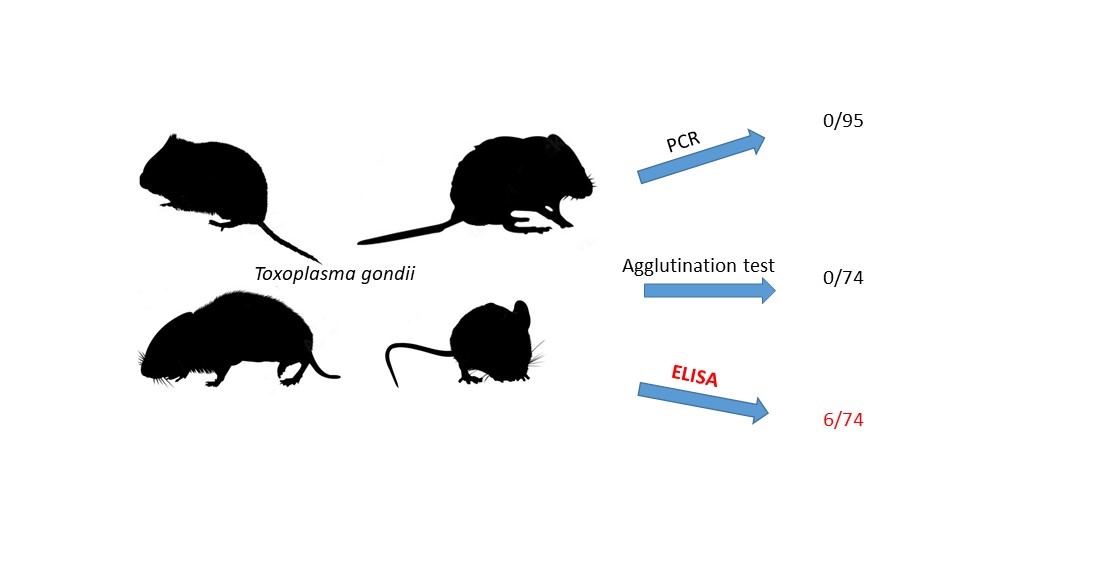
Firstly we tested 68 rodents from seven different species. These included
A. agrarius (n=18),
A. flavicollis (n=13),
A. sylvaticus (n=8),
M. glareolus (n=12),
M. arvalis (n=11),
M. agrestis (n=4), and
M. muscullus (n=2). We performed PCR screening using blood, spleen and brain tissues of these animals. We found no
T. gondii positive samples using molecular detection (
Figure 1).
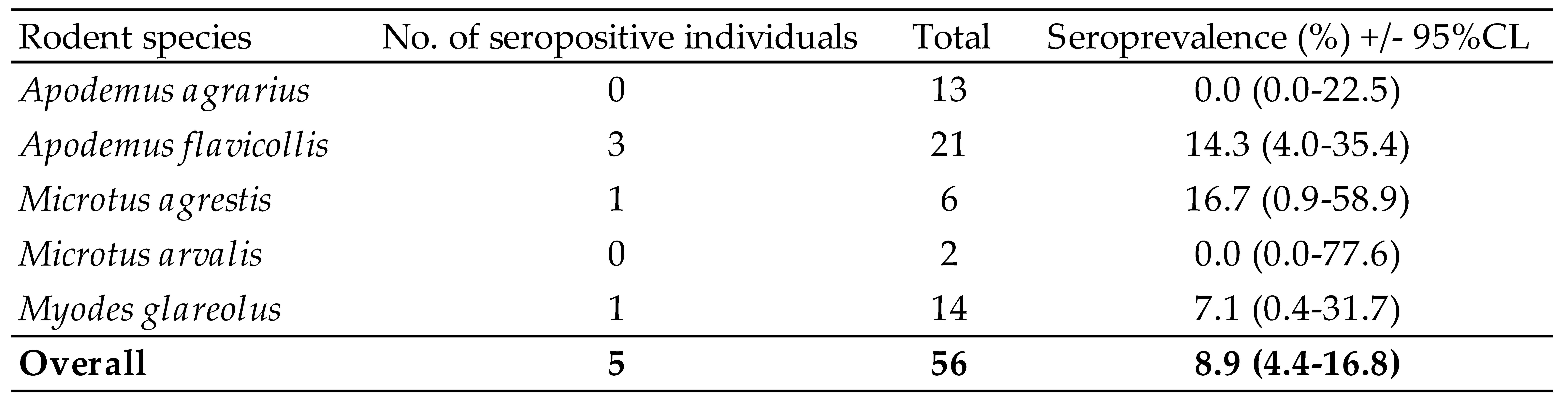
After molecular the approach we performed serological tests, with sera samples of 56 individuals, the agglutination and ELISA tests. The agglutination test did not detect any seropositive animals. However, using the ELISA test we found antibodies against
T. gondii in the sera of three rodents species (
A. flavicollis, M. agrestis and
M. glareolus), with an overall seroprevalence of 8.9% [4.4-16.8] (
Table 1).
Table 1.
Seroprevalence of T. gondii within investigated rodent species.
Table 1.
Seroprevalence of T. gondii within investigated rodent species.
4. Discussion
Our results confirm that wild rodents trapped in the Mazury Lake District region are exposed to
T. gondii and may pose a particular threat for carnivore pets, such as domestic cats, and thus also to humans. In this study, we report an overall seroprevalence of
T. gondii in small rodents of 8.9 %, based on the ELISA test. These results are consistent with our previous study [
8] in which we found 32 samples (5.5%) out of 545 seropositive to
T. gondii. No seropositivity was detected by the agglutination test.
Modified agglutination test (MAT) and ELISA are highly specific methods widely used for the detection of antibodies to
T. gondii, and applicable for serological diagnosis of infection as well as in epidemiological studies. Several authors compared ELISA and agglutination test for the detection of
T. gondii and declared lower specificity and sensitivity of MAT than that of ELISA [
33,
34]. Moreover, the agglutination test is able to detect only IgG antibodies, while goat Anti-Mouse Polyvalent Immunoglobulins (G, A, M) used for ELISA in the presented study, is capable to detect three classes of antibodies, IgG, IgM and IgA. While IgG antibodies indicate previous or chronic infection, IgM and IgA signalize the recent or acute phase. Thus, the difference observed between the results of the agglutination test and ELISA may be also associated with the detected different stages of the infection. The lack of seropositive samples in the agglutination test may be related to the lower positivity and titre of this test compared to the ELISA. In addition, the ELISA test is better at identifying different classes of antibodies than the agglutination test, so this method has a higher sensitivity and specificity [
35,
36].
Laboratory tests based on serological methods appear to be the best option for detecting
T. gondii [
37,
38]. Unfortunately, due to the small size of rodents, in some cases, it is not possible to obtain sufficient blood (serum) to enable serological testing. In our previous study [
8], we also tested rodent sera using the serological method (a bespoke ELISA test), and therefore here, we compared the results of serological tests with molecular ones. In small rodents,
T. gondii tissue cysts (bradyzoites) are mainly located in the olfactory bulb [
39,
40]. Based on this knowledge, the brains and also spleens and blood of seven rodent species were used in this study to detect
T. gondii DNA.
However, we failed to detect T. gondii DNA in any of these tissue samples from the rodents in our study.
Our results compare well with other studies. For example Ivovic et al. (2019), found that on the Istrian peninsula
T. gondii was rarely detectable among species of small rodents such as
A. sylvaticus,
A. flavicollis and
A. agrarius [
37]. Recent studies by Rizwan et al. (2023) based on molecular detection of
T. gondii via amplification of the B1 and the SAG3 genes by PCR and nested-PCR assays showed that only 14 (5.9%) of 236 rodents trapped in Pakistan showed signs of the presence of
T. gondii DNA [
41]. This is in line with results from rats tested at a mink farm in China. Zou et al. (2022) found 18 samples (7.93%) out of 227 samples positive for
T. gondii [
42]. However, a much higher prevalence of
T. gondii was found among wild rats in Nigeria – 64 (76.2%) of the 84 rodent individuals were positive [
43], but on the other hand, none of 78 rodents (
A. agrarius and
M. arvalis) tested by Herrmann et al. (2011) using both serological and molecular methods were seropositive or PCR positive. Only 15.9% of foxes tested seropositive in the PCR assay in the same study [
44].
Urbanization, global warming and globalization affect the maintenance and transmission of many diseases caused by parasites, including those caused by
T. gondii species [
45,
46]. The life cycle of
T. gondii is based on contamination of the environment with pathogen oocysts and on the prey-predator relationship [
47]. Anthropogenic and environmental factors affect the survival time and infectivity of oocysts [
12]. The environmental contamination by this parasite also depends on the size of the population of the intermediate and definitive hosts [
48]. Despite many studies on the impact of factors affecting the spread of
T. gondii, the mechanisms related to the promotion of the pathogen in the environment are still not fully known [
49]. Wild rodents are frequent prey of predators, including felid species. By introducing resources into natural environments, humans influence rodent population structure, which affects the circulation of
T. gondii in the wild environment [
9,
50]. However, the role of wild rodents in the transmission of
T. gondii is still underestimated, therefore further studies are necessary to reveal their impact on the emergence, transmission and distribution of the parasite.
In summary, we did not detect T. gondii in brain, spleen and blood samples using a molecular approach, however we found serological evidence for the presence of T. gondii in four vole species from wild rodent populations in NE Poland. The results of this study clearly indicate that the serological approach is the best option for biomonitoring T. gondii in small mammals. The ELISA test has the highest sensitivity and specificity of all the serological methods tested in this study.
5. Conclusions
Our study suggests that rodents living in Urwitałt in the Mazury Lake District in Northeastern Poland are exposed to
T. gondii, posing a potential public health risk to local residents and visitors to the region. Considering other recent reports [
41,
43,
51] based on molecular and serological techniques, further monitoring is needed to fully understand the status of
T. gondii in the wild and to assess comprehensively the risk of transmission of this pathogen to the human communites in the region [
5].
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
The study was conceived and designed by JN and MG. Supervision of the long-term monitoring of bank vole populations in the region was by MG, AB and JMB, Samples were collected in the field by JN, AG, MK, MG, and AB. Animal dissections by JN, MG, AG, MK and AB. Molecular analysis and laboratory work was conducted by JN, MK, BB, AL, AS, MG and AB. Data handling – MG. The manuscript was written by JN and MG in consultation with all co-authors. JN, MG, AB and JMB revised the manuscript. All authors accepted the final manuscript version.
Funding
This research was co-funded through the 2018–2019 BiodivERsA joint call for research proposals under the BiodivERsA3 ERA-Net COFUND program; the funding organisations ANR (France), DFG (Germany), EPA (Ireland), FWO (Belgium), and NCN (Poland). JN, MG and AG were supported by the National Science Centre, Poland, under the BiodivERsA3 programme (2019/31/Z/NZ8/04028). MK was supported by the National Science Centre, Poland, under the Preludium BIS programme 2020/39/O/NZ6/01777. JMB was supported by the Royal Society, the British Ecological Society and the Grabowski Fund.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was carried out in strict accordance with the recommendations in the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the Polish National Ethics Committee for Animal Experimentation and according to the Polish national law for field work involving the trapping and culling of wild unprotected vertebrates for scientific purposes (Resolution No. 12/2022 of Polish National Ethics Committee for Animal Experiments, 11th March 2022). The study was performed according to the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
We thank the Universities of Nottingham, Warsaw University and the Medical University of Gdansk for financial support. We thank The Masurian Center For Biodiversity and Nature Education in Urwitałt for hospitability in the field station.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Galeh, T.M.; Sarvi, S.; Montazeri, M.; Moosazadeh, M.; Nakhaei, M.; Shariatzadeh, S.A.; Daryani, A. Global Status of Toxoplasma gondii Seroprevalence in Rodents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, H.J.; Koshy, A.A. Latent Toxoplasmosis Effects on Rodents and Humans: How Much is Real and How Much is Media Hype? MBio 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennari, S.M.; Ogrzewalska, M.H.; Soares, H.S.; Saraiva, D.G.; Pinter, A.; Nieri-Bastos, F.A.; Labruna, M.B.; Szabó, M.P.J.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in wild rodents and marsupials from the Atlantic Forest, state of São Paulo, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Veterinária 2015, 24, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.H.; Pavey, C.; O’Handley, R.; Vyas, A. Behavioral biology of Toxoplasma gondii infection. Parasites {\&} Vectors 2021, 14, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Tenter, A.M.; Heckeroth, A.R.; Weiss, L.M. Toxoplasma gondii: from animals to humans. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1217–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, P.R.F.; de Melo, R.P.B.; de Oliveira, U.D.R.; Magalhães, F.J.R.; Junior, R.J.F.; Andrade, M.R.; Mota, R.A. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts in soil and risk mapping in an island environment in the Northeast of Brazil. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 3457–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupińska, M.; Antolová, D.; Tołkacz, K.; Szczepaniak, K.; Strachecka, A.; Goll, A.; Nowicka, J.; Baranowicz, K.; Bajer, A.; Behnke, J.M.; et al. Grassland versus forest dwelling rodents as indicators of environmental contamination with the zoonotic nematode Toxocara spp. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzybek, M.; Antolová, D.; Tołkacz, K.; Alsarraf, M.; Behnke-Borowczyk, J.; Nowicka, J.; Paleolog, J.; Biernat, B.; Behnke, J.M.; Bajer, A. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii among Sylvatic Rodents in Poland. Animals 2021, 11, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jittapalapong, S.; Sarataphan, N.; Maruyama, S.; Hugot, J.-P.; Morand, S.; Herbreteau, V. Toxoplasmosis in Rodents: Ecological Survey and First Evidences in Thailand. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOTTELAND, C.; CHAVAL, Y.; VILLENA, I.; GALAN, M.; GEERS, R.; AUBERT, D.; POULLE, M.-L.; CHARBONNEL, N.; GILOT-FROMONT, E. Species or local environment, what determines the infection of rodents by Toxoplasma gondii ? Parasitology 2014, 141, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AFONSO, E.; THULLIEZ, P.; PONTIER, D.; GILOT-FROMONT, E. Toxoplasmosis in prey species and consequences for prevalence in feral cats: not all prey species are equal. Parasitology 2007, 134, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerburg, B.G.; Singleton, G.R.; Kijlstra, A. Rodent-borne diseases and their risks for public health. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 35, 221–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S. , Naz F., Jan A., Ullah R., Khan S., Haseeb A., Ahmad I., Y.M. Seroprevalence and risk factors of toxoplasomosis among women in District Chitral, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. World J Zool 2016, 11, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Attias, M.; Teixeira, D.E.; Benchimol, M.; Vommaro, R.C.; Crepaldi, P.H.; De Souza, W. The life-cycle of Toxoplasma gondii reviewed using animations. Parasites {\&} Vectors 2020, 13, 588. [Google Scholar]
- Gilot-Fromont, E.; Llu, M.; Dard, M.-L.; Richomme, C.; Aubert, D.; Afonso, E.; Mercier, A.; Gotteland, C.; Ville, I. The Life Cycle of Toxoplasma gondii in the Natural Environment. In Toxoplasmosis - Recent Advances; InTech, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gering, E.; Laubach, Z.M.; Weber, P.S.D.; Soboll Hussey, G.; Lehmann, K.D.S.; Montgomery, T.M.; Turner, J.W.; Perng, W.; Pioon, M.O.; Holekamp, K.E.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii infections are associated with costly boldness toward felids in a wild host. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. The history and life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. In Toxoplasma gondii; Elsevier, 2020; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Waindok, P.; Özbakış-Beceriklisoy, G.; Janecek-Erfurth, E.; Springer, A.; Pfeffer, M.; Leschnik, M.; Strube, C. Parasites in brains of wild rodents (Arvicolinae and Murinae) in the city of Leipzig, Germany. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 10, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, J.G. Laboratory Diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii Infection and Toxoplasmosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, S73–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breeze, A.C. Infectious diseases of the fetus and newborn infant, 6th edn. Arch. Dis. Child. - Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2007, 92, F156–F156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lass, A.; Pietkiewicz, H.; Modzelewska, E.; Dumètre, A.; Szostakowska, B.; Myjak, P. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts in environmental soil samples using molecular methods. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. {\&} Infect. Dis. 2009, 28, 599–605. [Google Scholar]
- Grzybek, M.; Bajer, A.; Bednarska, M.M.; Al-Sarraf, M.; Behnke-Borowczyk, J.; Harris, P.D.; Price, S.J.; Brown, G.S.; Osborne, S.-J.; Siński, E.; et al. Long-term spatiotemporal stability and dynamic changes in helminth infracommunities of bank voles (Myodes glareolus) in NE Poland. Parasitology 2015, 142, 1722–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnke, J.M.; Barnard, C.J.; Bajer, A.; Bray, D.; Dinmore, J.; Frake, K.; Osmond, J.; Race, T.; Sinski, E. Variation in the helminth community structure in bank voles (Clethrionomys glareolus) from three comparable localities in the mazury lake istrict region of Poland. Parasitology 2001, 123, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzybek, M.; Bajer, A.; Behnke-Borowczyk, J.; Al-Sarraf, M.; Behnke, J.M. Female host sex-biased parasitism with the rodent stomach nematode Mastophorus muris in wild bank voles (Myodes glareolus). Parasitol. Res. 2014, 114, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tołkacz, K.; Bednarska, M.; Alsarraf, M.; Dwużnik, D.; Grzybek, M.; Welc-Falęciak, R.; Behnke, J.M.; Bajer, A. Prevalence, genetic identity and vertical transmission of Babesia microti in three naturally infected species of vole, Microtus spp. (Cricetidae). Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tołkacz, K.; Alsarraf, M.; Kowalec, M.; Dwużnik, D.; Grzybek, M.; Behnke, J.M.; Bajer, A. Bartonella infections in three species of Microtus: prevalence and genetic diversity, vertical transmission and the effect of concurrent Babesia microti infection on its success. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzybek, M.; Alsarraf, M.; Tołkacz, K.; Behnke-Borowczyk, J.; Biernat, B.; Stańczak, J.; Strachecka, A.; Guz, L.; Szczepaniak, K.; Paleolog, J.; et al. Seroprevalence of TBEV in bank voles from Poland—a long-term approach. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, K.J.; McDevitt, J.J. Development of a PCR-enzyme immunoassay oligoprobe detection method for Toxoplasma gondii oocysts, incorporating PCR controls. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5819–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burg, J.L.; Grover, C.M.; Pouletty, P.; Boothroyd, J.C. Direct and sensitive detection of a pathogenic protozoan, Toxoplasma gondii, by polymerase chain reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 1787–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, A.M.F.; Percipalle, M.; Giunta, R.P.; Salvaggio, A.; Caracappa, G.; Alfonzetti, T.; Aparo, A.; Reale, S. Development and validation of a real-time PCR assay for the detection of Toxoplasma gondii DNA in animal and meat samples. J. Vet. Diagnostic Investig. 2017, 29, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, H.P.; Van Knapen, F.; Atkinson, H.J.; Balfour, A.H.; Lee, D.L. A new soluble antigen preparation of Toxoplasma gondii and its use in serological diagnosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1982, 49, 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, F.J. Statistical Tables; W. H. Freeman: New York, 1995; ISBN 978-0716724124. [Google Scholar]
- Klun, I.; Djurković-Djaković, O.; Thulliez, P. Comparison of a Commercial ELISA with the Modified Agglutination Test for the Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Naturally Exposed Sheep. Zoonoses Public Health 2007, 54, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lu, H.; Jia, B.; Chang, Z.; Peng, S.; Yin, J.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, N. A comparative study of Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence in three healthy Chinese populations detected using native and recombinant antigens. Parasit. Vectors 2013, 6, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osoba, A.O.; Balkhy, H.; Memish, Z.; Khan, M.Y.; Al-Thagafi, A.; Al Shareef, B.; Al Mowallad, A.; Oni, G.A. Diagnostic Value of Brucella ELISA IgG and IgM in Bacteremic and Non-Bacteremic Patients with Brucellosis. J. Chemother. 2001, 13, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, M.; Feyzioğlu, B.; Kurtoğlu, M.G.; Doğan, M.; Dağı, H.T.; Yüksekkaya, Ş.; Keşli, R.; Baysal, B. A Comparison of Immuncapture Agglutination and ELISA Methods in Serological Diagnosis of Brucellosis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 8, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivovic, V.; Potusek, S.; Buzan, E. Prevalence and genotype identification of Toxoplasma gondii in suburban rodents collected at waste disposal sites. Parasite 2019, 26, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, W.L.; Vercammen, M.; De Braekeleer, J.; Verschueren, H. Identification of a 200- to 300-fold repetitive 529 bp DNA fragment in Toxoplasma gondii, and its use for diagnostic and quantitative PCR1Note: Nucleotide sequence data reported in this paper have been submitted to GenBankTM database with the accession nu. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenreiterová, M.; Flegr, J.; Kuběna, A.A.; Němec, P. The Distribution of Toxoplasma gondii Cysts in the Brain of a Mouse with Latent Toxoplasmosis: Implications for the Behavioral Manipulation Hypothesis. PLoS One 2011, 6, e28925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, D.J.; Graham, D.I.; Hutchison, W.M. Pathological changes in the brains of mice infected with Toxoplasma gondii: a histological, immunocytochemical and ultrastructural study. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 1991, 72, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Javid, A.; Rashid, M.I. Molecular detection of Toxoplasma gondii among commensal rodents from the Sahiwal division, Punjab, Pakistan. Parasitol. Res. 2023, 122, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Geng, H.-L.; Jia, H.-L.; Zhao, Q.; Qin, S.-Y.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Zhang, X.-X. The Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in Wild Rats ( Rattus norvegicus ) on Mink Farms in Shandong Province, Eastern China. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2022, 22, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ode, S.; Jarikre, T.; Jubril, A.J.; Ularamu, H.; Luka, P.; Adamu, M.; Emikpe, B. High prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Nigerian wild rats by molecular detection. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Reports 2022, 35, 100776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, D.C.; Maksimov, P.; Maksimov, A.; Sutor, A.; Schwarz, S.; Jaschke, W.; Schliephake, A.; Denzin, N.; Conraths, F.J.; Schares, G. Toxoplasma gondii in foxes and rodents from the German Federal States of Brandenburg and Saxony-Anhalt: Seroprevalence and genotypes. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 185, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patz, J.A.; Graczyk, T.K.; Geller, N.; Vittor, A.Y. Effects of environmental change on emerging parasitic diseases. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, B.M. How has agriculture influenced the geography and genetics of animal parasites? Trends Parasitol. 2009, 25, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, E.; Poulle, M.L.; Lemoine, M.; Villena, I.; Aubert, D.; Gilot-Fromont, E. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in small mammals from the Ardennes region, France. Folia Parasitol. (Praha). 2007, 54, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kijlstra, A.; Meerburg, B.; Cornelissen, J.; De Craeye, S.; Vereijken, P.; Jongert, E. The role of rodents and shrews in the transmission of Toxoplasma gondii to pigs. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 156, 183–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.K.; Johnson, P.T.J. Toxoplasmosis: Recent Advances in Understanding the Link Between Infection and Host Behavior. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 9, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BUZAN, E. CHANGES IN RODENT COMMUNITIES AS CONSEQUENCE OF URBANIZATION AND INAPPROPRIATE WASTE MANAGEMENT. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2017, 15, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soka, J. Occurrence of Toxoplasma gondii infection among free-living small rodents and insectivores in the Lublin Province – the role of these animals in epidemiology of toxoplasmosis. Med. Ogólna i Nauk. o Zdrowiu 2021, 27, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).