1. Introduction
Acacia erioloba, known as Giraffe Thorn or Camel Thorn, is an African species in the large and taxonomically controversial Acacia genus. The name is mistranslated from the Afrikaans "Kameeldoring", meaning Giraffe Thorn [
1]. This plant is a large genus of shrubs and trees in the pea family Fabaceae subfamily Mimosoideae. The seeds from the plant known as the Wattle or Acacia are popular. The Acacia trees are highly demanding for activated carbon (AC) and carbonaceous materials. AC is the most extensively used adsorbent in industries and for domestic applications capable of treating diverse effluents [
1]. Due to chronic water stress, since 1968, Windhoek, the capital of Namibia, has used treated wastewater to produce drinking water. Wastewater reuse for drinking purposes is not standard because only 4% of sewage is generally recycled, mainly for industrial needs [
2]. Windhoek's Goreagab Water Reclamation plant uses advanced "multi-barrier" technologies, including powdered and granular ACs [
3]. Powdered AC is added to the raw water to remove algae and dissolved organic matter like humic substances, enabling the removal by enhanced coagulation and partial deactivation of harmful microbiology [
4]. The remaining dissolved organic compounds in the water are then adsorbed onto the granular AC [
5], which demands considerable amounts of AC for wastewater treatment in Namibia.
To cope with the massive requirement of powdered and granular activated carbon, AC should be generated using locally available raw materials and a cost-effective production technique. The use of acacia tree material could be an additional benefit. It is the dominant tree, highly recognisable, on the Kalahari plains in Angola, Botswana, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Zambia, and Zimbabwe, often growing along and on the banks of riverbeds. Some Namibian companies have used some Acacia genus species to produce charcoal that has been used to purify water [
1]. Acacia seedpods make high-quality charcoal formed through slowly burning, producing little ash [
6].
Namibia faces the challenge that its traditionally open semi-arid savannah rangeland, characterised by a patchy mixture of trees, mainly acacia species, thickets of bush and extensive grassland, is gradually transforming into a dense, bush-encroached landscape. Bush encroachment affects more than 30 million hectares of land in Namibia, resulting in the decreased carrying capacity of the rangelands, loss of biodiversity, and in the medium term, a reduction of available groundwater due to the increased water uptake by the encroacher bushes among others [
7,
8]. The consequences are economic losses of around EUR 100 million annually and a high loss of jobs in agriculture [
3]. The bushes have created a natural and previously unused resource of an estimated 200 million tons of wood biomass.
Although many studies in the literature relate the preparation and characterisation of AC from carbonaceous materials [
9,
10,
11], there is limited information on the generation of AC using Acacia erioloba seedpods as the precursor material [
6]. The conversion of Acacia erioloba seedpods to AC offers a significant advantage in reducing the cost and the environmental damage resulting from the decay and disposal of these residues. Furthermore, carbon produced from acacia is more rigid and more resistant to attrition [
10]. AC can be prepared by physical or chemical activation. Physical activation is a two steps method in which raw material is first carbonised at a temperature between 400 ⁰C and 1000 ⁰C and then activated by steam, carbon dioxide, air or their mixtures [
12]. In chemical activation, the carbonisation and activation steps are carried out simultaneously. The method requires less heat, and a simple laboratory setup is sufficient with less complex operating conditions than physical or steam activation techniques [
12].
Recently, we reported the chemical preparation of activated carbon from Acacia eriooba seedpods using H
2SO
4 as impregnating agent for water treatment [
6]. Phosphoric acid (H
2PO
3), an activation of carbonaceous materials, has become increasingly used to manufacture AC [
13,
14]. H
2PO
3 activation has environmental benefits and several other advantages, such as ease of recovery compared to zinc chloride and sulfuric acid activation, low energy cost, and high char yield [
15]. Chemical activation with phosphoric acid was used to produce AC as it is relatively easy and does not require skilled and trained personnel [
16].
Providing safe drinking water is raising a lot of global concerns. In this paper, the chemical preparation of AC using Acacia erioloba seedpods as a carbonaceous precursor and H2PO3 as an activation agent. The effect of particle sizes on AC's adsorption properties is described. The prepared AC were sieved into different particle sizes. The adsorption properties of the material were characterised using various analytical techniques, including scanning electron microscopy (SEM) equipped with EDX, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET), proximate analysis, Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption isotherms, iodine number, and methylene blue index.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Used
H3PO4 (10%), HCl (0.1 M), methylene blue (C16H18ClN3S), potassium iodide (KI), potassium iodate (KIO3), sodium thiosulphate pentahydrate (Na2S2O3.5H2O), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), starch and iodine were procured from Sigma-Aldrich.
2.2. Preparation of Activated Carbon
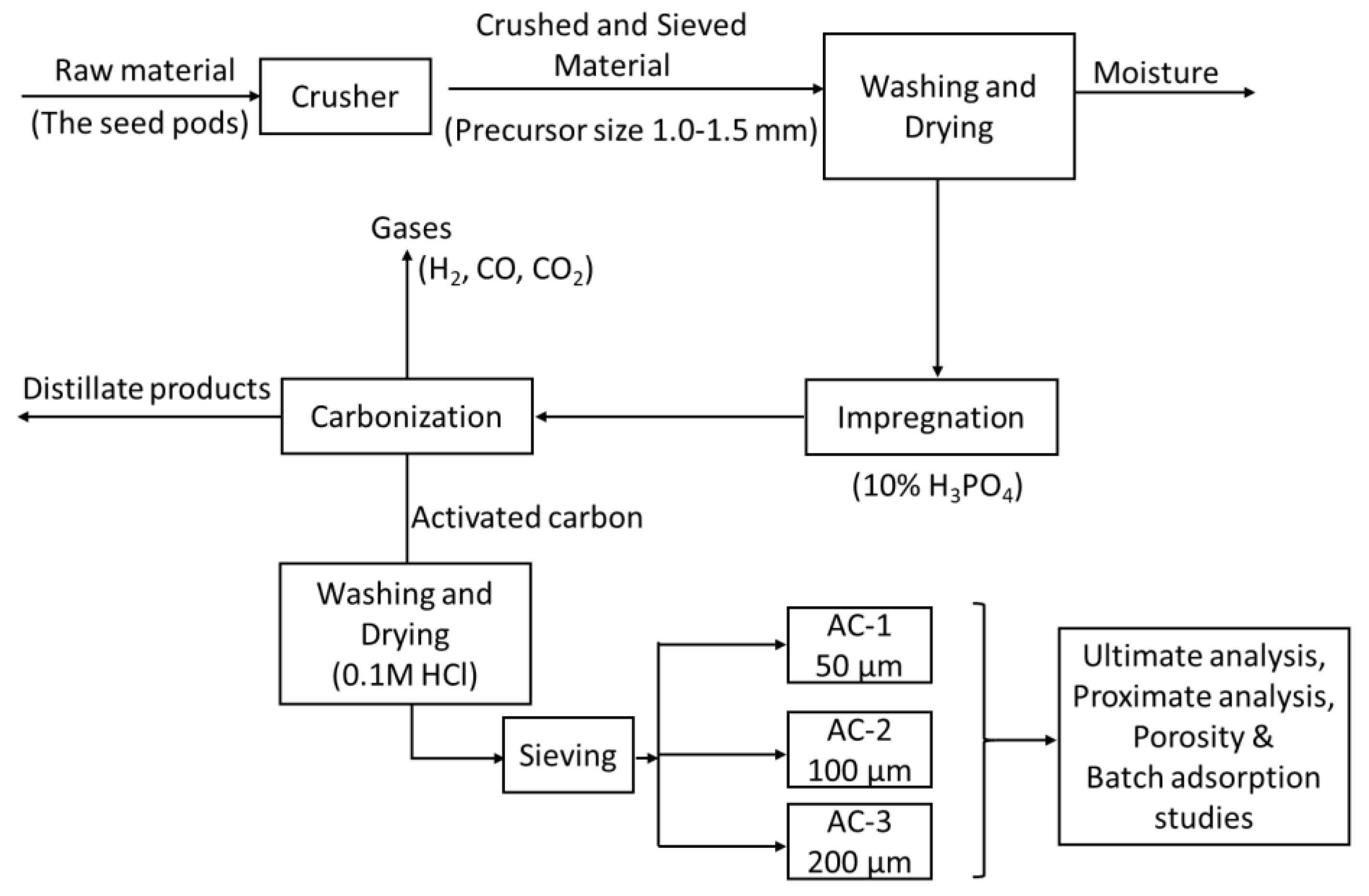
The seedpods were collected from a Camelthorn tree on the University of Namibia premises.
Scheme 1 shows the steps employed for the preparation of AC. The seedpods were sun-dried, crushed and ground in a ball mill to form a biomass precursor. The ground sample was sieved to obtain particles of uniform size, 1.0 – 1.5 mm in diameter. The precursor was washed with distilled water to remove surface bounded impurities and mud and then dried at 105 °C for 12 hours.
25 g of the dried precursor was impregnated with 150 mL 10% phosphoric acid (H
3PO
4) as an activation agent in a 500 mL flask. The calculated amount of the dried Acacia seedpod powder and the activating agent (H
3PO
4) were mixed, as per the impregnation ratio (IR), presented in Equation (1).
The mixture's flask was covered with aluminium foil and kept at room temperature overnight. After soaking, the samples were heated at 110 °C on a hot plate for 2 hours. The samples were filtered using suction filtration and washed with hot deionised water (about 80°C) until the pH was neutral. The material was then oven dried for 24 hours at 105 ± 5 ˚C. The dried sample in crucibles was then kept in the Muffle furnace for 1 hour and heated at a steady rate to attain the temperature of 500 ˚C to produce AC. The obtained sample was then washed with 100 ml of 0.1 M HCl to remove impurities and filtered by suction filtration and washed again with hot deionised water until pH was neutral. The residue was dried in an oven at 105 °C for 3 hours. The prepared AC samples were kept in airtight bottles for further characterisation.
The prepared activated carbon sample was then sieved into three different particle sizes of 50, 100 and 200 micrometres (µm) and was denoted as AC-1, AC-2 and AC-3, respectively, throughout this paper. The reason for sieving the material into three different sizes was to determine the effect of particular particle sizes on AC's adsorption properties.
Scheme 1 shows the schematic diagram for the preparation and activation of.
2.3. Ultimate and Proximate Analysis of the Prepared Activated Carbon
The percentage yield of the prepared AC was determined by using Equation 1 on a chemical-free basis and is regarded as an indicator of the process efficiency for the chemical activation process.
Where M1 and M2 are the masses of the carbonized sample before and after activation, respectively.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) coupled with Energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS) was used for elemental analysis. Proximate analysis was carried out in triplicate to determine the pH, moisture content, ash content, volatile matter, bulk density, and fixed carbon of AC-1, AC-2 and AC-3 samples as per literature methods [
11,
17].
To quantity, the pH, 0.5 g of each AC powder sample and 100 mL of distilled water in triplicate were placed in 500 mL Erlenmeyer flasks was stirred for 60 min, followed by pH measurement. For the moisture content, a 0.5 g AC sample was put into pre-weighed crucibles in triplicate and heated in an oven at 125˚C for 90 min. The crucible was left in the furnace for overnight to cool. After cooling, the weight of the dried sample was measured. The same procedure was repeated for the AC-2 and AC-3 powders, respectively. Equation 3 was employed [
11].
Where B = mass of crucible + original sample, F = mass of crucible + dried sample and G = mass of empty crucible.
The ash content was estimated by placing 0.5 g of AC-1, AC-2 and AC-3 powder into pre-weighed crucibles. The crucibles were heated in a muffle furnace to 750˚C for 90 min. During this heating process, the crucibles were left open. The crucibles were left to cool overnight and weighed. The procedure was repeated three times to obtain an average value. Equation 4 was used to calculate the average ash content [
11].
Where G = mass of empty crucible, B = mass of crucible + sample and F = mass of crucible+ ash sample.
The Volatile matter content was evaluated by placing a known quantity of AC-1 powder sample into a cylindrical crucible with a lid. It was then heated to 925˚C for 7 minutes in a muffle furnace. Then the crucible was left overnight for cooling and weighed. The following equation (Eqn. 5) was used [
11]. The process was repeated in triplicate to obtain an average value. The same procedure was repeated for the AC-2 and AC-3 powders, respectively.
Where B = mass of crucible, lid and sample before heating, F = mass of crucible, lid and contents after heating, G = mass of empty crucible & lid and M%= percentage of moisture determined in equation 3 above.
The Bulk Density (BD) was determined by estimating the mass of the measuring cylinder with and without 1 g of the AC-1 powder sample in triplicate Equation 6 (eqn.6) was employed [
11].
Where M1 = mass of measuring cylinder in grams, M2 = mass of measuring cylinder + its contents and V = volume of the measuring cylinder in litres.
Finally, the fixed carbon content was determined using equation 7 [
11]:
2.4. Porosity Study of the Prepared AC Based on Iodine Number Determination
Iodine number is the milligrams of iodine adsorbed by 1gram of AC from a standard 0.10 M iodine solution when the equilibrium iodine concentration is exactly 0.02 M. Iodine number is a measure of the micro-pore content of the activated carbon. A higher iodine number signifies a higher micro-porosity of the sample. ASTMD4607–94, gives the standard procedure for determining the iodine number of the activated carbon [
18]. 1 g of the AC-1 powder was mixed with 10 ml of 5% by weight of hydrochloric acid in a conical flask. The solution was swirled until the activated carbon was wetted. The mixture was boiled for 30 s in a water bath. The flask was cooled to room temperature, and then 100 ml of 0.10 M iodine solution was added and shaken vigorously for 30 s. The contents were filtered through a filter paper. 50 ml of the filtrate was discarded, and the remaining filtrate was collected in a clean beaker. Then 50 ml of this filtrate was titrated against 0.10 M sodium thiosulphate solution until pale yellow. 0.40 M starch indicator was added, and titration continued until the blue colour disappeared to estimate the concentration. This was repeated three times to obtain an average value. The same procedure was repeated for the AC-2 and AC-3 powders, respectively.
2.5. Batch Adsorption Studies
The methylene blue number is defined as the maximum amount of dye adsorbed on 1.0 g of adsorbent. It is also described in the literature as q
eq. Stock solution of methylene blue was prepared by dissolving 1.2 g of methylene blue dye into 1000 mL of distilled water and stirred overnight using a magnetic stirrer to obtain homogeneity. The respective solution was diluted to different concentrations: 10, 25, 50, 100 and 250 mg/L. A standard calibration plot was prepared by measuring the absorbance at 664 nm. From the diluted solutions, 10 mL aliquots were pipette into 5 labelled 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks. 0.01 g of the AC-1 powder was placed into each flask, closed with aluminium foil and left standing for 24 hours. The residual absorbance of methylene blue was measured using a UV/Vis spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 664 nm. The calibration curve was used to determine the final concentration of dye present in the solution. This was repeated three times to obtain an average value. The same procedure was repeated for the sieved AC-2 and AC-3 powders. The amount of methylene blue adsorbed was calculated using Equation 8 for isotherm parameters analysis [
19].
Where C0 (mg/ L) is the concentration of the methylene blue solution at starting time (t = 0), Ce (mg /L) is the concentration of the methylene blue solution at equilibrium time, V (L) is the volume of the solution treated, and M (g) is the mass of the adsorbent. All test runs were carried out in triplicates to reproduce the results.
To determine the methylene blue number for the Langmuir model, a q
eq plot is made in function of C
e. The Langmuir parameters (qmax and KL) are found by the least square fitting regression [
20].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Percentage (%) Yield, Ultimate Analysis and Morphological Properties of Prepared AC
The average % yield of prepared AC is 77.22. This result indicates that the acacia seedpod is a lignocellulosic material with high cellulose and low lignin content, an essential factor for preparing AC. The high yield of AC could be attributed to the H
3PO
4 as an impregnating reagent, where many carbons are removed as CO, CH
4, CO
2 and tar during the dehydration stage [
21].
Ultimate analysis results of the prepared AC from
A. erioloba seedpods with H
3PO
4 as the impregnating agent are presented in
Figure 1. Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDX) data highlight that the AC has a negligible amount of metals such as Al, Si and Ca (≥ 0.13%), low Cu and Na (≥0.26%) content with a high carbon (83.61%) and oxygen (15.60%) contents. Hence AC shows carbon as the dominant element among other elements. These results are comparable to some work on AC from
A. Erioloba seedpods using H
2SO
4 as an impregnating agent in which carbon content (82.09%) was reported [
6]. The high oxygen contents in AC could be due to the influence of H
3PO
4 as an impregnating agent during heat treatment.
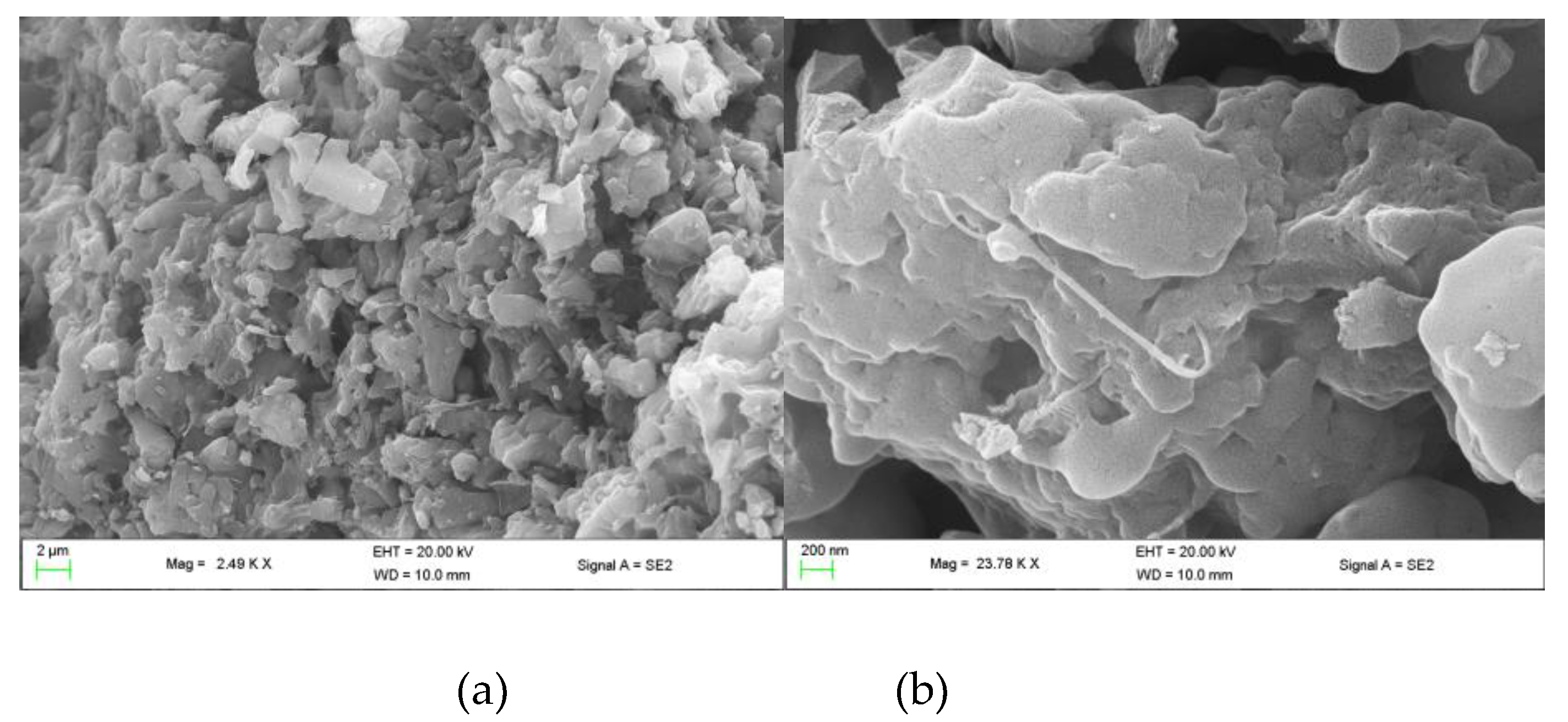
The external and internal surface of the prepared AC was studied using the SEM technique. SEM micrographs of the chemically activated carbons by H
3PO
4 are presented in
Figure 2.
The porous surface of the material is observable at higher magnification. The A and B SEM images show the pores in the micrometre (μm) diameter range. The prepared material also contains a highly developed internal surface area and porosity, with and rough texture and random pore size. These pores are mesoporous per
IUPAC standards [
22]. These pores and cavities result from evaporating the H
3PO
4 molecules during carbonisation, leaving the spaces previously occupied by H
3PO
4 on the surface of AC which causes the formation of soft spongy material [
23]. The presence of H
3PO
4 on the surface has resulted in white particles and impurities on the surface of the AC. This indicates that the acid introduced the pores on AC's surface, hence the increased surface area [
24].
The BET method was employed to study the specific surface area (SBET), the pore volume and the pore size, which reflect 387 m
2/g, 0.2081 cm
3/g, and 1.76 nm, respectively. The SBET agrees with most of the AC prepared by chemical activation [
6,
19]. As adopted from the report of Udayakumar and others [
25], the prepared AC powder in this study is microporous to mesoporous. The activating agent employed in this research effectively created well-developed pores leading to a large surface area and porous structure compared to H
2SO
4 that we reported previously [
6]. It is known that H
3PO
4 develop large mesopores and macropores. KOH can only modify the microporosity to more heterogeneous micropores.
In contrast, ZnCl
2 creates both wide micropores and low mesopores [
24]. These reflect the variation in the activation mode of each chemical, and H
3PO
4 is an excellent dehydrating reagent compared to the above-mentioned impregnating agents [
5,
14]. ACs should possess a high mesopore content and a high surface area for advanced applications.
3.2. Proximate Analysis of Prepared AC Sieved at a Different Size
For the proximate analysis, the prepared AC was sieved into various sizes, 50, 100 and 200 micrometres. The pH and percentages for moisture content, ash content, volatile matter, bulk density and fixed carbon of the prepared AC-1, AC-2 and AC-3 are tabulated in
Table 1.
Generally, the value of the power of hydrogen (pH) is one of the essential properties of an adsorbent that indicates its acidity/basicity of it and determines whether AC will develop a surface charge when submerged in an aqueous solution with a specific functional group. The prepared AC's pH indicates weak basicity with a pH range of 8.5—8.8. The basicity of AC's surface favours the adsorption of organic compounds such as methylene blue (MB) and catalysis processes [
26].
For the prepared AC-1, AC-2 and AC-3 samples, the moisture content was 23.24, 21.62 and 22.31 %, respectively. The moisture is due to various irregular porous characteristics (see SEM images), which can hold the water within. AC, with a large surface area and pore volume, will always adsorb moisture from the air unless preserved in airtight containers. AC-1, which has a 50-micrometre particle size, has the highest moisture content compared to other powders and a large surface area.
The ash content values represent the inorganic composition of the AC, which enhances the hydrophilic nature and can cause catalytic effects resulting in restructuring during the regeneration of AC. The ash content of the prepared AC-1, AC-2 and AC-3 samples are 27.10, 22.80, and 24.01 %, respectively. High ash content could be due to the less efficient removal of impurities during the chemical activation followed by the pyrolysis of raw materials [
6]. Generally, ash content above 10 % exhibits a larger surface area than low ash content [
27].
For the prepared AC-1, AC-2 and AC-3 samples, the volatile content was 21.50, 22.85, and 22.50 %, respectively. For the prepared AC samples, there is no significant difference between the volatile matter since all the carbon materials employed in this research were impregnated with 10% of phosphoric acid. It is well known that increasing % of impregnating agents increases the release of volatiles from the sample and decreases yield [
26]. Usually, the volatile values of the samples generated from acacia plant materials is around 35% [
6]. The lower value of volatile % experienced in this project could be due to the decrease in holding time. The gasification time was 1 hour. Increased adsorption time may weaken pore walls due to more evaporation of volatiles which destroys the pores. Consequently, promote the widens of the micropores and converts them into mesopores [
28,
29].
Fixed carbon is the amount of non-volatile carbon remaining in a carbonaceous sample. The fixed carbon for the prepared AC-1, AC-2 and AC-3 samples are 32.16, 32.73 and 31.18 %, respectively. Approximately 32 % of the prepared AC can be burned into a solid state, which is indeed beneficial to produce a higher yield of AC.
Bulk density provides a view regarding the floatability property of the adsorbent. The bulk density for the prepared AC-1, AC-2 and AC-3 samples are 0.58, 0.56, and 0.49%, respectively, which means the activated carbon, will float, resulting in poor contact with the adsorbent, thereby leading to a flawed adsorption process.
3.3. Batch Adsorption Dynamics and Equilibrium Studies of the Prepared ACs to Remove Organic Compounds in Water
The Iodine and methylene blue (MB) indices were employed to estimate the microporosity and mesoporosity of the prepared ACs.
3.3.1. Iodine Number and Number of Pores of Prepared ACs
The iodine number of prepared AC is presented in
Table 2 and is compared with a study that used the same materials and procedure [
6], but changed only the impregnating agent to H
2SO
4. The estimated Iodine number ANOVA analysis tables are incorporated in the appendix (
Table A1,
Table A2 and
Table A3).
The results in
Table 2 illustrate that the highest iodine number is 670 mg/g for AC-2 sample generated using H
3PO
4. AC sucks out the 670 mg/g volume of impurities, which means the number of pores depends on the AC particle size and the impregnating agent employed. The other factor could be the preparation conditions (activation temperature, for example). It is well reported that the iodine number decreases with higher pyrolysis temperatures (> 500 ºC) [
30]. The AC samples prepared using H
2SO
4 were heat treated at 600 ºC. The iodine number enhanced with increased activation temperature [
31]. However, to validate the above, analysis of variance (ANOVA) was applied at a confidence level of 95% to justify how adequate these results are. The ANOVA results showed that the equations did not adequately represent the relationship between each response and the significant variables. This is also evident from the adjusted R
2 values in
Table 2, which are far from 1, compared to the unadjusted values. The carbonisation temperature, the interaction between carbonisation and activation temperature, and the interaction between carbonisation temperature and impregnation ratio influence and lower the iodine number [
30].
3.3.2. Methylene Number, Adsorption Capacity and Surface Area of Prepared ACs
The adsorption capacity of the prepared activated carbon was determined using MB as an adsorbate. The increase in the initial MB solution concentration is the most used system for carrying out isotherm adsorption studies.
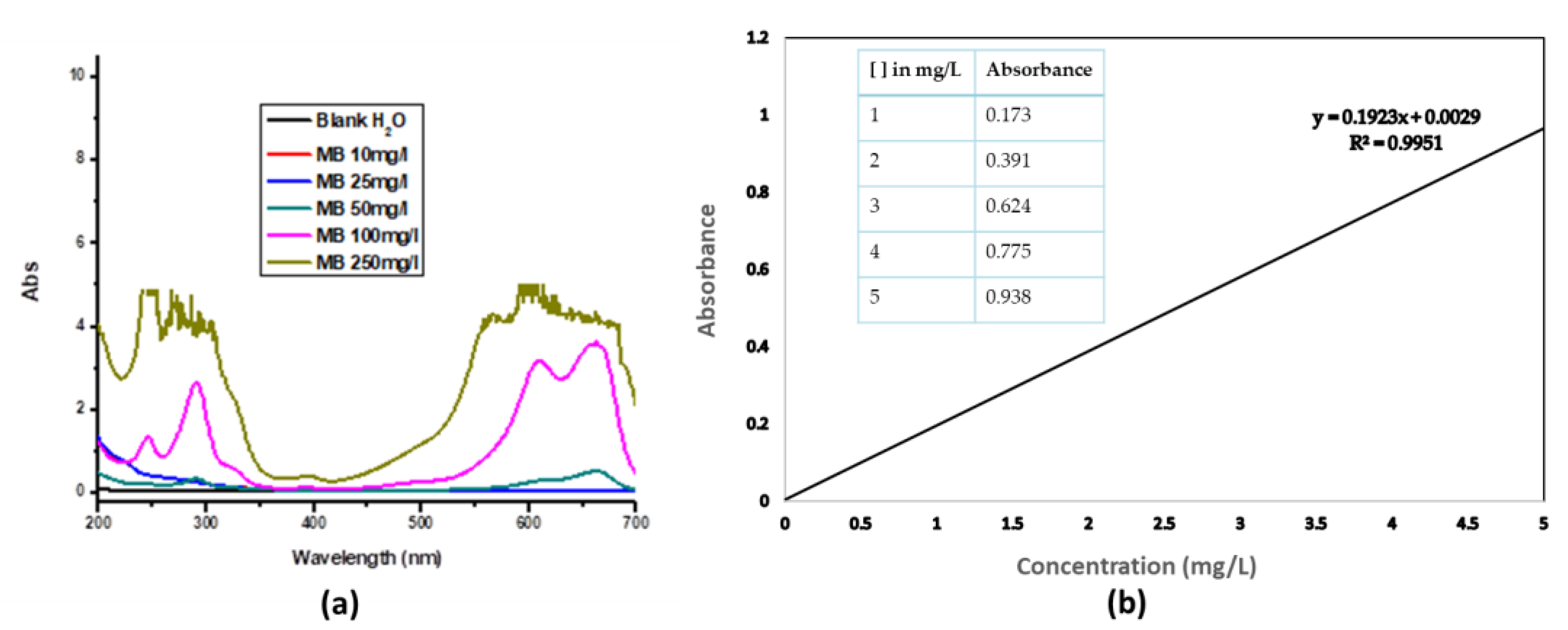
Figure 3 (a) shows the absorption spectra of MB at different concentrations. As can be observed from the absorbance spectra of methylene blue solution in
Figure 3 (a), at the specified light wavelength of 664 nm, the absorbance increased with the increase in the concentrations of the MB solution – which agrees with Beer-Lambert's law. Using these data (an inset in
Figure 3 (b), a calibration graph was obtained by plotting the absorbance of known concentrations of methylene blue solution and from which the equilibrium concentration (C
e) was determined.
For the adsorption isotherms analysis for this heterogeneous surface AC, the linear Langmuir isotherm (Eqn. 9) [
20] and the linear Freundlich isotherm (Eqn. 10) [
32] were employed, respectively.
C
e is the equilibrium concentration of dye solution (mg/L) [
9,
32].
KF and
n are the Freundlich adsorption constants, which indicate the capacity and intensity of the adsorption, respectively. Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption isotherms linear plots for preparing AC-1, 2 and 3 samples are presented in
Figure 4.
The changes in the MB concentration were used to plot the linear isotherms, and the raw data is provided in the appendix (
Table A4,
Table A5,
Table A6,
Table A7 and
Table A8). From the Langmuir and Freundlich linear plots in
Figure 4, the Langmuir and Freundlich constants were determined and presented in
Table 4.
Langmuir constants, q and b, are related to the monolayer adsorption capacity and the relative adsorption energy of adsorption, respectively. In contrast, Freundlich constants, K
F and n, are the relative indicators of adsorption capacity and adsorption intensity, respectively [
32]. The equilibrium concentration at time 't' was found by dividing the absorbance by the slope (Ce = (remaining concentration)/ (0.191)).
The correlation values (R
2) from the Langmuir and Freundlich linear plots are slightly close to 1. Thus, both models describe the system well, but the Freundlich isotherm model appeared to be much more suitable [
30,
32]. AC-2 recorded a better correlation among the Freundlich linear plots (R
2 = 0.9484). The fitness of the Freundlich model to the adsorption process indicates that methylene blue was adsorbed on a heterogeneous surface rather than on a monolayer surface and suggests sharing or exchanging electrons between the carbon surface and methylene blue molecules [
9]. The N values for the Freundlich plots close to 1 for AC-1 and AC-2 also support the favourable adsorption of methylene blue [
32]. However, sorption is very insignificant when
N is less than 1. Hence this can be deduced that adsorption on the prepared AC was a chemical rather than a physical process [
11].
The surface area of AC was determined further using the Langmuir isotherm method [
33] and compared to similar studies (
Table 5). A higher specific surface area, 620 ± 5.0 m
2/g, was recorded for AC-1, and the lowest was for AC-3 (632 ±3.6 m
2/g). Smaller activated carbon particle sizes can have a higher surface area than bigger particles. However, MB is a cationic dye. It might have been that ACs possess negatively charged functional groups; hence this chemical process favours the removal of MB [6. 9, 11].
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, activated carbon can be prepared from A. erioloba seedpods using phosphoric acid as activating agent. Compared to activation using H2SO4, H3PO4 prove superior in generating well-developed pores, leading to a mesoporosity and microporosity structure with a larger surface area. The iodine number of the prepared AC was higher. The adsorption of methylene blue on new AC material better fits with Langmuir's adsorption isotherm; hence, particles are adsorbed on well-pronounced heterogeneous surfaces. AC is an economical and eco-friendly green approach for wastewater treatment, especially for those in water-stressed countries such as Namibia. Specifically, the increasing demand for AC in Namibia can be solved by producing low-cost activated carbon from locally available waste materials such as Acacia seedpods. This strategy will provide low-cost activated carbon and help with the bush encroachment problem in Namibia.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, A.R., V.U. and L.S.D.; methodology, H.M.N., P.K., S.B.J.; validation, H.N.M., A.R. and L.S.D.; formal analysis, A.R. and L.S.D.; investigation, H.M.N.; resources, A.R., and L.S.D.; data curation, L.S.D.; writing—original draft preparation, A.R and L.S.D.; writing—review and editing, L.S.D. and S.B.J.; supervision, A.R.; project administration, A.R. and L.S.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received external funding from Perivoli Foundation, UK.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgement: Authors are grateful to the UNAM for providing support and facility to conduct this research and the Centre of Research Service (CRS) for providing technical help and support. This research did receive a specific grant from PERIVOLI Foundation,Research grant number…..
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
Table A1.
Analysis of variance for iodine number AC-1.
Table A1.
Analysis of variance for iodine number AC-1.
| |
df |
Sum of Squares |
Mean Square |
F value |
p-value prob>F |
| Regression |
1 |
62245.9 |
62245.9 |
1.802789 |
0.040753 |
| Residual |
1 |
34527.56 |
96773.46 |
2 |
|
Table A2.
Analysis of variance for iodine number AC-2.
Table A2.
Analysis of variance for iodine number AC-2.
| |
df |
Sum of Squares |
Mean Square |
F value |
p-value prob>F |
| Regression |
1 |
53376.47 |
53376.47 |
1.399579 |
0.446747 |
| Residual |
1 |
38137.53 |
91514 |
2 |
|
Table A3.
Analysis of variance for iodine number AC-3.
Table A3.
Analysis of variance for iodine number AC-3.
| |
df |
Sum of Squares |
Mean Square |
F value |
p-value prob>F |
| Regression |
1 |
62195.23 |
62195.23 |
1.796056 |
0.408104 |
| Residual |
1 |
34628.77 |
96824 |
2 |
|
Appendix B
Table A4.
Percent removal of methylene blue by AC-1 (10 mg).
Table A4.
Percent removal of methylene blue by AC-1 (10 mg).
Methylene Blue Concentration
(mg/L) |
Stock solution Absorbance before removal |
Stock solution
Absorbance after removal |
% Removal of
Blue
Methylene |
SD |
| 10 |
0.57213 |
0.000571 |
99.90 |
0.43 |
| 25 |
1.3480 |
0.003440 |
99.76 |
0.65 |
| 50 |
2.6770 |
0.003197 |
99.74 |
0.03 |
| 100 |
3.7882 |
0.007340 |
99.80 |
0.13 |
| 250 |
4.13 48 |
0.042950 |
98.97 |
1.02 |
Table A5.
Per cent removal of methylene blue by AC-2 (10 mg).
Table A5.
Per cent removal of methylene blue by AC-2 (10 mg).
Methylene Blue Concentration
(mg/L) |
Stock solution Absorbance before removal |
Stock solution
Absorbance after removal |
% Removal of
Blue
Methylene |
SD |
| 10 |
0.63123 |
0.000468 |
99.91 |
0.98 |
| 25 |
1.3400 |
0.001474 |
99.89 |
0.32 |
| 50 |
2.7670 |
0.003900 |
99.86 |
0.26 |
| 100 |
3.7595 |
0.006756 |
99.82 |
0.91 |
| 250 |
4.0148 |
0.039990 |
99.00 |
2.44 |
Table A6.
Per cent removal of methylene blue by AC-3 (10 mg).
Table A6.
Per cent removal of methylene blue by AC-3 (10 mg).
Methylene Blue Concentration
(mg/L) |
Stock solution Absorbance before removal |
Stock solution
Absorbance after removal |
% Removal of
Blue
Methylene |
SD |
| 10 |
0.6421 |
0.0005681 |
99.90 |
0.78 |
| 25 |
1.3540 |
0.0015769 |
99.88 |
0.27 |
| 50 |
2.7490 |
0.0039008 |
99.86 |
0.09 |
| 100 |
3.7425 |
0.0067569 |
99.84 |
0.32 |
| 250 |
4.0951 |
0.0393805 |
99.20 |
0.10 |
Appendix C
Table A7.
Isotherm data for MB removal by AC-2 (10 mg) for Langmuir adsorption isotherm.
Table A7.
Isotherm data for MB removal by AC-2 (10 mg) for Langmuir adsorption isotherm.
| Conc. (mg/L) |
Absorb.
(before removal) |
Absorbance
(after removal) |
Conc. (mg/L) |
Co-C
(mg/l) |
Ce
(mg/l) |
Qe
(mg/g) |
Ce/Qe (x10-3) (L/g) |
| 10 |
0.75123 |
0.002900 |
0.06408 |
3.2300 |
0.0069 |
3.2475 |
2.12 |
| 25 |
13500 |
0.0091694 |
0.04747 |
6.9725 |
0.0166 |
6.9347 |
2.40 |
| 50 |
2.7470 |
0.0093646 |
0.04850 |
14.452 |
0.0426 |
14.31 |
2.98 |
| 100 |
3.7695 |
0.02309700 |
0.06791 |
19.612 |
0.0601 |
19.370 |
3.07 |
Table A8.
Isotherm data for MB removal by AC-3 (10 mg) for Langmuir adsorption isotherm.
Table A8.
Isotherm data for MB removal by AC-3 (10 mg) for Langmuir adsorption isotherm.
| Conc. (mg/L) |
Absorb.
(before removal) |
Absorbance
(after removal) |
Conc. (mg/L) |
Co-C
(mg/l) |
Ce
(mg/l) |
Qe
(mg/g) |
Ce/Qe (x10-3) (L/g) |
| 10 |
0.6701 |
0.0029930 |
0.00701 |
3.2873 |
0.001677 |
3.2473 |
0.5 |
| 25 |
1.3451 |
0.0033928 |
0.01670 |
7.0033 |
0.016712 |
6.9271 |
1.87 |
| 50 |
2.8053 |
0.0041056 |
0.02097 |
14.459 |
0.016740 |
14.306 |
1.17 |
| 100 |
3.6950 |
0.0067562 |
0.0396 |
19.640 |
0.039560 |
19.427 |
2.04 |
Table A9.
Isotherm data for AC-1, 2 and 3 for Freundlich adsorption isotherm.
Table A9.
Isotherm data for AC-1, 2 and 3 for Freundlich adsorption isotherm.
| |
AC-1 (50 µm) |
AC-2 (100 µm) |
AC-3 (200 µm) |
Conc
(mg/L) |
Log Qe
|
log Ce
|
log Ce
|
Log Qe
|
log Ce
|
Log Qe
|
| 10 |
0.5182 |
-2.1520 |
0.5188 |
-2.149 |
0.5115 |
-2. 687 |
| 25 |
0.8406 |
-1.6782 |
0.9241 |
-1.752 |
0.8406 |
-1.782 |
| 50 |
1.1556 |
-1.4512 |
1.1176 |
-1.34 02 |
1.1555 |
-1.781 |
| 100 |
1.2884 |
-1.5260 |
1.2620 |
-1.324 |
1.2885 |
-1.4312 |
References
- Seymour, C., & Milton, S. A collation and overview of research information on Acacia erioloba (camelthorn) and identification of relevant research gaps to inform protection of the species. Contract, 2003, 31 (2003/089). Available from:https://cdn.24.co.za/files/Cms/General/d/7258/6ca73bb32e674a0b8179b6a89d0bf5a6.pdf.
- Birch, C., Harper-Simmonds, L., Lindeque, P., and Middleton, A. Benefits of bush control in Namibia. A national economic study for Namibia and a case for the Otjozondjupa Region. Report for the Economics of Land Degradation Initiative, 2016. Available from: www.eld-initiave.org.
- Maquet, C. Wastewater reuse: a solution with a future. Field Actions Science Reports. The journal of field actions, 2020 (Special Issue 22), 64-69. http://journals.openedition.org/factsreports/6341.
- Shutova, Y., Rao, N. R. H., Zamyadi, A., Baker, A., Bridgeman, J., Lau, B., & Henderson, R. K. Characterisation of dissolved organic matter to optimise powdered activated carbon and clarification removal efficiency. Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology, 2020, 6(8), 2065-2077. [CrossRef]
- Jjagwe, J., Olupot, P. W., Menya, E., & Kalibbala, H. M. (2021). Synthesis and application of Granular activated carbon from biomass waste materials for water treatment: A review. Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts, 2021, 6(4), 292-322. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A., Hango, H. J., Daniel, L. S., Uahengo, V., Jaime, S. J., Bhaskaruni, S. V., & Jonnalagadda, S. B. (2019). Chemical preparation of activated carbon from Acacia erioloba seed pods using H2SO4 as impregnating agent for water treatment: an environmentally benevolent approach. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 237, 117689. [CrossRef]
- Bester, F. V. Major problem-bush species and densities in Namibia. Agricola, 1999, 10, 1-3. Available from: https://www.nbri.org.na/sites/default/files/Agricola1998_99_No10_02_Bester.PDF.
- Shikangalah, R., & Mapani, B. A review of bush encroachment in Namibia: From a problem to an opportunity? Journal of Rangeland Science, 2020, 10(3), 251-266. https://dorl.net/dor/20.1001.1.20089996.2020.10.3.4.3.
- El-Shafey, E. I., Ali, S. N., Al-Busafi, S., & Al-Lawati, H. A. Preparation and characterisation of surface functionalised activated carbons from date palm leaflets and application for methylene blue removal. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2016, 4(3), 2713-2724. [CrossRef]
- Gratuito, M. K. B., Panyathanmaporn, T., Chumnanklang, R. A., Sirinuntawittaya, N. B., & Dutta, A. Production of activated carbon from coconut shell: optimisation using response surface methodology. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99(11), 4887-4895. [CrossRef]
- Tounsadi, H., Khalidi, A., Machrouhi, A., Farnane, M., Elmoubarki, R., Elhalil, A., ... & Barka, N. Highly efficient activated carbon from Glebionis coronaria L. biomass: Optimisation of preparation conditions and heavy metals removal using experimental design approach. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2016, 4(4), 4549-4564. [CrossRef]
- Song, M., Jin, B., Xiao, R., Yang, L., Wu, Y., Zhong, Z., & Huang, Y. (2013). The comparison of two activation techniques to prepare activated carbon from corn cob. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2013, 48, 250-256. [CrossRef]
- Rosas JM, Bedia J, Rodríguez-Mirasol J, Cordero T. HEMP-derived activated carbon fibers by chemical activation with phosphoric acid. Fuel 2009, 88:19–26. [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M., Ali, M., Siddiqi, Z., & Al Qahtani, A. S. Preparation of activated carbon from acacia (Vachellia seyal) Tree Branches and application to treat wastewater containing methylene blue dye. Modern Applied Science, 2019, 11(12), 102-108.
- Lim, W. C., Srinivasakannan, C., & Balasubramanian, N. Activation of palm shells by phosphoric acid impregnation for high yielding activated carbon. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2010, 88(2), 181-186. [CrossRef]
- Lupul, I., Yperman, J., Carleer, R., & Gryglewicz, G. Tailoring of porous texture of hemp stem-based activated carbon produced by phosphoric acid activation in steam atmosphere. Journal of Porous Materials, 2015, 22(1), 283-289. [CrossRef]
- Jagtoyen, M. Synthesis of activated carbons by the phosphoric acid activation of wood. Thesis, 1996, University of Kentucky.
- Gomez-Serrano, V., Valenzuela-Calahorro, C., & Pastor-Villegas, J. Characterization of rockrose wood, char and activated carbon. Biomass and Bioenergy, 1993, 4(5), 355-364. [CrossRef]
- ASTM Standards (2006), Designation D 4607-94, Standard TestMethod for Determination of Iodine Number of ActivatedCarbon. Designation D 2006, 4607-94,.
- Yaqubi, O., Tai, M. H., Mitra, D., Gerente, C., Neoh, K. G., Wang, C. H., & Andres, Y. Adsorptive removal of tetracycline and amoxicillin from aqueous solution by leached carbon black waste and chitosan-carbon composite beads. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(1), 104988.
- Rashed, M. N. Adsorption technique for the removal of organic pollutants from water and wastewater. Organic Pollutants-Monitoring, Risk and Treatment, 2013, 7, 167-194.
- Baig, M. M., & Gul, I. H. (2021). Conversion of wheat husk to high surface area activated carbon for energy storage in high-performance supercapacitors. Biomass and Bioenergy, 144, 105909. [CrossRef]
- Sher, F., Iqbal, S. Z., Albazzaz, S., Ali, U., Mortari, D. A., & Rashid, T. (2020). Development of biomass derived highly porous fast adsorbents for post-combustion CO2 capture. Fuel, 282, 118506. [CrossRef]
- Molina-Sabio, M., & Rodrıguez-Reinoso, F. Role of chemical activation in the development of carbon porosity. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2004, 241(1-3), 15-25. [CrossRef]
- Udayakumar, M., El Mrabate, B., Koos, T., Szemmelveisz, K., Kristaly, F., Lesko, M., ... & Nemeth, Z. Synthesis of activated carbon foams with high specific surface area using polyurethane elastomer templates for effective removal of methylene blue. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2021, 14(7), 103214. [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Utrilla, J., Sánchez-Polo, M., Gómez-Serrano, V., Álvarez, P. M., Alvim-Ferraz, M. C. M., & Dias, J. M. Activated carbon modifications to enhance its water treatment applications. An overview. Journal of hazardous materials, 2011, 187(1-3), 1-23. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., Song, X., Zhang, P., Gao, H., Ou, C., & Kong, X. Production of activated carbons from four wastes via one-step activation and their applications in Pb2+ adsorption: insight of ash content. Chemosphere, 2020, 245, 125587. [CrossRef]
- Liou, T. H. Development of mesoporous structure and high adsorption capacity of biomass-based activated carbon by phosphoric acid and zinc chloride activation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 158(2), 129-142. [CrossRef]
- Hu, S., Xiang, J., Sun, L., Xu, M., Qiu, J., & Fu, P. Characterization of char from rapid pyrolysis of rice husk. Fuel processing technology, 2008, 89(11), 1096-1105. [CrossRef]
- Esfandiari, A., Kaghazchi, T., & Soleimani, M.. Preparation and evaluation of activated carbons obtained by physical activation of polyethyleneterephthalate (PET) wastes. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2012, 43(4), 631-637.
- Shaarani, F. W., & Hameed, B. H. (2011). Ammonia-modified activated carbon for the adsorption of 2, 4-dichlorophenol. Chemical engineering journal, 2011, 169(1-3), 180-185. [CrossRef]
- Vuthaluru, H., Znad, H., & Ahmed, M. (2015). Removal of dissolved organic carbon from oily produced water by adsorption onto date seeds: equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 226(6), 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Itodo, A. U., Itodo, H. U., & Gafar, M. K. (2010). Estimation of specific surface area using Langmuir isotherm method. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management, 14(4). [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).