Submitted:
17 February 2023
Posted:
17 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. LIBs at low temperature
2.1. Limitations of LIBs at low temperatures
2.1.1. Electrolyte
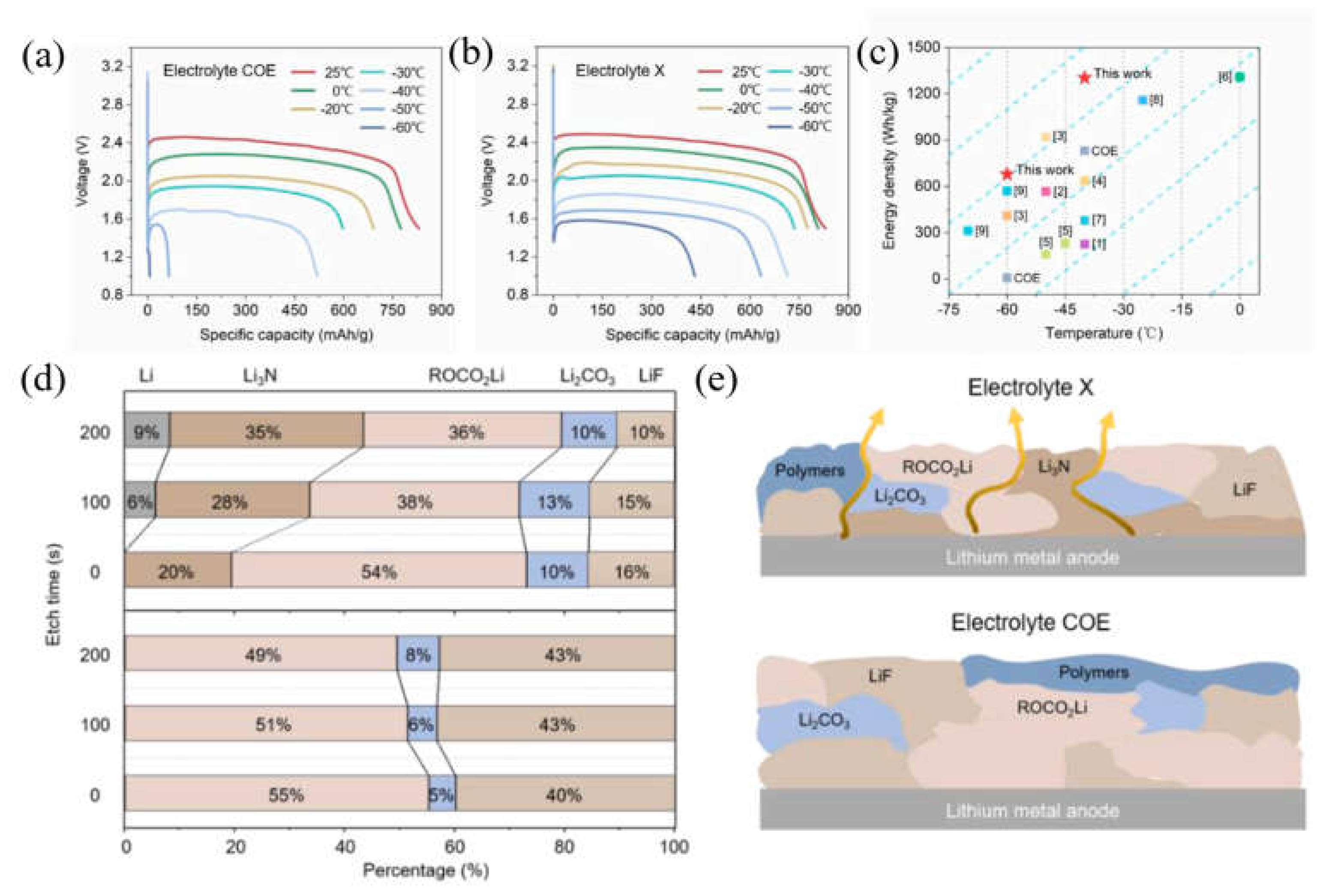
2.1.2. SEI film
2.1.3. Development of other low-temperature battery systems
2.1.4. Electrode
3. Modification of electrode materials
3.1. Carbon-based electrodes for LIBs
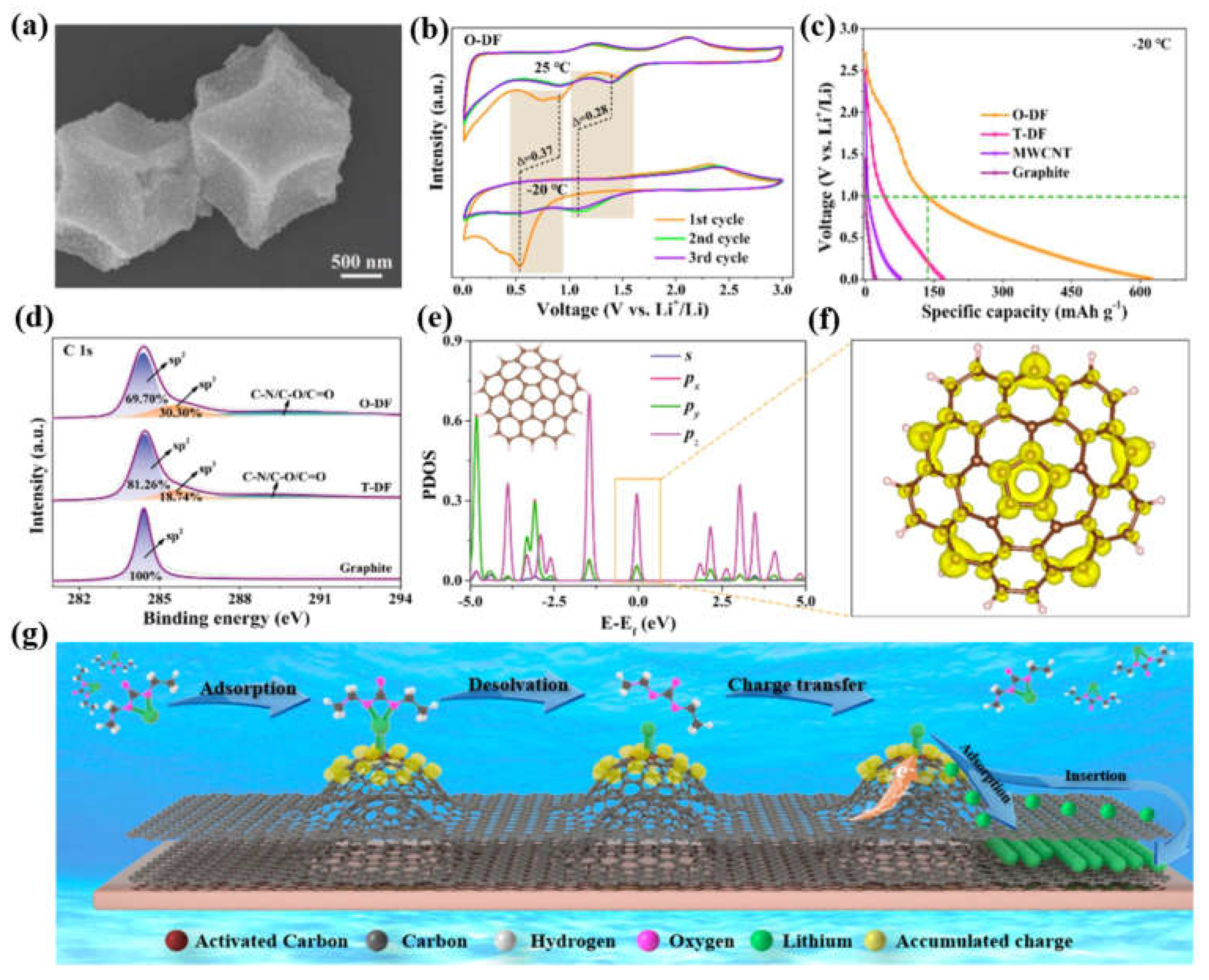
3.1.1. Electronic modulation of carbon-based anodes for low-temperature LIBs
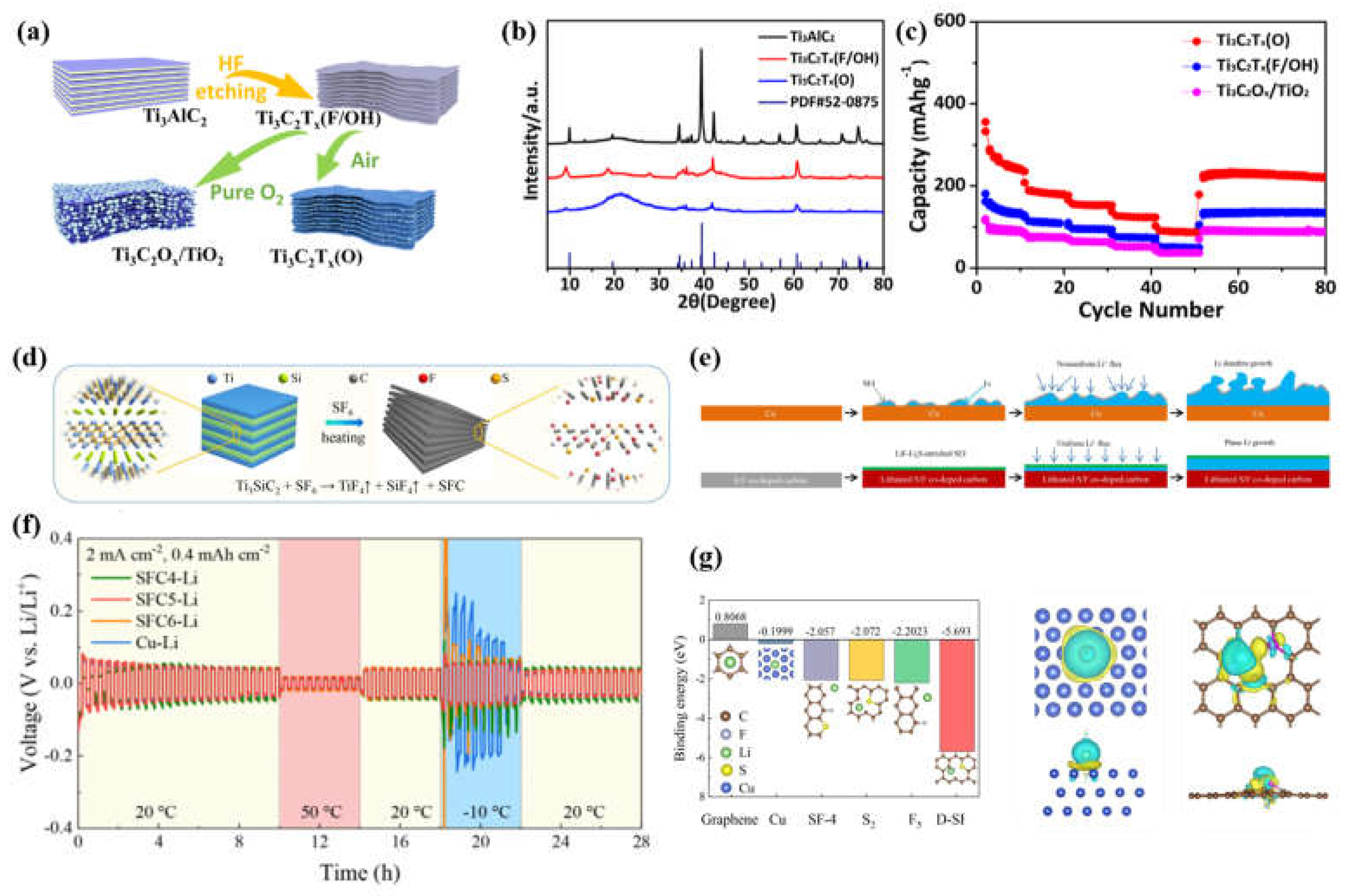
3.2. Structural engineering of carbon-based anodes for low-temperature LIBs
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of interest
References
- Li, M.; Lu, J.; Chen, Z.; Amine, K. 30 years of lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Lu, Y.-C. A retrospective on lithium-ion batteries. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Han, X.; Li, J.; Hua, J.; Ouyang, M. A review on the key issues for lithium-ion battery management in electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 2013, 226, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, R.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Seh, Z.W.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y. Promises and challenges of the practical implementation of prelithiation in lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2101565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, N.; Xu, Q.; Pearlie, L.S.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Yan, Q.; Dong, X. Bioinspired controlled synthesis of NiSe/Ni2P nanoparticles decorated 3D porous carbon for Li/Na ion batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 13217–13225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthiram, A. An outlook on lithium ion battery technology. ACS Central Sci. 2017, 3, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffner, F.; Kronemeyer, N.; Tübke, J.; Leker, J.; Winter, M.; Schmuch, R. Post-lithium-ion battery cell production and its compatibility with lithium-ion cell production infrastructure. Nat. Energy 2021, 6, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Iglesias, E.; Venet, P.; Pelissier, S. Modelling lithium-ion battery ageing in electric vehicle applications—calendar and cycling ageing combination effects. Batteries 2020, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-H.; Yi, K.-H. Space qualification of small satellite Li-ion battery system for the secured reliability. J. Korean Soc. Aerona. 2014, 42, 351–359. [Google Scholar]
- Depetro, A.; Gamble, G.; Moinuddin, K. Fire safety risk analysis of conventional submarines. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Jiang, M.; Tao, P.; Song, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Deng, T.; Shang, W. Temperature effect and thermal impact in lithium-ion batteries: A review. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2018, 28, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J. Fundamentals and challenges of lithium ion batteries at temperatures between− 40 and 60° C. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1904152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubble, D.; Brown, D.E.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, C.; Lau, J.; McCloskey, B.D.; Liu, G. Liquid electrolyte development for low-temperature lithium-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 550–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.-J.; Liu, Q.; Cohen, O.; Kim, M.; Persson, K.A.; Zhang, Z. Understanding the role of SEI layer in low-temperature performance of lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 11910–11918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Song, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Cui, X.; Wang, P.; Sun, J.; Cai, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, N. Insight into the competitive reaction between LiDFP and LiFSI in lithium-ion battery at low temperature. J. Power Sources 2022, 549, 232147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Tan, C.; Ou, T.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Ji, X. Constructing advanced electrode materials for low-temperature lithium-ion batteries: A review. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 4525–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Manthiram, A. Designing advanced lithium-based batteries for low-temperature Conditions. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2001972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liu, G.; Cheng, H.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ming, J. Low-Temperature Electrolyte Design for Lithium-Ion Batteries: Prospect and Challenges. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 15842–15865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, C.; Geng, J.; Sui, Y.; Wei, H.; Sun, C.; Geng, H.; Liu, Y. Nickel cobalt selenides on black phosphorene with fast electron transport for high-energy density sodium-ion half/full batteries. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z. Low temperature preheating techniques for Lithium-ion batteries: Recent advances and future challenges. Appl. Energy 2022, 313, 118832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.-T.F.; Babu, G.; Gullapalli, H.; Kalaga, K.; Sayed, F.N.; Kato, K.; Joyner, J.; Ajayan, P.M. A materials perspective on Li-ion batteries at extreme temperatures. Nat. Energy. 2017, 2, 17108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Deng, T.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, C.; Fan, X. Critical Review on Low-Temperature Li-Ion/Metal Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Wen, K.; Lv, W.; Zhou, X.; Liang, Y.; Yang, F.; Chen, Z.; Zou, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, W. Materials insights into low-temperature performances of lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources. 2015, 300, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, G.A.; Geaney, H.; Ryan, K.M. Alternative anodes for low temperature lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2021, 9, 14172–14213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selinis, P.; Farmakis, F. A Review on the Anode and Cathode Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries with Improved Subzero Temperature Performance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 010526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; Srivastava, S.K. Nanostructured anode materials for lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2015, 3, 2454–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Niu, Z.; Chen, J. Advanced nanostructured carbon-based materials for rechargeable lithium-sulfur batteries. Carbon. 2019, 141, 400–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselin, L.S.; Juang, R.-S.; Hsieh, C.-T.; Sagadevan, S.; Umar, A.; Selvin, R.; Hegazy, H.H. Recent advances and perspectives of carbon-based nanostructures as anode materials for Li-ion batteries. Materials. 2019, 12, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Dong, D.; Lu, Y.-C. Design strategies for low temperature aqueous electrolytes. Nano Res. Energy 2022, 1, e9120003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Li, Y. Towards practical lean-electrolyte Li–S batteries: Highly solvating electrolytes or sparingly solvating electrolytes. Nano Res. Energy 2022, 1, e9120012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Qin, T.; Li, Q.; Zan, M.; Yu, X.; Li, H. Exploiting the synergistic effects of multiple components with a uniform design method for developing low-temperature electrolytes. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 50, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Tai, L.; Wu, X.; Yang, J.; Geng, H. Boosting Pseudo-capacitive Sodium Storage in Ultrafine Titanium Dioxide by an In-situ Porous Forming Strategy. ChemNanoMat 2022, 8, e202200068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, T.; Sun, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Q.; Li, Y. The optimized LiBF4 based electrolytes for TiO2 (B) anode in lithium ion batteries with an excellent low temperature performance. J. Power Sources 2020, 453, 227908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Che, Y.; Lan, G.; Lan, J.; Li, J.; Xing, L.; Xu, K.; Fan, W.; Yu, L.; Li, W. Tailoring low-temperature performance of a lithium-ion battery via rational designing interphase on an anode. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 38285–38293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, T.; Shi, X.; Ma, Y.; Song, D.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L. Hierarchical Sulfide-Rich Modification Layer on SiO/C Anode for Low-Temperature Li-Ion Batteries. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2104531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Ehteshami, N.; Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Paillard, E. Improving the graphite/electrolyte interface in lithium-ion battery for fast charging and low temperature operation: Fluorosulfonyl isocyanate as electrolyte additive. J. Power Sources 2019, 429, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Miao, X.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, H. In-situ lattice tunnel intercalation of vanadium pentoxide for improving long-term performance of rechargeable magnesium batteries. ChemNanoMat 2022, 8, e202200025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, H.; Wei, H.; Ang, E.H.; Yang, J.; Miao, X.; Geng, H.; Zuo, X. Interface and structure engineering of bimetallic selenides toward high-performance sodium-ion half/full batteries. J. Power Sources 2021, 506, 230216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Yan, C.; Shao, P.; Dai, K.; Yang, J. Interface and electronic structure engineering induced Prussian blue analogues with ultra-stable capability for aqueous NH 4+ storage. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 8501–8509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Wang, D.; Dong, B.; Zhu, M.; Zhi, C. Building durable aqueous K-ion capacitors based on MXene family. Nano Res. Energy 2022, 1, e9120002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, L.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Zou, J.; Zhao, S.; Mao, J.; Guo, Z. Challenges and prospects of lithium–CO2 batteries. Nano Res. Energy 2022, 1, e9120001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payandeh, S.; Strauss, F.; Mazilkin, A.; Kondrakov, A.; Brezesinski, T. Tailoring the LiNbO 3 coating of Ni-rich cathode materials for stable and high-performance all-solid-state batteries. Nano Res. Energy 2022, 1, e9120016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenuwara, A.C.; Shetty, P.P.; Kondekar, N.; Sandoval, S.E.; Cavallaro, K.; May, R.; Yang, C.-T.; Marbella, L.E.; Qi, Y.; McDowell, M.T. Efficient low-temperature cycling of lithium metal anodes by tailoring the solid-electrolyte interphase. ACS Energy Lett. 2020, 5, 2411–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hou, W.; Pan, R.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y. The interfacial electronic engineering in polyhedral MOF derived Co-doped NiSe2 composite for upgrading rate and longevity performance of aqueous energy storage. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 897, 163187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tron, A.; Jeong, S.; Park, Y.D.; Mun, J. Aqueous lithium-ion battery of nano-LiFePO4 with antifreezing agent of ethyleneglycol for low-temperature operation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 14531–14538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.-F.; Gao, X.-W.; Du, T.; Gong, H.; Liu, L.-Y.; Luo, W.-B. Two-dimensional NbSSe as anode material for low-temperature sodium-ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Chi, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y. Cost attractive hydrogel electrolyte for low temperature aqueous sodium ion batteries. J. Energy Storage 2021, 40, 102701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J.; Geng, H. Structural engineering of bimetallic selenides for high-energy density sodium-ion half/full batteries. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 16898–16905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Yuan, N.; Hu, B.; Ding, J.; Ge, S. Graphite-based lithium ion battery with ultrafast charging and discharging and excellent low temperature performance. J. Power Sources 2019, 430, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dong, G.; Li, Y. Boosting the electrochemical performance of lithium titanate at sub-zero temperature with Mo, S doping, and addition of MXene. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 26, 101145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.J.; Yang, L.X.; Wang, W.J.; Liu, H.J.; Zeng, C.L. Molten salt disproportionation synthesis of nanosized VN wrapped onto carbon fibers with enhanced lithium-ion storage capabilities. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 919, 165796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Xie, J.; Zhuang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Hu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J. Improved low-temperature performance of surface modified lithium-rich Li1. 2Ni0. 13Co0. 13Mn0. 54O2 cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. Solid State Ionics 2020, 347, 115245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Qi, S.; Fan, X.-Y.; Ji, F.-D.; Feng, Y.-H.; Si, D.; Wang, D.-W.; Liu, M.; Han, X.; Wang, P.-F. Cobalt-Doped Spinel Cathode for High-Power Lithium-Ion Batteries Toward Expanded Low-Temperature Applications. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2022, 5, 12682–12692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Cai, M.; Xie, M.; Dong, H.; Dong, W.; Huang, F. Constructing Robust Cathode/Electrolyte Interphase for Ultrastable 4.6 V LiCoO2 under− 25° C. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 19561–19568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Yu, X.; Qin, Y.; Meng, T.; Hu, X. The pursuit of commercial silicon-based microparticle anodes for advanced lithium-ion batteries: A review. Nano Res. Energy 2022, 1, e9120037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Ren, D.; Wang, L.; He, X. Graphite as anode materials: Fundamental mechanism, recent progress and advances. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 36, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goriparti, S.; Miele, E.; De Angelis, F.; Di Fabrizio, E.; Zaccaria, R.P.; Capiglia, C. Review on recent progress of nanostructured anode materials for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 257, 421–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Li, J.; Zuo, Z. Advanced electrochemical energy storage and conversion on graphdiyne interface. Nano Res. Energy 2022, 1, e9120036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Tai, L.; Shen, C.; Yang, J.; Sun, C.; Geng, H.; Zuo, X. Constructing electronic interconnected bimetallic selenide-filled porous carbon nanosheets for stable and highly efficient sodium-ion half/full batteries. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 18578–18585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Zang, X.; Hou, W.; Li, C.; Huang, Q.; Hu, X.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Ma, F. Construction of three-dimensional electronic interconnected Na3V2 (PO4) 3/C as cathode for sodium ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 899, 163363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez de la Torre, M.D.; Melguizo Guijarro, M. Covalent bonds on activated carbon. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 2010, 5147–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.M.; Nascarella, M.A.; Valberg, P.A. Carbon black vs. black carbon and other airborne materials containing elemental carbon: Physical and chemical distinctions. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 181, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusof, N.; Ismail, A. Post spinning and pyrolysis processes of polyacrylonitrile (PAN)-based carbon fiber and activated carbon fiber: A review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 93, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X. Fabrication and properties of carbon fibers. Materials 2009, 2, 2369–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, A.D.; Omrani, E.; Menezes, P.L.; Rohatgi, P.K. Mechanical and tribological properties of self-lubricating metal matrix nanocomposites reinforced by carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and graphene–a review. Composites Part B 2015, 77, 402–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilgen, C.; Diederich, F. Structural aspects of fullerene chemistry a journey through fullerene chirality. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 5049–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, R.; Yang, B. Carbon dots: A new type of carbon-based nanomaterial with wide applications. ACS Central Sci. 2020, 6, 2179–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z. Carbon-based nanocages: a new platform for advanced energy storage and conversion. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1904177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheka, E.F.; Razbirin, B.S.; Starukhin, A.N.; Nelson, D.K.; Degunov, M.Y.; Lyubovskaya, R.N.; Troshin, P. Fullerene-cluster amplifiers and nanophotonics of fullerene solutions. J. Nanophotonics 2009, 3, 033501. [Google Scholar]
- Sekar, S.; Aqueel Ahmed, A.T.; Inamdar, A.I.; Lee, Y.; Im, H.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, S. Activated carbon-decorated spherical silicon nanocrystal composites synchronously-derived from rice husks for anodic source of lithium-ion battery. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, X.; Geng, J.; Tan, Y.; Lv, C.; Pei, C.; Wei, H.; Chen, D.; Yang, J. Phase engineering of vanadium sulfides as superior anodes for high-energy density sodium-ion half/full batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 934, 167826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Johannisson, W.; Johansen, M.; Liu, F.; Zenkert, D.; Lindbergh, G.; Asp, L.E. Characterization of the adhesive properties between structural battery electrolytes and carbon fibers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 188, 107962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardhana, N.; Dimov, N.; Sasidharan, M.; Park, G.-J.; Nakamura, H.; Yoshio, M. Suppression of lithium deposition at sub-zero temperatures on graphite by surface modification. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 1116–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Cha, R.; Yang, L.; Mou, K.; Jiang, X. Fabrication of cellulose/graphene paper as a stable-cycling anode materials without collector. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehrawat, P.; Julien, C.; Islam, S. Carbon nanotubes in Li-ion batteries: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2016, 213, 12–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Lee, S.-T. Carbon dots: advances in nanocarbon applications. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 19214–19224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, C.P.; Yin, Y.X.; Wan, L.J.; Guo, Y.G. Sulfur encapsulated in graphitic carbon nanocages for high-rate and long-cycle lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9539–9544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, X.; Xie, J. Fullerenes for rechargeable battery applications: Recent developments and future perspectives. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 55, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarayapalli, K.C.; Kaniyampati, P.V.; Lee, K.; Vattikuti, S.V.P.; Shim, J; Julien, C.M. Sonochemically synthesized nanostructured ternary electrode material for coin-cell-type supercapacitor applications. FlatChem. 2021, 30, 100304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vattikuti, S.V.P.; Reddy, B.P.; Byon, C.; Shim, J. Carbon/CuO nanosphere-anchored g-C3N4 nanosheets as ternary electrode material for supercapacitors. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 262, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarayapalli, K.C.; Lee, K.; Do, H.-B.; Dang, N.N.; Yoo, K.; Shim, J.; Vattikuti, S.V.P. Mesostructured g-C3N4 nanosheets interconnected with V2O5 nanobelts as electrode for coin-cell-type-asymmetric supercapacitor device. Mater. Today Energy. 2021, 21, 100699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Yuan, N.; Ding, J.; Qin, S.; Razal, J.M.; Wang, X.; Ge, S.; Gogotsi, Y. Extending the low temperature operational limit of Li-ion battery to −80 degrees C. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 23, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Lv, X.; Liu, D.H.; Dai, D.; Gu, J.; Yang, L.; Chen, Z. Two-dimensional NiO@ C-N nanosheets composite as a superior low-temperature anode material for advanced lithium-/sodium-Ion batteries. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 3616–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Du, L.; Yan, Y.; Wu, S. An Investigation into the Charge-Storage Mechanism of MnO@ Graphite as Anode for Lithium-Ion Batteries at Low Temperature. ChemElectroChem 2019, 6, 2248–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Zhou, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Yuan, N.; Ge, S.; Ding, J. Excellent Rate and Low Temperature Performance of Lithium-Ion Batteries based on Binder-Free Li4Ti5O12 Electrode. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xiao, C.; Razmjooy, N. Optimal operational strategy of hybrid PV/wind renewable energy system using homer: a case study. Int. J. Ambient Energy 2022, 43, 3953–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, C.; Ma, W.; Fan, W.; Sun, Y.; Yin, H.; Shi, X.; Liu, X.; Ding, Y. Enhanced low-temperature Li-ion storage in MXene titanium carbide by surface oxygen termination. 2D Mater. 2019, 6, 045025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, D.; Zou, G.; Liu, B.; John, S.T.; Li, L.; Ren, L.; Peng, Q. Lithiation MAX derivative electrodes with low overpotential and long-term cyclability in a wide-temperature range. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 47, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
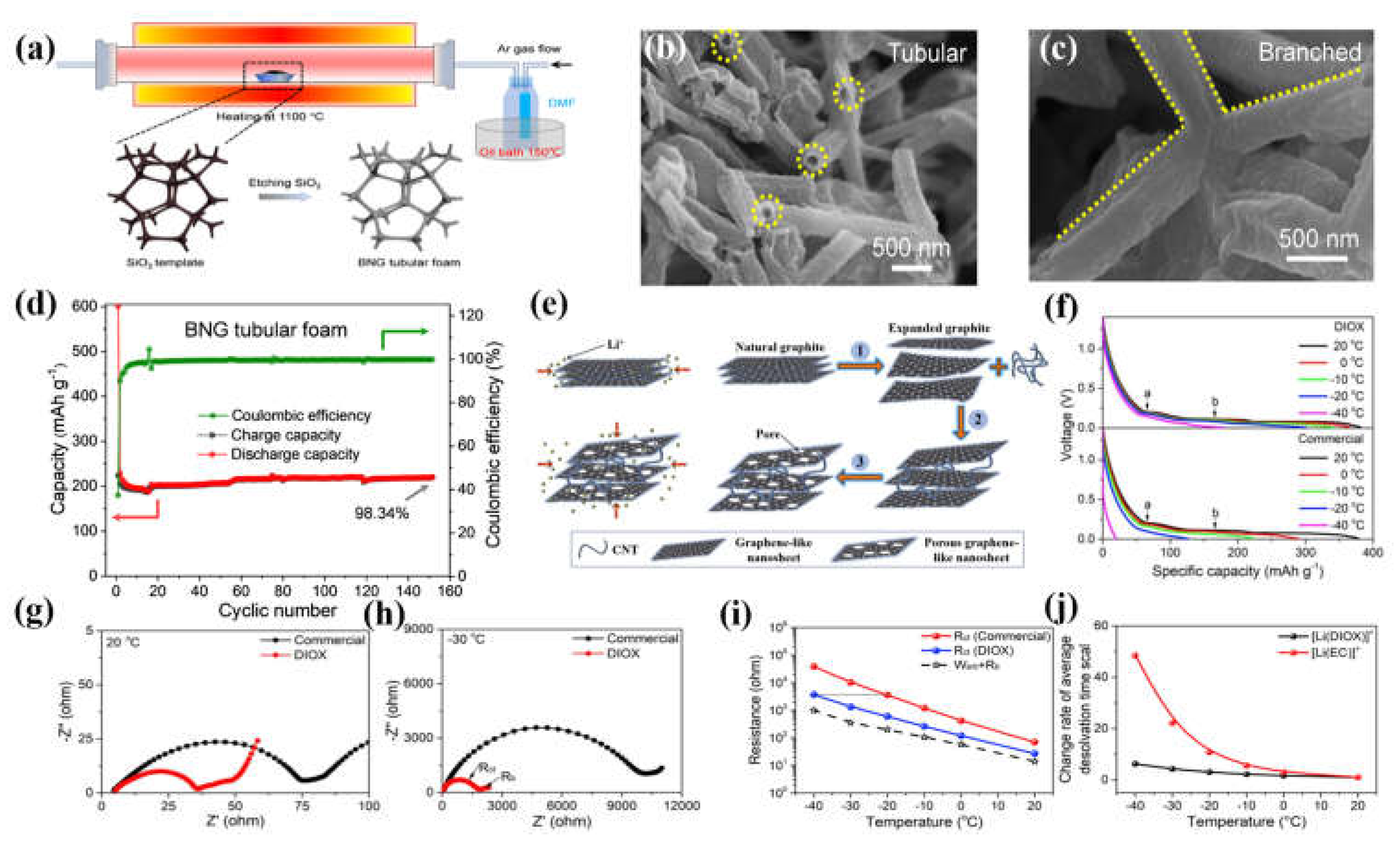
- Lu, F.; Liu, J.; Xia, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Engineering C–N Moieties in Branched Nitrogen-Doped Graphite Tubular Foam toward Stable Li+-Storage at Low Temperature. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 5858–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jin, Q.; Li, D.; Huan, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, G.; Zhao, J.; Yang, W.; Wu, Z.; Zhong, B. Mo2C-Embedded Carambola-like N, S-Rich Carbon Framework as the Interlayer Material for High-Rate Lithium–Sulfur Batteries in a Wide Temperature Range. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 22971–22980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Lan, Q.; Yang, Z.; Lv, X.-J. Multiple phase N-doped TiO2 nanotubes/TiN/graphene nanocomposites for high rate lithium ion batteries at low temperature. J. Power Sources 2019, 423, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Lin, C.; Dong, H.; Wei, H.; Yang, J.; Geng, H. Electronic modulation and structure engineered MoSe2 with multichannel paths as an advanced anode for sodium-ion half/full batteries. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 65, 2997–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, J.; Dong, H.; Wei, H.; Sun, C.; Yang, J.; Geng, H. Iron doping of NiSe2 nanosheets to accelerate reaction kinetics in sodium-ion half/full batteries. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, J.; Cheng, X.; Xie, W.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Yi, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Riemannian Surface on Carbon Anodes Enables Li-Ion Storage at −35° C. ACS Central Sci. 2022, 8, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, W.; Zhang, P.; Wei, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, K.; Liu, Z. Vacancy manipulating of molybdenum carbide MXenes to enhance Faraday reaction for high performance lithium-ion batteries. Nano Res. Energy 2022, 1, e9120026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, F.; Li, D.; Zhou, D.; Jing, P.; Du, F.; Qu, S. Carbon-dots-derived 3D highly nitrogen-doped porous carbon framework for high-performance lithium ion storage. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 9848–9856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, B.; Song, J.; Gao, H.; Wu, Z.; Shen, H.; Li, Y.; Lei, W.; Hao, Q. Synthesis of MnO–Sn cubes embedding in nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers with high lithium-ion storage performance. Nanotechnology 2021, 33, 115403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, W.; Wong, K.W.; Wu, J.; Chen, T.; Huang, S. Ultrafine ZnSe encapsulated in nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanofibers for superior Na-ion batteries with a long lifespan and low-temperature performance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 11705–11713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
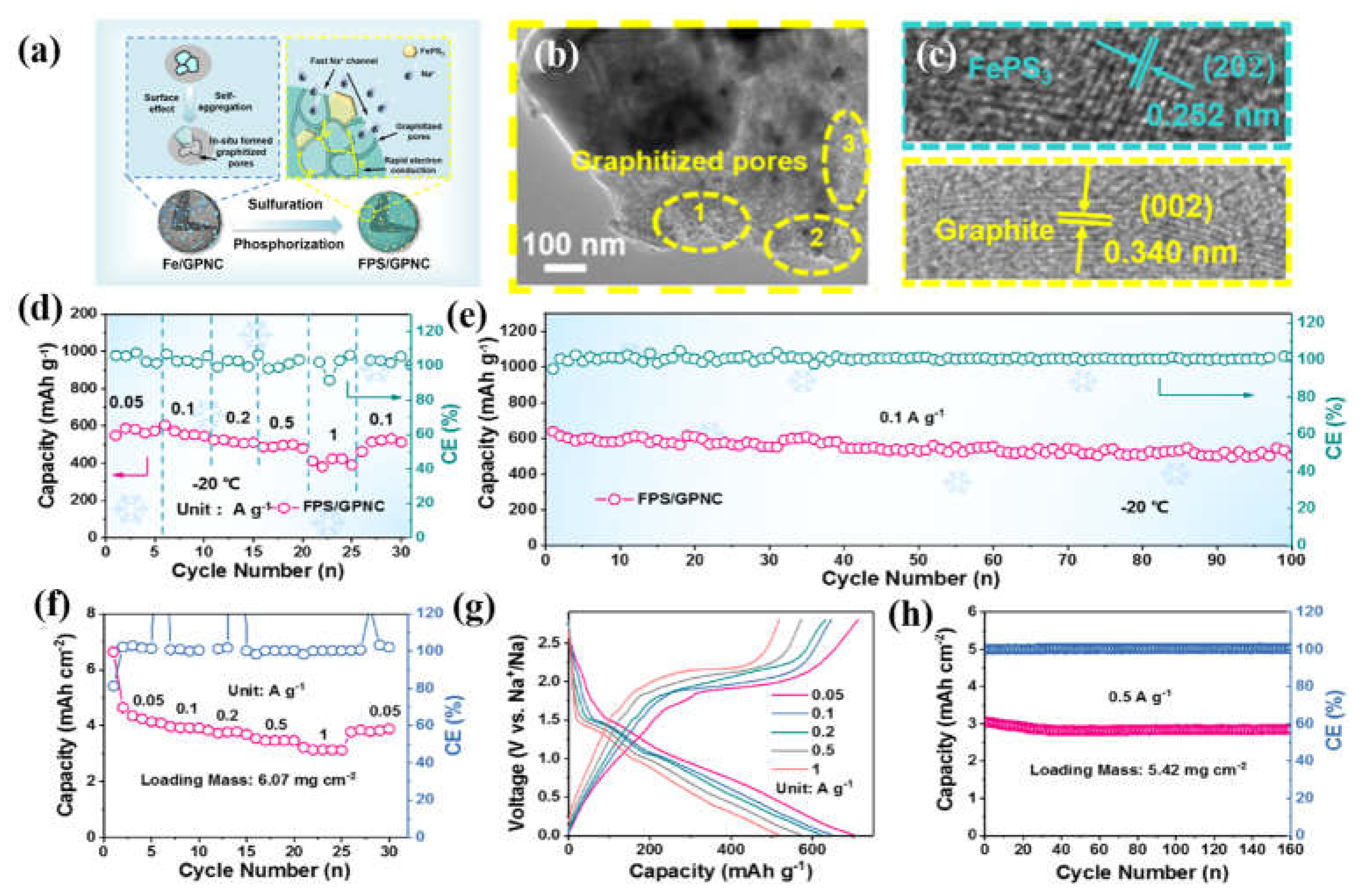
- Huang, S.; Ye, M.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, C.C. Achieving Ultrahigh-Rate and Low-Temperature Sodium Storage of FePS3 via In Situ Construction of Graphitized Porous N-Doped Carbon. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 42048–42056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
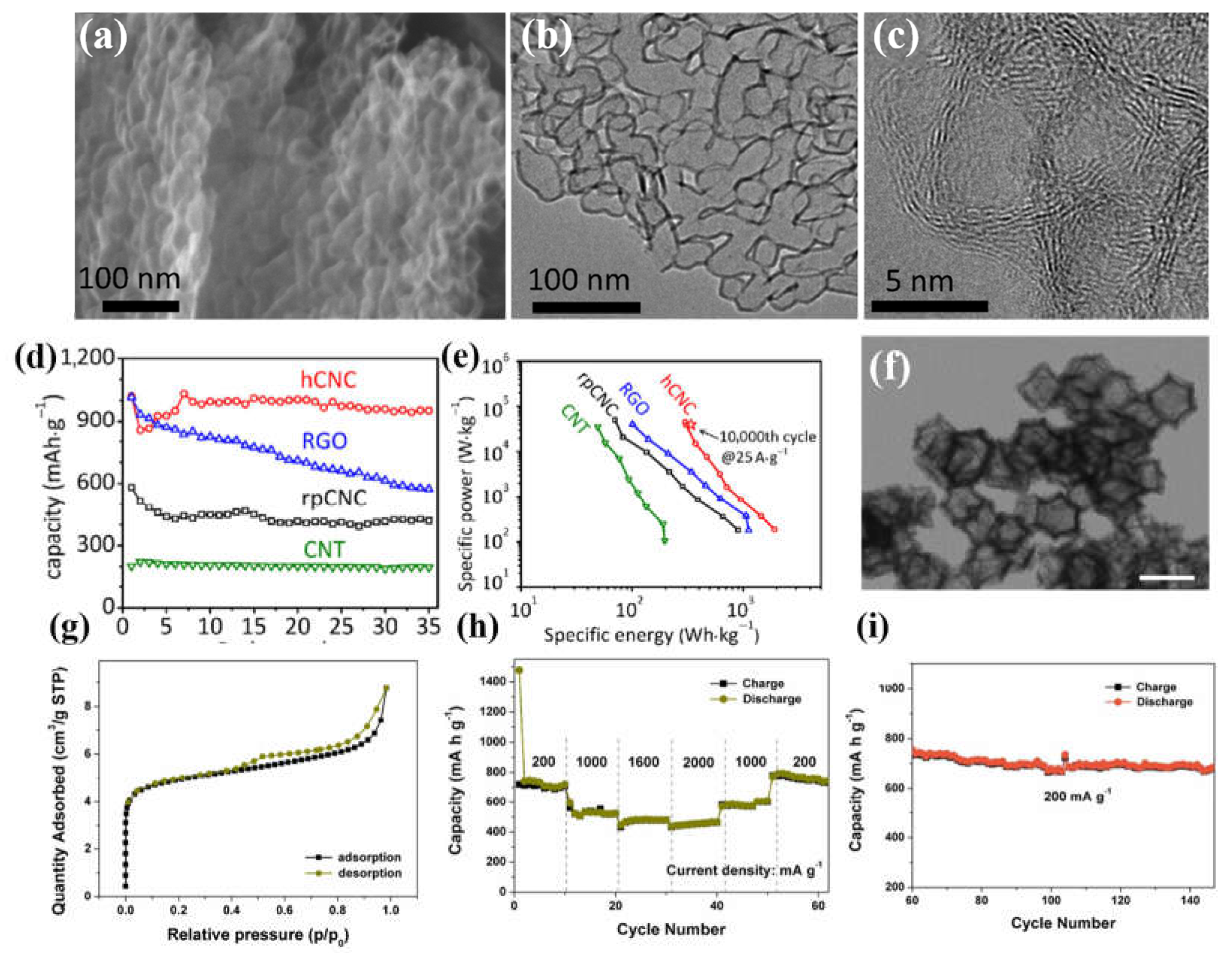
- Lyu, Z.; Yang, L.; Xu, D.; Zhao, J.; Lai, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z. Hierarchical carbon nanocages as high-rate anodes for Li-and Na-ion batteries. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 3535–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Mi, K.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Yu, T.; Yuan, A.; Kong, Q.; Xiong, S. MOF-derived bi-metal embedded N-doped carbon polyhedral nanocages with enhanced lithium storage. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, Y. Standing carbon-coated molybdenum dioxide nanosheets on graphene: morphology evolution and lithium ion storage properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 4706–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
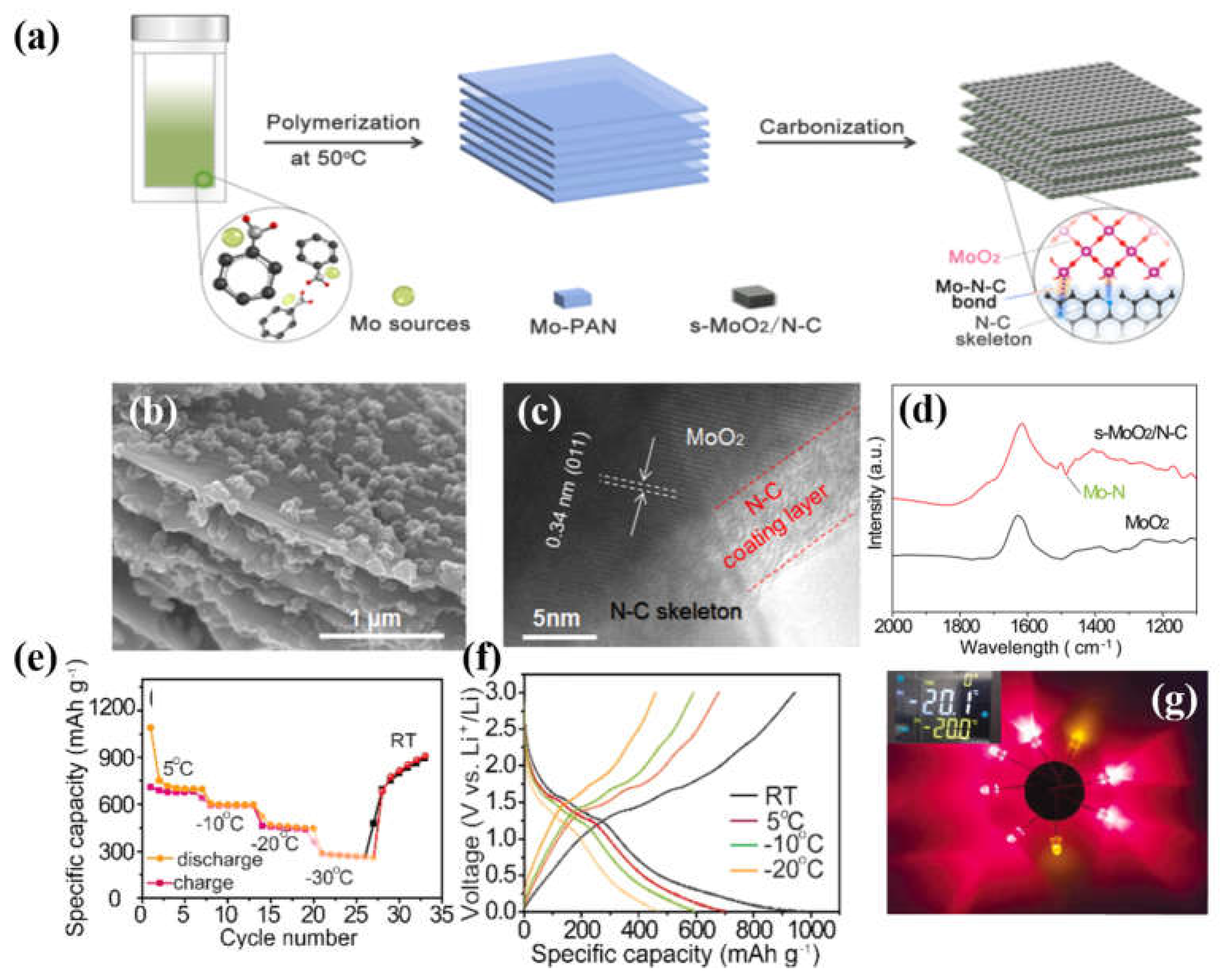
- Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, M.; Bai, G.; Ding, Y. Strongly surface-bonded MoO2 and N-doped hierarchical carbon nanoplates through interfacial Mo-NC bonds with superb room/low-temperature Li-storage performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 927, 166968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Carbon-Based Materials | Test temperature | Capacity | Current density | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PGN/CNT | -40 ℃ | 300 mAh g−1 | 20 C | Xu et al. [82] |
| NiO@C-N NSs | -40 ℃ | 428 mAh g−1 | 0.05 A g−1 | Bai et al. [83] |
| MnO@Graphite | -25 ℃ | 295 mAh g−1 | 0.1 A g−1 | Tian et al. [84] |
| LTO/Ag/CNT | -60 ℃ | 140 mAh g−1 | 0.2 C | Hu et al. [85] |
| TiO2(B)/Graphene | -30 ℃ | 240 mAh g−1 | 0.1 A g−1 | Zhang et al. [86] |
| Ti3C2Tx(O) | -20 ℃ | 88 mAh g−1 | 1 A g−1 | Wang et al. [87] |
| SFC | -10 ℃ | 76 mAh g−1 | 0.1 A g−1 | Wang et al. [88] |
| BNG | -10 ℃ | 223mAh g−1 | 0.2 C | Lu et al [89] |
| N, S−Mo2C/C-ACF | 5 ℃ | 405mAh g−1 | 5 C | Li et al. [90] |
| G/HTO | -20 ℃ | 211 mAh g−1 | 0.1 A g−1 | Li et al. [91] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).






