Submitted:
25 February 2023
Posted:
27 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
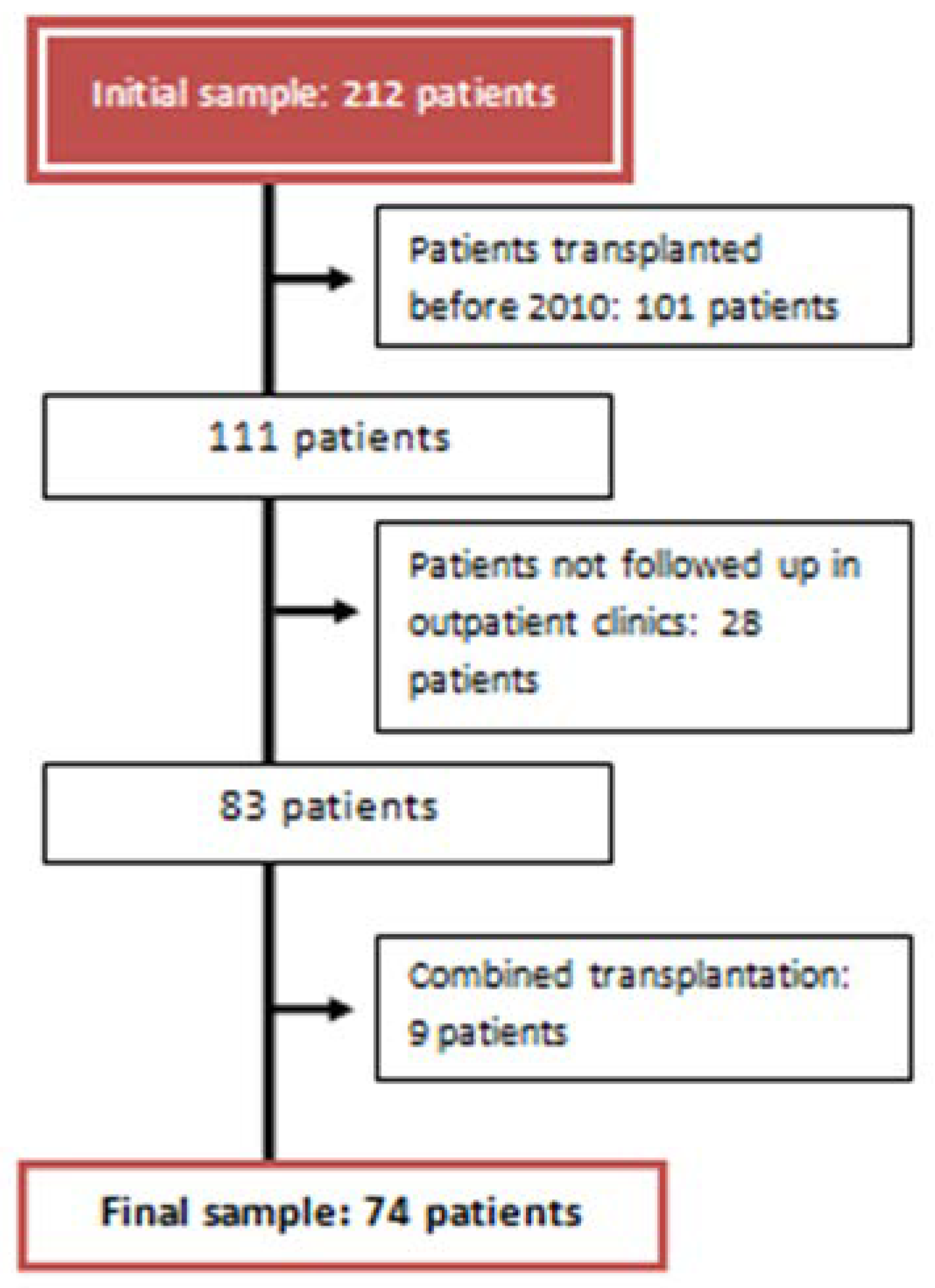
Study Population
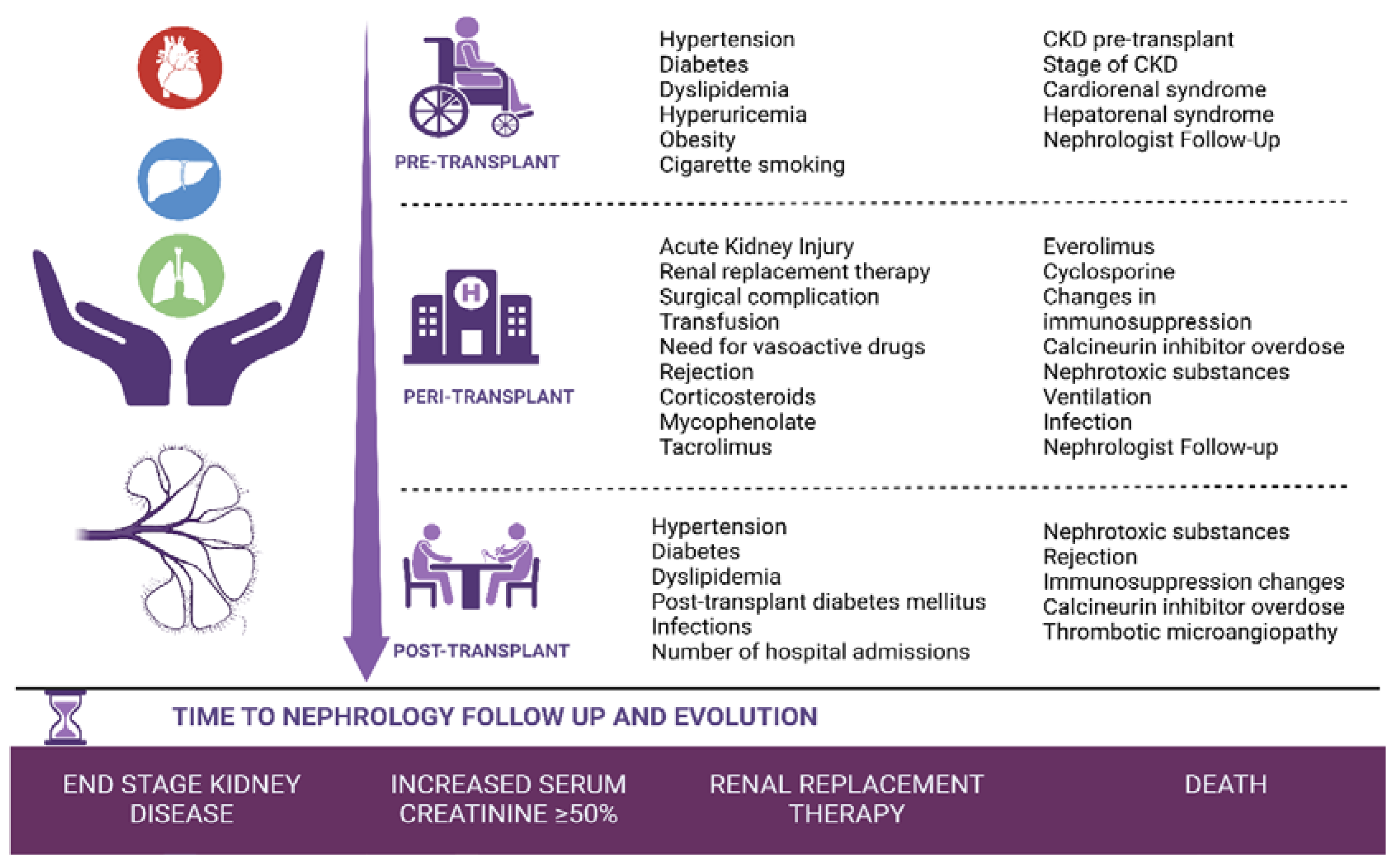
- Pre-transplant period: Clinical and analytical variables present before the solid organ transplant until day 0 of the transplant.
- Peri-transplant period: From the transplant to hospital discharge.
- Post-transplant period: From hospital discharge to one year of follow-up in nephrology consultations.
Data Collection
Statistical Analysis
Data Availability
3. Results
Baseline Characteristics
Increased Baseline Creatinine by 50%
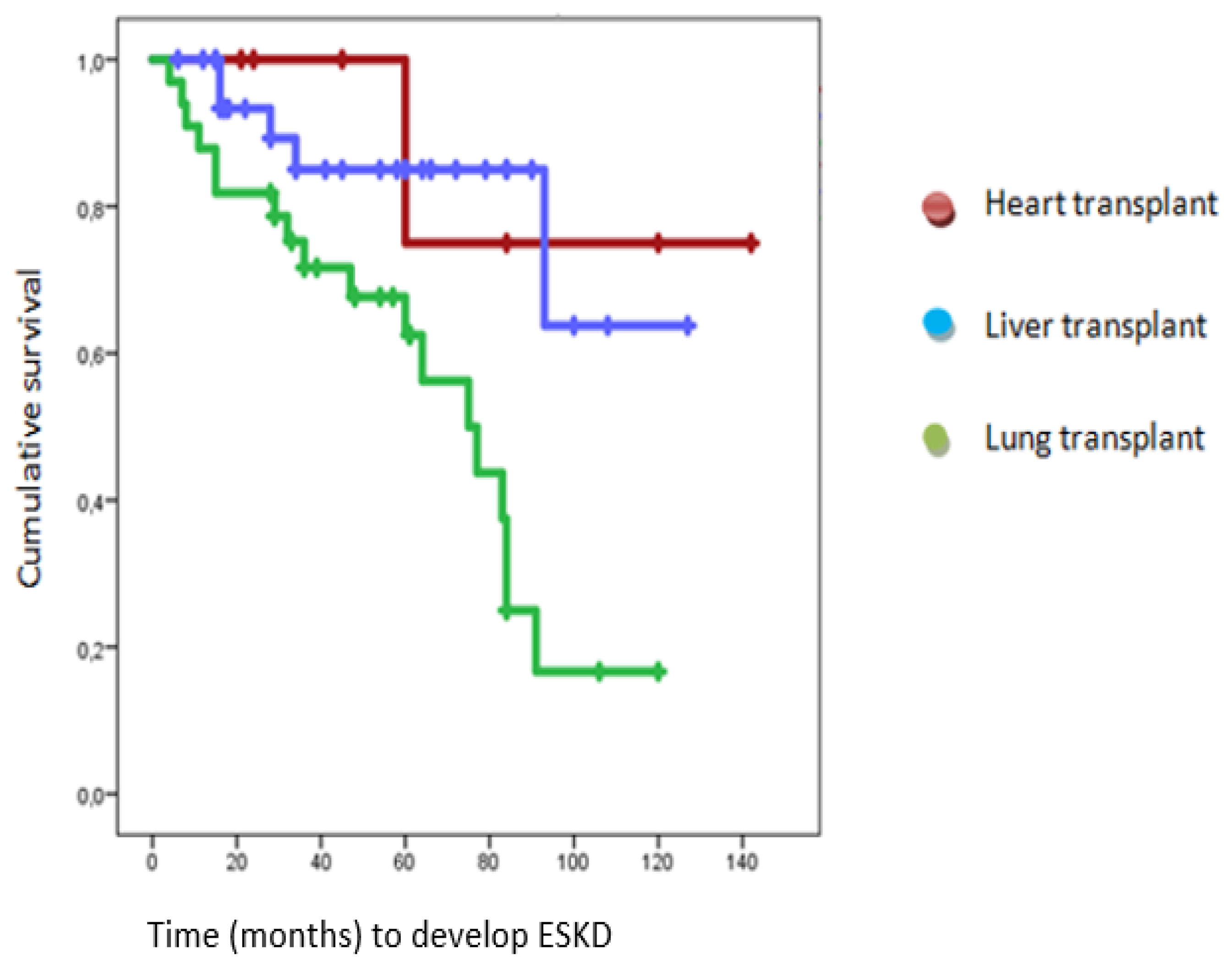
End Stage Kidney Disease (ESKD)
Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT)
Death
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bloom, R.D.; Reese, P.P. Chronic kidney disease after nonrenal solid-organ transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007, 18, 3031–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.W. Chronic kidney disease in solid-organ transplantation. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2006, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, A.O.; Held, P.J.; Port, F.K.; Wolfe, R.A.; Leichtman, A.B.; Young, E.W.; Arndorfer, J.; Christensen, L.; Merion, R.M. Chronic renal failure after transplantation of a nonrenal organ. N Engl J Med. 2003, 349, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Vílchez, F.; Almenar-Bonet, L.; Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; et al. Registro español de Trasplante Cardiaco. XXX Informe oficial de la Sección de Insuficiencia Cardiaca de la SEC (1984-2018). Rev Esp Cardiol. 2019, 72, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memoria de Resultados del Registro Español de Trasplante Hepático. Disponible en: http://www.sethepatico.org.
- Registro Español de Trasplante Pulmonar. Resultados 2001-2016. Disponible en: http://www.ont.es/.
- Kim, I.C.; Youn, J.C.; Kobashigawa, J.A. The Past, Present and Future of Heart Transplantation. Korean Circ J. 2018, 48, 565–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.H.; Sanchez-Fueyo, A.; Samuel, D. From immunosuppression to tolerance. J Hepatol. 2015, 62 (Suppl. 1), S170–S185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivulich, S.; Westall, G.; Dooley, M.; Snell, G. The Evolution of Lung Transplant Immunosuppression. Drugs 2018, 78, 965–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.; Haller, H.; Schmitt, R.; et al. Biopsy-diagnosed renal disease in patients after transplantation of other organs and tissues. Am. J. Transplant. Of. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2010, 10, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, A.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Crespo-Barrio, M.; De-Sequera-Ortiz, P.; Fernández-Giráldez, E.; García-Maset, R.; Macía-Heras, M.; Pérez-Fontán, M.; Rodríguez-Portillo, M.; Salgueira-Lazo, M.; Sánchez-Álvarez, E.; Santamaría-Olmo, R.; Simal-Blanco, F.; Pino-Pino, M.D. The Spanish Society of Nephrology (SENEFRO) commentary to the Spain GBD 2016 report: Keeping chronic kidney disease out of sight of health authorities will only magnify the problem. Nefrologia (Engl Ed) 2019, 39, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiseman, A.C. CKD in Recipients of Nonkidney Solid Organ Transplants: A Review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.T.; Kosirog, M.; Aghaulor, B.; Gregory, D.; Pine, S.; Daud, A.; Das, A.; Finn, D.J.; Levitsky, J.; Holl, J.L.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; VanWagner, L.B. Comanagement With Nephrologist Care Is Associated With Fewer Cardiovascular Events Among Liver Transplant Recipients With Chronic Kidney Disease. Transplant Direct. 2021, 7, e766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vondran, F.W.R.; Wintterle, S.; Bräsen, J.H.; Haller, H.; Klempnauer, J.; Richter, N.; Lehner, F.; Schiffer, M. Abdominalchirurgie trifft Nephrologie: Wichtige nephrologische Aspekte vor und nach Nieren- bzw. Lebertransplantation [Transplant Surgeon Meets Nephrologist: Important Nephrological Aspects Before and After Kidney or Liver Transplantation]. Zentralbl Chir. 2017, 142, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bloom, R.D.; Doyle, A.M. Kidney disease after heart and lung transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2006, 6, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahirwani, R.; Campbell, M.S.; Siropaides, T.; Markmann, J.; Olthoff, K.; Shaked, A.; Bloom, R.D.; Reddy, K.R. Transplantation: impact of pretransplant renal insufficiency. Liver Transpl. 2008, 14, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banga, A.; Mohanka, M.; Mullins, J.; Bollineni, S.; Kaza, V.; Torres, F.; Tanriover, B. Association of pretransplant kidney function with outcomes after lung transplantation. Clin Transplant. 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortrie, G.; Manintveld, O.C.; Caliskan, K.; Bekkers, J.A.; Betjes, M.G. Acute Kidney Injury as a Complication of Cardiac Transplantation: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Impact on 1-year Mortality and Renal Function. Transplantation 2016, 100, 1740–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, M.P.; Carneiro-D'Albuquerque, L.A.; Mazo, D.F. Current aspects of renal dysfunction after liver transplantation. World J Hepatol. 2022, 14, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atchade, E.; Barour, S.; Tran-Dinh, A.; Jean-Baptiste, S.; Tanaka, S.; Tashk, P.; Snauwaert, A.; Lortat-Jacob, B.; Mourin, G.; Mordant, P.; Castier, Y.; Mal, H.; De Tymowski, C.; Montravers, P. Acute Kidney Injury After Lung Transplantation: Perioperative Risk Factors and Outcome. Transplant Proc. 2020, 52, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, P.N.; Rocha, A.T.; Palmer, S.M.; Davis, R.D.; Smith, S.R. Acute renal failure after lung transplantation: incidence, predictors and impact on perioperative morbidity and mortality. Am J Transplant. 2005, 5, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevens, F.; Pirenne, J. Renal disease in the allograft recipient. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2020, 46–47, 101690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreassen, A.K.; Andersson, B.; Gustafsson, F.; Eiskjaer, H.; Rådegran, G.; Gude, E.; Jansson, K.; Solbu, D.; Karason, K.; Arora, S.; Dellgren, G.; Gullestad, L.; SCHEDULE Investigators. Everolimus Initiation With Early Calcineurin Inhibitor Withdrawal in De Novo Heart Transplant Recipients: Three-Year Results From the Randomized SCHEDULE Study. Am J Transplant. 2016, 16, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| GLOBAL (74) | HEART (7) | LIVER (34) | LUNG (33) | |
| Age (years) | 54.39 | 49.42 | 58.71 | 51 |
| Sex (%) | Men: 73 Women: 27 |
Men: 85.7 Women: 14.3 |
Men: 79.4 Women: 20.6 |
Man: 63.6 Women: 36.4 |
| Pre-transplantation | ||||
| Hypertension (%) | 37.8 | 57.1 | 39.4 | 33.3 |
| Diabetes (%) | 27.1 | 14.3 | 51.5 | 26.1 |
| Dyslipidemia (%) | 25.7 | 42.9 | 18.2 | 27.3 |
| Hyperuricemia (%) | 14.9 | 14.3 | 15.2 | 15.2 |
| Overweight (%) | 23 | 28.6 | 33.3 | 12.1 |
| Obesity (%) | 18.9 | 28.6 | 27.3 | 9.1 |
| Ex-smoker (%) | 55.4 | 42.9 | 42.4 | 72.7 |
| Smoker (%) | 8.1 | 28.6 | 12.1 | 0 |
| Cardiorenal syndrome (%) | 6.8 | 28.6 | 3 | 6.1 |
| Hepatorenal syndrome (%) | 18.9 | 0 | 39.4 | 0 |
| CKD (%) | 23 | 28.6 | 45.5 | 0 |
| Stage or CKD (%) | G3a: 65.21 G3b: 23.91 G4: 10.88 |
G3a: 100 G3b: 0 G4: 0 |
G3a: 60 G3b: 26.6 G4: 13.4 |
G3a: 0 G3b: 0 G4: 0 |
| Nephrologist Follow-up (%) | 14.9 | 28.6 | 18.2 | 6.1 |
| Peri-transplantation | ||||
| AKI (%) | 58.1 | 85.7 | 63.6 | 48.5 |
| RRT (%) | 5.4 | 28.6 | 0 | 6.1 |
| Surgical complications (%) | 51.4 | 57.1 | 30.3 | 72.7 |
| Transfusion requirements (%) | 87.8 | 71.4 | 97 | 81.8 |
| Vasoactive drugs (%) | 54.1 | 85.7 | 98.5 | 54.5 |
| Mechanical ventilation (%) | 44.6 | 42.9 | 15.2 | 75.8 |
| Infections (%) | 62.6 | 57.1 | 36.4 | 90.9 |
| Tacrolimus (%) | 81.8 | 57.1 | 78.8 | 87.9 |
| Cyclosporine (%) | 23 | 42.9 | 18.2 | 24.2 |
| Mycophenolate (%) | 98.6 | 100 | 97 | 100 |
| Everolimus (%) | 8.2 | 14.3 | 9.1 | 6.1 |
| Corticosteroids (%) | 90.5 | 100 | 78.8 | 100 |
| Changes in immunosuppression (%) | 14.9 | 28.6 | 12.1 | 15.2 |
| Graft rejection (%) | 20.3 | 71.4 | 9.1 | 21.2 |
| Calcineurin inhibitor overdose (%) | 50 | 42.9 | 21.2 | 81.8 |
| Nephrotoxic substances (%) | 64.9 | 100 | 33.3 | 91 |
|
NSAIDS (%) Antimicrobials (%) Intravenous contrast (%) Combinations of nephrotoxic (%) |
4.16 31.27 20.80 43.77 |
14.2 42.9 42.9 0 |
9 63.66 18.31 9 |
0 16.7 16.7 66.6 |
| Nephrologist Follow-up (%) | 18.9 | 42.9 | 21.2 | 12.1 |
| Post-transplantation | ||||
| New hypertension (%) | 23 | 28.6 | 15.1 | 30.3 |
| PTDM (%) | 23 | 28.6 | 15.2 | 30.3 |
| New dyslipidemia (%) | 17.5 | 57.1 | 12.1 | 18.2 |
| Admissions (mean) | 6.8 | 6.8 | 3.79 | 9.15 |
| Infections | 78.4 | 42.9 | 69.7 | 93.9 |
| Calcineurin inhibitor overdose (%) | 66.2 | 71.4 | 36.4 | 97 |
| Changes in immunosuppression (%) | 68.9 | 57.1 | 51.5 | 90.9 |
| Graft rejection (%) | 31.1 | 85.7 | 15.2 | 36.4 |
| Nephrotoxic substances (%) | 77 | 100 | 57.6 | 93.9 |
|
NSAIDS (%) Antimicrobials (%) Intravenous contrast (%) Others (%) Combinations of nephrotoxic (%) |
1.75 17.53 19.35 1.75 59.62 |
0 0 71.4 0 28.6 |
5.2 42.84 15.79 5.2 31.97 |
0 6.49 9.69 0 82.82 |
| TMA (%) | 9.5 | 14.3 | 0 | 18.2 |
| Final results | ||||
| Time to Nephrology follow up (mean, months) | 33.01 | 33.71 | 28.24 | 38.64 |
|
Worsened renal function (%) Improved or maintain renal function stable (%) |
45.9 54.1 |
28.57 74.43 |
44.11 55.89 |
51.5 48.5 |
| Increase in baseline creatinine by 50% (%) | 59.5 | 42.9 | 32.35 | 90.9 |
| ESKD (%) | 32.43 | 14.3 | 14.7 | 54.54 |
| RRT (%) | 10.8 | 14.3 | 6.1 | 15.2 |
| Exitus (%) | 28.4 | 0 | 32.35 | 30.3 |
| Factors | N | % | p-value | Hazard Ratio |
| Type of transplant | P < 0.05 | |||
| Heart transplantation | 3 | 42.9 | HR 0.075 [95% CI] 0.01 to 0.5 | |
| Liver transplantation | 11 | 32.4 | HR 0.048 [95% CI] 0.012 to 0.192 | |
| Lung transplantation | 30 | 90.9 | This parameter is set to zero because it is redundant. | |
| Pre-transplant period | ||||
| CKD | 3 | 17.6 | p<0.001 | HR 0.084 [95% CI] 0.021 to 0.331 |
| Not having follow-up by Nephrology | 41 | 65.1 | p<0.027 | HR 4.97 [95% CI] 1.196 to 20.651 |
| Peri-transplant period | ||||
| Mechanical ventilation | 27 | 81.8 | p<0.001 | HR 6.353 [95% CI] 2.155 to 18.726 |
| Calcineurin inhibitor overdose | 28 | 75.7 | p<0.006 | HR 4.083 [95% CI] 1.512 to 11.028 |
| Nephrotoxic | 33 | 68.8 | p<0.029 | HR 3 [95% CI] 1.116 to 8.064 |
| Antimicrobials | 26 | 74.3 | p<0.012 | HR 3.569 [95% CI] 1.324 to 9.62 |
| Intravenous contrast | 24 | 77.4 | p<0.009 | HR 3.943 [95% CI] 1.403 to 11.082 |
| No use of everolimus | 44 | 64.7 | P< 0.001 | HR 15722797292 |
| Not making changes in immunosuppression | 41 | 65.1 | p<0.027 | HR 4.97 [95% CI] 1.196 to 20.651 |
| Not having follow-up by Nephrology | 39 | 65 | P<0.046 | HR 3.34 [95% CI] 1.01 to 11.26 |
| Post-transplant period | ||||
| Calcineurin inhibitor overdose | 35 | 71.4 | p<0.004 | HR 4.444 [95% CI] 1.594 to 12.390 |
| Intravenous contrast | 31 | 70.5 | P<0.022 | HR 3.118 [95% CI] 1.182 to 8.226 |
| Number of hospital admissions | P< 0.006 | HR 1.169 [95% CI] 1.046 to 1.306 | ||
| Time until outpatient Nephrology consultation | P<0.002 | HR 1.032 [95% CI] 1.011 to 1.054 | ||
| Factors | N | % | p-value | Hazard Ratio |
| Type of transplant | P <0.001 | |||
| Heart transplantation | 1 | 14.3 | P<0.082 | HR 0.13 [95% CI] 0.015 to 1.28 |
| Liver transplantation | 5 | 14.7 | P< 0.001 | HR 0.144 [95% CI] 0.045 to 0.463 |
| Lung transplantation | 18 | 54.5 | This parameter is set to zero because it is redundant. | |
| Peri-transplant period | ||||
| Mechanical ventilation | 15 | 45.5 | P <0.035 | HR 2.963 [95% CI] 1.081 to 8.120 |
| Calcineurin inhibitor overdose | 17 | 45.9 | P<0.015 | HR 3.643 [95% CI] 1.27 to 10.372 |
| Antimicrobials | 16 | 45.7 | P< 0.028 | HR 3.158 [95% CI] 1.133 to 8.801 |
| Intravenous contrast | 16 | 51.6 | P< 0.004 | HR 4.667 [95% CI] 1.646 to 13.232 |
| Post-transplant period | ||||
| Calcineurin inhibitor overdose | 20 | 40.8 | P< 0.037 | HR 3.621 [95% CI] 1.078 to 12.161 |
| Antimicrobials | 18 | 42.9 | P<0.032 | HR 3.25 [95% CI] 1.106 to 9.548 |
| Number of hospital admissions | P< 0.020 | HR 1.103 [95% CI] 1.015 to 1.198 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





